diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index 0561ed02..e5429430 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -144,6 +144,7 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
| 0380 |[Insert Delete GetRandom O(1)](src/main/kotlin/g0301_0400/s0380_insert_delete_getrandom_o1)| Medium | Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Hash_Table, Math, Design, Randomized | 1326 | 68.23
+| 0622 |[Design Circular Queue](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0622_design_circular_queue)| Medium | Array, Design, Linked_List, Queue | 234 | 92.68
### Graph Theory I
@@ -230,6 +231,7 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0595 |[Big Countries](src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0595_big_countries)| Easy | Database | 417 | 56.09
| 0584 |[Find Customer Referee](src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0584_find_customer_referee)| Easy | Database | 779 | 43.48
| 0183 |[Customers Who Never Order](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0183_customers_who_never_order)| Easy | Database | 712 | 33.67
@@ -237,6 +239,7 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0627 |[Swap Salary](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0627_swap_salary)| Easy | Database | 400 | 51.04
| 0196 |[Delete Duplicate Emails](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0196_delete_duplicate_emails)| Easy | Database | 593 | 94.17
#### Day 3 String Processing Functions
@@ -248,6 +251,7 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0608 |[Tree Node](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0608_tree_node)| Medium | LeetCode_Curated_SQL_70, Database | 794 | 48.38
| 0176 |[Second Highest Salary](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0176_second_highest_salary)| Medium | Database | 219 | 92.54
#### Day 5 Union
@@ -261,6 +265,7 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
| 0197 |[Rising Temperature](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0197_rising_temperature)| Easy | Database | 394 | 94.15
+| 0607 |[Sales Person](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0607_sales_person)| Easy | LeetCode_Curated_SQL_70, Database | 2142 | 44.56
#### Day 7 Function
@@ -417,6 +422,7 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0621 |[Task Scheduler](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0621_task_scheduler)| Medium | Array, Hash_Table, Sorting, Greedy, Heap_Priority_Queue, Counting | 266 | 98.36
#### Day 6 Tree
@@ -569,6 +575,7 @@
| 0001 |[Two Sum](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0001_two_sum)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Hash_Table | 234 | 92.75
| 0217 |[Contains Duplicate](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0217_contains_duplicate)| Easy | Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Hash_Table, Sorting | 719 | 73.49
| 0058 |[Length of Last Word](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0058_length_of_last_word)| Easy | String | 243 | 63.33
+| 0605 |[Can Place Flowers](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0605_can_place_flowers)| Easy | Array, Greedy | 209 | 85.71
| 0122 |[Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0122_best_time_to_buy_and_sell_stock_ii)| Medium | Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming, Greedy | 197 | 95.10
| 0080 |[Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array II](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0080_remove_duplicates_from_sorted_array_ii)| Medium | Array, Two_Pointers | 357 | 44.78
| 0189 |[Rotate Array](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0189_rotate_array)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Math, Two_Pointers | 483 | 86.95
@@ -1022,6 +1029,7 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 0617 |[Merge Two Binary Trees](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0617_merge_two_binary_trees)| Easy | Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree | 243 | 72.83
| 0116 |[Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0116_populating_next_right_pointers_in_each_node)| Medium | Top_Interview_Questions, Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree, Linked_List | 355 | 69.02
#### Day 9 Breadth First Search Depth First Search
@@ -1276,6 +1284,7 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
| 0350 |[Intersection of Two Arrays II](src/main/kotlin/g0301_0400/s0350_intersection_of_two_arrays_ii)| Easy | Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Hash_Table, Sorting, Binary_Search, Two_Pointers | 321 | 73.37
+| 0633 |[Sum of Square Numbers](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0633_sum_of_square_numbers)| Medium | Math, Binary_Search, Two_Pointers | 126 | 100.00
#### Day 11
@@ -1296,6 +1305,7 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
| 0209 |[Minimum Size Subarray Sum](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0209_minimum_size_subarray_sum)| Medium | Array, Binary_Search, Prefix_Sum, Sliding_Window | 315 | 96.73
+| 0611 |[Valid Triangle Number](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0611_valid_triangle_number)| Medium | Array, Sorting, Greedy, Binary_Search, Two_Pointers | 203 | 100.00
#### Day 2
@@ -1631,7 +1641,43 @@
| 0864 |[Shortest Path to Get All Keys](src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0864_shortest_path_to_get_all_keys)| Hard | Breadth_First_Search, Bit_Manipulation | 176 | 100.00
| 0763 |[Partition Labels](src/main/kotlin/g0701_0800/s0763_partition_labels)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, String, Hash_Table, Greedy, Two_Pointers, Data_Structure_II_Day_7_String | 235 | 84.75
| 0739 |[Daily Temperatures](src/main/kotlin/g0701_0800/s0739_daily_temperatures)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Array, Stack, Monotonic_Stack, Programming_Skills_II_Day_6 | 936 | 80.54
+| 0648 |[Replace Words](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0648_replace_words)| Medium | Array, String, Hash_Table, Trie | 392 | 100.00
| 0647 |[Palindromic Substrings](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0647_palindromic_substrings)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, String, Dynamic_Programming | 266 | 67.83
+| 0646 |[Maximum Length of Pair Chain](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0646_maximum_length_of_pair_chain)| Medium | Array, Dynamic_Programming, Sorting, Greedy | 249 | 100.00
+| 0645 |[Set Mismatch](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0645_set_mismatch)| Easy | Array, Hash_Table, Sorting, Bit_Manipulation | 246 | 88.46
+| 0643 |[Maximum Average Subarray I](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0643_maximum_average_subarray_i)| Easy | Array, Sliding_Window | 494 | 98.65
+| 0641 |[Design Circular Deque](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0641_design_circular_deque)| Medium | Array, Design, Linked_List, Queue | 232 | 100.00
+| 0640 |[Solve the Equation](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0640_solve_the_equation)| Medium | String, Math, Simulation | 170 | 66.67
+| 0639 |[Decode Ways II](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0639_decode_ways_ii)| Hard | String, Dynamic_Programming | 259 | 100.00
+| 0638 |[Shopping Offers](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0638_shopping_offers)| Medium | Array, Dynamic_Programming, Bit_Manipulation, Backtracking, Bitmask, Memoization | 195 | 100.00
+| 0637 |[Average of Levels in Binary Tree](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0637_average_of_levels_in_binary_tree)| Easy | Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree | 249 | 100.00
+| 0636 |[Exclusive Time of Functions](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0636_exclusive_time_of_functions)| Medium | Array, Stack | 270 | 80.00
+| 0633 |[Sum of Square Numbers](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0633_sum_of_square_numbers)| Medium | Math, Binary_Search, Two_Pointers, Binary_Search_I_Day_10 | 126 | 100.00
+| 0632 |[Smallest Range Covering Elements from K Lists](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0632_smallest_range_covering_elements_from_k_lists)| Hard | Array, Hash_Table, Sorting, Greedy, Heap_Priority_Queue, Sliding_Window | 399 | 83.33
+| 0630 |[Course Schedule III](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0630_course_schedule_iii)| Hard | Array, Greedy, Heap_Priority_Queue | 536 | 100.00
+| 0629 |[K Inverse Pairs Array](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0629_k_inverse_pairs_array)| Hard | Dynamic_Programming | 155 | 100.00
+| 0628 |[Maximum Product of Three Numbers](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0628_maximum_product_of_three_numbers)| Easy | Array, Math, Sorting | 276 | 97.30
+| 0627 |[Swap Salary](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0627_swap_salary)| Easy | Database, SQL_I_Day_2_Select_and_Order | 400 | 51.04
+| 0626 |[Exchange Seats](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0626_exchange_seats)| Medium | Database | 502 | 50.56
+| 0623 |[Add One Row to Tree](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0623_add_one_row_to_tree)| Medium | Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree | 202 | 100.00
+| 0622 |[Design Circular Queue](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0622_design_circular_queue)| Medium | Array, Design, Linked_List, Queue, Programming_Skills_II_Day_20 | 234 | 92.68
+| 0621 |[Task Scheduler](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0621_task_scheduler)| Medium | Array, Hash_Table, Sorting, Greedy, Heap_Priority_Queue, Counting, Level_2_Day_5_Greedy | 266 | 98.36
+| 0620 |[Not Boring Movies](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0620_not_boring_movies)| Easy | Database | 305 | 59.80
+| 0617 |[Merge Two Binary Trees](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0617_merge_two_binary_trees)| Easy | Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree, Algorithm_I_Day_8_Breadth_First_Search_Depth_First_Search | 243 | 72.83
+| 0611 |[Valid Triangle Number](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0611_valid_triangle_number)| Medium | Array, Sorting, Greedy, Binary_Search, Two_Pointers, Binary_Search_II_Day_1 | 203 | 100.00
+| 0609 |[Find Duplicate File in System](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0609_find_duplicate_file_in_system)| Medium | Array, String, Hash_Table | 426 | 100.00
+| 0608 |[Tree Node](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0608_tree_node)| Medium | LeetCode_Curated_SQL_70, Database, SQL_I_Day_4_Union_and_Select | 794 | 48.38
+| 0607 |[Sales Person](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0607_sales_person)| Easy | LeetCode_Curated_SQL_70, Database, SQL_I_Day_6_Union | 2142 | 44.56
+| 0606 |[Construct String from Binary Tree](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0606_construct_string_from_binary_tree)| Easy | String, Depth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree | 187 | 100.00
+| 0605 |[Can Place Flowers](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0605_can_place_flowers)| Easy | Array, Greedy, Udemy_Arrays | 209 | 85.71
+| 0601 |[Human Traffic of Stadium](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0601_human_traffic_of_stadium)| Hard | Database | 529 | 51.80
+| 0600 |[Non-negative Integers without Consecutive Ones](src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0600_non_negative_integers_without_consecutive_ones)| Hard | Dynamic_Programming | 142 | 100.00
+| 0599 |[Minimum Index Sum of Two Lists](src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0599_minimum_index_sum_of_two_lists)| Easy | Array, String, Hash_Table | 293 | 100.00
+| 0598 |[Range Addition II](src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0598_range_addition_ii)| Easy | Array, Math | 176 | 66.67
+| 0596 |[Classes More Than 5 Students](src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0596_classes_more_than_5_students)| Easy | Database | 484 | 50.92
+| 0595 |[Big Countries](src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0595_big_countries)| Easy | Database, SQL_I_Day_1_Select | 417 | 56.09
+| 0594 |[Longest Harmonious Subsequence](src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0594_longest_harmonious_subsequence)| Easy | Array, Hash_Table, Sorting | 331 | 100.00
+| 0593 |[Valid Square](src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0593_valid_square)| Medium | Math, Geometry | 161 | 83.33
| 0592 |[Fraction Addition and Subtraction](src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0592_fraction_addition_and_subtraction)| Medium | String, Math, Simulation | 164 | 100.00
| 0591 |[Tag Validator](src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0591_tag_validator)| Hard | String, Stack | 177 | 100.00
| 0590 |[N-ary Tree Postorder Traversal](src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0590_n_ary_tree_postorder_traversal)| Easy | Depth_First_Search, Tree, Stack | 237 | 88.10
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0593_valid_square/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0593_valid_square/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8b4fc05c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0593_valid_square/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 593\. Valid Square
+
+Medium
+
+Given the coordinates of four points in 2D space `p1`, `p2`, `p3` and `p4`, return `true` _if the four points construct a square_.
+
+The coordinate of a point pi is represented as [xi, yi]. The input is **not** given in any order.
+
+A **valid square** has four equal sides with positive length and four equal angles (90-degree angles).
