diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index 00626a00..506f60b1 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -92,6 +92,7 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0209 |[Minimum Size Subarray Sum](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0209_minimum_size_subarray_sum)| Medium | Array, Binary_Search, Prefix_Sum, Sliding_Window | 315 | 96.73
#### Day 2
@@ -336,6 +337,7 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0191 |[Number of 1 Bits](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0191_number_of_1_bits)| Easy | Top_Interview_Questions, Bit_Manipulation | 237 | 68.44
#### Day 3 Conditional Statements
@@ -346,6 +348,7 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0202 |[Happy Number](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0202_happy_number)| Easy | Top_Interview_Questions, Hash_Table, Math, Two_Pointers | 261 | 45.08
#### Day 5 Function
@@ -595,6 +598,7 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0196 |[Delete Duplicate Emails](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0196_delete_duplicate_emails)| Easy | Database | 593 | 94.17
#### Day 3 String Processing Functions
@@ -617,6 +621,7 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0197 |[Rising Temperature](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0197_rising_temperature)| Easy | Database | 394 | 94.15
#### Day 7 Function
@@ -650,6 +655,7 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0205 |[Isomorphic Strings](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0205_isomorphic_strings)| Easy | String, Hash_Table | 278 | 79.96
#### Day 3 Linked List
@@ -734,6 +740,7 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0202 |[Happy Number](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0202_happy_number)| Easy | Top_Interview_Questions, Hash_Table, Math, Two_Pointers | 261 | 45.08
| 0054 |[Spiral Matrix](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0054_spiral_matrix)| Medium | Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Matrix, Simulation | 224 | 62.50
#### Day 2 String
@@ -800,6 +807,7 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0210 |[Course Schedule II](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0210_course_schedule_ii)| Medium | Top_Interview_Questions, Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Graph, Topological_Sort | 266 | 96.32
#### Day 12 Dynamic Programming
@@ -1025,6 +1033,8 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0191 |[Number of 1 Bits](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0191_number_of_1_bits)| Easy | Top_Interview_Questions, Bit_Manipulation | 237 | 68.44
+| 0190 |[Reverse Bits](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0190_reverse_bits)| Easy | Top_Interview_Questions, Bit_Manipulation, Divide_and_Conquer | 198 | 81.82
| 0338 |[Counting Bits](src/main/kotlin/g0301_0400/s0338_counting_bits)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Dynamic_Programming, Bit_Manipulation | 186 | 99.26
| 0029 |[Divide Two Integers](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0029_divide_two_integers)| Medium | Top_Interview_Questions, Math, Bit_Manipulation | 281 | 31.67
@@ -1079,6 +1089,7 @@
|-|-|-|-|-|-
| 0141 |[Linked List Cycle](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0141_linked_list_cycle)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Hash_Table, Two_Pointers, Linked_List | 223 | 91.85
| 0021 |[Merge Two Sorted Lists](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0021_merge_two_sorted_lists)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Linked_List, Recursion | 176 | 96.25
+| 0203 |[Remove Linked List Elements](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0203_remove_linked_list_elements)| Easy | Linked_List, Recursion | 233 | 91.22
#### Day 8 Linked List
@@ -1349,11 +1360,13 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0191 |[Number of 1 Bits](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0191_number_of_1_bits)| Easy | Top_Interview_Questions, Bit_Manipulation | 237 | 68.44
#### Day 14 Bit Manipulation
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0190 |[Reverse Bits](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0190_reverse_bits)| Easy | Top_Interview_Questions, Bit_Manipulation, Divide_and_Conquer | 198 | 81.82
| 0136 |[Single Number](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0136_single_number)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Bit_Manipulation | 344 | 83.63
### Algorithm II
@@ -1391,6 +1404,7 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
| 0438 |[Find All Anagrams in a String](src/main/kotlin/g0401_0500/s0438_find_all_anagrams_in_a_string)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, String, Hash_Table, Sliding_Window | 561 | 54.68
+| 0209 |[Minimum Size Subarray Sum](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0209_minimum_size_subarray_sum)| Medium | Array, Binary_Search, Prefix_Sum, Sliding_Window | 315 | 96.73
