diff --git a/docs/content/Configuration/Downstream/Superset.mdx b/docs/content/Configuration/Downstream/Superset.mdx
index eaaf41a9b21ac..a64f8f19a8262 100644
--- a/docs/content/Configuration/Downstream/Superset.mdx
+++ b/docs/content/Configuration/Downstream/Superset.mdx
@@ -135,7 +135,6 @@ To allow queries from Superset to match pre-aggregations in Cube, [the
must be set to `true` in the pre-aggregation definition. This is because
Superset uses loose date ranges when generating SQL queries.
-[ref-cube-getting-started-docker]: https://cube.dev/docs/getting-started/docker
[ref-getting-started]: /cloud/getting-started
[ref-schema-ref-preagg-allownonstrict]:
/schema/reference/pre-aggregations#allow-non-strict-date-range-match
diff --git a/docs/content/Getting-Started/Cloud/01-Overview.mdx b/docs/content/Getting-Started/Cloud/01-Overview.mdx
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..d4785a2f0274a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/content/Getting-Started/Cloud/01-Overview.mdx
@@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
+---
+title: Getting started with Cube Cloud
+permalink: /getting-started/cloud/overview
+category: Getting Started
+subCategory: Cube Cloud
+menuOrder: 2
+---
+
+First, we'll create a new deployment, connect it to a database, and generate a