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** p1 = [0,0], p2 = [1,1], p3 = [1,0], p4 = [0,1]
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** p1 = [0,0], p2 = [1,1], p3 = [1,0], p4 = [0,12]
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** p1 = [1,0], p2 = [-1,0], p3 = [0,1], p4 = [0,-1]
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `p1.length == p2.length == p3.length == p4.length == 2`
+* -104 <= xi, yi <= 104
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.Arrays
+
+class Solution {
+ fun validSquare(p1: IntArray, p2: IntArray, p3: IntArray, p4: IntArray): Boolean {
+ val distancesSquared = IntArray(6)
+ distancesSquared[0] = getDistanceSquared(p1, p2)
+ distancesSquared[1] = getDistanceSquared(p1, p3)
+ distancesSquared[2] = getDistanceSquared(p1, p4)
+ distancesSquared[3] = getDistanceSquared(p2, p3)
+ distancesSquared[4] = getDistanceSquared(p2, p4)
+ distancesSquared[5] = getDistanceSquared(p3, p4)
+ Arrays.sort(distancesSquared)
+ if (distancesSquared[0] == 0) {
+ return false
+ }
+ if (distancesSquared[0] != distancesSquared[3]) {
+ return false
+ }
+ return if (distancesSquared[4] != distancesSquared[5]) {
+ false
+ } else distancesSquared[5] == 2 * distancesSquared[0]
+ }
+
+ private fun getDistanceSquared(p1: IntArray, p2: IntArray): Int {
+ val deltaX = p2[0] - p1[0]
+ val deltaY = p2[1] - p1[1]
+ return deltaX * deltaX + deltaY * deltaY
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0594_longest_harmonious_subsequence/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0594_longest_harmonious_subsequence/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3dc1827a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0594_longest_harmonious_subsequence/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 594\. Longest Harmonious Subsequence
+
+Easy
+
+We define a harmonious array as an array where the difference between its maximum value and its minimum value is **exactly** `1`.
+
+Given an integer array `nums`, return _the length of its longest harmonious subsequence among all its possible subsequences_.
+
+A **subsequence** of array is a sequence that can be derived from the array by deleting some or no elements without changing the order of the remaining elements.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,3,2,2,5,2,3,7]
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Explanation:** The longest harmonious subsequence is [3,2,2,2,3].
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,3,4]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,1,1,1]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= nums.length <= 2 * 104
+* -109 <= nums[i] <= 109
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.Arrays
+
+class Solution {
+ fun findLHS(nums: IntArray): Int {
+ Arrays.sort(nums)
+ var max = 0
+ var lastN = 0
+ var curN = 1
+ var cur = nums[0]
+ for (i in 1 until nums.size) {
+ if (nums[i] > cur) {
+ if (lastN > 0 && curN > 0 && lastN + curN > max) {
+ max = lastN + curN
+ }
+ // if diff more than 1, don't count
+ lastN = if (nums[i] - cur == 1) curN else 0
+ curN = 1
+ cur = nums[i]
+ } else {
+ curN++
+ }
+ }
+ if (lastN > 0 && curN > 0 && lastN + curN > max) {
+ max = lastN + curN
+ }
+ return max
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0595_big_countries/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0595_big_countries/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d6d6ecf9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0595_big_countries/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,66 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 595\. Big Countries
+
+Easy
+
+SQL Schema
+
+Table: `World`
+
+ +-------------+---------+
+ | Column Name | Type |
+ +-------------+---------+
+ | name | varchar |
+ | continent | varchar |
+ | area | int |
+ | population | int |
+ | gdp | int |
+ +-------------+---------+
+ name is the primary key column for this table.
+ Each row of this table gives information about the name of a country, the continent to which it belongs,
+ its area, the population, and its GDP value.
+
+A country is **big** if:
+
+* it has an area of at least three million (i.e., 3000000 km2), or
+* it has a population of at least twenty-five million (i.e., `25000000`).
+
+Write an SQL query to report the name, population, and area of the **big countries**.
+
+Return the result table in **any order**.
+
+The query result format is in the following example.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:**
+
+ World table:
+ +-------------+-----------+---------+------------+--------------+
+ | name | continent | area | population | gdp |
+ +-------------+-----------+---------+------------+--------------+
+ | Afghanistan | Asia | 652230 | 25500100 | 20343000000 |
+ | Albania | Europe | 28748 | 2831741 | 12960000000 |
+ | Algeria | Africa | 2381741 | 37100000 | 188681000000 |
+ | Andorra | Europe | 468 | 78115 | 3712000000 |
+ | Angola | Africa | 1246700 | 20609294 | 100990000000 |
+ +-------------+-----------+---------+------------+--------------+
+
+**Output:**
+
+ +-------------+------------+---------+
+ | name | population | area |
+ +-------------+------------+---------+
+ | Afghanistan | 25500100 | 652230 |
+ | Algeria | 37100000 | 2381741 |
+ +-------------+------------+---------+
+
+## Solution
+
+```sql
+# Write your MySQL query statement below
+SELECT name,population,area FROM World
+WHERE area >= 3000000 or population >= 25000000;
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0596_classes_more_than_5_students/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0596_classes_more_than_5_students/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..95e75aea
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0596_classes_more_than_5_students/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 596\. Classes More Than 5 Students
+
+Easy
+
+SQL Schema
+
+Table: `Courses`
+
+ +-------------+---------+
+ | Column Name | Type |
+ +-------------+---------+
+ | student | varchar |
+ | class | varchar |
+ +-------------+---------+
+ (student, class) is the primary key column for this table.
+ Each row of this table indicates the name of a student and the class in which they are enrolled.
+
+Write an SQL query to report all the classes that have **at least five students**.
+
+Return the result table in **any order**.
+
+The query result format is in the following example.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:**
+
+ Courses table:
+ +---------+----------+
+ | student | class |
+ +---------+----------+
+ | A | Math |
+ | B | English |
+ | C | Math |
+ | D | Biology |
+ | E | Math |
+ | F | Computer |
+ | G | Math |
+ | H | Math |
+ | I | Math |
+ +---------+----------+
+
+**Output:**
+
+ +---------+
+ | class |
+ +---------+
+ | Math |
+ +---------+
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+ - Math has 6 students, so we include it.
+ - English has 1 student, so we do not include it.
+ - Biology has 1 student, so we do not include it.
+ - Computer has 1 student, so we do not include it.
+
+## Solution
+
+```sql
+# Write your MySQL query statement below
+select class
+from Courses
+group by class
+having count(student) >= 5
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0598_range_addition_ii/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0598_range_addition_ii/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..85acfe25
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0598_range_addition_ii/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 598\. Range Addition II
+
+Easy
+
+You are given an `m x n` matrix `M` initialized with all `0`'s and an array of operations `ops`, where ops[i] = [ai, bi] means `M[x][y]` should be incremented by one for all 0 <= x < ai and 0 <= y < bi.
+
+Count and return _the number of maximum integers in the matrix after performing all the operations_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
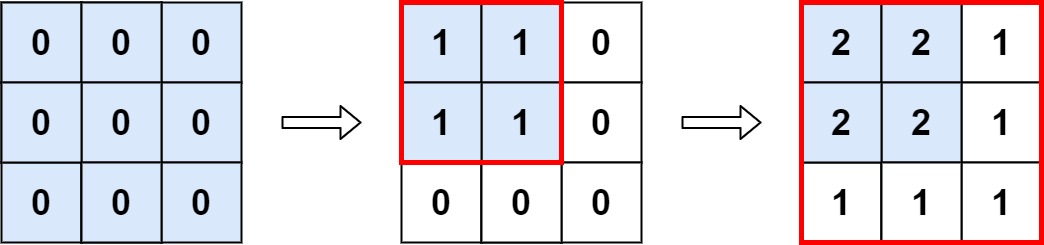
+
+
+**Input:** m = 3, n = 3, ops = \[\[2,2],[3,3]]
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:** The maximum integer in M is 2, and there are four of it in M. So return 4.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** m = 3, n = 3, ops = \[\[2,2],[3,3],[3,3],[3,3],[2,2],[3,3],[3,3],[3,3],[2,2],[3,3],[3,3],[3,3]]
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** m = 3, n = 3, ops = []
+
+**Output:** 9
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= m, n <= 4 * 104
+* 0 <= ops.length <= 104
+* `ops[i].length == 2`
+* 1 <= ai <= m
+* 1 <= bi <= n
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ /*
+ * Since the incrementing starts from zero to op[0] and op[1], we only need to find the range that
+ * has the most overlaps. Thus we keep finding the minimum of both x and y.
+ */
+ fun maxCount(m: Int, n: Int, ops: Array): Int {
+ var x = m
+ var y = n
+ for (op in ops) {
+ x = x.coerceAtMost(op[0])
+ y = y.coerceAtMost(op[1])
+ }
+ return x * y
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0599_minimum_index_sum_of_two_lists/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0599_minimum_index_sum_of_two_lists/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c40aa172
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0599_minimum_index_sum_of_two_lists/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 599\. Minimum Index Sum of Two Lists
+
+Easy
+
+Suppose Andy and Doris want to choose a restaurant for dinner, and they both have a list of favorite restaurants represented by strings.
+
+You need to help them find out their **common interest** with the **least list index sum**. If there is a choice tie between answers, output all of them with no order requirement. You could assume there always exists an answer.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** list1 = ["Shogun","Tapioca Express","Burger King","KFC"], list2 = ["Piatti","The Grill at Torrey Pines","Hungry Hunter Steakhouse","Shogun"]
+
+**Output:** ["Shogun"]
+
+**Explanation:** The only restaurant they both like is "Shogun".
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** list1 = ["Shogun","Tapioca Express","Burger King","KFC"], list2 = ["KFC","Shogun","Burger King"]
+
+**Output:** ["Shogun"]
+
+**Explanation:** The restaurant they both like and have the least index sum is "Shogun" with index sum 1 (0+1).
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= list1.length, list2.length <= 1000`
+* `1 <= list1[i].length, list2[i].length <= 30`
+* `list1[i]` and `list2[i]` consist of spaces `' '` and English letters.
+* All the stings of `list1` are **unique**.
+* All the stings of `list2` are **unique**.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun findRestaurant(list1: Array, list2: Array): Array {
+ var min = 1000000
+ val hm: MutableMap = HashMap()
+ val result: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ fillMap(list1, hm)
+ // find min value
+ for (i in list2.indices) {
+ if (hm.containsKey(list2[i])) {
+ val value = hm[list2[i]]!! + i
+ // a new min value was found
+ if (value < min) {
+ min = value
+ // Clean the arraylist
+ result.clear()
+ // add new min value
+ result.add(list2[i])
+ } else if (value == min) {
+ result.add(list2[i])
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return result.toTypedArray()
+ }
+
+ fun fillMap(a: Array, hm: MutableMap) {
+ for (i in a.indices) {
+ hm[a[i]] = i
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0600_non_negative_integers_without_consecutive_ones/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0600_non_negative_integers_without_consecutive_ones/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8c1da39a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0600_non_negative_integers_without_consecutive_ones/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 600\. Non-negative Integers without Consecutive Ones
+
+Hard
+
+Given a positive integer `n`, return the number of the integers in the range `[0, n]` whose binary representations **do not** contain consecutive ones.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 5
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+ Here are the non-negative integers <= 5 with their corresponding binary representations:
+ 0 : 0
+ 1 : 1
+ 2 : 10
+ 3 : 11
+ 4 : 100
+ 5 : 101
+ Among them, only integer 3 disobeys the rule (two consecutive ones) and the other 5 satisfy the rule.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 1
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** n = 2
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= n <= 109
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun findIntegers(n: Int): Int {
+ val f = IntArray(32)
+ f[0] = 1
+ f[1] = 2
+ var ans = 0
+ var preBit = 0
+ for (i in 2..31) {
+ f[i] = f[i - 1] + f[i - 2]
+ }
+ for (k in 31 downTo 0) {
+ if (n and (1 shl k) != 0) {
+ // if that bit is on
+ ans += f[k]
+ if (preBit != 0) {
+ return ans
+ }
+ preBit = 1
+ } else {
+ preBit = 0
+ }
+ }
+ return ans + 1
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0601_human_traffic_of_stadium/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0601_human_traffic_of_stadium/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c8646ec8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0601_human_traffic_of_stadium/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,82 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 601\. Human Traffic of Stadium
+
+Hard
+
+SQL Schema
+
+Table: `Stadium`
+
+ +---------------+---------+
+ | Column Name | Type |
+ +---------------+---------+
+ | id | int |
+ | visit_date | date |
+ | people | int |
+ +---------------+---------+
+ visit_date is the primary key for this table.
+ Each row of this table contains the visit date and visit id to the stadium with the number of people during
+ the visit.
+ No two rows will have the same visit_date, and as the id increases, the dates increase as well.
+
+Write an SQL query to display the records with three or more rows with **consecutive** `id`'s, and the number of people is greater than or equal to 100 for each.
