diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index 97048a76..a150d872 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -1,3 +1,1520 @@
[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
> ["For coding interview preparation, LeetCode is one of the best online resource providing a rich library of more than 300 real coding interview questions for you to practice from using one of the 7 supported languages - C, C++, Java, Python, C#, JavaScript, Ruby."](https://www.quora.com/How-effective-is-Leetcode-for-preparing-for-technical-interviews)
+
+* [Algorithm II](#algorithm-ii)
+* [Binary Search I](#binary-search-i)
+* [Binary Search II](#binary-search-ii)
+* [Dynamic Programming I](#dynamic-programming-i)
+* [Programming Skills I](#programming-skills-i)
+* [Programming Skills II](#programming-skills-ii)
+* [Graph Theory I](#graph-theory-i)
+* [SQL I](#sql-i)
+* [Level 1](#level-1)
+* [Level 2](#level-2)
+* [Udemy](#udemy)
+* [Data Structure I](#data-structure-i)
+* [Data Structure II](#data-structure-ii)
+* [Algorithm I](#algorithm-i)
+
+### Algorithm II
+
+#### Day 1 Binary Search
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0034 |[Find First and Last Position of Element in Sorted Array](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0034_find_first_and_last_position_of_element_in_sorted_array)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Binary_Search | 228 | 83.38
+| 0033 |[Search in Rotated Sorted Array](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0033_search_in_rotated_sorted_array)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Binary_Search | 184 | 86.08
+| 0074 |[Search a 2D Matrix](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0074_search_a_2d_matrix)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Array, Binary_Search, Matrix | 290 | 40.17
+
+#### Day 2 Binary Search
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0153 |[Find Minimum in Rotated Sorted Array](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0153_find_minimum_in_rotated_sorted_array)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Array, Binary_Search | 262 | 60.96
+
+#### Day 3 Two Pointers
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0015 |[3Sum](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0015_3sum)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Sorting, Two_Pointers | 1059 | 55.28
+
+#### Day 4 Two Pointers
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0011 |[Container With Most Water](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0011_container_with_most_water)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Greedy, Two_Pointers | 635 | 64.22
+
+#### Day 5 Sliding Window
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0438 |[Find All Anagrams in a String](src/main/kotlin/g0401_0500/s0438_find_all_anagrams_in_a_string)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, String, Hash_Table, Sliding_Window | 561 | 54.68
+
+#### Day 6 Breadth First Search Depth First Search
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0200 |[Number of Islands](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0200_number_of_islands)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Matrix, Union_Find | 252 | 95.41
+
+#### Day 7 Breadth First Search Depth First Search
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 8 Breadth First Search Depth First Search
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 9 Recursion Backtracking
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0078 |[Subsets](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0078_subsets)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Bit_Manipulation, Backtracking | 353 | 30.14
+
+#### Day 10 Recursion Backtracking
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0039 |[Combination Sum](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0039_combination_sum)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Array, Backtracking | 317 | 86.85
+
+#### Day 11 Recursion Backtracking
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0017 |[Letter Combinations of a Phone Number](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0017_letter_combinations_of_a_phone_number)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, String, Hash_Table, Backtracking | 132 | 100.00
+| 0022 |[Generate Parentheses](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0022_generate_parentheses)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, String, Dynamic_Programming, Backtracking | 210 | 78.51
+| 0079 |[Word Search](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0079_word_search)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Matrix, Backtracking | 463 | 68.49
+
+#### Day 12 Dynamic Programming
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0055 |[Jump Game](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0055_jump_game)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming, Greedy | 670 | 66.67
+
+#### Day 13 Dynamic Programming
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0045 |[Jump Game II](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0045_jump_game_ii)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming, Greedy | 227 | 98.14
+| 0062 |[Unique Paths](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0062_unique_paths)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Dynamic_Programming, Math, Combinatorics | 209 | 49.18
+
+#### Day 14 Dynamic Programming
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0005 |[Longest Palindromic Substring](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0005_longest_palindromic_substring)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, String, Dynamic_Programming | 359 | 69.08
+
+#### Day 15 Dynamic Programming
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0139 |[Word Break](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0139_word_break)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, String, Hash_Table, Dynamic_Programming, Trie, Memoization | 197 | 87.17
+
+#### Day 16 Dynamic Programming
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0300 |[Longest Increasing Subsequence](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0300_longest_increasing_subsequence)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming, Binary_Search | 318 | 82.28
+
+#### Day 17 Dynamic Programming
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 1143 |[Longest Common Subsequence](src/main/kotlin/g1101_1200/s1143_longest_common_subsequence)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, String, Dynamic_Programming | 307 | 38.36
+
+#### Day 18 Dynamic Programming
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0072 |[Edit Distance](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0072_edit_distance)| Hard | Top_100_Liked_Questions, String, Dynamic_Programming | 320 | 63.53
+| 0322 |[Coin Change](src/main/kotlin/g0301_0400/s0322_coin_change)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming, Breadth_First_Search | 332 | 50.68
+
+#### Day 19 Bit Manipulation
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 20 Others
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 21 Others
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+### Binary Search I
+
+#### Day 1
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 2
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0035 |[Search Insert Position](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0035_search_insert_position)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Array, Binary_Search | 267 | 50.32
+
+#### Day 3
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 4
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 5
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0034 |[Find First and Last Position of Element in Sorted Array](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0034_find_first_and_last_position_of_element_in_sorted_array)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Binary_Search | 228 | 83.38
+
+#### Day 6
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 7
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 8
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0074 |[Search a 2D Matrix](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0074_search_a_2d_matrix)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Array, Binary_Search, Matrix | 290 | 40.17
+
+#### Day 9
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 10
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 11
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0033 |[Search in Rotated Sorted Array](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0033_search_in_rotated_sorted_array)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Binary_Search | 184 | 86.08
+
+#### Day 12
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0153 |[Find Minimum in Rotated Sorted Array](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0153_find_minimum_in_rotated_sorted_array)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Array, Binary_Search | 262 | 60.96
+
+### Binary Search II
+
+#### Day 1
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 2
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 3
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0300 |[Longest Increasing Subsequence](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0300_longest_increasing_subsequence)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming, Binary_Search | 318 | 82.28
+
+#### Day 4
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 5
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0287 |[Find the Duplicate Number](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0287_find_the_duplicate_number)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Binary_Search, Two_Pointers, Bit_Manipulation | 656 | 66.21
+
+#### Day 6
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 7
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 8
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0240 |[Search a 2D Matrix II](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0240_search_a_2d_matrix_ii)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Binary_Search, Matrix, Divide_and_Conquer | 460 | 66.08
+
+#### Day 9
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 10
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 11
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 12
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 13
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 14
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 15
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 16
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 17
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 18
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 19
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 20
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+### Dynamic Programming I
+
+#### Day 1
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 2
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0070 |[Climbing Stairs](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0070_climbing_stairs)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Dynamic_Programming, Math, Memoization | 127 | 97.06
+
+#### Day 3
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0198 |[House Robber](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0198_house_robber)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming | 156 | 92.24
+
+#### Day 4
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0055 |[Jump Game](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0055_jump_game)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming, Greedy | 670 | 66.67
+| 0045 |[Jump Game II](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0045_jump_game_ii)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming, Greedy | 227 | 98.14
+
+#### Day 5
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0053 |[Maximum Subarray](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0053_maximum_subarray)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming, Divide_and_Conquer | 662 | 82.48
+
+#### Day 6
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0152 |[Maximum Product Subarray](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0152_maximum_product_subarray)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming | 253 | 88.42
+
+#### Day 7
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0121 |[Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0121_best_time_to_buy_and_sell_stock)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming | 609 | 94.06
+
+#### Day 8
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 9
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0139 |[Word Break](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0139_word_break)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, String, Hash_Table, Dynamic_Programming, Trie, Memoization | 197 | 87.17
+| 0042 |[Trapping Rain Water](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0042_trapping_rain_water)| Hard | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming, Two_Pointers, Stack, Monotonic_Stack | 196 | 100.00
+
+#### Day 10
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 11
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 12
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 13
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 14
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 15
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0062 |[Unique Paths](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0062_unique_paths)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Dynamic_Programming, Math, Combinatorics | 209 | 49.18
+
+#### Day 16
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0064 |[Minimum Path Sum](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0064_minimum_path_sum)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming, Matrix | 222 | 95.70
+| 0221 |[Maximal Square](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0221_maximal_square)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming, Matrix | 614 | 44.00
+
+#### Day 17
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0005 |[Longest Palindromic Substring](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0005_longest_palindromic_substring)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, String, Dynamic_Programming | 359 | 69.08
+
+#### Day 18
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0300 |[Longest Increasing Subsequence](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0300_longest_increasing_subsequence)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming, Binary_Search | 318 | 82.28
+
+#### Day 19
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 1143 |[Longest Common Subsequence](src/main/kotlin/g1101_1200/s1143_longest_common_subsequence)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, String, Dynamic_Programming | 307 | 38.36
+| 0072 |[Edit Distance](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0072_edit_distance)| Hard | Top_100_Liked_Questions, String, Dynamic_Programming | 320 | 63.53
+
+#### Day 20
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0322 |[Coin Change](src/main/kotlin/g0301_0400/s0322_coin_change)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming, Breadth_First_Search | 332 | 50.68
+
+#### Day 21
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+### Programming Skills I
+
+#### Day 1 Basic Data Type
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 2 Operator
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 3 Conditional Statements
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 4 Loop
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 5 Function
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 6 Array
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0283 |[Move Zeroes](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0283_move_zeroes)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Two_Pointers | 516 | 79.07
+
+#### Day 7 Array
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 8 String
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 9 String
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 10 Linked List and Tree
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 11 Containers and Libraries
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 12 Class and Object
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+### Programming Skills II
+
+#### Day 1
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 2
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 3
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 4
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 5
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 6
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0739 |[Daily Temperatures](src/main/kotlin/g0701_0800/s0739_daily_temperatures)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Array, Stack, Monotonic_Stack | 936 | 80.54
+
+#### Day 7
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0048 |[Rotate Image](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0048_rotate_image)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Math, Matrix | 287 | 46.50
+
+#### Day 8
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0054 |[Spiral Matrix](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0054_spiral_matrix)| Medium | Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Matrix, Simulation | 224 | 62.50
+
+#### Day 9
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 10
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 11
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0049 |[Group Anagrams](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0049_group_anagrams)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, String, Hash_Table, Sorting | 506 | 86.55
+
+#### Day 12
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0438 |[Find All Anagrams in a String](src/main/kotlin/g0401_0500/s0438_find_all_anagrams_in_a_string)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, String, Hash_Table, Sliding_Window | 561 | 54.68
+
+#### Day 13
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 14
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0138 |[Copy List with Random Pointer](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0138_copy_list_with_random_pointer)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Hash_Table, Linked_List | 274 | 80.58
+
+#### Day 15
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0002 |[Add Two Numbers](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0002_add_two_numbers)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Math, Linked_List, Recursion | 212 | 93.71
+
+#### Day 16
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 17
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 18
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0155 |[Min Stack](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0155_min_stack)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Stack, Design | 331 | 84.88
+
+#### Day 19
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 20
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+### Graph Theory I
+
+#### Day 1 Matrix Related Problems
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0200 |[Number of Islands](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0200_number_of_islands)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Matrix, Union_Find | 252 | 95.41
+
+#### Day 2 Matrix Related Problems
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 3 Matrix Related Problems
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 4 Matrix Related Problems
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 5 Matrix Related Problems
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 6 Matrix Related Problems
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 7 Standard Traversal
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 8 Standard Traversal
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 9 Standard Traversal
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 10 Standard Traversal
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 11 Breadth First Search
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 12 Breadth First Search
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 13 Graph Theory
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 14 Graph Theory
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+### SQL I
+
+#### Day 1 Select
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 2 Select and Order
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 3 String Processing Functions
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 4 Union and Select
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 5 Union
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 6 Union
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 7 Function
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 8 Function
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 9 Control of Flow
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 10 Where
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+### Level 1
+
+#### Day 1 Prefix Sum
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 2 String
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 3 Linked List
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0021 |[Merge Two Sorted Lists](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0021_merge_two_sorted_lists)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Linked_List, Recursion | 148 | 99.90
+| 0206 |[Reverse Linked List](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0206_reverse_linked_list)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Linked_List, Recursion | 309 | 15.90
+
+#### Day 4 Linked List
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0142 |[Linked List Cycle II](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0142_linked_list_cycle_ii)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Hash_Table, Two_Pointers, Linked_List | 192 | 63.39
+
+#### Day 5 Greedy
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0121 |[Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0121_best_time_to_buy_and_sell_stock)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming | 609 | 94.06
+
+#### Day 6 Tree
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0102 |[Binary Tree Level Order Traversal](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0102_binary_tree_level_order_traversal)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Breadth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree | 355 | 29.37
+
+#### Day 7 Binary Search
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 8 Binary Search Tree
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0098 |[Validate Binary Search Tree](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0098_validate_binary_search_tree)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Depth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree, Binary_Search_Tree | 330 | 41.38
+
+#### Day 9 Graph/BFS/DFS
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0200 |[Number of Islands](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0200_number_of_islands)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Matrix, Union_Find | 252 | 95.41
+
+#### Day 10 Dynamic Programming
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0070 |[Climbing Stairs](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0070_climbing_stairs)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Dynamic_Programming, Math, Memoization | 127 | 97.06
+
+#### Day 11 Dynamic Programming
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0062 |[Unique Paths](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0062_unique_paths)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Dynamic_Programming, Math, Combinatorics | 209 | 49.18
+
+#### Day 12 Sliding Window/Two Pointer
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0438 |[Find All Anagrams in a String](src/main/kotlin/g0401_0500/s0438_find_all_anagrams_in_a_string)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, String, Hash_Table, Sliding_Window | 561 | 54.68
+
+#### Day 13 Hashmap
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0001 |[Two Sum](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0001_two_sum)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Hash_Table | 234 | 92.75
+
+#### Day 14 Stack
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0394 |[Decode String](src/main/kotlin/g0301_0400/s0394_decode_string)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, String, Stack, Recursion | 268 | 23.13
+
+#### Day 15 Heap
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+### Level 2
+
+#### Day 1 Implementation/Simulation
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0054 |[Spiral Matrix](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0054_spiral_matrix)| Medium | Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Matrix, Simulation | 224 | 62.50
+
+#### Day 2 String
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0014 |[Longest Common Prefix](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0014_longest_common_prefix)| Easy | Top_Interview_Questions, String | 269 | 48.51
+
+#### Day 3 Linked List
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0019 |[Remove Nth Node From End of List](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0019_remove_nth_node_from_end_of_list)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Two_Pointers, Linked_List | 172 | 85.17
+| 0234 |[Palindrome Linked List](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0234_palindrome_linked_list)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Two_Pointers, Stack, Linked_List, Recursion | 809 | 20.12
+
+#### Day 4 Linked List
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0148 |[Sort List](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0148_sort_list)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Sorting, Two_Pointers, Linked_List, Divide_and_Conquer, Merge_Sort | 820 | 61.70
+
+#### Day 5 Greedy
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 6 Tree
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0226 |[Invert Binary Tree](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0226_invert_binary_tree)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree | 275 | 13.68
+
+#### Day 7 Tree
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0543 |[Diameter of Binary Tree](src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0543_diameter_of_binary_tree)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Depth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree | 307 | 43.93
+| 0437 |[Path Sum III](src/main/kotlin/g0401_0500/s0437_path_sum_iii)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Depth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree | 403 | 54.12
+
+#### Day 8 Binary Search
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0074 |[Search a 2D Matrix](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0074_search_a_2d_matrix)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Array, Binary_Search, Matrix | 290 | 40.17
+| 0033 |[Search in Rotated Sorted Array](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0033_search_in_rotated_sorted_array)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Binary_Search | 184 | 86.08
+
+#### Day 9 Binary Search Tree
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0230 |[Kth Smallest Element in a BST](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0230_kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Depth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree, Binary_Search_Tree | 393 | 33.33
+
+#### Day 10 Graph/BFS/DFS
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0994 |[Rotting Oranges](src/main/kotlin/g0901_1000/s0994_rotting_oranges)| Medium | Array, Breadth_First_Search, Matrix | 308 | 57.93
+
+#### Day 11 Graph/BFS/DFS
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 12 Dynamic Programming
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0198 |[House Robber](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0198_house_robber)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming | 156 | 92.24
+| 0322 |[Coin Change](src/main/kotlin/g0301_0400/s0322_coin_change)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming, Breadth_First_Search | 332 | 50.68
+
+#### Day 13 Dynamic Programming
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0416 |[Partition Equal Subset Sum](src/main/kotlin/g0401_0500/s0416_partition_equal_subset_sum)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming | 509 | 57.56
+| 0152 |[Maximum Product Subarray](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0152_maximum_product_subarray)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming | 253 | 88.42
+
+#### Day 14 Sliding Window/Two Pointer
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0003 |[Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0003_longest_substring_without_repeating_characters)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, String, Hash_Table, Sliding_Window | 212 | 91.24
+| 0016 |[3Sum Closest](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0016_3sum_closest)| Medium | Array, Sorting, Two_Pointers | 219 | 89.56
+| 0076 |[Minimum Window Substring](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0076_minimum_window_substring)| Hard | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, String, Hash_Table, Sliding_Window | 346 | 85.20
+
+#### Day 15 Tree
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0101 |[Symmetric Tree](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0101_symmetric_tree)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree | 290 | 26.98
+| 0199 |[Binary Tree Right Side View](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0199_binary_tree_right_side_view)| Medium | Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree | 194 | 92.89
+
+#### Day 16 Design
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0155 |[Min Stack](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0155_min_stack)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Stack, Design | 331 | 84.88
+| 0208 |[Implement Trie (Prefix Tree)](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0208_implement_trie_prefix_tree)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, String, Hash_Table, Design, Trie | 689 | 61.00
+
+#### Day 17 Interval
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0056 |[Merge Intervals](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0056_merge_intervals)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Sorting | 323 | 99.68
+
+#### Day 18 Stack
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 19 Union Find
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 20 Brute Force/Backtracking
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0039 |[Combination Sum](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0039_combination_sum)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Array, Backtracking | 317 | 86.85
+| 0046 |[Permutations](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0046_permutations)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Backtracking | 186 | 100.00
+
+### Udemy
+
+#### Udemy Integers
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0136 |[Single Number](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0136_single_number)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Bit_Manipulation | 344 | 83.63
+| 0007 |[Reverse Integer](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0007_reverse_integer)| Medium | Top_Interview_Questions, Math | 230 | 57.36
+| 0009 |[Palindrome Number](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0009_palindrome_number)| Easy | Math | 208 | 94.88
+
+#### Udemy Strings
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0014 |[Longest Common Prefix](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0014_longest_common_prefix)| Easy | Top_Interview_Questions, String | 269 | 48.51
+| 0003 |[Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0003_longest_substring_without_repeating_characters)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, String, Hash_Table, Sliding_Window | 212 | 91.24
+| 0020 |[Valid Parentheses](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0020_valid_parentheses)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, String, Stack | 196 | 71.08
+| 0005 |[Longest Palindromic Substring](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0005_longest_palindromic_substring)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, String, Dynamic_Programming | 359 | 69.08
+| 0394 |[Decode String](src/main/kotlin/g0301_0400/s0394_decode_string)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, String, Stack, Recursion | 268 | 23.13
+| 0049 |[Group Anagrams](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0049_group_anagrams)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, String, Hash_Table, Sorting | 506 | 86.55
+
+#### Udemy Binary Search
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0033 |[Search in Rotated Sorted Array](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0033_search_in_rotated_sorted_array)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Binary_Search | 184 | 86.08
+| 0153 |[Find Minimum in Rotated Sorted Array](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0153_find_minimum_in_rotated_sorted_array)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Array, Binary_Search | 262 | 60.96
+
+#### Udemy Arrays
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0121 |[Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0121_best_time_to_buy_and_sell_stock)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming | 609 | 94.06
+| 0283 |[Move Zeroes](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0283_move_zeroes)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Two_Pointers | 516 | 79.07
+| 0001 |[Two Sum](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0001_two_sum)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Hash_Table | 234 | 92.75
+| 0189 |[Rotate Array](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0189_rotate_array)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Math, Two_Pointers | 483 | 86.95
+| 0055 |[Jump Game](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0055_jump_game)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming, Greedy | 670 | 66.67
+| 0075 |[Sort Colors](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0075_sort_colors)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Sorting, Two_Pointers | 198 | 85.66
+| 0238 |[Product of Array Except Self](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0238_product_of_array_except_self)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Prefix_Sum | 669 | 48.96
+| 0041 |[First Missing Positive](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0041_first_missing_positive)| Hard | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Hash_Table | 345 | 100.00
+| 0239 |[Sliding Window Maximum](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0239_sliding_window_maximum)| Hard | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Heap_Priority_Queue, Sliding_Window, Queue, Monotonic_Queue | 1059 | 86.14
+
+#### Udemy Two Pointers
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0026 |[Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0026_remove_duplicates_from_sorted_array)| Easy | Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Two_Pointers | 361 | 77.19
+| 0042 |[Trapping Rain Water](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0042_trapping_rain_water)| Hard | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming, Two_Pointers, Stack, Monotonic_Stack | 196 | 100.00
+| 0015 |[3Sum](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0015_3sum)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Sorting, Two_Pointers | 1059 | 55.28
+
+#### Udemy Famous Algorithm
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0053 |[Maximum Subarray](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0053_maximum_subarray)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming, Divide_and_Conquer | 662 | 82.48
+| 0169 |[Majority Element](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0169_majority_element)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Hash_Table, Sorting, Counting, Divide_and_Conquer | 460 | 51.25
+
+#### Udemy Sorting Algorithms
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Udemy 2D Arrays/Matrix
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0074 |[Search a 2D Matrix](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0074_search_a_2d_matrix)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Array, Binary_Search, Matrix | 290 | 40.17
+| 0054 |[Spiral Matrix](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0054_spiral_matrix)| Medium | Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Matrix, Simulation | 224 | 62.50
+| 0048 |[Rotate Image](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0048_rotate_image)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Math, Matrix | 287 | 46.50
+| 0073 |[Set Matrix Zeroes](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0073_set_matrix_zeroes)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Hash_Table, Matrix | 255 | 100.00
+| 0056 |[Merge Intervals](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0056_merge_intervals)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Sorting | 323 | 99.68
+
+#### Udemy Linked List
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0114 |[Flatten Binary Tree to Linked List](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0114_flatten_binary_tree_to_linked_list)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Depth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree, Stack, Linked_List | 305 | 26.30
+| 0024 |[Swap Nodes in Pairs](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0024_swap_nodes_in_pairs)| Medium | Linked_List, Recursion | 173 | 83.13
+| 0142 |[Linked List Cycle II](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0142_linked_list_cycle_ii)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Hash_Table, Two_Pointers, Linked_List | 192 | 63.39
+| 0141 |[Linked List Cycle](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0141_linked_list_cycle)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Hash_Table, Two_Pointers, Linked_List | 425 | 10.15
+| 0206 |[Reverse Linked List](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0206_reverse_linked_list)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Linked_List, Recursion | 309 | 15.90
+| 0021 |[Merge Two Sorted Lists](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0021_merge_two_sorted_lists)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Linked_List, Recursion | 148 | 99.90
+| 0160 |[Intersection of Two Linked Lists](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0160_intersection_of_two_linked_lists)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Hash_Table, Two_Pointers, Linked_List | 262 | 83.50
+| 0234 |[Palindrome Linked List](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0234_palindrome_linked_list)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Two_Pointers, Stack, Linked_List, Recursion | 809 | 20.12
+| 0138 |[Copy List with Random Pointer](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0138_copy_list_with_random_pointer)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Hash_Table, Linked_List | 274 | 80.58
+| 0025 |[Reverse Nodes in k-Group](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0025_reverse_nodes_in_k_group)| Hard | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Linked_List, Recursion | 194 | 87.72
+| 0146 |[LRU Cache](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0146_lru_cache)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Hash_Table, Design, Linked_List, Doubly_Linked_List | 1116 | 97.93
+
+#### Udemy Tree Stack Queue
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0094 |[Largest Rectangle in Histogram](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0094_binary_tree_inorder_traversal)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Depth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree, Stack | 283 | 17.97
+| 0102 |[Binary Tree Level Order Traversal](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0102_binary_tree_level_order_traversal)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Breadth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree | 355 | 29.37
+| 0543 |[Diameter of Binary Tree](src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0543_diameter_of_binary_tree)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Depth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree | 307 | 43.93
+| 0226 |[Invert Binary Tree](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0226_invert_binary_tree)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree | 275 | 13.68
+| 0124 |[Binary Tree Maximum Path Sum](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0124_binary_tree_maximum_path_sum)| Hard | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Dynamic_Programming, Depth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree | 331 | 74.42
+| 0098 |[Validate Binary Search Tree](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0098_validate_binary_search_tree)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Depth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree, Binary_Search_Tree | 330 | 41.38
+| 0236 |[Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0236_lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_tree)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Depth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree | 386 | 45.21
+
+#### Udemy Trie and Heap
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0208 |[Implement Trie (Prefix Tree)](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0208_implement_trie_prefix_tree)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, String, Hash_Table, Design, Trie | 689 | 61.00
+
+#### Udemy Graph
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0200 |[Number of Islands](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0200_number_of_islands)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Matrix, Union_Find | 252 | 95.41
+
+#### Udemy Dynamic Programming
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0139 |[Word Break](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0139_word_break)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, String, Hash_Table, Dynamic_Programming, Trie, Memoization | 197 | 87.17
+| 0152 |[Maximum Product Subarray](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0152_maximum_product_subarray)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming | 253 | 88.42
+| 0198 |[House Robber](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0198_house_robber)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming | 156 | 92.24
+| 0070 |[Climbing Stairs](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0070_climbing_stairs)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Dynamic_Programming, Math, Memoization | 127 | 97.06
+| 0064 |[Minimum Path Sum](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0064_minimum_path_sum)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming, Matrix | 222 | 95.70
+| 0300 |[Longest Increasing Subsequence](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0300_longest_increasing_subsequence)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming, Binary_Search | 318 | 82.28
+| 1143 |[Longest Common Subsequence](src/main/kotlin/g1101_1200/s1143_longest_common_subsequence)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, String, Dynamic_Programming | 307 | 38.36
+| 0072 |[Edit Distance](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0072_edit_distance)| Hard | Top_100_Liked_Questions, String, Dynamic_Programming | 320 | 63.53
+| 0010 |[Regular Expression Matching](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0010_regular_expression_matching)| Hard | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, String, Dynamic_Programming, Recursion | 234 | 85.18
+
+#### Udemy Backtracking/Recursion
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0022 |[Generate Parentheses](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0022_generate_parentheses)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, String, Dynamic_Programming, Backtracking | 210 | 78.51
+| 0039 |[Combination Sum](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0039_combination_sum)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Array, Backtracking | 317 | 86.85
+| 0078 |[Subsets](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0078_subsets)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Bit_Manipulation, Backtracking | 353 | 30.14
