diff --git a/docs/integrations/containers-orchestration/opentelemetry/rabbitmq-opentelemetry.md b/docs/integrations/containers-orchestration/opentelemetry/rabbitmq-opentelemetry.md
index 9761804934..9e5152b4b1 100644
--- a/docs/integrations/containers-orchestration/opentelemetry/rabbitmq-opentelemetry.md
+++ b/docs/integrations/containers-orchestration/opentelemetry/rabbitmq-opentelemetry.md
@@ -11,7 +11,7 @@ import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
})
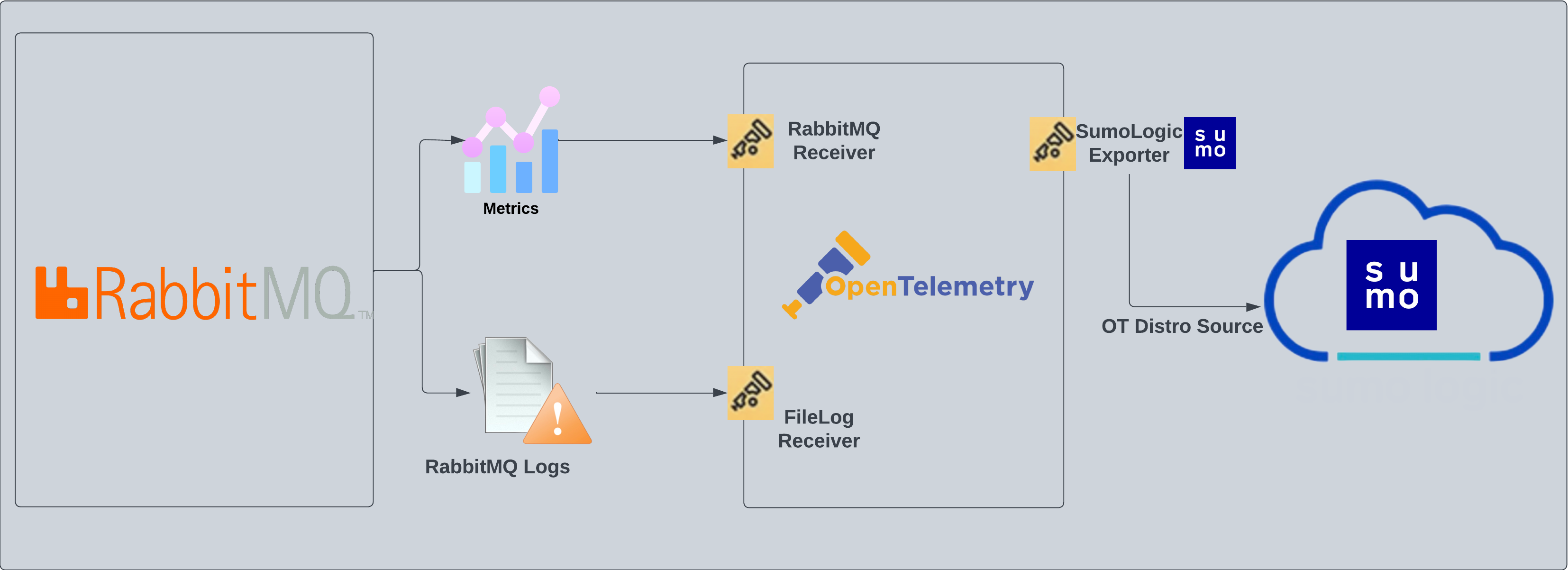
}) -The [RabbitMQ](https://www.rabbitmq.com/getstarted.html) app is a unified log app. Preconfigured dashboards provide insight into error logs. RabbitMQ logs are sent to Sumo Logic through OpenTelemetry [filelog receiver](https://github.com/open-telemetry/opentelemetry-collector-contrib/tree/main/receiver/filelogreceiver).
+RabbitMQ logs are sent to Sumo Logic through the OpenTelemetry [filelog receiver](https://github.com/open-telemetry/opentelemetry-collector-contrib/tree/main/receiver/filelogreceiver). RabbitMQ metrics are sent through the [RabbitMQ](https://github.com/open-telemetry/opentelemetry-collector-contrib/tree/main/receiver/rabbitmqreceiver) metrics receiver.
-The [RabbitMQ](https://www.rabbitmq.com/getstarted.html) app is a unified log app. Preconfigured dashboards provide insight into error logs. RabbitMQ logs are sent to Sumo Logic through OpenTelemetry [filelog receiver](https://github.com/open-telemetry/opentelemetry-collector-contrib/tree/main/receiver/filelogreceiver).
+RabbitMQ logs are sent to Sumo Logic through the OpenTelemetry [filelog receiver](https://github.com/open-telemetry/opentelemetry-collector-contrib/tree/main/receiver/filelogreceiver). RabbitMQ metrics are sent through the [RabbitMQ](https://github.com/open-telemetry/opentelemetry-collector-contrib/tree/main/receiver/rabbitmqreceiver) metrics receiver.
 @@ -19,17 +19,32 @@ The [RabbitMQ](https://www.rabbitmq.com/getstarted.html) app is a unified log ap
Following are the [Fields](/docs/manage/fields/) which will be created as part of RabbitMQ App install if not already present.
