diff --git "a/blog/Beginner\342\200\231s Guide to the Top 5 React Hooks.md" "b/blog/Beginner\342\200\231s Guide to the Top 5 React Hooks.md"
index 937914baa..44d17cf88 100644
--- "a/blog/Beginner\342\200\231s Guide to the Top 5 React Hooks.md"
+++ "b/blog/Beginner\342\200\231s Guide to the Top 5 React Hooks.md"
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
---
-title: 'A Beginner’s Guide to the Top 5 React Hooks'
+title: "A Beginner’s Guide to the Top 5 React Hooks"
sidebar_label: React hooks
authors: [dharshibalasubramaniyam]
tags: [react.js, react-hooks]
@@ -36,7 +36,7 @@ In this beginner’s guide, we’ll explore the top 5 React hooks that every Rea
### Importing useState hook from react:
```js
-import { useState } from 'react';
+import { useState } from "react";
```
### Declaring a state variable named count with an initial value of 0,
@@ -61,6 +61,7 @@ const Counter = () => {
);
};
```
+
- In above example, when the button is clicked, the onClick event handler calls the setCount function with the updated value of count (count + 1), causing the component to re-render with the new state value.
- Note: We cannot update a state variable like, count = count +1
@@ -71,29 +72,26 @@ const Counter = () => {
```js
const Counter = () => {
- const [person, setPerson] = useState({id: '1', name: 'John', age: 25});
+ const [person, setPerson] = useState({ id: "1", name: "John", age: 25 });
const updateName = (newName) => {
- setPerson(prevState => {
+ setPerson((prevState) => {
return { ...prevState, name: newName };
});
};
const updateAge = (newAge) => {
- setPerson(prevState => {
+ setPerson((prevState) => {
return { ...prevState, age: newAge };
});
};
- return (
-
- {/* form to update name and age */}
-
- );
+ return
{/* form to update name and age */}
;
};
```
## 2. ‘useEffect’ hook
+
- The useEffect hook in React enables functional components to perform side effects, such as data fetching, DOM manipulation, or subscriptions. It replaces lifecycle methods like componentDidMount, componentDidUpdate, and componentWillUnmount in class components.
### componentDidMount
@@ -105,7 +103,7 @@ const Counter = () => {
```js
useEffect(() => {
// Perform initialization or side effects
- console.log("The component is rendered initially.")
+ console.log("The component is rendered initially.");
}, []);
```
@@ -118,7 +116,7 @@ useEffect(() => {
```js
useEffect(() => {
// Effect runs after every render
- console.log("The component is rendered.")
+ console.log("The component is rendered.");
});
```
@@ -127,7 +125,7 @@ useEffect(() => {
```js
useEffect(() => {
// Perform side effects after state or props update
- console.log("dependency1 or dependency2 have updated.")
+ console.log("dependency1 or dependency2 have updated.");
}, [dependency1, dependency2]);
```
@@ -140,10 +138,10 @@ useEffect(() => {
```js
useEffect(() => {
// Perform side effects
- console.log("dependency is updated.")
+ console.log("dependency is updated.");
return () => {
// Cleanup tasks
- console.log("The component is unmounted.")
+ console.log("The component is unmounted.");
};
}, [dependency]);
```
@@ -158,7 +156,7 @@ useEffect(() => {
```js
// themeContext.js
-import React, { createContext } from 'react';
+import React, { createContext } from "react";
export const ThemeContext = createContext(null);
```
@@ -169,11 +167,11 @@ export const ThemeContext = createContext(null);
```js
function App() {
- const theme = 'dark';
+ const theme = "dark";
return (
-
+
);
}
@@ -184,20 +182,21 @@ function App() {
- Now, any component within the provider can access the context using the useContext hook.
```js
-import React, { useContext } from 'react';
-import ThemeContext from './ThemeContext';
+import React, { useContext } from "react";
+import ThemeContext from "./ThemeContext";
function MyComponent() {
const theme = useContext(ThemeContext);
- return
;
};
```
### Reducer Function
- You define a reducer function. This function takes two arguments: the current state and an action, and returns the new state based on the action. The reducer function is responsible for updating the state.
-
+
```js
// Step 2: Define reducer function
const reducer = (state, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
- case 'increment':
+ case "increment":
return { count: state.count + 1 };
- case 'decrement':
+ case "decrement":
return { count: state.count - 1 };
default:
throw new Error();
@@ -251,15 +246,15 @@ const reducer = (state, action) => {
```js
const Counter = () => {
const initialState = { count: 0 };
-
+
// Step 3: Use useReducer hook
const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(reducer, initialState);
return (
Count: {state.count}
-
-
+
+
);
};
@@ -276,7 +271,7 @@ const Counter = () => {
Example 1
```js
-import React, { useRef } from 'react';
+import React, { useRef } from "react";
function MyComponent() {
// Create a ref to store a DOM element
@@ -305,7 +300,7 @@ In this example, myInputRef is created using useRef, and it's attached to the in
Example 2
```js
-import React, { useState, useRef } from 'react';
+import React, { useState, useRef } from "react";
function Counter() {
// State for storing the count
@@ -320,10 +315,10 @@ function Counter() {
if (intervalIdRef.current !== null) {
return; // If already running, do nothing
}
-
+
// Start the counter
intervalIdRef.current = setInterval(() => {
- setCount(prevCount => prevCount + 1);
+ setCount((prevCount) => prevCount + 1);
}, 1000);
};
@@ -333,7 +328,7 @@ function Counter() {
if (intervalIdRef.current === null) {
return; // If not running, do nothing
}
-
+
// Stop the counter
clearInterval(intervalIdRef.current);
intervalIdRef.current = null;
@@ -350,6 +345,7 @@ function Counter() {
export default Counter;
```
+
- We have a state variable count that stores the current count.
- We create a ref named intervalIdRef using useRef(null). This ref will be used to store the ID returned by setInterval so that we can later clear the interval.
- startCounter function starts a timer using setInterval and increments the count every second. It first checks if the counter is already running to avoid starting multiple timers simultaneously.
diff --git a/blog/Cybersecurity-in-Cloud-Computing.md b/blog/Cybersecurity-in-Cloud-Computing.md
index c44bfa756..bca73d018 100644
--- a/blog/Cybersecurity-in-Cloud-Computing.md
+++ b/blog/Cybersecurity-in-Cloud-Computing.md
@@ -11,89 +11,113 @@ In this guide, we will explore the key aspects of cybersecurity in cloud computi
## Overview
+
Cloud computing offers scalable resources and convenience, but it also introduces unique cybersecurity challenges. This guide covers key aspects of cybersecurity in cloud computing, including common threats, best practices, and security frameworks.
## Table of Contents
## 1. Introduction to Cloud Computing
+
Cloud computing provides on-demand delivery of computing resources over the internet, enabling businesses to scale and innovate quickly. However, this flexibility comes with cybersecurity challenges that need to be addressed to protect sensitive data and applications.
## 2. Common Cloud Security Threats
### Data Breaches
+
Data breaches in the cloud can occur due to misconfigured storage, weak authentication, or vulnerabilities in the cloud infrastructure.
### Insider Threats
+
Insider threats involve malicious activities by employees or other trusted individuals who have access to sensitive data.
### Account Hijacking
+
Attackers can gain unauthorized access to cloud accounts through phishing, brute force attacks, or exploiting vulnerabilities.
### Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks
+
DoS attacks overwhelm cloud services with traffic, causing disruptions and potentially leading to data loss.
## 3. Cloud Security Models
### Shared Responsibility Model
+
The shared responsibility model divides security responsibilities between the cloud provider and the customer. Providers secure the infrastructure, while customers are responsible for securing their data and applications.
### Security as a Service (SECaaS)
+
SECaaS delivers security services through the cloud, offering solutions like antivirus, intrusion detection, and security monitoring.
## 4. Best Practices for Cloud Security
### Data Encryption
+
Encrypt data both in transit and at rest to protect it from unauthorized access.
### Identity and Access Management (IAM)
+
Implement strong IAM practices, including multi-factor authentication (MFA) and least privilege access, to control who can access cloud resources.
### Regular Audits and Compliance
+
Conduct regular security audits and ensure compliance with relevant standards and regulations.
### Secure Application Development
+
Follow secure coding practices and regularly update applications to fix security vulnerabilities.
## 5. Cloud Security Frameworks and Standards
### NIST Cloud Computing Security
+
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) provides guidelines and best practices for securing cloud environments.
### ISO/IEC 27017
+
This international standard offers guidelines for information security controls specific to cloud services.
### CSA Cloud Controls Matrix
+
The Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) provides a framework of security controls tailored to cloud computing environments.
## 6. Implementing Cloud Security
### Choosing a Secure Cloud Provider
+
Select a cloud provider with strong security measures, certifications, and a proven track record.
### Configuring Security Settings
+
Properly configure security settings, such as firewalls, encryption, and access controls, to protect cloud resources.
### Monitoring and Incident Response
+
Implement continuous monitoring and establish an incident response plan to quickly detect and respond to security incidents.
## 7. Case Studies of Cloud Security Breaches
### Analysis of Major Incidents
+
Examine major cloud security breaches to understand how they occurred and the impact they had.
### Lessons Learned
+
Learn from past incidents to improve security measures and prevent similar breaches in the future.
## 8. Future Trends in Cloud Security
### AI and Machine Learning
+
Artificial intelligence and machine learning can enhance cloud security by detecting and responding to threats in real-time.
### Quantum Computing
+
Quantum computing poses new challenges and opportunities for cloud security, particularly in the field of encryption.
### Zero Trust Architecture
+
Zero trust architecture assumes that threats can come from both outside and inside the network, and it implements strict access controls and continuous monitoring.
