From 3fd508048e0264dbabd247f11d876dc629db7c31 Mon Sep 17 00:00:00 2001
From: =?UTF-8?q?B=C3=B9i=20Minh=20=C4=90=E1=BB=A9c?=
<93396463+bmndc@users.noreply.github.com>
Date: Thu, 20 Jun 2024 21:31:17 +0700
Subject: [PATCH] webide: Move page from GitHub Wiki
---
webide.md | 291 ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
1 file changed, 291 insertions(+)
create mode 100644 webide.md
diff --git a/webide.md b/webide.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..e321846ee
--- /dev/null
+++ b/webide.md
@@ -0,0 +1,291 @@
+---
+layout: page
+title: "Sideloading and debugging third-party applications"
+---
+As with other KaiOS 2.5.4 devices, the Nokia 6300 4G is classified as debug-enabled; you can install and debug any apps from outside sources as you wish. This comes with a few caveats: you cannot install apps with 'forbidden' permissions (`embed-apps`, `embed-widgets` and `engmode-extension`, such as Wallace Toolbox), or debug apps that come with the phone using DevTools.
+
+Developers, nevertheless, can debug system information and see warnings and errors outside their apps with `adb logcat`.
+
+To turn on debugging mode on the 6300 4G, dial `*#*#33284#*#*`. You should see a bug icon in the status bar letting you know ~~your phone has bugs inside~~ you’re in debugging mode, and you're good to go. You can also switch to ADB and DevTools access under Debugger in [the hidden Developer menu].
+
+Dial the code again to exit debugging mode. *Tip: You can save the code and add it as one of the speed dial contacts.*
+
+Note that sideloading on-device with OmniSD, plus many Gerda apps which require `navigator.mozApps.mgmt.import` API that has been removed from KaiOS 2.5.2.2, will no longer work on this phone. OmniSD's Privileged factory reset feature, however, can be used after permanent rooting to gain privileged userspace session.
+
+## ADB and WebIDE
+
+*Not to be confused with [jailbreaking] on iOS devices, which is the act of using exploits to gain elevated permissions and bypass Apple's security restrictions on their devices.*
+
+Now, let's learn how to sideload and debug an application on your KaiOS phone using ADB and WebIDE. This will let us install apps which might be not available from KaiStore, or ones that you are developing.
+
+ADB, short for Android Debug Bridge, is a powerful toolset that can be used on Android-based devices to unlock access to a range of functions beyond what the typical user interface provides. It's mainly designed for app developers to get access to system logs and debug the performance of their apps, but it's also a great tools for power users and enthusiasts to control their phones through shell access, install third-party APKs, tweak the system and restore it from being a dead paperweight.
+
+While KaiOS and Firefox OS are not directly based on Android and you cannot install APKs on them, their Gonk layer [makes significant use of Android's well-established hardware compatibility], including the ability to use ADB to interact with the phone through a computer. This is for the sake of deploying the OS onto different hardware without raising the cost for development.
+
+Meanwhile, WebIDE, short for Web Integrated Development Environment, allows you to create, edit, run and debug web applications on Firefox OS (and later KaiOS) devices and simulators. It's [built on the former Firefox OS App Manager] but with additional functions such as a code editor, boilerplate code templates and manifest validation, and includes Firefox debugging tools. With it, you can also connect your browser to one or multiple "runtimes" where you can manage app installation.
+
+We'll refer to this guide as the main, officially supported method of installing third-party apps onto your KaiOS phone, for the sake of simplicity. Other methods, such as Luxferre's CLI `gdeploy`, are also available.
+
+> [!NOTE]
+> This guide is only applicable on debug-enabled KaiOS 2.5 devices, and is no longer relevant for recent versions. In 2021, [Mozilla partnered with KaiOS Technologies] to "modernize the old Boot2Gecko codebase to run atop a modern Gecko so that it can be used by KaiOS as a basis for their future phones", and redesigned WebIDE in the process (currently included in Firefox Developer Edition).
+>
+> For debug-enabled KaiOS 3 devices, follow the instructions for KaiOS’s `appscmd` on [the official Developer Portal].
+>
+> Before proceeding, make sure that your phone is debug-enabled, or you have taken steps to enable debugging capability on your phone. To check if your phone is debug-enabled, go to [Devices page on BananaHackers Wiki].