+data model from it. Then, we'll run queries using the Developer Playground and
+APIs. Finally, we'll add a pre-aggregation to optimize query latency down to
+milliseconds.
+
+This guide will walk you through the following tasks:
+
+- [Create a new deployment](/getting-started/cloud/create-a-deployment)
+- [Generate a data model from a connected data source](/getting-started/cloud/generate-models)
+- [Run queries using the Developer Playground and APIs](/getting-started/cloud/query-data)
+- [Add a pre-aggregation to optimize query performance](/getting-started/cloud/add-a-pre-aggregation)
+
+If you'd prefer to run Cube locally, then you can refer to [Getting Started
+using Cube Core][ref-getting-started-core-overview] instead.
+
+[ref-getting-started-core-overview]: /getting-started/core/overview
diff --git a/docs/content/Getting-Started/Cloud/02-Create-a-deployment.mdx b/docs/content/Getting-Started/Cloud/02-Create-a-deployment.mdx
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..ad46495d4c6d1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/content/Getting-Started/Cloud/02-Create-a-deployment.mdx
@@ -0,0 +1,125 @@
+---
+title: Create a deployment
+permalink: /getting-started/cloud/create-a-deployment
+category: Getting Started
+subCategory: Cube Cloud
+menuOrder: 3
+---
+
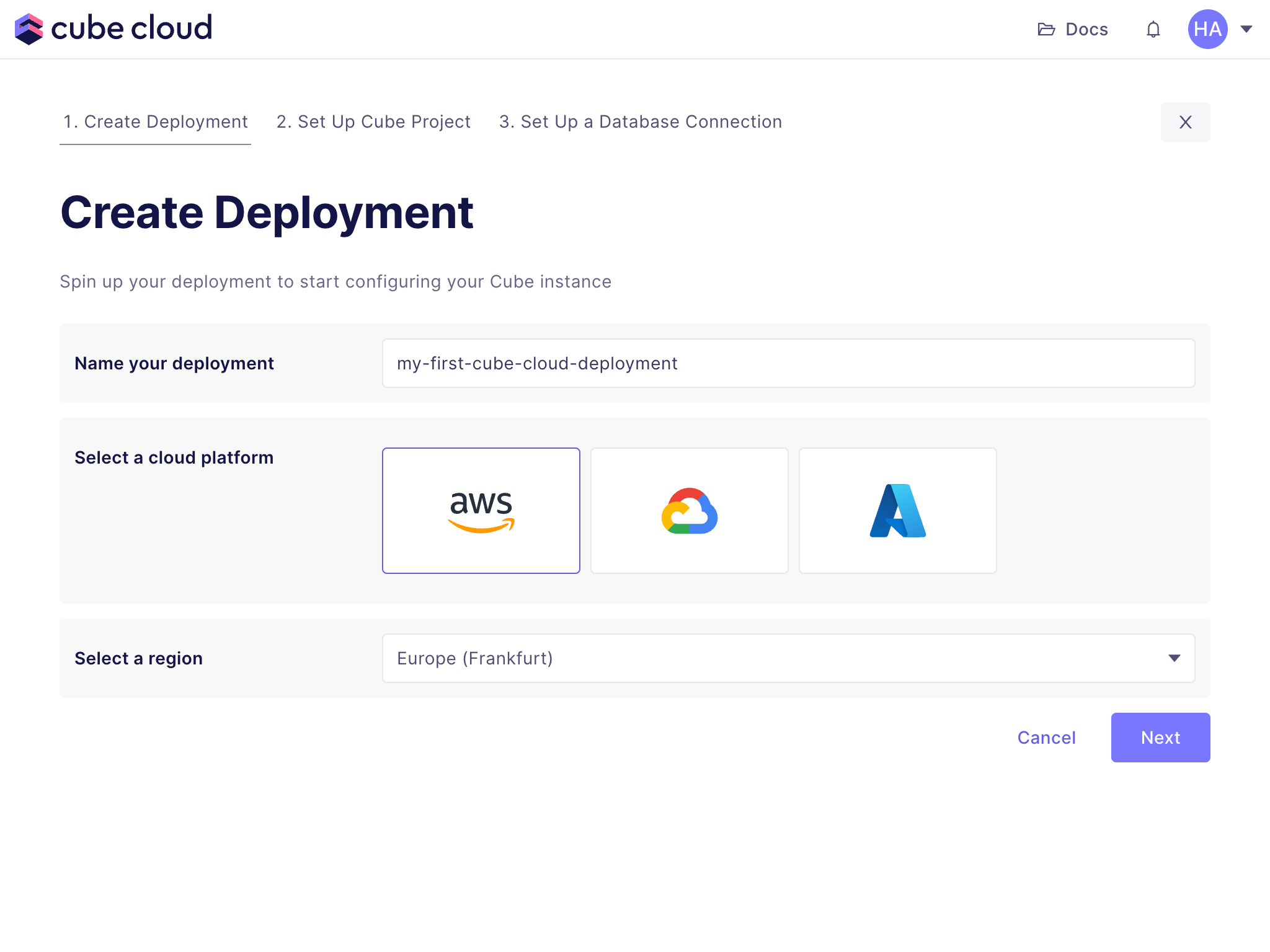
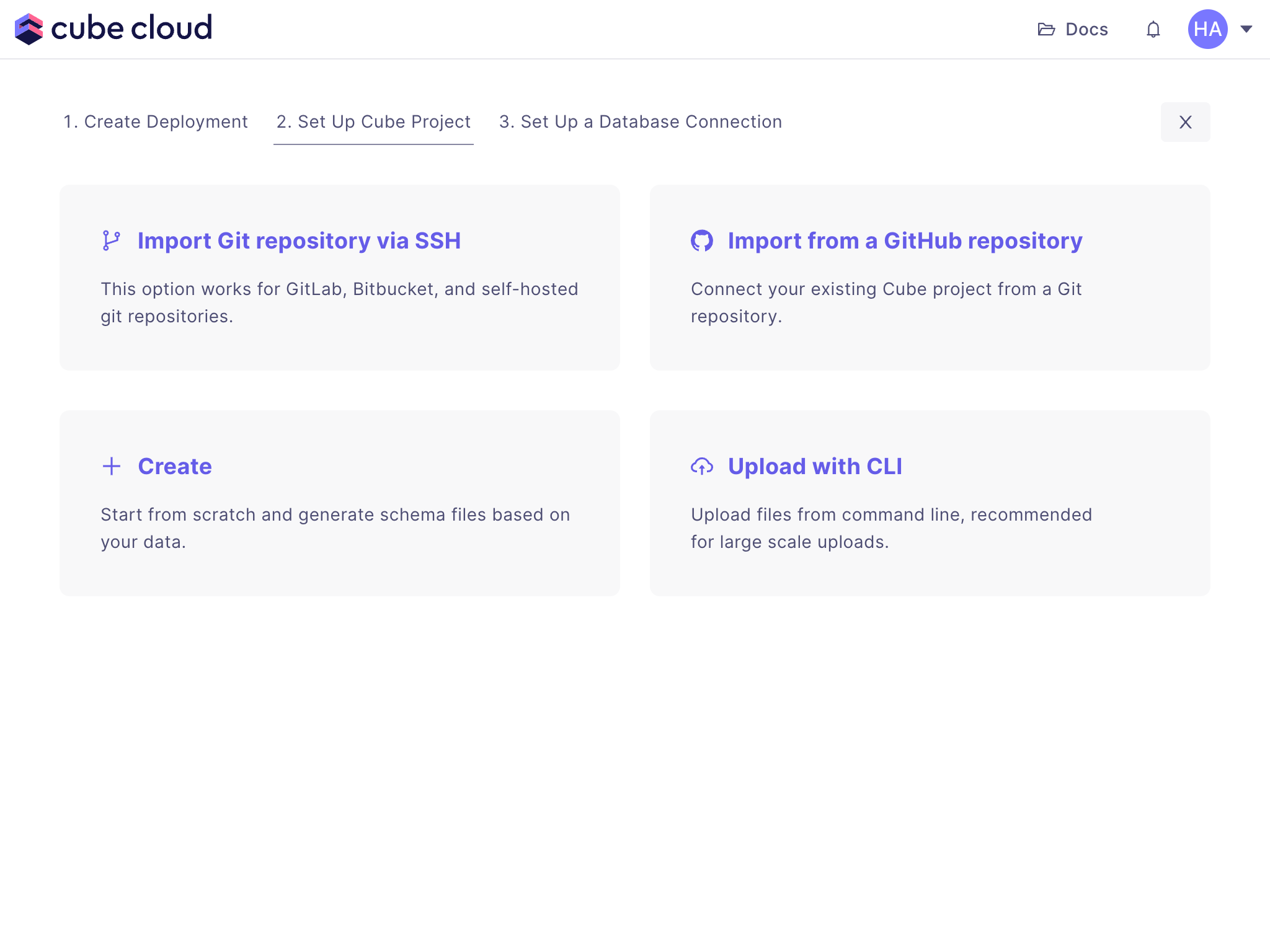
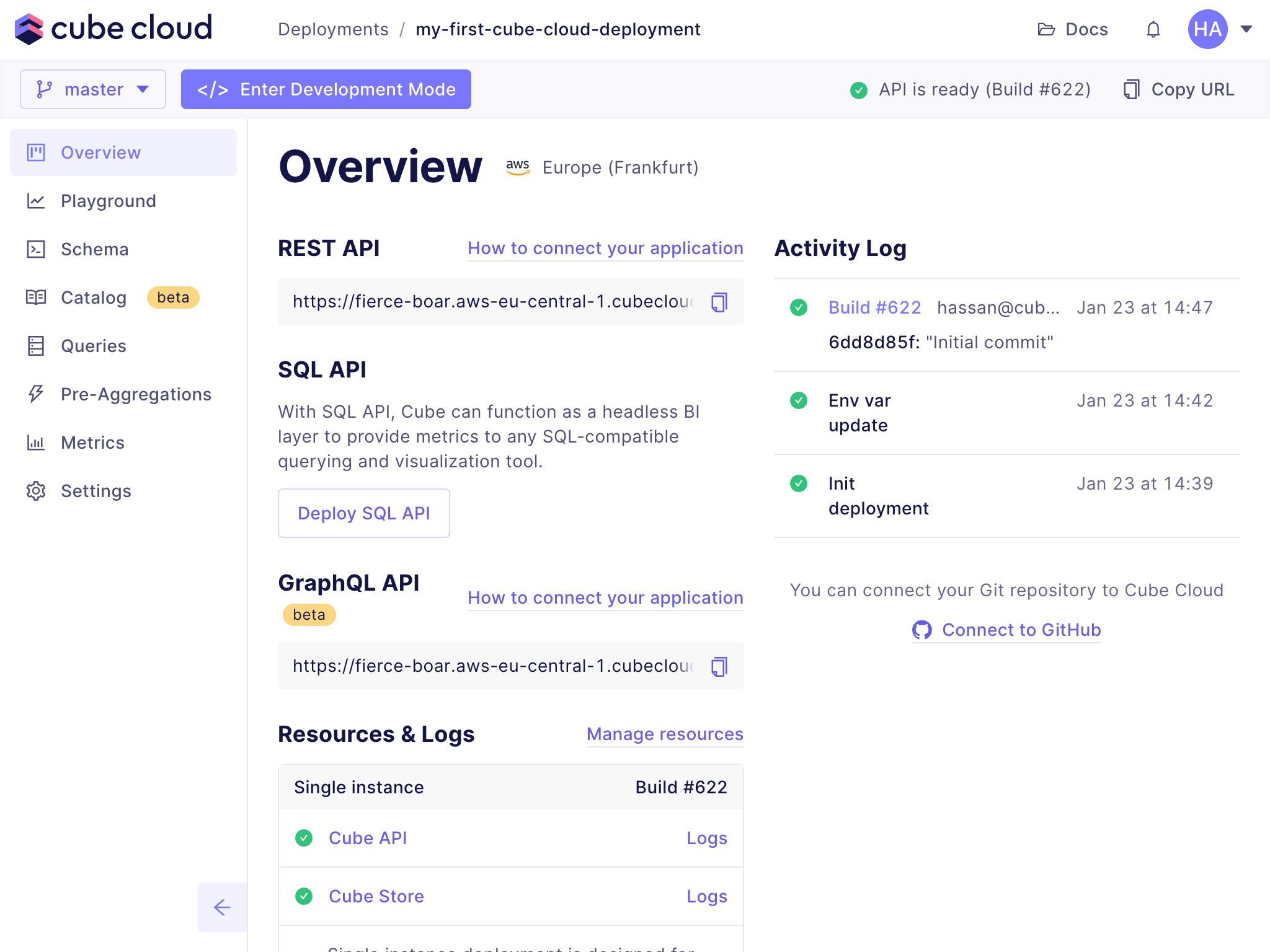
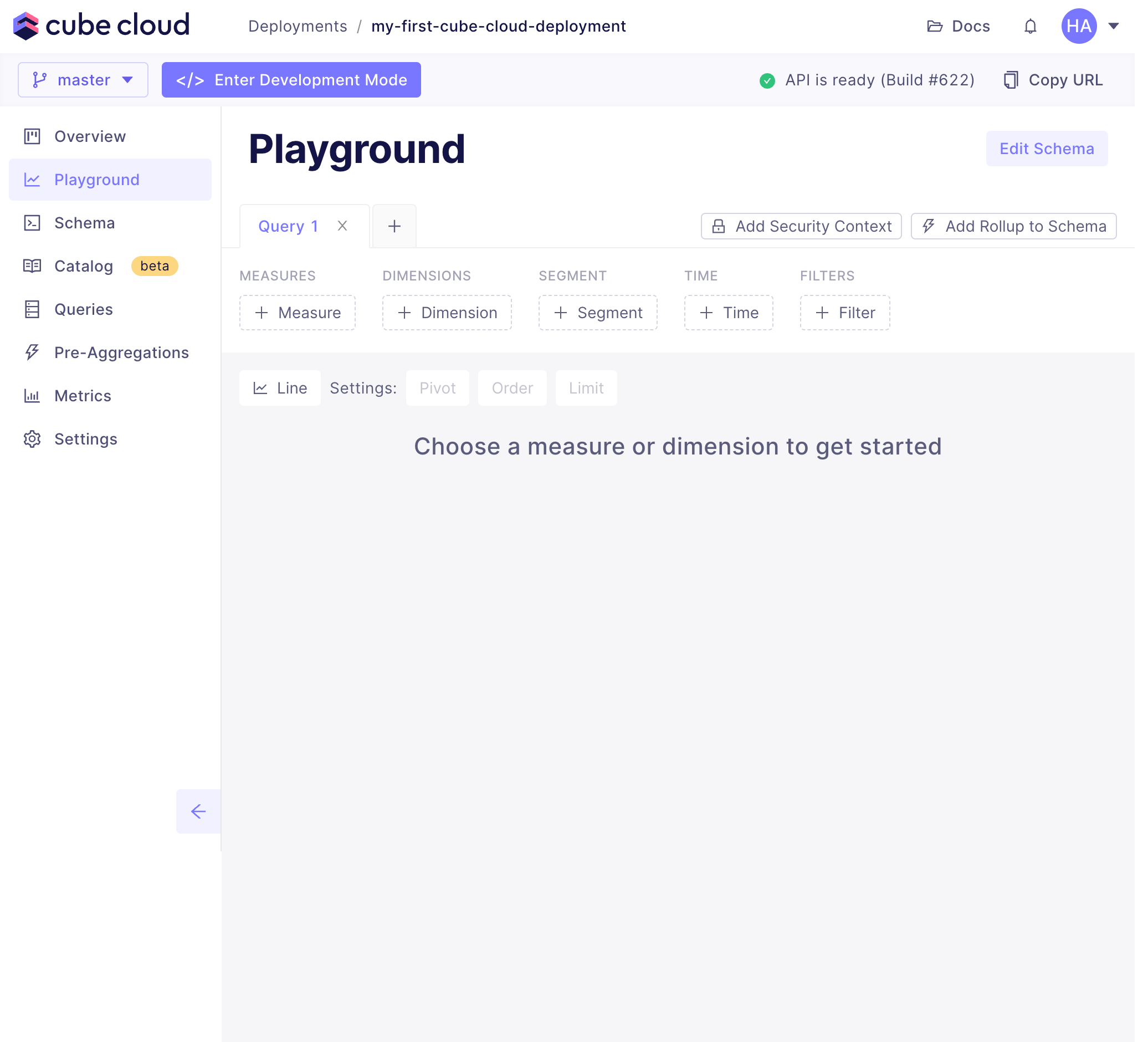
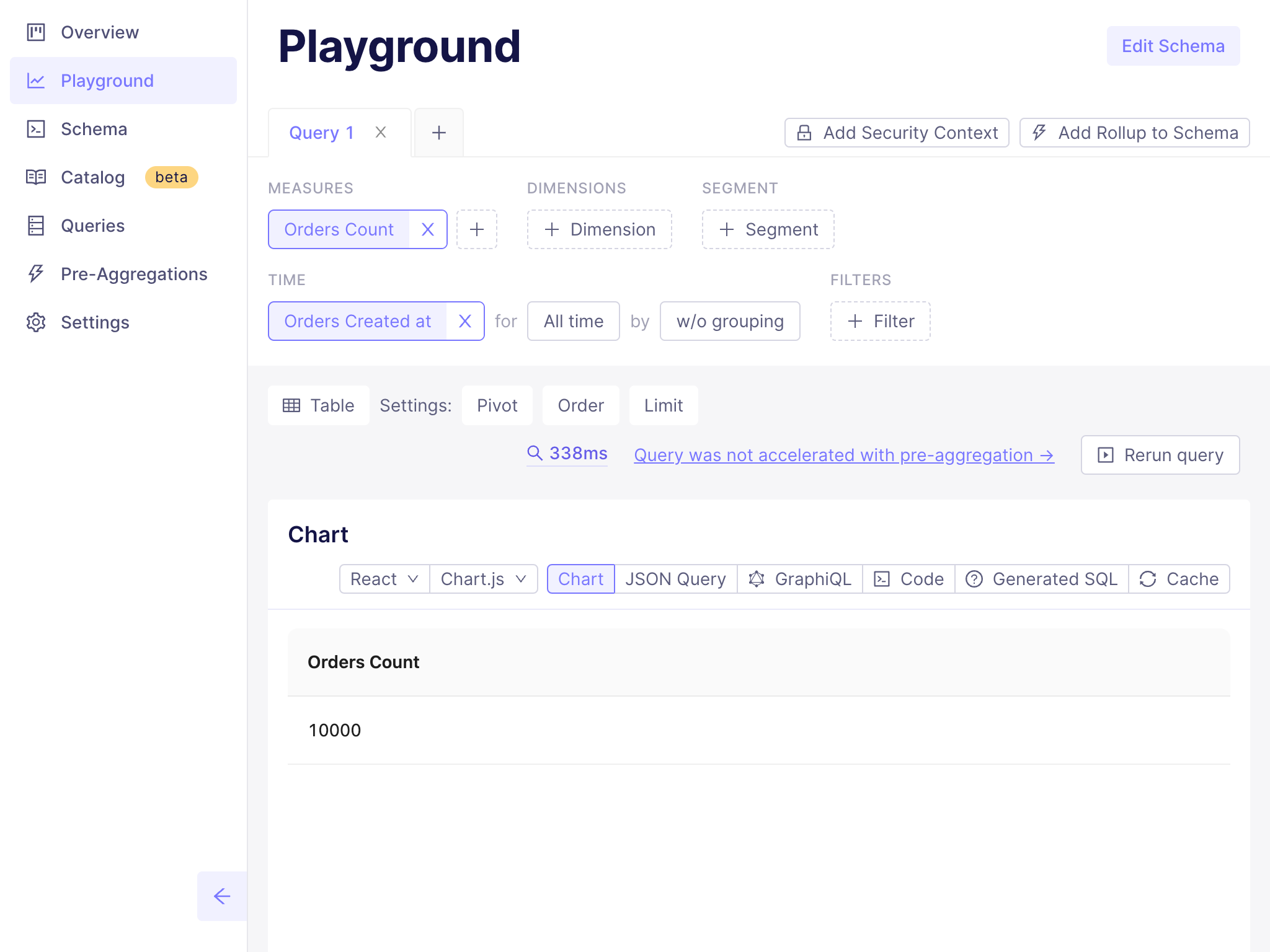
+In this step, we will create a new deployment in Cube Cloud. A deployment
+represents a data model, configuration, and managed infrastructure. We will use
+it to connect a data source and generate data models.
+
+## Create an account
+
+To continue with this guide, you'll need to have a Cube Cloud account. If you
+don't have one yet, [click here to sign up][cube-cloud-signup] for free.
+
+## Create a deployment
+
+First, [sign in to your Cube Cloud account][cube-cloud-signin]. Then,
+click Create Deployment:
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Field | Value |
+| -------- | ------------------ |
+| Host | `demo-db.cube.dev` |
+| Port | `5432` |
+| Database | `ecom` |
+| Username | `cube` |
+| Password | `12345` |
+
+
+
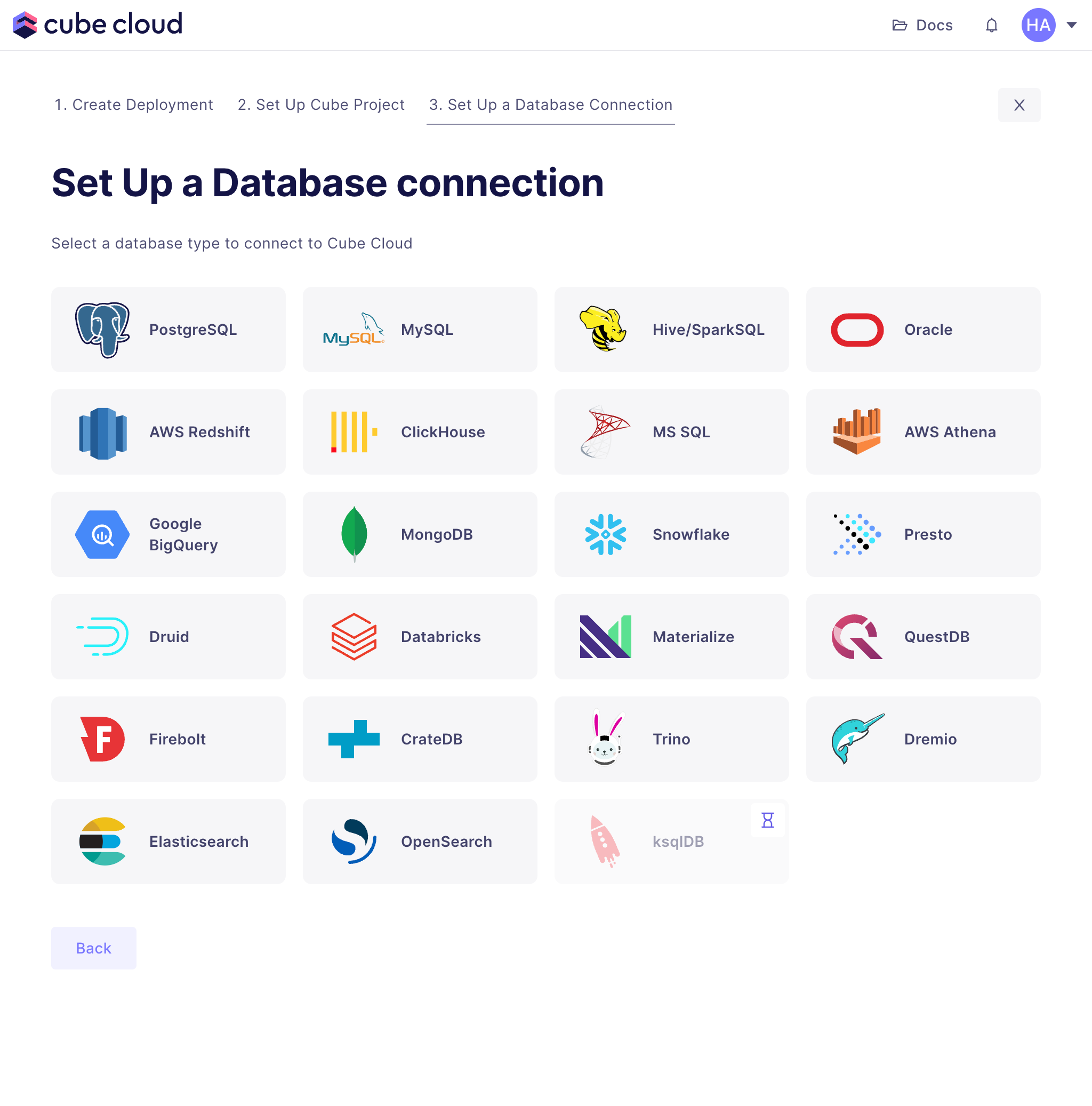
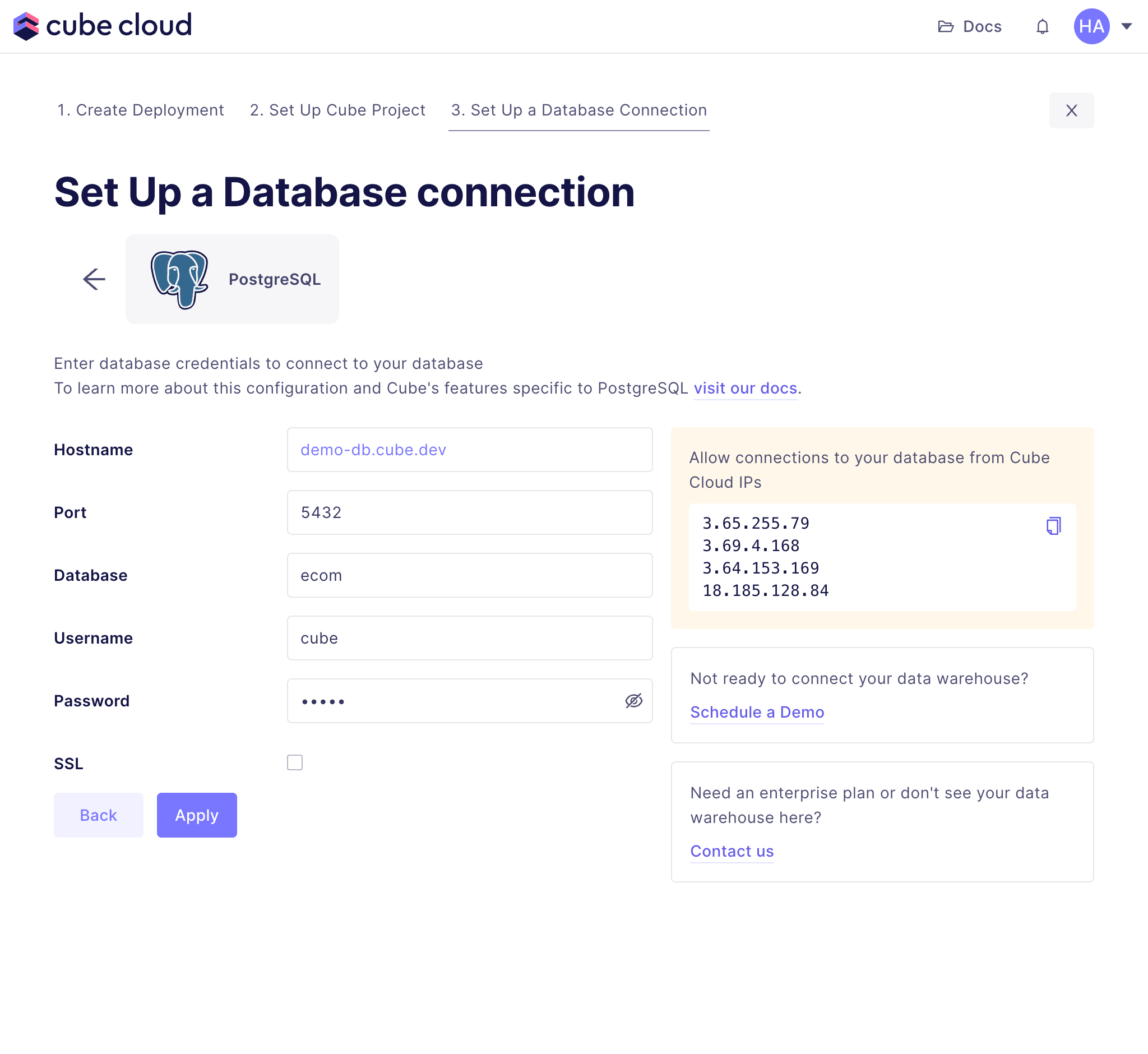
+After selecting the data source, enter valid credentials for it and
+click Apply. Check the [Connecting to Databases][ref-conf-db]
+page for more details on specific data sources.
+
+
+
+
+