## 9. Conclusion
+
Securing cloud environments is crucial for protecting sensitive data and maintaining trust. By understanding the unique challenges of cloud security and implementing best practices, organizations can leverage the benefits of cloud computing while minimizing risks.
diff --git a/blog/DOM manipulation in JavaScript.md b/blog/DOM manipulation in JavaScript.md
index 61adde58e..3a93c3b75 100644
--- a/blog/DOM manipulation in JavaScript.md
+++ b/blog/DOM manipulation in JavaScript.md
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
---
-title: 'DOM manipulation in JavaScript'
+title: "DOM manipulation in JavaScript"
sidebar_label: DOM-manipulation-in-JavaScript
authors: [dharshibalasubramaniyam]
tags: [dom, javascript]
@@ -17,30 +17,30 @@ In web development, the Document Object Model (DOM) is a crucial aspect of creat
- This model allows developers to interact with the document programmatically via scripting languages like JavaScript.
-- When a web page is loaded, the browser parses the HTML and creates the DOM.
+- When a web page is loaded, the browser parses the HTML and creates the DOM.
- The DOM represents the document as a tree of nodes, where each node is an object representing a part of the document:
-*Document Node*: Represents the entire document.
+_Document Node_: Represents the entire document.
-*Element Nodes*: Represent HTML elements like `
+
5. **Create Additional Components**: You can create additional components in the `src/components` folder to organize your code and reuse components across your app.
- ```bash
- mkdir src/components
- ```
+ ```bash
+ mkdir src/components
+ ```
-7. Now, create a new file called `Home.js` in the `src/components` folder and add the following code to create a simple home component.
+6. Now, create a new file called `Home.js` in the `src/components` folder and add the following code to create a simple home component.
- ```js title="src/components/Home.js"
- import React from 'react';
+ ```js title="src/components/Home.js"
+ import React from "react";
- const Home = () => {
- return (
-
-
Welcome to the Home Page
-
- );
- };
+ const Home = () => {
+ return (
+
+
Welcome to the Home Page
+
+ );
+ };
- export default Home;
- ```
+ export default Home;
+ ```
-8. **Update the `App.js` File**: Update your `App.js` file to use the `Home` component.
-
- ```js title="src/App.js"
- import React from 'react';
- import Home from './components/Home';
-
- function App() {
- return (
-
-
-
- );
- }
+7. **Update the `App.js` File**: Update your `App.js` file to use the `Home` component.
- export default App;
- ```
+ ```js title="src/App.js"
+ import React from "react";
+ import Home from "./components/Home";
+
+ function App() {
+ return (
+
+
+
+ );
+ }
+
+ export default App;
+ ```
-9. Now, you can see the `Home` component displayed on browser window.
+8. Now, you can see the `Home` component displayed on browser window.
-
-
-
Welcome to the Home Page
-
-
+
+
+
Welcome to the Home Page
+
+
## Setting a Proxy from your Backend API server to the Frontend React App
@@ -507,104 +508,109 @@ To set up a proxy, follow these steps:
1. **Update the `package.json` File**: Update the `package.json` file in your React app to include a proxy setting that points to your backend API server.
- ```json title="frontend/package.json"
- {
- "name": "frontend",
- "version": "0.1.0",
- "private": true,
- "proxy": "http://localhost:4000"
- }
- ```
+ ```json title="frontend/package.json"
+ {
+ "name": "frontend",
+ "version": "0.1.0",
+ "private": true,
+ "proxy": "http://localhost:4000"
+ }
+ ```
+
2. **Restart the React App**: Run `npm start` to restart the React app with the new proxy setting.
- ```bash
- npm start
- ```
+ ```bash
+ npm start
+ ```
+
3. **Test the Proxy**: Make a request to your backend API server from your frontend React app using the proxy setting.
- ```js title="src/components/Home.js"
- import React, { useEffect } from 'react';
-
- const Home = () => {
- useEffect(() => {
- fetch('/api/books')
- .then(response => response.json())
- .then(data => console.log(data))
- .catch(error => console.error(error));
- }, []);
-
- return (
-
+ );
+ };
+
+ export default Home;
+ ```
+
7. **Check the Browser Window**: Open the browser window to see the list of books fetched from your backend API server and displayed on the screen.
-
-
-
Welcome to the Home Page
-
-
Book 1
-
Book 2
-
Book 3
-
-
-
+
+
+
Welcome to the Home Page
+
+
Book 1
+
Book 2
+
Book 3
+
+
+
By setting up a proxy from your backend API server to your frontend React app, you can avoid issues related to cross-origin requests during development. This allows you to focus on building your application without worrying about the underlying infrastructure.
@@ -616,87 +622,89 @@ Here is a simple guide to styling and making requests from the frontend:
1. **Create a `styles.css` File**: Create a new file called `styles.css` in the `src` folder of your React app to add custom styles.
- ```css title="src/styles.css"
- body {
- font-family: 'Arial', sans-serif;
- background-color: #f0f0f0;
- margin: 0;
- padding: 0;
- }
+ ```css title="src/styles.css"
+ body {
+ font-family: "Arial", sans-serif;
+ background-color: #f0f0f0;
+ margin: 0;
+ padding: 0;
+ }
+
+ .container {
+ max-width: 800px;
+ margin: 0 auto;
+ padding: 20px;
+ }
+
+ .heading {
+ font-size: 24px;
+ font-weight: bold;
+ margin-bottom: 20px;
+ }
+
+ .list {
+ list-style-type: none;
+ padding: 0;
+ }
+
+ .item {
+ background-color: #fff;
+ border: 1px solid #ccc;
+ margin-bottom: 10px;
+ padding: 10px;
+ }
+ ```
- .container {
- max-width: 800px;
- margin: 0 auto;
- padding: 20px;
- }
-
- .heading {
- font-size: 24px;
- font-weight: bold;
- margin-bottom: 20px;
- }
-
- .list {
- list-style-type: none;
- padding: 0;
- }
-
- .item {
- background-color: #fff;
- border: 1px solid #ccc;
- margin-bottom: 10px;
- padding: 10px;
- }
- ```
2. **Update the `App.js` File**: Update your `App.js` file to include the custom styles.
- ```js title="src/App.js"
- import React, { useEffect, useState } from 'react';
- import './styles.css';
-
- const App = () => {
- const [books, setBooks] = useState([]);
-
- useEffect(() => {
- fetch('/api/books')
- .then(response => response.json())
- .then(data => setBooks(data))
- .catch(error => console.error(error));
- }, []);
-
- return (
-
+ );
+ };
+
+ export default App;
+ ```
3. **Check the Browser Window**: Open the browser window to see the list of books displayed with the custom styles applied.
-
-
-
Book List
-
-
Book 1
-
Book 2
-
Book 3
-
-
-
+
+
+
Book List
+
+
Book 1
+
Book 2
+
Book 3
+
+
+
By adding custom styles to your React app and making requests to the API endpoints, you can create a visually appealing and interactive user interface. You can experiment with different styles, layouts, and components to enhance the user experience and make your app more engaging.
Once you have styled your app and made requests to the API endpoints, you can continue to add more features, functionality, and components to build a full-fledged web application. You can also explore other libraries, frameworks, and tools to further enhance your app and take it to the next level.
-
:::tip
**Key Takeaways**
diff --git a/blog/getting-started-with-microservices/index.md b/blog/getting-started-with-microservices/index.md
index 43390f140..9e485427b 100644
--- a/blog/getting-started-with-microservices/index.md
+++ b/blog/getting-started-with-microservices/index.md
@@ -688,9 +688,9 @@ Then check the endpoints using postman to ensure that everything is working cool
- There will be no changes in the eureka dashboard. It will be display same as before.
- Let’s check the add expense endpoint from frontend.
- 
+ 
- 
+ 
- In wrapping up our discussion on microservices, there’s one critical aspect left to address: the challenge of accessing microservices individually via their own port numbers. This approach becomes impractical as the number of microservices, or instances thereof increases. That’s precisely where an API gateway steps in.
@@ -783,7 +783,7 @@ Now let’s see how we can develop an Api-gateway for our application.
- It matches the incoming request against the defined routes based on the configured predicates. In this case, it identifies that the request path starts with “/expense-service/”, indicating that it should be directed to the expense service.
- Before forwarding the request to the expense service, the API gateway rewrites the URI to match the expected format of the microservice. Since the expense service expects requests without the “/expense-service” prefix, the API gateway removes this prefix from the URI.
- Once the URI is properly formatted, the API gateway forwards the request to the identified microservice. In this example, it sends the request to the expense service, ensuring that it reaches the correct endpoint (“/expense/all”).
-
+
Let’s check this in post man.

diff --git a/blog/getting-started-with-nlp.md b/blog/getting-started-with-nlp.md
index 2504a9782..b2019b59f 100644
--- a/blog/getting-started-with-nlp.md
+++ b/blog/getting-started-with-nlp.md
@@ -1,11 +1,10 @@
---
-title: 'Getting Started with Natural Language Processing (NLPs)'
+title: "Getting Started with Natural Language Processing (NLPs)"
sidebar_label: NLP Basics
authors: [nayanika-mukherjee]
tags: [natural language processing, nlp, machine learning, technology]
date: 2024-07-27
hide_table_of_contents: true
-
---
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a field of artificial intelligence that focuses on the interaction between computers and humans through natural language. The goal of NLP is to enable computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language in a way that is valuable. This documentation provides an introduction to NLP, its basic concepts, techniques, tools, and practical applications.
@@ -32,6 +31,7 @@ Text preprocessing is a crucial step in NLP, involving cleaning and preparing te
- **Stemming and Lemmatization:** Reducing words to their base forms.