#### Day 6 Breadth First Search Depth First Search
@@ -1482,6 +1496,7 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0201 |[Bitwise AND of Numbers Range](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0201_bitwise_and_of_numbers_range)| Medium | Bit_Manipulation | 368 | 80.00
#### Day 20 Others
@@ -1492,6 +1507,7 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0202 |[Happy Number](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0202_happy_number)| Easy | Top_Interview_Questions, Hash_Table, Math, Two_Pointers | 261 | 45.08
| 0149 |[Max Points on a Line](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0149_max_points_on_a_line)| Hard | Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Hash_Table, Math, Geometry | 307 | 83.33
## Algorithms
@@ -1528,13 +1544,29 @@
| 0226 |[Invert Binary Tree](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0226_invert_binary_tree)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree, Data_Structure_I_Day_12_Tree, Level_2_Day_6_Tree, Udemy_Tree_Stack_Queue | 233 | 54.90
| 0221 |[Maximal Square](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0221_maximal_square)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming, Matrix, Dynamic_Programming_I_Day_16 | 614 | 44.00
| 0215 |[Kth Largest Element in an Array](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0215_kth_largest_element_in_an_array)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Sorting, Heap_Priority_Queue, Divide_and_Conquer, Quickselect, Data_Structure_II_Day_20_Heap_Priority_Queue | 839 | 34.43
+| 0210 |[Course Schedule II](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0210_course_schedule_ii)| Medium | Top_Interview_Questions, Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Graph, Topological_Sort, Level_2_Day_11_Graph/BFS/DFS | 266 | 96.32
+| 0209 |[Minimum Size Subarray Sum](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0209_minimum_size_subarray_sum)| Medium | Array, Binary_Search, Prefix_Sum, Sliding_Window, Algorithm_II_Day_5_Sliding_Window, Binary_Search_II_Day_1 | 315 | 96.73
| 0208 |[Implement Trie (Prefix Tree)](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0208_implement_trie_prefix_tree)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, String, Hash_Table, Design, Trie, Level_2_Day_16_Design, Udemy_Trie_and_Heap | 689 | 61.00
| 0207 |[Course Schedule](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0207_course_schedule)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Graph, Topological_Sort | 416 | 40.10
| 0206 |[Reverse Linked List](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0206_reverse_linked_list)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Linked_List, Recursion, Data_Structure_I_Day_8_Linked_List, Algorithm_I_Day_10_Recursion_Backtracking, Level_1_Day_3_Linked_List, Udemy_Linked_List | 279 | 45.78
+| 0205 |[Isomorphic Strings](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0205_isomorphic_strings)| Easy | String, Hash_Table, Level_1_Day_2_String | 278 | 79.96
+| 0204 |[Count Primes](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0204_count_primes)| Medium | Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Math, Enumeration, Number_Theory | 360 | 96.61
+| 0203 |[Remove Linked List Elements](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0203_remove_linked_list_elements)| Easy | Linked_List, Recursion, Data_Structure_I_Day_7_Linked_List | 233 | 91.22
+| 0202 |[Happy Number](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0202_happy_number)| Easy | Top_Interview_Questions, Hash_Table, Math, Two_Pointers, Algorithm_II_Day_21_Others, Programming_Skills_I_Day_4_Loop, Level_2_Day_1_Implementation/Simulation | 261 | 45.08
+| 0201 |[Bitwise AND of Numbers Range](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0201_bitwise_and_of_numbers_range)| Medium | Bit_Manipulation, Algorithm_II_Day_19_Bit_Manipulation | 368 | 80.00
| 0200 |[Number of Islands](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0200_number_of_islands)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Matrix, Union_Find, Algorithm_II_Day_6_Breadth_First_Search_Depth_First_Search, Graph_Theory_I_Day_1_Matrix_Related_Problems, Level_1_Day_9_Graph/BFS/DFS, Udemy_Graph | 252 | 95.41
| 0199 |[Binary Tree Right Side View](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0199_binary_tree_right_side_view)| Medium | Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree, Data_Structure_II_Day_16_Tree, Level_2_Day_15_Tree | 194 | 92.89
| 0198 |[House Robber](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0198_house_robber)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming, Algorithm_I_Day_12_Dynamic_Programming, Dynamic_Programming_I_Day_3, Level_2_Day_12_Dynamic_Programming, Udemy_Dynamic_Programming | 156 | 92.24
+| 0197 |[Rising Temperature](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0197_rising_temperature)| Easy | Database, SQL_I_Day_6_Union | 394 | 94.15