+
+

+
+

+
+

+
+

+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
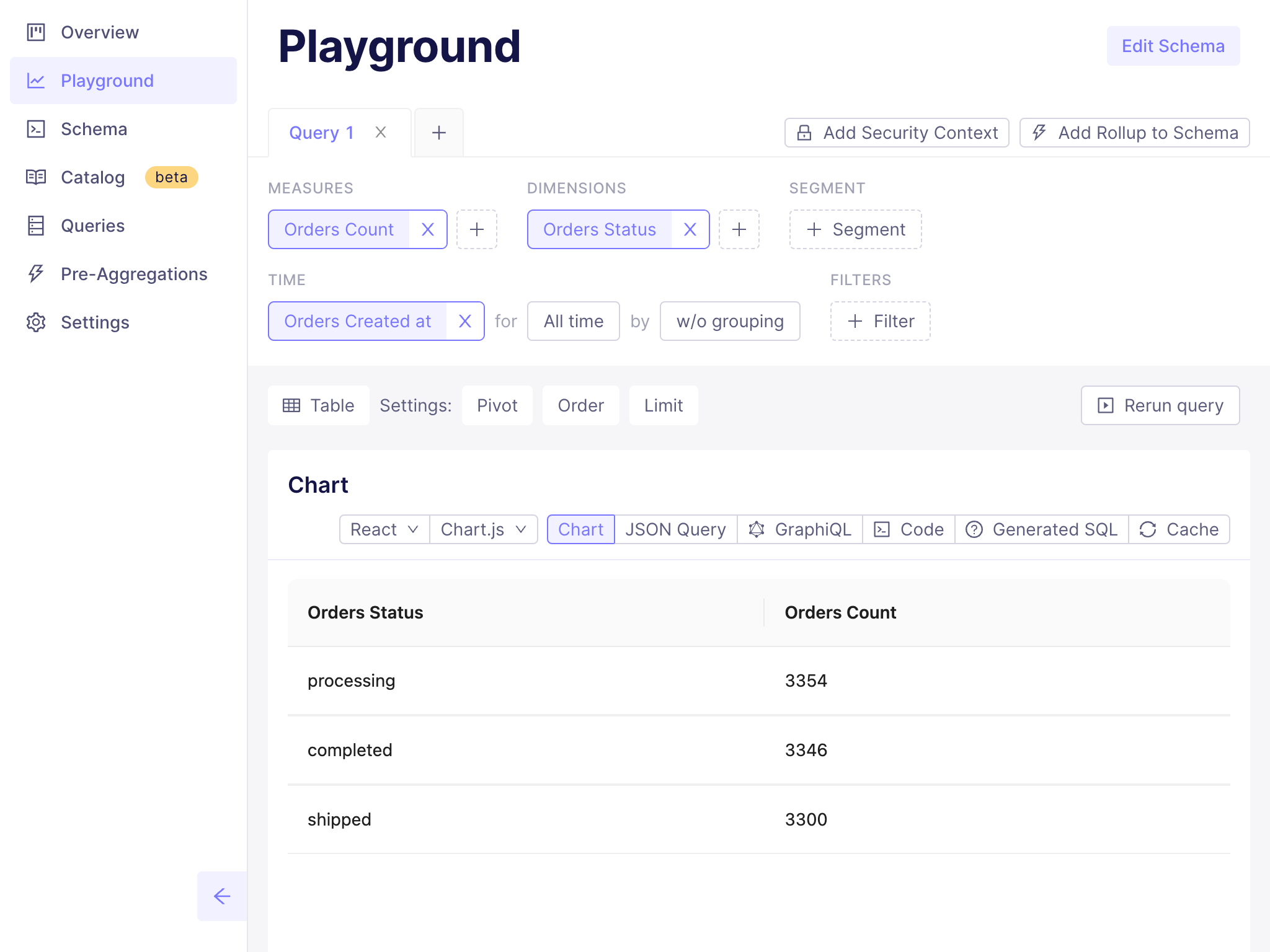
+
+