+>
+> **Be careful when installing apps from unknown sources**; it's never a bad practice to proof-read their source code. While there are certain security practices, such as prohibiting installing apps with `engmode-extension` permission, KaiOS is still [prone to] [malicious code] which can result in performance degradation, data loss or worse.
+
+## What we need
+
+- a phone running KaiOS 2.5 (again, KaiOS 3 users should NOT follow this guide);
+- a x86_64 computer running Windows, macOS or Linux;
+ - armhf/aarch64 users may need to use `gdeploy` or [build one of the browsers below from source]
+- an USB cable with data transferring capability;
+- an Internet connection for both your phone and computer;
+- an archiver: built-in file manager on macOS/Linux, [7-Zip] or WinRAR on Windows;
+- latest version of Android Debug Bridge (ADB): [Windows], [macOS], [Linux]
+ - you can also install from your operating system's package manager:
+ - Windows:
+ - [Chocolatey]: `choco install adb`
+ - Scoop: `scoop install main/adb`
+ - `winget` [prohibits installing executables with symlinks]
+ - [macOS (Homebrew)]: `brew install android-platform-tools`
+ - Debian/Ubuntu: `sudo apt-get install adb`
+ - [Fedora]: `sudo dnf install android-tools`
+ - [Arch]/Manjaro: `sudo pacman -S android-tools`
+ - Termux (terminal emulator on Android): `pkg install android-tools`
+ - *tip: If you download the SDK from Android Developers' website, [include the extracted folder in PATH for quick access]. This would be handled for you if you installed ADB via package manager.*
+- Mozilla got rid of the old WebIDE since Firefox 59, so we'll have to install an older version of Firefox:
+ - [Waterfox Classic]: the most recently maintained browser which still has old WebIDE
+ - [Pale Moon 28.6.1](https://archive.palemoon.org/palemoon/28.x/28.6.1/) (Windows/Linux): a popular fork of Firefox with older user interface, legacy Firefox add-on support and always runs in single-process mode.
+ - Firefox 59 (ESR 52.9): the last official Firefox version to be bundled with working WebIDE and other tools for development on Firefox OS devices, before Mozilla decided to kill the project in 2016. Archives of all Firefox releases can be found [here](https://archive.mozilla.org).
+ - [KaiOS RunTime] (Ubuntu): official development environment for KaiOS 2.5 made by KaiOS. It's also possible to get KaiOSRT to work on Windows 10 and later using Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSLg). [See this video on YouTube for action].
+
+*Need a video tutorial? If you’re on Linux, KaiOS Technologies officially made one for their own WebIDE client KaiOSRT which can be found [on their channel]. Alternatively, there’s also [one on BananaHackers’ YouTube channel].*
+
+---
+
+Begin by turning on debugging mode on your phone and connecting your phone to the computer with the USB cable. This step will differ for each device; if you're unsure, it's best to look up your phone on the [Devices page on BananaHackers Wiki].
+
+On your computer, install ADB from the package manager, or download the SDK Platform Tools from Android Developers' website, which should contain the latest version of ADB. Extract the downloaded archive to a folder, then navigate to the `platform-tools` folder using Command Prompt or Terminal.
+
+
+
+Start the ADB daemon by typing `adb devices`. ADB will automatically detect your phone in debugging mode. Proceed when you see a `device`, otherwise:
+
+- if the operating system states that `adb` is not a valid command, check if you're in the right folder and/or if `platform-tools` was properly added in PATH. You may need to specify `./adb.exe devices` to tell the OS where to look for ADB, or make ADB an executable: `chmod +x adb`.
+- if ADB executes but nothing appears under "List of devices attached" (as shown below), check if your phone is properly connected to the computer. On Windows, you may need to open Driver Manager (Win + R, `devmgmt.msc`) and look for any USB peripherals with missing drivers, and install accordingly.
+- if you’re connecting to a Linux-based computer, you may need to go to Settings, Storage and turn on USB Storage on the phone for `udev` to properly register your phone as an USB peripheral with external storage. An icon in the status bar will appear indicating storage access via USB. (If you don't wish to do this, see Setting up USB access on Linux below.)