-* `messaging.cluster.name`. User configured. Specify the user-friendly cluster name which RabbitMQ belongs to.
-* `sumo.datasource`. Has fixed value of **rabbitmq**.
+* **`sumo.datasource`**. Fixed value of **rabbitmq**.
+* **`messaging.system`**. Fixed value of **rabbitmq**.
+* **`deployment.environment`**. This is a user-configured field set at the time of collector installation. It identifies the environment where the rabbitmq env resides, such as `dev`, `prod`, or `qa`.
+* **`messaging.cluster.name`**. User configured. Enter a name to uniquely identify your RabbitMQ cluster. This cluster name will be shown in the Sumo Logic dashboards.
+* **`messaging.node.name`**. Includes the value of the hostname of the machine which is being monitored.
## Prerequisites
+### For metrics collection
+
+:::note
+The RabbitMQ receiver supports RabbitMQ versions `3.8` and `3.9`.
+:::
+
+Enable the RabbitMQ management plugin by following the instructions in the [RabbitMQ documentation](https://www.rabbitmq.com/management.html#getting-started). Also, make sure you at least have the [monitoring](https://www.rabbitmq.com/management.html#permissions) level permissions to monitor the metrics.
+
+
+### For logs collection
+
This section provides instructions for configuring log collection for RabbitMQ running on a non-Kubernetes environment for the Sumo Logic App for RabbitMQ. By default, RabbitMQ logs are stored in a log file.
Follow the instructions to set up log collection:
-1. **Configure logging in RabbitMQ**. RabbitMQ supports logging via the following methods: local text log files, syslog and stdout. RabbitMQ logs have six levels of verbosity: debug, info, warning, error, critical, none. For details please visit this [page](https://www.rabbitmq.com/logging.html#log-levels). For the dashboards to work properly, log level needs to be set to **debug**. Default log level is **info**. All logging settings are located in [RabbitMQ.conf](https://www.rabbitmq.com/logging.html).
-2. **Configure RabbitMQ to write log lines to a local file**. By default, RabbitMQ logs are stored in `/var/log/rabbitmq/rabbit@.log`. The default directory for log files is listed in the `RabbitMQ.conf` file. To configure the log output destination to a log file, use one of the following settings, either in the [configuration file](https://www.rabbitmq.com/logging.html). Edit or create `/etc/rabbitmq/rabbitmq.conf` file config:
+
+1. RabbitMQ logs have six levels of verbosity: debug, info, warning, error, critical, and none. For more information, refer to the [RabbitMQ documentation](https://www.rabbitmq.com/logging.html#log-levels). To make sure the dashboard work properly, the log level needs to be set to **debug**. Default log level is **info**. All logging settings are located in [RabbitMQ.conf](https://www.rabbitmq.com/logging.html).
+2. Configure RabbitMQ to write log lines to a local file. By default, RabbitMQ logs are stored in `/var/log/rabbitmq/rabbit@.log`. The default directory for log files is listed in the `RabbitMQ.conf` file. To configure the log output destination to a log file, use one of the following settings, either in the [configuration file](https://www.rabbitmq.com/logging.html). Edit or create `/etc/rabbitmq/rabbitmq.conf` file config:
```
log.dir = /var/log/rabbitmq