+
+Return the result table ordered by `visit_date` in **ascending order**.
+
+The query result format is in the following example.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:**
+
+ Stadium table:
+ +------+------------+-----------+
+ | id | visit_date | people |
+ +------+------------+-----------+
+ | 1 | 2017-01-01 | 10 |
+ | 2 | 2017-01-02 | 109 |
+ | 3 | 2017-01-03 | 150 |
+ | 4 | 2017-01-04 | 99 |
+ | 5 | 2017-01-05 | 145 |
+ | 6 | 2017-01-06 | 1455 |
+ | 7 | 2017-01-07 | 199 |
+ | 8 | 2017-01-09 | 188 |
+ +------+------------+-----------+
+
+**Output:**
+
+ +------+------------+-----------+
+ | id | visit_date | people |
+ +------+------------+-----------+
+ | 5 | 2017-01-05 | 145 |
+ | 6 | 2017-01-06 | 1455 |
+ | 7 | 2017-01-07 | 199 |
+ | 8 | 2017-01-09 | 188 |
+ +------+------------+-----------+
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+ The four rows with ids 5, 6, 7, and 8 have consecutive ids and each of them has >= 100 people attended.
+ Note that row 8 was included even though the visit\_date was not the next day after row 7.
+ The rows with ids 2 and 3 are not included because we need at least three consecutive ids.
+
+## Solution
+
+```sql
+# Write your MySQL query statement below
+with new_group as(
+ select id,visit_date,people,id - row_number() over(order by id) as new
+ from Stadium
+ where people >= 100
+ )
+ select id,visit_date,people
+ from new_group
+ where new in(
+ select new
+ from new_group
+ group by new
+ having count(id) >= 3
+ );
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0605_can_place_flowers/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0605_can_place_flowers/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..877ad31d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0605_can_place_flowers/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 605\. Can Place Flowers
+
+Easy
+
+You have a long flowerbed in which some of the plots are planted, and some are not. However, flowers cannot be planted in **adjacent** plots.
+
+Given an integer array `flowerbed` containing `0`'s and `1`'s, where `0` means empty and `1` means not empty, and an integer `n`, return _if_ `n` new flowers can be planted in the `flowerbed` without violating the no-adjacent-flowers rule.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** flowerbed = [1,0,0,0,1], n = 1
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** flowerbed = [1,0,0,0,1], n = 2
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= flowerbed.length <= 2 * 104
+* `flowerbed[i]` is `0` or `1`.
+* There are no two adjacent flowers in `flowerbed`.
+* `0 <= n <= flowerbed.length`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+@Suppress("NAME_SHADOWING")
+class Solution {
+ fun canPlaceFlowers(flowerbed: IntArray, n: Int): Boolean {
+ var n = n
+ for (i in flowerbed.indices) {
+ if (flowerbed[i] == 0 && n > 0) {
+ val left = i == 0 || flowerbed[i - 1] == 0
+ val right = i == flowerbed.size - 1 || flowerbed[i + 1] == 0
+ if (left && right) {
+ flowerbed[i] = 1
+ n--
+ }
+ }
+ if (n == 0) {
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ return n == 0
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0606_construct_string_from_binary_tree/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0606_construct_string_from_binary_tree/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..9849a210
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0606_construct_string_from_binary_tree/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,82 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 606\. Construct String from Binary Tree
+
+Easy
+
+Given the `root` of a binary tree, construct a string consisting of parenthesis and integers from a binary tree with the preorder traversal way, and return it.
+
+Omit all the empty parenthesis pairs that do not affect the one-to-one mapping relationship between the string and the original binary tree.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
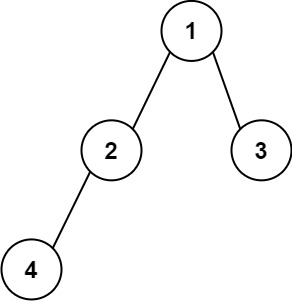
+
+
+**Input:** root = [1,2,3,4]
+
+**Output:** "1(2(4))(3)"
+
+**Explanation:** Originally, it needs to be "1(2(4)())(3()())", but you need to omit all the unnecessary empty parenthesis pairs. And it will be "1(2(4))(3)"
+
+**Example 2:**
+
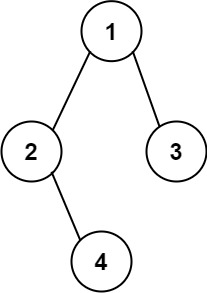
+
+
+**Input:** root = [1,2,3,null,4]
+
+**Output:** "1(2()(4))(3)"
+
+**Explanation:** Almost the same as the first example, except we cannot omit the first parenthesis pair to break the one-to-one mapping relationship between the input and the output.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 104].
+* `-1000 <= Node.val <= 1000`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode
+
+/*
+ * Example:
+ * var ti = TreeNode(5)
+ * var v = ti.`val`
+ * Definition for a binary tree node.
+ * class TreeNode(var `val`: Int) {
+ * var left: TreeNode? = null
+ * var right: TreeNode? = null
+ * }
+ */
+class Solution {
+ fun tree2str(t: TreeNode?): String {
+ if (t == null) {
+ return ""
+ }
+ val sb = StringBuilder()
+ preorder(t, sb)
+ return sb.toString()
+ }
+
+ private fun preorder(root: TreeNode?, sb: StringBuilder) {
+ if (root == null) {
+ return
+ }
+ sb.append(root.`val`)
+ if (root.left != null) {
+ sb.append("(")
+ preorder(root.left, sb)
+ sb.append(")")
+ }
+ if (root.right != null) {
+ if (root.left == null) {
+ sb.append("()")
+ }
+ sb.append("(")
+ preorder(root.right, sb)
+ sb.append(")")
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0607_sales_person/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0607_sales_person/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d1d1da04
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0607_sales_person/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,120 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 607\. Sales Person
+
+Easy
+
+SQL Schema
+
+Table: `SalesPerson`
+
+ +-----------------+---------+
+ | Column Name | Type |
+ +-----------------+---------+
+ | sales_id | int |
+ | name | varchar |
+ | salary | int |
+ | commission_rate | int |
+ | hire_date | date |
+ +-----------------+---------+
+ sales_id is the primary key column for this table.
+ Each row of this table indicates the name and the ID of a salesperson alongside their salary, commission rate, and hire date.
+
+Table: `Company`
+
+ +-------------+---------+
+ | Column Name | Type |
+ +-------------+---------+
+ | com_id | int |
+ | name | varchar |
+ | city | varchar |
+ +-------------+---------+
+ com_id is the primary key column for this table.
+ Each row of this table indicates the name and the ID of a company and the city in which the company is located.
+
+Table: `Orders`
+
+ +-------------+------+
+ | Column Name | Type |
+ +-------------+------+
+ | order_id | int |
+ | order_date | date |
+ | com_id | int |
+ | sales_id | int |
+ | amount | int |
+ +-------------+------+
+ order_id is the primary key column for this table.
+ com_id is a foreign key to com_id from the Company table.
+ sales_id is a foreign key to com_id from the SalesPerson table.
+ Each row of this table contains information about one order. This includes the ID of the company, the ID of the salesperson, the date of the order, and the amount paid.
+
+Write an SQL query to report the names of all the salespersons who did not have any orders related to the company with the name **"RED"**.
+
+Return the result table in **any order**.
+
+The query result format is in the following example.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:**
+
+ SalesPerson table:
+ +----------+------+--------+-----------------+------------+
+ | sales_id | name | salary | commission_rate | hire_date |
+ +----------+------+--------+-----------------+------------+
+ | 1 | John | 100000 | 6 | 4/1/2006 |
+ | 2 | Amy | 12000 | 5 | 5/1/2010 |
+ | 3 | Mark | 65000 | 12 | 12/25/2008 |
+ | 4 | Pam | 25000 | 25 | 1/1/2005 |
+ | 5 | Alex | 5000 | 10 | 2/3/2007 |
+ +----------+------+--------+-----------------+------------+
+
+ Company table:
+
+ +--------+--------+----------+
+ | com_id | name | city |
+ +--------+--------+----------+
+ | 1 | RED | Boston |
+ | 2 | ORANGE | New York |
+ | 3 | YELLOW | Boston |
+ | 4 | GREEN | Austin |
+ +--------+--------+----------+
+
+ Orders table:
+ +----------+------------+--------+----------+--------+
+ | order_id | order_date | com_id | sales_id | amount |
+ +----------+------------+--------+----------+--------+
+ | 1 | 1/1/2014 | 3 | 4 | 10000 |
+ | 2 | 2/1/2014 | 4 | 5 | 5000 |
+ | 3 | 3/1/2014 | 1 | 1 | 50000 |
+ | 4 | 4/1/2014 | 1 | 4 | 25000 |
+ +----------+------------+--------+----------+--------+
+
+**Output:**
+
+ +------+
+ | name |
+ +------+
+ | Amy |
+ | Mark |
+ | Alex |
+ +------+
+
+**Explanation:** According to orders 3 and 4 in the Orders table,
+it is easy to tell that only salesperson John and Pam have sales to company RED, so we report all the other names in the table salesperson.
+
+## Solution
+
+```sql
+# Write your MySQL query statement below
+SELECT NAME
+FROM
+SALESPERSON
+WHERE SALES_ID NOT IN
+(
+SELECT O.SALES_ID FROM ORDERS AS O LEFT JOIN COMPANY C
+ON O.COM_ID = C.COM_ID
+WHERE C.NAME = 'RED'
+)
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0608_tree_node/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0608_tree_node/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d4e7628d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0608_tree_node/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,106 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 608\. Tree Node
+
+Medium
+
+SQL Schema
+
+Table: `Tree`
+
+ +-------------+------+
+ | Column Name | Type |
+ +-------------+------+
+ | id | int |
+ | p_id | int |
+ +-------------+------+
+ id is the primary key column for this table.
+ Each row of this table contains information about the id of a node and the id of its parent node in a tree.
+ The given structure is always a valid tree.
+
+Each node in the tree can be one of three types:
+
+* **"Leaf"**: if the node is a leaf node.
+* **"Root"**: if the node is the root of the tree.
+* **"Inner"**: If the node is neither a leaf node nor a root node.
+
+Write an SQL query to report the type of each node in the tree.
+
+Return the result table in **any order**.
+
+The query result format is in the following example.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
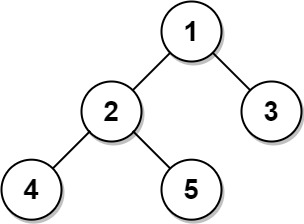
+
+
+**Input:**
+
+ Tree table:
+ +----+------+
+ | id | p_id |
+ +----+------+
+ | 1 | null |
+ | 2 | 1 |
+ | 3 | 1 |
+ | 4 | 2 |
+ | 5 | 2 |
+ +----+------+
+
+**Output:**
+
+ +----+-------+
+ | id | type |
+ +----+-------+
+ | 1 | Root |
+ | 2 | Inner |
+ | 3 | Leaf |
+ | 4 | Leaf |
+ | 5 | Leaf |
+ +----+-------+
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Node 1 is the root node because its parent node is null and it has child nodes 2 and 3.
+
+Node 2 is an inner node because it has parent node 1 and child node 4 and 5.
+
+Nodes 3, 4, and 5 are leaf nodes because they have parent nodes and they do not have child nodes.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:**
+
+ Tree table:
+ +----+------+
+ | id | p_id |
+ +----+------+
+ | 1 | null |
+ +----+------+
+
+**Output:**
+
+ +----+-------+
+ | id | type |
+ +----+-------+
+ | 1 | Root |
+ +----+-------+
+
+**Explanation:** If there is only one node on the tree, you only need to output its root attributes.
+
+## Solution
+
+```sql
+# Write your MySQL query statement below
+SELECT
+ id,
+ CASE
+ WHEN p_id IS NULL THEN 'Root'
+ WHEN p_id IN (SELECT id FROM Tree) AND id IN (SELECT p_id FROM Tree) THEN 'Inner'
+ ELSE 'Leaf'
+ END AS type
+FROM Tree
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0609_find_duplicate_file_in_system/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0609_find_duplicate_file_in_system/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3891ef1d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0609_find_duplicate_file_in_system/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,77 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 609\. Find Duplicate File in System
+
+Medium
+
+Given a list `paths` of directory info, including the directory path, and all the files with contents in this directory, return _all the duplicate files in the file system in terms of their paths_. You may return the answer in **any order**.