+- on macOS and Linux, `udev` and `lsusb` are your friends to troubleshoot any USB connection issues here
+- if a device appears as `unauthorized`, it means that you need to approve the ADB connection to your phone with a pop-up on your phone's screen. Except... KaiOS does not have such thing! You're pretty much stuck here until someone figures out how to get your phone accessible by ADB.
+
+```console
+$ adb devices
+* daemon not running; starting now at tcp:5037
+* daemon started successfully
+List of devices attached
+1a2b3c4d device
+```
+
+Connect to ADB over Wi-Fi
+
+---
+
+*I was not able to get this to work. Proceed with caution.*
+
+If you are in a rush and wish to connect to your phone wirelessly, turn on Wi-Fi on your phone, set the TCP/IP socket on the phone to 5555:
+
+```console
+$ adb tcpip 5555
+restarting in TCP mode port: 5555
+```
+
+Disconnect the USB cable, wait a moment, then run:
+
+```console
+$ adb connect 192.168.1.14:5555
+connected to 192.168.1.14:5555
+
+$ adb devices
+List of devices attached
+192.168.1.14:5555 device
+
+$ adb forward tcp:6000 localfilesystem:/data/local/debugger-socket
+6000
+```
+
+Replace `192.168.1.14` with your phone's IP address assigned by local network—the same network your computer is on.
+
+You can find your phone's local IP address (192.168.1.x) by going to Settings, Network & Connectivity, Wi-Fi, Available networks, click on the connected Wi-Fi access point and look under IP address; or download N4NO’s [My IP Address] from KaiStore.
+
+It's also possible to connect to your phone entirely without an USB cable, though the connection will be less reliable. See [Connect to ADB wirelessly on Launch hidden settings] page for more details.
+
+---
+
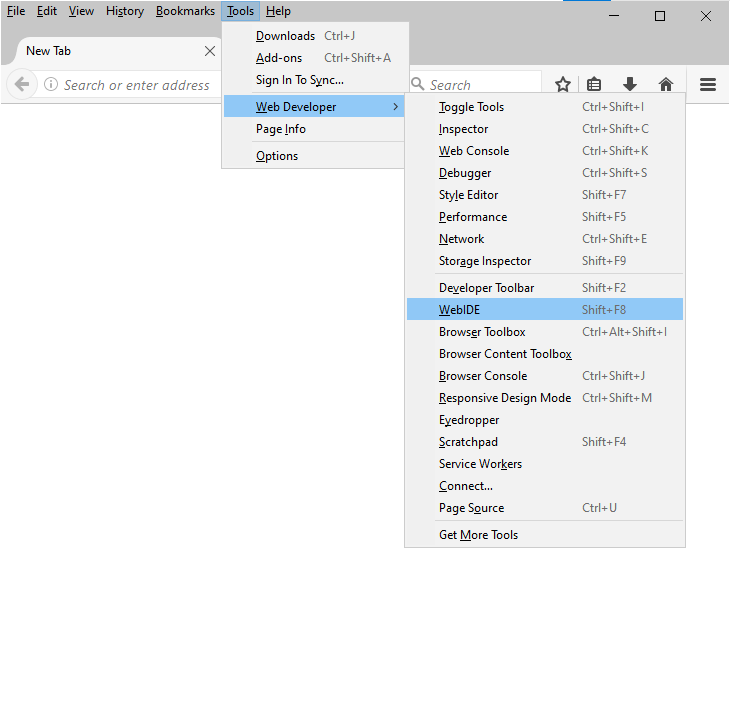
+
+
+Your phone’s name should appear in the right pane as an option under USB Devices. Click it to connect.
