diff --git a/solution/2900-2999/2946.Matrix Similarity After Cyclic Shifts/README.md b/solution/2900-2999/2946.Matrix Similarity After Cyclic Shifts/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..aac4e770111a1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2900-2999/2946.Matrix Similarity After Cyclic Shifts/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,96 @@
+# [2946. 循环移位后的矩阵相似检查](https://leetcode.cn/problems/matrix-similarity-after-cyclic-shifts)
+
+[English Version](/solution/2900-2999/2946.Matrix%20Similarity%20After%20Cyclic%20Shifts/README_EN.md)
+
+## 题目描述
+
+
+
+给你一个大小为 m x n 的整数矩阵 mat 和一个整数 k 。请你将矩阵中的 奇数 行循环 右 移 k 次,偶数 行循环 左 移 k 次。
+
+如果初始矩阵和最终矩阵完全相同,则返回 true ,否则返回 false 。
+
+
+
+示例 1:
+
+
+输入:mat = [[1,2,1,2],[5,5,5,5],[6,3,6,3]], k = 2
+输出:true
+解释:
+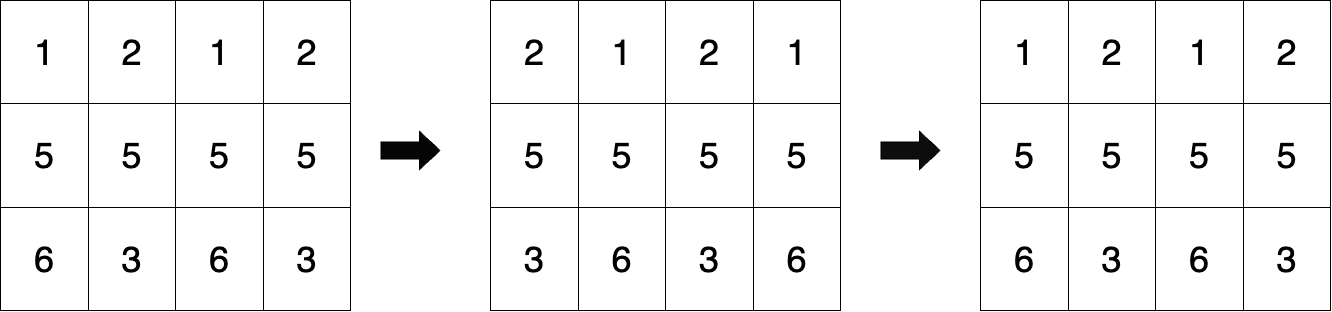 +
+初始矩阵如图一所示。
+图二表示对奇数行右移一次且对偶数行左移一次后的矩阵状态。
+图三是经过两次循环移位后的最终矩阵状态,与初始矩阵相同。
+因此,返回 true 。
+
+
+初始矩阵如图一所示。
+图二表示对奇数行右移一次且对偶数行左移一次后的矩阵状态。
+图三是经过两次循环移位后的最终矩阵状态,与初始矩阵相同。
+因此,返回 true 。
+
+
+示例 2:
+
+
+输入:mat = [[2,2],[2,2]], k = 3
+输出:true
+解释:由于矩阵中的所有值都相等,即使进行循环移位,矩阵仍然保持不变。因此,返回 true 。
+
+
+示例 3:
+
+
+输入:mat = [[1,2]], k = 1
+输出:false
+解释:循环移位一次后,mat = [[2,1]],与初始矩阵不相等。因此,返回 false 。
+
+
+
+
+提示:
+
+
+ 1 <= mat.length <= 251 <= mat[i].length <= 251 <= mat[i][j] <= 251 <= k <= 50
+
+## 解法
+
+
+
+
+
+### **Python3**
+
+
+
+```python
+
+```
+
+### **Java**
+
+
+
+```java
+
+```
+
+### **C++**
+
+```cpp
+
+```
+
+### **Go**
+
+```go
+
+```
+
+### **...**
+
+```
+
+```
+
+
diff --git a/solution/2900-2999/2946.Matrix Similarity After Cyclic Shifts/README_EN.md b/solution/2900-2999/2946.Matrix Similarity After Cyclic Shifts/README_EN.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..885c720f84045
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2900-2999/2946.Matrix Similarity After Cyclic Shifts/README_EN.md
@@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
+# [2946. Matrix Similarity After Cyclic Shifts](https://leetcode.com/problems/matrix-similarity-after-cyclic-shifts)
+
+[中文文档](/solution/2900-2999/2946.Matrix%20Similarity%20After%20Cyclic%20Shifts/README.md)
+
+## Description
+
+You are given a 0-indexed m x n integer matrix mat and an integer k. You have to cyclically right shift odd indexed rows k times and cyclically left shift even indexed rows k times.
+
+Return true if the initial and final matrix are exactly the same and false otherwise.