+| 0196 |[Delete Duplicate Emails](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0196_delete_duplicate_emails)| Easy | Database, SQL_I_Day_2_Select_and_Order | 593 | 94.17
+| 0195 |[Tenth Line](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0195_tenth_line)| Easy | Shell | 36 | 87.50
+| 0194 |[Transpose File](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0194_transpose_file)| Medium | Shell | 477 | 28.60
+| 0193 |[Valid Phone Numbers](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0193_valid_phone_numbers)| Easy | Shell | 98 | 88.64
+| 0192 |[Word Frequency](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0192_word_frequency)| Medium | Shell | 114 | 73.60
+| 0191 |[Number of 1 Bits](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0191_number_of_1_bits)| Easy | Top_Interview_Questions, Bit_Manipulation, Algorithm_I_Day_13_Bit_Manipulation, Programming_Skills_I_Day_2_Operator, Udemy_Bit_Manipulation | 237 | 68.44
+| 0190 |[Reverse Bits](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0190_reverse_bits)| Easy | Top_Interview_Questions, Bit_Manipulation, Divide_and_Conquer, Algorithm_I_Day_14_Bit_Manipulation, Udemy_Bit_Manipulation | 198 | 81.82
| 0189 |[Rotate Array](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0189_rotate_array)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Math, Two_Pointers, Algorithm_I_Day_2_Two_Pointers, Udemy_Arrays | 483 | 86.95
+| 0188 |[Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock IV](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0188_best_time_to_buy_and_sell_stock_iv)| Hard | Array, Dynamic_Programming | 293 | 68.31
| 0187 |[Repeated DNA Sequences](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0187_repeated_dna_sequences)| Medium | String, Hash_Table, Bit_Manipulation, Sliding_Window, Hash_Function, Rolling_Hash, Data_Structure_II_Day_9_String, Udemy_Strings | 319 | 79.03
| 0185 |[Department Top Three Salaries](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0185_department_top_three_salaries)| Hard | Database | 757 | 87.06
| 0184 |[Department Highest Salary](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0184_department_highest_salary)| Medium | Database | 637 | 76.01
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0177_nth_highest_salary/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0177_nth_highest_salary/readme.md
index ba7fc476..798ef2b6 100644
--- a/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0177_nth_highest_salary/readme.md
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0177_nth_highest_salary/readme.md
@@ -75,4 +75,4 @@ SET M=N-1;
SELECT DISTINCT Salary FROM Employee ORDER BY Salary DESC LIMIT M, 1
);
END
-```
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0188_best_time_to_buy_and_sell_stock_iv/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0188_best_time_to_buy_and_sell_stock_iv/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..4d66dde6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0188_best_time_to_buy_and_sell_stock_iv/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 188\. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock IV
+
+Hard
+
+You are given an integer array `prices` where `prices[i]` is the price of a given stock on the ith day, and an integer `k`.
+
+Find the maximum profit you can achieve. You may complete at most `k` transactions.
+
+**Note:** You may not engage in multiple transactions simultaneously (i.e., you must sell the stock before you buy again).
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** k = 2, prices = [2,4,1]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** Buy on day 1 (price = 2) and sell on day 2 (price = 4), profit = 4-2 = 2.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** k = 2, prices = [3,2,6,5,0,3]
+
+**Output:** 7
+
+**Explanation:** Buy on day 2 (price = 2) and sell on day 3 (price = 6), profit = 6-2 = 4. Then buy on day 5 (price = 0) and sell on day 6 (price = 3), profit = 3-0 = 3.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= k <= 100`
+* `1 <= prices.length <= 1000`
+* `0 <= prices[i] <= 1000`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun maxProfit(k: Int, prices: IntArray): Int {
+ val n = prices.size
+ val dp = IntArray(k + 1)
+ val maxdp = IntArray(k + 1)
+ for (i in 0..k) {
+ maxdp[i] = Int.MIN_VALUE
+ }
+ for (i in 1..n) {
+ maxdp[0] = Math.max(maxdp[0], dp[0] - prices[i - 1])
+ for (j in k downTo 1) {
+ maxdp[j] = Math.max(maxdp[j], dp[j] - prices[i - 1])
+ dp[j] = Math.max(maxdp[j - 1] + prices[i - 1], dp[j])
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[k]
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0190_reverse_bits/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0190_reverse_bits/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..4d5d06e5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0190_reverse_bits/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 190\. Reverse Bits
+
+Easy
+
+Reverse bits of a given 32 bits unsigned integer.