+
+If you don't see any devices, either because you're setting up WebIDE for the first time, or your browser doesn't have a working `adbd` daemon, forward ADB access to TCP socket 6000:
+
+```console
+$ adb forward tcp:6000 localfilesystem:/data/local/debugger-socket
+6000
+```
+
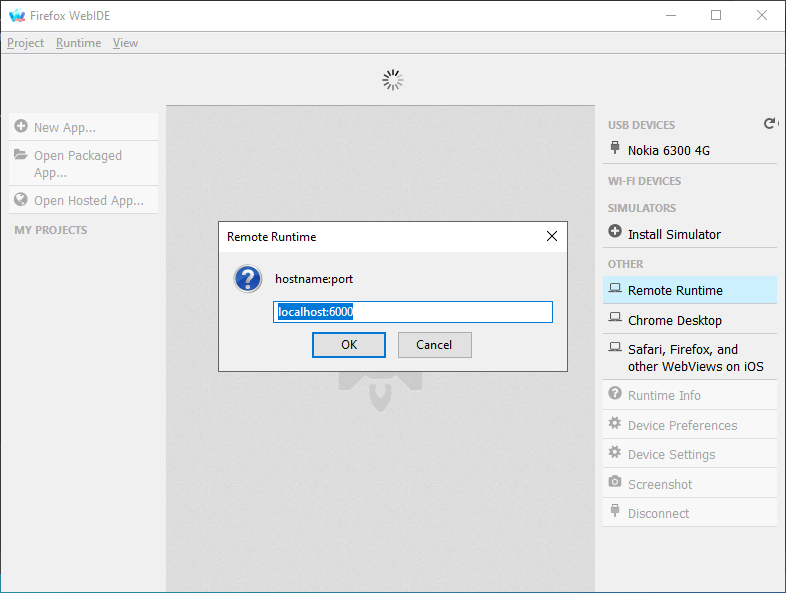
+Then, click Remote Runtime in the right pane, leave it as default at `localhost:6000` and press OK. If you still see a yellow banner stating "Operation failed: Connecting to Remote Runtime", either you set the incorrect socket or your phone rejected DevTools access.
+
+
+
+*If you’re using older browsers to access WebIDE such as Firefox v59 or Pale Moon <28.6.1, at this point you may see a warning header about mismatched build date. You can safely ignore it as WebIDE was mainly designed to support Firefox OS device builds released alongside that Firefox/Pale Moon versions.*
+
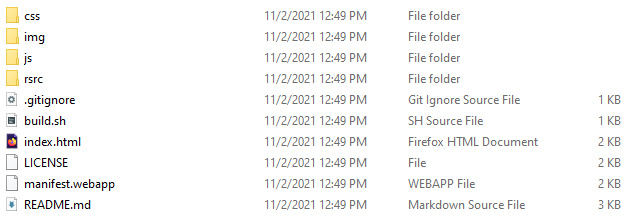
+To sideload an application, download a packaged file (you can find great apps on [BananaHackers Store] and GitHub!) and extract it into a dedicated folder. Make sure that there's a `manifest.webapp` at the root of the extracted folder. If you see an `application.zip` (which indicates the app was packaged for OmniSD), unzip it.
+
+
+
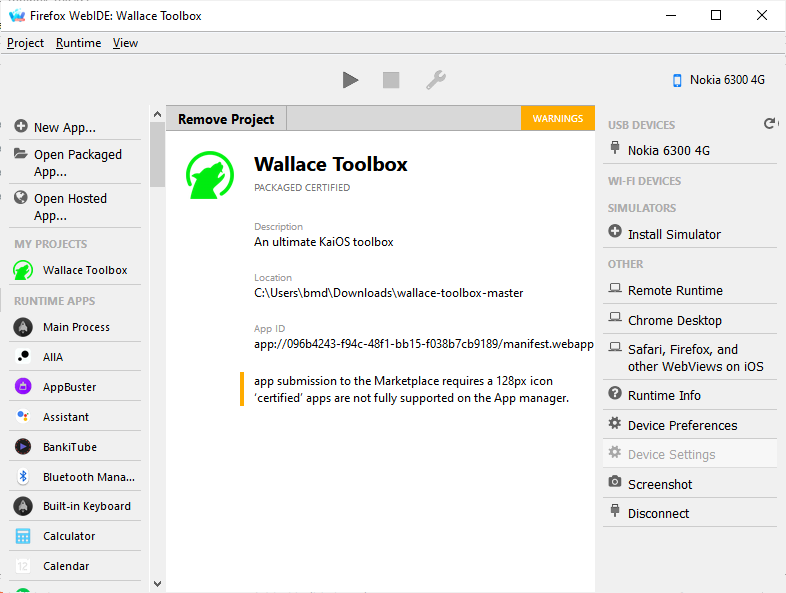
+In WebIDE, select Open Packaged App in its left sidebar and navigate to the root of the app folder you just extracted (again, make sure that there's a `manifest.webapp` at its root!)
+
+
+
+Once you get the app loaded with no errors, press the triangle Install and Run in the top bar to sideload.