log.file = rabbitmq.log
@@ -74,9 +89,22 @@ import SetupColl from '../../../reuse/apps/opentelemetry/set-up-collector.md';
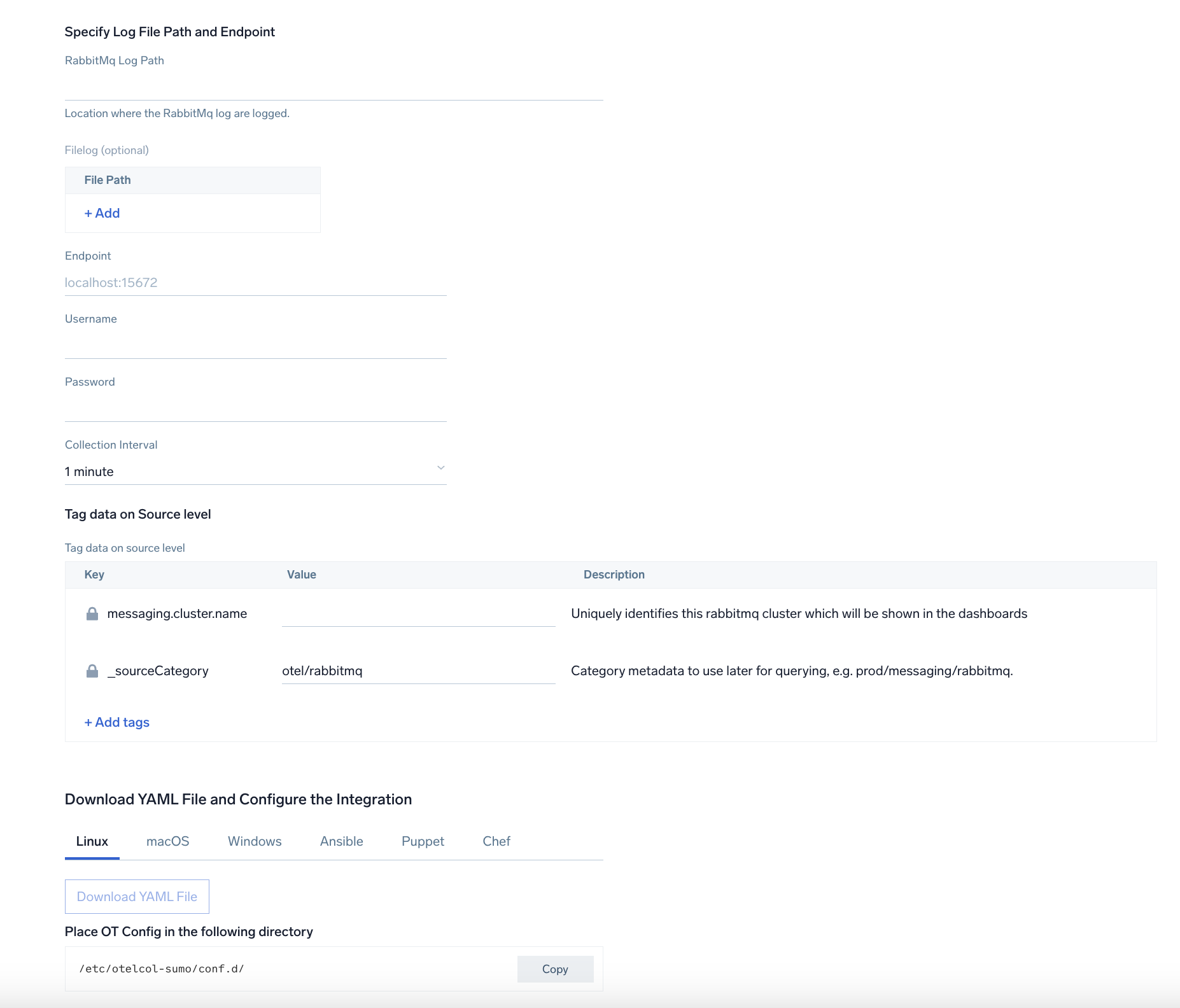
### Step 2: Configure integration
-In this step, we will be configuring the yaml file required for RabbitMQ Collection. Path of the log file configured to capture RabbitMQ logs is needed to be given here.
+OpenTelemetry works with a [configuration](https://opentelemetry.io/docs/collector/configuration/) yaml file with all the details concerning the data that needs to be collected. For example, it specifies the location of a log file that is read and sent to the Sumo Logic platform.
+
+In this step, you will configure the yaml file required for RabbitMQ collection.
+
+Below are the inputs required:
+
+- **`endpoint (no default)`**. The hostname and port of the RabbitMQ instance, separated by a colon. (For example: `localhost:15672`.)
+- **RabbitMQ logs Path**. Enter the path to the log file for your RabbitMQ instance.
+- **username**. Enter the RabbitMQ username.
+- **password**. Enter the RabbitMQ password.
+
+The log file path configured to capture RabbitMQ logs must be given here. The files are typically located in `/var/log/rabbitmq/rabbit@.log`. If you are using a customized path, check the [`rabbitmq.conf`](https://www.rabbitmq.com/logging.html) file for this information.
-The files are typically located in `/var/log/rabbitmq/rabbit@.log`. You can add any custom fields which you want to tag along with the data ingested in sumo. Click on the **Download YAML File** button to get the yaml file.
+You can add any custom fields which you want to tag along with the data ingested in sumo. Click on the **Download YAML File** button to get the yaml file.
+
+For Linux platform, click **Download Environment Variables File** to get the file with the password which is supposed to be set as environment variable.
@@ -19,17 +19,32 @@ The [RabbitMQ](https://www.rabbitmq.com/getstarted.html) app is a unified log ap
Following are the [Fields](/docs/manage/fields/) which will be created as part of RabbitMQ App install if not already present.
-* `messaging.cluster.name`. User configured. Specify the user-friendly cluster name which RabbitMQ belongs to.
-* `sumo.datasource`. Has fixed value of **rabbitmq**.
+* **`sumo.datasource`**. Fixed value of **rabbitmq**.
+* **`messaging.system`**. Fixed value of **rabbitmq**.
+* **`deployment.environment`**. This is a user-configured field set at the time of collector installation. It identifies the environment where the rabbitmq env resides, such as `dev`, `prod`, or `qa`.
+* **`messaging.cluster.name`**. User configured. Enter a name to uniquely identify your RabbitMQ cluster. This cluster name will be shown in the Sumo Logic dashboards.
+* **`messaging.node.name`**. Includes the value of the hostname of the machine which is being monitored.
## Prerequisites
+### For metrics collection
+
+:::note
+The RabbitMQ receiver supports RabbitMQ versions `3.8` and `3.9`.
+:::
+
+Enable the RabbitMQ management plugin by following the instructions in the [RabbitMQ documentation](https://www.rabbitmq.com/management.html#getting-started). Also, make sure you at least have the [monitoring](https://www.rabbitmq.com/management.html#permissions) level permissions to monitor the metrics.