Example of text preprocessing in Python:
+
```python
import nltk
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
@@ -76,6 +76,7 @@ To build a simple NLP model, follow these steps:
6. **Evaluation:** Evaluate the model's performance using appropriate metrics.
Example of text classification using scikit-learn:
+
```python
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB
@@ -140,10 +141,11 @@ Future trends in NLP include:
- **Human-AI Collaboration:** Combining human expertise with AI for better results.
:::tip
+
- Start Simple: Begin with basic NLP tasks and gradually move to complex ones.
- Experiment: Try different preprocessing techniques, models, and libraries.
- Stay Updated: Follow the latest advancements in NLP through research papers and conferences.
-:::
+ :::
## Resources for Further Learning
diff --git a/blog/getting-started-with-serverless-architecture.md b/blog/getting-started-with-serverless-architecture.md
index 37f1b1286..7bf09adf0 100644
--- a/blog/getting-started-with-serverless-architecture.md
+++ b/blog/getting-started-with-serverless-architecture.md
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
---
-title: 'Getting Started with Serverless Architecture Using AWS Lambda'
+title: "Getting Started with Serverless Architecture Using AWS Lambda"
sidebar_label: Serverless Architecture and AWS Lambda
authors: [nayanika-mukherjee]
tags: [serverless, AWS Lambda, cloud computing, Python, technology]
@@ -42,7 +42,9 @@ Before creating a Lambda function, you need an IAM role that Lambda assumes when
```bash
aws iam create-role --role-name lambda-execution-role --assume-role-policy-document file://trust-policy.json
```
+
`trust-policy.json`:
+
```json
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
@@ -57,7 +59,9 @@ aws iam create-role --role-name lambda-execution-role --assume-role-policy-docum
]
}
```
+
Attach the necessary policies to the role:
+
```bash
aws iam attach-role-policy --role-name lambda-execution-role --policy-arn arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/service-role/AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole
```
@@ -65,9 +69,11 @@ aws iam attach-role-policy --role-name lambda-execution-role --policy-arn arn:aw
## Writing and Deploying Lambda Functions
### Basic Lambda Function
+
Here is a simple Python function that returns a greeting.
`lambda_function.py`:
+
```python
def lambda_handler(event, context):
return {
@@ -77,12 +83,15 @@ def lambda_handler(event, context):
```
### Creating and Deploying the Function
+
- Create a ZIP file containing your code:
+
```bash
zip function.zip lambda_function.py
```
- Deploy the Lambda Function:
+
```bash
aws lambda create-function --function-name HelloWorldFunction \
--zip-file fileb://function.zip --handler lambda_function.lambda_handler \
@@ -98,34 +107,44 @@ Lambda functions have an execution model that includes:
- Execution Duration: You can configure the timeout for your function (default is 3 seconds, maximum is 15 minutes).
## Managing Lambda Functions
+
- Updating a Function
-To update the function code:
+ To update the function code:
+
```bash
zip function.zip lambda_function.py
aws lambda update-function-code --function-name HelloWorldFunction --zip-file fileb://function.zip
```
- Monitoring and Logging
-AWS Lambda integrates with Amazon CloudWatch to provide monitoring and logging. You can view logs by navigating to the CloudWatch Logs in the AWS Management Console.
+ AWS Lambda integrates with Amazon CloudWatch to provide monitoring and logging. You can view logs by navigating to the CloudWatch Logs in the AWS Management Console.
## Advanced Topics
### Environment Variables
+
You can use environment variables to pass configuration settings to your Lambda function.
+
```bash
aws lambda update-function-configuration --function-name HelloWorldFunction \
--environment "Variables={ENV_VAR1=value1,ENV_VAR2=value2}"
```
+
### Layers
+
Lambda layers allow you to package libraries and other dependencies separately from your function code.
- Create a layer:
+
```bash
zip -r myLayer.zip python/
aws lambda publish-layer-version --layer-name myLayer --zip-file fileb://myLayer.zip
```
+
### VPC Integration
+
You can configure your Lambda function to access resources in a VPC.
+
```bash
aws lambda update-function-configuration --function-name HelloWorldFunction \
--vpc-config SubnetIds=subnet-abc123,SecurityGroupIds=sg-abc123
@@ -134,26 +153,34 @@ aws lambda update-function-configuration --function-name HelloWorldFunction \
## Performance and Scaling
### Cold Starts
+
A cold start occurs when a new instance of the function is invoked after being idle. To mitigate cold starts:
- Optimize initialization code.
- Use Provisioned Concurrency for predictable performance.
### Concurrency Limits
+
You can configure reserved concurrency to limit the number of concurrent executions:
+
```bash
aws lambda put-function-concurrency --function-name HelloWorldFunction --reserved-concurrent-executions 10
```
+
## Testing and Debugging
### Local Testing
+
Use the AWS SAM CLI to test Lambda functions locally:
+
```bash
sam local invoke HelloWorldFunction -e event.json
```
### Debugging
+
Utilize CloudWatch Logs to debug issues by adding log statements in your code:
+
```python
import logging
logger = logging.getLogger()
@@ -166,10 +193,13 @@ def lambda_handler(event, context):
'body': 'Hello, World!'
}
```
+
## Real-World Examples
### S3 Event Trigger
+
Trigger a Lambda function when an object is uploaded to an S3 bucket:
+
```python
import json
@@ -186,7 +216,9 @@ def lambda_handler(event, context):
```
### DynamoDB Stream
+
Process DynamoDB stream events:
+
```python
import json
diff --git a/blog/getting-started-with-vite/index.md b/blog/getting-started-with-vite/index.md
index 105461d91..bb8d8e6a1 100644
--- a/blog/getting-started-with-vite/index.md
+++ b/blog/getting-started-with-vite/index.md
@@ -134,4 +134,4 @@ To learn more about Vite, visit the official [Vite documentation](https://vitejs
## Conclusion
-In this blog post, we learned how to get started with React by creating a new app using Vite. We followed the steps to set up our development environment and build our first React application. We explored the advantages of using Vite for React development and discussed its features, benefits, and community support. We also learned about the project structure of a new React application created with Vite and how to build our first React application. We hope this blog post has provided you with valuable insights into using Vite for React development and has inspired you to explore the possibilities of building modern web applications with Vite and React.
\ No newline at end of file
+In this blog post, we learned how to get started with React by creating a new app using Vite. We followed the steps to set up our development environment and build our first React application. We explored the advantages of using Vite for React development and discussed its features, benefits, and community support. We also learned about the project structure of a new React application created with Vite and how to build our first React application. We hope this blog post has provided you with valuable insights into using Vite for React development and has inspired you to explore the possibilities of building modern web applications with Vite and React.
diff --git a/blog/git-best-practicies.md b/blog/git-best-practicies.md
index d5c4f6bca..7ed547f33 100644
--- a/blog/git-best-practicies.md
+++ b/blog/git-best-practicies.md
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
---
-title: ' Git Best Practices: Commit Often, Perfect Later, Publish Once'
+title: " Git Best Practices: Commit Often, Perfect Later, Publish Once"
sidebar_label: Git Best Practicies
authors: [ajay-dhangar]
tags: [git, best practicies]
@@ -41,4 +41,4 @@ When you're collaborating with others, it's important to communicate effectively
## Conclusion
-Git is a powerful tool for managing the development of software projects, but it can be challenging to use effectively. By following best practices for using Git, such as committing often, structuring your commits, managing your branches, and collaborating with others, you can make your development process more efficient and less error-prone. By doing this, you can make it easier to understand the evolution of your codebase, to track down bugs, and to collaborate with others. Happy coding!
\ No newline at end of file
+Git is a powerful tool for managing the development of software projects, but it can be challenging to use effectively. By following best practices for using Git, such as committing often, structuring your commits, managing your branches, and collaborating with others, you can make your development process more efficient and less error-prone. By doing this, you can make it easier to understand the evolution of your codebase, to track down bugs, and to collaborate with others. Happy coding!
diff --git a/blog/install-mongodb-linux.md b/blog/install-mongodb-linux.md
index 8f9db2710..4d856397a 100644
--- a/blog/install-mongodb-linux.md
+++ b/blog/install-mongodb-linux.md
@@ -77,4 +77,4 @@ sudo apt install -y mongosh
## Conclusion
-Congratulations! You have successfully installed MongoDB and `mongosh` on your Debian Bullseye system. You can now start using MongoDB to store and manage your data. If you have any questions or run into any issues, feel free to consult the official [MongoDB documentation](https://docs.mongodb.com/). Happy coding!
\ No newline at end of file
+Congratulations! You have successfully installed MongoDB and `mongosh` on your Debian Bullseye system. You can now start using MongoDB to store and manage your data. If you have any questions or run into any issues, feel free to consult the official [MongoDB documentation](https://docs.mongodb.com/). Happy coding!
diff --git a/blog/install-mongodb-windows.md b/blog/install-mongodb-windows.md
index e96633c5f..63f180752 100644
--- a/blog/install-mongodb-windows.md
+++ b/blog/install-mongodb-windows.md
@@ -60,4 +60,4 @@ mongosh
This will open the mongosh shell, and you can start interacting with the MongoDB server using JavaScript-like syntax.
-Congratulations! You have successfully installed MongoDB and mongosh on your Windows system. You are now ready to start building powerful applications with MongoDB as your database. Happy coding!