+| 0017 |[Letter Combinations of a Phone Number](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0017_letter_combinations_of_a_phone_number)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, String, Hash_Table, Backtracking | 132 | 100.00
+| 0046 |[Permutations](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0046_permutations)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Backtracking | 186 | 100.00
+
+#### Udemy Bit Manipulation
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Udemy Design
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0155 |[Min Stack](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0155_min_stack)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Stack, Design | 331 | 84.88
+
+### Data Structure I
+
+#### Day 1 Array
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0053 |[Maximum Subarray](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0053_maximum_subarray)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming, Divide_and_Conquer | 662 | 82.48
+
+#### Day 2 Array
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0001 |[Two Sum](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0001_two_sum)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Hash_Table | 234 | 92.75
+
+#### Day 3 Array
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0121 |[Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0121_best_time_to_buy_and_sell_stock)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming | 609 | 94.06
+
+#### Day 4 Array
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 5 Array
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0074 |[Search a 2D Matrix](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0074_search_a_2d_matrix)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Array, Binary_Search, Matrix | 290 | 40.17
+
+#### Day 6 String
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 7 Linked List
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0141 |[Linked List Cycle](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0141_linked_list_cycle)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Hash_Table, Two_Pointers, Linked_List | 425 | 10.15
+| 0021 |[Merge Two Sorted Lists](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0021_merge_two_sorted_lists)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Linked_List, Recursion | 148 | 99.90
+
+#### Day 8 Linked List
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0206 |[Reverse Linked List](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0206_reverse_linked_list)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Linked_List, Recursion | 309 | 15.90
+
+#### Day 9 Stack Queue
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0020 |[Valid Parentheses](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0020_valid_parentheses)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, String, Stack | 196 | 71.08
+
+#### Day 10 Tree
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0094 |[Largest Rectangle in Histogram](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0094_binary_tree_inorder_traversal)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Depth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree, Stack | 283 | 17.97
+
+#### Day 11 Tree
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0102 |[Binary Tree Level Order Traversal](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0102_binary_tree_level_order_traversal)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Breadth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree | 355 | 29.37
+| 0101 |[Symmetric Tree](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0101_symmetric_tree)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree | 290 | 26.98
+
+#### Day 12 Tree
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0226 |[Invert Binary Tree](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0226_invert_binary_tree)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree | 275 | 13.68
+
+#### Day 13 Tree
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 14 Tree
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0098 |[Validate Binary Search Tree](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0098_validate_binary_search_tree)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Depth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree, Binary_Search_Tree | 330 | 41.38
+
+### Data Structure II
+
+#### Day 1 Array
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0136 |[Single Number](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0136_single_number)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Bit_Manipulation | 344 | 83.63
+| 0169 |[Majority Element](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0169_majority_element)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Hash_Table, Sorting, Counting, Divide_and_Conquer | 460 | 51.25
+| 0015 |[3Sum](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0015_3sum)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Sorting, Two_Pointers | 1059 | 55.28
+
+#### Day 2 Array
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0075 |[Sort Colors](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0075_sort_colors)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Sorting, Two_Pointers | 198 | 85.66
+| 0056 |[Merge Intervals](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0056_merge_intervals)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Sorting | 323 | 99.68
+
+#### Day 3 Array
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0048 |[Rotate Image](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0048_rotate_image)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Math, Matrix | 287 | 46.50
+
+#### Day 4 Array
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0240 |[Search a 2D Matrix II](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0240_search_a_2d_matrix_ii)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Binary_Search, Matrix, Divide_and_Conquer | 460 | 66.08
+
+#### Day 5 Array
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0238 |[Product of Array Except Self](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0238_product_of_array_except_self)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Prefix_Sum | 669 | 48.96
+| 0560 |[Subarray Sum Equals K](src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0560_subarray_sum_equals_k)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Array, Hash_Table, Prefix_Sum | 692 | 53.27
+
+#### Day 6 String
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 7 String
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0763 |[Partition Labels](src/main/kotlin/g0701_0800/s0763_partition_labels)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, String, Hash_Table, Greedy, Two_Pointers | 235 | 84.75
+
+#### Day 8 String
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0049 |[Group Anagrams](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0049_group_anagrams)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, String, Hash_Table, Sorting | 506 | 86.55
+
+#### Day 9 String
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0005 |[Longest Palindromic Substring](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0005_longest_palindromic_substring)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, String, Dynamic_Programming | 359 | 69.08
+
+#### Day 10 Linked List
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0002 |[Add Two Numbers](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0002_add_two_numbers)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Math, Linked_List, Recursion | 212 | 93.71
+| 0142 |[Linked List Cycle II](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0142_linked_list_cycle_ii)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Hash_Table, Two_Pointers, Linked_List | 192 | 63.39
+
+#### Day 11 Linked List
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0160 |[Intersection of Two Linked Lists](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0160_intersection_of_two_linked_lists)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Hash_Table, Two_Pointers, Linked_List | 262 | 83.50
+
+#### Day 12 Linked List
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0024 |[Swap Nodes in Pairs](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0024_swap_nodes_in_pairs)| Medium | Linked_List, Recursion | 173 | 83.13
+
+#### Day 13 Linked List
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0025 |[Reverse Nodes in k-Group](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0025_reverse_nodes_in_k_group)| Hard | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Linked_List, Recursion | 194 | 87.72
+
+#### Day 14 Stack Queue
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0155 |[Min Stack](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0155_min_stack)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Stack, Design | 331 | 84.88
+
+#### Day 15 Tree
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0105 |[Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Inorder Traversal](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0105_construct_binary_tree_from_preorder_and_inorder_traversal)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Hash_Table, Tree, Binary_Tree, Divide_and_Conquer | 370 | 58.31
+
+#### Day 16 Tree
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0199 |[Binary Tree Right Side View](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0199_binary_tree_right_side_view)| Medium | Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree | 194 | 92.89
+
+#### Day 17 Tree
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0230 |[Kth Smallest Element in a BST](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0230_kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Depth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree, Binary_Search_Tree | 393 | 33.33
+
+#### Day 18 Tree
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0236 |[Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0236_lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_tree)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Depth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree | 386 | 45.21
+
+#### Day 19 Graph
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 20 Heap Priority Queue
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0215 |[Kth Largest Element in an Array](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0215_kth_largest_element_in_an_array)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Sorting, Heap_Priority_Queue, Divide_and_Conquer, Quickselect | 839 | 34.43
+| 0347 |[Top K Frequent Elements](src/main/kotlin/g0301_0400/s0347_top_k_frequent_elements)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Hash_Table, Sorting, Heap_Priority_Queue, Counting, Divide_and_Conquer, Quickselect, Bucket_Sort | 268 | 99.74
+
+#### Day 21 Heap Priority Queue
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+### Algorithm I
+
+#### Day 1 Binary Search
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0035 |[Search Insert Position](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0035_search_insert_position)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Array, Binary_Search | 267 | 50.32
+
+#### Day 2 Two Pointers
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0189 |[Rotate Array](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0189_rotate_array)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Math, Two_Pointers | 483 | 86.95
+
+#### Day 3 Two Pointers
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0283 |[Move Zeroes](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0283_move_zeroes)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Two_Pointers | 516 | 79.07
+
+#### Day 4 Two Pointers
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 5 Two Pointers
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0019 |[Remove Nth Node From End of List](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0019_remove_nth_node_from_end_of_list)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Two_Pointers, Linked_List | 172 | 85.17
+
+#### Day 6 Sliding Window
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0003 |[Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0003_longest_substring_without_repeating_characters)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, String, Hash_Table, Sliding_Window | 212 | 91.24
+
+#### Day 7 Breadth First Search Depth First Search
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 8 Breadth First Search Depth First Search
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 9 Breadth First Search Depth First Search
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0994 |[Rotting Oranges](src/main/kotlin/g0901_1000/s0994_rotting_oranges)| Medium | Array, Breadth_First_Search, Matrix | 308 | 57.93
+
+#### Day 10 Recursion Backtracking
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0021 |[Merge Two Sorted Lists](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0021_merge_two_sorted_lists)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Linked_List, Recursion | 148 | 99.90
+| 0206 |[Reverse Linked List](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0206_reverse_linked_list)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Linked_List, Recursion | 309 | 15.90
+
+#### Day 11 Recursion Backtracking
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0046 |[Permutations](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0046_permutations)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Backtracking | 186 | 100.00
+
+#### Day 12 Dynamic Programming
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0070 |[Climbing Stairs](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0070_climbing_stairs)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Dynamic_Programming, Math, Memoization | 127 | 97.06
+| 0198 |[House Robber](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0198_house_robber)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming | 156 | 92.24
+
+#### Day 13 Bit Manipulation
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+
+#### Day 14 Bit Manipulation
+
+| | | | | |
+|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0136 |[Single Number](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0136_single_number)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Bit_Manipulation | 344 | 83.63
+
+## Algorithms
+
+| # | Title | Difficulty | Tag | Time, ms | Time, %
+|------|----------------|-------------|-------------|----------|--------
+| 1143 |[Longest Common Subsequence](src/main/kotlin/g1101_1200/s1143_longest_common_subsequence)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, String, Dynamic_Programming, Algorithm_II_Day_17_Dynamic_Programming, Dynamic_Programming_I_Day_19, Udemy_Dynamic_Programming | 307 | 38.36
+| 0994 |[Rotting Oranges](src/main/kotlin/g0901_1000/s0994_rotting_oranges)| Medium | Array, Breadth_First_Search, Matrix, Algorithm_I_Day_9_Breadth_First_Search_Depth_First_Search, Level_2_Day_10_Graph/BFS/DFS | 308 | 57.93
+| 0864 |[Shortest Path to Get All Keys](src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0864_shortest_path_to_get_all_keys)| Hard | Breadth_First_Search, Bit_Manipulation | 176 | 100.00
+| 0763 |[Partition Labels](src/main/kotlin/g0701_0800/s0763_partition_labels)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, String, Hash_Table, Greedy, Two_Pointers, Data_Structure_II_Day_7_String | 235 | 84.75
+| 0739 |[Daily Temperatures](src/main/kotlin/g0701_0800/s0739_daily_temperatures)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Array, Stack, Monotonic_Stack, Programming_Skills_II_Day_6 | 936 | 80.54
+| 0647 |[Palindromic Substrings](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0647_palindromic_substrings)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, String, Dynamic_Programming | 266 | 67.83
+| 0560 |[Subarray Sum Equals K](src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0560_subarray_sum_equals_k)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Array, Hash_Table, Prefix_Sum, Data_Structure_II_Day_5_Array | 692 | 53.27
+| 0543 |[Diameter of Binary Tree](src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0543_diameter_of_binary_tree)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Depth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree, Level_2_Day_7_Tree, Udemy_Tree_Stack_Queue | 307 | 43.93
+| 0438 |[Find All Anagrams in a String](src/main/kotlin/g0401_0500/s0438_find_all_anagrams_in_a_string)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, String, Hash_Table, Sliding_Window, Algorithm_II_Day_5_Sliding_Window, Programming_Skills_II_Day_12, Level_1_Day_12_Sliding_Window/Two_Pointer | 561 | 54.68
+| 0437 |[Path Sum III](src/main/kotlin/g0401_0500/s0437_path_sum_iii)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Depth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree, Level_2_Day_7_Tree | 403 | 54.12
+| 0416 |[Partition Equal Subset Sum](src/main/kotlin/g0401_0500/s0416_partition_equal_subset_sum)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming, Level_2_Day_13_Dynamic_Programming | 509 | 57.56
+| 0394 |[Decode String](src/main/kotlin/g0301_0400/s0394_decode_string)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, String, Stack, Recursion, Level_1_Day_14_Stack, Udemy_Strings | 268 | 23.13
+| 0378 |[Kth Smallest Element in a Sorted Matrix](src/main/kotlin/g0301_0400/s0378_kth_smallest_element_in_a_sorted_matrix)| Medium | Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Sorting, Binary_Search, Matrix, Heap_Priority_Queue | 522 | 59.78
+| 0347 |[Top K Frequent Elements](src/main/kotlin/g0301_0400/s0347_top_k_frequent_elements)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Hash_Table, Sorting, Heap_Priority_Queue, Counting, Divide_and_Conquer, Quickselect, Bucket_Sort, Data_Structure_II_Day_20_Heap_Priority_Queue | 268 | 99.74
+| 0322 |[Coin Change](src/main/kotlin/g0301_0400/s0322_coin_change)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming, Breadth_First_Search, Algorithm_II_Day_18_Dynamic_Programming, Dynamic_Programming_I_Day_20, Level_2_Day_12_Dynamic_Programming | 332 | 50.68
+| 0300 |[Longest Increasing Subsequence](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0300_longest_increasing_subsequence)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming, Binary_Search, Algorithm_II_Day_16_Dynamic_Programming, Binary_Search_II_Day_3, Dynamic_Programming_I_Day_18, Udemy_Dynamic_Programming | 318 | 82.28
+| 0295 |[Find Median from Data Stream](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0295_find_median_from_data_stream)| Hard | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Sorting, Two_Pointers, Design, Heap_Priority_Queue, Data_Stream | 2289 | 33.60
+| 0287 |[Find the Duplicate Number](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0287_find_the_duplicate_number)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Binary_Search, Two_Pointers, Bit_Manipulation, Binary_Search_II_Day_5 | 656 | 66.21
+| 0283 |[Move Zeroes](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0283_move_zeroes)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Two_Pointers, Algorithm_I_Day_3_Two_Pointers, Programming_Skills_I_Day_6_Array, Udemy_Arrays | 516 | 79.07
+| 0240 |[Search a 2D Matrix II](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0240_search_a_2d_matrix_ii)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Binary_Search, Matrix, Divide_and_Conquer, Data_Structure_II_Day_4_Array, Binary_Search_II_Day_8 | 460 | 66.08
+| 0239 |[Sliding Window Maximum](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0239_sliding_window_maximum)| Hard | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Heap_Priority_Queue, Sliding_Window, Queue, Monotonic_Queue, Udemy_Arrays | 1059 | 86.14
+| 0238 |[Product of Array Except Self](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0238_product_of_array_except_self)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Prefix_Sum, Data_Structure_II_Day_5_Array, Udemy_Arrays | 669 | 48.96
+| 0236 |[Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0236_lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_tree)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Depth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree, Data_Structure_II_Day_18_Tree, Udemy_Tree_Stack_Queue | 386 | 45.21
+| 0234 |[Palindrome Linked List](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0234_palindrome_linked_list)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Two_Pointers, Stack, Linked_List, Recursion, Level_2_Day_3_Linked_List, Udemy_Linked_List | 809 | 20.12
+| 0230 |[Kth Smallest Element in a BST](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0230_kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Depth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree, Binary_Search_Tree, Data_Structure_II_Day_17_Tree, Level_2_Day_9_Binary_Search_Tree | 393 | 33.33
+| 0226 |[Invert Binary Tree](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0226_invert_binary_tree)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree, Data_Structure_I_Day_12_Tree, Level_2_Day_6_Tree, Udemy_Tree_Stack_Queue | 275 | 13.68
+| 0221 |[Maximal Square](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0221_maximal_square)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming, Matrix, Dynamic_Programming_I_Day_16 | 614 | 44.00
+| 0215 |[Kth Largest Element in an Array](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0215_kth_largest_element_in_an_array)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Sorting, Heap_Priority_Queue, Divide_and_Conquer, Quickselect, Data_Structure_II_Day_20_Heap_Priority_Queue | 839 | 34.43
+| 0208 |[Implement Trie (Prefix Tree)](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0208_implement_trie_prefix_tree)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, String, Hash_Table, Design, Trie, Level_2_Day_16_Design, Udemy_Trie_and_Heap | 689 | 61.00
+| 0207 |[Course Schedule](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0207_course_schedule)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Graph, Topological_Sort | 416 | 40.10
+| 0206 |[Reverse Linked List](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0206_reverse_linked_list)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Linked_List, Recursion, Data_Structure_I_Day_8_Linked_List, Algorithm_I_Day_10_Recursion_Backtracking, Level_1_Day_3_Linked_List, Udemy_Linked_List | 309 | 15.90
+| 0200 |[Number of Islands](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0200_number_of_islands)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Matrix, Union_Find, Algorithm_II_Day_6_Breadth_First_Search_Depth_First_Search, Graph_Theory_I_Day_1_Matrix_Related_Problems, Level_1_Day_9_Graph/BFS/DFS, Udemy_Graph | 252 | 95.41
+| 0199 |[Binary Tree Right Side View](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0199_binary_tree_right_side_view)| Medium | Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree, Data_Structure_II_Day_16_Tree, Level_2_Day_15_Tree | 194 | 92.89
+| 0198 |[House Robber](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0198_house_robber)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming, Algorithm_I_Day_12_Dynamic_Programming, Dynamic_Programming_I_Day_3, Level_2_Day_12_Dynamic_Programming, Udemy_Dynamic_Programming | 156 | 92.24
+| 0189 |[Rotate Array](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0189_rotate_array)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Math, Two_Pointers, Algorithm_I_Day_2_Two_Pointers, Udemy_Arrays | 483 | 86.95
+| 0169 |[Majority Element](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0169_majority_element)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Hash_Table, Sorting, Counting, Divide_and_Conquer, Data_Structure_II_Day_1_Array, Udemy_Famous_Algorithm | 460 | 51.25
+| 0160 |[Intersection of Two Linked Lists](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0160_intersection_of_two_linked_lists)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Hash_Table, Two_Pointers, Linked_List, Data_Structure_II_Day_11_Linked_List, Udemy_Linked_List | 262 | 83.50
+| 0155 |[Min Stack](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0155_min_stack)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Stack, Design, Data_Structure_II_Day_14_Stack_Queue, Programming_Skills_II_Day_18, Level_2_Day_16_Design, Udemy_Design | 331 | 84.88
+| 0153 |[Find Minimum in Rotated Sorted Array](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0153_find_minimum_in_rotated_sorted_array)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Array, Binary_Search, Algorithm_II_Day_2_Binary_Search, Binary_Search_I_Day_12, Udemy_Binary_Search | 262 | 60.96
+| 0152 |[Maximum Product Subarray](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0152_maximum_product_subarray)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming, Dynamic_Programming_I_Day_6, Level_2_Day_13_Dynamic_Programming, Udemy_Dynamic_Programming | 253 | 88.42
+| 0148 |[Sort List](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0148_sort_list)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Sorting, Two_Pointers, Linked_List, Divide_and_Conquer, Merge_Sort, Level_2_Day_4_Linked_List | 820 | 61.70
+| 0146 |[LRU Cache](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0146_lru_cache)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Hash_Table, Design, Linked_List, Doubly_Linked_List, Udemy_Linked_List | 1116 | 97.93
+| 0142 |[Linked List Cycle II](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0142_linked_list_cycle_ii)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Hash_Table, Two_Pointers, Linked_List, Data_Structure_II_Day_10_Linked_List, Level_1_Day_4_Linked_List, Udemy_Linked_List | 192 | 63.39
+| 0141 |[Linked List Cycle](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0141_linked_list_cycle)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Hash_Table, Two_Pointers, Linked_List, Data_Structure_I_Day_7_Linked_List, Udemy_Linked_List | 425 | 10.15
+| 0139 |[Word Break](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0139_word_break)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, String, Hash_Table, Dynamic_Programming, Trie, Memoization, Algorithm_II_Day_15_Dynamic_Programming, Dynamic_Programming_I_Day_9, Udemy_Dynamic_Programming | 197 | 87.17
+| 0138 |[Copy List with Random Pointer](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0138_copy_list_with_random_pointer)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Hash_Table, Linked_List, Programming_Skills_II_Day_14, Udemy_Linked_List | 274 | 80.58
+| 0136 |[Single Number](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0136_single_number)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Bit_Manipulation, Data_Structure_II_Day_1_Array, Algorithm_I_Day_14_Bit_Manipulation, Udemy_Integers | 344 | 83.63
+| 0131 |[Palindrome Partitioning](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0131_palindrome_partitioning)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, String, Dynamic_Programming, Backtracking | 820 | 87.27
+| 0128 |[Longest Consecutive Sequence](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0128_longest_consecutive_sequence)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Hash_Table, Union_Find | 460 | 97.77
+| 0124 |[Binary Tree Maximum Path Sum](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0124_binary_tree_maximum_path_sum)| Hard | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Dynamic_Programming, Depth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree, Udemy_Tree_Stack_Queue | 331 | 74.42
+| 0121 |[Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0121_best_time_to_buy_and_sell_stock)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming, Data_Structure_I_Day_3_Array, Dynamic_Programming_I_Day_7, Level_1_Day_5_Greedy, Udemy_Arrays | 609 | 94.06
+| 0114 |[Flatten Binary Tree to Linked List](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0114_flatten_binary_tree_to_linked_list)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Depth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree, Stack, Linked_List, Udemy_Linked_List | 305 | 26.30
+| 0105 |[Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Inorder Traversal](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0105_construct_binary_tree_from_preorder_and_inorder_traversal)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Hash_Table, Tree, Binary_Tree, Divide_and_Conquer, Data_Structure_II_Day_15_Tree | 370 | 58.31
+| 0102 |[Binary Tree Level Order Traversal](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0102_binary_tree_level_order_traversal)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Breadth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree, Data_Structure_I_Day_11_Tree, Level_1_Day_6_Tree, Udemy_Tree_Stack_Queue | 355 | 29.37
+| 0101 |[Symmetric Tree](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0101_symmetric_tree)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree, Data_Structure_I_Day_11_Tree, Level_2_Day_15_Tree | 290 | 26.98
+| 0098 |[Validate Binary Search Tree](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0098_validate_binary_search_tree)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Depth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree, Binary_Search_Tree, Data_Structure_I_Day_14_Tree, Level_1_Day_8_Binary_Search_Tree, Udemy_Tree_Stack_Queue | 330 | 41.38
+| 0094 |[Largest Rectangle in Histogram](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0094_binary_tree_inorder_traversal)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Depth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree, Stack, Data_Structure_I_Day_10_Tree, Udemy_Tree_Stack_Queue | 283 | 17.97
+| 0084 |[Largest Rectangle in Histogram](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0084_largest_rectangle_in_histogram)| Hard | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Stack, Monotonic_Stack | 525 | 100.00
+| 0079 |[Word Search](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0079_word_search)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Matrix, Backtracking, Algorithm_II_Day_11_Recursion_Backtracking | 463 | 68.49
+| 0078 |[Subsets](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0078_subsets)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Bit_Manipulation, Backtracking, Algorithm_II_Day_9_Recursion_Backtracking, Udemy_Backtracking/Recursion | 353 | 30.14
+| 0076 |[Minimum Window Substring](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0076_minimum_window_substring)| Hard | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, String, Hash_Table, Sliding_Window, Level_2_Day_14_Sliding_Window/Two_Pointer | 346 | 85.20
+| 0075 |[Sort Colors](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0075_sort_colors)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Sorting, Two_Pointers, Data_Structure_II_Day_2_Array, Udemy_Arrays | 198 | 85.66
+| 0074 |[Search a 2D Matrix](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0074_search_a_2d_matrix)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Array, Binary_Search, Matrix, Data_Structure_I_Day_5_Array, Algorithm_II_Day_1_Binary_Search, Binary_Search_I_Day_8, Level_2_Day_8_Binary_Search, Udemy_2D_Arrays/Matrix | 290 | 40.17
+| 0073 |[Set Matrix Zeroes](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0073_set_matrix_zeroes)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Hash_Table, Matrix, Udemy_2D_Arrays/Matrix | 255 | 100.00
+| 0072 |[Edit Distance](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0072_edit_distance)| Hard | Top_100_Liked_Questions, String, Dynamic_Programming, Algorithm_II_Day_18_Dynamic_Programming, Dynamic_Programming_I_Day_19, Udemy_Dynamic_Programming | 320 | 63.53
+| 0070 |[Climbing Stairs](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0070_climbing_stairs)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Dynamic_Programming, Math, Memoization, Algorithm_I_Day_12_Dynamic_Programming, Dynamic_Programming_I_Day_2, Level_1_Day_10_Dynamic_Programming, Udemy_Dynamic_Programming | 127 | 97.06
+| 0064 |[Minimum Path Sum](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0064_minimum_path_sum)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming, Matrix, Dynamic_Programming_I_Day_16, Udemy_Dynamic_Programming | 222 | 95.70
+| 0062 |[Unique Paths](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0062_unique_paths)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Dynamic_Programming, Math, Combinatorics, Algorithm_II_Day_13_Dynamic_Programming, Dynamic_Programming_I_Day_15, Level_1_Day_11_Dynamic_Programming | 209 | 49.18
+| 0056 |[Merge Intervals](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0056_merge_intervals)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Sorting, Data_Structure_II_Day_2_Array, Level_2_Day_17_Interval, Udemy_2D_Arrays/Matrix | 323 | 99.68
+| 0055 |[Jump Game](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0055_jump_game)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming, Greedy, Algorithm_II_Day_12_Dynamic_Programming, Dynamic_Programming_I_Day_4, Udemy_Arrays | 670 | 66.67
+| 0054 |[Spiral Matrix](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0054_spiral_matrix)| Medium | Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Matrix, Simulation, Programming_Skills_II_Day_8, Level_2_Day_1_Implementation/Simulation, Udemy_2D_Arrays/Matrix | 224 | 62.50
+| 0053 |[Maximum Subarray](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0053_maximum_subarray)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming, Divide_and_Conquer, Data_Structure_I_Day_1_Array, Dynamic_Programming_I_Day_5, Udemy_Famous_Algorithm | 662 | 82.48
+| 0051 |[N-Queens](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0051_n_queens)| Hard | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Array, Backtracking | 243 | 95.10
+| 0049 |[Group Anagrams](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0049_group_anagrams)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, String, Hash_Table, Sorting, Data_Structure_II_Day_8_String, Programming_Skills_II_Day_11, Udemy_Strings | 506 | 86.55
+| 0048 |[Rotate Image](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0048_rotate_image)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Math, Matrix, Data_Structure_II_Day_3_Array, Programming_Skills_II_Day_7, Udemy_2D_Arrays/Matrix | 287 | 46.50
+| 0046 |[Permutations](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0046_permutations)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Backtracking, Algorithm_I_Day_11_Recursion_Backtracking, Level_2_Day_20_Brute_Force/Backtracking, Udemy_Backtracking/Recursion | 186 | 100.00
+| 0045 |[Jump Game II](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0045_jump_game_ii)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming, Greedy, Algorithm_II_Day_13_Dynamic_Programming, Dynamic_Programming_I_Day_4 | 227 | 98.14
+| 0042 |[Trapping Rain Water](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0042_trapping_rain_water)| Hard | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming, Two_Pointers, Stack, Monotonic_Stack, Dynamic_Programming_I_Day_9, Udemy_Two_Pointers | 196 | 100.00
+| 0041 |[First Missing Positive](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0041_first_missing_positive)| Hard | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Hash_Table, Udemy_Arrays | 345 | 100.00
+| 0039 |[Combination Sum](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0039_combination_sum)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Array, Backtracking, Algorithm_II_Day_10_Recursion_Backtracking, Level_2_Day_20_Brute_Force/Backtracking, Udemy_Backtracking/Recursion | 317 | 86.85
+| 0035 |[Search Insert Position](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0035_search_insert_position)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Array, Binary_Search, Algorithm_I_Day_1_Binary_Search, Binary_Search_I_Day_2 | 267 | 50.32
+| 0034 |[Find First and Last Position of Element in Sorted Array](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0034_find_first_and_last_position_of_element_in_sorted_array)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Binary_Search, Algorithm_II_Day_1_Binary_Search, Binary_Search_I_Day_5 | 228 | 83.38
+| 0033 |[Search in Rotated Sorted Array](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0033_search_in_rotated_sorted_array)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Binary_Search, Algorithm_II_Day_1_Binary_Search | 184 | 86.08
+| 0026 |[Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0026_remove_duplicates_from_sorted_array)| Easy | Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Two_Pointers | 361 | 77.19
+| 0025 |[Reverse Nodes in k-Group](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0025_reverse_nodes_in_k_group)| Hard | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Linked_List, Recursion, Data_Structure_II_Day_13_Linked_List | 194 | 87.72
+| 0024 |[Swap Nodes in Pairs](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0024_swap_nodes_in_pairs)| Medium | Linked_List, Recursion, Data_Structure_II_Day_12_Linked_List | 173 | 83.13
+| 0023 |[Merge k Sorted Lists](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0023_merge_k_sorted_lists)| Hard | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Heap_Priority_Queue, Linked_List, Divide_and_Conquer, Merge_Sort | 323 | 75.14
+| 0022 |[Generate Parentheses](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0022_generate_parentheses)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, String, Dynamic_Programming, Backtracking, Algorithm_II_Day_11_Recursion_Backtracking | 210 | 78.51
+| 0021 |[Merge Two Sorted Lists](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0021_merge_two_sorted_lists)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Linked_List, Recursion, Data_Structure_I_Day_7_Linked_List, Algorithm_I_Day_10_Recursion_Backtracking | 148 | 99.90
+| 0020 |[Valid Parentheses](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0020_valid_parentheses)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, String, Stack, Data_Structure_I_Day_9_Stack_Queue | 196 | 71.08
+| 0019 |[Remove Nth Node From End of List](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0019_remove_nth_node_from_end_of_list)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Two_Pointers, Linked_List, Algorithm_I_Day_5_Two_Pointers | 172 | 85.17
+| 0018 |[4Sum](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0018_4sum)| Medium | Array, Sorting, Two_Pointers | 467 | 81.25
+| 0017 |[Letter Combinations of a Phone Number](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0017_letter_combinations_of_a_phone_number)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, String, Hash_Table, Backtracking, Algorithm_II_Day_11_Recursion_Backtracking | 132 | 100.00
+| 0016 |[3Sum Closest](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0016_3sum_closest)| Medium | Array, Sorting, Two_Pointers | 219 | 89.56
+| 0015 |[3Sum](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0015_3sum)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Sorting, Two_Pointers, Data_Structure_II_Day_1_Array, Algorithm_II_Day_3_Two_Pointers | 1059 | 55.28
+| 0014 |[Longest Common Prefix](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0014_longest_common_prefix)| Easy | Top_Interview_Questions, String | 269 | 48.51
+| 0013 |[Roman to Integer](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0013_roman_to_integer)| Easy | Top_Interview_Questions, String, Hash_Table, Math | 293 | 78.06
+| 0012 |[Integer to Roman](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0012_integer_to_roman)| Medium | String, Hash_Table, Math | 300 | 72.89
+| 0011 |[Container With Most Water](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0011_container_with_most_water)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Greedy, Two_Pointers, Algorithm_II_Day_4_Two_Pointers | 635 | 64.22
+| 0010 |[Regular Expression Matching](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0010_regular_expression_matching)| Hard | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, String, Dynamic_Programming, Recursion | 234 | 85.18
+| 0009 |[Palindrome Number](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0009_palindrome_number)| Easy | Math | 208 | 94.88
+| 0008 |[String to Integer (atoi)](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0008_string_to_integer_atoi)| Medium | Top_Interview_Questions, String | 152 | 99.64
+| 0007 |[Reverse Integer](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0007_reverse_integer)| Medium | Top_Interview_Questions, Math | 230 | 57.36
+| 0006 |[Zigzag Conversion](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0006_zigzag_conversion)| Medium | String | 351 | 78.99
+| 0005 |[Longest Palindromic Substring](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0005_longest_palindromic_substring)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, String, Dynamic_Programming, Data_Structure_II_Day_9_String, Algorithm_II_Day_14_Dynamic_Programming, Dynamic_Programming_I_Day_17 | 359 | 69.08
+| 0004 |[Median of Two Sorted Arrays](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0004_median_of_two_sorted_arrays)| Hard | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Binary_Search, Divide_and_Conquer | 276 | 91.12
+| 0003 |[Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0003_longest_substring_without_repeating_characters)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, String, Hash_Table, Sliding_Window, Algorithm_I_Day_6_Sliding_Window | 212 | 91.24
+| 0002 |[Add Two Numbers](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0002_add_two_numbers)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Math, Linked_List, Recursion, Data_Structure_II_Day_10_Linked_List, Programming_Skills_II_Day_15 | 212 | 93.71
+| 0001 |[Two Sum](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0001_two_sum)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Hash_Table, Data_Structure_I_Day_2_Array, Level_1_Day_13_Hashmap, Udemy_Arrays | 234 | 92.75
+
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0001_two_sum/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0001_two_sum/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0d6afa88
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0001_two_sum/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1\. Two Sum
+
+Easy
+
+Given an array of integers `nums` and an integer `target`, return _indices of the two numbers such that they add up to `target`_.
+
+You may assume that each input would have **_exactly_ one solution**, and you may not use the _same_ element twice.
+
+You can return the answer in any order.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9
+
+**Output:** [0,1]
+
+**Output:** Because nums[0] + nums[1] == 9, we return [0, 1].
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [3,2,4], target = 6
+
+**Output:** [1,2]
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [3,3], target = 6
+
+**Output:** [0,1]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 2 <= nums.length <= 104
+* -109 <= nums[i] <= 109
+* -109 <= target <= 109
+* **Only one valid answer exists.**
+
+**Follow-up:** Can you come up with an algorithm that is less than O(n2) time complexity?
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun twoSum(numbers: IntArray, target: Int): IntArray {
+ val indexMap: MutableMap = HashMap()
+ for (i in numbers.indices) {
+ val requiredNum = target - numbers[i]
+ if (indexMap.containsKey(requiredNum)) {
+ return intArrayOf(indexMap[requiredNum]!!, i)
+ }
+ indexMap[numbers[i]] = i
+ }
+ return intArrayOf(-1, -1)
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0002_add_two_numbers/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0002_add_two_numbers/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0e10de72
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0002_add_two_numbers/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 2\. Add Two Numbers
+
+Medium
+
+You are given two **non-empty** linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The digits are stored in **reverse order**, and each of their nodes contains a single digit. Add the two numbers and return the sum as a linked list.
+
+You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4]
+
+**Output:** [7,0,8]
+
+**Explanation:** 342 + 465 = 807.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** l1 = [0], l2 = [0]
+
+**Output:** [0]
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** l1 = [9,9,9,9,9,9,9], l2 = [9,9,9,9]
+
+**Output:** [8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* The number of nodes in each linked list is in the range `[1, 100]`.
+* `0 <= Node.val <= 9`
+* It is guaranteed that the list represents a number that does not have leading zeros.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import com_github_leetcode.ListNode
+
+/*
+ * Definition for singly-linked list.
