SafePayAI is an advanced fraud detection and prevention application designed to safeguard digital transactions using cutting-edge artificial intelligence techniques. With seamless integration of machine learning models and user-friendly interfaces, SafePayAI offers robust solutions for real-time fraud detection and mitigation.
By leveraging Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) for synthetic data generation and Random Forest classifiers for accurate predictions, SafePayAI ensures unparalleled security and efficiency in transaction monitoring.
-
1st Place Winner at DigiPay Pro NPCI Competition IIT Bombay Techfest 2024
-
SafePayAI proudly secured 1st place in the prestigious DigiPay Pro NPCI Competition, organized by NPCI during the IIT Bombay Techfest 2024.
-
Event Highlights
- 🎯 Objective:
- Develop Generative AI or Privacy-Preserving AI solutions for:
- Synthetic Data Generation to improve fraud detection accuracy while ensuring privacy.
- Fraud Detection to address evolving fraud patterns using AI-driven insights.
- 🎯 Objective:
-
💰 Prize Pool: ₹1,00,000.
-
📅 Key Dates:
- Registration Deadline: December 5, 2024
- Round 1 Submission: December 6, 2024
- Final Presentation at IIT bombay TechFest: December 18, 2024
Why SafePayAI Stood Out
- 🚀 Innovative Approach: Combined GANs and Random Forest models to achieve 95% accuracy in fraud detection.
- 🌍 Real-World Applicability: Designed a scalable, future-proof fraud detection solution adaptable to payment systems like UPI.
- 👩💻 User-Centric Design: Created a responsive UI with Google Sign-In, dashboards, and real-time alerts.
Our team receiving the award at IIT Bombay Techfest 2024.
Team SafePayAI with the event coordinator at the IIT Bombay Techfest.
- 🔒 User Authentication: Secure login using Google Sign-In.
- 📊 Transaction Dashboard: View and analyze transaction history.
- 📱 Responsive UI: Optimized for both mobile and desktop with Tailwind CSS.
- 🎨 Animations: Interactive transitions powered by Framer Motion.
- 🧪 AI-Powered Fraud Detection: Integrated GANs and Random Forest classifiers for fraud detection.
- ⚡ Real-Time Analysis: Instant fraud predictions through APIs with pre-trained models.
- 🔄 Data Augmentation: GANs generate synthetic datasets for improved model performance.
- 📂 Database Integration: Firebase backend to store UPI IDs, transaction history, and analytics.
- 🌟 React
- ⚡ Vite
- 🎨 Tailwind CSS
- 🎭 Framer Motion
- 🛠️ Radix UI
Our SafePay AI User Dashboard UI
Our SafePay AI Fraud Detection Warning UI
Our SafePay Recent Transaction UI
- Clone the Main repository:
git clone https://github.com/Shabopp/FraudDetectionUsingGAN.git
- Navigate to the project directory:
cd FraudDetectionUsingGAN
- Navigate to the Frontend directory:
cd fraudAI_Frontend_React - Install dependencies:
npm install
- Start the development server:
npm run dev
- Open the app in your browser at http://localhost:3000.
- Navigate to the backend directory:
cd ../AI_model_server_Flask - Install required Python packages:
pip install -r requirements.txt
- Ensure the trained model file
best_rf_model.pklis present in the directory. - Start the Flask server:
python app.py
- The API will be accessible at http://127.0.0.1:5000/.