\ No newline at end of file
+Congratulations! You have successfully installed MongoDB and mongosh on your Windows system. You are now ready to start building powerful applications with MongoDB as your database. Happy coding!
diff --git a/blog/introduction-to-the-Linux-development-and-cyber-security.md b/blog/introduction-to-the-Linux-development-and-cyber-security.md
index 3ddcab9cf..bb96ec9bf 100644
--- a/blog/introduction-to-the-Linux-development-and-cyber-security.md
+++ b/blog/introduction-to-the-Linux-development-and-cyber-security.md
@@ -1,12 +1,11 @@
-
---
-title: 'Comprehensive Documentation on Linux Development and Cybersecurity'
+title: "Comprehensive Documentation on Linux Development and Cybersecurity"
sidebar_label: Linux development and cyber security
authors: [pujan-sarkar]
-tags: [cyber security, Linux , internet, technology]
+tags: [cyber security, Linux, internet, technology]
date: 2024-06-23
hide_table_of_contents: true
----
+---
Linux, renowned for its stability, security, and open-source nature, plays a pivotal role in modern computing environments, particularly in development and cybersecurity. This documentation explores how Linux facilitates software development processes and serves as a secure foundation for cybersecurity operations.
diff --git a/blog/introduction-to-web-assembly.md b/blog/introduction-to-web-assembly.md
index e3b16e424..b2985043c 100644
--- a/blog/introduction-to-web-assembly.md
+++ b/blog/introduction-to-web-assembly.md
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
---
-title: 'Introduction to WebAssembly: Enhancing Web Performance'
+title: "Introduction to WebAssembly: Enhancing Web Performance"
sidebar_label: WebAssembly and Web Performance
authors: [nayanika-mukherjee]
tags: [webassembly, wasm, web performance, technology]
@@ -50,10 +50,12 @@ To compile your code to WebAssembly, follow these steps:
```bash
emcc your_code.c -o your_code.wasm
```
-For Rust:
+ For Rust:
+
```
rustc --target wasm32-unknown-unknown -O your_code.rs
```
+
## Interfacing with JavaScript
WebAssembly can interact with JavaScript, enabling you to call Wasm functions from JavaScript and vice versa. Use the JavaScript WebAssembly API to load and instantiate Wasm modules.
diff --git a/blog/iot-integration-and-application-development.md b/blog/iot-integration-and-application-development.md
index ceb48121c..3f758c03b 100644
--- a/blog/iot-integration-and-application-development.md
+++ b/blog/iot-integration-and-application-development.md
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
---
-title: 'IoT (Internet of Things): Integration and Application Development'
-slidebar_label: 'IoT: Integration and Application Development'
+title: "IoT (Internet of Things): Integration and Application Development"
+slidebar_label: "IoT: Integration and Application Development"
authors: [nayanika-mukherjee]
tags: [IoT, Internet of Things, Sensors, Actuators, Cloud, Edge Computing]
date: 2024-07-31
@@ -23,7 +23,7 @@ The Internet of Things (IoT) is a transformative technology that connects physic
- **Network Layer**: Transmits data between devices and the cloud.
- **Data Layer**: Manages data storage, processing, and analytics.
- **Application Layer**: Interfaces where users interact with the IoT system.
-
+
### Example: Simple IoT Architecture Diagram
```plaintext
@@ -41,18 +41,18 @@ The Internet of Things (IoT) is a transformative technology that connects physic
### Example: Basic MQTT Communication
```javascript
-const mqtt = require('mqtt');
-const client = mqtt.connect('mqtt://broker.hivemq.com');
+const mqtt = require("mqtt");
+const client = mqtt.connect("mqtt://broker.hivemq.com");
-client.on('connect', () => {
- client.subscribe('sensor/data', (err) => {
+client.on("connect", () => {
+ client.subscribe("sensor/data", (err) => {
if (!err) {
- client.publish('sensor/data', 'Temperature: 22°C');
+ client.publish("sensor/data", "Temperature: 22°C");
}
});
});
-client.on('message', (topic, message) => {
+client.on("message", (topic, message) => {
console.log(message.toString());
});
```
@@ -134,15 +134,16 @@ print(f'Encrypted data: {encrypted}')
```javascript
// Example: Sending sensor data to a server
-const axios = require('axios');
+const axios = require("axios");
const data = { temperature: 22, humidity: 55 };
-axios.post('https://example.com/api/sensor-data', data)
- .then(response => {
- console.log('Data sent successfully:', response.data);
+axios
+ .post("https://example.com/api/sensor-data", data)
+ .then((response) => {
+ console.log("Data sent successfully:", response.data);
})
- .catch(error => {
- console.error('Error sending data:', error);
+ .catch((error) => {
+ console.error("Error sending data:", error);
});
```
@@ -196,4 +197,4 @@ axios.post('https://example.com/api/sensor-data', data)
## Conclusion
-The IoT landscape is vast and ever-evolving, offering exciting opportunities to innovate across various industries. By understanding the architecture, communication protocols, and security challenges, you can develop robust IoT applications that can make a real-world impact.
\ No newline at end of file
+The IoT landscape is vast and ever-evolving, offering exciting opportunities to innovate across various industries. By understanding the architecture, communication protocols, and security challenges, you can develop robust IoT applications that can make a real-world impact.
diff --git a/blog/leveraging-gpt-models-for-microfrontends.md b/blog/leveraging-gpt-models-for-microfrontends.md
index 7d76a0e93..98890e998 100644
--- a/blog/leveraging-gpt-models-for-microfrontends.md
+++ b/blog/leveraging-gpt-models-for-microfrontends.md
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
---
-title: 'Leveraging GPT Model for Microfrontends: Architecting Front-End at Scale'
+title: "Leveraging GPT Model for Microfrontends: Architecting Front-End at Scale"
sidebar_label: Microfrontends and GPT
authors: [nayanika-mukherjee]
tags: [microfrontends, GPT, front-end, architecture, technology]
@@ -114,4 +114,3 @@ For further learning and exploration, consider the following resources:
## Conclusion
Leveraging GPT models for microfrontends offers a scalable, flexible approach to frontend development. By understanding the principles and best practices outlined in this documentation, developers can architect robust, maintainable front-end applications that meet the demands of modern web development.
-
diff --git a/blog/microservices-architecture.md b/blog/microservices-architecture.md
index ed4fde11a..6316d70e0 100644
--- a/blog/microservices-architecture.md
+++ b/blog/microservices-architecture.md
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
---
-title: 'Microservices Architecture: Design, Implementation, and Monitoring'
+title: "Microservices Architecture: Design, Implementation, and Monitoring"
sidebar_label: Microservices Basics
authors: [nayanika-mukherjee]
tags: [microservices, architecture, spring boot, docker, kubernetes, monitoring]
@@ -42,6 +42,7 @@ public class ExampleController {
}
}
```
+
### Example: Dockerizing a Spring Boot Application
```dockerfile
@@ -57,6 +58,7 @@ COPY target/myapp.jar /app/myapp.jar
# Run the application
ENTRYPOINT ["java", "-jar", "myapp.jar"]
```
+
### Example: Deploying to Kubernetes
```yaml
@@ -75,10 +77,10 @@ spec:
app: myapp
spec:
containers:
- - name: myapp
- image: myapp:latest
- ports:
- - containerPort: 8080
+ - name: myapp
+ image: myapp:latest
+ ports:
+ - containerPort: 8080
```
## Monitoring and Managing Microservices
@@ -137,6 +139,7 @@ spec:
## Real-World Examples and Performance Considerations
### Choosing the Right Tools and Frameworks
+
Selecting the appropriate tools and frameworks depends on factors like:
- **Language Preferences:** Spring Boot for Java, Flask for Python, Express for Node.js.
@@ -144,6 +147,7 @@ Selecting the appropriate tools and frameworks depends on factors like:
- **Orchestration Requirements:** Kubernetes for managing containerized applications.
### Monitoring and Managing Microservices
+
To ensure reliability and performance:
- **Health Checks:** Regularly check the health of services using Kubernetes liveness and readiness probes.
@@ -151,16 +155,19 @@ To ensure reliability and performance:
- **Circuit Breakers:** Implement fault tolerance with tools like Hystrix.
### Real-World Examples
+
Several companies have successfully implemented microservices:
- **Netflix:** Uses microservices to handle massive traffic and deliver streaming content.
- **Amazon:** Migrated from a monolithic architecture to microservices to improve scalability and resilience.
They have faced challenges such as:
+
- **Complexity:** Managing numerous services can be complex.
- **Data Consistency:** Ensuring consistency across distributed services.
### Performance Considerations
+
Scaling microservices involves:
- **Load Balancing:** Distributing traffic evenly across services using tools like NGINX or Kubernetes Ingress.
@@ -178,4 +185,4 @@ For further learning:
- **Books:** "Building Microservices" by Sam Newman, "Microservices Patterns" by Chris Richardson.
- **Online Courses:** Udemy, Coursera, and Pluralsight offer courses on microservices.
-- **Communities:** Join microservices communities and forums to connect with other practitioners.
\ No newline at end of file
+- **Communities:** Join microservices communities and forums to connect with other practitioners.
diff --git a/blog/piracy-preserving-ai.md b/blog/piracy-preserving-ai.md
index d2a4eb785..9956c4aaa 100644
--- a/blog/piracy-preserving-ai.md
+++ b/blog/piracy-preserving-ai.md
@@ -1,11 +1,11 @@
---
-title: 'Privacy-Preserving AI: Techniques and Applications'
+title: "Privacy-Preserving AI: Techniques and Applications"
sidebar_label: Privacy-Preserving AI
authors: [nayanika-mukherjee]
tags: [AI, privacy, technology, machine learning]
date: 2024-08-01
hide_table_of_contents: true
----
+---
Privacy-Preserving AI is an emerging field focused on protecting individuals' privacy while enabling the use of AI for data analysis and decision-making. This documentation covers various techniques and applications, exploring how AI can be developed and deployed without compromising data privacy.