+
+
+### For logs collection
+
This section provides instructions for configuring log collection for RabbitMQ running on a non-Kubernetes environment for the Sumo Logic App for RabbitMQ. By default, RabbitMQ logs are stored in a log file.
Follow the instructions to set up log collection:
-1. **Configure logging in RabbitMQ**. RabbitMQ supports logging via the following methods: local text log files, syslog and stdout. RabbitMQ logs have six levels of verbosity: debug, info, warning, error, critical, none. For details please visit this [page](https://www.rabbitmq.com/logging.html#log-levels). For the dashboards to work properly, log level needs to be set to **debug**. Default log level is **info**. All logging settings are located in [RabbitMQ.conf](https://www.rabbitmq.com/logging.html).
-2. **Configure RabbitMQ to write log lines to a local file**. By default, RabbitMQ logs are stored in `/var/log/rabbitmq/rabbit@.log`. The default directory for log files is listed in the `RabbitMQ.conf` file. To configure the log output destination to a log file, use one of the following settings, either in the [configuration file](https://www.rabbitmq.com/logging.html). Edit or create `/etc/rabbitmq/rabbitmq.conf` file config:
+
+1. RabbitMQ logs have six levels of verbosity: debug, info, warning, error, critical, and none. For more information, refer to the [RabbitMQ documentation](https://www.rabbitmq.com/logging.html#log-levels). To make sure the dashboard work properly, the log level needs to be set to **debug**. Default log level is **info**. All logging settings are located in [RabbitMQ.conf](https://www.rabbitmq.com/logging.html).
+2. Configure RabbitMQ to write log lines to a local file. By default, RabbitMQ logs are stored in `/var/log/rabbitmq/rabbit@.log`. The default directory for log files is listed in the `RabbitMQ.conf` file. To configure the log output destination to a log file, use one of the following settings, either in the [configuration file](https://www.rabbitmq.com/logging.html). Edit or create `/etc/rabbitmq/rabbitmq.conf` file config:
```
log.dir = /var/log/rabbitmq
log.file = rabbitmq.log
@@ -74,9 +89,22 @@ import SetupColl from '../../../reuse/apps/opentelemetry/set-up-collector.md';
### Step 2: Configure integration
-In this step, we will be configuring the yaml file required for RabbitMQ Collection. Path of the log file configured to capture RabbitMQ logs is needed to be given here.
+OpenTelemetry works with a [configuration](https://opentelemetry.io/docs/collector/configuration/) yaml file with all the details concerning the data that needs to be collected. For example, it specifies the location of a log file that is read and sent to the Sumo Logic platform.
+
+In this step, you will configure the yaml file required for RabbitMQ collection.
+
+Below are the inputs required:
+
+- **`endpoint (no default)`**. The hostname and port of the RabbitMQ instance, separated by a colon. (For example: `localhost:15672`.)
+- **RabbitMQ logs Path**. Enter the path to the log file for your RabbitMQ instance.
+- **username**. Enter the RabbitMQ username.
+- **password**. Enter the RabbitMQ password.
+
+The log file path configured to capture RabbitMQ logs must be given here. The files are typically located in `/var/log/rabbitmq/rabbit@.log`. If you are using a customized path, check the [`rabbitmq.conf`](https://www.rabbitmq.com/logging.html) file for this information.
-The files are typically located in `/var/log/rabbitmq/rabbit@.log`. You can add any custom fields which you want to tag along with the data ingested in sumo. Click on the **Download YAML File** button to get the yaml file.
+You can add any custom fields which you want to tag along with the data ingested in sumo. Click on the **Download YAML File** button to get the yaml file.
+
+For Linux platform, click **Download Environment Variables File** to get the file with the password which is supposed to be set as environment variable.
 @@ -164,6 +192,8 @@ Here's a sample log message you'd find in Non-Kubernetes environments.
## Sample queries
+### Logs
+
This sample Query is from the **RabbitMQ - Logs dashboard** > **Events** by Severity panel.
```sql title="Query String"
@@ -173,10 +203,26 @@ This sample Query is from the **RabbitMQ - Logs dashboard** > **Events** by Seve
| parse "* * [*]" as date,time,severity | count by severity
```
+### Metrics
+
+This sample query is from the **Average Number of Consumers** panel in **RabbitMQ - Metrics** dashboard.