+
+**Note:**
+
+* Note that in some languages, such as Java, there is no unsigned integer type. In this case, both input and output will be given as a signed integer type. They should not affect your implementation, as the integer's internal binary representation is the same, whether it is signed or unsigned.
+* In Java, the compiler represents the signed integers using [2's complement notation](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Two%27s_complement). Therefore, in **Example 2** above, the input represents the signed integer `-3` and the output represents the signed integer `-1073741825`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 00000010100101000001111010011100
+
+**Output:** 964176192 (00111001011110000010100101000000)
+
+**Explanation:** The input binary string **00000010100101000001111010011100** represents the unsigned integer 43261596, so return 964176192 which its binary representation is **00111001011110000010100101000000**.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 11111111111111111111111111111101
+
+**Output:** 3221225471 (10111111111111111111111111111111)
+
+**Explanation:** The input binary string **11111111111111111111111111111101** represents the unsigned integer 4294967293, so return 3221225471 which its binary representation is **10111111111111111111111111111111**.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* The input must be a **binary string** of length `32`
+
+**Follow up:** If this function is called many times, how would you optimize it?
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+@Suppress("NAME_SHADOWING")
+class Solution {
+ // you need treat n as an unsigned value
+ fun reverseBits(n: Int): Int {
+ var n = n
+ var ret = 0
+ // because there are 32 bits in total
+ for (i in 0..31) {
+ ret = ret shl 1
+ // If the bit is 1 we OR it with 1, ie add 1
+ if (n and 1 > 0) {
+ ret = ret or 1
+ }
+ n = n ushr 1
+ }
+ return ret
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0191_number_of_1_bits/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0191_number_of_1_bits/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2d12a9a0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0191_number_of_1_bits/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 191\. Number of 1 Bits
+
+Easy
+
+Write a function that takes an unsigned integer and returns the number of '1' bits it has (also known as the [Hamming weight](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hamming_weight)).
+
+**Note:**
+
+* Note that in some languages, such as Java, there is no unsigned integer type. In this case, the input will be given as a signed integer type. It should not affect your implementation, as the integer's internal binary representation is the same, whether it is signed or unsigned.
+* In Java, the compiler represents the signed integers using [2's complement notation](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Two%27s_complement). Therefore, in **Example 3**, the input represents the signed integer. `-3`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 00000000000000000000000000001011
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** The input binary string **00000000000000000000000000001011** has a total of three '1' bits.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 00000000000000000000000010000000
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:** The input binary string **00000000000000000000000010000000** has a total of one '1' bit.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** n = 11111111111111111111111111111101
+
+**Output:** 31
+
+**Explanation:** The input binary string **11111111111111111111111111111101** has a total of thirty one '1' bits.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* The input must be a **binary string** of length `32`.
+
+**Follow up:** If this function is called many times, how would you optimize it?
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun hammingWeight(n: Int): Int {
+ val str = Integer.toBinaryString(n).filter { it == '1' }
+ return str.length
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0192_word_frequency/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0192_word_frequency/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a172dc48
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0192_word_frequency/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 192\. Word Frequency
+
+Medium
+
+Write a bash script to calculate the frequency of each word in a text file `words.txt`.
+
+For simplicity sake, you may assume:
+
+* `words.txt` contains only lowercase characters and space `' '` characters.
+* Each word must consist of lowercase characters only.
+* Words are separated by one or more whitespace characters.
+
+**Example:**
+
+Assume that `words.txt` has the following content:
+
+ the day is sunny the the
+ the sunny is is
+
+Your script should output the following, sorted by descending frequency:
+
+ the 4
+ is 3
+ sunny 2
+ day 1
+
+**Note:**
+
+* Don't worry about handling ties, it is guaranteed that each word's frequency count is unique.
+* Could you write it in one-line using [Unix pipes](http://tldp.org/HOWTO/Bash-Prog-Intro-HOWTO-4.html)?