@@ -14,72 +14,89 @@ Privacy-Preserving AI is an emerging field focused on protecting individuals' pr
## Differential Privacy
### Overview
+
Differential privacy ensures that the output of an algorithm does not reveal whether any individual’s data was included in the input. It adds noise to the data, providing privacy guarantees while retaining the data's utility.
### Applications
+
- **Data Analysis:** Used in statistical analysis to protect individual records.
- **Machine Learning:** Applied to training data to prevent model inversion attacks.
## Homomorphic Encryption
### Overview
+
Homomorphic encryption allows computations to be performed on encrypted data without decrypting it. The results, when decrypted, match the output of operations performed on the plaintext.
### Applications
+
- **Secure Data Processing:** Enables computation on sensitive data without exposure.
- **Cloud Computing:** Allows cloud providers to process encrypted data without accessing the raw data.
## Federated Learning
### Overview
+
Federated learning trains machine learning models across multiple decentralized devices or servers while keeping the data localized. This approach enhances privacy by ensuring data never leaves its source.
### Applications
+
- **Healthcare:** Aggregating patient data from multiple hospitals for model training.
- **Mobile Devices:** Training models across users' devices without data centralization.
## Privacy-Preserving Data Sharing
### Overview
+
Techniques for privacy-preserving data sharing include anonymization, pseudonymization, and secure multi-party computation. These methods allow data to be shared and analyzed without compromising individual privacy.
### Applications
+
- **Collaborative Research:** Sharing data between institutions while maintaining privacy.
- **Public Data Releases:** Releasing datasets for public use with privacy protections.
## AI Model Privacy Attacks and Defenses
### Overview
+
AI models can be vulnerable to privacy attacks such as membership inference and model inversion. Defenses include differential privacy, secure enclaves, and adversarial training.
### Applications
+
- **Model Security:** Enhancing the robustness of AI models against privacy attacks.
- **Data Protection:** Ensuring sensitive information is not leaked through model outputs.
## Ethical Considerations in Privacy-Preserving AI
### Overview
+
Ethical considerations involve balancing the benefits of AI with the need to protect individual privacy. This includes transparency, consent, and fairness in AI applications.
### Applications
+
- **Regulatory Compliance:** Ensuring AI systems comply with privacy laws and regulations.
- **Trust Building:** Enhancing user trust in AI systems by prioritizing privacy.
## Privacy-Preserving AI in Various Fields
### Healthcare
+
Privacy-preserving techniques are critical in healthcare for protecting patient data while enabling research and personalized medicine.
### Finance
+
In finance, these techniques allow for secure transactions and fraud detection without exposing sensitive financial data.
### Social Media
+
Protecting user data on social media platforms while enabling personalized content and advertising.
## Tools and Frameworks for Privacy-Preserving AI
### Overview
+
There are several tools and frameworks designed to facilitate privacy-preserving AI, including:
+
- **PySyft:** A Python library for secure and private deep learning.
- **TF Encrypted:** TensorFlow library for encrypted machine learning.
- **OpenMined:** An open-source community focused on privacy-preserving AI.
@@ -87,43 +104,52 @@ There are several tools and frameworks designed to facilitate privacy-preserving
## Future Trends in Privacy-Preserving AI
### Overview
+
Future trends include advancements in federated learning, improved encryption techniques, and the integration of privacy-preserving methods into AI development pipelines.
### Applications
+
- **Smart Cities:** Enabling data-driven urban planning without compromising privacy.
- **Personal Assistants:** Developing AI that respects user privacy while providing personalized services.
## Challenges and Limitations
### Overview
+
Challenges include computational overhead, scalability issues, and the complexity of implementing privacy-preserving techniques.
### Applications
+
- **Performance Trade-offs:** Balancing privacy with the efficiency of AI models.
- **Complexity:** Navigating the technical complexities of advanced privacy techniques.
## Case Studies and Real-World Applications
### Healthcare
+
Case studies on how privacy-preserving AI is being used to aggregate and analyze patient data while maintaining privacy.
### Finance
+
Examples of privacy-preserving AI in fraud detection and secure financial transactions.
### Social Media
+
How social media platforms implement privacy-preserving techniques to protect user data.
## Resources
### Books
+
- "Privacy-Preserving Machine Learning" by J. Smith
- "Introduction to Differential Privacy" by C. Dwork
### Online Courses
+
- "Privacy in Machine Learning" by Coursera
- "Federated Learning and Differential Privacy" by edX
### Research Papers
+
- "The Algorithmic Foundations of Differential Privacy" by C. Dwork and A. Roth
- "Federated Learning: Challenges, Methods, and Future Directions" by Q. Yang et al.
-
diff --git a/blog/react-js.md b/blog/react-js.md
index 163eed6eb..fc499227e 100644
--- a/blog/react-js.md
+++ b/blog/react-js.md
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
---
-title: 'React JS'
+title: "React JS"
sidebar_label: React JS
authors: [hitesh-gahanolia]
-tags: [javascript , framework , frontend , react , node ]
+tags: [javascript, framework, frontend, react, node]
date: 2024-06-13 12:29
hide_table_of_contents: true
---
@@ -14,6 +14,7 @@ React is a JavaScript library primarily used for building user interfaces in sin
React offers various extensions for entire application architectural support, such as Flux and React Native, beyond mere UI.
## Why React?
+
- Declarative Nature: React's declarative approach allows developers to describe the desired UI state, and React handles the rendering efficiently. This simplifies the development process by abstracting away the manual DOM manipulation.
- Improved Performance: React uses Virtual DOM, a lightweight representation of the actual DOM. By comparing the previous and current states of this Virtual DOM, React determines the minimal set of DOM operations needed to update the UI, resulting in faster rendering and better performance.
@@ -26,54 +27,66 @@ React offers various extensions for entire application architectural support, su
- Developer Tools: React is supported by dedicated developer tools like the React Developer Tools extension for Chrome. These tools facilitate debugging by providing insights into component hierarchies, state changes, and performance optimizations.
-
-
## ReactJS History
+
When compared to other technologies on the market, React is a new technology. React was created by Jordan Walke, a software engineer at Facebook, in 2011.Initially implemented in Facebook's News Feed, its success quickly led to its adoption in Instagram, showcasing its power and versatility in building dynamic user interfaces.
## React Features
+
Currently, ReactJS gaining quick popularity as the best JavaScript framework among web developers. It is playing an essential role in the front-end ecosystem. The important features of ReactJS are as following.
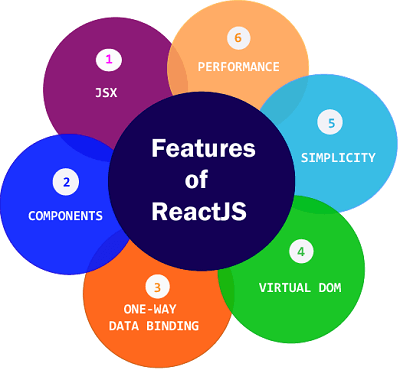
- ### JSX
+### JSX
+
JSX is a syntax extension for JavaScript that allows developers to write HTML-like code within JavaScript. This makes it easier to create and understand the structure of React components, as it closely resembles the final output in the browser. While not mandatory, using JSX is recommended in React development because it enhances readability and simplifies the creation of user interfaces.
### Components
+
React components enable reusability and encapsulation by breaking down UIs into self-contained pieces with their own structure, style, and behavior. This promotes code reuse, as components can be used across different parts of the application, enhancing maintainability and reducing bugs, while ensuring a clean separation of concerns.
### One-way Data Binding
- One-way data binding is a pattern where data flows in a single direction, typically from the model to the view. This ensures that the state of an application is predictable and easier to manage. In the context of JavaScript frameworks, Flux and Redux are popular architectures that facilitate one-way data binding and state management.
+
+One-way data binding is a pattern where data flows in a single direction, typically from the model to the view. This ensures that the state of an application is predictable and easier to manage. In the context of JavaScript frameworks, Flux and Redux are popular architectures that facilitate one-way data binding and state management.
#### Flux
+
Flux is an architecture pattern created by Facebook for building client-side web applications. It emphasizes unidirectional data flow and is composed of four key components:
##### Action:
+
- Actions are plain JavaScript objects or functions that contain the type of event and any associated data (payload). Actions are the only source of information for the store.
##### Dispatcher:
+
- The dispatcher is a central hub that manages all the data flow in a Flux application. When an action is created, it is dispatched to all stores that have registered with the dispatcher. The dispatcher’s role is to handle these actions and ensure they reach the appropriate store.
##### Store:
+
- Stores hold the application state and logic. They listen for actions from the dispatcher and update their state accordingly. Stores then emit a change event to notify the view layer to re-render. Each store manages a specific portion of the application's state.
##### View:
+
- The view is the presentation layer, typically composed of React components. Views listen to changes from the stores and re-render themselves accordingly. They can also generate new actions based on user interactions and send them to the dispatcher.
### Virtual DOM
+
A virtual DOM object is a representation of the original DOM object. It works like a one-way data binding. Whenever any modifications happen in the web application, the entire UI is re-rendered in virtual DOM representation. Then it checks the difference between the previous DOM representation and new DOM. Once it has done, the real DOM will update only the things that have actually changed. This makes the application faster, and there is no wastage of memory.
### Simplicity
+
ReactJS uses JSX file which makes the application simple and to code as well as understand. We know that ReactJS is a component-based approach which makes the code reusable as your need. This makes it simple to use and learn.
### Performance
-ReactJS is known to be a great performer. This feature makes it much better than other frameworks out there today. The reason behind this is that it manages a virtual DOM. The DOM is a cross-platform and programming API which deals with HTML, XML or XHTML. The DOM exists entirely in memory. Due to this, when we create a component, we did not write directly to the DOM. Instead, we are writing virtual components that will turn into the DOM leading to smoother and faster performance.