+
+```sql sumo.datasource=rabbitmq metric=rabbitmq.consumer.count deployment.environment=* messaging.cluster.name=* messaging.node.name=* rabbitmq.queue.name=* rabbitmq.vhost.name=*
+| avg by messaging.cluster.name
+| sum
+```
+
+
## Viewing RabbitMQ Dashboards
-### Overview
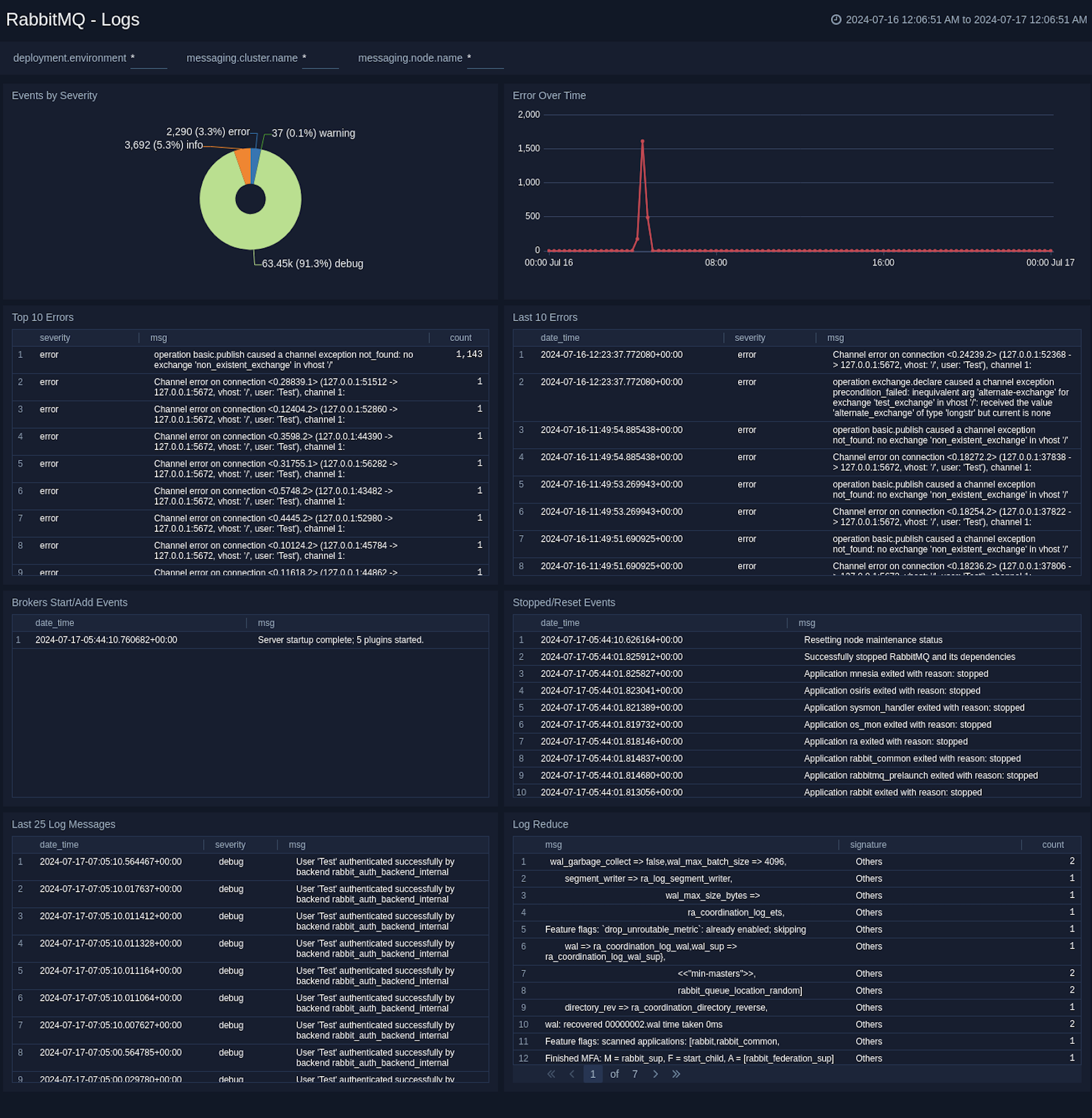
+### Logs
+
+The **RabbitMQ - Logs** dashboard gives you an at-a-glance view of error messages, error by severity, top and last 10 errors, broker, and Event Start/Add log messages.
+
+
@@ -164,6 +192,8 @@ Here's a sample log message you'd find in Non-Kubernetes environments.
## Sample queries
+### Logs
+
This sample Query is from the **RabbitMQ - Logs dashboard** > **Events** by Severity panel.
```sql title="Query String"
@@ -173,10 +203,26 @@ This sample Query is from the **RabbitMQ - Logs dashboard** > **Events** by Seve
| parse "* * [*]" as date,time,severity | count by severity
```
+### Metrics
+
+This sample query is from the **Average Number of Consumers** panel in **RabbitMQ - Metrics** dashboard.
+
+```sql sumo.datasource=rabbitmq metric=rabbitmq.consumer.count deployment.environment=* messaging.cluster.name=* messaging.node.name=* rabbitmq.queue.name=* rabbitmq.vhost.name=*
+| avg by messaging.cluster.name
+| sum
+```
+
+
## Viewing RabbitMQ Dashboards
-### Overview
+### Logs
+
+The **RabbitMQ - Logs** dashboard gives you an at-a-glance view of error messages, error by severity, top and last 10 errors, broker, and Event Start/Add log messages.