+
+*Feel free to ignore this warning: "app submission to the Marketplace requires a [size in px] icon". if you were to upload your apps to the Firefox Marketplace, a 128px icon is required to display your app in the splash screen. While KaiStore also requires app icons to be in certain sizes, a 128px icon is no longer necessary, [only 56px and 112px]. You can get rid of this error by including a 128px icon in the app's manifest.*
+
+## gdeploy
+
+`gdeploy` is a small cross-platform command-line utility developed by Luxferre as an alternative to the graphical WebIDE, and can even be used as NodeJS module/library. According to Luxferre, 'it uses the same `firefox-client` backend but has much simpler architecture for application management'.
+
+For Windows 10 version 1709 and later, type these commands one by one into Command Prompt, with [DIR_PATH] replaced by the extracted folder directory of the app you want to install (see step 8 above):
+
+```console
+winget install Git.Git
+winget install OpenJS.NodeJS.LTS
+cd /d "%USERPROFILE%\Desktop"
+git clone https://gitlab.com/suborg/gdeploy.git
+curl -Lo platform-tools.zip https://dl.google.com/android/repository/platform-tools-latest-windows.zip
+tar -xf platform-tools.zip
+cd platform-tools\
+adb devices
+adb forward tcp:6000 localfilesystem:/data/local/debugger-socket
+cd ..\gdeploy\
+npm i && npm link
+gdeploy install [DIR_PATH]
+```
+
+For macOS and Linux, if you have Homebrew installed as a package manager:
+
+```console
+brew install git node android-platform-tools
+cd ~/Desktop
+git clone https://gitlab.com/suborg/gdeploy.git
+adb devices
+adb forward tcp:6000 localfilesystem:/data/local/debugger-socket
+cd gdeploy
+npm i && npm link
+gdeploy install [DIR_PATH]
+```
+
+## Setting up USB access on Linux
+
+Dedicated to those adrenaline-fueled who want to complicate their lives.
+
+For security reasons, if you want to plug in your phone for debugging only and without USB Storage on, which would grant your computer access to the phone's internal storage, you will need to set `udev` rules to grant `plugdev` read-write access to the socket on your phone.
+
+Initialise `udev` rules by installing `android-sdk-platform-tools-common` on Debian and Ubuntu, or `android-tools` (`android-tools-git` on AUR) on Arch-based distros. Otherwise, you can also install `wget` and `coreutils` if they're not already installed, then manually download and install `51-android.rules` by typing:
+
+```console
+$ wget -S -O - https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cm-b2g/B2G/1230463/tools/51-android.rules | sudo tee >/dev/null /etc/udev/rules.d/51-android.rules; sudo udevadm control --reload-rules
+```
+
+`wget` will fetch a list of `udev` rules from cm-b2g/B2G, then pass the result to `tee` which will write the content onto `/etc/udev/rules.d/51-android.rules` without displaying any output in Terminal, and `udevadm` will then reload the rules from configured locations.
+
+Plug your phone to the computer using an USB cable and obtain the Vendor ID of the phone:
+
+```console
+$ lsusb
+Bus 001 Device 007: ID 05c6:f003 Qualcomm, Inc. Nokia 8110 4G
+ ^^^^
+```
+
+In our case, the Qualcomm-based Nokia 8110 4G has the Vendor ID of `05c6`.
+
+Open `/etc/udev/rules.d/51-android.rules` in your preferred text editor with root privileges. Append this line, replace `05c6` with the Vendor ID you got above:
+
+```
+SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTR{idVendor}=="05c6", MODE="0664", GROUP="plugdev"
+```
+
+This will allow read-write access to the USB device with vendor ID `05c6` for the system and users in the `plugdev` group, and read-only access for others (`rw-rw-r--`). Add yourself in the `plugdev` group:
+
+```console
+# usermod -aG plugdev $LOGNAME
+```
+
+Execute this command as root to make `51-android.rules` read-only for all users on the system:
+
+```
+# chmod a+r /etc/udev/rules.d/51-android.rules
+```
+
+Now, create `~/.android/adb_usb.ini` in your HOME directory. Open it using your preferred text editor and put the obtained Vendor ID value in HEX: `0xABCD`, whereas `ABCD` is Vendor ID.
+
+```console
+$ echo "0x05c6" > ~/.android/adb_usb.ini
+```
+
+Finally, re-run `adb devices`.