+ReactJS is known to be a great performer. This feature makes it much better than other frameworks out there today. The reason behind this is that it manages a virtual DOM. The DOM is a cross-platform and programming API which deals with HTML, XML or XHTML. The DOM exists entirely in memory. Due to this, when we create a component, we did not write directly to the DOM. Instead, we are writing virtual components that will turn into the DOM leading to smoother and faster performance.
## React Ecosystem
+
The React ecosystem is vast and diverse, encompassing a wide range of libraries and tools that enhance and extend the capabilities of React. These tools help in state management, routing, form handling, styling, and more, making React a robust framework for building complex and feature-rich applications. Here are some of the most popular libraries and tools commonly used with React:
### State Management
+
#### Redux
Description: Redux is a state management library that provides a predictable state container for JavaScript apps. It helps manage application state and enables powerful debugging capabilities through tools like the Redux DevTools.
@@ -93,12 +106,15 @@ Description: Recoil is a state management library for React developed by Faceboo
Key Features: Atoms, selectors, asynchronous state management.
### Routing
+
#### React Router
+
Description: React Router is the most widely used routing library for React. It allows for dynamic routing in a web application, enabling navigation between different components and views.
Key Features: Nested routes, dynamic routing, query parameters.
### Form Handling
+
#### Formik
Description: Formik is a library that simplifies form management in React applications. It helps with form validation, error handling, and form submission.
@@ -112,6 +128,7 @@ Description: React Hook Form is a performant, flexible library for managing form
Key Features: Minimal re-renders, easy integration with UI libraries, built-in validation support.
### Styling
+
#### Styled Components
Description: Styled Components is a library for styling React applications using tagged template literals. It allows for writing actual CSS to style components, keeping styles scoped and maintaining a clean component structure.
@@ -125,6 +142,7 @@ Description: Emotion is a flexible and powerful library for writing CSS styles w
Key Features: Performant styles, server-side rendering, powerful theming capabilities.
### Testing
+
#### Jest
Description: Jest is a JavaScript testing framework developed by Facebook, designed to ensure correctness of any JavaScript codebase. It works seamlessly with React, providing a simple and efficient way to test components and applications.
@@ -138,6 +156,7 @@ Description: React Testing Library is a testing utility that encourages testing
Key Features: Lightweight, integrates with Jest, emphasizes testing UI from the user’s perspective.
### Build and Tooling
+
#### Create React App
Description: Create React App (CRA) is a CLI tool that sets up a new React project with a sensible default configuration. It handles configuration for tools like Webpack, Babel, ESLint, and more.
@@ -153,14 +172,19 @@ Key Features: Server-side rendering, static site generation, API routes, fast re
The React ecosystem is continuously evolving, with new tools and libraries emerging to address various needs and challenges in modern web development. These tools help streamline the development process, enhance performance, and ensure maintainability of React applications.
## Pros and Cons of ReactJS
+
Today, ReactJS is the highly used open-source JavaScript Library. It helps in creating impressive web apps that require minimal effort and coding. The main objective of ReactJS is to develop User Interfaces (UI) that improves the speed of the apps. There are important pros and cons of ReactJS given as following:
Advantage of ReactJS
+
### Easy to Learn and Use
+
ReactJS is much easier to learn and use. It comes with a good supply of documentation, tutorials, and training resources. Any developer who comes from a JavaScript background can easily understand and start creating web apps using React in a few days. It is the V(view part) in the MVC (Model-View-Controller) model, and referred to as ?one of the JavaScript frameworks.? It is not fully featured but has the advantage of open-source JavaScript User Interface(UI) library, which helps to execute the task in a better manner.
### Creating Dynamic Web Applications Becomes Easier
-#### JSX for Readability and Maintainability:
+
+#### JSX for Readability and Maintainability:
+
- JSX (JavaScript XML) allows developers to write HTML elements in JavaScript. This mixture of HTML and JavaScript makes the code more readable and maintainable. For example, instead of splitting code between HTML and JavaScript files, JSX enables developers to write them together, making it easier to understand and work with the code.
### Reusable Components
@@ -170,7 +194,9 @@ A ReactJS web application is made up of multiple components, and each component
### Performance Enhancement
#### Virtual DOM vs. Real DOM:
-- React uses a virtual DOM to optimize updates and rendering. When the state of a component changes, React first updates the virtual DOM, a lightweight copy of the real DOM. It then compares this virtual DOM with a snapshot of the real DOM before applying only the necessary changes to the real DOM.Instead of re-rendering the entire DOM tree, React only updates the parts that have changed, which significantly boosts performance, especially in complex applications.
+
+- React uses a virtual DOM to optimize updates and rendering. When the state of a component changes, React first updates the virtual DOM, a lightweight copy of the real DOM. It then compares this virtual DOM with a snapshot of the real DOM before applying only the necessary changes to the real DOM.Instead of re-rendering the entire DOM tree, React only updates the parts that have changed, which significantly boosts performance, especially in complex applications.
+
### Known to be SEO Friendly
Traditional JavaScript frameworks have an issue in dealing with SEO. The search engines generally having trouble in reading JavaScript-heavy applications. Many web developers have often complained about this problem. ReactJS overcomes this problem that helps developers to be easily navigated on various search engines. It is because React.js applications can run on the server, and the virtual DOM will be rendering and returning to the browser as a regular web page.
@@ -179,27 +205,32 @@ Traditional JavaScript frameworks have an issue in dealing with SEO. The search
Today, ReactJS is choosing by most of the web developers. It is because it is offering a very rich JavaScript library. The JavaScript library provides more flexibility to the web developers to choose the way they want.
-
## Disadvantage of ReactJS
+
### The high pace of development
+
#### Continuous Learning and Updates:
+
- The React ecosystem evolves rapidly, with frequent updates and new releases. While these updates bring improvements and new features, they also mean developers need to constantly learn and adapt. For example, React Hooks, introduced in version 16.8, brought a significant change in how state and side effects are handled.
Developers had to quickly learn and integrate this new feature, which can be challenging and time-consuming.
### Poor Documentation
+
#### Rapid Updates Leading to Outdated Information:
- - While the official React documentation has improved, the rapid pace of updates can sometimes lead to outdated or incomplete information. For example, when new features like Concurrent Mode or Suspense are introduced, documentation might lag behind, making it difficult for developers to find accurate and up-to-date information.
- Developers might need to rely on community forums, blog posts, or other unofficial sources to fill in the gaps, which can be frustrating and time-consuming.
+- While the official React documentation has improved, the rapid pace of updates can sometimes lead to outdated or incomplete information. For example, when new features like Concurrent Mode or Suspense are introduced, documentation might lag behind, making it difficult for developers to find accurate and up-to-date information.
+
+Developers might need to rely on community forums, blog posts, or other unofficial sources to fill in the gaps, which can be frustrating and time-consuming.
### View Part
+
ReactJS Covers only the UI Layers of the app and nothing else. So you still need to choose some other technologies to get a complete tooling set for development in the project.
### JSX as a barrier
ReactJS uses JSX. It's a syntax extension that allows HTML with JavaScript mixed together. This approach has its own benefits, but some members of the development community consider JSX as a barrier, especially for new developers. Developers complain about its complexity in the learning curve.
+### Official Documentation
-### Official Documentation
- - https://react.dev/
\ No newline at end of file
+- https://react.dev/
diff --git a/blog/reactjs-mongodb-chrome-extension.md b/blog/reactjs-mongodb-chrome-extension.md
index 6e928c991..e5195f681 100644
--- a/blog/reactjs-mongodb-chrome-extension.md
+++ b/blog/reactjs-mongodb-chrome-extension.md
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
---
-title: 'Chrome Extension Using MERN'
+title: "Chrome Extension Using MERN"
sidebar_label: Chrome Extension Using MERN
authors: [khushi-kalra]
tags: [chrome extension, web dev, React, Express, MongoDB, Node, UI]
@@ -18,6 +18,7 @@ Here's a step-by-step guide based on my experience:
## Creating Frontend of the Extension
### Step 1: Create a React App
+
First, you'll need to set up a basic React application. You can do this using Create React App:
```bash
@@ -26,25 +27,25 @@ cd my-chrome-extension
```
### Step 2: Change the Manifest JSON File
+
The manifest.json file is crucial for Chrome extensions as it contains metadata about your extension. Update the manifest.json file in the public folder with the following content:
```json
{
- "manifest_version":3,
- "name":"Chrome Extension",
- "version":"1.0.0",
- "description":"My First Chrome Extension Using MERN",
+ "manifest_version": 3,
+ "name": "Chrome Extension",
+ "version": "1.0.0",
+ "description": "My First Chrome Extension Using MERN",
"action": {
"default_popup": "index.html",
"default_title": "Open"
},
- "permissions":[
- "scripting"
- ]
+ "permissions": ["scripting"]
}
```
### Step 3: Add Height and Width
+
To ensure your extension has the proper dimensions, update the index.css file in the src folder and add height and width:
```css
@@ -55,7 +56,9 @@ body {
```
### Check Point
-To check if you have followed all the steps properly. You can go try to run the extension in browser.
+
+To check if you have followed all the steps properly. You can go try to run the extension in browser.
+
1. Run `npm build` in the terminal.
2. Open Chrome and go to chrome://extensions/.
3. Enable "Developer mode" in the top right corner.
@@ -63,7 +66,9 @@ To check if you have followed all the steps properly. You can go try to run the
5. See if can see the default React page in the height and width you gave.
### Step 4: Change Rendering to MemoryRouter
+
This is the most crucial step. BrowserRouter is not supported for the Chrome Extensions, which is default in React applications. We are going to change that too MemoryRouter.