+
+## Solution
+
+```bash
+# Read from the file words.txt and output the word frequency list to stdout.
+sed -e '/^$/d' | sort | uniq -c | sort -r | awk '{print $2" "$1}'
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0193_valid_phone_numbers/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0193_valid_phone_numbers/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..60420744
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0193_valid_phone_numbers/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 193\. Valid Phone Numbers
+
+Easy
+
+Given a text file `file.txt` that contains a list of phone numbers (one per line), write a one-liner bash script to print all valid phone numbers.
+
+You may assume that a valid phone number must appear in one of the following two formats: (xxx) xxx-xxxx or xxx-xxx-xxxx. (x means a digit)
+
+You may also assume each line in the text file must not contain leading or trailing white spaces.
+
+**Example:**
+
+Assume that `file.txt` has the following content:
+
+ 987-123-4567
+ 123 456 7890
+ (123) 456-7890
+
+Your script should output the following valid phone numbers:
+
+ 987-123-4567
+ (123) 456-7890
+
+## Solution
+
+```bash
+# Read from the file file.txt and output all valid phone numbers to stdout.
+egrep '^[0-9]{3}-[0-9]{3}-[0-9]{4}$|^\([0-9]{3}\)\s[0-9]{3}-[0-9]{4}$' file.txt
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0194_transpose_file/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0194_transpose_file/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..05c507c1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0194_transpose_file/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 194\. Transpose File
+
+Medium
+
+Given a text file `file.txt`, transpose its content.
+
+You may assume that each row has the same number of columns, and each field is separated by the `' '` character.
+
+**Example:**
+
+If `file.txt` has the following content:
+
+ name age
+ alice 21
+ ryan 30
+
+Output the following:
+
+ name alice ryan
+ age 21 30
+
+## Solution
+
+```bash
+# Read from the file file.txt and print its transposed content to stdout.
+wordcount=$(head -1 file.txt | wc -w)
+col_n=1
+while [[ $col_n -le $wordcount ]]; do
+ awk "{ print \$$col_n }" file.txt | paste -sd " "
+ col_n=$((col_n + 1))
+done
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0195_tenth_line/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0195_tenth_line/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..267a2cba
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0195_tenth_line/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 195\. Tenth Line
+
+Easy
+
+Given a text file `file.txt`, print just the 10th line of the file.
+
+**Example:**
+
+Assume that `file.txt` has the following content:
+
+Line 1 Line 2 Line 3 Line 4 Line 5 Line 6 Line 7 Line 8 Line 9 Line 10
+
+Your script should output the tenth line, which is:
+
+Line 10
+
+**Note:**
+1\. If the file contains less than 10 lines, what should you output?
+2\. There's at least three different solutions. Try to explore all possibilities.
+
+## Solution
+
+```bash
+# Read from the file file.txt and output the tenth line to stdout.
+sed -n 10p file.txt
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0196_delete_duplicate_emails/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0196_delete_duplicate_emails/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..9c21b98d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0196_delete_duplicate_emails/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 196\. Delete Duplicate Emails
+
+Easy
+
+SQL Schema
+
+Table: `Person`
+
+ +-------------+---------+
+ | Column Name | Type |
+ +-------------+---------+
+ | id | int |
+ | email | varchar |
+ +-------------+---------+
+ id is the primary key column for this table.
+ Each row of this table contains an email. The emails will not contain uppercase letters.
+
+Write an SQL query to **delete** all the duplicate emails, keeping only one unique email with the smallest `id`.
+
+Return the result table in **any order**.
+
+The query result format is in the following example.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:**
+
+ Person table:
+ +----+------------------+
+ | id | email |
+ +----+------------------+
+ | 1 | john@example.com |
+ | 2 | bob@example.com |
+ | 3 | john@example.com |
+ +----+------------------+
+
+**Output:**
+
+ +----+------------------+
+ | id | email |
+ +----+------------------+
+ | 1 | john@example.com |
+ | 2 | bob@example.com |
+ +----+------------------+
+
+**Explanation:** john@example.com is repeated two times. We keep the row with the smallest Id = 1.