+
+A group of duplicate files consists of at least two files that have the same content.
+
+A single directory info string in the input list has the following format:
+
+* `"root/d1/d2/.../dm f1.txt(f1_content) f2.txt(f2_content) ... fn.txt(fn_content)"`
+
+It means there are `n` files `(f1.txt, f2.txt ... fn.txt)` with content `(f1_content, f2_content ... fn_content)` respectively in the directory "`root/d1/d2/.../dm"`. Note that `n >= 1` and `m >= 0`. If `m = 0`, it means the directory is just the root directory.
+
+The output is a list of groups of duplicate file paths. For each group, it contains all the file paths of the files that have the same content. A file path is a string that has the following format:
+
+* `"directory_path/file_name.txt"`
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** paths = ["root/a 1.txt(abcd) 2.txt(efgh)","root/c 3.txt(abcd)","root/c/d 4.txt(efgh)","root 4.txt(efgh)"]
+
+**Output:** [["root/a/2.txt","root/c/d/4.txt","root/4.txt"],["root/a/1.txt","root/c/3.txt"]]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** paths = ["root/a 1.txt(abcd) 2.txt(efgh)","root/c 3.txt(abcd)","root/c/d 4.txt(efgh)"]
+
+**Output:** [["root/a/2.txt","root/c/d/4.txt"],["root/a/1.txt","root/c/3.txt"]]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= paths.length <= 2 * 104
+* `1 <= paths[i].length <= 3000`
+* 1 <= sum(paths[i].length) <= 5 * 105
+* `paths[i]` consist of English letters, digits, `'/'`, `'.'`, `'('`, `')'`, and `' '`.
+* You may assume no files or directories share the same name in the same directory.
+* You may assume each given directory info represents a unique directory. A single blank space separates the directory path and file info.
+
+**Follow up:**
+
+* Imagine you are given a real file system, how will you search files? DFS or BFS?
+* If the file content is very large (GB level), how will you modify your solution?
+* If you can only read the file by 1kb each time, how will you modify your solution?
+* What is the time complexity of your modified solution? What is the most time-consuming part and memory-consuming part of it? How to optimize?
+* How to make sure the duplicated files you find are not false positive?
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun findDuplicate(paths: Array): List> {
+ val map: MutableMap> = HashMap()
+ for (path in paths) {
+ val pathComponents = path.split(" ".toRegex()).dropLastWhile { it.isEmpty() }.toTypedArray()
+ val root = pathComponents[0]
+ for (i in 1 until pathComponents.size) {
+ val startIndex = pathComponents[i].indexOf("(")
+ val endIndex = pathComponents[i].lastIndexOf(")")
+ val content = pathComponents[i].substring(startIndex, endIndex)
+ map.putIfAbsent(content, ArrayList())
+ map[content]!!.add(root + "/" + pathComponents[i].substring(0, startIndex))
+ }
+ }
+ val result: MutableList> = ArrayList()
+ for (list in map.values) {
+ if (list.size > 1) {
+ result.add(list)
+ }
+ }
+ return result
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0611_valid_triangle_number/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0611_valid_triangle_number/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ad36ae63
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0611_valid_triangle_number/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 611\. Valid Triangle Number
+
+Medium
+
+Given an integer array `nums`, return _the number of triplets chosen from the array that can make triangles if we take them as side lengths of a triangle_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [2,2,3,4]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** Valid combinations are:
+
+2,3,4 (using the first 2)
+
+2,3,4 (using the second 2)
+
+2,2,3
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [4,2,3,4]
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= nums.length <= 1000`
+* `0 <= nums[i] <= 1000`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun triangleNumber(nums: IntArray): Int {
+ val n: Int
+ var max = 0
+ val count = IntArray(1001)
+ for (i in nums) {
+ count[i]++
+ max = Math.max(max, i)
+ }
+ count[0] = 0
+ var idx = 0
+ for (i in 1..max) {
+ var j = 0
+ while (j < count[i]) {
+ nums[idx] = i
+ ++j
+ ++idx
+ }
+ count[i] += count[i - 1]
+ }
+ n = idx
+ var r = 0
+ for (i in 0 until n - 2) {
+ for (j in i + 1 until n - 1) {
+ if (nums[i] + nums[j] > max) {
+ r += (n - j) * (n - j - 1) / 2
+ break
+ }
+ r += count[nums[i] + nums[j] - 1] - j - 1
+ }
+ }
+ return r
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0617_merge_two_binary_trees/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0617_merge_two_binary_trees/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0b30db80
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0617_merge_two_binary_trees/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 617\. Merge Two Binary Trees
+
+Easy
+
+You are given two binary trees `root1` and `root2`.
+
+Imagine that when you put one of them to cover the other, some nodes of the two trees are overlapped while the others are not. You need to merge the two trees into a new binary tree. The merge rule is that if two nodes overlap, then sum node values up as the new value of the merged node. Otherwise, the NOT null node will be used as the node of the new tree.
+
+Return _the merged tree_.
+
+**Note:** The merging process must start from the root nodes of both trees.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** root1 = [1,3,2,5], root2 = [2,1,3,null,4,null,7]
+
+**Output:** [3,4,5,5,4,null,7]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** root1 = [1], root2 = [1,2]
+
+**Output:** [2,2]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* The number of nodes in both trees is in the range `[0, 2000]`.
+* -104 <= Node.val <= 104
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode
+
+/*
+ * Example:
+ * var ti = TreeNode(5)
+ * var v = ti.`val`
+ * Definition for a binary tree node.
+ * class TreeNode(var `val`: Int) {
+ * var left: TreeNode? = null
+ * var right: TreeNode? = null
+ * }
+ */
+class Solution {
+ fun mergeTrees(root1: TreeNode?, root2: TreeNode?): TreeNode? {
+ if (root1 == null) {
+ return root2
+ }
+ return if (root2 == null) {
+ root1
+ } else TreeNode(
+ root1.`val` + root2.`val`,
+ mergeTrees(root1.left, root2.left),
+ mergeTrees(root1.right, root2.right)
+ )
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0620_not_boring_movies/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0620_not_boring_movies/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a1e89819
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0620_not_boring_movies/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 620\. Not Boring Movies
+
+Easy
+
+SQL Schema
+
+Table: `Cinema`
+
+ +----------------+----------+
+ | Column Name | Type |
+ +----------------+----------+
+ | id | int |
+ | movie | varchar |
+ | description | varchar |
+ | rating | float |
+ +----------------+----------+
+ id is the primary key for this table.
+ Each row contains information about the name of a movie, its genre, and its rating.
+ rating is a 2 decimal places float in the range [0, 10]
+
+Write an SQL query to report the movies with an odd-numbered ID and a description that is not `"boring"`.
+
+Return the result table ordered by `rating` **in descending order**.
+
+The query result format is in the following example.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:**
+Cinema table:
++----+------------+-------------+--------+
+\| id \| movie \| description \| rating \|
++----+------------+-------------+--------+
+\| 1 \| War \| great 3D \| 8.9 \|
+\| 2 \| Science \| fiction \| 8.5 \|
+\| 3 \| irish \| boring \| 6.2 \|
+\| 4 \| Ice song \| Fantacy \| 8.6 \|
+\| 5 \| House card \| Interesting \| 9.1 \|
++----+------------+-------------+--------+
+
+**Output:**
+
+ +----+------------+-------------+--------+
+ | id | movie | description | rating |
+ +----+------------+-------------+--------+
+ | 5 | House card | Interesting | 9.1 |
+ | 1 | War | great 3D | 8.9 |
+ +----+------------+-------------+--------+
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+ We have three movies with odd-numbered IDs: 1, 3, and 5. The movie with ID = 3 is boring so we do not
+ include it in the answer.
+
+## Solution
+
+```sql
+# Write your MySQL query statement below
+select id, movie, description, rating from Cinema
+WHERE mod(id,2) = 1
+and
+description not LIKE '%boring%'
+order by rating DESC;
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0621_task_scheduler/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0621_task_scheduler/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..9ccd9b82
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0621_task_scheduler/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 621\. Task Scheduler
+
+Medium
+
+Given a characters array `tasks`, representing the tasks a CPU needs to do, where each letter represents a different task. Tasks could be done in any order. Each task is done in one unit of time. For each unit of time, the CPU could complete either one task or just be idle.
+
+However, there is a non-negative integer `n` that represents the cooldown period between two **same tasks** (the same letter in the array), that is that there must be at least `n` units of time between any two same tasks.
+
+Return _the least number of units of times that the CPU will take to finish all the given tasks_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** tasks = ["A","A","A","B","B","B"], n = 2
+
+**Output:** 8
+
+**Explanation:** A -> B -> idle -> A -> B -> idle -> A -> B There is at least 2 units of time between any two same tasks.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** tasks = ["A","A","A","B","B","B"], n = 0
+
+**Output:** 6
+
+**Explanation:** On this case any permutation of size 6 would work since n = 0. ["A","A","A","B","B","B"] ["A","B","A","B","A","B"] ["B","B","B","A","A","A"] ... And so on.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** tasks = ["A","A","A","A","A","A","B","C","D","E","F","G"], n = 2
+
+**Output:** 16
+
+**Explanation:** One possible solution is A -> B -> C -> A -> D -> E -> A -> F -> G -> A -> idle -> idle -> A -> idle -> idle -> A
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= task.length <= 104
+* `tasks[i]` is upper-case English letter.
+* The integer `n` is in the range `[0, 100]`.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun leastInterval(tasks: CharArray, n: Int): Int {
+ if (n <= 0) {
+ return tasks.size
+ }
+ val counters = IntArray(26)
+ var maxCount = 0
+ for (task in tasks) {
+ val idx = task.code - 'A'.code
+ counters[idx]++
+ maxCount = Math.max(maxCount, counters[idx])
+ }
+ var maxNum = 0
+ for (counter in counters) {
+ if (counter == maxCount) {
+ maxNum++
+ }
+ }
+ return Math.max(tasks.size, (maxCount - 1) * (n + 1) + maxNum)
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0622_design_circular_queue/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0622_design_circular_queue/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f26284ff
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0622_design_circular_queue/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,111 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 622\. Design Circular Queue
+
+Medium
+
+Design your implementation of the circular queue. The circular queue is a linear data structure in which the operations are performed based on FIFO (First In First Out) principle and the last position is connected back to the first position to make a circle. It is also called "Ring Buffer".
+
+One of the benefits of the circular queue is that we can make use of the spaces in front of the queue. In a normal queue, once the queue becomes full, we cannot insert the next element even if there is a space in front of the queue. But using the circular queue, we can use the space to store new values.
+
+Implementation the `MyCircularQueue` class:
+
+* `MyCircularQueue(k)` Initializes the object with the size of the queue to be `k`.
+* `int Front()` Gets the front item from the queue. If the queue is empty, return `-1`.
+* `int Rear()` Gets the last item from the queue. If the queue is empty, return `-1`.
+* `boolean enQueue(int value)` Inserts an element into the circular queue. Return `true` if the operation is successful.
+* `boolean deQueue()` Deletes an element from the circular queue. Return `true` if the operation is successful.
+* `boolean isEmpty()` Checks whether the circular queue is empty or not.
+* `boolean isFull()` Checks whether the circular queue is full or not.