+
+ +
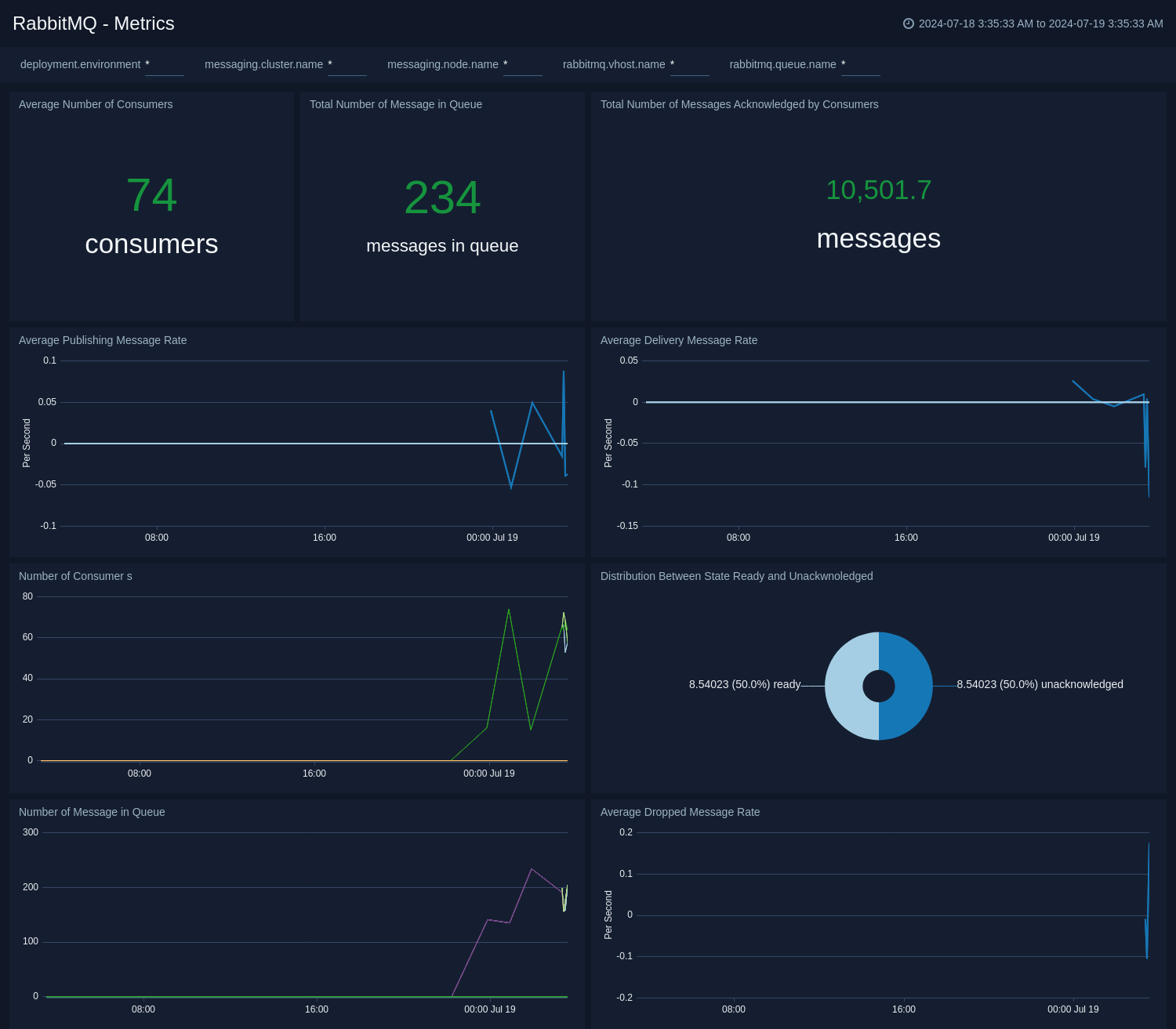
+### Metrics
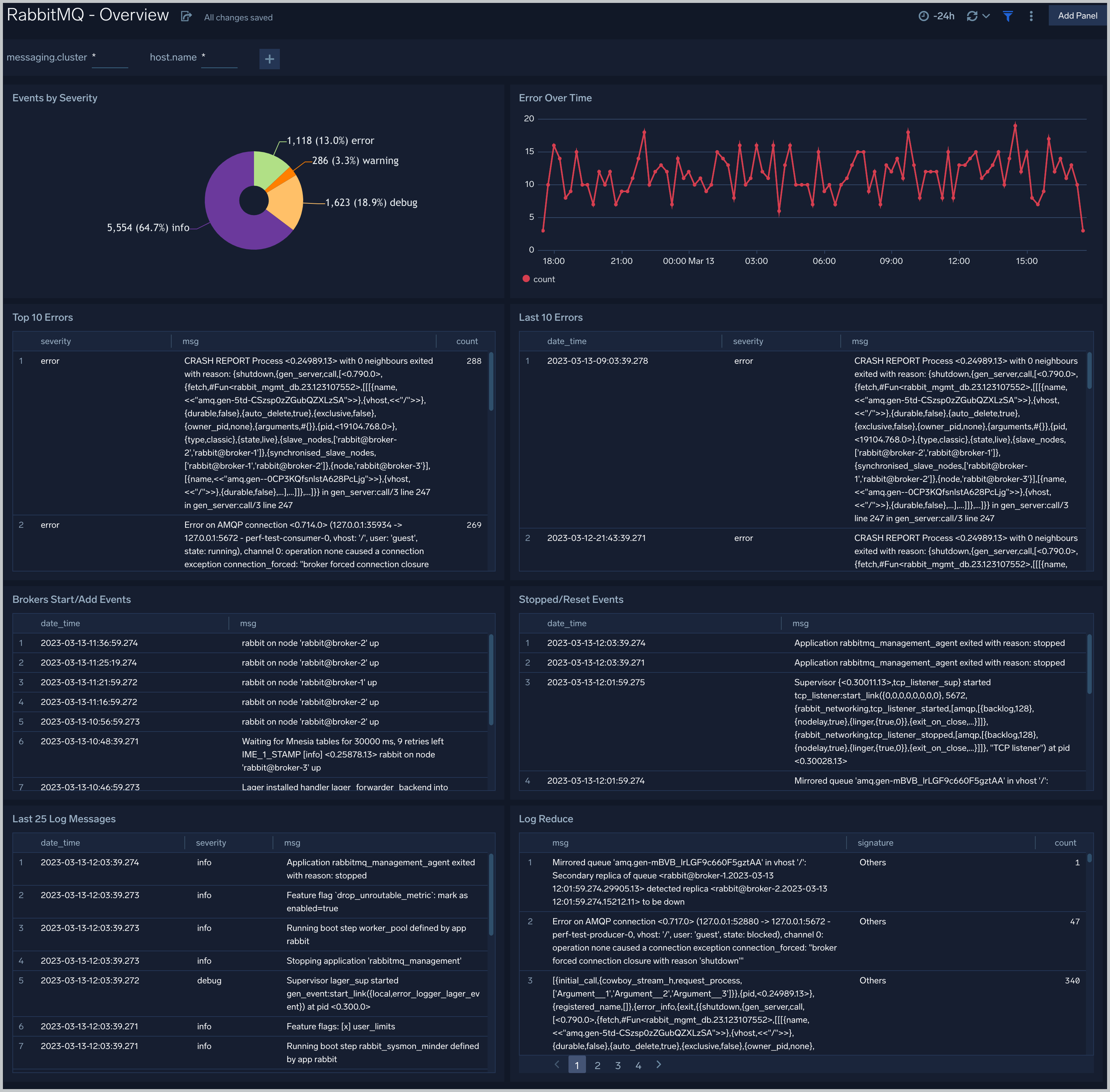
-The **RabbitMQ - Overview** dashboard gives you an at-a-glance view of Error messages, error by severity, top and last 10 errors, Broker and Event Start/Add log messages.
+The **RabbitMQ - Metrics** dashboard gives you an at-a-glance view of your RabbitMQ deployment across brokers, queue, exchange, consumer, and messages.
-
+
+### Metrics
-The **RabbitMQ - Overview** dashboard gives you an at-a-glance view of Error messages, error by severity, top and last 10 errors, Broker and Event Start/Add log messages.
+The **RabbitMQ - Metrics** dashboard gives you an at-a-glance view of your RabbitMQ deployment across brokers, queue, exchange, consumer, and messages.
- +
+
 @@ -164,6 +192,8 @@ Here's a sample log message you'd find in Non-Kubernetes environments.
## Sample queries
+### Logs
+
This sample Query is from the **RabbitMQ - Logs dashboard** > **Events** by Severity panel.
```sql title="Query String"
@@ -173,10 +203,26 @@ This sample Query is from the **RabbitMQ - Logs dashboard** > **Events** by Seve
| parse "* * [*]" as date,time,severity | count by severity
```
+### Metrics
+
+This sample query is from the **Average Number of Consumers** panel in **RabbitMQ - Metrics** dashboard.
+
+```sql sumo.datasource=rabbitmq metric=rabbitmq.consumer.count deployment.environment=* messaging.cluster.name=* messaging.node.name=* rabbitmq.queue.name=* rabbitmq.vhost.name=*