+
+
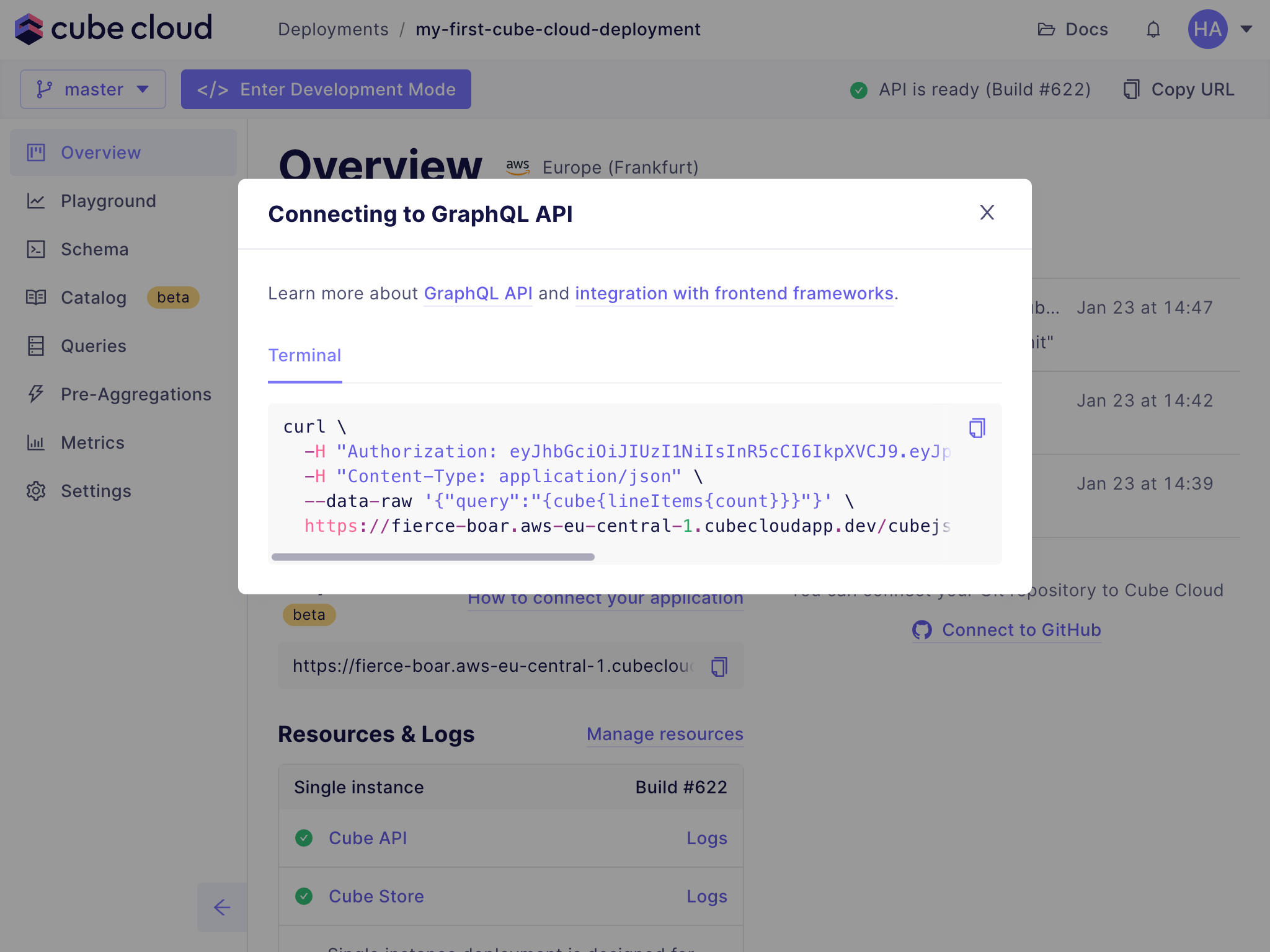
+
+

+
+
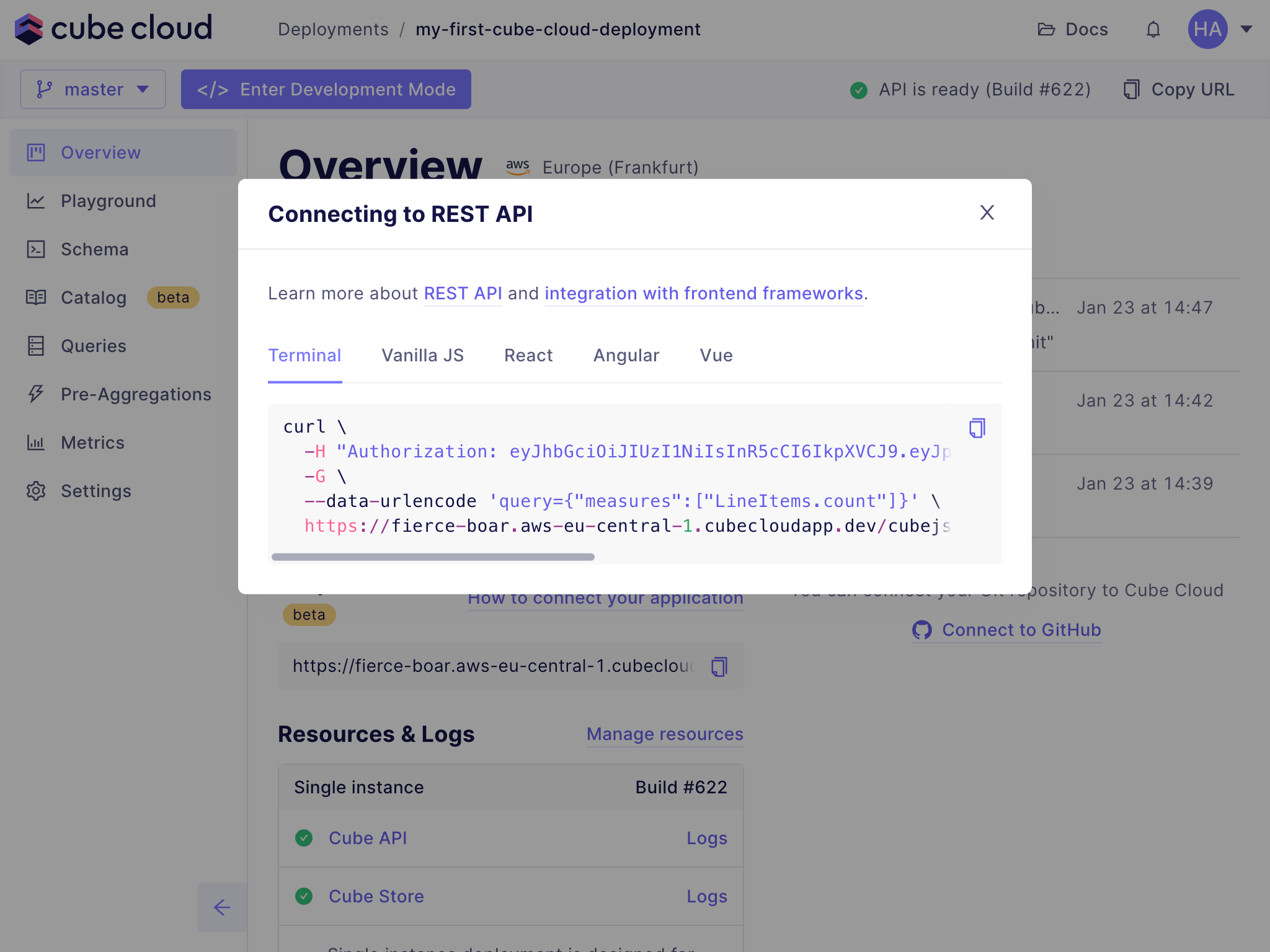
