| title | description | services | author | ms.service | ms.topic | ms.date | ms.author |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Azure Application Gateway listener configuration |
This article describes how to configure Azure Application Gateway listeners. |
application-gateway |
vhorne |
application-gateway |
conceptual |
09/09/2020 |
surmb |
[!INCLUDE updated-for-az]
A listener is a logical entity that checks for incoming connection requests by using the port, protocol, host, and IP address. When you configure the listener, you must enter values for these that match the corresponding values in the incoming request on the gateway.
When you create an application gateway by using the Azure portal, you also create a default listener by choosing the protocol and port for the listener. You can choose whether to enable HTTP2 support on the listener. After you create the application gateway, you can edit the settings of that default listener (appGatewayHttpListener) or create new listeners.
When you create a new listener, you choose between basic and multi-site.
-
If you want all of your requests (for any domain) to be accepted and forwarded to backend pools, choose basic. Learn how to create an application gateway with a basic listener.
-
If you want to forward requests to different backend pools based on the host header or host names, choose multi-site listener, where you must also specify a host name that matches with the incoming request. This is because Application Gateway relies on HTTP 1.1 host headers to host more than one website on the same public IP address and port. To learn more, see hosting multiple sites using Application Gateway.
For the v1 SKU, requests are matched according to the order of the rules and the type of listener. If a rule with basic listener comes first in the order, it's processed first and will accept any request for that port and IP combination. To avoid this, configure the rules with multi-site listeners first and push the rule with the basic listener to the last in the list.
For the v2 SKU, multi-site listeners are processed before basic listeners.
Choose the front-end IP address that you plan to associate with this listener. The listener will listen to incoming requests on this IP.
Choose the front-end port. Select an existing port or create a new one. Choose any value from the allowed range of ports. You can use not only well-known ports, such as 80 and 443, but any allowed custom port that's suitable. A port can be used for public-facing listeners or private-facing listeners.
Choose HTTP or HTTPS:
-
If you choose HTTP, the traffic between the client and the application gateway is unencrypted.
-
Choose HTTPS if you want TLS termination or end-to-end TLS encryption. The traffic between the client and the application gateway is encrypted. And the TLS connection terminates at the application gateway. If you want end-to-end TLS encryption, you must choose HTTPS and configure the back-end HTTP setting. This ensures that traffic is re-encrypted when it travels from the application gateway to the back end.
To configure TLS termination and end-to-end TLS encryption, you must add a certificate to the listener to enable the application gateway to derive a symmetric key. This is dictated by the TLS protocol specification. The symmetric key is used to encrypt and decrypt the traffic that's sent to the gateway. The gateway certificate must be in Personal Information Exchange (PFX) format. This format lets you export the private key that the gateway uses to encrypt and decrypt traffic.
See Overview of TLS termination and end to end TLS with Application Gateway
HTTP/2 protocol support is available to clients that connect to application gateway listeners only. The communication to back-end server pools is over HTTP/1.1. By default, HTTP/2 support is disabled. The following Azure PowerShell code snippet shows how to enable this:
$gw = Get-AzApplicationGateway -Name test -ResourceGroupName hm
$gw.EnableHttp2 = $true
Set-AzApplicationGateway -ApplicationGateway $gw
WebSocket support is enabled by default. There's no user-configurable setting to enable or disable it. You can use WebSockets with both HTTP and HTTPS listeners.
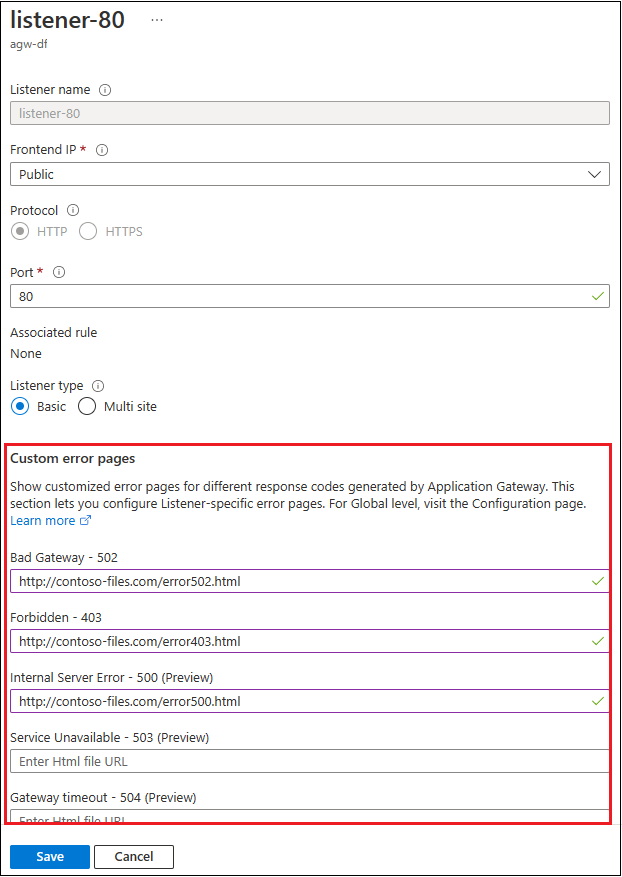
You can define custom error at the global level or the listener level. But creating global-level custom error pages from the Azure portal is currently not supported. You can configure a custom error page for a 403 web application firewall error or a 502 maintenance page at the listener level. You must also specify a publicly accessible blob URL for the given error status code. For more information, see Create Application Gateway custom error pages.
To configure a global custom error page, see Azure PowerShell configuration.
You can centralize TLS/SSL certificate management and reduce encryption-decryption overhead for a back-end server farm. Centralized TLS handling also lets you specify a central TLS policy that's suited to your security requirements. You can choose default, predefined, or custom TLS policy.
You configure TLS policy to control TLS protocol versions. You can configure an application gateway to use a minimum protocol version for TLS handshakes from TLS1.0, TLS1.1, and TLS1.2. By default, SSL 2.0 and 3.0 are disabled and aren't configurable. For more information, see Application Gateway TLS policy overview.
After you create a listener, you associate it with a request-routing rule. That rule determines how requests that are received on the listener are routed to the back end.