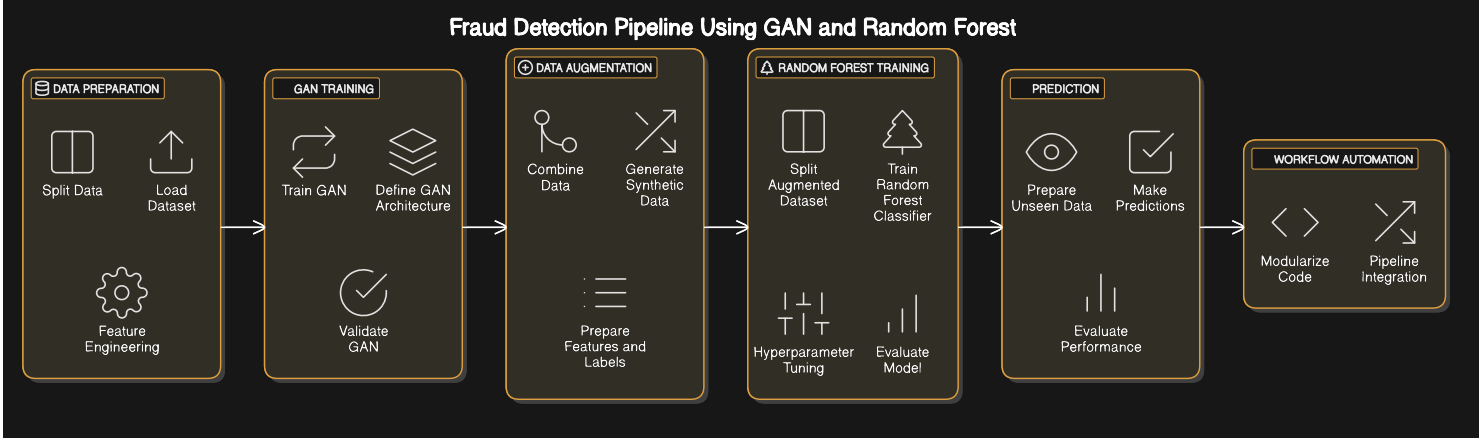
The core of SafePayAI lies in its AI-driven fraud detection mechanism, developed using a combination of GAN and Random Forest models. Here’s an in-depth breakdown:
- Load Dataset: Start with a transactional dataset containing both fraudulent and non-fraudulent records. Ensure it is preprocessed (e.g., handling missing values, scaling, and encoding).
- Split Data: Divide into training (80%) and testing (20%) sets.
- Feature Engineering: Normalize numerical features and one-hot encode categorical variables.
- GAN Architecture:
- Generator: Creates synthetic transaction data from random noise.
- Discriminator: Differentiates between real and synthetic data.
- Training Process:
- Alternate between training the discriminator on real and synthetic data and training the generator to fool the discriminator.
- Use Binary Cross-Entropy (BCE) loss for both.
- Validation: Evaluate synthetic data quality through visualization and statistical metrics.
- Generate Synthetic Data: Use the trained GAN to create synthetic transactions for both fraud and non-fraud labels.
- Merge Data: Combine synthetic and real data to balance the dataset and reduce class imbalance.
- Dataset Splitting: Split the augmented dataset into training and validation sets.
- Training: Train the Random Forest model using the sklearn library.
- Hyperparameter Tuning: Optimize parameters (e.g., n_estimators, max_depth) using cross-validation.
- Evaluation: Assess model performance using metrics like accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, and AUC-ROC.
- Input Processing: Preprocess transaction data received from the frontend.
- Prediction: Pass processed data through the trained Random Forest model to classify transactions as
FraudorNot Fraud. - Output: Display results on the frontend dashboard in real time.
- Modularized preprocessing, GAN training, synthetic data generation, and Random Forest training into reusable functions.
- Integrated the workflow into a script for seamless execution.
📊 Fraud Detection Parameters
-
Transaction Amount Anomalies: Detects transactions that significantly deviate from a user's historical average or usual behavior.
-
Transaction Frequency: Flags unusual spikes in the number of transactions within a short time period (e.g., multiple transactions in minutes).
-
Recipient Verification Status: Checks whether the recipient is verified, registered recently, or flagged as suspicious.
-
Recipient Blacklist Status: Identifies transactions to or from blacklisted UPI IDs, accounts, or merchants.
-
Device Fingerprinting: Analyzes mismatches in the device ID, browser, or OS used for the transaction compared to prior user sessions.
-
VPN or Proxy Usage: Flags transactions originating from masked IP addresses, indicating possible fraud attempts.
-
Geo-Location Flags: Identifies if transactions are initiated from unusual or high-risk geolocations.
-
Behavioral Biometrics: Monitors user interaction patterns, such as typing speed or mouse movement, for deviations from typical behavior.
-
Time Since Last Transaction with Recipient: Evaluates if the recipient is a new contact or there has been a significant time gap since the last transaction.
-
Social Trust Score: Scores recipients based on their relationship with the user (e.g., presence in contact list or prior transactions).
-
Account Age: Analyzes the age of the user’s account, flagging newly created accounts performing high-risk transactions.
-
High-Risk Transaction Times: Flags transactions occurring during non-business hours or at unusual times.
-
Past Fraudulent Behavior Flags: Checks if the user or recipient has been flagged for prior fraudulent activity.