+
+
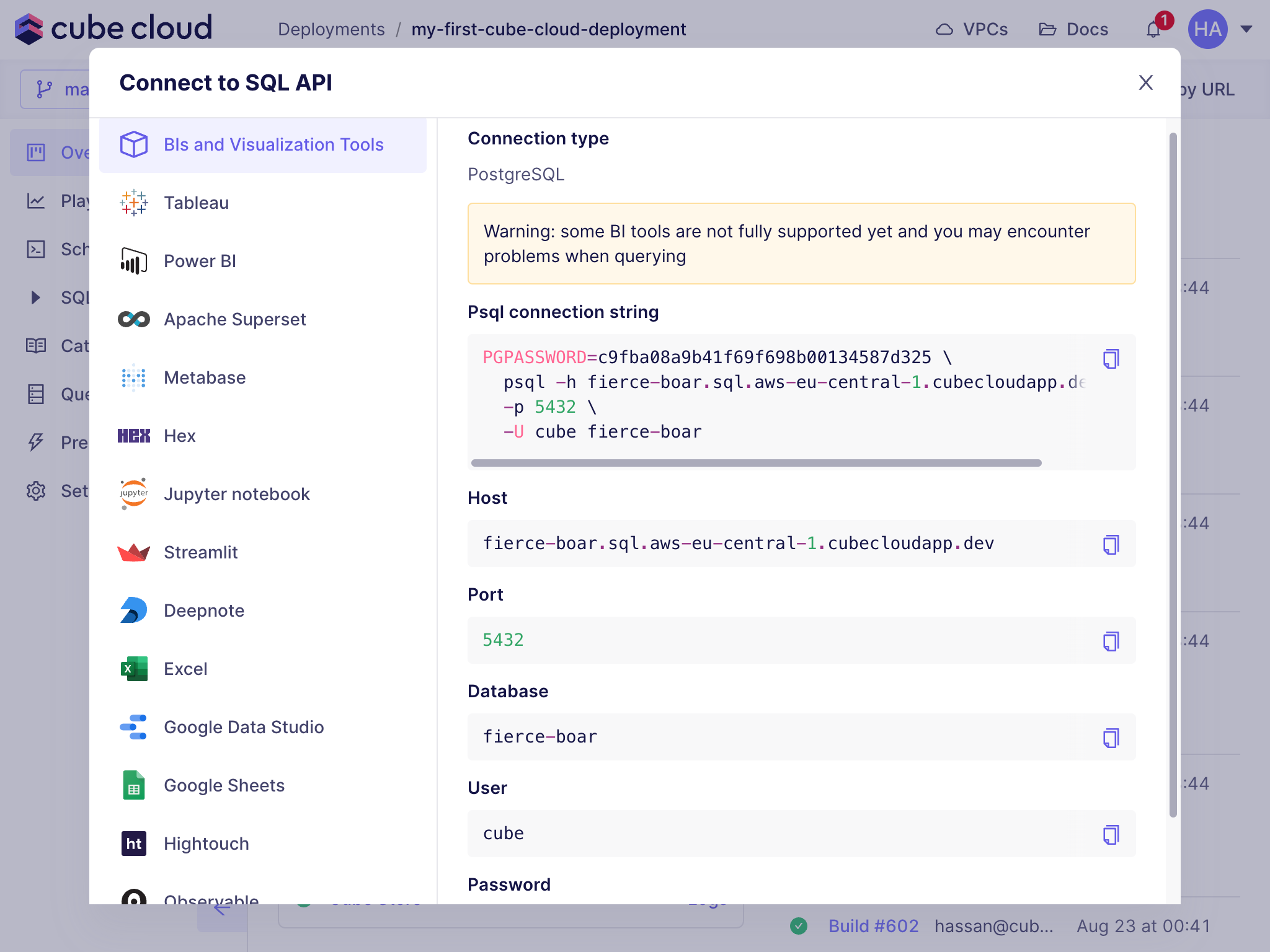
+
+
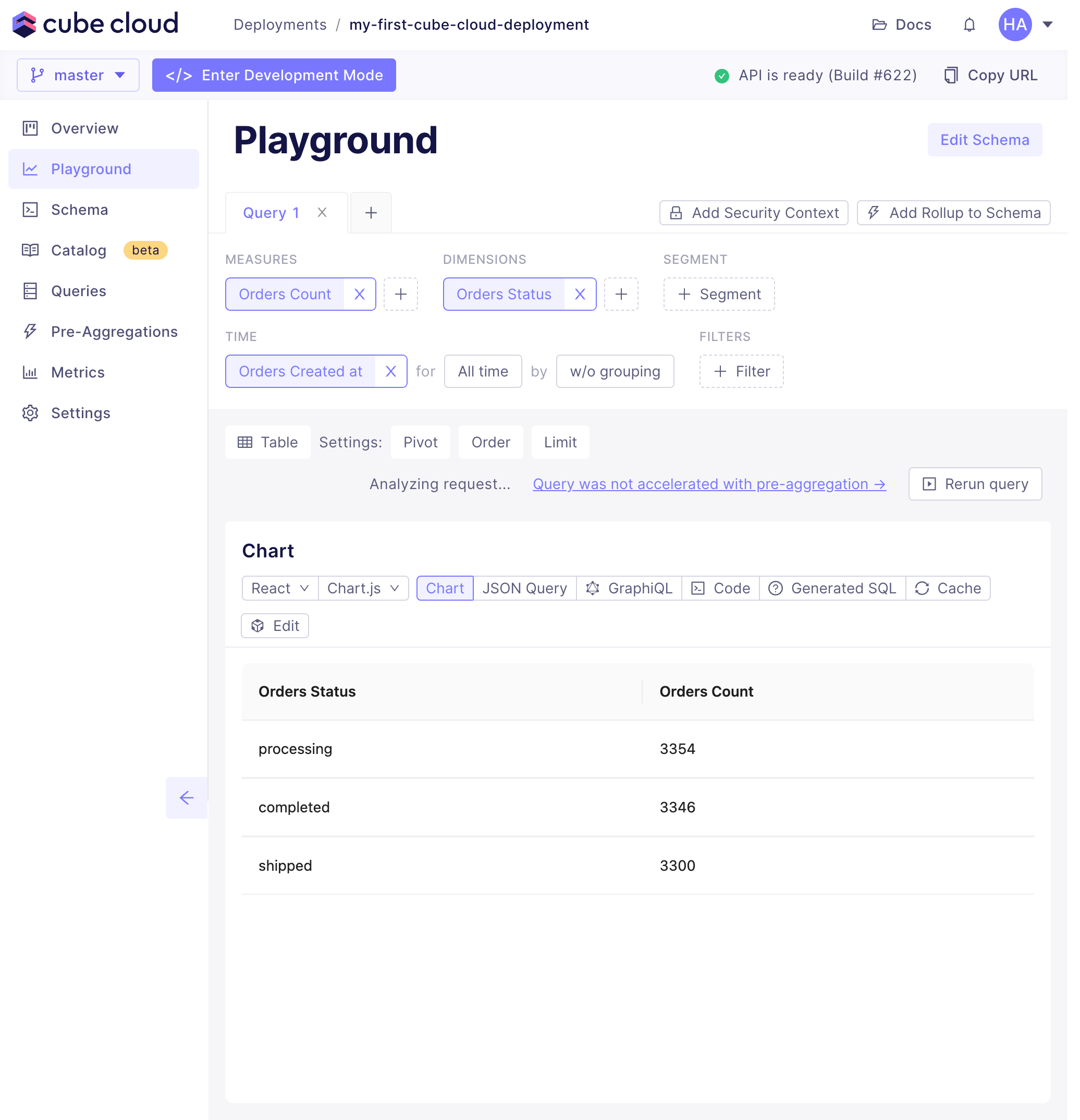
+