+
+
+Example 1:
+
+
+Input: mat = [[1,2,1,2],[5,5,5,5],[6,3,6,3]], k = 2
+Output: true
+Explanation:
+ +
+Initially, the matrix looks like the first figure.
+Second figure represents the state of the matrix after one right and left cyclic shifts to even and odd indexed rows.
+Third figure is the final state of the matrix after two cyclic shifts which is similar to the initial matrix.
+Therefore, return true.
+
+
+Initially, the matrix looks like the first figure.
+Second figure represents the state of the matrix after one right and left cyclic shifts to even and odd indexed rows.
+Third figure is the final state of the matrix after two cyclic shifts which is similar to the initial matrix.
+Therefore, return true.
+
+
+Example 2:
+
+
+Input: mat = [[2,2],[2,2]], k = 3
+Output: true
+Explanation: As all the values are equal in the matrix, even after performing cyclic shifts the matrix will remain the same. Therefeore, we return true.
+
+
+Example 3:
+
+
+Input: mat = [[1,2]], k = 1
+Output: false
+Explanation: After one cyclic shift, mat = [[2,1]] which is not equal to the initial matrix. Therefore we return false.
+
+
+
+Constraints:
+
+
+ 1 <= mat.length <= 251 <= mat[i].length <= 251 <= mat[i][j] <= 251 <= k <= 50
+
+## Solutions
+
+
+
+### **Python3**
+
+```python
+
+```
+
+### **Java**
+
+```java
+
+```
+
+### **C++**
+
+```cpp
+
+```
+
+### **Go**
+
+```go
+
+```
+
+### **...**
+
+```
+
+```
+
+
diff --git a/solution/2900-2999/2946.Matrix Similarity After Cyclic Shifts/images/similarmatrix.png b/solution/2900-2999/2946.Matrix Similarity After Cyclic Shifts/images/similarmatrix.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..7e3eebe38965b
Binary files /dev/null and b/solution/2900-2999/2946.Matrix Similarity After Cyclic Shifts/images/similarmatrix.png differ
diff --git a/solution/2900-2999/2947.Count Beautiful Substrings I/README.md b/solution/2900-2999/2947.Count Beautiful Substrings I/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..3292f65ccd8fe
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2900-2999/2947.Count Beautiful Substrings I/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
+# [2947. 统计美丽子字符串 I](https://leetcode.cn/problems/count-beautiful-substrings-i)
+
+[English Version](/solution/2900-2999/2947.Count%20Beautiful%20Substrings%20I/README_EN.md)
+
+## 题目描述
+
+
+
+给你一个字符串 s 和一个正整数 k 。
+
+用 vowels 和 consonants 分别表示字符串中元音字母和辅音字母的数量。
+
+如果某个字符串满足以下条件,则称其为 美丽字符串 :
+
+
+ vowels == consonants,即元音字母和辅音字母的数量相等。(vowels * consonants) % k == 0,即元音字母和辅音字母的数量的乘积能被 k 整除。
+
+返回字符串 s 中 非空美丽子字符串 的数量。
+
+子字符串是字符串中的一个连续字符序列。
+
+英语中的 元音字母 为 'a'、'e'、'i'、'o' 和 'u' 。
+
+英语中的 辅音字母 为除了元音字母之外的所有字母。
+
+
+
+示例 1:
+
+
+输入:s = "baeyh", k = 2
+输出:2
+解释:字符串 s 中有 2 个美丽子字符串。
+- 子字符串 "baeyh",vowels = 2(["a","e"]),consonants = 2(["y","h"])。
+可以看出字符串 "aeyh" 是美丽字符串,因为 vowels == consonants 且 vowels * consonants % k == 0 。
+- 子字符串 "baeyh",vowels = 2(["a","e"]),consonants = 2(["b","y"])。
+可以看出字符串 "baey" 是美丽字符串,因为 vowels == consonants 且 vowels * consonants % k == 0 。
+可以证明字符串 s 中只有 2 个美丽子字符串。
+
+
+示例 2:
+
+
+输入:s = "abba", k = 1
+输出:3
+解释:字符串 s 中有 3 个美丽子字符串。
+- 子字符串 "abba",vowels = 1(["a"]),consonants = 1(["b"])。
+- 子字符串 "abba",vowels = 1(["a"]),consonants = 1(["b"])。
+- 子字符串 "abba",vowels = 2(["a","a"]),consonants = 2(["b","b"])。
+可以证明字符串 s 中只有 3 个美丽子字符串。
+
+
+示例 3:
+
+
+输入:s = "bcdf", k = 1
+输出:0
+解释:字符串 s 中没有美丽子字符串。
+
+
+
+
+提示:
+
+
+ 1 <= s.length <= 10001 <= k <= 1000s 仅由小写英文字母组成。
+
+## 解法
+
+
+
+
+
+### **Python3**
+
+
+
+```python
+
+```
+
+### **Java**
+
+
+
+```java
+
+```
+
+### **C++**
+
+```cpp
+
+```
+
+### **Go**
+
+```go
+
+```
+
+### **...**
+
+```
+
+```
+
+
diff --git a/solution/2900-2999/2947.Count Beautiful Substrings I/README_EN.md b/solution/2900-2999/2947.Count Beautiful Substrings I/README_EN.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..c42d163d30c74
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2900-2999/2947.Count Beautiful Substrings I/README_EN.md
@@ -0,0 +1,103 @@
+# [2947. Count Beautiful Substrings I](https://leetcode.com/problems/count-beautiful-substrings-i)
+
+[中文文档](/solution/2900-2999/2947.Count%20Beautiful%20Substrings%20I/README.md)
+
+## Description
+
+You are given a string s and a positive integer k.