+
+## Solution
+
+```sql
+# Write your MySQL query statement below
+DELETE FROM Person
+WHERE Id NOT IN (SELECT id FROM (SELECT Email, MIN(Id) AS id FROM Person GROUP BY Email) t)
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0197_rising_temperature/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0197_rising_temperature/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3caa8bda
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0197_rising_temperature/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 197\. Rising Temperature
+
+Easy
+
+SQL Schema
+
+Table: `Weather`
+
+ +---------------+---------+
+ | Column Name | Type |
+ +---------------+---------+
+ | id | int |
+ | recordDate | date |
+ | temperature | int |
+ +---------------+---------+
+ id is the primary key for this table.
+ This table contains information about the temperature on a certain day.
+
+Write an SQL query to find all dates' `Id` with higher temperatures compared to its previous dates (yesterday).
+
+Return the result table in **any order**.
+
+The query result format is in the following example.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:**
+
+ Weather table:
+ +----+------------+-------------+
+ | id | recordDate | temperature |
+ +----+------------+-------------+
+ | 1 | 2015-01-01 | 10 |
+ | 2 | 2015-01-02 | 25 |
+ | 3 | 2015-01-03 | 20 |
+ | 4 | 2015-01-04 | 30 |
+ +----+------------+-------------+
+
+**Output:**
+
+ +----+
+ | id |
+ +----+
+ | 2 |
+ | 4 |
+ +----+
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+ In 2015-01-02, the temperature was higher than the previous day (10 -> 25).
+ In 2015-01-04, the temperature was higher than the previous day (20 -> 30).
+
+## Solution
+
+```sql
+# Write your MySQL query statement below
+SELECT SecondDate.id as Id
+FROM Weather SecondDate JOIN Weather FirstDate
+ON ADDDATE(FirstDate.recordDate,1) = SecondDate.recordDate
+AND SecondDate.temperature > FirstDate.temperature;
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0201_bitwise_and_of_numbers_range/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0201_bitwise_and_of_numbers_range/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1690dbb3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0201_bitwise_and_of_numbers_range/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,77 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 201\. Bitwise AND of Numbers Range
+
+Medium
+
+Given two integers `left` and `right` that represent the range `[left, right]`, return _the bitwise AND of all numbers in this range, inclusive_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** left = 5, right = 7
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** left = 0, right = 0
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** left = 1, right = 2147483647
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 0 <= left <= right <= 231 - 1
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun rangeBitwiseAnd(left: Int, right: Int): Int {
+ return if (left == right) left else right and MASKS[Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(left xor right)]
+ }
+
+ companion object {
+ private val MASKS = intArrayOf(
+ 0,
+ -0x80000000,
+ -0x40000000,
+ -0x20000000,
+ -0x10000000,
+ -0x8000000,
+ -0x4000000,
+ -0x2000000,
+ -0x1000000,
+ -0x800000,
+ -0x400000,
+ -0x200000,
+ -0x100000,
+ -0x80000,
+ -0x40000,
+ -0x20000,
+ -0x10000,
+ -0x8000,
+ -0x4000,
+ -0x2000,
+ -0x1000,
+ -0x800,
+ -0x400,
+ -0x200,
+ -0x100,
+ -0x80,
+ -0x40,
+ -0x20,
+ -0x10,
+ -0x8,
+ -0x4,
+ -0x2
+ )
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0202_happy_number/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0202_happy_number/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e980fd4f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0202_happy_number/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 202\. Happy Number
+
+Easy
+
+Write an algorithm to determine if a number `n` is happy.
+
+A **happy number** is a number defined by the following process:
+
+* Starting with any positive integer, replace the number by the sum of the squares of its digits.
+* Repeat the process until the number equals 1 (where it will stay), or it **loops endlessly in a cycle** which does not include 1.
+* Those numbers for which this process **ends in 1** are happy.