+
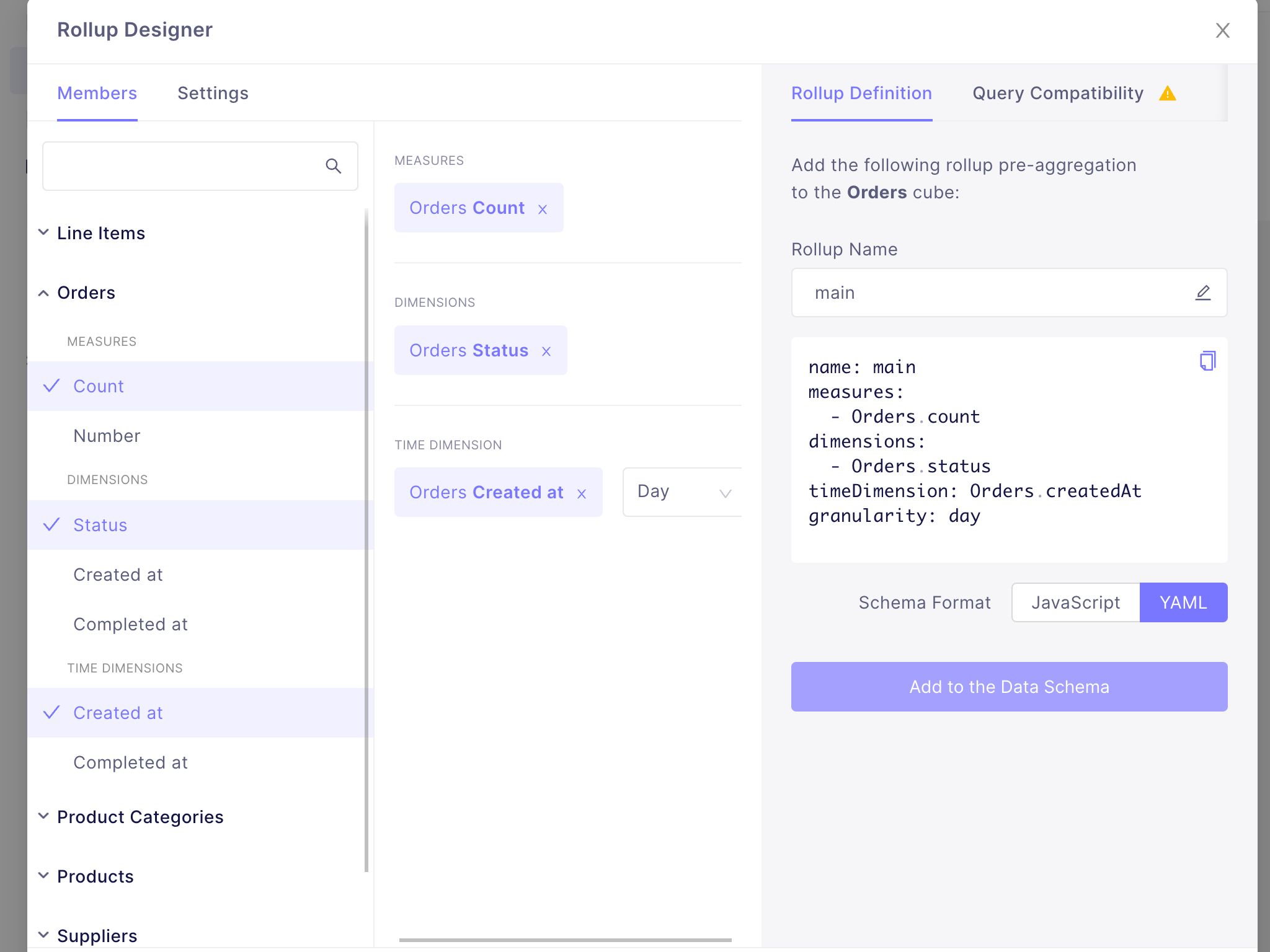
+
+
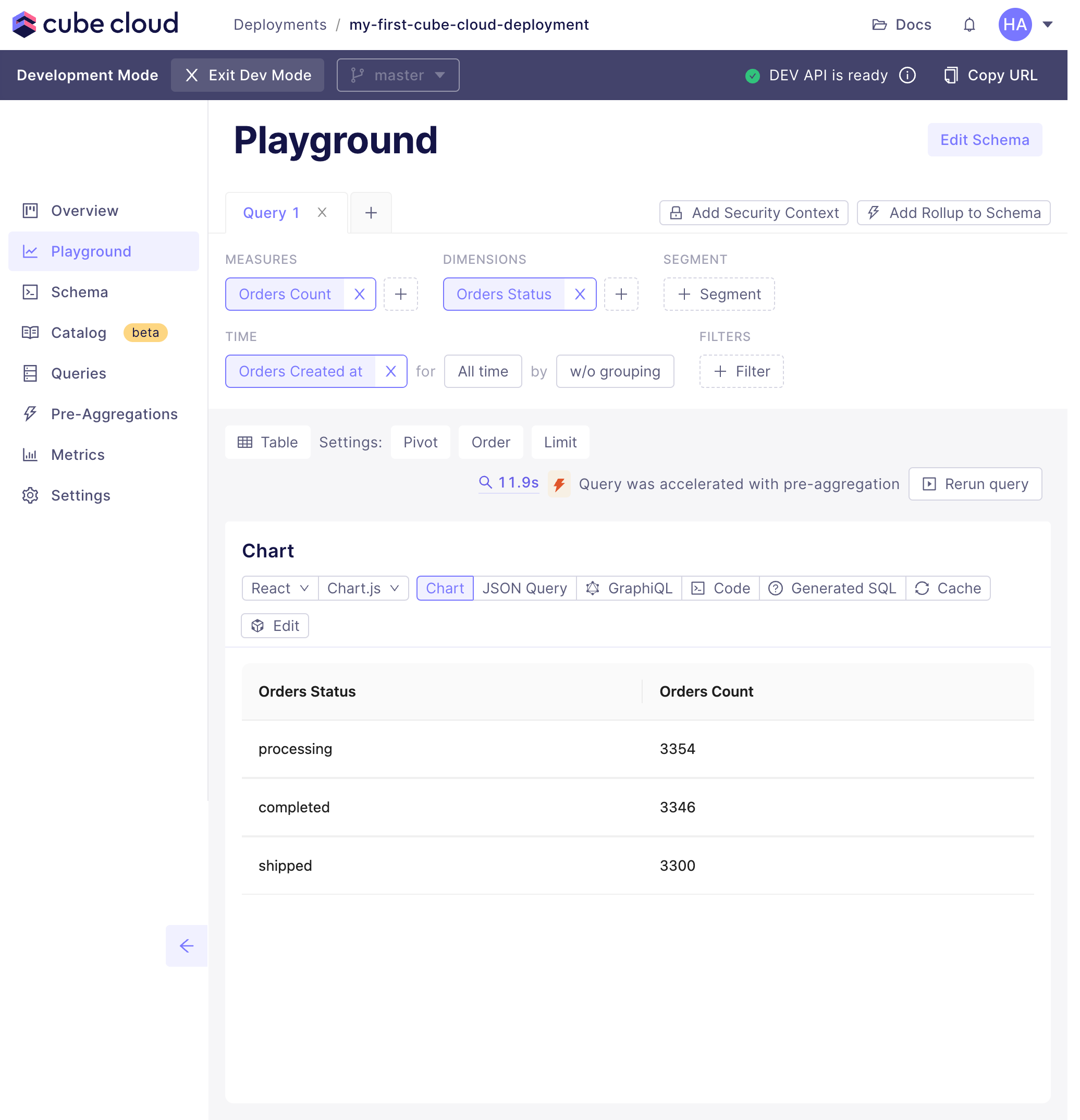
+
+