+| avg by messaging.cluster.name
+| sum
+```
+
+
## Viewing RabbitMQ Dashboards
-### Overview
+### Logs
+
+The **RabbitMQ - Logs** dashboard gives you an at-a-glance view of error messages, error by severity, top and last 10 errors, broker, and Event Start/Add log messages.
+
+
@@ -164,6 +192,8 @@ Here's a sample log message you'd find in Non-Kubernetes environments.
## Sample queries
+### Logs
+
This sample Query is from the **RabbitMQ - Logs dashboard** > **Events** by Severity panel.
```sql title="Query String"
@@ -173,10 +203,26 @@ This sample Query is from the **RabbitMQ - Logs dashboard** > **Events** by Seve
| parse "* * [*]" as date,time,severity | count by severity
```
+### Metrics
+
+This sample query is from the **Average Number of Consumers** panel in **RabbitMQ - Metrics** dashboard.
+
+```sql sumo.datasource=rabbitmq metric=rabbitmq.consumer.count deployment.environment=* messaging.cluster.name=* messaging.node.name=* rabbitmq.queue.name=* rabbitmq.vhost.name=*
+| avg by messaging.cluster.name
+| sum
+```
+
+
## Viewing RabbitMQ Dashboards
-### Overview
+### Logs
+
+The **RabbitMQ - Logs** dashboard gives you an at-a-glance view of error messages, error by severity, top and last 10 errors, broker, and Event Start/Add log messages.
+
+ +
+### Metrics
-The **RabbitMQ - Overview** dashboard gives you an at-a-glance view of Error messages, error by severity, top and last 10 errors, Broker and Event Start/Add log messages.