+
+Return `true` _if_ `n` _is a happy number, and_ `false` _if not_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 19
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** 12 + 92 = 82 82 + 22 = 68 62 + 82 = 100 12 + 02 + 02 = 1
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 2
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= n <= 231 - 1
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ private val set = mutableSetOf()
+
+ tailrec fun isHappy(n: Int): Boolean {
+ var num = n
+ var squareSum = 0
+ while (num > 0) {
+ val digit = num % 10
+ squareSum += digit * digit
+ num /= 10
+ }
+ if (squareSum == 1) {
+ return true
+ }
+ if (set.contains(squareSum)) {
+ return false
+ }
+ set.add(squareSum)
+ return isHappy(squareSum)
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0203_remove_linked_list_elements/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0203_remove_linked_list_elements/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..65705786
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0203_remove_linked_list_elements/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 203\. Remove Linked List Elements
+
+Easy
+
+Given the `head` of a linked list and an integer `val`, remove all the nodes of the linked list that has `Node.val == val`, and return _the new head_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+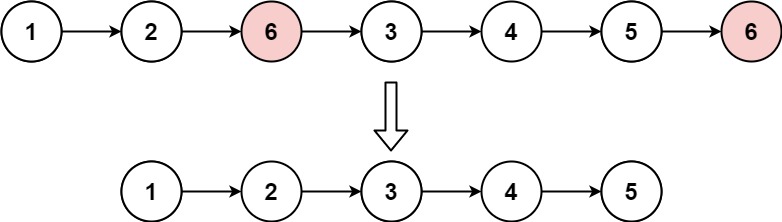
+
+**Input:** head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6
+
+**Output:** [1,2,3,4,5]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** head = [], val = 1
+
+**Output:** []
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** head = [7,7,7,7], val = 7
+
+**Output:** []
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* The number of nodes in the list is in the range [0, 104].
+* `1 <= Node.val <= 50`
+* `0 <= val <= 50`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import com_github_leetcode.ListNode
+
+/*
+ * Example:
+ * var li = ListNode(5)
+ * var v = li.`val`
+ * Definition for singly-linked list.
+ * class ListNode(var `val`: Int) {
+ * var next: ListNode? = null
+ * }
+ */
+class Solution {
+ fun removeElements(head: ListNode?, `val`: Int): ListNode? {
+ val sentinel = ListNode(-1)
+ sentinel.next = head
+ var next = head
+ var prev = sentinel
+ while (next != null) {
+ if (next.`val` == `val`) {
+ prev.next = next.next
+ } else {
+ prev = next
+ }
+ next = next.next
+ }
+ return sentinel.next
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0204_count_primes/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0204_count_primes/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2bc94f6f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0204_count_primes/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 204\. Count Primes
+
+Medium
+
+Given an integer `n`, return _the number of prime numbers that are strictly less than_ `n`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 10
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:** There are 4 prime numbers less than 10, they are 2, 3, 5, 7.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 0
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** n = 1
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 0 <= n <= 5 * 106
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun countPrimes(n: Int): Int {
+ val isprime = BooleanArray(n)
+ var count = 0
+ run {
+ var i = 2
+ while (i * i <= n) {
+ if (!isprime[i]) {
+ var j = i * 2
+ while (j < n) {
+ isprime[j] = true
+ j += i
+ }
+ }
+ i++
+ }
+ }
+ for (i in 2 until isprime.size) {
+ if (!isprime[i]) {
+ count++
+ }
+ }
+ return count
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0205_isomorphic_strings/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0205_isomorphic_strings/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d443e00d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0205_isomorphic_strings/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,74 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 205\. Isomorphic Strings
+
+Easy
+
+Given two strings `s` and `t`, _determine if they are isomorphic_.
+
+Two strings `s` and `t` are isomorphic if the characters in `s` can be replaced to get `t`.