+
1. Install React Router:
```bash
@@ -73,26 +78,28 @@ npm install react-router-dom
2. Update index.js to include routes:
```jsx
-import React from 'react';
-import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
-import App from './App';
+import React from "react";
+import ReactDOM from "react-dom";
+import App from "./App";
-import { MemoryRouter as Router } from 'react-router-dom';
+import { MemoryRouter as Router } from "react-router-dom";
ReactDOM.render(
-
-
-
-
- ,
- document.querySelector('#root')
+
+
+
+
+ ,
+ document.querySelector("#root"),
);
```
### Step 5: Adding Routing
+
1. We will make a "Components" folder in src and a Home.jsx.
+
```jsx
-import React from 'react';
+import React from "react";
function Home() {
return (
@@ -107,10 +114,11 @@ export default Home;
```
2. We will update our App.js as:
+
```js
-import React from 'react';
-import { Routes, Route } from 'react-router-dom';
-import Home from './Components/Home.jsx';
+import React from "react";
+import { Routes, Route } from "react-router-dom";
+import Home from "./Components/Home.jsx";
function App() {
return (
@@ -124,11 +132,13 @@ function App() {
export default App;
```
+
**Note: You can run "npm build" again and reload the build folder to see the changes made.**
-
+
## Adding Backend to the Extension
### Step 1: Create a Backend Folder
+
In your project root, create a new folder called backend:
```bash
@@ -137,24 +147,29 @@ cd backend
```
### Step 2: Add server.js
+
Create a server.js file in the backend folder:
```javascript
-const express = require('express');
-const mongoose = require('mongoose');
-const cors = require('cors');
+const express = require("express");
+const mongoose = require("mongoose");
+const cors = require("cors");
const app = express();
app.use(cors());
app.use(express.json());
-mongoose.connect(process.env.MONGO_URI, { useNewUrlParser: true, useUnifiedTopology: true })
- .then(() => console.log('MongoDB connected'))
- .catch(err => console.log(err));
+mongoose
+ .connect(process.env.MONGO_URI, {
+ useNewUrlParser: true,
+ useUnifiedTopology: true,
+ })
+ .then(() => console.log("MongoDB connected"))
+ .catch((err) => console.log(err));
-app.get('/', (req, res) => {
- res.send('Hello, world!');
+app.get("/", (req, res) => {
+ res.send("Hello, world!");
});
const PORT = process.env.PORT || 5000;
@@ -162,6 +177,7 @@ app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`Server is running on port ${PORT}`);
});
```
+
### Step 3: Add a .env file
```env
diff --git a/blog/sed-normalize-md-file-with-regex.md b/blog/sed-normalize-md-file-with-regex.md
index 88fd726cb..fbda35899 100644
--- a/blog/sed-normalize-md-file-with-regex.md
+++ b/blog/sed-normalize-md-file-with-regex.md
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
---
-title: 'Sed: Normalize markdown file with Regex'
+title: "Sed: Normalize markdown file with Regex"
author: ajay-dhangar
tags: [sed, regex, web clipper]
date: 2024-03-15 14:37:46
@@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ One of the common issues I encounter is inconsistent formatting of the front mat
```markdown
---
-title: 'Sed: Normalize markdown file with Regex'
+title: "Sed: Normalize markdown file with Regex"
author: Ajay Dhangar
tags: [sed, regex, web clipper]
date: 2020-11-26 21:13:28
@@ -41,4 +41,4 @@ Let's break down the regular expression:
When I run this command on a markdown file, it removes the existing front matter and leaves me with just the content of the file. This is exactly what I want, as I can then manually add a consistent front matter to the file.
-I hope this example gives you an idea of how powerful regular expressions can be when used with command-line utilities like `sed`. With a little bit of practice, you can write regular expressions to perform complex text manipulations with ease. If you're interested in learning more about regular expressions, I highly recommend checking out the [RegexOne](https://regexone.com/) interactive tutorial, which is a great resource for beginners.
\ No newline at end of file
+I hope this example gives you an idea of how powerful regular expressions can be when used with command-line utilities like `sed`. With a little bit of practice, you can write regular expressions to perform complex text manipulations with ease. If you're interested in learning more about regular expressions, I highly recommend checking out the [RegexOne](https://regexone.com/) interactive tutorial, which is a great resource for beginners.
diff --git a/blog/sql.md b/blog/sql.md
index 6fb6da295..394cdbe29 100644
--- a/blog/sql.md
+++ b/blog/sql.md
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
---
-title: 'SQL'
+title: "SQL"
sidebar_label: SQL - Structured Query Language
authors: [hitesh-gahanolia]
-tags: [sql , databases , data]
+tags: [sql, databases, data]
date: 2024-06-12 5:17
hide_table_of_contents: true
---
@@ -16,13 +16,15 @@ Structured query language (SQL) is a programming language for storing and proces
Structured query language (SQL) is a popular query language that is frequently used in all types of applications. Data analysts and developers learn and use SQL because it integrates well with different programming languages. For example, they can embed SQL queries with the Java programming language to build high-performing data processing applications with major SQL database systems such as Oracle or MS SQL Server. SQL is also fairly easy to learn as it uses common English keywords in its statements
### History
-SQL was invented in the 1970s based on the relational data model. It was initially known as the structured English query language (SEQUEL). The term was later shortened to SQL. Oracle, formerly known as Relational Software, became the first vendor to offer a commercial SQL relational database management system.
+SQL was invented in the 1970s based on the relational data model. It was initially known as the structured English query language (SEQUEL). The term was later shortened to SQL. Oracle, formerly known as Relational Software, became the first vendor to offer a commercial SQL relational database management system.
## Process of SQL
+
When we are executing the command of SQL on any Relational database management system, then the system automatically finds the best routine to carry out our request, and the SQL engine determines how to interpret that particular command.
Structured Query Language contains the following four components in its process:
+
- Query Dispatcher
- Optimization Engines
- Classic Query Engine
@@ -32,16 +34,18 @@ A classic query engine allows data professionals and users to maintain non-SQL q
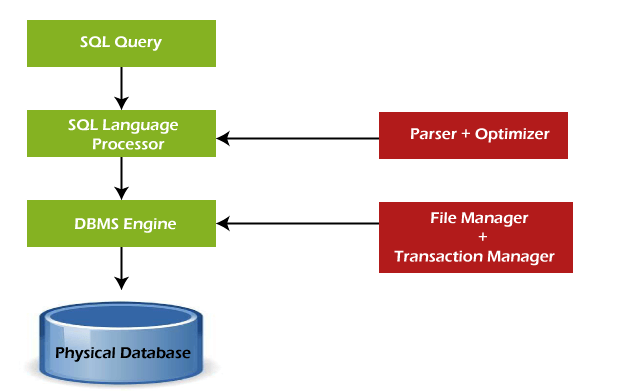
## What are the components of a SQL system?
-Relational database management systems use structured query language (SQL) to store and manage data. The system stores multiple database tables that relate to each other. MS SQL Server, MySQL, or MS Access are examples of relational database management systems. The following are the components of such a system.
+
+Relational database management systems use structured query language (SQL) to store and manage data. The system stores multiple database tables that relate to each other. MS SQL Server, MySQL, or MS Access are examples of relational database management systems. The following are the components of such a system.
### SQL table
+
A SQL table is the basic element of a relational database. The SQL database table consists of rows and columns. Database engineers create relationships between multiple database tables to optimize data storage space.
-For example, the database engineer creates a SQL table for products in a store:
+For example, the database engineer creates a SQL table for products in a store:

-
### SQL statements
+
SQL statements, or SQL queries, are valid instructions that relational database management systems understand. Software developers build SQL statements by using different SQL language elements. SQL language elements are components such as identifiers, variables, and search conditions that form a correct SQL statement.
For example, the following SQL statement uses a SQL INSERT command to store Mattress Brand A, priced $499, into a table named Mattress_table, with column names brand_name and cost:
@@ -51,39 +55,51 @@ INSERT INTO Mattress_table (brand_name, cost)
`VALUES(‘A’,’499’);`
### Stored procedures
-Stored procedures are a collection of one or more SQL statements stored in the relational database. Software developers use stored procedures to improve efficiency and performance. For example, they can create a stored procedure for updating sales tables instead of writing the same SQL statement in different applications.
+
+Stored procedures are a collection of one or more SQL statements stored in the relational database. Software developers use stored procedures to improve efficiency and performance. For example, they can create a stored procedure for updating sales tables instead of writing the same SQL statement in different applications.
## What are SQL commands?
+
Structured query language (SQL) commands are specific keywords or SQL statements that developers use to manipulate the data stored in a relational database. You can categorize SQL commands as follows.
-### Data definition language
+### Data definition language
+
Data definition language (DDL) refers to SQL commands that design the database structure. Database engineers use DDL to create and modify database objects based on the business requirements. For example, the database engineer uses the CREATE command to create database objects such as tables, views, and indexes.
### Data query language
-Data query language (DQL) consists of instructions for retrieving data stored in relational databases. Software applications use the SELECT command to filter and return specific results from a SQL table.
+
+Data query language (DQL) consists of instructions for retrieving data stored in relational databases. Software applications use the SELECT command to filter and return specific results from a SQL table.
### Data manipulation language
+
Data manipulation language (DML) statements write new information or modify existing records in a relational database. For example, an application uses the INSERT command to store a new record in the database.
### Data control language
-Database administrators use data control language (DCL) to manage or authorize database access for other users. For example, they can use the GRANT command to permit certain applications to manipulate one or more tables.
+
+Database administrators use data control language (DCL) to manage or authorize database access for other users. For example, they can use the GRANT command to permit certain applications to manipulate one or more tables.