-
Location-Inconsistent Transactions: Detects transactions initiated from multiple geolocations in a short time frame, indicating compromised credentials.
-
Normalized Transaction Amount: Compares the transaction amount against normalized values for similar users or demographic profiles.
-
Transaction Context Anomalies: Flags transactions that do not align with the user's typical spending habits (e.g., sudden large purchases).
-
Fraud Complaints Count: Analyzes the frequency of fraud complaints linked to a UPI ID, device, or account.
-
Merchant Category Mismatch: Checks if the merchant's behavior aligns with their declared category (e.g., high-value transactions for a low-value merchant).
-
User Daily Limit Exceeded: Flags transactions that exceed predefined daily transaction limits.
-
Recent High-Value Transaction Flags: Detects if the user recently performed a high-value transaction, increasing risk for subsequent fraudulent activity.
- GET
/- Returns a welcome message.
- POST
/predict- Request Body: JSON object containing features for prediction.
{ "features": [value1, value2, value3, ...] } - Response: JSON object containing the prediction.
{ "prediction": ["Fraud" or "Not Fraud"] } - Error Responses:
- 400: No input data provided.
- 500: Internal server error.
- Request Body: JSON object containing features for prediction.
-
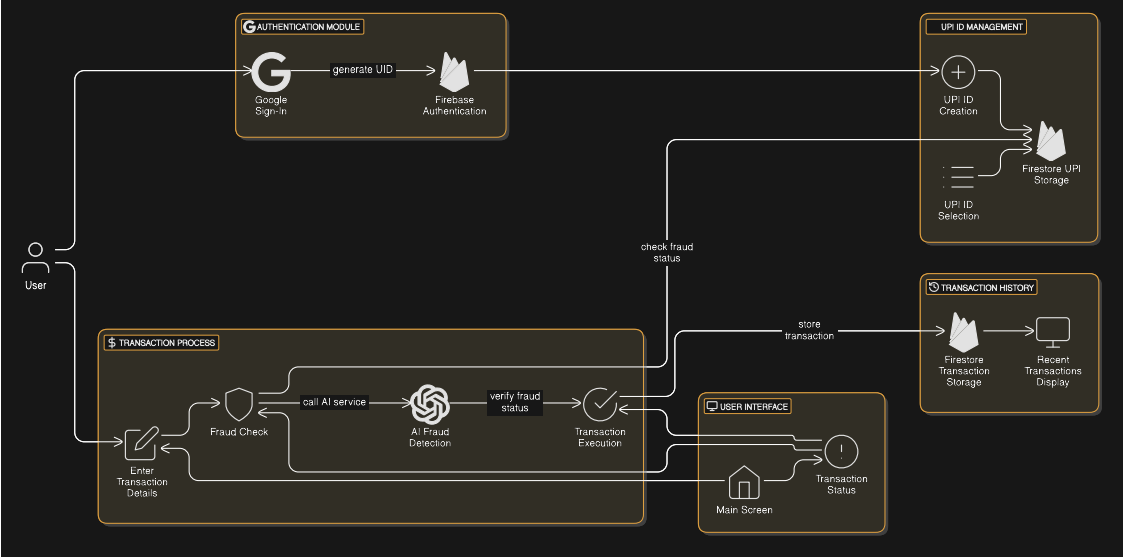
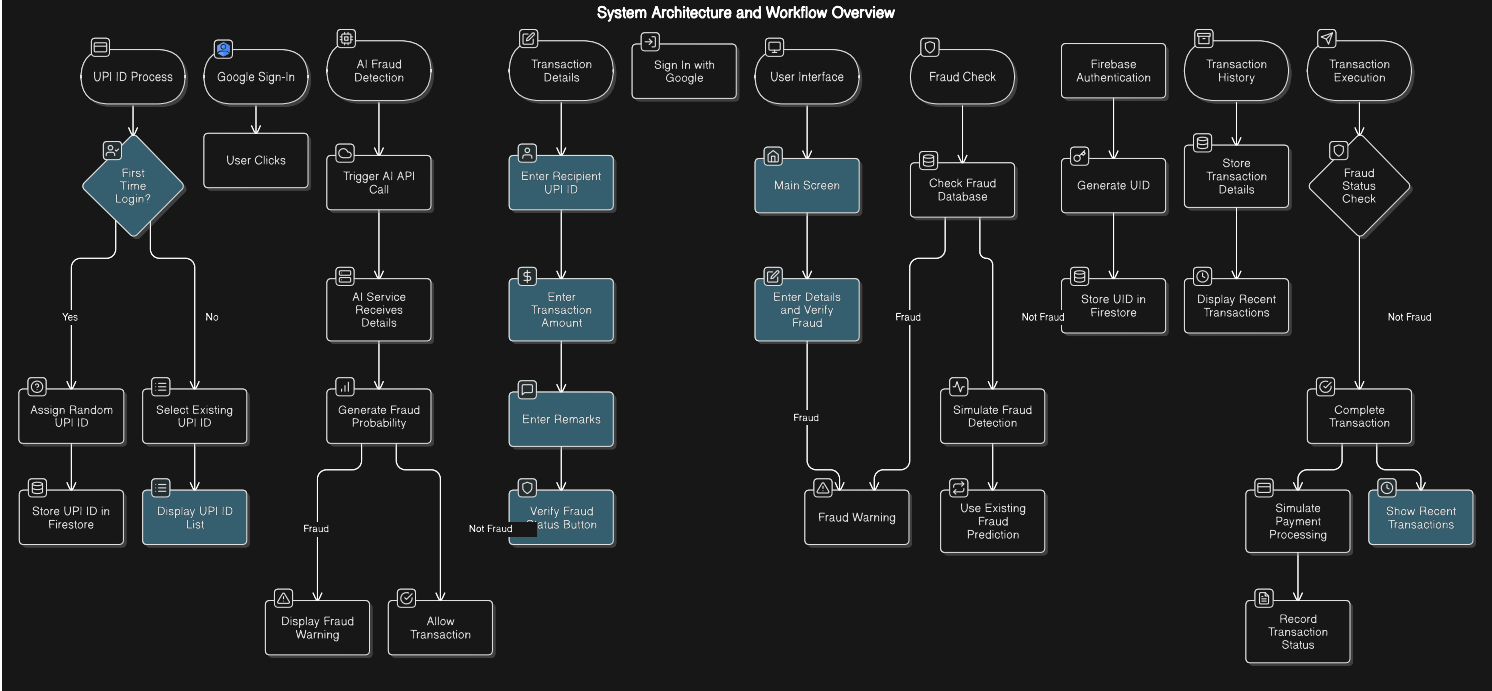
Google Sign-In (Authentication) Purpose: Enables secure user authentication using Google accounts. Workflow: Users authenticate via Google, generating a unique user ID (UID). This UID is linked to the user's data in Firebase Firestore.
-
Creating/Selecting UPI ID Purpose: Assigns a unique UPI ID to users upon first login or allows selection from existing ones. Details: First-time users are automatically assigned a UPI ID (e.g., user12345@bank). Existing users can select from their linked UPI IDs. UPI IDs are stored under the user's profile in Firestore.