+
+You must solve the problem without using the built-in queue data structure in your programming language.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input** ["MyCircularQueue", "enQueue", "enQueue", "enQueue", "enQueue", "Rear", "isFull", "deQueue", "enQueue", "Rear"] [[3], [1], [2], [3], [4], [], [], [], [4], []]
+
+**Output:** [null, true, true, true, false, 3, true, true, true, 4]
+
+**Explanation:** MyCircularQueue myCircularQueue = new MyCircularQueue(3); myCircularQueue.enQueue(1); // return True myCircularQueue.enQueue(2); // return True myCircularQueue.enQueue(3); // return True myCircularQueue.enQueue(4); // return False myCircularQueue.Rear(); // return 3 myCircularQueue.isFull(); // return True myCircularQueue.deQueue(); // return True myCircularQueue.enQueue(4); // return True myCircularQueue.Rear(); // return 4
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= k <= 1000`
+* `0 <= value <= 1000`
+* At most `3000` calls will be made to `enQueue`, `deQueue`, `Front`, `Rear`, `isEmpty`, and `isFull`.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class MyCircularQueue(private val maxSize: Int) {
+ private val dumyHead = DoubleLinkedNode(0)
+ private var size = 0
+
+ init {
+ dumyHead.left = dumyHead
+ dumyHead.right = dumyHead
+ }
+
+ fun enQueue(value: Int): Boolean {
+ if (size == maxSize) {
+ return false
+ }
+ val node = DoubleLinkedNode(value)
+ val right = dumyHead.right
+ dumyHead.right = node
+ node.left = dumyHead
+ node.right = right
+ right!!.left = node
+ size++
+ return true
+ }
+
+ fun deQueue(): Boolean {
+ if (size == 0) {
+ return false
+ }
+ val left = dumyHead.left
+ dumyHead.left = left!!.left
+ dumyHead.left!!.right = dumyHead
+ size--
+ return true
+ }
+
+ fun Rear(): Int {
+ return if (size == 0) {
+ -1
+ } else dumyHead.right!!.`val`
+ }
+
+ fun Front(): Int {
+ return if (size == 0) {
+ -1
+ } else dumyHead.left!!.`val`
+ }
+
+ fun isEmpty(): Boolean {
+ return size == 0
+ }
+
+ fun isFull(): Boolean {
+ return size == maxSize
+ }
+
+ internal class DoubleLinkedNode(val `val`: Int) {
+ var left: DoubleLinkedNode? = null
+ var right: DoubleLinkedNode? = null
+ }
+}
+
+/*
+ * Your MyCircularQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
+ * var obj = MyCircularQueue(k)
+ * var param_1 = obj.enQueue(value)
+ * var param_2 = obj.deQueue()
+ * var param_3 = obj.Front()
+ * var param_4 = obj.Rear()
+ * var param_5 = obj.isEmpty()
+ * var param_6 = obj.isFull()
+ */
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0623_add_one_row_to_tree/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0623_add_one_row_to_tree/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..9256ecdf
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0623_add_one_row_to_tree/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,87 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 623\. Add One Row to Tree
+
+Medium
+
+Given the `root` of a binary tree and two integers `val` and `depth`, add a row of nodes with value `val` at the given depth `depth`.
+
+Note that the `root` node is at depth `1`.
+
+The adding rule is:
+
+* Given the integer `depth`, for each not null tree node `cur` at the depth `depth - 1`, create two tree nodes with value `val` as `cur`'s left subtree root and right subtree root.
+* `cur`'s original left subtree should be the left subtree of the new left subtree root.
+* `cur`'s original right subtree should be the right subtree of the new right subtree root.
+* If `depth == 1` that means there is no depth `depth - 1` at all, then create a tree node with value `val` as the new root of the whole original tree, and the original tree is the new root's left subtree.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+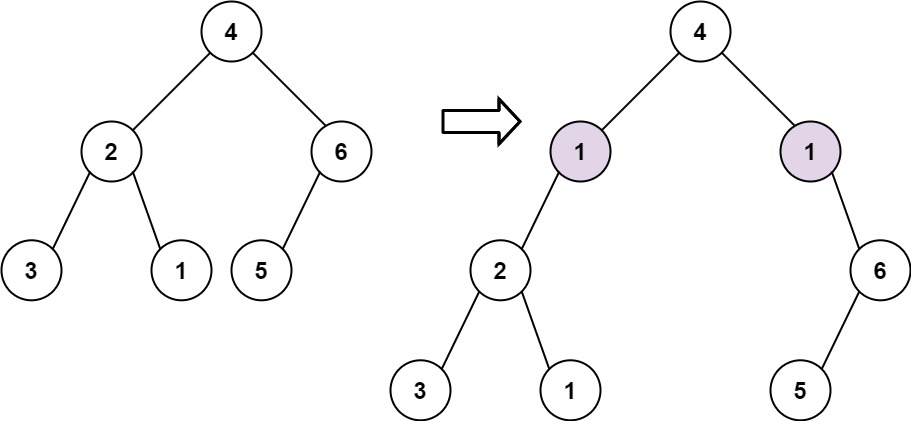
+
+**Input:** root = [4,2,6,3,1,5], val = 1, depth = 2
+
+**Output:** [4,1,1,2,null,null,6,3,1,5]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+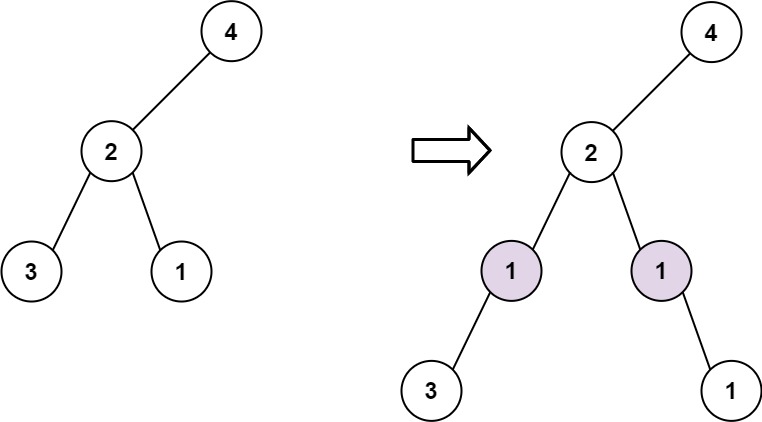
+
+**Input:** root = [4,2,null,3,1], val = 1, depth = 3
+
+**Output:** [4,2,null,1,1,3,null,null,1]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 104].
+* The depth of the tree is in the range [1, 104].
+* `-100 <= Node.val <= 100`
+* -105 <= val <= 105
+* `1 <= depth <= the depth of tree + 1`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode
+
+/*
+ * Example:
+ * var ti = TreeNode(5)
+ * var v = ti.`val`
+ * Definition for a binary tree node.
+ * class TreeNode(var `val`: Int) {
+ * var left: TreeNode? = null
+ * var right: TreeNode? = null
+ * }
+ */
+class Solution {
+ fun addOneRow(root: TreeNode?, `val`: Int, depth: Int): TreeNode? {
+ if (depth == 1) {
+ val newRoot = TreeNode(`val`)
+ newRoot.left = root
+ return newRoot
+ }
+ dfs(root!!, depth - 2, `val`)
+ return root
+ }
+
+ private fun dfs(node: TreeNode, depth: Int, `val`: Int) {
+ if (depth == 0) {
+ val left = TreeNode(`val`)
+ val right = TreeNode(`val`)
+ left.left = node.left
+ right.right = node.right
+ node.left = left
+ node.right = right
+ } else {
+ if (node.left != null) {
+ dfs(node.left!!, depth - 1, `val`)
+ }
+ if (node.right != null) {
+ dfs(node.right!!, depth - 1, `val`)
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0626_exchange_seats/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0626_exchange_seats/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1ad96b3f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0626_exchange_seats/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 626\. Exchange Seats
+
+Medium
+
+SQL Schema
+
+Table: `Seat`
+
+ +-------------+---------+
+ | Column Name | Type |
+ +-------------+---------+
+ | id | int |
+ | name | varchar |
+ +-------------+---------+
+ id is the primary key column for this table.
+ Each row of this table indicates the name and the ID of a student.
+ id is a continuous increment.
+
+Write an SQL query to swap the seat id of every two consecutive students. If the number of students is odd, the id of the last student is not swapped.
+
+Return the result table ordered by `id` **in ascending order**.
+
+The query result format is in the following example.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:**
+
+ Seat table:
+ +----+---------+
+ | id | student |
+ +----+---------+
+ | 1 | Abbot |
+ | 2 | Doris |
+ | 3 | Emerson |
+ | 4 | Green |
+ | 5 | Jeames |
+ +----+---------+
+
+**Output:**
+
+ +----+---------+
+ | id | student |
+ +----+---------+
+ | 1 | Doris |
+ | 2 | Abbot |
+ | 3 | Green |
+ | 4 | Emerson |
+ | 5 | Jeames |
+ +----+---------+
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Note that if the number of students is odd, there is no need to change the last one's seat.
+
+## Solution
+
+```sql
+# Write your MySQL query statement below
+SELECT CASE
+ WHEN s.id = ( SELECT COUNT(*) FROM Seat ) AND MOD(s.id,2) = 1 THEN s.id
+ WHEN MOD(s.id,2) = 0 THEN s.id - 1
+ ELSE s.id + 1
+ END AS id,
+ s.student
+FROM Seat AS s
+ORDER BY id
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0627_swap_salary/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0627_swap_salary/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..801c629f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0627_swap_salary/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 627\. Swap Salary
+
+Easy
+
+SQL Schema
+
+Table: `Salary`
+
+ +-------------+----------+
+ | Column Name | Type |
+ +-------------+----------+
+ | id | int |
+ | name | varchar |
+ | sex | ENUM |
+ | salary | int |
+ +-------------+----------+
+ id is the primary key for this table.
+ The sex column is ENUM value of type ('m', 'f').
+ The table contains information about an employee.
+
+Write an SQL query to swap all `'f'` and `'m'` values (i.e., change all `'f'` values to `'m'` and vice versa) with a **single update statement** and no intermediate temporary tables.
+
+Note that you must write a single update statement, **do not** write any select statement for this problem.
+
+The query result format is in the following example.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:**
+
+ Salary table:
+ +----+------+-----+--------+
+ | id | name | sex | salary |
+ +----+------+-----+--------+
+ | 1 | A | m | 2500 |
+ | 2 | B | f | 1500 |
+ | 3 | C | m | 5500 |
+ | 4 | D | f | 500 |
+ +----+------+-----+--------+
+
+**Output:**
+
+ +----+------+-----+--------+
+ | id | name | sex | salary |
+ +----+------+-----+--------+
+ | 1 | A | f | 2500 |
+ | 2 | B | m | 1500 |
+ | 3 | C | f | 5500 |
+ | 4 | D | m | 500 |
+ +----+------+-----+--------+
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+ (1, A) and (3, C) were changed from 'm' to 'f'.
+ (2, B) and (4, D) were changed from 'f' to 'm'.
+
+## Solution
+
+```sql
+# Write your MySQL query statement below
+UPDATE Salary SET sex = CASE WHEN sex = 'm' THEN 'f' ELSE 'm' END WHERE TRUE;
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0628_maximum_product_of_three_numbers/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0628_maximum_product_of_three_numbers/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f0a426d9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0628_maximum_product_of_three_numbers/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 628\. Maximum Product of Three Numbers
+
+Easy
+
+Given an integer array `nums`, _find three numbers whose product is maximum and return the maximum product_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,3]
+
+**Output:** 6
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,3,4]
+
+**Output:** 24
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [-1,-2,-3]
+
+**Output:** -6
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 3 <= nums.length <= 104
+* `-1000 <= nums[i] <= 1000`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun maximumProduct(nums: IntArray): Int {
+ var min1 = Int.MAX_VALUE
+ var min2 = Int.MAX_VALUE
+ var max1 = Int.MIN_VALUE
+ var max2 = Int.MIN_VALUE
+ var max3 = Int.MIN_VALUE
+ for (i in nums) {
+ if (i > max1) {
+ max3 = max2
+ max2 = max1
+ max1 = i
+ } else if (i > max2) {
+ max3 = max2
+ max2 = i
+ } else if (i > max3) {
+ max3 = i
+ }
+ if (i < min1) {
+ min2 = min1
+ min1 = i
+ } else if (i < min2) {
+ min2 = i
+ }
+ }
+ return Math.max(min1 * min2 * max1, max1 * max2 * max3)
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0629_k_inverse_pairs_array/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0629_k_inverse_pairs_array/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..046d2ecd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0629_k_inverse_pairs_array/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,66 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 629\. K Inverse Pairs Array
+
+Hard
+
+For an integer array `nums`, an **inverse pair** is a pair of integers `[i, j]` where `0 <= i < j < nums.length` and `nums[i] > nums[j]`.