+ * public class ListNode {
+ * int val;
+ * ListNode next;
+ * ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
+ * }
+ */
+class Solution {
+ fun addTwoNumbers(l1: ListNode?, l2: ListNode?): ListNode? {
+ val dummyHead = ListNode(0)
+ var p = l1
+ var q = l2
+ var curr: ListNode? = dummyHead
+ var carry = 0
+ while (p != null || q != null) {
+ val x = p?.`val` ?: 0
+ val y = q?.`val` ?: 0
+ val sum = carry + x + y
+ carry = sum / 10
+ curr!!.next = ListNode(sum % 10)
+ curr = curr.next
+ if (p != null) {
+ p = p.next
+ }
+ if (q != null) {
+ q = q.next
+ }
+ }
+ if (carry > 0) {
+ curr!!.next = ListNode(carry)
+ }
+ return dummyHead.next
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0003_longest_substring_without_repeating_characters/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0003_longest_substring_without_repeating_characters/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..232900a3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0003_longest_substring_without_repeating_characters/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 3\. Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters
+
+Medium
+
+Given a string `s`, find the length of the **longest substring** without repeating characters.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "abcabcbb"
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** The answer is "abc", with the length of 3.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "bbbbb"
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:** The answer is "b", with the length of 1.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** s = "pwwkew"
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** The answer is "wke", with the length of 3. Notice that the answer must be a substring, "pwke" is a subsequence and not a substring.
+
+**Example 4:**
+
+**Input:** s = ""
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 0 <= s.length <= 5 * 104
+* `s` consists of English letters, digits, symbols and spaces.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun lengthOfLongestSubstring(s: String): Int {
+ var i = 0
+ var j = 0
+ var longest = 0
+ // 1. if string empty, return 0
+ if (s.isEmpty()) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ while (j < s.length) {
+ // 2. if the char at index j already seen, update the longest if needs
+ if (i != j && s.substring(i, j).indexOf(s[j]) > -1) {
+ longest = Math.max(j - i, longest)
+ i++
+ } else {
+ // 3. j out of bound already, update longest
+ if (++j == s.length) {
+ longest = Math.max(s.length - i, longest)
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return longest
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0004_median_of_two_sorted_arrays/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0004_median_of_two_sorted_arrays/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f012edbd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0004_median_of_two_sorted_arrays/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 4\. Median of Two Sorted Arrays
+
+Hard
+
+Given two sorted arrays `nums1` and `nums2` of size `m` and `n` respectively, return **the median** of the two sorted arrays.
+
+The overall run time complexity should be `O(log (m+n))`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums1 = [1,3], nums2 = [2]
+
+**Output:** 2.00000
+
+**Explanation:** merged array = [1,2,3] and median is 2.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums1 = [1,2], nums2 = [3,4]
+
+**Output:** 2.50000
+
+**Explanation:** merged array = [1,2,3,4] and median is (2 + 3) / 2 = 2.5.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums1 = [0,0], nums2 = [0,0]
+
+**Output:** 0.00000
+
+**Example 4:**
+
+**Input:** nums1 = [], nums2 = [1]
+
+**Output:** 1.00000
+
+**Example 5:**
+
+**Input:** nums1 = [2], nums2 = []
+
+**Output:** 2.00000
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `nums1.length == m`
+* `nums2.length == n`
+* `0 <= m <= 1000`
+* `0 <= n <= 1000`
+* `1 <= m + n <= 2000`
+* -106 <= nums1[i], nums2[i] <= 106
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import kotlin.collections.ArrayList
+
+class Solution {
+ fun findMedianSortedArrays(nums1: IntArray, nums2: IntArray): Double {
+ val l: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ val f: Double
+ for (j in nums1) {
+ l.add(j)
+ }
+ for (i in nums2) {
+ l.add(i)
+ }
+ l.sort()
+ val k = l.size
+ f = if (k % 2 == 0) {
+ (l[k / 2 - 1] + l[k / 2]).toDouble() / 2
+ } else {
+ l[(k + 1) / 2 - 1].toDouble()
+ }
+ return f
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0005_longest_palindromic_substring/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0005_longest_palindromic_substring/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c8133a2b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0005_longest_palindromic_substring/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,75 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 5\. Longest Palindromic Substring
+
+Medium
+
+Given a string `s`, return _the longest palindromic substring_ in `s`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "babad"
+
+**Output:** "bab" **Note:** "aba" is also a valid answer.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "cbbd"
+
+**Output:** "bb"
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** s = "a"
+
+**Output:** "a"
+
+**Example 4:**
+
+**Input:** s = "ac"
+
+**Output:** "a"
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= s.length <= 1000`
+* `s` consist of only digits and English letters.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun longestPalindrome(s: String): String {
+ val newStr = CharArray(s.length * 2 + 1)
+ newStr[0] = '#'
+ for (i in s.indices) {
+ newStr[2 * i + 1] = s[i]
+ newStr[2 * i + 2] = '#'
+ }
+ val dp = IntArray(newStr.size)
+ var friendCenter = 0
+ var friendRadius = 0
+ var lpsCenter = 0
+ var lpsRadius = 0
+ for (i in newStr.indices) {
+ dp[i] = if (friendCenter + friendRadius > i) Math.min(
+ dp[friendCenter * 2 - i],
+ friendCenter + friendRadius - i
+ ) else 1
+ while (i + dp[i] < newStr.size && i - dp[i] >= 0 && newStr[i + dp[i]] == newStr[i - dp[i]]) {
+ dp[i]++
+ }
+ if (friendCenter + friendRadius < i + dp[i]) {
+ friendCenter = i
+ friendRadius = dp[i]
+ }
+ if (lpsRadius < dp[i]) {
+ lpsCenter = i
+ lpsRadius = dp[i]
+ }
+ }
+ return s.substring((lpsCenter - lpsRadius + 1) / 2, (lpsCenter + lpsRadius - 1) / 2)
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0006_zigzag_conversion/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0006_zigzag_conversion/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1e993367
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0006_zigzag_conversion/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,77 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 6\. Zigzag Conversion
+
+Medium
+
+The string `"PAYPALISHIRING"` is written in a zigzag pattern on a given number of rows like this: (you may want to display this pattern in a fixed font for better legibility)
+
+P A H N A P L S I I G Y I R
+
+And then read line by line: `"PAHNAPLSIIGYIR"`
+
+Write the code that will take a string and make this conversion given a number of rows:
+
+string convert(string s, int numRows);
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "PAYPALISHIRING", numRows = 3
+
+**Output:** "PAHNAPLSIIGYIR"
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "PAYPALISHIRING", numRows = 4
+
+**Output:** "PINALSIGYAHRPI"
+
+**Explanation:** P I N A L S I G Y A H R P I
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** s = "A", numRows = 1
+
+**Output:** "A"
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= s.length <= 1000`
+* `s` consists of English letters (lower-case and upper-case), `','` and `'.'`.
+* `1 <= numRows <= 1000`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun convert(s: String, numRows: Int): String {
+ val sLen = s.length
+ if (numRows == 1) {
+ return s
+ }
+ val maxDist = numRows * 2 - 2
+ val buf = StringBuilder()
+ for (i in 0 until numRows) {
+ var index = i
+ if (i == 0 || i == numRows - 1) {
+ while (index < sLen) {
+ buf.append(s[index])
+ index += maxDist
+ }
+ } else {
+ while (index < sLen) {
+ buf.append(s[index])
+ index += maxDist - i * 2
+ if (index >= sLen) {
+ break
+ }
+ buf.append(s[index])
+ index += i * 2
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return buf.toString()
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0007_reverse_integer/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0007_reverse_integer/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d0bd7f57
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0007_reverse_integer/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 7\. Reverse Integer
+
+Medium
+
+Given a signed 32-bit integer `x`, return `x` _with its digits reversed_. If reversing `x` causes the value to go outside the signed 32-bit integer range [-231, 231 - 1], then return `0`.
+
+**Assume the environment does not allow you to store 64-bit integers (signed or unsigned).**
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** x = 123
+
+**Output:** 321
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** x = -123
+
+**Output:** -321
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** x = 120
+
+**Output:** 21
+
+**Example 4:**
+
+**Input:** x = 0
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* -231 <= x <= 231 - 1
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun reverse(x: Int): Int {
+ var rev: Long = 0
+ var localX = x
+ while (localX != 0) {
+ rev = (rev * 10) + (localX % 10)
+ localX /= 10
+ }
+ if (rev > Integer.MAX_VALUE || rev < Integer.MIN_VALUE) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ return rev.toInt()
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0008_string_to_integer_atoi/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0008_string_to_integer_atoi/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1da64488
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0008_string_to_integer_atoi/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,160 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 8\. String to Integer (atoi)
+
+Medium
+
+Implement the `myAtoi(string s)` function, which converts a string to a 32-bit signed integer (similar to C/C++'s `atoi` function).
+
+The algorithm for `myAtoi(string s)` is as follows:
+
+1. Read in and ignore any leading whitespace.
+2. Check if the next character (if not already at the end of the string) is `'-'` or `'+'`. Read this character in if it is either. This determines if the final result is negative or positive respectively. Assume the result is positive if neither is present.
+3. Read in next the characters until the next non-digit character or the end of the input is reached. The rest of the string is ignored.
+4. Convert these digits into an integer (i.e. `"123" -> 123`, `"0032" -> 32`). If no digits were read, then the integer is `0`. Change the sign as necessary (from step 2).
+5. If the integer is out of the 32-bit signed integer range [-231, 231 - 1], then clamp the integer so that it remains in the range. Specifically, integers less than -231 should be clamped to -231, and integers greater than 231 - 1 should be clamped to 231 - 1.
+6. Return the integer as the final result.
+
+**Note:**
+
+* Only the space character `' '` is considered a whitespace character.
+* **Do not ignore** any characters other than the leading whitespace or the rest of the string after the digits.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "42"
+
+**Output:** 42
+
+**Explanation:** The underlined characters are what is read in, the caret is the current reader position.
+
+ Step 1: "42" (no characters read because there is no leading whitespace)
+ ^
+ Step 2: "42" (no characters read because there is neither a '-' nor '+')
+ ^
+ Step 3: "42" ("42" is read in)
+ ^
+
+The parsed integer is 42. Since 42 is in the range [-231, 231 - 1], the final result is 42.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = " -42"
+
+**Output:** -42
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+ Step 1: " -42" (leading whitespace is read and ignored)
+ ^
+ Step 2: " -42" ('-' is read, so the result should be negative)
+ ^
+ Step 3: " -42" ("42" is read in)
+ ^
+ The parsed integer is -42.
+
+Since -42 is in the range [-231, 231 - 1], the final result is -42.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** s = "4193 with words"
+
+**Output:** 4193
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+ Step 1: "4193 with words" (no characters read because there is no leading whitespace)
+ ^
+ Step 2: "4193 with words" (no characters read because there is neither a '-' nor '+')
+ ^
+ Step 3: "4193 with words" ("4193" is read in; reading stops because the next character is a non-digit)
+ ^
+ The parsed integer is 4193.
+
+Since 4193 is in the range [-231, 231 - 1], the final result is 4193.
+
+**Example 4:**
+
+**Input:** s = "words and 987"
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+ Step 1: "words and 987" (no characters read because there is no leading whitespace)
+ ^
+ Step 2: "words and 987" (no characters read because there is neither a '-' nor '+')
+ ^
+ Step 3: "words and 987" (reading stops immediately because there is a non-digit 'w')
+ ^
+ The parsed integer is 0 because no digits were read.
+
+Since 0 is in the range [-231, 231 - 1], the final result is 0.
+
+**Example 5:**
+
+**Input:** s = "-91283472332"
+
+**Output:** -2147483648
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+ Step 1: "-91283472332" (no characters read because there is no leading whitespace)
+ ^
+ Step 2: "-91283472332" ('-' is read, so the result should be negative)
+ ^
+ Step 3: "-91283472332" ("91283472332" is read in)
+ ^
+ The parsed integer is -91283472332.
+
+Since -91283472332 is less than the lower bound of the range [-231, 231 - 1], the final result is clamped to -231 = -2147483648.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `0 <= s.length <= 200`
+* `s` consists of English letters (lower-case and upper-case), digits (`0-9`), `' '`, `'+'`, `'-'`, and `'.'`.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun myAtoi(str: String?): Int {
+ if (str.isNullOrEmpty()) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ var i = 0
+ var negativeSign = false
+ val input = str.toCharArray()
+ while (i < input.size && input[i] == ' ') {
+ i++
+ }
+ if (i == input.size) {
+ return 0
+ } else if (input[i] == '+') {
+ i++
+ } else if (input[i] == '-') {
+ i++
+ negativeSign = true
+ }
+ var num = 0
+ while (i < input.size && input[i] <= '9' && input[i] >= '0') {
+ // current char
+ var tem = input[i] - '0'
+ tem = if (negativeSign) -tem else tem
+ // avoid invalid number like 038
+ if (num == 0 && tem == '0'.code) {
+ i++
+ } else if (num == Int.MIN_VALUE / 10 && tem <= -8 || num < Int.MIN_VALUE / 10) {
+ return Int.MIN_VALUE
+ } else if (num == Int.MAX_VALUE / 10 && tem >= 7 || num > Int.MAX_VALUE / 10) {
+ return Int.MAX_VALUE
+ } else {
+ num = num * 10 + tem
+ i++
+ }
+ }
+ return num
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0009_palindrome_number/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0009_palindrome_number/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2d80eda5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0009_palindrome_number/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 9\. Palindrome Number
+
+Easy
+
+Given an integer `x`, return `true` if `x` is palindrome integer.
+
+An integer is a **palindrome** when it reads the same backward as forward. For example, `121` is palindrome while `123` is not.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** x = 121
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** x = -121
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Explanation:** From left to right, it reads -121. From right to left, it becomes 121-. Therefore it is not a palindrome.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** x = 10
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Explanation:** Reads 01 from right to left. Therefore it is not a palindrome.
+
+**Example 4:**
+
+**Input:** x = -101
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* -231 <= x <= 231 - 1
+
+**Follow up:** Could you solve it without converting the integer to a string?
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun isPalindrome(x: Int): Boolean {
+ if (x < 0) return false
+ var rev = 0
+ var localX = x
+ while (localX > 0) {
+ rev *= 10
+ rev += localX % 10
+ localX /= 10
+ }
+ return rev == x
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0010_regular_expression_matching/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0010_regular_expression_matching/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..322f8e12
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0010_regular_expression_matching/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,100 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 10\. Regular Expression Matching
+
+Hard
+
+Given an input string `s` and a pattern `p`, implement regular expression matching with support for `'.'` and `'*'` where:
+
+* `'.'` Matches any single character.
+* `'*'` Matches zero or more of the preceding element.
+
+The matching should cover the **entire** input string (not partial).
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "aa", p = "a"
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Explanation:** "a" does not match the entire string "aa".
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "aa", p = "a\*"
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** '\*' means zero or more of the preceding element, 'a'. Therefore, by repeating 'a' once, it becomes "aa".
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** s = "ab", p = ".\*"
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** ".\*" means "zero or more (\*) of any character (.)".
+
+**Example 4:**
+
+**Input:** s = "aab", p = "c\*a\*b"
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** c can be repeated 0 times, a can be repeated 1 time. Therefore, it matches "aab".
+
+**Example 5:**
+
+**Input:** s = "mississippi", p = "mis\*is\*p\*."
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= s.length <= 20`
+* `1 <= p.length <= 30`
+* `s` contains only lowercase English letters.
+* `p` contains only lowercase English letters, `'.'`, and `'*'`.
+* It is guaranteed for each appearance of the character `'*'`, there will be a previous valid character to match.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun isMatch(s: String, p: String): Boolean {
+ val n = s.length
+ val m = p.length
+ return solve(n - 1, m - 1, s, p)
+ }
+
+ private fun solve(i: Int, j: Int, s: String, p: String): Boolean {
+ if (j < 0) {
+ return i < 0
+ }
+ if (i < 0) {
+ return p[j] == '*' && solve(i, j - 2, s, p)
+ }
+ // simple char matching
+ // if s char matchs with p char or it can be '.'
+ if (s[i] == p[j] || p[j] == '.') {
+ return solve(i - 1, j - 1, s, p)
+ }
+ return if (p[j] == '*') {
+ // if s char matches with p char or it can be '.'
+ if (s[i] == p[j - 1] || p[j - 1] == '.') {
+ solve(i - 1, j, s, p) || solve(i, j - 2, s, p)
+ } else {
+ solve(
+ i,
+ j - 2,
+ s,
+ p
+ )
+ }
+ } else {
+ false
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0011_container_with_most_water/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0011_container_with_most_water/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..53a05a4a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0011_container_with_most_water/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 11\. Container With Most Water
+
+Medium
+
+Given `n` non-negative integers a1, a2, ..., an , where each represents a point at coordinate (i, ai). `n` vertical lines are drawn such that the two endpoints of the line `i` is at (i, ai) and `(i, 0)`. Find two lines, which, together with the x-axis forms a container, such that the container contains the most water.
+
+**Notice** that you may not slant the container.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** height = [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]
+
+**Output:** 49
+
+**Explanation:** The above vertical lines are represented by array [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]. In this case, the max area of water (blue section) the container can contain is 49.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** height = [1,1]
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** height = [4,3,2,1,4]
+
+**Output:** 16
+
+**Example 4:**
+
+**Input:** height = [1,2,1]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `n == height.length`
+* 2 <= n <= 105
+* 0 <= height[i] <= 104
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun maxArea(height: IntArray): Int {
+ var max = 0
+ if (height.isNotEmpty()) {
+ var left = 0
+ var right = height.size - 1
+ while (left < right) {
+ // next two if conditions are to make sure there are two non-zero containers to
+ // hold water. If not move next to find one
+ if (height[left] == 0) {
+ left++
+ continue
+ }
+ if (height[right] == 0) {
+ right--
+ continue
+ }
+ // if control came here that means left and right containers are non zero and
+ // can hold water. Get the count of containers and multiple by lower container
+ if (height[left] < height[right]) {
+ max = Math.max(max, (right - left) * height[left])
+ left++
+ } else {
+ max = Math.max(max, (right - left) * height[right])
+ right--
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return max
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0012_integer_to_roman/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0012_integer_to_roman/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..5fe24d14
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0012_integer_to_roman/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,126 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 12\. Integer to Roman
+
+Medium
+
+Roman numerals are represented by seven different symbols: `I`, `V`, `X`, `L`, `C`, `D` and `M`.
+
+ Symbol Value
+ I 1
+ V 5
+ X 10
+ L 50
+ C 100
+ D 500
+ M 1000
+
+For example, `2` is written as `II` in Roman numeral, just two one's added together. `12` is written as `XII`, which is simply `X + II`. The number `27` is written as `XXVII`, which is `XX + V + II`.
+
+Roman numerals are usually written largest to smallest from left to right. However, the numeral for four is not `IIII`. Instead, the number four is written as `IV`. Because the one is before the five we subtract it making four. The same principle applies to the number nine, which is written as `IX`. There are six instances where subtraction is used:
+
+* `I` can be placed before `V` (5) and `X` (10) to make 4 and 9.
+* `X` can be placed before `L` (50) and `C` (100) to make 40 and 90.
+* `C` can be placed before `D` (500) and `M` (1000) to make 400 and 900.
+
+Given an integer, convert it to a roman numeral.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** num = 3
+
+**Output:** "III"
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** num = 4
+
+**Output:** "IV"
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** num = 9
+
+**Output:** "IX"
+
+**Example 4:**
+
+**Input:** num = 58
+
+**Output:** "LVIII"
+
+**Explanation:** L = 50, V = 5, III = 3.
+
+**Example 5:**
+
+**Input:** num = 1994
+
+**Output:** "MCMXCIV"
+
+**Explanation:** M = 1000, CM = 900, XC = 90 and IV = 4.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= num <= 3999`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun intToRoman(num: Int): String? {
+ var localNum = num
+ val sb = StringBuilder()
+ val m = 1000
+ val c = 100
+ val x = 10
+ val i = 1
+ localNum = numerals(sb, localNum, m, ' ', ' ', 'M')
+ localNum = numerals(sb, localNum, c, 'M', 'D', 'C')
+ localNum = numerals(sb, localNum, x, 'C', 'L', 'X')
+ numerals(sb, localNum, i, 'X', 'V', 'I')
+ return sb.toString()
+ }
+
+ private fun numerals(sb: StringBuilder, num: Int, one: Int, cTen: Char, cFive: Char, cOne: Char): Int {
+ val div = num / one
+ when (div) {
+ 9 -> {
+ sb.append(cOne)
+ sb.append(cTen)
+ }
+ 8 -> {
+ sb.append(cFive)
+ sb.append(cOne)
+ sb.append(cOne)
+ sb.append(cOne)
+ }
+ 7 -> {
+ sb.append(cFive)
+ sb.append(cOne)
+ sb.append(cOne)
+ }
+ 6 -> {
+ sb.append(cFive)
+ sb.append(cOne)
+ }
+ 5 -> sb.append(cFive)
+ 4 -> {
+ sb.append(cOne)
+ sb.append(cFive)
+ }
+ 3 -> {
+ sb.append(cOne)
+ sb.append(cOne)
+ sb.append(cOne)
+ }
+ 2 -> {
+ sb.append(cOne)
+ sb.append(cOne)
+ }
+ 1 -> sb.append(cOne)
+ }
+ return num - div * one
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0013_roman_to_integer/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0013_roman_to_integer/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c78ae2ca
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0013_roman_to_integer/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,105 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 13\. Roman to Integer
+
+Easy
+
+Roman numerals are represented by seven different symbols: `I`, `V`, `X`, `L`, `C`, `D` and `M`.
+
+ Symbol Value
+ I 1
+ V 5
+ X 10
+ L 50
+ C 100
+ D 500
+ M 1000
+
+For example, `2` is written as `II` in Roman numeral, just two one's added together. `12` is written as `XII`, which is simply `X + II`. The number `27` is written as `XXVII`, which is `XX + V + II`.
+
+Roman numerals are usually written largest to smallest from left to right. However, the numeral for four is not `IIII`. Instead, the number four is written as `IV`. Because the one is before the five we subtract it making four. The same principle applies to the number nine, which is written as `IX`. There are six instances where subtraction is used:
+
+* `I` can be placed before `V` (5) and `X` (10) to make 4 and 9.
+* `X` can be placed before `L` (50) and `C` (100) to make 40 and 90.
+* `C` can be placed before `D` (500) and `M` (1000) to make 400 and 900.
+
+Given a roman numeral, convert it to an integer.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "III"
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "IV"
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** s = "IX"
+
+**Output:** 9
+
+**Example 4:**
+
+**Input:** s = "LVIII"
+
+**Output:** 58
+
+**Explanation:** L = 50, V= 5, III = 3.
+
+**Example 5:**
+
+**Input:** s = "MCMXCIV"
+
+**Output:** 1994
+
+**Explanation:** M = 1000, CM = 900, XC = 90 and IV = 4.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= s.length <= 15`
+* `s` contains only the characters `('I', 'V', 'X', 'L', 'C', 'D', 'M')`.
+* It is **guaranteed** that `s` is a valid roman numeral in the range `[1, 3999]`.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun romanToInt(s: String): Int {
+ var x = 0
+ var y: Char
+ for (i in s.indices) {
+ y = s[i]
+ when (y) {
+ 'I' -> x = getX(s, x, i, 1, 'V', 'X')
+ 'V' -> x += 5
+ 'X' -> x = getX(s, x, i, 10, 'L', 'C')
+ 'L' -> x += 50
+ 'C' -> x = getX(s, x, i, 100, 'D', 'M')
+ 'D' -> x += 500
+ 'M' -> x += 1000
+ }
+ }
+ return x
+ }
+
+ private fun getX(s: String, x: Int, i: Int, i2: Int, v: Char, x2: Char): Int {
+ var localX = x
+ if (i + 1 == s.length) {
+ localX += i2
+ } else if (s[i + 1] == v) {
+ localX -= i2
+ } else if (s[i + 1] == x2) {
+ localX -= i2
+ } else {
+ localX += i2
+ }
+ return localX
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0014_longest_common_prefix/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0014_longest_common_prefix/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e11612ad
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0014_longest_common_prefix/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 14\. Longest Common Prefix
+
+Easy
+
+Write a function to find the longest common prefix string amongst an array of strings.
+
+If there is no common prefix, return an empty string `""`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** strs = ["flower","flow","flight"]
+
+**Output:** "fl"
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** strs = ["dog","racecar","car"]
+
+**Output:** ""
+
+**Explanation:** There is no common prefix among the input strings.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= strs.length <= 200`
+* `0 <= strs[i].length <= 200`
+* `strs[i]` consists of only lower-case English letters.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun longestCommonPrefix(strs: Array): String {
+ if (strs.isEmpty()) {
+ return ""
+ }
+ if (strs.size == 1) {
+ return strs[0]
+ }
+ var temp = strs[0]
+ var i = 1
+ var cur: String
+ while (temp.length > 0 && i < strs.size) {
+ if (temp.length > strs[i].length) {
+ temp = temp.substring(0, strs[i].length)
+ }
+ cur = strs[i].substring(0, temp.length)
+ if (cur != temp) {
+ temp = temp.substring(0, temp.length - 1)
+ } else {
+ i++
+ }
+ }
+ return temp
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0015_3sum/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0015_3sum/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..03b85e4b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0015_3sum/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,82 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 15\. 3Sum
+
+Medium
+
+Given an integer array nums, return all the triplets `[nums[i], nums[j], nums[k]]` such that `i != j`, `i != k`, and `j != k`, and `nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k] == 0`.
+
+Notice that the solution set must not contain duplicate triplets.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [-1,0,1,2,-1,-4]
+
+**Output:** [[-1,-1,2],[-1,0,1]]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = []
+
+**Output:** []
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [0]
+
+**Output:** []
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `0 <= nums.length <= 3000`
+* -105 <= nums[i] <= 105
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.Arrays
+import kotlin.collections.ArrayList
+
+class Solution {
+ fun threeSum(nums: IntArray): List> {
+ Arrays.sort(nums)
+ val len = nums.size
+ val result: MutableList> = ArrayList()
+ var l: Int
+ var r: Int
+ var i = 0
+ while (i < len - 2) {
+ l = i + 1
+ r = len - 1
+ while (r > l) {
+ val sum = nums[i] + nums[l] + nums[r]
+ if (sum < 0) {
+ l++
+ } else if (sum > 0) {
+ r--
+ } else {
+ val list: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ list.add(nums[i])
+ list.add(nums[l])
+ list.add(nums[r])
+ result.add(list)
+ while (l < r && nums[l + 1] == nums[l]) {
+ l++
+ }
+ while (r > l && nums[r - 1] == nums[r]) {
+ r--
+ }
+ l++
+ r--
+ }
+ }
+ while (i < len - 1 && nums[i + 1] == nums[i]) {
+ i++
+ }
+ i++
+ }
+ return result
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0016_3sum_closest/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0016_3sum_closest/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a80dc861
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0016_3sum_closest/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 16\. 3Sum Closest
+
+Medium
+
+Given an integer array `nums` of length `n` and an integer `target`, find three integers in `nums` such that the sum is closest to `target`.
+
+Return _the sum of the three integers_.
+
+You may assume that each input would have exactly one solution.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [-1,2,1,-4], target = 1
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** The sum that is closest to the target is 2. (-1 + 2 + 1 = 2).
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [0,0,0], target = 1
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `3 <= nums.length <= 1000`
+* `-1000 <= nums[i] <= 1000`
+* -104 <= target <= 104
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.Arrays
+
+class Solution {
+ fun threeSumClosest(nums: IntArray?, target: Int): Int {
+ if (nums == null || nums.size < 3) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ if (nums.size == 3) {
+ return nums[0] + nums[1] + nums[2]
+ }
+ Arrays.sort(nums)
+ val n = nums.size
+ var sum = nums[0] + nums[1] + nums[2]
+ for (i in 0 until n - 2) {
+ if (nums[i] + nums[n - 1] + nums[n - 2] < target) {
+ sum = nums[i] + nums[n - 1] + nums[n - 2]
+ continue
+ }
+ if (nums[i] + nums[i + 1] + nums[i + 2] > target) {
+ val temp = nums[i] + nums[i + 1] + nums[i + 2]
+ return lessGap(sum, temp, target)
+ }
+ var j = i + 1
+ var k = n - 1
+ while (j < k) {
+ val temp = nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k]
+ if (temp == target) {
+ return target
+ }
+ if (temp < target) {
+ j++
+ } else {
+ k--
+ }
+ sum = lessGap(sum, temp, target)
+ }
+ }
+ return sum
+ }
+
+ private fun lessGap(sum: Int, temp: Int, target: Int): Int {
+ return if (Math.abs(sum - target) < Math.abs(temp - target)) sum else temp
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0017_letter_combinations_of_a_phone_number/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0017_letter_combinations_of_a_phone_number/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0a4ff4db
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0017_letter_combinations_of_a_phone_number/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 17\. Letter Combinations of a Phone Number
+
+Medium
+
+Given a string containing digits from `2-9` inclusive, return all possible letter combinations that the number could represent. Return the answer in **any order**.
+
+A mapping of digit to letters (just like on the telephone buttons) is given below. Note that 1 does not map to any letters.
+
+
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** digits = "23"
+
+**Output:** ["ad","ae","af","bd","be","bf","cd","ce","cf"]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** digits = ""
+
+**Output:** []
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** digits = "2"
+
+**Output:** ["a","b","c"]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `0 <= digits.length <= 4`
+* `digits[i]` is a digit in the range `['2', '9']`.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun letterCombinations(digits: String): List {
+ if (digits.isEmpty()) return ArrayList()
+ val letters = arrayOf("", "", "abc", "def", "ghi", "jkl", "mno", "pqrs", "tuv", "wxyz")
+ val ans: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ val sb = StringBuilder()
+ findCombinations(0, digits, letters, sb, ans)
+ return ans
+ }
+
+ private fun findCombinations(
+ start: Int,
+ nums: String,
+ letters: Array,
+ curr: StringBuilder,
+ ans: MutableList
+ ) {
+ if (curr.length == nums.length) {
+ ans.add(curr.toString())
+ return
+ }
+ for (i in start until nums.length) {
+ val n = Character.getNumericValue(nums[i])
+ for (j in 0 until letters[n].length) {
+ val ch = letters[n][j]
+ curr.append(ch)
+ findCombinations(i + 1, nums, letters, curr, ans)
+ curr.deleteCharAt(curr.length - 1)
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0018_4sum/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0018_4sum/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..53515e69
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0018_4sum/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,87 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 18\. 4Sum
+
+Medium
+
+Given an array `nums` of `n` integers, return _an array of all the **unique** quadruplets_ `[nums[a], nums[b], nums[c], nums[d]]` such that:
+
+* `0 <= a, b, c, d < n`
+* `a`, `b`, `c`, and `d` are **distinct**.