+
+> jkelol111's [Make KaiOS Install] is another command-line tool to install apps using KaiOS's remote debugging protocol. Instructions on using this tool can be found on the repository's README.
+
+**References used for this page**
+
+- [ADB & Fastboot](https://ivan-hc.github.io/bananahackers/adb.html) and [WebIDE and other Development tools](https://ivan-hc.github.io/bananahackers/webide.html) on BananaHackers website
+- Martin Kaptein's [Side-loading and deploying custom apps to KaiOS](https://mk24.me/blog/sideloading-and-deploying-apps-to-kai-os/) blog post
+- [Android Debug Bridge](https://wiki.archlinux.org/title/Android_Debug_Bridge) on Arch Linux Wiki, distributed under GNU Free Documentation License 1.3
+- [Run apps on a hardware device](https://developer.android.com/studio/run/device) on Android Developers' website, distributed under Apache 2.0 License
+
+[the hidden Developer menu]: https://w2d.bananahackers.net
+[jailbreaking]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IOS_jailbreaking
+[makes significant use of Android's well-established hardware compatibility]: https://kaios.dev/2024/03/kaios-system-properties/
+[built on the former Firefox OS App Manager]: https://www.infoq.com/news/2014/06/webide/
+[Mozilla partnered with KaiOS Technologies]: https://wiki.mozilla.org/KaiOS
+[the official Developer Portal]: https://developer.kaiostech.com/docs/sfp-3.0/getting-started/env-setup/os-env-setup
+[Devices page on BananaHackers Wiki]: https://wiki.bananahackers.net/devices
+[prone to]: https://www.reddit.com/r/KaiOS/comments/1d0iur3/security_analysis_of_the_kaios_feature_phone/ "Note: Fabrice Desré, former Chief Architect of KaiOS Technologies, confirmed that there are factual errors in the report i.e. apps are handled in their own processes rather than in the same runtime, and that the research team never contacted KaiOS."
+[malicious code]: https://research.nccgroup.com/2020/08/24/whitepaper-exploring-the-security-of-kaios-mobile-applications/
+[build one of the browsers below from source]: https://new.reddit.com/r/KaiOS/comments/rawwhz/webide_capable_program_linux_arm/
+[7-Zip]: https://www.7-zip.org/download.html
+[Windows]: https://dl.google.com/android/repository/platform-tools-latest-windows.zip
+[macOS]: https://dl.google.com/android/repository/platform-tools-latest-darwin.zip
+[Linux]: https://dl.google.com/android/repository/platform-tools-latest-linux.zip
+[Chocolatey]: https://community.chocolatey.org/packages/adb
+[prohibits installing executables with symlinks]: https://github.com/microsoft/winget-pkgs/issues/4082
+[macOS (Homebrew)]: https://formulae.brew.sh/cask/android-platform-tools
+[Fedora]: https://packages.fedoraproject.org/pkgs/android-tools/android-tools
+[Arch]: https://archlinux.org/packages/extra/x86_64/android-tools
+[include the extracted folder in PATH for quick access]: https://gist.github.com/nex3/c395b2f8fd4b02068be37c961301caa7
+[Waterfox Classic]: https://classic.waterfox.net
+[Pale Moon 28.6.1]: https://archive.palemoon.org/palemoon/28.x/28.6.1/
+[KaiOS RunTime]: https://s3.amazonaws.com/kaicloudsimulatordl/developer-portal/simulator/Kaiosrt_ubuntu.tar.bz2
+[See this video on YouTube for action]: https://youtu.be/eg2SOCTMxYU
+[on their channel]: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wI-HW2cLrew
+[one on BananaHackers’ YouTube channel]: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SoKD7IBTvM4
+[My IP Address]: https://www.kaiostech.com/store/apps/?bundle_id=com.n4no.myipaddress
+[Connect to ADB wirelessly on Launch hidden settings]: https://bmndc.github.io/nokia-leo/w2d#connect-to-adb-wirelessly
+[BananaHackers Store]: https://store.bananahackers.net
+[only 56px and 112px]: https://developer.kaiostech.com/docs/distribution/submission-guideline/
+[Make KaiOS Install]: https://github.com/jkelol111/make-kaios-install
\ No newline at end of file