+
+Given two integers n and k, return the number of different arrays consist of numbers from `1` to `n` such that there are exactly `k` **inverse pairs**. Since the answer can be huge, return it **modulo** 109 + 7.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 3, k = 0
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:** Only the array [1,2,3] which consists of numbers from 1 to 3 has exactly 0 inverse pairs.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 3, k = 1
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** The array [1,3,2] and [2,1,3] have exactly 1 inverse pair.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= n <= 1000`
+* `0 <= k <= 1000`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+@Suppress("NAME_SHADOWING")
+class Solution {
+ fun kInversePairs(n: Int, k: Int): Int {
+ var k = k
+ k = Math.min(k, n * (n - 1) / 2 - k)
+ if (k < 0) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ var dp = IntArray(k + 1)
+ var dp1 = IntArray(k + 1)
+ dp[0] = 1
+ dp1[0] = 1
+ val mod = 1000000007
+ for (i in 1..n) {
+ val temp = dp
+ dp = dp1
+ dp1 = temp
+ var j = 1
+ val m = Math.min(k, i * (i - 1) / 2)
+ while (j <= m) {
+ dp[j] = (dp1[j] + dp[j - 1] - if (j >= i) dp1[j - i] else 0) % mod
+ if (dp[j] < 0) {
+ dp[j] += mod
+ }
+ j++
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[k]
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0630_course_schedule_iii/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0630_course_schedule_iii/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..121c71ff
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0630_course_schedule_iii/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,89 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 630\. Course Schedule III
+
+Hard
+
+There are `n` different online courses numbered from `1` to `n`. You are given an array `courses` where courses[i] = [durationi, lastDayi] indicate that the ith course should be taken **continuously** for durationi days and must be finished before or on lastDayi.
+
+You will start on the 1st day and you cannot take two or more courses simultaneously.
+
+Return _the maximum number of courses that you can take_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** courses = \[\[100,200],[200,1300],[1000,1250],[2000,3200]]
+
+**Output:** 3 Explanation: There are totally 4 courses, but you can take 3 courses at most: First, take the 1st course, it costs 100 days so you will finish it on the 100th day, and ready to take the next course on the 101st day. Second, take the 3rd course, it costs 1000 days so you will finish it on the 1100th day, and ready to take the next course on the 1101st day. Third, take the 2nd course, it costs 200 days so you will finish it on the 1300th day. The 4th course cannot be taken now, since you will finish it on the 3300th day, which exceeds the closed date.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** courses = \[\[1,2]]
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** courses = \[\[3,2],[4,3]]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= courses.length <= 104
+* 1 <= durationi, lastDayi <= 104
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.Arrays
+import java.util.PriorityQueue
+
+class Solution {
+ fun scheduleCourse(courses: Array): Int {
+ // Sort the courses based on their deadline date.
+ Arrays.sort(courses) { a: IntArray, b: IntArray ->
+ a[1] - b[1]
+ }
+ // Only the duration is stored. We don't care which course
+ // is the longest, we only care about the total courses can
+ // be taken.
+ // If the question wants the course ids to be returned.
+ // Consider use a Pair int pair.
+ val pq = PriorityQueue { a: Int, b: Int -> b - a }
+ // Total time consumed.
+ var time = 0
+ // At the given time `course`, the overall "time limit" is
+ // course[1]. All courses in pq is already 'valid'. But
+ // adding this course[0] might exceed the course[1] limit.
+ for (course in courses) {
+ // If adding this course doesn't exceed. Let's add it
+ // for now. (Greedy algo). We might remove it later if
+ // we have a "better" solution at that time.
+ if (time + course[0] <= course[1]) {
+ time += course[0]
+ pq.offer(course[0])
+ } else {
+ // If adding this ecxeeds the limit. We can still add it
+ // if-and-only-if there are courses longer than current
+ // one. If so, by removing a longer course, current shorter
+ // course can fit in for sure. Although the total course
+ // count is the same, the overall time consumed is shorter.
+ // Which gives us more room for future courses.
+ // Remove any course that is longer than current course
+ // will work, but we remove the longest one with the help
+ // of heap (pq).
+ if (!pq.isEmpty() && pq.peek() > course[0]) {
+ time -= pq.poll()
+ time += course[0]
+ pq.offer(course[0])
+ }
+ // If no course in consider (pq) is shorter than the
+ // current course. It is safe to discard it.
+ }
+ }
+ return pq.size
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0632_smallest_range_covering_elements_from_k_lists/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0632_smallest_range_covering_elements_from_k_lists/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8a52b2ee
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0632_smallest_range_covering_elements_from_k_lists/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,88 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 632\. Smallest Range Covering Elements from K Lists
+
+Hard
+
+You have `k` lists of sorted integers in **non-decreasing order**. Find the **smallest** range that includes at least one number from each of the `k` lists.
+
+We define the range `[a, b]` is smaller than range `[c, d]` if `b - a < d - c` **or** `a < c` if `b - a == d - c`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = \[\[4,10,15,24,26],[0,9,12,20],[5,18,22,30]]
+
+**Output:** [20,24]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+List 1: [4, 10, 15, 24,26], 24 is in range [20,24].
+
+List 2: [0, 9, 12, 20], 20 is in range [20,24].
+
+List 3: [5, 18, 22, 30], 22 is in range [20,24].
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = \[\[1,2,3],[1,2,3],[1,2,3]]
+
+**Output:** [1,1]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `nums.length == k`
+* `1 <= k <= 3500`
+* `1 <= nums[i].length <= 50`
+* -105 <= nums[i][j] <= 105
+* `nums[i]` is sorted in **non-decreasing** order.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.Objects
+import java.util.PriorityQueue
+
+class Solution {
+ internal class Triplet(var value: Int, var row: Int, var idx: Int) : Comparable {
+ override operator fun compareTo(other: Triplet?): Int {
+ return value - other!!.value
+ }
+ }
+
+ fun smallestRange(nums: List>): IntArray {
+ val pq = PriorityQueue()
+ var maxInPq = Int.MIN_VALUE
+ for (i in nums.indices) {
+ pq.add(Triplet(nums[i][0], i, 0))
+ if (maxInPq < nums[i][0]) {
+ maxInPq = nums[i][0]
+ }
+ }
+ var rangeSize = maxInPq - Objects.requireNonNull(pq.peek()).value + 1
+ var rangeLeft = Objects.requireNonNull(pq.peek()).value
+ var rangeRight = maxInPq
+ while (true) {
+ val nextNumber = pq.remove()
+ if (nextNumber.idx + 1 < nums[nextNumber.row].size) {
+ val `val` = nums[nextNumber.row][nextNumber.idx + 1]
+ if (`val` > maxInPq) {
+ maxInPq = `val`
+ }
+ pq.add(Triplet(`val`, nextNumber.row, nextNumber.idx + 1))
+ if (maxInPq - Objects.requireNonNull(pq.peek()).value + 1 < rangeSize) {
+ rangeSize = maxInPq - pq.peek().value + 1
+ rangeLeft = maxInPq
+ rangeRight = pq.peek().value
+ }
+ } else {
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ val answer = IntArray(2)
+ answer[0] = rangeLeft
+ answer[1] = rangeRight
+ return answer
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0633_sum_of_square_numbers/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0633_sum_of_square_numbers/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1f80171d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0633_sum_of_square_numbers/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 633\. Sum of Square Numbers
+
+Medium
+
+Given a non-negative integer `c`, decide whether there're two integers `a` and `b` such that a2 + b2 = c.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** c = 5
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** 1 \* 1 + 2 \* 2 = 5
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** c = 3
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 0 <= c <= 231 - 1
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import kotlin.math.sqrt
+
+class Solution {
+ fun judgeSquareSum(c: Int): Boolean {
+ val right = sqrt(c.toDouble()).toInt()
+ val left = sqrt(c.toDouble() / 2).toInt()
+ for (i in left..right) {
+ val j = sqrt(c - (i * i).toDouble()).toInt()
+ if (i * i + j * j == c) {
+ return true
+ }
+ }
+ return false
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0636_exclusive_time_of_functions/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0636_exclusive_time_of_functions/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..85cde8ec
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0636_exclusive_time_of_functions/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,126 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 636\. Exclusive Time of Functions
+
+Medium
+
+On a **single-threaded** CPU, we execute a program containing `n` functions. Each function has a unique ID between `0` and `n-1`.
+
+Function calls are **stored in a [call stack](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Call_stack)**: when a function call starts, its ID is pushed onto the stack, and when a function call ends, its ID is popped off the stack. The function whose ID is at the top of the stack is **the current function being executed**. Each time a function starts or ends, we write a log with the ID, whether it started or ended, and the timestamp.
+
+You are given a list `logs`, where `logs[i]` represents the ith log message formatted as a string `"{function_id}:{"start" | "end"}:{timestamp}"`. For example, `"0:start:3"` means a function call with function ID `0` **started at the beginning** of timestamp `3`, and `"1:end:2"` means a function call with function ID `1` **ended at the end** of timestamp `2`. Note that a function can be called **multiple times, possibly recursively**.
+
+A function's **exclusive time** is the sum of execution times for all function calls in the program. For example, if a function is called twice, one call executing for `2` time units and another call executing for `1` time unit, the **exclusive time** is `2 + 1 = 3`.
+
+Return _the **exclusive time** of each function in an array, where the value at the_ ith _index represents the exclusive time for the function with ID_ `i`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** n = 2, logs = ["0:start:0","1:start:2","1:end:5","0:end:6"]
+
+**Output:** [3,4]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Function 0 starts at the beginning of time 0, then it executes 2 for units of time and reaches the end of time 1.
+
+Function 1 starts at the beginning of time 2, executes for 4 units of time, and ends at the end of time 5.
+
+Function 0 resumes execution at the beginning of time 6 and executes for 1 unit of time.
+
+So function 0 spends 2 + 1 = 3 units of total time executing, and function 1 spends 4 units of total time executing.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 1, logs = ["0:start:0","0:start:2","0:end:5","0:start:6","0:end:6","0:end:7"]
+
+**Output:** [8]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Function 0 starts at the beginning of time 0, executes for 2 units of time, and recursively calls itself.
+
+Function 0 (recursive call) starts at the beginning of time 2 and executes for 4 units of time.
+
+Function 0 (initial call) resumes execution then immediately calls itself again.
+
+Function 0 (2nd recursive call) starts at the beginning of time 6 and executes for 1 unit of time.
+
+Function 0 (initial call) resumes execution at the beginning of time 7 and executes for 1 unit of time.
+
+So function 0 spends 2 + 4 + 1 + 1 = 8 units of total time executing.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** n = 2, logs = ["0:start:0","0:start:2","0:end:5","1:start:6","1:end:6","0:end:7"]
+
+**Output:** [7,1]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Function 0 starts at the beginning of time 0, executes for 2 units of time, and recursively calls itself.
+
+Function 0 (recursive call) starts at the beginning of time 2 and executes for 4 units of time.
+
+Function 0 (initial call) resumes execution then immediately calls function 1.
+
+Function 1 starts at the beginning of time 6, executes 1 unit of time, and ends at the end of time 6.
+
+Function 0 resumes execution at the beginning of time 6 and executes for 2 units of time.
+
+So function 0 spends 2 + 4 + 1 = 7 units of total time executing, and function 1 spends 1 unit of total time executing.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= n <= 100`
+* `1 <= logs.length <= 500`
+* `0 <= function_id < n`
+* 0 <= timestamp <= 109
+* No two start events will happen at the same timestamp.
+* No two end events will happen at the same timestamp.