+* `nums[a] + nums[b] + nums[c] + nums[d] == target`
+
+You may return the answer in **any order**.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,0,-1,0,-2,2], target = 0
+
+**Output:** [[-2,-1,1,2],[-2,0,0,2],[-1,0,0,1]]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [2,2,2,2,2], target = 8
+
+**Output:** [[2,2,2,2]]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= nums.length <= 200`
+* -109 <= nums[i] <= 109
+* -109 <= target <= 109
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.Arrays
+
+class Solution {
+ fun fourSum(nums: IntArray, target: Int): List?> {
+ var list: MutableList?> = ArrayList()
+ var j: Int
+ var k: Int
+ var l: Int
+ Arrays.sort(nums)
+ var i: Int = 0
+ while (i < nums.size - 3) {
+ if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) {
+ i++
+ continue
+ }
+ j = i + 1
+ while (j < nums.size - 2) {
+ if (j > i + 1 && nums[j] == nums[j - 1]) {
+ j++
+ continue
+ }
+ k = j + 1
+ l = nums.size - 1
+ while (k < l) {
+ val sum = nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k] + nums[l]
+ if (sum == target) {
+ val l1 = ArrayList()
+ l1.add(nums[i])
+ l1.add(nums[j])
+ l1.add(nums[k])
+ l1.add(nums[l])
+ list.add(l1)
+ l--
+ if (k < l && nums[l] == nums[l + 1]) {
+ l--
+ }
+ } else if (sum > target) {
+ l--
+ } else {
+ k++
+ }
+ }
+ j++
+ }
+ i++
+ }
+ list = ArrayList(LinkedHashSet(list))
+ return list
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0019_remove_nth_node_from_end_of_list/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0019_remove_nth_node_from_end_of_list/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..83e130e2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0019_remove_nth_node_from_end_of_list/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,74 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 19\. Remove Nth Node From End of List
+
+Medium
+
+Given the `head` of a linked list, remove the `nth` node from the end of the list and return its head.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2
+
+**Output:** [1,2,3,5]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** head = [1], n = 1
+
+**Output:** []
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** head = [1,2], n = 1
+
+**Output:** [1]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* The number of nodes in the list is `sz`.
+* `1 <= sz <= 30`
+* `0 <= Node.val <= 100`
+* `1 <= n <= sz`
+
+**Follow up:** Could you do this in one pass?
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import com_github_leetcode.ListNode
+
+/*
+ * Example:
+ * var li = ListNode(5)
+ * var v = li.`val`
+ * Definition for singly-linked list.
+ * class ListNode(var `val`: Int) {
+ * var next: ListNode? = null
+ * }
+ */
+class Solution {
+ private var n = 0
+
+ fun removeNthFromEnd(head: ListNode?, n: Int): ListNode? {
+ this.n = n
+ val node = ListNode(0, head)
+ removeNth(node)
+ return node.next
+ }
+
+ private fun removeNth(node: ListNode?) {
+ if (node?.next == null) {
+ return
+ }
+ removeNth(node.next)
+ n--
+ if (n == 0) {
+ node.next = node.next?.next
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0020_valid_parentheses/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0020_valid_parentheses/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e85d23b1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0020_valid_parentheses/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,75 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 20\. Valid Parentheses
+
+Easy
+
+Given a string `s` containing just the characters `'('`, `')'`, `'{'`, `'}'`, `'['` and `']'`, determine if the input string is valid.
+
+An input string is valid if:
+
+1. Open brackets must be closed by the same type of brackets.
+2. Open brackets must be closed in the correct order.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "()"
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "()[]{}"
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** s = "(]"
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Example 4:**
+
+**Input:** s = "([)]"
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Example 5:**
+
+**Input:** s = "{[]}"
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= s.length <= 104
+* `s` consists of parentheses only `'()[]{}'`.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.Stack
+
+class Solution {
+ fun isValid(s: String): Boolean {
+ val stack = Stack()
+ for (element in s) {
+ val c = element
+ if (c == '(' || c == '[' || c == '{') {
+ stack.push(c)
+ } else if (c == ')' && !stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() == '(') {
+ stack.pop()
+ } else if (c == '}' && !stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() == '{') {
+ stack.pop()
+ } else if (c == ']' && !stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() == '[') {
+ stack.pop()
+ } else {
+ return false
+ }
+ }
+ return stack.isEmpty()
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0021_merge_two_sorted_lists/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0021_merge_two_sorted_lists/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a509760d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0021_merge_two_sorted_lists/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,77 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 21\. Merge Two Sorted Lists
+
+Easy
+
+Merge two sorted linked lists and return it as a **sorted** list. The list should be made by splicing together the nodes of the first two lists.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4]
+
+**Output:** [1,1,2,3,4,4]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** l1 = [], l2 = []
+
+**Output:** []
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** l1 = [], l2 = [0]
+
+**Output:** [0]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* The number of nodes in both lists is in the range `[0, 50]`.
+* `-100 <= Node.val <= 100`
+* Both `l1` and `l2` are sorted in **non-decreasing** order.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import com_github_leetcode.ListNode
+
+/*
+ * Example:
+ * var li = ListNode(5)
+ * var v = li.`val`
+ * Definition for singly-linked list.
+ * class ListNode(var `val`: Int) {
+ * var next: ListNode? = null
+ * }
+ */
+class Solution {
+ fun mergeTwoLists(list1: ListNode?, list2: ListNode?): ListNode? {
+ var l1 = list1
+ var l2 = list2
+ var list: ListNode? = ListNode(-1)
+ val head = list
+ while (l1 != null || l2 != null) {
+ if (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
+ if (l1.`val` <= l2.`val`) {
+ list!!.next = ListNode(l1.`val`)
+ l1 = l1.next
+ } else {
+ list!!.next = ListNode(l2.`val`)
+ l2 = l2.next
+ }
+ } else if (l1 != null) {
+ list!!.next = ListNode(l1.`val`)
+ l1 = l1.next
+ } else {
+ list!!.next = ListNode(l2!!.`val`)
+ l2 = l2.next
+ }
+ list = list.next
+ }
+ return head!!.next
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0022_generate_parentheses/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0022_generate_parentheses/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..4abef88b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0022_generate_parentheses/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 22\. Generate Parentheses
+
+Medium
+
+Given `n` pairs of parentheses, write a function to _generate all combinations of well-formed parentheses_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 3
+
+**Output:** ["((()))","(()())","(())()","()(())","()()()"]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 1
+
+**Output:** ["()"]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= n <= 8`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun generateParenthesis(n: Int): List {
+ val sb = StringBuilder()
+ val ans: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ return generate(sb, ans, n, n)
+ }
+
+ private fun generate(sb: StringBuilder, str: MutableList, open: Int, close: Int): List {
+ if (open == 0 && close == 0) {
+ str.add(sb.toString())
+ return str
+ }
+ if (open > 0) {
+ sb.append('(')
+ generate(sb, str, open - 1, close)
+ sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length - 1)
+ }
+ if (close > 0 && open < close) {
+ sb.append(')')
+ generate(sb, str, open, close - 1)
+ sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length - 1)
+ }
+ return str
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0023_merge_k_sorted_lists/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0023_merge_k_sorted_lists/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..98dd7386
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0023_merge_k_sorted_lists/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,103 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 23\. Merge k Sorted Lists
+
+Hard
+
+You are given an array of `k` linked-lists `lists`, each linked-list is sorted in ascending order.
+
+_Merge all the linked-lists into one sorted linked-list and return it._
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** lists = \[\[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]]
+
+**Output:** [1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6]
+
+**Explanation:** The linked-lists are: [ 1->4->5, 1->3->4, 2->6 ] merging them into one sorted list: 1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** lists = []
+
+**Output:** []
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** lists = \[\[]]
+
+**Output:** []
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `k == lists.length`
+* `0 <= k <= 10^4`
+* `0 <= lists[i].length <= 500`
+* `-10^4 <= lists[i][j] <= 10^4`
+* `lists[i]` is sorted in **ascending order**.
+* The sum of `lists[i].length` won't exceed `10^4`.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import com_github_leetcode.ListNode
+
+class Solution {
+ fun mergeKLists(lists: Array): ListNode? {
+ return if (lists.isEmpty()) {
+ null
+ } else mergeKLists(lists, 0, lists.size)
+ }
+
+ private fun mergeKLists(lists: Array, leftIndex: Int, rightIndex: Int): ListNode? {
+ return if (rightIndex > leftIndex + 1) {
+ val mid = (leftIndex + rightIndex) / 2
+ val left = mergeKLists(lists, leftIndex, mid)
+ val right = mergeKLists(lists, mid, rightIndex)
+ mergeTwoLists(left, right)
+ } else {
+ lists[leftIndex]
+ }
+ }
+
+ private fun mergeTwoLists(leftLocal: ListNode?, rightLocal: ListNode?): ListNode? {
+ var left = leftLocal
+ var right = rightLocal
+ if (left == null) {
+ return right
+ }
+ if (right == null) {
+ return left
+ }
+ val res: ListNode
+ if (left.`val` <= right.`val`) {
+ res = left
+ left = left.next
+ } else {
+ res = right
+ right = right.next
+ }
+ var node: ListNode? = res
+ while (left != null || right != null) {
+ if (left == null) {
+ node!!.next = right
+ right = right!!.next
+ } else if (right == null) {
+ node!!.next = left
+ left = left.next
+ } else {
+ if (left.`val` <= right.`val`) {
+ node!!.next = left
+ left = left.next
+ } else {
+ node!!.next = right
+ right = right.next
+ }
+ }
+ node = node.next
+ }
+ return res
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0024_swap_nodes_in_pairs/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0024_swap_nodes_in_pairs/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..6bd1783c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0024_swap_nodes_in_pairs/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 24\. Swap Nodes in Pairs
+
+Medium
+
+Given a linked list, swap every two adjacent nodes and return its head. You must solve the problem without modifying the values in the list's nodes (i.e., only nodes themselves may be changed.)
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** head = [1,2,3,4]
+
+**Output:** [2,1,4,3]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** head = []
+
+**Output:** []
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** head = [1]
+
+**Output:** [1]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* The number of nodes in the list is in the range `[0, 100]`.
+* `0 <= Node.val <= 100`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import com_github_leetcode.ListNode
+
+class Solution {
+ fun swapPairs(head: ListNode?): ListNode? {
+ if (head == null) {
+ return null
+ }
+ val len = getLength(head)
+ return reverse(head, len)
+ }
+
+ private fun getLength(currLocal: ListNode): Int {
+ var curr: ListNode? = currLocal
+ var cnt = 0
+ while (curr != null) {
+ cnt++
+ curr = curr.next
+ }
+ return cnt
+ }
+
+ // Recursive function to reverse in groups
+ private fun reverse(head: ListNode?, len: Int): ListNode? {
+ // base case
+ if (len < 2) {
+ return head
+ }
+ var curr = head
+ var prev: ListNode? = null
+ var next: ListNode?
+ for (i in 0..1) {
+ // reverse linked list code
+ next = curr!!.next
+ curr.next = prev
+ prev = curr
+ curr = next
+ }
+ head!!.next = reverse(curr, len - 2)
+ return prev
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0025_reverse_nodes_in_k_group/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0025_reverse_nodes_in_k_group/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..9d4a745c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0025_reverse_nodes_in_k_group/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 25\. Reverse Nodes in k-Group
+
+Hard
+
+Given a linked list, reverse the nodes of a linked list _k_ at a time and return its modified list.
+
+_k_ is a positive integer and is less than or equal to the length of the linked list. If the number of nodes is not a multiple of _k_ then left-out nodes, in the end, should remain as it is.
+
+You may not alter the values in the list's nodes, only nodes themselves may be changed.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2
+
+**Output:** [2,1,4,3,5]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 3
+
+**Output:** [3,2,1,4,5]
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 1
+
+**Output:** [1,2,3,4,5]
+
+**Example 4:**
+
+**Input:** head = [1], k = 1
+
+**Output:** [1]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* The number of nodes in the list is in the range `sz`.
+* `1 <= sz <= 5000`
+* `0 <= Node.val <= 1000`
+* `1 <= k <= sz`
+
+**Follow-up:** Can you solve the problem in O(1) extra memory space?
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import com_github_leetcode.ListNode
+
+class Solution {
+ fun reverseKGroup(head: ListNode?, k: Int): ListNode? {
+ if (head?.next == null || k == 1) {
+ return head
+ }
+ var j = 0
+ var len = head
+ // loop for checking the length of the linklist, if the linklist is less than k, then return
+ // as it is.
+ while (j < k) {
+ if (len == null) {
+ return head
+ }
+ len = len.next
+ j++
+ }
+ // Reverse linked list logic applied here.
+ var c = head
+ var n: ListNode? = null
+ var prev: ListNode? = null
+ var i = 0
+ // Traverse the while loop for K times to reverse the node in K groups.
+ while (i != k) {
+ n = c!!.next
+ c.next = prev
+ prev = c
+ c = n
+ i++
+ }
+ // C1 is pointing to 1st node of K group, which is now going to point to the next K group
+ // linklist.
+ // recursion, for futher remaining linked list.
+ head.next = reverseKGroup(n, k)
+ return prev
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0026_remove_duplicates_from_sorted_array/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0026_remove_duplicates_from_sorted_array/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..adb085c4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0026_remove_duplicates_from_sorted_array/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,75 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 26\. Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array
+
+Easy
+
+Given an integer array `nums` sorted in **non-decreasing order**, remove the duplicates [**in-place**](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/In-place_algorithm) such that each unique element appears only **once**. The **relative order** of the elements should be kept the **same**.
+
+Since it is impossible to change the length of the array in some languages, you must instead have the result be placed in the **first part** of the array `nums`. More formally, if there are `k` elements after removing the duplicates, then the first `k` elements of `nums` should hold the final result. It does not matter what you leave beyond the first `k` elements.
+
+Return `k` _after placing the final result in the first_ `k` _slots of_ `nums`.
+
+Do **not** allocate extra space for another array. You must do this by **modifying the input array [in-place](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/In-place_algorithm)** with O(1) extra memory.
+
+**Custom Judge:**
+
+The judge will test your solution with the following code:
+
+ int[] nums = [...]; // Input array
+ int[] expectedNums = [...]; // The expected answer with correct length
+
+ int k = removeDuplicates(nums); // Calls your implementation
+
+ assert k == expectedNums.length;
+ for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
+ assert nums[i] == expectedNums[i];
+ }
+
+If all assertions pass, then your solution will be **accepted**.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,1,2]
+
+**Output:** 2, nums = [1,2,\_]
+
+**Explanation:** Your function should return k = 2, with the first two elements of nums being 1 and 2 respectively. It does not matter what you leave beyond the returned k (hence they are underscores).
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [0,0,1,1,1,2,2,3,3,4]
+
+**Output:** 5, nums = [0,1,2,3,4,\_,\_,\_,\_,\_]
+
+**Explanation:** Your function should return k = 5, with the first five elements of nums being 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively. It does not matter what you leave beyond the returned k (hence they are underscores).
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 0 <= nums.length <= 3 * 104
+* `-100 <= nums[i] <= 100`
+* `nums` is sorted in **non-decreasing** order.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun removeDuplicates(nums: IntArray): Int {
+ val n = nums.size
+ var i = 0
+ var j = 1
+ if (n <= 1) {
+ return n
+ }
+ while (j <= n - 1) {
+ if (nums[i] != nums[j]) {
+ nums[i + 1] = nums[j]
+ i++
+ }
+ j++
+ }
+ return i + 1
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0033_search_in_rotated_sorted_array/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0033_search_in_rotated_sorted_array/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..abc76775
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0033_search_in_rotated_sorted_array/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,77 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 33\. Search in Rotated Sorted Array
+
+Medium
+
+There is an integer array `nums` sorted in ascending order (with **distinct** values).
+
+Prior to being passed to your function, `nums` is **possibly rotated** at an unknown pivot index `k` (`1 <= k < nums.length`) such that the resulting array is `[nums[k], nums[k+1], ..., nums[n-1], nums[0], nums[1], ..., nums[k-1]]` (**0-indexed**). For example, `[0,1,2,4,5,6,7]` might be rotated at pivot index `3` and become `[4,5,6,7,0,1,2]`.
+
+Given the array `nums` **after** the possible rotation and an integer `target`, return _the index of_ `target` _if it is in_ `nums`_, or_ `-1` _if it is not in_ `nums`.
+
+You must write an algorithm with `O(log n)` runtime complexity.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 0
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 3
+
+**Output:** -1
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1], target = 0
+
+**Output:** -1
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= nums.length <= 5000`
+* -104 <= nums[i] <= 104
+* All values of `nums` are **unique**.
+* `nums` is an ascending array that is possibly rotated.
+* -104 <= target <= 104
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun search(nums: IntArray, target: Int): Int {
+ var mid: Int
+ var lo = 0
+ var hi = nums.size - 1
+ while (lo <= hi) {
+ mid = (hi - lo shr 1) + lo
+ if (target == nums[mid]) {
+ return mid
+ }
+ // if this is true, then the possible rotation can only be in the second half
+ if (nums[lo] <= nums[mid]) {
+ // the target is in the first half only if it's
+ if (nums[lo] <= target && target <= nums[mid]) {
+ // included
+ hi = mid - 1
+ } else {
+ // between nums[lo] and nums[mid]
+ lo = mid + 1
+ }
+ // otherwise, the possible rotation can only be in the first half
+ } else if (nums[mid] <= target && target <= nums[hi]) {
+ // the target is in the second half only if it's included
+ lo = mid + 1
+ } else {
+ // between nums[hi] and nums[mid]
+ hi = mid - 1
+ }
+ }
+ return -1
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0034_find_first_and_last_position_of_element_in_sorted_array/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0034_find_first_and_last_position_of_element_in_sorted_array/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d5d1abed
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0034_find_first_and_last_position_of_element_in_sorted_array/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 34\. Find First and Last Position of Element in Sorted Array
+
+Medium
+
+Given an array of integers `nums` sorted in non-decreasing order, find the starting and ending position of a given `target` value.
+
+If `target` is not found in the array, return `[-1, -1]`.
+
+You must write an algorithm with `O(log n)` runtime complexity.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [5,7,7,8,8,10], target = 8
+
+**Output:** [3,4]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [5,7,7,8,8,10], target = 6
+
+**Output:** [-1,-1]
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [], target = 0
+
+**Output:** [-1,-1]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 0 <= nums.length <= 105
+* -109 <= nums[i] <= 109
+* `nums` is a non-decreasing array.
+* -109 <= target <= 109
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution constructor() {
+ fun searchRange(nums: IntArray, target: Int): IntArray {
+ val ans = IntArray(2)
+ ans[0] = helper(nums, target, false)
+ ans[1] = helper(nums, target, true)
+ return ans
+ }
+
+ private fun helper(nums: IntArray, target: Int, equals: Boolean): Int {
+ var l = 0
+ var r: Int = nums.size - 1
+ var result: Int = -1
+ while (l <= r) {
+ val mid: Int = l + (r - l) / 2
+ if (nums[mid] == target) {
+ result = mid
+ }
+ if (nums[mid] < target || (nums[mid] == target && equals)) {
+ l = mid + 1
+ } else {
+ r = mid - 1
+ }
+ }
+ return result
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0035_search_insert_position/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0035_search_insert_position/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8c20c2de
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0035_search_insert_position/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 35\. Search Insert Position
+
+Easy
+
+Given a sorted array of distinct integers and a target value, return the index if the target is found. If not, return the index where it would be if it were inserted in order.
+
+You must write an algorithm with `O(log n)` runtime complexity.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,3,5,6], target = 5
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,3,5,6], target = 2
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,3,5,6], target = 7
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Example 4:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,3,5,6], target = 0
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Example 5:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1], target = 0
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= nums.length <= 104
+* -104 <= nums[i] <= 104
+* `nums` contains **distinct** values sorted in **ascending** order.
+* -104 <= target <= 104
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun searchInsert(nums: IntArray, target: Int): Int {
+ var lo = 0
+ var hi = nums.size - 1
+ while (lo <= hi) {
+ val mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2
+ if (target == nums[mid]) {
+ return mid
+ } else if (target < nums[mid]) {
+ hi = mid - 1
+ } else if (target > nums[mid]) {
+ lo = mid + 1
+ }
+ }
+ return lo
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0039_combination_sum/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0039_combination_sum/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..05add0fa
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0039_combination_sum/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 39\. Combination Sum
+
+Medium
+
+Given an array of **distinct** integers `candidates` and a target integer `target`, return _a list of all **unique combinations** of_ `candidates` _where the chosen numbers sum to_ `target`_._ You may return the combinations in **any order**.
+
+The **same** number may be chosen from `candidates` an **unlimited number of times**. Two combinations are unique if the frequency of at least one of the chosen numbers is different.
+
+It is **guaranteed** that the number of unique combinations that sum up to `target` is less than `150` combinations for the given input.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7
+
+**Output:** [[2,2,3],[7]]
+
+**Explanation:**
+2 and 3 are candidates, and 2 + 2 + 3 = 7. Note that 2 can be used multiple times.
+
+7 is a candidate, and 7 = 7.
+
+These are the only two combinations.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** candidates = [2,3,5], target = 8
+
+**Output:** [[2,2,2,2],[2,3,3],[3,5]]
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** candidates = [2], target = 1
+
+**Output:** []
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= candidates.length <= 30`
+* `1 <= candidates[i] <= 200`
+* All elements of `candidates` are **distinct**.
+* `1 <= target <= 500`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun combinationSum(candidates: IntArray, target: Int): List> {
+ val result = mutableListOf>()
+ fun backtrack(start: Int, case: MutableList, sum: Int) {
+ if (sum >= target) {
+ if (sum == target) {
+ result.add(case.toList())
+ }
+ return
+ }
+ for (i in start until candidates.size) {
+ case.add(candidates[i])
+ backtrack(i, case, sum + candidates[i])
+ case.removeAt(case.size - 1)
+ }
+ }
+ backtrack(0, mutableListOf(), 0)
+ return result
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0041_first_missing_positive/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0041_first_missing_positive/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..b3dc561e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0041_first_missing_positive/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,74 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 41\. First Missing Positive
+
+Hard
+
+Given an unsorted integer array `nums`, return the smallest missing positive integer.
+
+You must implement an algorithm that runs in `O(n)` time and uses constant extra space.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,0]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** The numbers in the range [1,2] are all in the array.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [3,4,-1,1]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** 1 is in the array but 2 is missing.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [7,8,9,11,12]
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:** The smallest positive integer 1 is missing.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= nums.length <= 105
+* -231 <= nums[i] <= 231 - 1
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun firstMissingPositive(nums: IntArray): Int {
+ var noOne = true
+ for (i in 0 until nums.size) {
+ if (noOne && nums[i] == 1) {
+ noOne = false
+ } else if (nums[i] <= 0) {
+ nums[i] = 1
+ }
+ }
+ if (noOne) {
+ return 1
+ }
+ var high = 0
+ var k: Int
+ for (x in nums) {
+ k = kotlin.math.abs(x)
+ high = kotlin.math.max(high, k)
+ if (k - 1 < nums.size) {
+ nums[k - 1] = -1 * kotlin.math.abs(nums[k - 1])
+ }
+ }
+ for (i in nums.indices) {
+ if (nums[i] > 0) {
+ return i + 1
+ }
+ }
+ return high + 1
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0042_trapping_rain_water/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0042_trapping_rain_water/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a9400423
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0042_trapping_rain_water/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 42\. Trapping Rain Water
+
+Hard
+
+Given `n` non-negative integers representing an elevation map where the width of each bar is `1`, compute how much water it can trap after raining.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** height = [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]
+
+**Output:** 6
+
+**Explanation:** The above elevation map (black section) is represented by array [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]. In this case, 6 units of rain water (blue section) are being trapped.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** height = [4,2,0,3,2,5]
+
+**Output:** 9
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `n == height.length`
+* 1 <= n <= 2 * 104
+* 0 <= height[i] <= 105
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun trap(height: IntArray): Int {
+ val size = height.size
+ var maxLeft = 0
+ var maxRight = 0
+ var totalWater = 0
+ var leftPtr = 0
+ var rightPtr = size - 1
+ while (leftPtr < rightPtr) {
+ if (height[leftPtr] <= height[rightPtr]) {
+ if (maxLeft > height[leftPtr]) {
+ totalWater = totalWater + maxLeft - height[leftPtr]
+ } else {
+ maxLeft = height[leftPtr]
+ }
+ ++leftPtr
+ } else {
+ if (maxRight > height[rightPtr]) {
+ totalWater = totalWater + maxRight - height[rightPtr]
+ } else {
+ maxRight = height[rightPtr]
+ }
+ --rightPtr
+ }
+ }
+ return totalWater
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0045_jump_game_ii/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0045_jump_game_ii/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..473c5498
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0045_jump_game_ii/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 45\. Jump Game II
+
+Medium
+
+Given an array of non-negative integers `nums`, you are initially positioned at the first index of the array.
+
+Each element in the array represents your maximum jump length at that position.
+
+Your goal is to reach the last index in the minimum number of jumps.
+
+You can assume that you can always reach the last index.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [2,3,1,1,4]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** The minimum number of jumps to reach the last index is 2. Jump 1 step from index 0 to 1, then 3 steps to the last index.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [2,3,0,1,4]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= nums.length <= 104
+* `0 <= nums[i] <= 1000`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun jump(nums: IntArray): Int {
+ var length = 0
+ var maxLength = 0
+ var minJump = 0
+ for (i in 0 until nums.size - 1) {
+ length--
+ maxLength--
+ maxLength = Math.max(maxLength, nums[i])
+ if (length <= 0) {
+ length = maxLength
+ minJump++
+ }
+ if (length >= nums.size - i - 1) {
+ return minJump
+ }
+ }
+ return minJump
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0046_permutations/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0046_permutations/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..7dcaddb7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0046_permutations/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 46\. Permutations
+
+Medium
+
+Given an array `nums` of distinct integers, return _all the possible permutations_. You can return the answer in **any order**.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,3]
+
+**Output:** [[1,2,3],[1,3,2],[2,1,3],[2,3,1],[3,1,2],[3,2,1]]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [0,1]
+
+**Output:** [[0,1],[1,0]]
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1]
+
+**Output:** [[1]]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= nums.length <= 6`
+* `-10 <= nums[i] <= 10`
+* All the integers of `nums` are **unique**.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun permute(nums: IntArray): List> {
+ if (nums.isEmpty()) {
+ return ArrayList()
+ }
+ val finalResult: MutableList> = ArrayList()
+ permuteRecur(nums, finalResult, ArrayList(), BooleanArray(nums.size))
+ return finalResult
+ }
+
+ private fun permuteRecur(
+ nums: IntArray,
+ finalResult: MutableList>,
+ currResult: MutableList,
+ used: BooleanArray
+ ) {
+ if (currResult.size == nums.size) {
+ finalResult.add(ArrayList(currResult))
+ return
+ }
+ for (i in nums.indices) {
+ if (used[i]) {
+ continue
+ }
+ currResult.add(nums[i])
+ used[i] = true
+ permuteRecur(nums, finalResult, currResult, used)
+ used[i] = false
+ currResult.removeAt(currResult.size - 1)
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0048_rotate_image/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0048_rotate_image/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2a457ff8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0048_rotate_image/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 48\. Rotate Image
+
+Medium
+
+You are given an `n x n` 2D `matrix` representing an image, rotate the image by **90** degrees (clockwise).
+
+You have to rotate the image [**in-place**](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/In-place_algorithm), which means you have to modify the input 2D matrix directly. **DO NOT** allocate another 2D matrix and do the rotation.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** matrix = \[\[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
+
+**Output:** [[7,4,1],[8,5,2],[9,6,3]]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** matrix = \[\[5,1,9,11],[2,4,8,10],[13,3,6,7],[15,14,12,16]]
+
+**Output:** [[15,13,2,5],[14,3,4,1],[12,6,8,9],[16,7,10,11]]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `n == matrix.length == matrix[i].length`
+* `1 <= n <= 20`
+* `-1000 <= matrix[i][j] <= 1000`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun rotate(matrix: Array) {
+ val n: Int = matrix.size
+ for (i in 0 until n / 2) {
+ for (j in i until n - i - 1) {
+ val pos = arrayOf(
+ intArrayOf(i, j),
+ intArrayOf(j, n - 1 - i),
+ intArrayOf(n - 1 - i, n - 1 - j),
+ intArrayOf(n - 1 - j, i)
+ )
+ var t = matrix[pos[0][0]][pos[0][1]]
+ for (k in 1 until pos.size) {
+ val temp = matrix[pos[k][0]][pos[k][1]]
+ matrix[pos[k][0]][pos[k][1]] = t
+ t = temp
+ }
+ matrix[pos[0][0]][pos[0][1]] = t
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0049_group_anagrams/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0049_group_anagrams/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..90235862
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0049_group_anagrams/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 49\. Group Anagrams
+
+Medium
+
+Given an array of strings `strs`, group **the anagrams** together. You can return the answer in **any order**.
+
+An **Anagram** is a word or phrase formed by rearranging the letters of a different word or phrase, typically using all the original letters exactly once.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** strs = ["eat","tea","tan","ate","nat","bat"]
+
+**Output:** [["bat"],["nat","tan"],["ate","eat","tea"]]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** strs = [""]
+
+**Output:** [[""]]
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** strs = ["a"]
+
+**Output:** [["a"]]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= strs.length <= 104
+* `0 <= strs[i].length <= 100`
+* `strs[i]` consists of lowercase English letters.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.Arrays
+
+class Solution {
+ fun groupAnagrams(strs: Array): List> {
+ val hm: MutableMap> = HashMap()
+ for (s in strs) {
+ val ch = s.toCharArray()
+ Arrays.sort(ch)
+ val temp = String(ch)
+ hm.computeIfAbsent(
+ temp
+ ) { _: String? -> ArrayList() }
+ hm[temp]!!.add(s)
+ }
+ return ArrayList>(hm.values)
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0051_n_queens/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0051_n_queens/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..59c7aba5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0051_n_queens/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 51\. N-Queens
+
+Hard
+
+The **n-queens** puzzle is the problem of placing `n` queens on an `n x n` chessboard such that no two queens attack each other.
+
+Given an integer `n`, return _all distinct solutions to the **n-queens puzzle**_. You may return the answer in **any order**.
+
+Each solution contains a distinct board configuration of the n-queens' placement, where `'Q'` and `'.'` both indicate a queen and an empty space, respectively.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** n = 4
+
+**Output:** [[".Q..","...Q","Q...","..Q."],["..Q.","Q...","...Q",".Q.."]]
+
+**Explanation:** There exist two distinct solutions to the 4-queens puzzle as shown above
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 1
+
+**Output:** [["Q"]]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= n <= 9`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.Arrays
+
+class Solution {
+ fun solveNQueens(n: Int): List> {
+ val pos = BooleanArray(n + 2 * n - 1 + 2 * n - 1)
+ val pos2 = IntArray(n)
+ val ans: MutableList> = ArrayList()
+ helper(n, 0, pos, pos2, ans)
+ return ans
+ }
+
+ private fun helper(n: Int, row: Int, pos: BooleanArray, pos2: IntArray, ans: MutableList>) {
+ if (row == n) {
+ construct(n, pos2, ans)
+ return
+ }
+ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ val index = n + 2 * n - 1 + n - 1 + i - row
+ if (pos[i] || pos[n + i + row] || pos[index]) {
+ continue
+ }
+ pos[i] = true
+ pos[n + i + row] = true
+ pos[index] = true
+ pos2[row] = i
+ helper(n, row + 1, pos, pos2, ans)
+ pos[i] = false
+ pos[n + i + row] = false
+ pos[index] = false
+ }
+ }
+
+ private fun construct(n: Int, pos: IntArray, ans: MutableList>) {
+ val sol: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ for (r in 0 until n) {
+ val queenRow = CharArray(n)
+ Arrays.fill(queenRow, '.')
