“Creational design patterns are design patterns that deal with object creation mechanisms, trying to create objects in a manner suitable to the situation. The basic form of object creation could result in design problems or added complexity to the design. Creational design patterns solve this problem by somehow controlling this object creation.”
• When a class can't anticipate which kind of
class of object it should create
• When the classes to be created are derived
from the same superclass/interface
• When you want to insulate the client from the
actual type that is being instantiated
java.util.Calendar, java.util.ResourceBundle and java.text.NumberFormat
• Requires keeping factory methods in sync with
domain classes
• No way to change an implementing class
without recompiling
• Is often used when there is a need to use different sets of objects and where those objects could be added or changed some time during the lifetime of an application
javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory and javax.xml.xpath.XPathFactory
the possibility of unnecessary complexity and extra work during the initial implementation
• Is often used when you want to hide the actual creation process from clients • The construction process should allow different representations of the resulting object
java.lang.StringBuilder#append and java.lang.StringBuffer#append
• “It does create more code (and could introduce more complexity) in the DTO than if you had for example contructor arguments and/or setters/getters.”1
• When a system needs to be independent of how the objects are created • Adding and removing objects at runtime • Specifying new objects by changing an existing structure
• There are no real implementation of the Prototype Pattern in JDK, but Object.clone() is a good candidate which follows the design
• Each subclass of Prototype must implement the Clone operation • Could be difficult with existing classes which have some internal objects with circular references, or which do not support copying
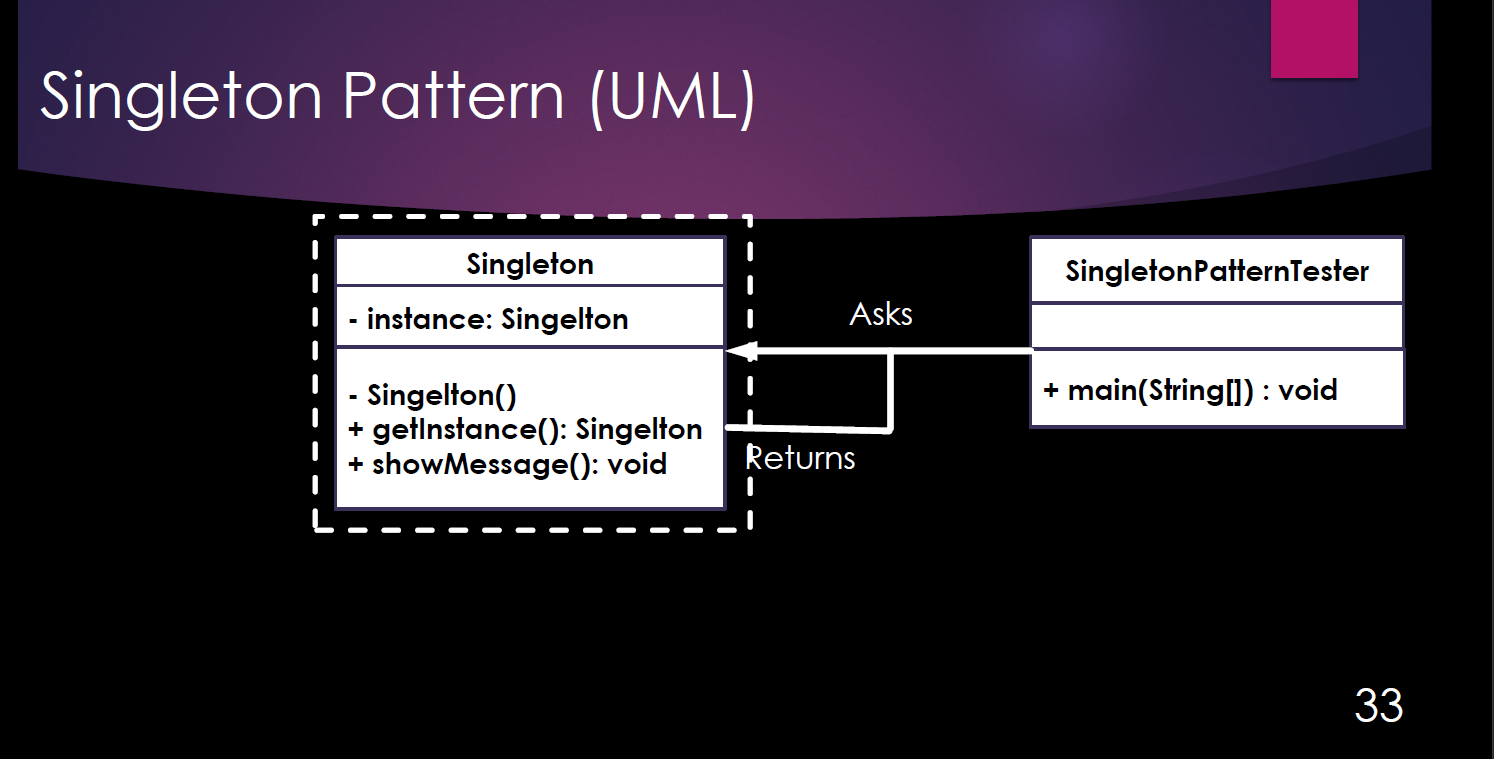
• When only one instance or a specific number of instances of a class are permitted
java.lang.Runtime#getRuntime()and java.awt.Desktop#getDesktop()
• Are generally used as a global instances à Try to avoid having global variables