+* Each function has an `"end"` log for each `"start"` log.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.ArrayDeque
+import java.util.Deque
+
+class Solution {
+ fun exclusiveTime(n: Int, logs: List): IntArray {
+ val stack: Deque = ArrayDeque()
+ val result = IntArray(n)
+ for (content in logs) {
+ val log = Log(content)
+ if (log.isStart) {
+ stack.push(log)
+ } else {
+ val top = stack.pop()
+ val executionTime = log.time - top.time + 1
+ result[top.id] += executionTime - top.waitingTime
+ if (!stack.isEmpty()) {
+ stack.peek().waitingTime += executionTime
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return result
+ }
+
+ private class Log internal constructor(content: String) {
+ var id: Int
+ var isStart: Boolean
+ var time: Int
+ var waitingTime: Int
+ init {
+ val tokens = content.split(":".toRegex()).dropLastWhile { it.isEmpty() }.toTypedArray()
+ id = tokens[0].toInt()
+ isStart = tokens[1] == "start"
+ time = tokens[2].toInt()
+ waitingTime = 0
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0637_average_of_levels_in_binary_tree/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0637_average_of_levels_in_binary_tree/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a18bb21c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0637_average_of_levels_in_binary_tree/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 637\. Average of Levels in Binary Tree
+
+Easy
+
+Given the `root` of a binary tree, return _the average value of the nodes on each level in the form of an array_. Answers within 10-5 of the actual answer will be accepted.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+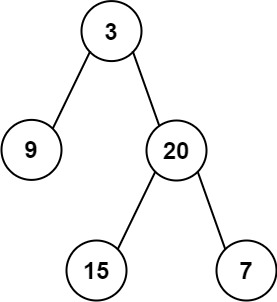
+
+**Input:** root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
+
+**Output:** [3.00000,14.50000,11.00000] Explanation: The average value of nodes on level 0 is 3, on level 1 is 14.5, and on level 2 is 11. Hence return [3, 14.5, 11].
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+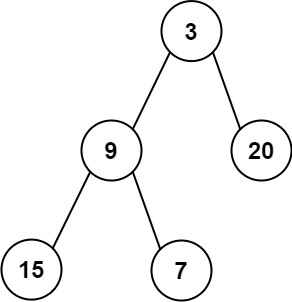
+
+**Input:** root = [3,9,20,15,7]
+
+**Output:** [3.00000,14.50000,11.00000]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 104].
+* -231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode
+
+/*
+ * Example:
+ * var ti = TreeNode(5)
+ * var v = ti.`val`
+ * Definition for a binary tree node.
+ * class TreeNode(var `val`: Int) {
+ * var left: TreeNode? = null
+ * var right: TreeNode? = null
+ * }
+ */
+class Solution {
+ fun averageOfLevels(root: TreeNode?): List {
+ val map: MutableMap> = HashMap()
+ helper(root, map, 0)
+ val result: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ for (pair in map.values) {
+ val avg = pair[1] / pair[0]
+ result.add(avg)
+ }
+ return result
+ }
+
+ private fun helper(root: TreeNode?, map: MutableMap>, level: Int) {
+ if (root == null) {
+ return
+ }
+ val pair = if (map.containsKey(level)) map[level]!! else arrayOf(0.0, 0.0)
+ pair[0] += 1.0
+ pair[1] = pair[1] + root.`val`
+ map[level] = pair
+ helper(root.left, map, level + 1)
+ helper(root.right, map, level + 1)
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0638_shopping_offers/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0638_shopping_offers/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..5581d1dd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0638_shopping_offers/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,118 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 638\. Shopping Offers
+
+Medium
+
+In LeetCode Store, there are `n` items to sell. Each item has a price. However, there are some special offers, and a special offer consists of one or more different kinds of items with a sale price.
+
+You are given an integer array `price` where `price[i]` is the price of the ith item, and an integer array `needs` where `needs[i]` is the number of pieces of the ith item you want to buy.
+
+You are also given an array `special` where `special[i]` is of size `n + 1` where `special[i][j]` is the number of pieces of the jth item in the ith offer and `special[i][n]` (i.e., the last integer in the array) is the price of the ith offer.
+
+Return _the lowest price you have to pay for exactly certain items as given, where you could make optimal use of the special offers_. You are not allowed to buy more items than you want, even if that would lower the overall price. You could use any of the special offers as many times as you want.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** price = [2,5], special = \[\[3,0,5],[1,2,10]], needs = [3,2]
+
+**Output:** 14
+
+**Explanation:** There are two kinds of items, A and B. Their prices are $2 and $5 respectively.
+
+In special offer 1, you can pay $5 for 3A and 0B In special offer 2, you can pay $10 for 1A and 2B.
+
+You need to buy 3A and 2B, so you may pay $10 for 1A and 2B (special offer #2), and $4 for 2A.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** price = [2,3,4], special = \[\[1,1,0,4],[2,2,1,9]], needs = [1,2,1]
+
+**Output:** 11
+
+**Explanation:** The price of A is $2, and $3 for B, $4 for C.
+
+You may pay $4 for 1A and 1B, and $9 for 2A ,2B and 1C.
+
+You need to buy 1A ,2B and 1C, so you may pay $4 for 1A and 1B (special offer #1), and $3 for 1B, $4 for 1C.
+
+You cannot add more items, though only $9 for 2A ,2B and 1C.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `n == price.length == needs.length`
+* `1 <= n <= 6`
+* `0 <= price[i], needs[i] <= 10`
+* `1 <= special.length <= 100`
+* `special[i].length == n + 1`
+* `0 <= special[i][j] <= 50`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution() {
+ fun shoppingOffers(
+ price: List,
+ special: List>,
+ needs: List
+ ): Int {
+ val map: MutableMap, Int> = HashMap()
+ shoppingOffersUtil(price, special, needs, map)
+ return map[needs]!!
+ }
+
+ private fun shoppingOffersUtil(
+ price: List,
+ special: List>,
+ needs: List,
+ map: MutableMap, Int>
+ ): Int {
+ if (map.containsKey(needs)) {
+ return map[needs]!!
+ }
+ var ans = computePrice(price, needs)
+ for (i in special.indices) {
+ if (verify(special[i], needs)) {
+ ans = Math.min(
+ special[i][needs.size] +
+ shoppingOffersUtil(
+ price,
+ special,
+ updatedNeeds(needs, special[i]),
+ map
+ ),
+ ans
+ )
+ }
+ }
+ map[needs] = ans
+ return (map[needs])!!
+ }
+
+ private fun updatedNeeds(needs: List, special: List): List {
+ val updatedNeeds: MutableList = ArrayList(needs)
+ for (i in needs.indices) {
+ updatedNeeds[i] = updatedNeeds[i] - special[i]
+ }
+ return updatedNeeds
+ }
+
+ private fun verify(special: List, needs: List): Boolean {
+ for (i in needs.indices) {
+ if (special[i] > needs[i]) {
+ return false
+ }
+ }
+ return true
+ }
+
+ private fun computePrice(price: List, needs: List): Int {
+ var ans = 0
+ for (i in needs.indices) {
+ ans += (needs[i] * price[i])
+ }
+ return ans
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0639_decode_ways_ii/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0639_decode_ways_ii/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..572eaaf7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0639_decode_ways_ii/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 639\. Decode Ways II
+
+Hard
+
+A message containing letters from `A-Z` can be **encoded** into numbers using the following mapping:
+
+'A' -> "1" 'B' -> "2" ... 'Z' -> "26"
+
+To **decode** an encoded message, all the digits must be grouped then mapped back into letters using the reverse of the mapping above (there may be multiple ways). For example, `"11106"` can be mapped into:
+
+* `"AAJF"` with the grouping `(1 1 10 6)`
+* `"KJF"` with the grouping `(11 10 6)`
+
+Note that the grouping `(1 11 06)` is invalid because `"06"` cannot be mapped into `'F'` since `"6"` is different from `"06"`.
+
+**In addition** to the mapping above, an encoded message may contain the `'*'` character, which can represent any digit from `'1'` to `'9'` (`'0'` is excluded). For example, the encoded message `"1*"` may represent any of the encoded messages `"11"`, `"12"`, `"13"`, `"14"`, `"15"`, `"16"`, `"17"`, `"18"`, or `"19"`. Decoding `"1*"` is equivalent to decoding **any** of the encoded messages it can represent.
+
+Given a string `s` consisting of digits and `'*'` characters, return _the **number** of ways to **decode** it_.
+
+Since the answer may be very large, return it **modulo** 109 + 7.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "\*"
+
+**Output:** 9
+
+**Explanation:** The encoded message can represent any of the encoded messages "1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", or "9". Each of these can be decoded to the strings "A", "B", "C", "D", "E", "F", "G", "H", and "I" respectively. Hence, there are a total of 9 ways to decode "\*".
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "1\*"
+
+**Output:** 18
+
+**Explanation:** The encoded message can represent any of the encoded messages "11", "12", "13", "14", "15", "16", "17", "18", or "19". Each of these encoded messages have 2 ways to be decoded (e.g. "11" can be decoded to "AA" or "K"). Hence, there are a total of 9 \* 2 = 18 ways to decode "1\*".
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** s = "2\*"
+
+**Output:** 15
+
+**Explanation:** The encoded message can represent any of the encoded messages "21", "22", "23", "24", "25", "26", "27", "28", or "29". "21", "22", "23", "24", "25", and "26" have 2 ways of being decoded, but "27", "28", and "29" only have 1 way. Hence, there are a total of (6 \* 2) + (3 \* 1) = 12 + 3 = 15 ways to decode "2\*".
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= s.length <= 105
+* `s[i]` is a digit or `'*'`.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun numDecodings(s: String): Int {
+ if (s[0] == '0') {
+ return 0
+ }
+ val dp = LongArray(s.length + 1)
+ dp[0] = 1
+ dp[1] = (if (s[0] == '*') 9 else 1).toLong()
+ val ch = s.toCharArray()
+ for (i in 2..ch.size) {
+ if (ch[i - 1] == '0') {
+ if (ch[i - 2] == '1' || ch[i - 2] == '2') {
+ dp[i] = dp[i - 2]
+ } else if (ch[i - 2] == '*') {
+ dp[i] = 2 * dp[i - 2]
+ } else {
+ return 0
+ }
+ } else if (ch[i - 1] >= '1' && ch[i - 1] <= '6') {
+ dp[i] = dp[i - 1]
+ if (ch[i - 2] == '1' || ch[i - 2] == '2') {
+ dp[i] += dp[i - 2]
+ } else if (ch[i - 2] == '*') {
+ dp[i] += 2 * dp[i - 2]
+ }
+ } else if (ch[i - 1] >= '7' && ch[i - 1] <= '9') {
+ dp[i] = dp[i - 1]
+ if (ch[i - 2] == '1' || ch[i - 2] == '*') {
+ dp[i] += dp[i - 2]
+ }
+ } else if (ch[i - 1] == '*') {
+ dp[i] = 9 * dp[i - 1]
+ if (ch[i - 2] == '1') {
+ dp[i] += 9 * dp[i - 2]
+ } else if (ch[i - 2] == '2') {
+ dp[i] += 6 * dp[i - 2]
+ } else if (ch[i - 2] == '*') {
+ dp[i] += 15 * dp[i - 2]
+ }
+ }
+ dp[i] = dp[i] % 1000000007
+ }
+ return dp[s.length].toInt()
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0640_solve_the_equation/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0640_solve_the_equation/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..b78365c6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0640_solve_the_equation/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,103 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 640\. Solve the Equation
+
+Medium
+
+Solve a given equation and return the value of `'x'` in the form of a string `"x=#value"`. The equation contains only `'+'`, `'-'` operation, the variable `'x'` and its coefficient. You should return `"No solution"` if there is no solution for the equation, or `"Infinite solutions"` if there are infinite solutions for the equation.
+
+If there is exactly one solution for the equation, we ensure that the value of `'x'` is an integer.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** equation = "x+5-3+x=6+x-2"
+
+**Output:** "x=2"
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** equation = "x=x"
+
+**Output:** "Infinite solutions"
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** equation = "2x=x"
+
+**Output:** "x=0"
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `3 <= equation.length <= 1000`
+* `equation` has exactly one `'='`.