+ queenRow[pos[r]] = 'Q'
+ sol.add(String(queenRow))
+ }
+ ans.add(sol)
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0053_maximum_subarray/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0053_maximum_subarray/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..40a08f3c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0053_maximum_subarray/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 53\. Maximum Subarray
+
+Medium
+
+Given an integer array `nums`, find the contiguous subarray (containing at least one number) which has the largest sum and return _its sum_.
+
+A **subarray** is a **contiguous** part of an array.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4]
+
+**Output:** 6
+
+**Explanation:** [4,-1,2,1] has the largest sum = 6.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1]
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [5,4,-1,7,8]
+
+**Output:** 23
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= nums.length <= 105
+* -104 <= nums[i] <= 104
+
+**Follow up:** If you have figured out the `O(n)` solution, try coding another solution using the **divide and conquer** approach, which is more subtle.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun maxSubArray(nums: IntArray): Int {
+ var nextMax = nums[0]
+ var curMax = nums[0]
+ for (i in 1 until nums.size) {
+ nextMax += nums[i]
+ if (nextMax < nums[i]) {
+ nextMax = nums[i]
+ }
+ if (nextMax > curMax) {
+ curMax = nextMax
+ }
+ }
+ return curMax
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0054_spiral_matrix/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0054_spiral_matrix/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..85b036aa
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0054_spiral_matrix/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 54\. Spiral Matrix
+
+Medium
+
+Given an `m x n` `matrix`, return _all elements of the_ `matrix` _in spiral order_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** matrix = \[\[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
+
+**Output:** [1,2,3,6,9,8,7,4,5]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** matrix = \[\[1,2,3,4],[5,6,7,8],[9,10,11,12]]
+
+**Output:** [1,2,3,4,8,12,11,10,9,5,6,7]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `m == matrix.length`
+* `n == matrix[i].length`
+* `1 <= m, n <= 10`
+* `-100 <= matrix[i][j] <= 100`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun spiralOrder(matrix: Array): List {
+ val list: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ var r = 0
+ var c = 0
+ var bigR = matrix.size - 1
+ var bigC: Int = matrix[0].size - 1
+ while (r <= bigR && c <= bigC) {
+ for (i in c..bigC) {
+ list.add(matrix[r][i])
+ }
+ r++
+ for (i in r..bigR) {
+ list.add(matrix[i][bigC])
+ }
+ bigC--
+ run {
+ var i = bigC
+ while (i >= c && r <= bigR) {
+ list.add(matrix[bigR][i])
+ i--
+ }
+ }
+ bigR--
+ var i = bigR
+ while (i >= r && c <= bigC) {
+ list.add(matrix[i][c])
+ i--
+ }
+ c++
+ }
+ return list
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0055_jump_game/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0055_jump_game/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d7ac9fd0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0055_jump_game/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 55\. Jump Game
+
+Medium
+
+You are given an integer array `nums`. You are initially positioned at the array's **first index**, and each element in the array represents your maximum jump length at that position.
+
+Return `true` _if you can reach the last index, or_ `false` _otherwise_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [2,3,1,1,4]
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** Jump 1 step from index 0 to 1, then 3 steps to the last index.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [3,2,1,0,4]
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Explanation:** You will always arrive at index 3 no matter what. Its maximum jump length is 0, which makes it impossible to reach the last index.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= nums.length <= 104
+* 0 <= nums[i] <= 105
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun canJump(nums: IntArray): Boolean {
+ val sz = nums.size
+ // we set 1 so it won't break on the first iteration
+ var tmp = 1
+ for (i in 0 until sz) {
+ // we always deduct tmp for every iteration
+ tmp--
+ if (tmp < 0) {
+ // if from previous iteration tmp is already 0, it will be <0 here
+ // leading to false value
+ return false
+ }
+ // we get the maximum value because this value is supposed
+ // to be our iterator, if both values are 0, then the next
+ // iteration we will return false
+ // if either both or one of them are not 0 then we will keep doing this and check.
+
+ // We can stop the whole iteration with this condition. without this condition the code
+ // runs in 2ms 79.6%, adding this condition improves the performance into 1ms 100%
+ // because if the test case jump value is quite large, instead of just iterate, we can
+ // just check using this condition
+ // example: [10, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0] -> we can just jump to the end without
+ // iterating whole array
+ tmp = Math.max(tmp, nums[i])
+ if (i + tmp >= sz - 1) {
+ return true
+ }
+ }
+ // we can just return true at the end, because if tmp is 0 on previous
+ // iteration,
+ // even though the next iteration index is the last one, it will return false under the
+ // tmp<0 condition
+ return true
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0056_merge_intervals/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0056_merge_intervals/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..6afc1ec3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0056_merge_intervals/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 56\. Merge Intervals
+
+Medium
+
+Given an array of `intervals` where intervals[i] = [starti, endi], merge all overlapping intervals, and return _an array of the non-overlapping intervals that cover all the intervals in the input_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** intervals = \[\[1,3],[2,6],[8,10],[15,18]]
+
+**Output:** [[1,6],[8,10],[15,18]]
+
+**Explanation:** Since intervals [1,3] and [2,6] overlap, merge them into [1,6].
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** intervals = \[\[1,4],[4,5]]
+
+**Output:** [[1,5]]
+
+**Explanation:** Intervals [1,4] and [4,5] are considered overlapping.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= intervals.length <= 104
+* `intervals[i].length == 2`
+* 0 <= starti <= endi <= 104
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.Arrays
+
+class Solution {
+ fun merge(intervals: Array): Array {
+ Arrays.sort(
+ intervals
+ ) { a: IntArray, b: IntArray ->
+ Integer.compare(
+ a[0],
+ b[0]
+ )
+ }
+ val list: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ var current = intervals[0]
+ list.add(current)
+ for (next in intervals) {
+ if (current[1] >= next[0]) {
+ current[1] = Math.max(current[1], next[1])
+ } else {
+ current = next
+ list.add(current)
+ }
+ }
+ return list.toTypedArray()
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0062_unique_paths/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0062_unique_paths/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2a67cd88
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0062_unique_paths/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 62\. Unique Paths
+
+Medium
+
+There is a robot on an `m x n` grid. The robot is initially located at the **top-left corner** (i.e., `grid[0][0]`). The robot tries to move to the **bottom-right corner** (i.e., `grid[m - 1][n - 1]`). The robot can only move either down or right at any point in time.
+
+Given the two integers `m` and `n`, return _the number of possible unique paths that the robot can take to reach the bottom-right corner_.
+
+The test cases are generated so that the answer will be less than or equal to 2 * 109.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** m = 3, n = 7
+
+**Output:** 28
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** m = 3, n = 2
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** From the top-left corner, there are a total of 3 ways to reach the bottom-right corner:
+
+1. Right -> Down -> Down
+
+2. Down -> Down -> Right
+
+3. Down -> Right -> Down
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= m, n <= 100`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun uniquePaths(m: Int, n: Int): Int {
+ val dp = Array(m) { IntArray(n) }
+ for (i in 0 until m) {
+ dp[i][0] = 1
+ }
+ for (j in 0 until n) {
+ dp[0][j] = 1
+ }
+ for (i in 1 until m) {
+ for (j in 1 until n) {
+ dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i][j - 1]
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[m - 1][n - 1]
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0064_minimum_path_sum/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0064_minimum_path_sum/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3bddeb47
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0064_minimum_path_sum/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 64\. Minimum Path Sum
+
+Medium
+
+Given a `m x n` `grid` filled with non-negative numbers, find a path from top left to bottom right, which minimizes the sum of all numbers along its path.
+
+**Note:** You can only move either down or right at any point in time.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** grid = \[\[1,3,1],[1,5,1],[4,2,1]]
+
+**Output:** 7
+
+**Explanation:** Because the path 1 → 3 → 1 → 1 → 1 minimizes the sum.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** grid = \[\[1,2,3],[4,5,6]]
+
+**Output:** 12
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `m == grid.length`
+* `n == grid[i].length`
+* `1 <= m, n <= 200`
+* `0 <= grid[i][j] <= 100`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun minPathSum(grid: Array): Int {
+ val m = grid.size
+ val n = grid[0].size
+ val dp = Array(m) { Array(n) { 0 } }
+ for (i in 0 until m) {
+ for (j in 0 until n) {
+ if (i == 0 && j == 0) {
+ dp[i][j] = grid[i][j]
+ } else if (i == 0) {
+ dp[i][j] = dp[i][j - 1] + grid[i][j]
+ } else if (j == 0) {
+ dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] + grid[i][j]
+ } else {
+ dp[i][j] = minOf(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]) + grid[i][j]
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[m - 1][n - 1]
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0070_climbing_stairs/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0070_climbing_stairs/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..da172a1d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0070_climbing_stairs/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,66 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 70\. Climbing Stairs
+
+Easy
+
+You are climbing a staircase. It takes `n` steps to reach the top.
+
+Each time you can either climb `1` or `2` steps. In how many distinct ways can you climb to the top?
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 2
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** There are two ways to climb to the top.
+
+1. 1 step + 1 step
+
+2. 2 steps
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 3
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** There are three ways to climb to the top.
+
+1. 1 step + 1 step + 1 step
+
+2. 1 step + 2 steps
+
+3. 2 steps + 1 step
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= n <= 45`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun climbStairs(n: Int): Int {
+ if (n < 2) {
+ return n
+ }
+ val cache = IntArray(n)
+ // creating a cache or DP to store the result
+ // so that we dont have to iterate multiple times
+ // for the same values;
+
+ // for 0 and 1 the result array i.e cache values would be 1 and 2
+ // in loop we are just getting ith values i.e 5th step values from
+ // i-1 and i-2 which are 4th step and 3rd step values.
+ cache[0] = 1
+ cache[1] = 2
+ for (i in 2 until n) {
+ cache[i] = cache[i - 1] + cache[i - 2]
+ }
+ return cache[n - 1]
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0072_edit_distance/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0072_edit_distance/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e9268eca
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0072_edit_distance/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 72\. Edit Distance
+
+Hard
+
+Given two strings `word1` and `word2`, return _the minimum number of operations required to convert `word1` to `word2`_.
+
+You have the following three operations permitted on a word:
+
+* Insert a character
+* Delete a character
+* Replace a character
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** word1 = "horse", word2 = "ros"
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+horse -> rorse (replace 'h' with 'r')
+
+rorse -> rose (remove 'r')
+
+rose -> ros (remove 'e')
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** word1 = "intention", word2 = "execution"
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+intention -> inention (remove 't')
+
+inention -> enention (replace 'i' with 'e')
+
+enention -> exention (replace 'n' with 'x')
+
+exention -> exection (replace 'n' with 'c')
+
+exection -> execution (insert 'u')
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `0 <= word1.length, word2.length <= 500`
+* `word1` and `word2` consist of lowercase English letters.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun minDistance(w1: String, w2: String): Int {
+ val n1 = w1.length
+ val n2 = w2.length
+ if (n2 > n1) {
+ return minDistance(w2, w1)
+ }
+ val dp = IntArray(n2 + 1)
+ for (j in 0..n2) {
+ dp[j] = j
+ }
+ for (i in 1..n1) {
+ var pre = dp[0]
+ dp[0] = i
+ for (j in 1..n2) {
+ val tmp = dp[j]
+ dp[j] = if (w1[i - 1] != w2[j - 1]) 1 + Math.min(pre, Math.min(dp[j], dp[j - 1])) else pre
+ pre = tmp
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[n2]
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0073_set_matrix_zeroes/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0073_set_matrix_zeroes/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..38126999
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0073_set_matrix_zeroes/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,97 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 73\. Set Matrix Zeroes
+
+Medium
+
+Given an `m x n` integer matrix `matrix`, if an element is `0`, set its entire row and column to `0`'s.
+
+You must do it [in place](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/In-place_algorithm).
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** matrix = \[\[1,1,1],[1,0,1],[1,1,1]]
+
+**Output:** [[1,0,1],[0,0,0],[1,0,1]]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** matrix = \[\[0,1,2,0],[3,4,5,2],[1,3,1,5]]
+
+**Output:** [[0,0,0,0],[0,4,5,0],[0,3,1,0]]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `m == matrix.length`
+* `n == matrix[0].length`
+* `1 <= m, n <= 200`
+* -231 <= matrix[i][j] <= 231 - 1
+
+**Follow up:**
+
+* A straightforward solution using `O(mn)` space is probably a bad idea.
+* A simple improvement uses `O(m + n)` space, but still not the best solution.
+* Could you devise a constant space solution?
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ // Approach: Use first row and first column for storing whether in future
+ // the entire row or column needs to be marked 0
+ fun setZeroes(matrix: Array) {
+ val m = matrix.size
+ val n: Int = matrix[0].size
+ var row0 = false
+ var col0 = false
+ // Check if 0th col needs to be market all 0s in future
+ for (ints in matrix) {
+ if (ints[0] == 0) {
+ col0 = true
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ // Check if 0th row needs to be market all 0s in future
+ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ if (matrix[0][i] == 0) {
+ row0 = true
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ // Store the signals in 0th row and column
+ for (i in 1 until m) {
+ for (j in 1 until n) {
+ if (matrix[i][j] == 0) {
+ matrix[i][0] = 0
+ matrix[0][j] = 0
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ // Mark 0 for all cells based on signal from 0th row and 0th column
+ for (i in 1 until m) {
+ for (j in 1 until n) {
+ if (matrix[i][0] == 0 || matrix[0][j] == 0) {
+ matrix[i][j] = 0
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ // Set 0th column
+ for (i in 0 until m) {
+ if (col0) {
+ matrix[i][0] = 0
+ }
+ }
+ // Set 0th row
+ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ if (row0) {
+ matrix[0][i] = 0
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0074_search_a_2d_matrix/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0074_search_a_2d_matrix/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e2df7d9f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0074_search_a_2d_matrix/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 74\. Search a 2D Matrix
+
+Medium
+
+Write an efficient algorithm that searches for a value `target` in an `m x n` integer matrix `matrix`. This matrix has the following properties:
+
+* Integers in each row are sorted from left to right.
+* The first integer of each row is greater than the last integer of the previous row.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** matrix = \[\[1,3,5,7],[10,11,16,20],[23,30,34,60]], target = 3
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** matrix = \[\[1,3,5,7],[10,11,16,20],[23,30,34,60]], target = 13
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `m == matrix.length`
+* `n == matrix[i].length`
+* `1 <= m, n <= 100`
+* -104 <= matrix[i][j], target <= 104
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun searchMatrix(matrix: Array, target: Int): Boolean {
+ val endRow = matrix.size
+ val endCol: Int = matrix[0].size
+ var targetRow = 0
+ var result = false
+ for (i in 0 until endRow) {
+ if (matrix[i][endCol - 1] >= target) {
+ targetRow = i
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ for (i in 0 until endCol) {
+ if (matrix[targetRow][i] == target) {
+ result = true
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ return result
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0075_sort_colors/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0075_sort_colors/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..876d66c3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0075_sort_colors/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 75\. Sort Colors
+
+Medium
+
+Given an array `nums` with `n` objects colored red, white, or blue, sort them **[in-place](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/In-place_algorithm)** so that objects of the same color are adjacent, with the colors in the order red, white, and blue.
+
+We will use the integers `0`, `1`, and `2` to represent the color red, white, and blue, respectively.
+
+You must solve this problem without using the library's sort function.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [2,0,2,1,1,0]
+
+**Output:** [0,0,1,1,2,2]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [2,0,1]
+
+**Output:** [0,1,2]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `n == nums.length`
+* `1 <= n <= 300`
+* `nums[i]` is either `0`, `1`, or `2`.
+
+**Follow up:** Could you come up with a one-pass algorithm using only constant extra space?
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun sortColors(nums: IntArray) {
+ var zeroes = 0
+ var ones = 0
+ for (i in nums.indices) {
+ if (nums[i] == 0) {
+ nums[zeroes++] = 0
+ } else if (nums[i] == 1) {
+ ones++
+ }
+ }
+ for (j in zeroes until zeroes + ones) {
+ nums[j] = 1
+ }
+ for (k in zeroes + ones until nums.size) {
+ nums[k] = 2
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0076_minimum_window_substring/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0076_minimum_window_substring/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c4fcf42f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0076_minimum_window_substring/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,78 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 76\. Minimum Window Substring
+
+Hard
+
+Given two strings `s` and `t` of lengths `m` and `n` respectively, return _the **minimum window substring** of_ `s` _such that every character in_ `t` _(**including duplicates**) is included in the window. If there is no such substring__, return the empty string_ `""`_._
+
+The testcases will be generated such that the answer is **unique**.
+
+A **substring** is a contiguous sequence of characters within the string.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "ADOBECODEBANC", t = "ABC"
+
+**Output:** "BANC"
+
+**Explanation:** The minimum window substring "BANC" includes 'A', 'B', and 'C' from string t.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "a", t = "a"
+
+**Output:** "a"
+
+**Explanation:** The entire string s is the minimum window.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** s = "a", t = "aa"
+
+**Output:** ""
+
+**Explanation:** Both 'a's from t must be included in the window. Since the largest window of s only has one 'a', return empty string.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `m == s.length`
+* `n == t.length`
+* 1 <= m, n <= 105
+* `s` and `t` consist of uppercase and lowercase English letters.
+
+**Follow up:** Could you find an algorithm that runs in `O(m + n)` time?
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun minWindow(s: String, t: String): String {
+ val map = IntArray(128)
+ for (element in t) {
+ map[element - 'A']++
+ }
+ var count = t.length
+ var begin = 0
+ var end = 0
+ var d = Int.MAX_VALUE
+ var head = 0
+ while (end < s.length) {
+ if (map[s[end++] - 'A']-- > 0) {
+ count--
+ }
+ while (count == 0) {
+ if (end - begin < d) {
+ d = end - begin
+ head = begin
+ }
+ if (map[s[begin++] - 'A']++ == 0) {
+ count++
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return if (d == Int.MAX_VALUE) "" else s.substring(head, head + d)
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0078_subsets/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0078_subsets/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..34a553a8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0078_subsets/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 78\. Subsets
+
+Medium
+
+Given an integer array `nums` of **unique** elements, return _all possible subsets (the power set)_.
+
+The solution set **must not** contain duplicate subsets. Return the solution in **any order**.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,3]
+
+**Output:** [[],[1],[2],[1,2],[3],[1,3],[2,3],[1,2,3]]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [0]
+
+**Output:** [[],[0]]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= nums.length <= 10`
+* `-10 <= nums[i] <= 10`
+* All the numbers of `nums` are **unique**.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun subsets(nums: IntArray): List> {
+ val res: MutableList> = ArrayList()
+ solve(nums, ArrayList(), res, 0)
+ return res
+ }
+
+ private fun solve(nums: IntArray, temp: MutableList, res: MutableList>, start: Int) {
+ res.add(ArrayList(temp))
+ for (i in start until nums.size) {
+ temp.add(nums[i])
+ solve(nums, temp, res, i + 1)
+ temp.removeAt(temp.size - 1)
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0079_word_search/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0079_word_search/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..975f085e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0079_word_search/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,98 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 79\. Word Search
+
+Medium
+
+Given an `m x n` grid of characters `board` and a string `word`, return `true` _if_ `word` _exists in the grid_.
+
+The word can be constructed from letters of sequentially adjacent cells, where adjacent cells are horizontally or vertically neighboring. The same letter cell may not be used more than once.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** board = \[\["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "ABCCED"
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** board = \[\["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "SEE"
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** board = \[\["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "ABCB"
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `m == board.length`
+* `n = board[i].length`
+* `1 <= m, n <= 6`
+* `1 <= word.length <= 15`
+* `board` and `word` consists of only lowercase and uppercase English letters.
+
+**Follow up:** Could you use search pruning to make your solution faster with a larger `board`?
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ private fun backtrace(
+ board: Array,
+ visited: Array,
+ word: String,
+ index: Int,
+ x: Int,
+ y: Int
+ ): Boolean {
+ if (index == word.length) {
+ return true
+ }
+ if (x < 0 || x >= board.size || y < 0 || y >= board[0].size || visited[x][y]) {
+ return false
+ }
+ visited[x][y] = true
+ return if (word[index] == board[x][y]) {
+ val res = (
+ backtrace(board, visited, word, index + 1, x, y + 1) ||
+ backtrace(board, visited, word, index + 1, x, y - 1) ||
+ backtrace(board, visited, word, index + 1, x + 1, y) ||
+ backtrace(board, visited, word, index + 1, x - 1, y)
+ )
+ if (!res) {
+ visited[x][y] = false
+ }
+ res
+ } else {
+ visited[x][y] = false
+ false
+ }
+ }
+
+ fun exist(board: Array, word: String): Boolean {
+ val visited = Array(board.size) {
+ BooleanArray(
+ board[0].size
+ )
+ }
+ for (i in board.indices) {
+ for (j in board[0].indices) {
+ if (backtrace(board, visited, word, 0, i, j)) {
+ return true
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return false
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0084_largest_rectangle_in_histogram/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0084_largest_rectangle_in_histogram/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0667b45e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0084_largest_rectangle_in_histogram/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,103 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 84\. Largest Rectangle in Histogram
+
+Hard
+
+Given an array of integers `heights` representing the histogram's bar height where the width of each bar is `1`, return _the area of the largest rectangle in the histogram_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** heights = [2,1,5,6,2,3]
+
+**Output:** 10
+
+**Explanation:** The above is a histogram where width of each bar is 1.
+
+The largest rectangle is shown in the red area, which has an area = 10 units.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** heights = [2,4]
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= heights.length <= 105
+* 0 <= heights[i] <= 104
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import kotlin.math.max
+
+class Solution {
+ fun largestRectangleArea(heights: IntArray): Int {
+ return largestArea(heights, 0, heights.size)
+ }
+
+ private fun largestArea(a: IntArray, start: Int, limit: Int): Int {
+ if (a.isEmpty()) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ if (start == limit) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ if (limit - start == 1) {
+ return a[start]
+ }
+ if (limit - start == 2) {
+ val maxOfTwoBars = Math.max(a[start], a[start + 1])
+ val areaFromTwo = Math.min(a[start], a[start + 1]) * 2
+ return Math.max(maxOfTwoBars, areaFromTwo)
+ }
+ return if (checkIfSorted(a, start, limit)) {
+ var maxWhenSorted = 0
+ for (i in start until limit) {
+ if (a[i] * (limit - i) > maxWhenSorted) {
+ maxWhenSorted = a[i] * (limit - i)
+ }
+ }
+ maxWhenSorted
+ } else {
+ val minInd = findMinInArray(a, start, limit)
+ maxOfThreeNums(
+ largestArea(a, start, minInd),
+ a[minInd] * (limit - start),
+ largestArea(a, minInd + 1, limit)
+ )
+ }
+ }
+
+ private fun findMinInArray(a: IntArray, start: Int, limit: Int): Int {
+ var min = Int.MAX_VALUE
+ var minIndex = -1
+ for (index in start until limit) {
+ if (a[index] < min) {
+ min = a[index]
+ minIndex = index
+ }
+ }
+ return minIndex
+ }
+
+ private fun checkIfSorted(a: IntArray, start: Int, limit: Int): Boolean {
+ for (i in start + 1 until limit) {
+ if (a[i] < a[i - 1]) {
+ return false
+ }
+ }
+ return true
+ }
+
+ private fun maxOfThreeNums(a: Int, b: Int, c: Int): Int {
+ return max(max(a, b), c)
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0094_binary_tree_inorder_traversal/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0094_binary_tree_inorder_traversal/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..7910e22e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0094_binary_tree_inorder_traversal/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 84\. Largest Rectangle in Histogram
+
+Hard
+
+Given an array of integers `heights` representing the histogram's bar height where the width of each bar is `1`, return _the area of the largest rectangle in the histogram_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** heights = [2,1,5,6,2,3]
+
+**Output:** 10
+
+**Explanation:** The above is a histogram where width of each bar is 1.
+
+The largest rectangle is shown in the red area, which has an area = 10 units.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** heights = [2,4]
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= heights.length <= 105
+* 0 <= heights[i] <= 104
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode
+
+class Solution {
+ fun inorderTraversal(root: TreeNode?): List {
+ if (root == null) {
+ return emptyList()
+ }
+ val answer: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ inorderTraversal(root, answer)
+ return answer
+ }
+
+ private fun inorderTraversal(root: TreeNode?, answer: MutableList) {
+ if (root == null) {
+ return
+ }
+ if (root.left != null) {
+ inorderTraversal(root.left, answer)
+ }
+ answer.add(root.`val`)
+ if (root.right != null) {
+ inorderTraversal(root.right, answer)
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0098_validate_binary_search_tree/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0098_validate_binary_search_tree/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f09a2de6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0098_validate_binary_search_tree/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 98\. Validate Binary Search Tree
+
+Medium
+
+Given the `root` of a binary tree, _determine if it is a valid binary search tree (BST)_.
+
+A **valid BST** is defined as follows:
+
+* The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys **less than** the node's key.
+* The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys **greater than** the node's key.
+* Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** root = [2,1,3]
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** root = [5,1,4,null,null,3,6]
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Explanation:** The root node's value is 5 but its right child's value is 4.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 104].
+* -231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode
+
+class Solution {
+ fun isValidBST(root: TreeNode?): Boolean {
+ return solve(root, Long.MIN_VALUE, Long.MAX_VALUE)
+ }
+
+ // we will send a valid range and check whether the root lies in the range
+ // and update the range for the subtrees
+ private fun solve(root: TreeNode?, left: Long, right: Long): Boolean {
+ if (root == null) {
+ return true
+ }
+ return if (root.`val` <= left || root.`val` >= right) {
+ false
+ } else solve(root.left, left, root.`val`.toLong()) && solve(root.right, root.`val`.toLong(), right)
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0101_symmetric_tree/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0101_symmetric_tree/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8e1d831a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0101_symmetric_tree/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 101\. Symmetric Tree
+
+Easy
+
+Given the `root` of a binary tree, _check whether it is a mirror of itself_ (i.e., symmetric around its center).
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** root = [1,2,2,3,4,4,3]
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** root = [1,2,2,null,3,null,3]
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* The number of nodes in the tree is in the range `[1, 1000]`.
+* `-100 <= Node.val <= 100`
+
+**Follow up:** Could you solve it both recursively and iteratively?
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode
+
+class Solution {
+ fun isSymmetric(root: TreeNode?): Boolean {
+ return if (root == null) {
+ true
+ } else helper(root.left, root.right)
+ }
+
+ private fun helper(leftNode: TreeNode?, rightNode: TreeNode?): Boolean {
+ if (leftNode == null || rightNode == null) {
+ return leftNode == null && rightNode == null
+ }
+ return if (leftNode.`val` != rightNode.`val`) {
+ false
+ } else helper(leftNode.left, rightNode.right) && helper(leftNode.right, rightNode.left)
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0102_binary_tree_level_order_traversal/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0102_binary_tree_level_order_traversal/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8e3e145e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0102_binary_tree_level_order_traversal/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,75 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 102\. Binary Tree Level Order Traversal
+
+Medium
+
+Given the `root` of a binary tree, return _the level order traversal of its nodes' values_. (i.e., from left to right, level by level).
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
+
+**Output:** [[3],[9,20],[15,7]]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** root = [1]
+
+**Output:** [[1]]
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** root = []
+
+**Output:** []
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* The number of nodes in the tree is in the range `[0, 2000]`.
+* `-1000 <= Node.val <= 1000`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode
+import java.util.ArrayList
+import java.util.LinkedList
+import java.util.Queue
+
+class Solution {
+ fun levelOrder(root: TreeNode?): List> {
+ var localRoot: TreeNode? = root
+ val result: MutableList> = ArrayList()
+ if (localRoot == null) {
+ return result
+ }
+ val queue: Queue = LinkedList()
+ queue.add(localRoot)
+ queue.add(null)
+ var level: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
+ localRoot = queue.remove()
+ while (!queue.isEmpty() && localRoot != null) {
+ level.add(localRoot.`val`)
+ if (localRoot.left != null) {
+ queue.add(localRoot.left)
+ }
+ if (localRoot.right != null) {
+ queue.add(localRoot.right)
+ }
+ localRoot = queue.remove()
+ }
+ result.add(level)
+ level = ArrayList()
+ if (!queue.isEmpty()) {
+ queue.add(null)
+ }
+ }
+ return result
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0105_construct_binary_tree_from_preorder_and_inorder_traversal/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0105_construct_binary_tree_from_preorder_and_inorder_traversal/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d0f7fd87
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0105_construct_binary_tree_from_preorder_and_inorder_traversal/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 105\. Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Inorder Traversal
+
+Medium
+
+Given two integer arrays `preorder` and `inorder` where `preorder` is the preorder traversal of a binary tree and `inorder` is the inorder traversal of the same tree, construct and return _the binary tree_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** preorder = [3,9,20,15,7], inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
+
+**Output:** [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** preorder = [-1], inorder = [-1]
+
+**Output:** [-1]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= preorder.length <= 3000`
+* `inorder.length == preorder.length`
+* `-3000 <= preorder[i], inorder[i] <= 3000`
+* `preorder` and `inorder` consist of **unique** values.
+* Each value of `inorder` also appears in `preorder`.
+* `preorder` is **guaranteed** to be the preorder traversal of the tree.
+* `inorder` is **guaranteed** to be the inorder traversal of the tree.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode
+import java.util.HashMap
+
+class Solution {
+ private var j = 0
+ private val map: MutableMap = HashMap()
+ fun get(key: Int): Int {
+ return map[key]!!
+ }
+
+ private fun answer(preorder: IntArray, inorder: IntArray, start: Int, end: Int): TreeNode? {
+ if (start > end || j > preorder.size) {
+ return null
+ }
+ val value = preorder[j++]
+ val index = get(value)
+ val node = TreeNode(value)
+ node.left = answer(preorder, inorder, start, index - 1)
+ node.right = answer(preorder, inorder, index + 1, end)
+ return node
+ }
+
+ fun buildTree(preorder: IntArray, inorder: IntArray): TreeNode? {
+ j = 0
+ for (i in preorder.indices) {
+ map[inorder[i]] = i
+ }
+ return answer(preorder, inorder, 0, preorder.size - 1)
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0114_flatten_binary_tree_to_linked_list/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0114_flatten_binary_tree_to_linked_list/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..68bd2bb1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0114_flatten_binary_tree_to_linked_list/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,74 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 114\. Flatten Binary Tree to Linked List
+
+Medium
+
+Given the `root` of a binary tree, flatten the tree into a "linked list":
+
+* The "linked list" should use the same `TreeNode` class where the `right` child pointer points to the next node in the list and the `left` child pointer is always `null`.
+* The "linked list" should be in the same order as a [**pre-order** **traversal**](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tree_traversal#Pre-order,_NLR) of the binary tree.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** root = [1,2,5,3,4,null,6]
+
+**Output:** [1,null,2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** root = []
+
+**Output:** []
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** root = [0]
+
+**Output:** [0]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* The number of nodes in the tree is in the range `[0, 2000]`.