### Transaction control language
-The relational engine uses transaction control language (TCL) to automatically make database changes. For example, the database uses the ROLLBACK command to undo an erroneous transaction.
+
+The relational engine uses transaction control language (TCL) to automatically make database changes. For example, the database uses the ROLLBACK command to undo an erroneous transaction.
## What is MySQL?
-MySQL is an open-source relational database management system offered by Oracle. Developers can download and use MySQL without paying a licensing fee. They can install MySQL on different operating systems or cloud servers. MySQL is a popular database system for web applications.
+
+MySQL is an open-source relational database management system offered by Oracle. Developers can download and use MySQL without paying a licensing fee. They can install MySQL on different operating systems or cloud servers. MySQL is a popular database system for web applications.
### SQL vs. MySQL
+
Structured query language (SQL) is a standard language for database creation and manipulation. MySQL is a relational database program that uses SQL queries. While SQL commands are defined by international standards, the MySQL software undergoes continual upgrades and improvements.
## What is NoSQL?
+
NoSQL refers to non-relational databases that don't use tables to store data. Developers store information in different types of NoSQL databases, including graphs, documents, and key-values. NoSQL databases are popular for modern applications because they are horizontally scalable. Horizontal scaling means increasing the processing power by adding more computers that run NoSQL software.
### SQL vs. NoSQL
-Structured query language (SQL) provides a uniform data manipulation language, but NoSQL implementation is dependent on different technologies. Developers use SQL for transactional and analytical applications, whereas NoSQL is suitable for responsive, heavy-usage applications.
+
+Structured query language (SQL) provides a uniform data manipulation language, but NoSQL implementation is dependent on different technologies. Developers use SQL for transactional and analytical applications, whereas NoSQL is suitable for responsive, heavy-usage applications.
## Advantages of SQL
+
SQL provides various advantages which make it more popular in the field of data science. It is a perfect query language which allows data professionals and users to communicate with the database. Following are the best advantages or benefits of Structured Query Language:
1. No programming needed
@@ -111,6 +127,7 @@ We can easily learn and understand the SQL language. We can also use this langua
The SQL language also helps in making the multiple views of the database structure for the different database users.
## Disadvantages of SQL
+
With the advantages of SQL, it also has some disadvantages, which are as follows:
1. Cost
@@ -123,4 +140,4 @@ Another big disadvantage is that the interface of Structured query language is d
3. Partial Database control
-The business rules are hidden. So, the data professionals and users who are using this query language cannot have full database control.
\ No newline at end of file
+The business rules are hidden. So, the data professionals and users who are using this query language cannot have full database control.
diff --git a/docs/javascript/data-types/primitive-types/string.md b/docs/javascript/data-types/primitive-types/string.md
index 1e231b99d..39e728e48 100644
--- a/docs/javascript/data-types/primitive-types/string.md
+++ b/docs/javascript/data-types/primitive-types/string.md
@@ -16,18 +16,17 @@ In JavaScript, a string is a sequence of characters enclosed within single or do
You can create strings in JavaScript using single quotes (`'`), double quotes (`"`), or backticks (`` ` ``). Here are examples of each:
```javascript title="app.js"
-let singleQuoted = 'Hello, World!';
+let singleQuoted = "Hello, World!";
let doubleQuoted = "Hello, World!";
let backticks = `Hello, World!`;
```
-
### Single Quotes
Strings enclosed within single quotes are the most common way to create strings in JavaScript. You can use single quotes to represent text data:
```javascript title="app.js"
-let singleQuoted = 'Hello, World!';
+let singleQuoted = "Hello, World!";
console.log(singleQuoted); // Output: Hello, World!
```
@@ -61,11 +60,11 @@ Strings in JavaScript support various operations, such as concatenation, interpo
String concatenation is the process of combining two or more strings into a single string. You can use the `+` operator or template literals for string concatenation:
```javascript title="app.js"
-let firstName = 'John';
-let lastName = 'Doe';
+let firstName = "John";
+let lastName = "Doe";
// Using the + operator
-let fullName = firstName + ' ' + lastName;
+let fullName = firstName + " " + lastName;
console.log(fullName); // Output: John Doe
// Using template literals
@@ -78,7 +77,7 @@ console.log(fullNameTemplate); // Output: John Doe
String interpolation allows you to embed expressions within a string. You can use template literals to interpolate variables and expressions directly within the string:
```javascript title="app.js"
-let name = 'Alice';
+let name = "Alice";
let greeting = `Hello, ${name}!`;
console.log(greeting); // Output: Hello, Alice!
@@ -111,20 +110,20 @@ JavaScript provides built-in methods for working with strings. Here are some com
Here's an example using some of these string methods:
```javascript title="app.js"
-let text = 'Hello, World!';
+let text = "Hello, World!";
let substring = text.substring(0, 5); // Extracts 'Hello'
let uppercaseText = text.toUpperCase(); // Converts text to uppercase
-let replacedText = text.replace('World', 'JavaScript'); // Replaces 'World' with 'JavaScript'
-let splitText = text.split(','); // Splits text into an array ['Hello', ' World!']
-let includesText = text.includes('Hello'); // Checks if text contains 'Hello' (returns true)
-let indexOfText = text.indexOf('World'); // Returns the index of 'World' (returns 7)
+let replacedText = text.replace("World", "JavaScript"); // Replaces 'World' with 'JavaScript'
+let splitText = text.split(","); // Splits text into an array ['Hello', ' World!']
+let includesText = text.includes("Hello"); // Checks if text contains 'Hello' (returns true)
+let indexOfText = text.indexOf("World"); // Returns the index of 'World' (returns 7)
let length = text.length; // Returns the length of the text (returns 13)
let charAt = text.charAt(7); // Returns the character at index 7 (returns 'W')
-let startsWith = text.startsWith('Hello'); // Checks if text starts with 'Hello' (returns true)
-let endsWith = text.endsWith('World!'); // Checks if text ends with 'World!' (returns true)
+let startsWith = text.startsWith("Hello"); // Checks if text starts with 'Hello' (returns true)
+let endsWith = text.endsWith("World!"); // Checks if text ends with 'World!' (returns true)
let repeatText = text.repeat(2); // Repeats text twice ('Hello, World!Hello, World!')
-let paddedText = text.padStart(20, '*'); // Pads text with '*' until it reaches a length of 20 from the start
-let trimmedText = ' Hello, World! '.trim(); // Removes whitespace from the beginning and end of the text
+let paddedText = text.padStart(20, "*"); // Pads text with '*' until it reaches a length of 20 from the start
+let trimmedText = " Hello, World! ".trim(); // Removes whitespace from the beginning and end of the text
console.log(substring);
console.log(uppercaseText);
@@ -151,4 +150,4 @@ Strings are versatile and powerful data types in JavaScript, and mastering strin
## Conclusion
-Strings are a fundamental data type in JavaScript used to represent text data. You can create strings using single quotes, double quotes, or backticks. Strings support various operations such as concatenation, interpolation, and methods for manipulating string data.
\ No newline at end of file
+Strings are a fundamental data type in JavaScript used to represent text data. You can create strings using single quotes, double quotes, or backticks. Strings support various operations such as concatenation, interpolation, and methods for manipulating string data.
diff --git a/docs/javascript/data-types/primitive-types/undefined.md b/docs/javascript/data-types/primitive-types/undefined.md
index de8ff26e0..f48b0b90b 100644
--- a/docs/javascript/data-types/primitive-types/undefined.md
+++ b/docs/javascript/data-types/primitive-types/undefined.md
@@ -41,7 +41,7 @@ You can also use the `typeof` operator to check if a variable is `undefined`. Th
```javascript title="app.js"
let undefinedValue;
-console.log(typeof undefinedValue === 'undefined'); // Output: true
+console.log(typeof undefinedValue === "undefined"); // Output: true
```
## Common Operations with Undefined Values
@@ -73,7 +73,7 @@ console.log(noReturnValue()); // Output: undefined
You can delete properties from an object using the `delete` operator. After deleting a property, accessing the property will return `undefined`. Here's an example:
```javascript title="app.js"
-let person = { name: 'Alice', age: 30 };
+let person = { name: "Alice", age: 30 };
delete person.age;
@@ -85,9 +85,9 @@ console.log(person.age); // Output: undefined
You can check if an object has a property with an `undefined` value using the `in` operator. The `in` operator returns `true` if the property exists in the object, even if its value is `undefined`. Here's an example:
```javascript title="app.js"
-let person = { name: 'Alice', age: undefined };
+let person = { name: "Alice", age: undefined };
-console.log('age' in person); // Output: true
+console.log("age" in person); // Output: true
```
### Passing Undefined Arguments
@@ -99,7 +99,7 @@ function greet(name, message) {
console.log(`Hello, ${name}! ${message}`);
}
-greet('Alice'); // Output: Hello, Alice! undefined
+greet("Alice"); // Output: Hello, Alice! undefined
```
In this example, the `greet` function is called with one argument (`'Alice'`) instead of two. The `message` parameter is assigned the value `undefined` because it is missing in the function call.
@@ -108,4 +108,4 @@ Understanding the `undefined` data type and how it behaves in JavaScript is esse
## Conclusion
-In this tutorial, you learned about the `undefined` data type in JavaScript, how to create `undefined` values, and common operations with `undefined` values. You also explored various scenarios where `undefined` values are used and how to handle them effectively in your JavaScript code.
\ No newline at end of file
+In this tutorial, you learned about the `undefined` data type in JavaScript, how to create `undefined` values, and common operations with `undefined` values. You also explored various scenarios where `undefined` values are used and how to handle them effectively in your JavaScript code.