+The **RabbitMQ - Metrics** dashboard gives you an at-a-glance view of your RabbitMQ deployment across brokers, queue, exchange, consumer, and messages.
-
+
+### Metrics
-The **RabbitMQ - Overview** dashboard gives you an at-a-glance view of Error messages, error by severity, top and last 10 errors, Broker and Event Start/Add log messages.
+The **RabbitMQ - Metrics** dashboard gives you an at-a-glance view of your RabbitMQ deployment across brokers, queue, exchange, consumer, and messages.
- +
+
 @@ -19,17 +19,32 @@ The [RabbitMQ](https://www.rabbitmq.com/getstarted.html) app is a unified log ap
Following are the [Fields](/docs/manage/fields/) which will be created as part of RabbitMQ App install if not already present.
-* `messaging.cluster.name`. User configured. Specify the user-friendly cluster name which RabbitMQ belongs to.
-* `sumo.datasource`. Has fixed value of **rabbitmq**.
+* **`sumo.datasource`**. Fixed value of **rabbitmq**.
+* **`messaging.system`**. Fixed value of **rabbitmq**.
+* **`deployment.environment`**. This is a user-configured field set at the time of collector installation. It identifies the environment where the rabbitmq env resides, such as `dev`, `prod`, or `qa`.
+* **`messaging.cluster.name`**. User configured. Enter a name to uniquely identify your RabbitMQ cluster. This cluster name will be shown in the Sumo Logic dashboards.
+* **`messaging.node.name`**. Includes the value of the hostname of the machine which is being monitored.
## Prerequisites
+### For metrics collection
+
+:::note
+The RabbitMQ receiver supports RabbitMQ versions `3.8` and `3.9`.
+:::
+
+Enable the RabbitMQ management plugin by following the instructions in the [RabbitMQ documentation](https://www.rabbitmq.com/management.html#getting-started). Also, make sure you at least have the [monitoring](https://www.rabbitmq.com/management.html#permissions) level permissions to monitor the metrics.
+
+
+### For logs collection
+
This section provides instructions for configuring log collection for RabbitMQ running on a non-Kubernetes environment for the Sumo Logic App for RabbitMQ. By default, RabbitMQ logs are stored in a log file.
Follow the instructions to set up log collection:
-1. **Configure logging in RabbitMQ**. RabbitMQ supports logging via the following methods: local text log files, syslog and stdout. RabbitMQ logs have six levels of verbosity: debug, info, warning, error, critical, none. For details please visit this [page](https://www.rabbitmq.com/logging.html#log-levels). For the dashboards to work properly, log level needs to be set to **debug**. Default log level is **info**. All logging settings are located in [RabbitMQ.conf](https://www.rabbitmq.com/logging.html).
-2. **Configure RabbitMQ to write log lines to a local file**. By default, RabbitMQ logs are stored in `/var/log/rabbitmq/rabbit@
@@ -19,17 +19,32 @@ The [RabbitMQ](https://www.rabbitmq.com/getstarted.html) app is a unified log ap
Following are the [Fields](/docs/manage/fields/) which will be created as part of RabbitMQ App install if not already present.
-* `messaging.cluster.name`. User configured. Specify the user-friendly cluster name which RabbitMQ belongs to.
-* `sumo.datasource`. Has fixed value of **rabbitmq**.
+* **`sumo.datasource`**. Fixed value of **rabbitmq**.
+* **`messaging.system`**. Fixed value of **rabbitmq**.
+* **`deployment.environment`**. This is a user-configured field set at the time of collector installation. It identifies the environment where the rabbitmq env resides, such as `dev`, `prod`, or `qa`.
+* **`messaging.cluster.name`**. User configured. Enter a name to uniquely identify your RabbitMQ cluster. This cluster name will be shown in the Sumo Logic dashboards.
+* **`messaging.node.name`**. Includes the value of the hostname of the machine which is being monitored.
## Prerequisites
+### For metrics collection
+
+:::note
+The RabbitMQ receiver supports RabbitMQ versions `3.8` and `3.9`.
+:::
+
+Enable the RabbitMQ management plugin by following the instructions in the [RabbitMQ documentation](https://www.rabbitmq.com/management.html#getting-started). Also, make sure you at least have the [monitoring](https://www.rabbitmq.com/management.html#permissions) level permissions to monitor the metrics.
+
+
+### For logs collection
+
This section provides instructions for configuring log collection for RabbitMQ running on a non-Kubernetes environment for the Sumo Logic App for RabbitMQ. By default, RabbitMQ logs are stored in a log file.
Follow the instructions to set up log collection:
-1. **Configure logging in RabbitMQ**. RabbitMQ supports logging via the following methods: local text log files, syslog and stdout. RabbitMQ logs have six levels of verbosity: debug, info, warning, error, critical, none. For details please visit this [page](https://www.rabbitmq.com/logging.html#log-levels). For the dashboards to work properly, log level needs to be set to **debug**. Default log level is **info**. All logging settings are located in [RabbitMQ.conf](https://www.rabbitmq.com/logging.html).
-2. **Configure RabbitMQ to write log lines to a local file**. By default, RabbitMQ logs are stored in `/var/log/rabbitmq/rabbit@