+* `-100 <= Node.val <= 100`
+
+**Follow up:** Can you flatten the tree in-place (with `O(1)` extra space)?
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode
+
+class Solution {
+ fun flatten(root: TreeNode?) {
+ if (root != null) {
+ findTail(root)
+ }
+ }
+
+ private fun findTail(root: TreeNode): TreeNode {
+ val left: TreeNode? = root.left
+ val right: TreeNode? = root.right
+ val tail: TreeNode
+ // find the tail of left subtree, tail means the most left leaf
+ if (left != null) {
+ tail = findTail(left)
+ // stitch the right subtree below the tail
+ root.left = null
+ root.right = left
+ tail.right = right
+ } else {
+ tail = root
+ }
+ // find tail of the right subtree
+ return if (tail.right == null) {
+ tail
+ } else {
+ findTail(tail.right!!)
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0121_best_time_to_buy_and_sell_stock/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0121_best_time_to_buy_and_sell_stock/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..aefdbece
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0121_best_time_to_buy_and_sell_stock/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 121\. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock
+
+Easy
+
+You are given an array `prices` where `prices[i]` is the price of a given stock on the ith day.
+
+You want to maximize your profit by choosing a **single day** to buy one stock and choosing a **different day in the future** to sell that stock.
+
+Return _the maximum profit you can achieve from this transaction_. If you cannot achieve any profit, return `0`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** prices = [7,1,5,3,6,4]
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Explanation:** Buy on day 2 (price = 1) and sell on day 5 (price = 6), profit = 6-1 = 5.
+
+Note that buying on day 2 and selling on day 1 is not allowed because you must buy before you sell.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** prices = [7,6,4,3,1]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:** In this case, no transactions are done and the max profit = 0.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= prices.length <= 105
+* 0 <= prices[i] <= 104
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun maxProfit(prices: IntArray): Int {
+ var maxProfit = 0
+ var min = prices[0]
+ for (i in 1 until prices.size) {
+ if (prices[i] > min) {
+ maxProfit = Math.max(maxProfit, prices[i] - min)
+ } else {
+ min = prices[i]
+ }
+ }
+ return maxProfit
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0124_binary_tree_maximum_path_sum/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0124_binary_tree_maximum_path_sum/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..98fc3dfb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0124_binary_tree_maximum_path_sum/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 124\. Binary Tree Maximum Path Sum
+
+Hard
+
+A **path** in a binary tree is a sequence of nodes where each pair of adjacent nodes in the sequence has an edge connecting them. A node can only appear in the sequence **at most once**. Note that the path does not need to pass through the root.
+
+The **path sum** of a path is the sum of the node's values in the path.
+
+Given the `root` of a binary tree, return _the maximum **path sum** of any **non-empty** path_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** root = [1,2,3]
+
+**Output:** 6
+
+**Explanation:** The optimal path is 2 -> 1 -> 3 with a path sum of 2 + 1 + 3 = 6.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** root = [-10,9,20,null,null,15,7]
+
+**Output:** 42
+
+**Explanation:** The optimal path is 15 -> 20 -> 7 with a path sum of 15 + 20 + 7 = 42.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 3 * 104].
+* `-1000 <= Node.val <= 1000`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode
+
+class Solution {
+ private var max = Int.MIN_VALUE
+ private fun helper(root: TreeNode?): Int {
+ if (root == null) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ // to avoid the -ve values in left side we will compare them with 0
+ val left = Math.max(0, helper(root.left))
+ val right = Math.max(0, helper(root.right))
+ val current: Int = root.`val` + left + right
+ if (current > max) {
+ max = current
+ }
+ return root.`val` + Math.max(left, right)
+ }
+
+ fun maxPathSum(root: TreeNode?): Int {
+ helper(root)
+ return max
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0128_longest_consecutive_sequence/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0128_longest_consecutive_sequence/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..56c26795
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0128_longest_consecutive_sequence/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 128\. Longest Consecutive Sequence
+
+Medium
+
+Given an unsorted array of integers `nums`, return _the length of the longest consecutive elements sequence._
+
+You must write an algorithm that runs in `O(n)` time.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [100,4,200,1,3,2]
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:** The longest consecutive elements sequence is `[1, 2, 3, 4]`. Therefore its length is 4.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [0,3,7,2,5,8,4,6,0,1]
+
+**Output:** 9
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 0 <= nums.length <= 105
+* -109 <= nums[i] <= 109
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.PriorityQueue
+
+class Solution {
+ fun longestConsecutive(nums: IntArray): Int {
+ if (nums.isEmpty()) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ val queue = PriorityQueue()
+ nums.forEach {
+ queue.add(it)
+ }
+ var lastNum = Integer.MIN_VALUE
+ var length = 0
+ var maxLength = 1
+ while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
+ val num = queue.poll()
+ if (num == lastNum) {
+ continue
+ }
+ length ++
+ if (num - lastNum > 1) {
+ length = 1
+ }
+ lastNum = num
+ maxLength = maxOf(maxLength, length)
+ }
+ return maxLength
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0131_palindrome_partitioning/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0131_palindrome_partitioning/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..26e10d57
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0131_palindrome_partitioning/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 131\. Palindrome Partitioning
+
+Medium
+
+Given a string `s`, partition `s` such that every substring of the partition is a **palindrome**. Return all possible palindrome partitioning of `s`.
+
+A **palindrome** string is a string that reads the same backward as forward.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "aab"
+
+**Output:** [["a","a","b"],["aa","b"]]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "a"
+
+**Output:** [["a"]]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= s.length <= 16`
+* `s` contains only lowercase English letters.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+@Suppress("NAME_SHADOWING")
+class Solution {
+ fun partition(s: String): List> {
+ val res = ArrayList>()
+ val mem = Array(s.length) { IntArray(s.length) }
+
+ fun isPalindrome(i: Int, j: Int): Boolean {
+ if (i > j) {
+ return true
+ }
+ return when (mem[i][j]) {
+ 1 -> true
+ 2 -> false
+ else -> {
+ val res = s[i] == s[j] && isPalindrome(i + 1, j - 1)
+ mem[i][j] = if (res) 1 else 2
+ res
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ fun dfs(start: Int, path: ArrayList) {
+ if (start == s.length) {
+ res.add(path.toList())
+ return
+ }
+
+ for (i in start..s.length - 1) {
+ if (!isPalindrome(start, i)) {
+ continue
+ }
+ path.add(s.substring(start..i))
+ dfs(i + 1, path)
+ path.removeAt(path.size - 1)
+ }
+ }
+ dfs(0, ArrayList())
+ return res
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0136_single_number/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0136_single_number/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..4c592813
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0136_single_number/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 136\. Single Number
+
+Easy
+
+Given a **non-empty** array of integers `nums`, every element appears _twice_ except for one. Find that single one.
+
+You must implement a solution with a linear runtime complexity and use only constant extra space.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [2,2,1]
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [4,1,2,1,2]
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1]
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= nums.length <= 3 * 104
+* -3 * 104 <= nums[i] <= 3 * 104
+* Each element in the array appears twice except for one element which appears only once.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun singleNumber(nums: IntArray): Int {
+ var num = 0
+ for (x in nums) {
+ num = num xor x
+ }
+ return num
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0138_copy_list_with_random_pointer/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0138_copy_list_with_random_pointer/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..fae6bbd0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0138_copy_list_with_random_pointer/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,105 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 138\. Copy List with Random Pointer
+
+Medium
+
+A linked list of length `n` is given such that each node contains an additional random pointer, which could point to any node in the list, or `null`.
+
+Construct a [**deep copy**](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Object_copying#Deep_copy) of the list. The deep copy should consist of exactly `n` **brand new** nodes, where each new node has its value set to the value of its corresponding original node. Both the `next` and `random` pointer of the new nodes should point to new nodes in the copied list such that the pointers in the original list and copied list represent the same list state. **None of the pointers in the new list should point to nodes in the original list**.
+
+For example, if there are two nodes `X` and `Y` in the original list, where `X.random --> Y`, then for the corresponding two nodes `x` and `y` in the copied list, `x.random --> y`.
+
+Return _the head of the copied linked list_.
+
+The linked list is represented in the input/output as a list of `n` nodes. Each node is represented as a pair of `[val, random_index]` where:
+
+* `val`: an integer representing `Node.val`
+* `random_index`: the index of the node (range from `0` to `n-1`) that the `random` pointer points to, or `null` if it does not point to any node.
+
+Your code will **only** be given the `head` of the original linked list.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+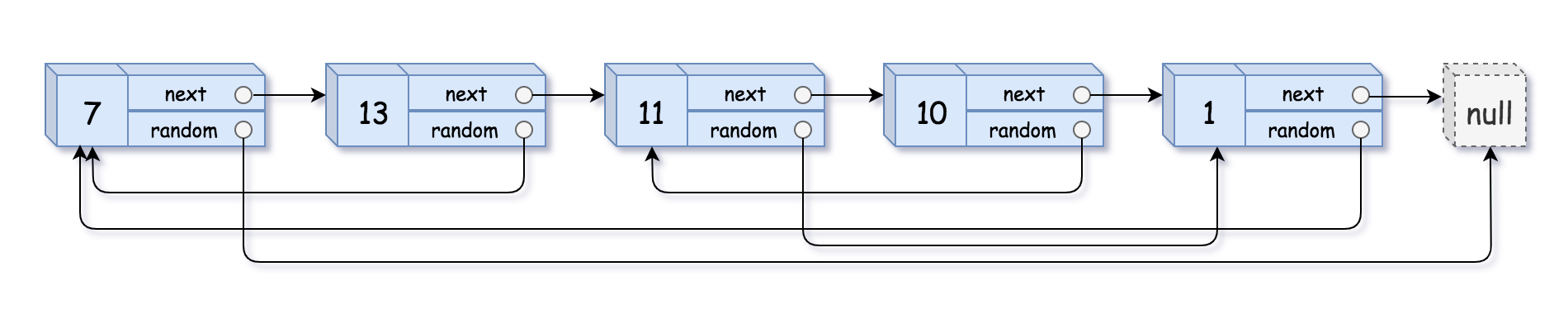
+
+**Input:** head = \[\[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
+
+**Output:** [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+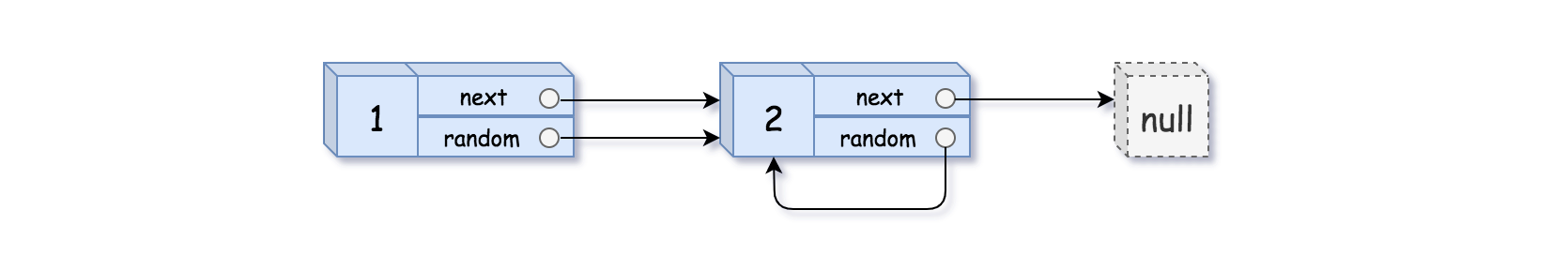
+
+**Input:** head = \[\[1,1],[2,1]]
+
+**Output:** [[1,1],[2,1]]
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**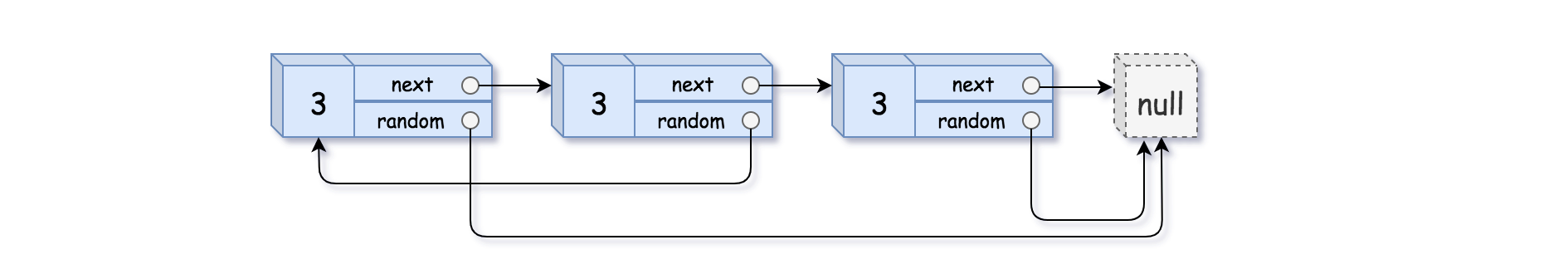**
+
+**Input:** head = \[\[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
+
+**Output:** [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `0 <= n <= 1000`
+* -104 <= Node.val <= 104
+* `Node.random` is `null` or is pointing to some node in the linked list.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import com_github_leetcode.Node
+
+class Solution {
+ fun copyRandomList(head: Node?): Node? {
+ if (head == null) {
+ return null
+ }
+ // first pass to have a clone node point to the next node. ie A->B becomes A->clonedNode->B
+ var curr: Node? = head
+ while (curr != null) {
+ val clonedNode = Node(curr.`val`)
+ clonedNode.next = curr.next
+ curr.next = clonedNode
+ curr = clonedNode.next
+ }
+ curr = head
+ // second pass to make the cloned node's random pointer point to the orginal node's randome
+ // pointer.
+ // ie. A's random pointer becomes ClonedNode's random pointer
+ while (curr != null) {
+ if (curr.random != null) {
+ curr.next?.random = curr.random!!.next
+ } else {
+ curr.next?.random = null
+ }
+ curr = curr.next?.next
+ }
+ curr = head
+ // third pass to restore the links and return the head of the cloned nodes' list.
+ var newHead: Node? = null
+ while (curr != null) {
+ var clonedNode: Node
+ if (newHead == null) {
+ clonedNode = curr.next!!
+ newHead = clonedNode
+ } else {
+ clonedNode = curr.next!!
+ }
+ curr.next = clonedNode.next
+ if (curr.next != null) {
+ clonedNode.next = curr.next!!.next
+ } else {
+ clonedNode.next = null
+ }
+ curr = curr.next
+ }
+ return newHead
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0139_word_break/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0139_word_break/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f8581df5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0139_word_break/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 139\. Word Break
+
+Medium
+
+Given a string `s` and a dictionary of strings `wordDict`, return `true` if `s` can be segmented into a space-separated sequence of one or more dictionary words.
+
+**Note** that the same word in the dictionary may be reused multiple times in the segmentation.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "leetcode", wordDict = ["leet","code"]
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** Return true because "leetcode" can be segmented as "leet code".
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "applepenapple", wordDict = ["apple","pen"]
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** Return true because "applepenapple" can be segmented as "apple pen apple".
+
+Note that you are allowed to reuse a dictionary word.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** s = "catsandog", wordDict = ["cats","dog","sand","and","cat"]
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= s.length <= 300`
+* `1 <= wordDict.length <= 1000`
+* `1 <= wordDict[i].length <= 20`
+* `s` and `wordDict[i]` consist of only lowercase English letters.
+* All the strings of `wordDict` are **unique**.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.HashSet
+
+class Solution {
+ fun wordBreak(s: String, wordDict: List): Boolean {
+ val set: MutableSet = HashSet()
+ var max = 0
+ val flag = BooleanArray(s.length + 1)
+ for (st in wordDict) {
+ set.add(st)
+ if (max < st.length) {
+ max = st.length
+ }
+ }
+ for (i in 1..max) {
+ if (dfs(s, 0, i, max, set, flag)) {
+ return true
+ }
+ }
+ return false
+ }
+
+ private fun dfs(s: String, start: Int, end: Int, max: Int, set: Set, flag: BooleanArray): Boolean {
+ if (!flag[end] && set.contains(s.substring(start, end))) {
+ flag[end] = true
+ if (end == s.length) {
+ return true
+ }
+ for (i in 1..max) {
+ if (end + i <= s.length && dfs(s, end, end + i, max, set, flag)) {
+ return true
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return false
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0141_linked_list_cycle/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0141_linked_list_cycle/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..145c3f81
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0141_linked_list_cycle/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,74 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 141\. Linked List Cycle
+
+Easy
+
+Given `head`, the head of a linked list, determine if the linked list has a cycle in it.
+
+There is a cycle in a linked list if there is some node in the list that can be reached again by continuously following the `next` pointer. Internally, `pos` is used to denote the index of the node that tail's `next` pointer is connected to. **Note that `pos` is not passed as a parameter**.
+
+Return `true` _if there is a cycle in the linked list_. Otherwise, return `false`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** There is a cycle in the linked list, where the tail connects to the 1st node (0-indexed).
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** head = [1,2], pos = 0
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** There is a cycle in the linked list, where the tail connects to the 0th node.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** head = [1], pos = -1
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Explanation:** There is no cycle in the linked list.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* The number of the nodes in the list is in the range [0, 104].
+* -105 <= Node.val <= 105
+* `pos` is `-1` or a **valid index** in the linked-list.
+
+**Follow up:** Can you solve it using `O(1)` (i.e. constant) memory?
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import com_github_leetcode.ListNode
+
+class Solution {
+ fun hasCycle(head: ListNode?): Boolean {
+ if (head == null) {
+ return false
+ }
+ var fast = head.next
+ var slow = head
+ while (fast?.next != null) {
+ if (fast == slow) {
+ return true
+ }
+ fast = fast.next!!.next
+ slow = slow!!.next
+ }
+ return false
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0142_linked_list_cycle_ii/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0142_linked_list_cycle_ii/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1de663eb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0142_linked_list_cycle_ii/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 142\. Linked List Cycle II
+
+Medium
+
+Given the `head` of a linked list, return _the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return_ `null`.
+
+There is a cycle in a linked list if there is some node in the list that can be reached again by continuously following the `next` pointer. Internally, `pos` is used to denote the index of the node that tail's `next` pointer is connected to (**0-indexed**). It is `-1` if there is no cycle. **Note that** `pos` **is not passed as a parameter**.
+
+**Do not modify** the linked list.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
+
+**Output:** tail connects to node index 1
+
+**Explanation:** There is a cycle in the linked list, where tail connects to the second node.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** head = [1,2], pos = 0
+
+**Output:** tail connects to node index 0
+
+**Explanation:** There is a cycle in the linked list, where tail connects to the first node.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** head = [1], pos = -1
+
+**Output:** no cycle
+
+**Explanation:** There is no cycle in the linked list.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* The number of the nodes in the list is in the range [0, 104].
+* -105 <= Node.val <= 105
+* `pos` is `-1` or a **valid index** in the linked-list.
+
+**Follow up:** Can you solve it using `O(1)` (i.e. constant) memory?
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import com_github_leetcode.ListNode
+
+class Solution {
+ fun detectCycle(head: ListNode?): ListNode? {
+ if (head?.next == null) {
+ return null
+ }
+ var slow = head
+ var fast = head
+ while (fast?.next != null) {
+ fast = fast.next!!.next
+ slow = slow!!.next
+ // intersected inside the loop.
+ if (slow == fast) {
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ if (fast?.next == null) {
+ return null
+ }
+ slow = head
+ while (slow != fast) {
+ slow = slow!!.next
+ fast = fast!!.next
+ }
+ return slow
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0146_lru_cache/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0146_lru_cache/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..9d16df87
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0146_lru_cache/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,119 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 146\. LRU Cache
+
+Medium
+
+Design a data structure that follows the constraints of a **[Least Recently Used (LRU) cache](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cache_replacement_policies#LRU)**.
+
+Implement the `LRUCache` class:
+
+* `LRUCache(int capacity)` Initialize the LRU cache with **positive** size `capacity`.
+* `int get(int key)` Return the value of the `key` if the key exists, otherwise return `-1`.
+* `void put(int key, int value)` Update the value of the `key` if the `key` exists. Otherwise, add the `key-value` pair to the cache. If the number of keys exceeds the `capacity` from this operation, **evict** the least recently used key.
+
+The functions `get` and `put` must each run in `O(1)` average time complexity.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input** ["LRUCache", "put", "put", "get", "put", "get", "put", "get", "get", "get"] [[2], [1, 1], [2, 2], [1], [3, 3], [2], [4, 4], [1], [3], [4]]
+
+**Output:** [null, null, null, 1, null, -1, null, -1, 3, 4]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+LRUCache lRUCache = new LRUCache(2);
+
+lRUCache.put(1, 1); // cache is {1=1}
+
+lRUCache.put(2, 2); // cache is {1=1, 2=2}
+
+lRUCache.get(1); // return 1
+
+lRUCache.put(3, 3); // LRU key was 2, evicts key 2, cache is {1=1, 3=3}
+
+lRUCache.get(2); // returns -1 (not found)
+
+lRUCache.put(4, 4); // LRU key was 1, evicts key 1, cache is {4=4, 3=3}
+
+lRUCache.get(1); // return -1 (not found)
+
+lRUCache.get(3); // return 3
+
+lRUCache.get(4); // return 4
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= capacity <= 3000`
+* 0 <= key <= 104
+* 0 <= value <= 105
+* At most 2 * 105 calls will be made to `get` and `put`.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class LRUCache(capacity: Int) {
+
+ private val nodeMap = HashMap()
+ val head = Node()
+ private val tail = Node()
+ var cacheCapacity = 0
+
+ init {
+ head.next = tail
+ tail.prev = head
+ cacheCapacity = capacity
+ }
+
+ fun get(key: Int): Int {
+ return if (!nodeMap.containsKey(key)) {
+ -1
+ } else {
+ val requiredNode = nodeMap.getValue(key)
+ update(requiredNode)
+ requiredNode.value
+ }
+ }
+
+ fun put(key: Int, value: Int) {
+ if (nodeMap.containsKey(key)) {
+ val requiredNode = nodeMap.getValue(key)
+ requiredNode.value = value
+ update(requiredNode)
+ } else {
+ val newNode = Node(key = key, value = value)
+ if (nodeMap.size >= cacheCapacity) {
+ val nodeToDelete = tail.prev!!
+ remove(nodeToDelete)
+ nodeMap.remove(nodeToDelete.key)
+ }
+ add(newNode)
+ nodeMap.put(key, newNode)
+ }
+ }
+
+ fun add(node: Node) {
+ val after = head.next
+ head.next = node
+ node.prev = head
+ node.next = after
+ after?.prev = node
+ }
+
+ private fun remove(node: Node) {
+ val before = node.prev
+ val after = node.next
+
+ before?.next = after
+ after?.prev = before
+ }
+
+ private fun update(node: Node) {
+ remove(node)
+ add(node)
+ }
+
+ data class Node(var key: Int = -1, var value: Int = -1, var next: Node? = null, var prev: Node? = null)
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0148_sort_list/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0148_sort_list/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0b43fe28
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0148_sort_list/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,100 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 148\. Sort List
+
+Medium
+
+Given the `head` of a linked list, return _the list after sorting it in **ascending order**_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** head = [4,2,1,3]
+
+**Output:** [1,2,3,4]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** head = [-1,5,3,4,0]
+
+**Output:** [-1,0,3,4,5]
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** head = []
+
+**Output:** []
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* The number of nodes in the list is in the range [0, 5 * 104].
+* -105 <= Node.val <= 105
+
+**Follow up:** Can you sort the linked list in `O(n logn)` time and `O(1)` memory (i.e. constant space)?
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import com_github_leetcode.ListNode
+
+/*
+ * Example:
+ * var li = ListNode(5)
+ * var v = li.`val`
+ * Definition for singly-linked list.
+ * class ListNode(var `val`: Int) {
+ * var next: ListNode? = null
+ * }
+ */
+@Suppress("NAME_SHADOWING")
+class Solution {
+ fun sortList(head: ListNode?): ListNode? {
+ if (head == null || head.next == null) {
+ return head
+ }
+ // Step 1: split the list into halves
+ var prev: ListNode? = null
+ var slow = head
+ var fast = head
+ while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
+ prev = slow
+ fast = fast.next!!.next
+ slow = slow!!.next
+ }
+ prev!!.next = null
+ // step 2: sort each half
+ val l1 = sortList(head)
+ val l2 = sortList(slow)
+ // step 3: merge the two halves
+ return merge(l1, l2)
+ }
+
+ private fun merge(l1: ListNode?, l2: ListNode?): ListNode? {
+ var l1 = l1
+ var l2 = l2
+ val result = ListNode(0)
+ var tmp: ListNode? = result
+ while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
+ if (l1.`val` < l2.`val`) {
+ tmp!!.next = l1
+ l1 = l1.next
+ } else {
+ tmp!!.next = l2
+ l2 = l2.next
+ }
+ tmp = tmp.next
+ }
+ if (l1 != null) {
+ tmp!!.next = l1
+ }
+ if (l2 != null) {
+ tmp!!.next = l2
+ }
+ return result.next
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0152_maximum_product_subarray/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0152_maximum_product_subarray/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..5474d814
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0152_maximum_product_subarray/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 152\. Maximum Product Subarray
+
+Medium
+
+Given an integer array `nums`, find a contiguous non-empty subarray within the array that has the largest product, and return _the product_.
+
+The test cases are generated so that the answer will fit in a **32-bit** integer.
+
+A **subarray** is a contiguous subsequence of the array.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [2,3,-2,4]
+
+**Output:** 6
+
+**Explanation:** [2,3] has the largest product 6.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [-2,0,-1]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:** The result cannot be 2, because [-2,-1] is not a subarray.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= nums.length <= 2 * 104
+* `-10 <= nums[i] <= 10`
+* The product of any prefix or suffix of `nums` is **guaranteed** to fit in a **32-bit** integer.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun maxProduct(nums: IntArray): Int {
+ var pos = nums[0]
+ var neg = nums[0]
+ var max = nums[0]
+ for (i in 1 until nums.size) {
+ val temp = pos
+ pos = Math.max(nums[i], nums[i] * if (nums[i] >= 0) pos else neg)
+ neg = Math.min(nums[i], nums[i] * if (nums[i] >= 0) neg else temp)
+ max = Math.max(max, pos)
+ }
+ return max
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0153_find_minimum_in_rotated_sorted_array/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0153_find_minimum_in_rotated_sorted_array/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e1eeee65
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0153_find_minimum_in_rotated_sorted_array/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 153\. Find Minimum in Rotated Sorted Array
+
+Medium
+
+Suppose an array of length `n` sorted in ascending order is **rotated** between `1` and `n` times. For example, the array `nums = [0,1,2,4,5,6,7]` might become:
+
+* `[4,5,6,7,0,1,2]` if it was rotated `4` times.
+* `[0,1,2,4,5,6,7]` if it was rotated `7` times.
+
+Notice that **rotating** an array `[a[0], a[1], a[2], ..., a[n-1]]` 1 time results in the array `[a[n-1], a[0], a[1], a[2], ..., a[n-2]]`.
+
+Given the sorted rotated array `nums` of **unique** elements, return _the minimum element of this array_.
+
+You must write an algorithm that runs in `O(log n) time.`
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [3,4,5,1,2]
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:** The original array was [1,2,3,4,5] rotated 3 times.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:** The original array was [0,1,2,4,5,6,7] and it was rotated 4 times.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [11,13,15,17]
+
+**Output:** 11
+
+**Explanation:** The original array was [11,13,15,17] and it was rotated 4 times.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `n == nums.length`
+* `1 <= n <= 5000`
+* `-5000 <= nums[i] <= 5000`
+* All the integers of `nums` are **unique**.
+* `nums` is sorted and rotated between `1` and `n` times.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ private fun findMinUtil(nums: IntArray, l: Int, r: Int): Int {
+ if (l == r) {
+ return nums[l]
+ }
+ val mid = (l + r) / 2
+ if (mid == l && nums[mid] < nums[r]) {
+ return nums[l]
+ }
+ if (mid - 1 >= 0 && nums[mid - 1] > nums[mid]) {
+ return nums[mid]
+ }
+ if (nums[mid] < nums[l]) {
+ return findMinUtil(nums, l, mid - 1)
+ } else if (nums[mid] > nums[r]) {
+ return findMinUtil(nums, mid + 1, r)
+ }
+ return findMinUtil(nums, l, mid - 1)
+ }
+
+ fun findMin(nums: IntArray): Int {
+ val l = 0
+ val r = nums.size - 1
+ return findMinUtil(nums, l, r)
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0155_min_stack/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0155_min_stack/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..da052ead
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0155_min_stack/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 155\. Min Stack
+
+Easy
+
+Design a stack that supports push, pop, top, and retrieving the minimum element in constant time.
+
+Implement the `MinStack` class:
+
+* `MinStack()` initializes the stack object.
+* `void push(int val)` pushes the element `val` onto the stack.
+* `void pop()` removes the element on the top of the stack.
+* `int top()` gets the top element of the stack.
+* `int getMin()` retrieves the minimum element in the stack.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input**
+
+ ["MinStack","push","push","push","getMin","pop","top","getMin"]
+ [[],[-2],[0],[-3],[],[],[],[]]
+
+**Output:** [null,null,null,null,-3,null,0,-2]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+ MinStack minStack = new MinStack();
+ minStack.push(-2);
+ minStack.push(0);
+ minStack.push(-3);
+ minStack.getMin(); // return -3
+ minStack.pop();
+ minStack.top(); // return 0
+ minStack.getMin(); // return -2
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* -231 <= val <= 231 - 1
+* Methods `pop`, `top` and `getMin` operations will always be called on **non-empty** stacks.
+* At most 3 * 104 calls will be made to `push`, `pop`, `top`, and `getMin`.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.Stack
+
+class MinStack() {
+ private val stack: Stack> = Stack()
+
+ fun push(x: Int) {
+ val min: Int = if (stack.isEmpty()) x
+ else getMin()
+
+ stack.push(x to minOf(min, x))
+ }
+
+ fun pop() {
+ stack.pop()
+ }
+
+ fun top(): Int {
+ return stack
+ .peek()
+ .first
+ }
+
+ fun getMin(): Int {
+ return stack
+ .peek()
+ .second
+ }
+}
+
+/*
+ * Your MinStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
+ * var obj = MinStack()
+ * obj.push(`val`)
+ * obj.pop()
+ * var param_3 = obj.top()
+ * var param_4 = obj.getMin()
+ */
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0160_intersection_of_two_linked_lists/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0160_intersection_of_two_linked_lists/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d8689bc8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0160_intersection_of_two_linked_lists/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 160\. Intersection of Two Linked Lists
+
+Easy
+
+Given the heads of two singly linked-lists `headA` and `headB`, return _the node at which the two lists intersect_. If the two linked lists have no intersection at all, return `null`.