-
Entering Transaction Details Purpose: Allows users to input recipient UPI ID, transaction amount, and remarks. Workflow: Users manually enter or select the recipient's UPI ID. Fraud detection verification is triggered via a "Verify Fraud Status" button.
-
Fraud Check (Verification Process) Purpose: Determines whether the recipient's UPI ID is flagged for fraud. Workflow: System checks the Firestore fraud database for the recipient UPI ID. If unflagged, simulated fraud detection is applied for new UPI IDs or reuses prior predictions for existing ones.
-
AI Fraud Detection Call Purpose: Utilizes AI to analyze transaction details and predict fraud. Workflow: Transaction data is sent to the AI service for fraud probability analysis. Based on the AI’s response: Fraud: User sees a warning. Not Fraud: Transaction proceeds.
-
Transaction Execution Purpose: Processes verified transactions. Workflow: If deemed not fraudulent, the system processes the transaction (simulated in this demo). Status is recorded in the transaction history.
-
Storing Transaction History Purpose: Maintains a record of transactions for auditing and display. Workflow: Details such as amount, recipient, timestamp, and fraud status are saved in Firestore. History is accessible under the user’s profile and displayed in the app's UI.
-
User Interface (UI) Workflow Main Screen: Displays the "Send Money" page with inputs for transaction details and fraud verification. Transaction Status: Fraudulent transactions show warnings and are blocked. Verified transactions activate the "Send Money" button. Recent Transactions: Displays historical data, including recipient, amount, date, and fraud status.