+
+
+| Field | Value |
+| -------- | ------------------ |
+| Host | `demo-db.cube.dev` |
+| Port | `5432` |
+| Database | `ecom` |
+| Username | `cube` |
+| Password | `12345` |
+
+
+
+After selecting the data source, enter valid credentials for it and
+click Apply. Check the [Connecting to Databases][ref-conf-db]
+page for more details on specific data sources.
+
+
+

+
+

+
+

+
+

+
+

+
+

+
+

+
+

+
-

-
-

-
-

-
-

-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-```
-
-#### Angular
-
-Add CubejsClientModule to your `app.module.ts` file:
-
-```typescript
-import { CubejsClientModule } from '@cubejs-client/ngx';
-import { environment } from '../../environments/environment';
-
-const cubejsOptions = {
- token: environment.CUBEJS_API_TOKEN,
- options: { apiUrl: environment.CUBEJS_API_URL }
-};
-
-@NgModule({
- declarations: [
- ...
- ],
- imports: [
- ...,
- CubejsClientModule.forRoot(cubejsOptions)
- ],
- providers: [...],
- bootstrap: [...]
-})
-export class AppModule { }
-```
-
-Then you can inject `CubejsClient` into your components or services:
-
-```typescript
-import { CubejsClient } from '@cubejs-client/ngx';
-
-export class AppComponent {
- constructor(private cubejs: CubejsClient) {}
-
- ngOnInit() {
- this.cubejs
- .load({
- measures: ['some_measure'],
- })
- .subscribe(
- (resultSet) => {
- this.data = resultSet.chartPivot();
- },
- (err) => console.log('HTTP Error', err)
- );
- }
-}
-```
-
-## 4. Deploy to Production
-
-Cube has first-class deployment support for [Docker][link-docker]:
-
-```bash{outputLines: 2-12}
-docker run --rm \
- --name cubejs-docker-demo \
- -e CUBEJS_API_SECRET= \
- -e CUBEJS_DB_HOST= \
- -e CUBEJS_DB_NAME= \
- -e CUBEJS_DB_USER= \
- -e CUBEJS_DB_PASS= \
- -e CUBEJS_DB_TYPE=postgres \
- --volume "$(pwd):/cube/conf" \
- /cubejs-docker-demo
-```
-
-For more information on deploying our official Docker image, please consult the
-[Deployment Guide][ref-docker-deployment-guide].
-
-[link-docker]: https://www.docker.com/
-[link-nodejs]: https://nodejs.org/en/
-[ref-dev-playground]: /dev-tools/dev-playground
-[ref-frontend-intro]: /frontend-introduction
-[ref-docker-deployment-guide]: /deployment/platforms/docker
-[ref-connecting-to-the-database]: /connecting-to-the-database
-[ref-cubejs-schema]: /schema/getting-started
diff --git a/docs/content/Getting-Started/Overview.mdx b/docs/content/Getting-Started/Overview.mdx
index 44ade2950fda7..2ea4240c14233 100644
--- a/docs/content/Getting-Started/Overview.mdx
+++ b/docs/content/Getting-Started/Overview.mdx
@@ -1,29 +1,32 @@
---
-title: Getting Started
+title: Overview
permalink: /getting-started
category: Getting Started
menuOrder: 1
-isDisableFeedbackBlock: true
+isDisableFeedbackBlock: false
---
-You can get started with Cube locally or self-host it with Docker.
+You can get started with Cube in one of two ways.
-Alternatively, you can get started with [Cube Cloud](https://cube.dev/cloud/).
-It provides managed experience for Cube and has a free tier for development
-projects and proofs of concept.
+We recommend using [Cube Cloud][cube-cloud], our managed platform for Cube,
+because it's the easiest way to build, test, deploy, and manage Cube projects.
+Cube Cloud includes features such as collaboration for teams, a web-based IDE,
+auto-scaling, and observability. Cube Cloud also comes with a free tier for
+development and proof-of-concept projects.
-
-
+Alternatively, you can run Cube on your own infrastructure.
+
+
+
-There's also a legacy option to get started with
-[Node.js](getting-started/nodejs).
+[cube-cloud]: https://cube.dev/cloud/
diff --git a/docs/content/SQL-API/Getting-Started.mdx b/docs/content/SQL-API/Getting-Started.mdx
deleted file mode 100644
index af949f8a21717..0000000000000
--- a/docs/content/SQL-API/Getting-Started.mdx
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,73 +0,0 @@
----
-title: Getting Started
-category: SQL API
-permalink: /backend/sql/getting-started
-menuOrder: 2
----
-
-## Cube Cloud
-
-The first step to get started with the SQL API in Cube Cloud is to create a
-deployment. You can follow this
-[step-by-step guide on creating a deployment within Cube Cloud](/cloud/getting-started/create).
-
-Once the deployment is ready, click **How to connect** link on the Overview
-page. It will open a modal with instructions on different ways to connect to
-Cube. Navigate to the SQL API tab and enable the SQL API.
-
-Once it is enabled, you should see a screen like the one below with your
-connection credentials.
-
-
-
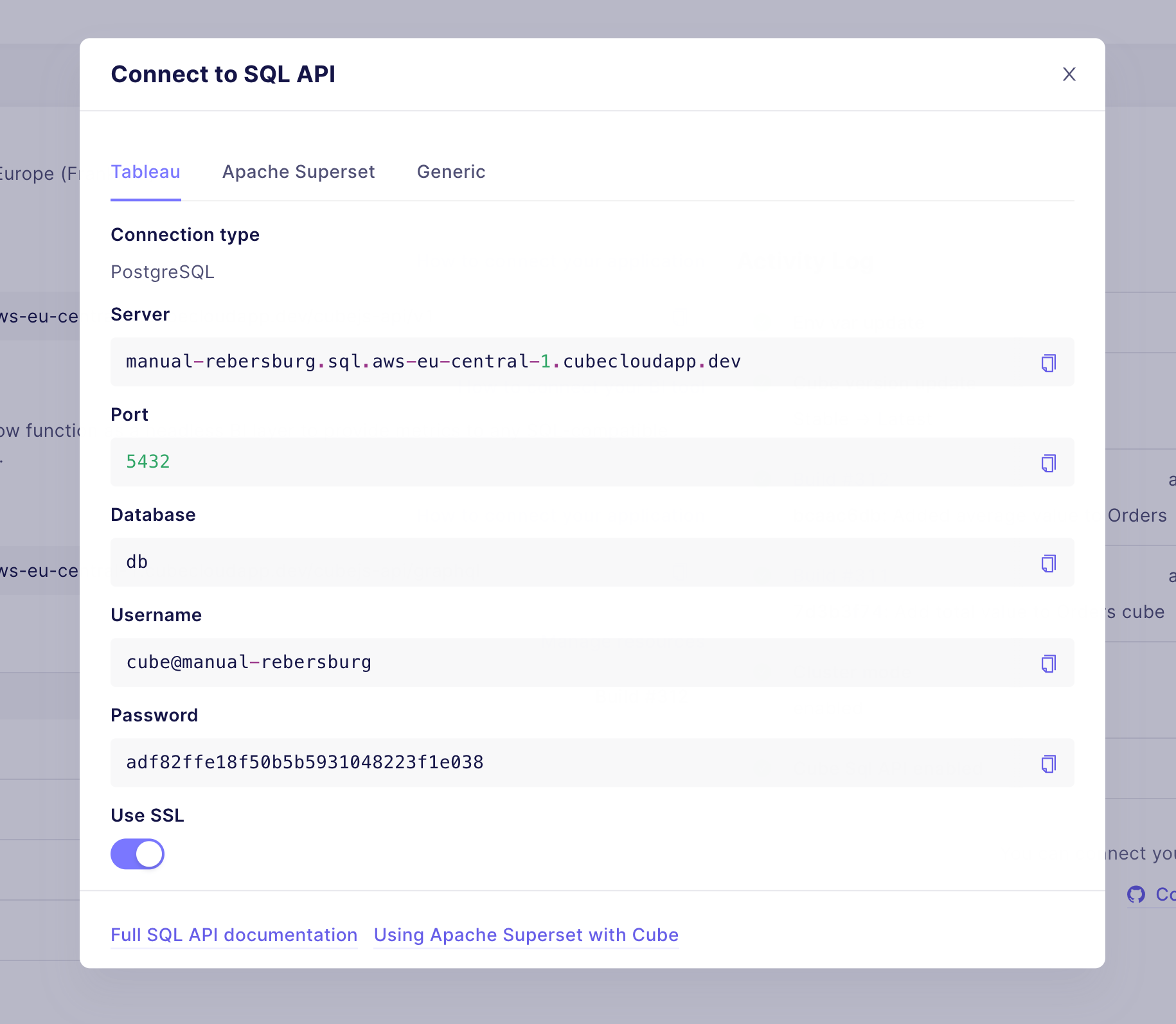
-
{children}
);
@@ -68,6 +69,7 @@ const components = {
h3: ScrollSpyH3,
h4: MyH4,
CodeTabs,
+ Btn: InlineButton,
};
const MDX = (props) => (
diff --git a/docs/static/styles/_layout.scss b/docs/static/styles/_layout.scss
index 2ffe4fb4c7ecb..c3a188fb579b4 100644
--- a/docs/static/styles/_layout.scss
+++ b/docs/static/styles/_layout.scss
@@ -87,7 +87,7 @@ a {
img:not(.mainTabImg) {
border: 1px solid #ECECF0;
border-radius: 4px;
- max-width: 100%;
+ width: 100%;
margin: 24px 0;
box-shadow: none !important;
}
diff --git a/docs/static/styles/variables.scss b/docs/static/styles/variables.scss
index 471e908e57731..cc2d9cc8c851e 100644
--- a/docs/static/styles/variables.scss
+++ b/docs/static/styles/variables.scss
@@ -4,6 +4,7 @@ $purple-04: #CAC9FF;
$purple-text: #665DE8;
$dark-01: #141446;
$dark-04: #A1A1B5;
+$dark-05: #E5E5EC;
$pink: #FF6492;
$pink-02: #FF83A8;
$pink-04: #FFC1D3;