+
+For example, the following two linked lists begin to intersect at node `c1`:
+
+
+
+The test cases are generated such that there are no cycles anywhere in the entire linked structure.
+
+**Note** that the linked lists must **retain their original structure** after the function returns.
+
+**Custom Judge:**
+
+The inputs to the **judge** are given as follows (your program is **not** given these inputs):
+
+* `intersectVal` - The value of the node where the intersection occurs. This is `0` if there is no intersected node.
+* `listA` - The first linked list.
+* `listB` - The second linked list.
+* `skipA` - The number of nodes to skip ahead in `listA` (starting from the head) to get to the intersected node.
+* `skipB` - The number of nodes to skip ahead in `listB` (starting from the head) to get to the intersected node.
+
+The judge will then create the linked structure based on these inputs and pass the two heads, `headA` and `headB` to your program. If you correctly return the intersected node, then your solution will be **accepted**.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,6,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
+
+**Output:** Intersected at '8'
+
+**Explanation:** The intersected node's value is 8 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [4,1,8,4,5]. From the head of B, it reads as [5,6,1,8,4,5]. There are 2 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in B.
+
+- Note that the intersected node's value is not 1 because the nodes with value 1 in A and B (2nd node in A and 3rd node in B) are different node references. In other words, they point to two different locations in memory, while the nodes with value 8 in A and B (3rd node in A and 4th node in B) point to the same location in memory.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** intersectVal = 2, listA = [1,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
+
+**Output:** Intersected at '2'
+
+**Explanation:** The intersected node's value is 2 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect).
+
+From the head of A, it reads as [1,9,1,2,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [3,2,4]. There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 1 node before the intersected node in B.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
+
+**Output:** No intersection
+
+**Explanation:** From the head of A, it reads as [2,6,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [1,5]. Since the two lists do not intersect, intersectVal must be 0, while skipA and skipB can be arbitrary values. Explanation: The two lists do not intersect, so return null.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* The number of nodes of `listA` is in the `m`.
+* The number of nodes of `listB` is in the `n`.
+* 1 <= m, n <= 3 * 104
+* 1 <= Node.val <= 105
+* `0 <= skipA < m`
+* `0 <= skipB < n`
+* `intersectVal` is `0` if `listA` and `listB` do not intersect.
+* `intersectVal == listA[skipA] == listB[skipB]` if `listA` and `listB` intersect.
+
+**Follow up:** Could you write a solution that runs in `O(m + n)` time and use only `O(1)` memory?
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import com_github_leetcode.ListNode
+
+/*
+ * Example:
+ * var li = ListNode(5)
+ * var v = li.`val`
+ * Definition for singly-linked list.
+ * class ListNode(var `val`: Int) {
+ * var next: ListNode? = null
+ * }
+ */
+class Solution {
+ fun getIntersectionNode(headA: ListNode?, headB: ListNode?): ListNode? {
+ var node1 = headA
+ var node2 = headB
+ while (node1 !== node2) {
+ node1 = if (node1 == null) headB else node1.next
+ node2 = if (node2 == null) headA else node2.next
+ }
+ return node1
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0169_majority_element/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0169_majority_element/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..61a95bb9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0169_majority_element/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 169\. Majority Element
+
+Easy
+
+Given an array `nums` of size `n`, return _the majority element_.
+
+The majority element is the element that appears more than `⌊n / 2⌋` times. You may assume that the majority element always exists in the array.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [3,2,3]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [2,2,1,1,1,2,2]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `n == nums.length`
+* 1 <= n <= 5 * 104
+* -109 <= nums[i] <= 109
+
+**Follow-up:** Could you solve the problem in linear time and in `O(1)` space?
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun majorityElement(arr: IntArray): Int {
+ var count = 1
+ var majority = arr[0]
+ // For Potential Majority Element
+ for (i in 1 until arr.size) {
+ if (arr[i] == majority) {
+ count++
+ } else {
+ if (count > 1) {
+ count--
+ } else {
+ majority = arr[i]
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ // For Confirmation
+ count = 0
+ for (j in arr) {
+ if (j == majority) {
+ count++
+ }
+ }
+ return if (count >= arr.size / 2 + 1) {
+ majority
+ } else {
+ -1
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0189_rotate_array/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0189_rotate_array/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..42cd6e9c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0189_rotate_array/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 189\. Rotate Array
+
+Medium
+
+Given an array, rotate the array to the right by `k` steps, where `k` is non-negative.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7], k = 3
+
+**Output:** [5,6,7,1,2,3,4]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+rotate 1 steps to the right: [7,1,2,3,4,5,6]
+
+rotate 2 steps to the right: [6,7,1,2,3,4,5]
+
+rotate 3 steps to the right: [5,6,7,1,2,3,4]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [-1,-100,3,99], k = 2
+
+**Output:** [3,99,-1,-100]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+rotate 1 steps to the right: [99,-1,-100,3]
+
+rotate 2 steps to the right: [3,99,-1,-100]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= nums.length <= 105
+* -231 <= nums[i] <= 231 - 1
+* 0 <= k <= 105
+
+**Follow up:**
+
+* Try to come up with as many solutions as you can. There are at least **three** different ways to solve this problem.
+* Could you do it in-place with `O(1)` extra space?
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+@Suppress("NAME_SHADOWING")
+class Solution {
+ private fun reverse(nums: IntArray, l: Int, r: Int) {
+ var l = l
+ var r = r
+ while (l <= r) {
+ val temp = nums[l]
+ nums[l] = nums[r]
+ nums[r] = temp
+ l++
+ r--
+ }
+ }
+
+ fun rotate(nums: IntArray, k: Int) {
+ val n = nums.size
+ val t = n - k % n
+ reverse(nums, 0, t - 1)
+ reverse(nums, t, n - 1)
+ reverse(nums, 0, n - 1)
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0198_house_robber/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0198_house_robber/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..66daebda
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0198_house_robber/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 198\. House Robber
+
+Medium
+
+You are a professional robber planning to rob houses along a street. Each house has a certain amount of money stashed, the only constraint stopping you from robbing each of them is that adjacent houses have security systems connected and **it will automatically contact the police if two adjacent houses were broken into on the same night**.
+
+Given an integer array `nums` representing the amount of money of each house, return _the maximum amount of money you can rob tonight **without alerting the police**_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,3,1]
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:** Rob house 1 (money = 1) and then rob house 3 (money = 3). Total amount you can rob = 1 + 3 = 4.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [2,7,9,3,1]
+
+**Output:** 12
+
+**Explanation:** Rob house 1 (money = 2), rob house 3 (money = 9) and rob house 5 (money = 1). Total amount you can rob = 2 + 9 + 1 = 12.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= nums.length <= 100`
+* `0 <= nums[i] <= 400`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun rob(nums: IntArray): Int {
+ if (nums.size == 0) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ if (nums.size == 1) {
+ return nums[0]
+ }
+ if (nums.size == 2) {
+ return Math.max(nums[0], nums[1])
+ }
+ val profit = IntArray(nums.size)
+ profit[0] = nums[0]
+ profit[1] = Math.max(nums[1], nums[0])
+ for (i in 2 until nums.size) {
+ profit[i] = Math.max(profit[i - 1], nums[i] + profit[i - 2])
+ }
+ return profit[nums.size - 1]
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0199_binary_tree_right_side_view/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0199_binary_tree_right_side_view/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..fd8588a5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0199_binary_tree_right_side_view/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 199\. Binary Tree Right Side View
+
+Medium
+
+Given the `root` of a binary tree, imagine yourself standing on the **right side** of it, return _the values of the nodes you can see ordered from top to bottom_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** root = [1,2,3,null,5,null,4]
+
+**Output:** [1,3,4]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** root = [1,null,3]
+
+**Output:** [1,3]
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** root = []
+
+**Output:** []
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* The number of nodes in the tree is in the range `[0, 100]`.
+* `-100 <= Node.val <= 100`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode
+
+/*
+ * Example:
+ * var ti = TreeNode(5)
+ * var v = ti.`val`
+ * Definition for a binary tree node.
+ * class TreeNode(var `val`: Int) {
+ * var left: TreeNode? = null
+ * var right: TreeNode? = null
+ * }
+ */
+class Solution {
+ fun rightSideView(root: TreeNode?): List {
+ val list: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ recurse(root, 0, list)
+ return list
+ }
+
+ private fun recurse(node: TreeNode?, level: Int, list: MutableList) {
+ if (node != null) {
+ if (list.size < level + 1) {
+ list.add(node.`val`)
+ }
+ recurse(node.right, level + 1, list)
+ recurse(node.left, level + 1, list)
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0200_number_of_islands/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0200_number_of_islands/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..7f86550b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0200_number_of_islands/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 200\. Number of Islands
+
+Medium
+
+Given an `m x n` 2D binary grid `grid` which represents a map of `'1'`s (land) and `'0'`s (water), return _the number of islands_.
+
+An **island** is surrounded by water and is formed by connecting adjacent lands horizontally or vertically. You may assume all four edges of the grid are all surrounded by water.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** grid = [
+
+["1","1","1","1","0"],
+
+["1","1","0","1","0"],
+
+["1","1","0","0","0"],
+
+["0","0","0","0","0"]
+
+]
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** grid = [
+
+["1","1","0","0","0"],
+
+["1","1","0","0","0"],
+
+["0","0","1","0","0"],
+
+["0","0","0","1","1"]
+
+]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `m == grid.length`
+* `n == grid[i].length`
+* `1 <= m, n <= 300`
+* `grid[i][j]` is `'0'` or `'1'`.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun numIslands(grid: Array): Int {
+ var islands = 0
+ if (grid.isNotEmpty() && grid[0].isNotEmpty()) {
+ for (i in grid.indices) {
+ for (j in grid[0].indices) {
+ if (grid[i][j] == '1') {
+ dfs(grid, i, j)
+ islands++
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return islands
+ }
+
+ private fun dfs(grid: Array, x: Int, y: Int) {
+ if (x < 0 || grid.size <= x || y < 0 || grid[0].size <= y || grid[x][y] != '1') {
+ return
+ }
+ grid[x][y] = 'x'
+ dfs(grid, x + 1, y)
+ dfs(grid, x - 1, y)
+ dfs(grid, x, y + 1)
+ dfs(grid, x, y - 1)
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0206_reverse_linked_list/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0206_reverse_linked_list/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..da6a416f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0206_reverse_linked_list/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,66 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 206\. Reverse Linked List
+
+Easy
+
+Given the `head` of a singly linked list, reverse the list, and return _the reversed list_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** head = [1,2,3,4,5]
+
+**Output:** [5,4,3,2,1]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** head = [1,2]
+
+**Output:** [2,1]
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** head = []
+
+**Output:** []
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* The number of nodes in the list is the range `[0, 5000]`.
+* `-5000 <= Node.val <= 5000`
+
+**Follow up:** A linked list can be reversed either iteratively or recursively. Could you implement both?
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import com_github_leetcode.ListNode
+
+/*
+ * Example:
+ * var li = ListNode(5)
+ * var v = li.`val`
+ * Definition for singly-linked list.
+ * class ListNode(var `val`: Int) {
+ * var next: ListNode? = null
+ * }
+ */
+class Solution {
+ fun reverseList(head: ListNode?): ListNode? {
+ var prev: ListNode? = null
+ var curr = head
+ while (curr !== null) {
+ val next = curr.next
+ curr.next = prev
+ prev = curr
+ curr = next
+ }
+ return prev
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0207_course_schedule/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0207_course_schedule/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..722dfecd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0207_course_schedule/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 207\. Course Schedule
+
+Medium
+
+There are a total of `numCourses` courses you have to take, labeled from `0` to `numCourses - 1`. You are given an array `prerequisites` where prerequisites[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that you **must** take course bi first if you want to take course ai.
+
+* For example, the pair `[0, 1]`, indicates that to take course `0` you have to first take course `1`.
+
+Return `true` if you can finish all courses. Otherwise, return `false`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** numCourses = 2, prerequisites = \[\[1,0]]
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** There are a total of 2 courses to take. To take course 1 you should have finished course 0. So it is possible.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** numCourses = 2, prerequisites = \[\[1,0],[0,1]]
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Explanation:** There are a total of 2 courses to take. To take course 1 you should have finished course 0, and to take course 0 you should also have finished course 1. So it is impossible.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= numCourses <= 2000`
+* `0 <= prerequisites.length <= 5000`
+* `prerequisites[i].length == 2`
+* 0 <= ai, bi < numCourses
+* All the pairs prerequisites[i] are **unique**.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun canFinish(numCourses: Int, prerequisites: Array): Boolean {
+ val adj: Array?> = arrayOfNulls>(numCourses)
+ for (i in 0 until numCourses) {
+ adj[i] = ArrayList()
+ }
+ for (pre in prerequisites) {
+ adj[pre[1]]?.add(pre[0])
+ }
+ val colors = IntArray(numCourses)
+ for (i in 0 until numCourses) {
+ if (colors[i] == WHITE && !adj[i]?.isEmpty()!! && hasCycle(adj, i, colors)) {
+ return false
+ }
+ }
+ return true
+ }
+
+ private fun hasCycle(adj: Array?>, node: Int, colors: IntArray): Boolean {
+ colors[node] = GRAY
+ for (nei in adj[node]!!) {
+ if (colors[nei] == GRAY) {
+ return true
+ }
+ if (colors[nei] == WHITE && hasCycle(adj, nei, colors)) {
+ return true
+ }
+ }
+ colors[node] = BLACK
+ return false
+ }
+
+ companion object {
+ private const val WHITE = 0
+ private const val GRAY = 1
+ private const val BLACK = 2
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0208_implement_trie_prefix_tree/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0208_implement_trie_prefix_tree/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..b56397f5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0208_implement_trie_prefix_tree/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,105 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 208\. Implement Trie (Prefix Tree)
+
+Medium
+
+A [**trie**](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trie) (pronounced as "try") or **prefix tree** is a tree data structure used to efficiently store and retrieve keys in a dataset of strings. There are various applications of this data structure, such as autocomplete and spellchecker.
+
+Implement the Trie class:
+
+* `Trie()` Initializes the trie object.
+* `void insert(String word)` Inserts the string `word` into the trie.
+* `boolean search(String word)` Returns `true` if the string `word` is in the trie (i.e., was inserted before), and `false` otherwise.
+* `boolean startsWith(String prefix)` Returns `true` if there is a previously inserted string `word` that has the prefix `prefix`, and `false` otherwise.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input** ["Trie", "insert", "search", "search", "startsWith", "insert", "search"] [[], ["apple"], ["apple"], ["app"], ["app"], ["app"], ["app"]]
+
+**Output:** [null, null, true, false, true, null, true]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Trie trie = new Trie();
+
+trie.insert("apple");
+
+trie.search("apple"); // return True
+
+trie.search("app"); // return False
+
+trie.startsWith("app"); // return True
+
+trie.insert("app");
+
+trie.search("app"); // return True
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= word.length, prefix.length <= 2000`
+* `word` and `prefix` consist only of lowercase English letters.
+* At most 3 * 104 calls **in total** will be made to `insert`, `search`, and `startsWith`.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Trie {
+ private val root: TrieNode
+ private var startWith = false
+
+ class TrieNode {
+ // Initialize your data structure here.
+ var children: Array
+ var isWord = false
+
+ init {
+ children = arrayOfNulls(26)
+ }
+ }
+
+ // Inserts a word into the trie.
+ fun insert(word: String) {
+ insert(word, root, 0)
+ }
+
+ private fun insert(word: String, root: TrieNode?, idx: Int) {
+ if (idx == word.length) {
+ root!!.isWord = true
+ return
+ }
+ val index = word[idx] - 'a'
+ if (root!!.children[index] == null) {
+ root.children[index] = TrieNode()
+ }
+ insert(word, root.children[index], idx + 1)
+ }
+
+ // Returns if the word is in the trie.
+ @JvmOverloads
+ fun search(word: String, root: TrieNode? = this.root, idx: Int = 0): Boolean {
+ if (idx == word.length) {
+ startWith = true
+ return root!!.isWord
+ }
+ val index = word[idx] - 'a'
+ if (root!!.children[index] == null) {
+ startWith = false
+ return false
+ }
+ return search(word, root.children[index], idx + 1)
+ }
+
+ // Returns if there is any word in the trie
+ // that starts with the given prefix.
+ fun startsWith(prefix: String): Boolean {
+ search(prefix)
+ return startWith
+ }
+
+ init {
+ root = TrieNode()
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0215_kth_largest_element_in_an_array/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0215_kth_largest_element_in_an_array/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..73f8680c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0215_kth_largest_element_in_an_array/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 215\. Kth Largest Element in an Array
+
+Medium
+
+Given an integer array `nums` and an integer `k`, return _the_ kth _largest element in the array_.
+
+Note that it is the kth largest element in the sorted order, not the kth distinct element.
+
+You must solve it in `O(n)` time complexity.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [3,2,1,5,6,4], k = 2
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [3,2,3,1,2,4,5,5,6], k = 4
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= k <= nums.length <= 105
+* -104 <= nums[i] <= 104
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.Arrays
+
+class Solution {
+ fun findKthLargest(nums: IntArray, k: Int): Int {
+ val n = nums.size
+ Arrays.sort(nums)
+ return nums[n - k]
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0221_maximal_square/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0221_maximal_square/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..9bb9cb39
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0221_maximal_square/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 221\. Maximal Square
+
+Medium
+
+Given an `m x n` binary `matrix` filled with `0`'s and `1`'s, _find the largest square containing only_ `1`'s _and return its area_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** matrix = \[\["1","0","1","0","0"],["1","0","1","1","1"],["1","1","1","1","1"],["1","0","0","1","0"]]
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** matrix = \[\["0","1"],["1","0"]]
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** matrix = \[\["0"]]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `m == matrix.length`
+* `n == matrix[i].length`
+* `1 <= m, n <= 300`
+* `matrix[i][j]` is `'0'` or `'1'`.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun maximalSquare(matrix: Array): Int {
+ val m = matrix.size
+ if (m == 0) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ val n: Int = matrix[0].size
+ if (n == 0) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ val dp = Array(m + 1) { IntArray(n + 1) }
+ var max = 0
+ for (i in 0 until m) {
+ for (j in 0 until n) {
+ if (matrix[i][j] == '1') {
+ // 1 + minimum from cell above, cell to the left, cell diagonal upper-left
+ val next = 1 + Math.min(dp[i][j], Math.min(dp[i + 1][j], dp[i][j + 1]))
+ // keep track of the maximum value seen
+ if (next > max) {
+ max = next
+ }
+ dp[i + 1][j + 1] = next
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return max * max
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0226_invert_binary_tree/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0226_invert_binary_tree/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ebd4fa89
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0226_invert_binary_tree/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 226\. Invert Binary Tree
+
+Easy
+
+Given the `root` of a binary tree, invert the tree, and return _its root_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** root = [4,2,7,1,3,6,9]
+
+**Output:** [4,7,2,9,6,3,1]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** root = [2,1,3]
+
+**Output:** [2,3,1]
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** root = []
+
+**Output:** []
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* The number of nodes in the tree is in the range `[0, 100]`.
+* `-100 <= Node.val <= 100`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode
+
+class Solution {
+ fun invertTree(root: TreeNode?): TreeNode? {
+ if (root == null) {
+ return null
+ }
+ val temp: TreeNode? = root.left
+ root.left = invertTree(root.right)
+ root.right = invertTree(temp)
+ return root
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0230_kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0230_kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..16a0e790
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0230_kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 230\. Kth Smallest Element in a BST
+
+Medium
+
+Given the `root` of a binary search tree, and an integer `k`, return _the_ kth _smallest value (**1-indexed**) of all the values of the nodes in the tree_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** root = [3,1,4,null,2], k = 1
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,null,1], k = 3
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* The number of nodes in the tree is `n`.
+* 1 <= k <= n <= 104
+* 0 <= Node.val <= 104
+
+**Follow up:** If the BST is modified often (i.e., we can do insert and delete operations) and you need to find the kth smallest frequently, how would you optimize?
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode
+
+class Solution {
+ private var k = 0
+ private var count = 0
+ private var `val` = 0
+ fun kthSmallest(root: TreeNode, k: Int): Int {
+ this.k = k
+ calculate(root)
+ return `val`
+ }
+
+ private fun calculate(node: TreeNode) {
+ if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
+ count++
+ if (count == k) {
+ `val` = node.`val`
+ }
+ return
+ }
+ if (node.left != null) {
+ calculate(node.left!!)
+ }
+ count++
+ if (count == k) {
+ `val` = node.`val`
+ return
+ }
+ if (node.right != null) {
+ calculate(node.right!!)
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0234_palindrome_linked_list/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0234_palindrome_linked_list/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..7c2c647c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0234_palindrome_linked_list/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 234\. Palindrome Linked List
+
+Easy
+
+Given the `head` of a singly linked list, return `true` _if it is a palindrome or_ `false` _otherwise_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** head = [1,2,2,1]
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** head = [1,2]
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* The number of nodes in the list is in the range [1, 105].
+* `0 <= Node.val <= 9`
+
+**Follow up:** Could you do it in `O(n)` time and `O(1)` space?
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import com_github_leetcode.ListNode
+
+/*
+ * Example:
+ * var li = ListNode(5)
+ * var v = li.`val`
+ * Definition for singly-linked list.
+ * class ListNode(var `val`: Int) {
+ * var next: ListNode? = null
+ * }
+ */
+@Suppress("NAME_SHADOWING")
+class Solution {
+ fun isPalindrome(head: ListNode?): Boolean {
+ var head = head
+ var len = 0
+ var right = head
+ // Calculate the length
+ while (right != null) {
+ right = right.next
+ len++
+ }
+ // Reverse the right half of the list
+ len = len / 2
+ right = head
+ for (i in 0 until len) {
+ right = right!!.next
+ }
+ var prev: ListNode? = null
+ while (right != null) {
+ val next = right.next
+ right.next = prev
+ prev = right
+ right = next
+ }
+ // Compare left half and right half
+ for (i in 0 until len) {
+ if (prev != null && head!!.`val` == prev.`val`) {
+ head = head.next
+ prev = prev.next
+ } else {
+ return false
+ }
+ }
+ return true
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0236_lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_tree/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0236_lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_tree/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..7614728d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0236_lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_tree/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 236\. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree
+
+Medium
+
+Given a binary tree, find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two given nodes in the tree.
+
+According to the [definition of LCA on Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lowest_common_ancestor): “The lowest common ancestor is defined between two nodes `p` and `q` as the lowest node in `T` that has both `p` and `q` as descendants (where we allow **a node to be a descendant of itself**).”
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** The LCA of nodes 5 and 1 is 3.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 4
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Explanation:** The LCA of nodes 5 and 4 is 5, since a node can be a descendant of itself according to the LCA definition.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** root = [1,2], p = 1, q = 2
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [2, 105].
+* -109 <= Node.val <= 109
+* All `Node.val` are **unique**.
+* `p != q`
+* `p` and `q` will exist in the tree.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode
+
+class Solution {
+ fun lowestCommonAncestor(root: TreeNode?, p: TreeNode, q: TreeNode): TreeNode? {
+ if (root == null) {
+ return null
+ }
+ if (root.`val` == p.`val` || root.`val` == q.`val`) {
+ return root
+ }
+ val left: TreeNode? = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q)
+ val right: TreeNode? = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q)
+ if (left != null && right != null) {
+ return root
+ }
+ return left ?: right
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0238_product_of_array_except_self/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0238_product_of_array_except_self/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a588977f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0238_product_of_array_except_self/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 238\. Product of Array Except Self
+
+Medium
+
+Given an integer array `nums`, return _an array_ `answer` _such that_ `answer[i]` _is equal to the product of all the elements of_ `nums` _except_ `nums[i]`.
+
+The product of any prefix or suffix of `nums` is **guaranteed** to fit in a **32-bit** integer.
+
+You must write an algorithm that runs in `O(n)` time and without using the division operation.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,3,4]
+
+**Output:** [24,12,8,6]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [-1,1,0,-3,3]
+
+**Output:** [0,0,9,0,0]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 2 <= nums.length <= 105
+* `-30 <= nums[i] <= 30`
+* The product of any prefix or suffix of `nums` is **guaranteed** to fit in a **32-bit** integer.
+
+**Follow up:** Can you solve the problem in `O(1) `extra space complexity? (The output array **does not** count as extra space for space complexity analysis.)
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun productExceptSelf(nums: IntArray): IntArray {
+ var product = 1
+ val ans = IntArray(nums.size)
+ for (num in nums) {
+ product = product * num
+ }
+ for (i in nums.indices) {
+ if (nums[i] != 0) {
+ ans[i] = product / nums[i]
+ } else {
+ var p = 1
+ for (j in nums.indices) {
+ if (j != i) {
+ p = p * nums[j]
+ }
+ }
+ ans[i] = p
+ }
+ }
+ return ans
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0239_sliding_window_maximum/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0239_sliding_window_maximum/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f5405846
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0239_sliding_window_maximum/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 239\. Sliding Window Maximum
+
+Hard
+
+You are given an array of integers `nums`, there is a sliding window of size `k` which is moving from the very left of the array to the very right. You can only see the `k` numbers in the window. Each time the sliding window moves right by one position.
+
+Return _the max sliding window_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,3,-1,-3,5,3,6,7], k = 3
+
+**Output:** [3,3,5,5,6,7]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Window position Max
+
+--------------- -----
+
+[1 3 -1] -3 5 3 6 7 **3**
+
+1 [3 -1 -3] 5 3 6 7 **3**
+
+1 3 [-1 -3 5] 3 6 7 **5**
+
+1 3 -1 [-3 5 3] 6 7 **5**
+
+1 3 -1 -3 [5 3 6] 7 **6**
+
+1 3 -1 -3 5 [3 6 7] **7**
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1], k = 1
+
+**Output:** [1]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= nums.length <= 105
+* -104 <= nums[i] <= 104
+* `1 <= k <= nums.length`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.LinkedList
+
+class Solution {
+ fun maxSlidingWindow(nums: IntArray, k: Int): IntArray {
+ val n = nums.size
+ val res = IntArray(n - k + 1)
+ var x = 0
+ val dq = LinkedList()
+ var i = 0
+ var j = 0
+ while (j < nums.size) {
+ while (!dq.isEmpty() && dq.peekLast() < nums[j]) {
+ dq.pollLast()
+ }
+ dq.addLast(nums[j])
+ if (j - i + 1 == k) {
+ res[x] = dq.peekFirst()
+ ++x
+ if (dq.peekFirst() == nums[i]) {
+ dq.pollFirst()
+ }
+ ++i
+ }
+ ++j
+ }
+ return res
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0240_search_a_2d_matrix_ii/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0240_search_a_2d_matrix_ii/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..245d9a6d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0240_search_a_2d_matrix_ii/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 240\. Search a 2D Matrix II
+
+Medium
+
+Write an efficient algorithm that searches for a value `target` in an `m x n` integer matrix `matrix`. This matrix has the following properties:
+
+* Integers in each row are sorted in ascending from left to right.
+* Integers in each column are sorted in ascending from top to bottom.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** matrix = \[\[1,4,7,11,15],[2,5,8,12,19],[3,6,9,16,22],[10,13,14,17,24],[18,21,23,26,30]], target = 5
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** matrix = \[\[1,4,7,11,15],[2,5,8,12,19],[3,6,9,16,22],[10,13,14,17,24],[18,21,23,26,30]], target = 20
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `m == matrix.length`
+* `n == matrix[i].length`
+* `1 <= n, m <= 300`
+* -109 <= matrix[i][j] <= 109
+* All the integers in each row are **sorted** in ascending order.
+* All the integers in each column are **sorted** in ascending order.
+* -109 <= target <= 109
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun searchMatrix(matrix: Array, target: Int): Boolean {
+ var r = 0
+ var c: Int = matrix[0].size - 1
+ while (r < matrix.size && c >= 0) {
+ if (matrix[r][c] == target) {
+ return true
+ } else if (matrix[r][c] > target) {
+ c--
+ } else {
+ r++
+ }
+ }
+ return false
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0283_move_zeroes/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0283_move_zeroes/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1f85d47b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0283_move_zeroes/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 283\. Move Zeroes
+
+Easy
+
+Given an integer array `nums`, move all `0`'s to the end of it while maintaining the relative order of the non-zero elements.
+
+**Note** that you must do this in-place without making a copy of the array.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [0,1,0,3,12]
+
+**Output:** [1,3,12,0,0]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [0]
+
+**Output:** [0]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= nums.length <= 104
+* -231 <= nums[i] <= 231 - 1
+
+**Follow up:** Could you minimize the total number of operations done?
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun moveZeroes(nums: IntArray) {
+ var firstZero = 0
+ for (i in nums.indices) {
+ if (nums[i] != 0) {
+ swap(firstZero, i, nums)
+ firstZero++
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ private fun swap(index1: Int, index2: Int, numbers: IntArray) {
+ val val2 = numbers[index2]
+ numbers[index2] = numbers[index1]
+ numbers[index1] = val2
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0287_find_the_duplicate_number/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0287_find_the_duplicate_number/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e601a598
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0287_find_the_duplicate_number/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 287\. Find the Duplicate Number
+
+Medium
+
+Given an array of integers `nums` containing `n + 1` integers where each integer is in the range `[1, n]` inclusive.
+
+There is only **one repeated number** in `nums`, return _this repeated number_.
+
+You must solve the problem **without** modifying the array `nums` and uses only constant extra space.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,3,4,2,2]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [3,1,3,4,2]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= n <= 105
+* `nums.length == n + 1`
+* `1 <= nums[i] <= n`
+* All the integers in `nums` appear only **once** except for **precisely one integer** which appears **two or more** times.
+
+**Follow up:**
+
+* How can we prove that at least one duplicate number must exist in `nums`?
+* Can you solve the problem in linear runtime complexity?
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun findDuplicate(nums: IntArray): Int {
+ val arr = IntArray(nums.size + 1)
+ for (num in nums) {
+ arr[num] += 1
+ if (arr[num] == 2) {
+ return num
+ }
+ }
+ return 0
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0295_find_median_from_data_stream/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0295_find_median_from_data_stream/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0531209a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0295_find_median_from_data_stream/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 295\. Find Median from Data Stream
+
+Hard
+
+The **median** is the middle value in an ordered integer list. If the size of the list is even, there is no middle value and the median is the mean of the two middle values.
+
+* For example, for `arr = [2,3,4]`, the median is `3`.
+* For example, for `arr = [2,3]`, the median is `(2 + 3) / 2 = 2.5`.
+
+Implement the MedianFinder class:
+
+* `MedianFinder()` initializes the `MedianFinder` object.
+* `void addNum(int num)` adds the integer `num` from the data stream to the data structure.
+* `double findMedian()` returns the median of all elements so far. Answers within 10-5 of the actual answer will be accepted.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input** ["MedianFinder", "addNum", "addNum", "findMedian", "addNum", "findMedian"] [[], [1], [2], [], [3], []]
+
+**Output:** [null, null, null, 1.5, null, 2.0]
+
+**Explanation:** MedianFinder medianFinder = new MedianFinder(); medianFinder.addNum(1); // arr = [1] medianFinder.addNum(2); // arr = [1, 2] medianFinder.findMedian(); // return 1.5 (i.e., (1 + 2) / 2) medianFinder.addNum(3); // arr[1, 2, 3] medianFinder.findMedian(); // return 2.0
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* -105 <= num <= 105
+* There will be at least one element in the data structure before calling `findMedian`.