+* `equation` consists of integers with an absolute value in the range `[0, 100]` without any leading zeros, and the variable `'x'`.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun solveEquation(equation: String): String {
+ val eqs = equation.split("=".toRegex()).dropLastWhile { it.isEmpty() }.toTypedArray()
+ val arr1 = evaluate(eqs[0])
+ val arr2 = evaluate(eqs[1])
+ return if (arr1[0] == arr2[0] && arr1[1] == arr2[1]) {
+ "Infinite solutions"
+ } else if (arr1[0] == arr2[0]) {
+ "No solution"
+ } else {
+ "x=" + (arr2[1] - arr1[1]) / (arr1[0] - arr2[0])
+ }
+ }
+
+ private fun evaluate(eq: String): IntArray {
+ val arr = eq.toCharArray()
+ var f = false
+ var a = 0
+ var b = 0
+ var i = 0
+ if (arr[0] == '-') {
+ f = true
+ i++
+ }
+ while (i < arr.size) {
+ if (arr[i] == '-') {
+ f = true
+ i++
+ } else if (arr[i] == '+') {
+ i++
+ }
+ val sb = StringBuilder()
+ while (i < arr.size && Character.isDigit(arr[i])) {
+ sb.append(arr[i])
+ i++
+ }
+ val n = sb.toString()
+ if (i < arr.size && arr[i] == 'x') {
+ var number: Int
+ number = if (n == "") {
+ 1
+ } else {
+ n.toInt()
+ }
+ if (f) {
+ number = -number
+ }
+ a += number
+ i++
+ } else {
+ var number = n.toInt()
+ if (f) {
+ number = -number
+ }
+ b += number
+ }
+ f = false
+ }
+ val op = IntArray(2)
+ op[0] = a
+ op[1] = b
+ return op
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0641_design_circular_deque/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0641_design_circular_deque/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3a99cc89
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0641_design_circular_deque/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,146 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 641\. Design Circular Deque
+
+Medium
+
+Design your implementation of the circular double-ended queue (deque).
+
+Implement the `MyCircularDeque` class:
+
+* `MyCircularDeque(int k)` Initializes the deque with a maximum size of `k`.
+* `boolean insertFront()` Adds an item at the front of Deque. Returns `true` if the operation is successful, or `false` otherwise.
+* `boolean insertLast()` Adds an item at the rear of Deque. Returns `true` if the operation is successful, or `false` otherwise.
+* `boolean deleteFront()` Deletes an item from the front of Deque. Returns `true` if the operation is successful, or `false` otherwise.
+* `boolean deleteLast()` Deletes an item from the rear of Deque. Returns `true` if the operation is successful, or `false` otherwise.
+* `int getFront()` Returns the front item from the Deque. Returns `-1` if the deque is empty.
+* `int getRear()` Returns the last item from Deque. Returns `-1` if the deque is empty.
+* `boolean isEmpty()` Returns `true` if the deque is empty, or `false` otherwise.
+* `boolean isFull()` Returns `true` if the deque is full, or `false` otherwise.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input**
+
+["MyCircularDeque", "insertLast", "insertLast", "insertFront", "insertFront", "getRear", "isFull", "deleteLast", "insertFront", "getFront"]
+
+[[3], [1], [2], [3], [4], [], [], [], [4], []]
+
+**Output:** [null, true, true, true, false, 2, true, true, true, 4]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+MyCircularDeque myCircularDeque = new MyCircularDeque(3);
+
+myCircularDeque.insertLast(1); // return True
+
+myCircularDeque.insertLast(2); // return True
+
+myCircularDeque.insertFront(3); // return True
+
+myCircularDeque.insertFront(4); // return False, the queue is full.
+
+myCircularDeque.getRear(); // return 2
+
+myCircularDeque.isFull(); // return True
+
+myCircularDeque.deleteLast(); // return True
+
+myCircularDeque.insertFront(4); // return True
+
+myCircularDeque.getFront(); // return 4
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= k <= 1000`
+* `0 <= value <= 1000`
+* At most `2000` calls will be made to `insertFront`, `insertLast`, `deleteFront`, `deleteLast`, `getFront`, `getRear`, `isEmpty`, `isFull`.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class MyCircularDeque(k: Int) {
+ private val data: IntArray
+ private var front: Int
+ private var rear: Int
+ private var size: Int
+
+ init {
+ data = IntArray(k)
+ front = 0
+ rear = k - 1
+ size = 0
+ }
+
+ fun insertFront(value: Int): Boolean {
+ if (size == data.size) {
+ return false
+ }
+ data[front] = value
+ front = (front + 1) % data.size
+ size++
+ return true
+ }
+
+ fun insertLast(value: Int): Boolean {
+ if (size == data.size) {
+ return false
+ }
+ data[rear] = value
+ rear = (rear - 1 + data.size) % data.size
+ size++
+ return true
+ }
+
+ fun deleteFront(): Boolean {
+ if (size == 0) {
+ return false
+ }
+ front = (front - 1 + data.size) % data.size
+ size--
+ return true
+ }
+
+ fun deleteLast(): Boolean {
+ if (size == 0) {
+ return false
+ }
+ rear = (rear + 1) % data.size
+ size--
+ return true
+ }
+
+ fun getFront(): Int {
+ return if (size == 0) {
+ -1
+ } else data[(front - 1 + data.size) % data.size]
+ }
+
+ fun getRear(): Int {
+ return if (size == 0) {
+ -1
+ } else data[(rear + 1) % data.size]
+ }
+
+ fun isEmpty(): Boolean {
+ return size == 0
+ }
+ fun isFull(): Boolean {
+ return size == data.size
+ }
+}
+
+/*
+ * Your MyCircularDeque object will be instantiated and called as such:
+ * var obj = MyCircularDeque(k)
+ * var param_1 = obj.insertFront(value)
+ * var param_2 = obj.insertLast(value)
+ * var param_3 = obj.deleteFront()
+ * var param_4 = obj.deleteLast()
+ * var param_5 = obj.getFront()
+ * var param_6 = obj.getRear()
+ * var param_7 = obj.isEmpty()
+ * var param_8 = obj.isFull()
+ */
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0643_maximum_average_subarray_i/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0643_maximum_average_subarray_i/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..611bf0e0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0643_maximum_average_subarray_i/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 643\. Maximum Average Subarray I
+
+Easy
+
+You are given an integer array `nums` consisting of `n` elements, and an integer `k`.
+
+Find a contiguous subarray whose **length is equal to** `k` that has the maximum average value and return _this value_. Any answer with a calculation error less than 10-5 will be accepted.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,12,-5,-6,50,3], k = 4
+
+**Output:** 12.75000
+
+**Explanation:** Maximum average is (12 - 5 - 6 + 50) / 4 = 51 / 4 = 12.75
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [5], k = 1
+
+**Output:** 5.00000
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `n == nums.length`
+* 1 <= k <= n <= 105
+* -104 <= nums[i] <= 104
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun findMaxAverage(nums: IntArray, k: Int): Double {
+ var windowSum = 0.0
+ var windowStart = 0
+ var max = Int.MIN_VALUE.toDouble()
+ for (windowEnd in nums.indices) {
+ windowSum += nums[windowEnd].toDouble()
+ if (windowEnd >= k - 1) {
+ val candidate = windowSum / k
+ max = Math.max(candidate, max)
+ windowSum -= nums[windowStart].toDouble()
+ windowStart++
+ }
+ }
+ return max
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0645_set_mismatch/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0645_set_mismatch/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..cec0392a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0645_set_mismatch/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 645\. Set Mismatch
+
+Easy
+
+You have a set of integers `s`, which originally contains all the numbers from `1` to `n`. Unfortunately, due to some error, one of the numbers in `s` got duplicated to another number in the set, which results in **repetition of one** number and **loss of another** number.
+
+You are given an integer array `nums` representing the data status of this set after the error.
+
+Find the number that occurs twice and the number that is missing and return _them in the form of an array_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,2,4]
+
+**Output:** [2,3]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,1]
+
+**Output:** [1,2]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 2 <= nums.length <= 104
+* 1 <= nums[i] <= 104
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun findErrorNums(nums: IntArray): IntArray {
+ val ans = IntArray(2)
+ var i = 0
+ while (i < nums.size) {
+ val correct = nums[i] - 1
+ if (nums[i] != nums[correct]) {
+ val temp = nums[i]
+ nums[i] = nums[correct]
+ nums[correct] = temp
+ } else {
+ i++
+ }
+ }
+ for (a in nums.indices) {
+ if (nums[a] != a + 1) {
+ ans[0] = nums[a]
+ ans[1] = a + 1
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ return ans
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0646_maximum_length_of_pair_chain/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0646_maximum_length_of_pair_chain/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e957eff3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0646_maximum_length_of_pair_chain/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 646\. Maximum Length of Pair Chain
+
+Medium
+
+You are given an array of `n` pairs `pairs` where pairs[i] = [lefti, righti] and lefti < righti.
+
+A pair `p2 = [c, d]` **follows** a pair `p1 = [a, b]` if `b < c`. A **chain** of pairs can be formed in this fashion.
+
+Return _the length longest chain which can be formed_.
+
+You do not need to use up all the given intervals. You can select pairs in any order.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** pairs = \[\[1,2],[2,3],[3,4]]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** The longest chain is [1,2] -> [3,4].
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** pairs = \[\[1,2],[7,8],[4,5]]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** The longest chain is [1,2] -> [4,5] -> [7,8].
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `n == pairs.length`
+* `1 <= n <= 1000`
+* -1000 <= lefti < righti <= 1000
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.Arrays
+
+class Solution {
+ fun findLongestChain(pairs: Array): Int {
+ if (pairs.size == 1) {
+ return 1
+ }
+ Arrays.sort(pairs) { a: IntArray, b: IntArray ->
+ a[1] - b[1]
+ }
+ var min = pairs[0][1]
+ var max = 1
+ for (i in 1 until pairs.size) {
+ if (pairs[i][0] > min) {
+ max++
+ min = pairs[i][1]
+ }
+ }
+ return max
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0648_replace_words/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0648_replace_words/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e549935a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0648_replace_words/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,103 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 648\. Replace Words
+
+Medium
+
+In English, we have a concept called **root**, which can be followed by some other word to form another longer word - let's call this word **successor**. For example, when the **root** `"an"` is followed by the **successor** word `"other"`, we can form a new word `"another"`.
+
+Given a `dictionary` consisting of many **roots** and a `sentence` consisting of words separated by spaces, replace all the **successors** in the sentence with the **root** forming it. If a **successor** can be replaced by more than one **root**, replace it with the **root** that has **the shortest length**.
+
+Return _the `sentence`_ after the replacement.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** dictionary = ["cat","bat","rat"], sentence = "the cattle was rattled by the battery"
+
+**Output:** "the cat was rat by the bat"
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** dictionary = ["a","b","c"], sentence = "aadsfasf absbs bbab cadsfafs"
+
+**Output:** "a a b c"
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= dictionary.length <= 1000`
+* `1 <= dictionary[i].length <= 100`
+* `dictionary[i]` consists of only lower-case letters.
+* 1 <= sentence.length <= 106
+* `sentence` consists of only lower-case letters and spaces.
+* The number of words in `sentence` is in the range `[1, 1000]`
+* The length of each word in `sentence` is in the range `[1, 1000]`
+* Every two consecutive words in `sentence` will be separated by exactly one space.
+* `sentence` does not have leading or trailing spaces.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.function.Consumer
+
+class Solution {
+ fun replaceWords(dictionary: List, sentence: String): String {
+ val trie = Trie()
+ dictionary.forEach(Consumer { word: String -> trie.insert(word) })
+ val allWords = sentence.split(" ".toRegex()).dropLastWhile { it.isEmpty() }.toTypedArray()
+ for (i in allWords.indices) {
+ allWords[i] = trie.getRootForWord(allWords[i])
+ }
+ return java.lang.String.join(" ", *allWords)
+ }
+
+ internal class Node {
+ var links = arrayOfNulls(26)
+ var isWordCompleted = false
+
+ fun containsKey(ch: Char): Boolean {
+ return links[ch.code - 'a'.code] != null
+ }
+
+ fun put(ch: Char, node: Node?) {
+ links[ch.code - 'a'.code] = node
+ }
+
+ operator fun get(ch: Char): Node? {
+ return links[ch.code - 'a'.code]
+ }
+ }
+
+ internal class Trie {
+ var root: Node = Node()
+
+ fun insert(word: String) {
+ var node: Node? = root
+ for (i in word.indices) {
+ if (!node!!.containsKey(word[i])) {
+ node.put(word[i], Node())
+ }
+ node = node[word[i]]
+ }
+ node!!.isWordCompleted = true
+ }
+
+ fun getRootForWord(word: String): String {
+ var node: Node? = root
+ val rootWord = StringBuilder()
+ for (i in word.indices) {
+ if (node!!.containsKey(word[i])) {
+ rootWord.append(word[i])
+ node = node[word[i]]
+ if (node!!.isWordCompleted) {
+ return rootWord.toString()
+ }
+ } else {
+ return word
+ }
+ }
+ return word
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file