+
+All occurrences of a character must be replaced with another character while preserving the order of characters. No two characters may map to the same character, but a character may map to itself.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "egg", t = "add"
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "foo", t = "bar"
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** s = "paper", t = "title"
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= s.length <= 5 * 104
+* `t.length == s.length`
+* `s` and `t` consist of any valid ascii character.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun isIsomorphic(s: String, t: String): Boolean {
+ val map = IntArray(128)
+ val str = s.toCharArray()
+ val tar = t.toCharArray()
+ val n = str.size
+ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ if (map[tar[i].code] == 0) {
+ if (search(map, str[i].code, tar[i].code) != -1) {
+ return false
+ }
+ map[tar[i].code] = str[i].code
+ } else {
+ if (map[tar[i].code] != str[i].code) {
+ return false
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return true
+ }
+
+ private fun search(map: IntArray, tar: Int, skip: Int): Int {
+ for (i in 0..127) {
+ if (i == skip) {
+ continue
+ }
+ if (map[i] != 0 && map[i] == tar) {
+ return i
+ }
+ }
+ return -1
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0209_minimum_size_subarray_sum/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0209_minimum_size_subarray_sum/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c385b5f3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0209_minimum_size_subarray_sum/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 209\. Minimum Size Subarray Sum
+
+Medium
+
+Given an array of positive integers `nums` and a positive integer `target`, return the minimal length of a **contiguous subarray** [numsl, numsl+1, ..., numsr-1, numsr] of which the sum is greater than or equal to `target`. If there is no such subarray, return `0` instead.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** target = 7, nums = [2,3,1,2,4,3]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** The subarray [4,3] has the minimal length under the problem constraint.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** target = 4, nums = [1,4,4]
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** target = 11, nums = [1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= target <= 109
+* 1 <= nums.length <= 105
+* 1 <= nums[i] <= 104
+
+**Follow up:** If you have figured out the `O(n)` solution, try coding another solution of which the time complexity is `O(n log(n))`.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun minSubArrayLen(s: Int, nums: IntArray): Int {
+ var sum = 0
+ var start = 0
+ var minLength = Integer.MAX_VALUE
+ var end = 0
+ if (nums.size < 1) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ while (end < nums.size) {
+ sum += nums[end]
+ while (sum >= s) {
+ minLength = Math.min(minLength, end - start + 1)
+ sum -= nums[start++]
+ }
+ end++
+ }
+ return if (start > 0) minLength else 0
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0210_course_schedule_ii/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0210_course_schedule_ii/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..88312c79
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0210_course_schedule_ii/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,88 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 210\. Course Schedule II
+
+Medium
+
+There are a total of `numCourses` courses you have to take, labeled from `0` to `numCourses - 1`. You are given an array `prerequisites` where prerequisites[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that you **must** take course bi first if you want to take course ai.
+
+* For example, the pair `[0, 1]`, indicates that to take course `0` you have to first take course `1`.
+
+Return _the ordering of courses you should take to finish all courses_. If there are many valid answers, return **any** of them. If it is impossible to finish all courses, return **an empty array**.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** numCourses = 2, prerequisites = \[\[1,0]]
+
+**Output:** [0,1]
+
+**Explanation:** There are a total of 2 courses to take. To take course 1 you should have finished course 0. So the correct course order is [0,1].
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** numCourses = 4, prerequisites = \[\[1,0],[2,0],[3,1],[3,2]]
+
+**Output:** [0,2,1,3]
+
+**Explanation:** There are a total of 4 courses to take. To take course 3 you should have finished both courses 1 and 2. Both courses 1 and 2 should be taken after you finished course 0. So one correct course order is [0,1,2,3]. Another correct ordering is [0,2,1,3].
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** numCourses = 1, prerequisites = []
+
+**Output:** [0]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= numCourses <= 2000`
+* `0 <= prerequisites.length <= numCourses * (numCourses - 1)`
+* `prerequisites[i].length == 2`
+* 0 <= ai, bi < numCourses
+* ai != bi
+* All the pairs [ai, bi] are **distinct**.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun findOrder(numCourses: Int, prerequisites: Array): IntArray {
+ val indegrees = IntArray(numCourses) { 0 }
+ val graph = buildGraph(numCourses, prerequisites, indegrees)
+ val queue = ArrayDeque()
+ for ((idx, indegree) in indegrees.withIndex()) {
+ if (indegree == 0) {
+ queue.addLast(idx)
+ }
+ }
+ val ans = IntArray(numCourses) { 0 }
+ var idx = 0
+ while (queue.isNotEmpty()) {
+ val cur = queue.removeFirst()
+ ans[idx++] = cur
+ for (pre in graph[cur]) {
+ if (--indegrees[pre] == 0) {
+ queue.addLast(pre)
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ if (idx < numCourses) {
+ return intArrayOf()
+ }
+ return ans
+ }
+
+ private fun buildGraph(
+ numCourses: Int,
+ prerequisites: Array,
+ indegrees: IntArray
+ ): List> {
+ val graph = List(numCourses) { mutableListOf() }
+ for ((cur, prev) in prerequisites) {
+ graph[prev].add(cur)
+ ++indegrees[cur]
+ }
+ return graph
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file