+* At most 5 * 104 calls will be made to `addNum` and `findMedian`.
+
+**Follow up:**
+
+* If all integer numbers from the stream are in the range `[0, 100]`, how would you optimize your solution?
+* If `99%` of all integer numbers from the stream are in the range `[0, 100]`, how would you optimize your solution?
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.PriorityQueue
+
+class MedianFinder {
+ // take two queues one is for storing upper half and the other is for lowerhalf
+ // max stores the lower half
+ // min heap stores the upper half
+ private val maxHeap: PriorityQueue = PriorityQueue { a: Int, b: Int -> b - a }
+ private val minHeap: PriorityQueue = PriorityQueue()
+ fun addNum(num: Int) {
+ if (maxHeap.isEmpty() || maxHeap.peek() > num) {
+ maxHeap.offer(num)
+ } else {
+ minHeap.offer(num)
+ }
+ if (Math.abs(maxHeap.size - minHeap.size) > 1) {
+ balance(maxHeap, minHeap)
+ }
+ }
+
+ fun balance(maxHeap: PriorityQueue, minHeap: PriorityQueue) {
+ val large = if (maxHeap.size > minHeap.size) maxHeap else minHeap
+ val small = if (maxHeap.size > minHeap.size) minHeap else maxHeap
+ small.offer(large.poll())
+ }
+
+ fun findMedian(): Double {
+ val large = if (maxHeap.size > minHeap.size) maxHeap else minHeap
+ val small = if (maxHeap.size > minHeap.size) minHeap else maxHeap
+ return if (large.size == small.size) {
+ (large.peek() + small.peek()).toDouble() / 2
+ } else {
+ large.peek().toDouble()
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+/*
+ * Your MedianFinder object will be instantiated and called as such:
+ * MedianFinder obj = new MedianFinder();
+ * obj.addNum(num);
+ * double param_2 = obj.findMedian();
+ */
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0300_longest_increasing_subsequence/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0300_longest_increasing_subsequence/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3c665e7b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0300_longest_increasing_subsequence/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 300\. Longest Increasing Subsequence
+
+Medium
+
+Given an integer array `nums`, return the length of the longest strictly increasing subsequence.
+
+A **subsequence** is a sequence that can be derived from an array by deleting some or no elements without changing the order of the remaining elements. For example, `[3,6,2,7]` is a subsequence of the array `[0,3,1,6,2,2,7]`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [10,9,2,5,3,7,101,18]
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:** The longest increasing subsequence is [2,3,7,101], therefore the length is 4.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [0,1,0,3,2,3]
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [7,7,7,7,7,7,7]
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= nums.length <= 2500`
+* -104 <= nums[i] <= 104
+
+**Follow up:** Can you come up with an algorithm that runs in `O(n log(n))` time complexity?
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun lengthOfLIS(nums: IntArray): Int {
+ if (nums.isEmpty()) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ val dp = IntArray(nums.size + 1)
+ // prefill the dp table
+ for (i in 1 until dp.size) {
+ dp[i] = Int.MAX_VALUE
+ }
+ val left = 1
+ var right = 1
+ for (curr in nums) {
+ var start = left
+ var end = right
+ // binary search, find the one that is lower than curr
+ while (start + 1 < end) {
+ val mid = start + (end - start) / 2
+ if (dp[mid] > curr) {
+ end = mid
+ } else {
+ start = mid
+ }
+ }
+ // update our dp table
+ if (dp[start] > curr) {
+ dp[start] = curr
+ } else if (curr > dp[start] && curr < dp[end]) {
+ dp[end] = curr
+ } else if (curr > dp[end]) {
+ dp[++end] = curr
+ right++
+ }
+ }
+ return right
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0301_0400/s0322_coin_change/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0301_0400/s0322_coin_change/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a0b40b81
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0301_0400/s0322_coin_change/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 322\. Coin Change
+
+Medium
+
+You are given an integer array `coins` representing coins of different denominations and an integer `amount` representing a total amount of money.
+
+Return _the fewest number of coins that you need to make up that amount_. If that amount of money cannot be made up by any combination of the coins, return `-1`.
+
+You may assume that you have an infinite number of each kind of coin.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** coins = [1,2,5], amount = 11
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** 11 = 5 + 5 + 1
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** coins = [2], amount = 3
+
+**Output:** -1
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** coins = [1], amount = 0
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= coins.length <= 12`
+* 1 <= coins[i] <= 231 - 1
+* 0 <= amount <= 104
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun coinChange(coins: IntArray, amount: Int): Int {
+ val dp = IntArray(amount + 1)
+ dp[0] = 1
+ for (coin in coins) {
+ for (i in coin..amount) {
+ val prev = dp[i - coin]
+ if (prev > 0) {
+ if (dp[i] == 0) {
+ dp[i] = prev + 1
+ } else {
+ dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i], prev + 1)
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[amount] - 1
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0301_0400/s0347_top_k_frequent_elements/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0301_0400/s0347_top_k_frequent_elements/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..34401e72
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0301_0400/s0347_top_k_frequent_elements/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 347\. Top K Frequent Elements
+
+Medium
+
+Given an integer array `nums` and an integer `k`, return _the_ `k` _most frequent elements_. You may return the answer in **any order**.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,1,1,2,2,3], k = 2
+
+**Output:** [1,2]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1], k = 1
+
+**Output:** [1]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= nums.length <= 105
+* -104 <= nums[i] <= 104
+* `k` is in the range `[1, the number of unique elements in the array]`.
+* It is **guaranteed** that the answer is **unique**.
+
+**Follow up:** Your algorithm's time complexity must be better than `O(n log n)`, where n is the array's size.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.Arrays
+import java.util.PriorityQueue
+import java.util.Queue
+
+class Solution {
+ fun topKFrequent(nums: IntArray, k: Int): IntArray {
+ Arrays.sort(nums)
+ // Min heap of
+ val queue: Queue = PriorityQueue(k + 1) { a: IntArray, b: IntArray -> a[1] - b[1] }
+ // Filter with min heap
+ var j = 0
+ for (i in 0..nums.size) {
+ if (i == nums.size || nums[i] != nums[j]) {
+ queue.offer(intArrayOf(nums[j], i - j))
+ if (queue.size > k) {
+ queue.poll()
+ }
+ j = i
+ }
+ }
+ // Convert to int array
+ val result = IntArray(k)
+ for (i in k - 1 downTo 0) {
+ result[i] = queue.poll().get(0)
+ }
+ return result
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0301_0400/s0378_kth_smallest_element_in_a_sorted_matrix/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0301_0400/s0378_kth_smallest_element_in_a_sorted_matrix/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..587d9936
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0301_0400/s0378_kth_smallest_element_in_a_sorted_matrix/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 378\. Kth Smallest Element in a Sorted Matrix
+
+Medium
+
+Given an `n x n` `matrix` where each of the rows and columns is sorted in ascending order, return _the_ kth _smallest element in the matrix_.
+
+Note that it is the kth smallest element **in the sorted order**, not the kth **distinct** element.
+
+You must find a solution with a memory complexity better than O(n2).
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** matrix = \[\[1,5,9],[10,11,13],[12,13,15]], k = 8
+
+**Output:** 13
+
+**Explanation:** The elements in the matrix are [1,5,9,10,11,12,13,**13**,15], and the 8th smallest number is 13
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** matrix = \[\[-5]], k = 1
+
+**Output:** -5
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `n == matrix.length == matrix[i].length`
+* `1 <= n <= 300`
+* -109 <= matrix[i][j] <= 109
+* All the rows and columns of `matrix` are **guaranteed** to be sorted in **non-decreasing order**.
+* 1 <= k <= n2
+
+**Follow up:**
+
+* Could you solve the problem with a constant memory (i.e., `O(1)` memory complexity)?
+* Could you solve the problem in `O(n)` time complexity? The solution may be too advanced for an interview but you may find reading [this paper](http://www.cse.yorku.ca/~andy/pubs/X+Y.pdf) fun.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun kthSmallest(matrix: Array?, k: Int): Int {
+ if (matrix == null || matrix.size == 0) {
+ return -1
+ }
+ var start = matrix[0][0]
+ var end = matrix[matrix.size - 1][matrix[0].size - 1]
+ // O(log(max-min)) time
+ while (start + 1 < end) {
+ val mid = start + (end - start) / 2
+ if (countLessEqual(matrix, mid) < k) {
+ // look towards end
+ start = mid
+ } else {
+ // look towards start
+ end = mid
+ }
+ }
+
+ // leave only with start and end, one of them must be the answer
+ // try to see if start fits the criteria first
+ return if (countLessEqual(matrix, start) >= k) {
+ start
+ } else {
+ end
+ }
+ }
+
+ // countLessEqual
+ // O(n) Time
+ private fun countLessEqual(matrix: Array, target: Int): Int {
+ // binary elimination from top right
+ var row = 0
+ var col: Int = matrix[0].size - 1
+ var count = 0
+ while (row < matrix.size && col >= 0) {
+ if (matrix[row][col] <= target) {
+ // get the count in current row
+ count += col + 1
+ row++
+ } else if (matrix[row][col] > target) {
+ // eliminate the current col
+ col--
+ }
+ }
+ return count
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0301_0400/s0394_decode_string/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0301_0400/s0394_decode_string/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..995b1b59
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0301_0400/s0394_decode_string/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 394\. Decode String
+
+Medium
+
+Given an encoded string, return its decoded string.
+
+The encoding rule is: `k[encoded_string]`, where the `encoded_string` inside the square brackets is being repeated exactly `k` times. Note that `k` is guaranteed to be a positive integer.
+
+You may assume that the input string is always valid; there are no extra white spaces, square brackets are well-formed, etc. Furthermore, you may assume that the original data does not contain any digits and that digits are only for those repeat numbers, `k`. For example, there will not be input like `3a` or `2[4]`.
+
+The test cases are generated so that the length of the output will never exceed 105.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "3[a]2[bc]"
+
+**Output:** "aaabcbc"
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "3[a2[c]]"
+
+**Output:** "accaccacc"
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** s = "2[abc]3[cd]ef"
+
+**Output:** "abcabccdcdcdef"
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= s.length <= 30`
+* `s` consists of lowercase English letters, digits, and square brackets `'[]'`.
+* `s` is guaranteed to be **a valid** input.
+* All the integers in `s` are in the range `[1, 300]`.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ private var i = 0
+
+ fun decodeString(s: String): String {
+ var count = 0
+ val sb = StringBuilder()
+ while (i < s.length) {
+ val c = s[i]
+ i++
+ if (Character.isLetter(c)) {
+ sb.append(c)
+ } else if (Character.isDigit(c)) {
+ count = count * 10 + Character.getNumericValue(c)
+ } else if (c == ']') {
+ break
+ } else if (c == '[') {
+ // sub problem
+ val repeat = decodeString(s)
+ while (count > 0) {
+ sb.append(repeat)
+ count--
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return sb.toString()
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0401_0500/s0416_partition_equal_subset_sum/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0401_0500/s0416_partition_equal_subset_sum/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d33c587b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0401_0500/s0416_partition_equal_subset_sum/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 416\. Partition Equal Subset Sum
+
+Medium
+
+Given a **non-empty** array `nums` containing **only positive integers**, find if the array can be partitioned into two subsets such that the sum of elements in both subsets is equal.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,5,11,5]
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** The array can be partitioned as [1, 5, 5] and [11].
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,3,5]
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Explanation:** The array cannot be partitioned into equal sum subsets.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= nums.length <= 200`
+* `1 <= nums[i] <= 100`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun canPartition(nums: IntArray): Boolean {
+ var sum = 0
+ for (num in nums) {
+ sum += num
+ }
+ if (sum % 2 != 0) {
+ return false
+ }
+ sum /= 2
+ // if use primitive boolean array will make default value to false
+ // we need the default value "null" to help us to do the memo
+ val dp = arrayOfNulls(sum + 1)
+ return sumTo(nums, sum, 0, dp)
+ }
+
+ private fun sumTo(nums: IntArray, sum: Int, index: Int, dp: Array): Boolean {
+ if (sum == 0) {
+ return true
+ }
+ if (sum < 0) {
+ return false
+ }
+ if (index == nums.size) {
+ return false
+ }
+ if (dp[sum] != null) {
+ return dp[sum]!!
+ }
+ // use the number or not use the number
+ dp[sum] = sumTo(nums, sum - nums[index], index + 1, dp) || sumTo(nums, sum, index + 1, dp)
+ return dp[sum]!!
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0401_0500/s0437_path_sum_iii/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0401_0500/s0437_path_sum_iii/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..50db943c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0401_0500/s0437_path_sum_iii/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,77 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 437\. Path Sum III
+
+Medium
+
+Given the `root` of a binary tree and an integer `targetSum`, return _the number of paths where the sum of the values along the path equals_ `targetSum`.
+
+The path does not need to start or end at the root or a leaf, but it must go downwards (i.e., traveling only from parent nodes to child nodes).
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** root = [10,5,-3,3,2,null,11,3,-2,null,1], targetSum = 8
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** The paths that sum to 8 are shown.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,5,1], targetSum = 22
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* The number of nodes in the tree is in the range `[0, 1000]`.
+* -109 <= Node.val <= 109
+* `-1000 <= targetSum <= 1000`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode
+
+/*
+ * Example:
+ * var ti = TreeNode(5)
+ * var v = ti.`val`
+ * Definition for a binary tree node.
+ * class TreeNode(var `val`: Int) {
+ * var left: TreeNode? = null
+ * var right: TreeNode? = null
+ * }
+ */
+@Suppress("NAME_SHADOWING")
+class Solution {
+ private var count = 0
+
+ fun pathSum(root: TreeNode?, targetSum: Int): Int {
+ if (root == null) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ helper(root, targetSum, 0)
+ pathSum(root.left, targetSum)
+ pathSum(root.right, targetSum)
+ return count
+ }
+
+ fun helper(node: TreeNode, targetSum: Int, currSum: Long) {
+ var currSum = currSum
+ currSum += node.`val`
+ if (targetSum.toLong() == currSum) {
+ count++
+ }
+ if (node.left != null) {
+ helper(node.left!!, targetSum, currSum)
+ }
+ if (node.right != null) {
+ helper(node.right!!, targetSum, currSum)
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0401_0500/s0438_find_all_anagrams_in_a_string/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0401_0500/s0438_find_all_anagrams_in_a_string/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..57012266
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0401_0500/s0438_find_all_anagrams_in_a_string/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 438\. Find All Anagrams in a String
+
+Medium
+
+Given two strings `s` and `p`, return _an array of all the start indices of_ `p`_'s anagrams in_ `s`. You may return the answer in **any order**.
+
+An **Anagram** is a word or phrase formed by rearranging the letters of a different word or phrase, typically using all the original letters exactly once.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "cbaebabacd", p = "abc"
+
+**Output:** [0,6]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The substring with start index = 0 is "cba", which is an anagram of "abc".
+
+The substring with start index = 6 is "bac", which is an anagram of "abc".
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "abab", p = "ab"
+
+**Output:** [0,1,2]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The substring with start index = 0 is "ab", which is an anagram of "ab".
+
+The substring with start index = 1 is "ba", which is an anagram of "ab".
+
+The substring with start index = 2 is "ab", which is an anagram of "ab".
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= s.length, p.length <= 3 * 104
+* `s` and `p` consist of lowercase English letters.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun findAnagrams(s: String, p: String): List {
+ val map = IntArray(26)
+ for (i in 0 until p.length) {
+ map[p[i] - 'a']++
+ }
+ val res: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ var i = 0
+ var j = 0
+ while (i < s.length) {
+ val idx = s[i] - 'a'
+ // add the new character
+ map[idx]--
+ // if the length is greater than windows length, pop the left charcater in the window
+ if (i >= p.length) {
+ map[s[j++] - 'a']++
+ }
+ var finish = true
+ for (k in 0..25) {
+ // if it is not an anagram of string p
+ if (map[k] != 0) {
+ finish = false
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ if (i >= p.length - 1 && finish) {
+ res.add(j)
+ }
+ i++
+ }
+ return res
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0543_diameter_of_binary_tree/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0543_diameter_of_binary_tree/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..b90b8f4c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0543_diameter_of_binary_tree/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 543\. Diameter of Binary Tree
+
+Easy
+
+Given the `root` of a binary tree, return _the length of the **diameter** of the tree_.
+
+The **diameter** of a binary tree is the **length** of the longest path between any two nodes in a tree. This path may or may not pass through the `root`.
+
+The **length** of a path between two nodes is represented by the number of edges between them.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** root = [1,2,3,4,5]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** 3 is the length of the path [4,2,1,3] or [5,2,1,3].
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** root = [1,2]
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 104].
+* `-100 <= Node.val <= 100`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode
+
+/*
+ * Example:
+ * var ti = TreeNode(5)
+ * var v = ti.`val`
+ * Definition for a binary tree node.
+ * class TreeNode(var `val`: Int) {
+ * var left: TreeNode? = null
+ * var right: TreeNode? = null
+ * }
+ */
+class Solution {
+ private var diameter = 0
+
+ fun diameterOfBinaryTree(root: TreeNode?): Int {
+ diameter = 0
+ diameterOfBinaryTreeUtil(root)
+ return diameter
+ }
+
+ private fun diameterOfBinaryTreeUtil(root: TreeNode?): Int {
+ if (root == null) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ val leftLength = if (root.left != null) 1 + diameterOfBinaryTreeUtil(root.left) else 0
+ val rightLength = if (root.right != null) 1 + diameterOfBinaryTreeUtil(root.right) else 0
+ diameter = Math.max(diameter, leftLength + rightLength)
+ return Math.max(leftLength, rightLength)
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0560_subarray_sum_equals_k/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0560_subarray_sum_equals_k/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0f356ad9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0560_subarray_sum_equals_k/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 560\. Subarray Sum Equals K
+
+Medium
+
+Given an array of integers `nums` and an integer `k`, return _the total number of subarrays whose sum equals to_ `k`.
+
+A subarray is a contiguous **non-empty** sequence of elements within an array.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,1,1], k = 2
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,3], k = 3
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= nums.length <= 2 * 104
+* `-1000 <= nums[i] <= 1000`
+* -107 <= k <= 107
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun subarraySum(nums: IntArray, k: Int): Int {
+ var tempSum = 0
+ var ret = 0
+ val sumCount: MutableMap = HashMap()
+ sumCount[0] = 1
+ for (i in nums) {
+ tempSum += i
+ if (sumCount.containsKey(tempSum - k)) {
+ ret += sumCount[tempSum - k]!!
+ }
+ if (sumCount[tempSum] != null) {
+ sumCount[tempSum] = sumCount[tempSum]!! + 1
+ } else {
+ sumCount[tempSum] = 1
+ }
+ }
+ return ret
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0647_palindromic_substrings/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0647_palindromic_substrings/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..5f0ce328
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0647_palindromic_substrings/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 647\. Palindromic Substrings
+
+Medium
+
+Given a string `s`, return _the number of **palindromic substrings** in it_.
+
+A string is a **palindrome** when it reads the same backward as forward.
+
+A **substring** is a contiguous sequence of characters within the string.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "abc"
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** Three palindromic strings: "a", "b", "c".
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "aaa"
+
+**Output:** 6
+
+**Explanation:** Six palindromic strings: "a", "a", "a", "aa", "aa", "aaa".
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= s.length <= 1000`
+* `s` consists of lowercase English letters.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ private fun expand(a: CharArray, l: Int, r: Int, res: IntArray) {
+ var left = l
+ var right = r
+ while (left >= 0 && right < a.size) {
+ if (a[left] != a[right]) {
+ return
+ } else {
+ res[0]++
+ left--
+ right++
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ fun countSubstrings(s: String): Int {
+ val a = s.toCharArray()
+ val res = intArrayOf(0)
+ for (i in a.indices) {
+ expand(a, i, i, res)
+ expand(a, i, i + 1, res)
+ }
+ return res[0]
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0701_0800/s0739_daily_temperatures/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0701_0800/s0739_daily_temperatures/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c9a79a65
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0701_0800/s0739_daily_temperatures/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 739\. Daily Temperatures
+
+Medium
+
+Given an array of integers `temperatures` represents the daily temperatures, return _an array_ `answer` _such that_ `answer[i]` _is the number of days you have to wait after the_ ith _day to get a warmer temperature_. If there is no future day for which this is possible, keep `answer[i] == 0` instead.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** temperatures = [73,74,75,71,69,72,76,73]
+
+**Output:** [1,1,4,2,1,1,0,0]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** temperatures = [30,40,50,60]
+
+**Output:** [1,1,1,0]
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** temperatures = [30,60,90]
+
+**Output:** [1,1,0]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= temperatures.length <= 105
+* `30 <= temperatures[i] <= 100`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun dailyTemperatures(temperatures: IntArray): IntArray {
+ val sol = IntArray(temperatures.size)
+ sol[temperatures.size - 1] = 0
+ for (i in sol.size - 2 downTo 0) {
+ var j = i + 1
+ while (j <= sol.size) {
+ if (temperatures[i] < temperatures[j]) {
+ sol[i] = j - i
+ break
+ } else {
+ if (sol[j] == 0) {
+ break
+ }
+ j = j + sol[j]
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return sol
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0701_0800/s0763_partition_labels/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0701_0800/s0763_partition_labels/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..b024af7f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0701_0800/s0763_partition_labels/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 763\. Partition Labels
+
+Medium
+
+You are given a string `s`. We want to partition the string into as many parts as possible so that each letter appears in at most one part.
+
+Note that the partition is done so that after concatenating all the parts in order, the resultant string should be `s`.
+
+Return _a list of integers representing the size of these parts_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "ababcbacadefegdehijhklij"
+
+**Output:** [9,7,8]
+
+**Explanation:** The partition is "ababcbaca", "defegde", "hijhklij". This is a partition so that each letter appears in at most one part. A partition like "ababcbacadefegde", "hijhklij" is incorrect, because it splits s into less parts.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "eccbbbbdec"
+
+**Output:** [10]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= s.length <= 500`
+* `s` consists of lowercase English letters.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun partitionLabels(s: String): List {
+ val letters = s.toCharArray()
+ val result: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ val position = IntArray(26)
+ for (i in letters.indices) {
+ position[letters[i] - 'a'] = i
+ }
+ var i = 0
+ var prev = -1
+ var max = 0
+ while (i < letters.size) {
+ if (position[letters[i] - 'a'] > max) {
+ max = position[letters[i] - 'a']
+ }
+ if (i == max) {
+ result.add(i - prev)
+ prev = i
+ }
+ i++
+ }
+ return result
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0864_shortest_path_to_get_all_keys/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0864_shortest_path_to_get_all_keys/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..da6c0098
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0864_shortest_path_to_get_all_keys/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,156 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 864\. Shortest Path to Get All Keys
+
+Hard
+
+You are given an `m x n` grid `grid` where:
+
+* `'.'` is an empty cell.
+* `'#'` is a wall.
+* `'@'` is the starting point.
+* Lowercase letters represent keys.
+* Uppercase letters represent locks.
+
+You start at the starting point and one move consists of walking one space in one of the four cardinal directions. You cannot walk outside the grid, or walk into a wall.
+
+If you walk over a key, you can pick it up and you cannot walk over a lock unless you have its corresponding key.
+
+For some `1 <= k <= 6`, there is exactly one lowercase and one uppercase letter of the first `k` letters of the English alphabet in the grid. This means that there is exactly one key for each lock, and one lock for each key; and also that the letters used to represent the keys and locks were chosen in the same order as the English alphabet.
+
+Return _the lowest number of moves to acquire all keys_. If it is impossible, return `-1`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** grid = ["@.a.#","###.#","b.A.B"]
+
+**Output:** 8
+
+**Explanation:** Note that the goal is to obtain all the keys not to open all the locks.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** grid = ["@..aA","..B#.","....b"]
+
+**Output:** 6
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** grid = ["@Aa"]
+
+**Output:** -1
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `m == grid.length`
+* `n == grid[i].length`
+* `1 <= m, n <= 30`
+* `grid[i][j]` is either an English letter, `'.'`, `'#'`, or `'@'`.
+* The number of keys in the grid is in the range `[1, 6]`.
+* Each key in the grid is **unique**.
+* Each key in the grid has a matching lock.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.LinkedList
+import java.util.Queue
+
+class Solution {
+ private var m = 0
+ private var n = 0
+ fun shortestPathAllKeys(stringGrid: Array): Int {
+ // strategy: BFS + masking
+ m = stringGrid.size
+ n = stringGrid[0].length
+ val grid = Array(m) { CharArray(n) }
+ var index = 0
+ // convert to char Array
+ for (s in stringGrid) {
+ grid[index++] = s.toCharArray()
+ }
+ // number of keys
+ var count = 0
+ val q: Queue = LinkedList()
+ for (i in 0 until m) {
+ for (j in 0 until n) {
+ // find starting position
+ if (grid[i][j] == '@') {
+ q.add(intArrayOf(i, j, 0))
+ }
+ // count number of keys
+ if (grid[i][j] in 'a'..'f') {
+ count++
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ val dx = intArrayOf(-1, 0, 1, 0)
+ val dy = intArrayOf(0, -1, 0, 1)
+ // this is the amt of keys we need
+ val target = (1 shl count) - 1
+ // keep track of position and current state
+ val visited = Array(m) {
+ Array(n) {
+ BooleanArray(target + 1)
+ }
+ }
+ // set initial position and state to true
+ visited[q.peek()[0]][q.peek()[1]][0] = true
+ var steps = 0
+ while (!q.isEmpty()) {
+ // use size to make sure everything is on one level
+ var size = q.size
+ while (--size >= 0) {
+ val curr = q.poll()
+ val x = curr[0]
+ val y = curr[1]
+ val state = curr[2]
+ // found all keys
+ if (state == target) {
+ return steps
+ }
+ for (i in 0..3) {
+ val nx = x + dx[i]
+ val ny = y + dy[i]
+ // use new state so we don't mess up current state
+ var nState = state
+ // out of bounds or reached wall
+ if (!inBounds(nx, ny) || grid[nx][ny] == '#') {
+ continue
+ }
+ // found key
+ // use OR to add key to our current state because if we already had the key the
+ // digit would still be 1/true
+ if (grid[nx][ny] in 'a'..'f') {
+ // bit mask our found key
+ nState = state or (1 shl grid[nx][ny] - 'a')
+ }
+ // found lock
+ // use & to see if we have the key
+ // 0 means that the digit we are looking at is 0
+ // need a 1 at the digit spot which means there is a key there
+ if (('A' > grid[nx][ny] || grid[nx][ny] > 'F' || nState and (1 shl grid[nx][ny] - 'A') != 0) &&
+ !visited[nx][ny][nState]
+ ) {
+ q.add(intArrayOf(nx, ny, nState))
+ visited[nx][ny][nState] = true
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ steps++
+ }
+ return -1
+ }
+
+ private fun inBounds(x: Int, y: Int): Boolean {
+ return x in 0 until m && y >= 0 && y < n
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0901_1000/s0994_rotting_oranges/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0901_1000/s0994_rotting_oranges/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..bfa1a123
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0901_1000/s0994_rotting_oranges/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,100 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 994\. Rotting Oranges
+
+Medium
+
+You are given an `m x n` `grid` where each cell can have one of three values:
+
+* `0` representing an empty cell,
+* `1` representing a fresh orange, or
+* `2` representing a rotten orange.
+
+Every minute, any fresh orange that is **4-directionally adjacent** to a rotten orange becomes rotten.
+
+Return _the minimum number of minutes that must elapse until no cell has a fresh orange_. If _this is impossible, return_ `-1`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** grid = \[\[2,1,1],[1,1,0],[0,1,1]]
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** grid = \[\[2,1,1],[0,1,1],[1,0,1]]
+
+**Output:** -1
+
+**Explanation:** The orange in the bottom left corner (row 2, column 0) is never rotten, because rotting only happens 4-directionally.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** grid = \[\[0,2]]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:** Since there are already no fresh oranges at minute 0, the answer is just 0.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `m == grid.length`
+* `n == grid[i].length`
+* `1 <= m, n <= 10`
+* `grid[i][j]` is `0`, `1`, or `2`.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.LinkedList
+import java.util.Queue
+
+class Solution {
+ fun orangesRotting(grid: Array): Int {
+ val queue: Queue = LinkedList()
+ val row = grid.size
+ val col: Int = grid[0].size
+ var countActive = 0
+ for (i in 0 until row) {
+ for (j in 0 until col) {
+ if (grid[i][j] == 2) {
+ queue.add(intArrayOf(i, j))
+ }
+ if (grid[i][j] != 0) {
+ countActive++
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ if (countActive == 0) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ var countCurrent = 0
+ var count = 0
+ val dx = intArrayOf(0, 0, 1, -1)
+ val dy = intArrayOf(1, -1, 0, 0)
+ while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
+ val size: Int = queue.size
+ count += size
+ for (i in 0 until size) {
+ val arr: IntArray = queue.poll()
+ for (j in 0..3) {
+ val x = arr[0] + dx[j]
+ val y = arr[1] + dy[j]
+ if (x < 0 || y < 0 || x >= row || y >= col || grid[x][y] != 1) {
+ continue
+ }
+ grid[x][y] = 2
+ queue.add(intArrayOf(x, y))
+ }
+ }
+ if (!queue.isEmpty()) {
+ countCurrent++
+ }
+ }
+ return if (countActive == count) countCurrent else -1
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1101_1200/s1143_longest_common_subsequence/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1101_1200/s1143_longest_common_subsequence/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..7d304644
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1101_1200/s1143_longest_common_subsequence/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1143\. Longest Common Subsequence
+
+Medium
+
+Given two strings `text1` and `text2`, return _the length of their longest **common subsequence**._ If there is no **common subsequence**, return `0`.
+
+A **subsequence** of a string is a new string generated from the original string with some characters (can be none) deleted without changing the relative order of the remaining characters.
+
+* For example, `"ace"` is a subsequence of `"abcde"`.
+
+A **common subsequence** of two strings is a subsequence that is common to both strings.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** text1 = "abcde", text2 = "ace"
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** The longest common subsequence is "ace" and its length is 3.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** text1 = "abc", text2 = "abc"
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** The longest common subsequence is "abc" and its length is 3.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** text1 = "abc", text2 = "def"
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:** There is no such common subsequence, so the result is 0.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= text1.length, text2.length <= 1000`
+* `text1` and `text2` consist of only lowercase English characters.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun longestCommonSubsequence(text1: String, text2: String): Int {
+ val n = text1.length
+ val m = text2.length
+ val dp = Array(n + 1) { IntArray(m + 1) }
+ for (i in 1..n) {
+ for (j in 1..m) {
+ if (text1[i - 1] == text2[j - 1]) {
+ dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1
+ } else {
+ dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1])
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[n][m]
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file