+
+Let vowels and consonants be the number of vowels and consonants in a string.
+
+A string is beautiful if:
+
+
+ vowels == consonants.(vowels * consonants) % k == 0, in other terms the multiplication of vowels and consonants is divisible by k.
+
+Return the number of non-empty beautiful substrings in the given string s.
+
+A substring is a contiguous sequence of characters in a string.
+
+Vowel letters in English are 'a', 'e', 'i', 'o', and 'u'.
+
+Consonant letters in English are every letter except vowels.
+
+
+Example 1:
+
+
+Input: s = "baeyh", k = 2
+Output: 2
+Explanation: There are 2 beautiful substrings in the given string.
+- Substring "baeyh", vowels = 2 (["a",e"]), consonants = 2 (["y","h"]).
+You can see that string "aeyh" is beautiful as vowels == consonants and vowels * consonants % k == 0.
+- Substring "baeyh", vowels = 2 (["a",e"]), consonants = 2 (["b","y"]).
+You can see that string "baey" is beautiful as vowels == consonants and vowels * consonants % k == 0.
+It can be shown that there are only 2 beautiful substrings in the given string.
+
+
+Example 2:
+
+
+Input: s = "abba", k = 1
+Output: 3
+Explanation: There are 3 beautiful substrings in the given string.
+- Substring "abba", vowels = 1 (["a"]), consonants = 1 (["b"]).
+- Substring "abba", vowels = 1 (["a"]), consonants = 1 (["b"]).
+- Substring "abba", vowels = 2 (["a","a"]), consonants = 2 (["b","b"]).
+It can be shown that there are only 3 beautiful substrings in the given string.
+
+
+Example 3:
+
+
+Input: s = "bcdf", k = 1
+Output: 0
+Explanation: There are no beautiful substrings in the given string.
+
+
+
+Constraints:
+
+
+ 1 <= s.length <= 10001 <= k <= 1000s consists of only English lowercase letters.
+
+## Solutions
+
+
+
+### **Python3**
+
+```python
+
+```
+
+### **Java**
+
+```java
+
+```
+
+### **C++**
+
+```cpp
+
+```
+
+### **Go**
+
+```go
+
+```
+
+### **...**
+
+```
+
+```
+
+
diff --git a/solution/2900-2999/2948.Make Lexicographically Smallest Array by Swapping Elements/README.md b/solution/2900-2999/2948.Make Lexicographically Smallest Array by Swapping Elements/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..39cdaade9fb30
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2900-2999/2948.Make Lexicographically Smallest Array by Swapping Elements/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,101 @@
+# [2948. 交换得到字典序最小的数组](https://leetcode.cn/problems/make-lexicographically-smallest-array-by-swapping-elements)
+
+[English Version](/solution/2900-2999/2948.Make%20Lexicographically%20Smallest%20Array%20by%20Swapping%20Elements/README_EN.md)
+
+## 题目描述
+
+
+
+给你一个下标从 0 开始的 正整数 数组 nums 和一个 正整数 limit 。
+
+在一次操作中,你可以选择任意两个下标 i 和 j,如果 满足 |nums[i] - nums[j]| <= limit ,则交换 nums[i] 和 nums[j] 。
+
+返回执行任意次操作后能得到的 字典序最小的数组 。
+
+如果在数组 a 和数组 b 第一个不同的位置上,数组 a 中的对应字符比数组 b 中的对应字符的字典序更小,则认为数组 a 就比数组 b 字典序更小。例如,数组 [2,10,3] 比数组 [10,2,3] 字典序更小,下标 0 处是两个数组第一个不同的位置,且 2 < 10 。
+
+
+
+示例 1:
+
+
+输入:nums = [1,5,3,9,8], limit = 2
+输出:[1,3,5,8,9]
+解释:执行 2 次操作:
+- 交换 nums[1] 和 nums[2] 。数组变为 [1,3,5,9,8] 。
+- 交换 nums[3] 和 nums[4] 。数组变为 [1,3,5,8,9] 。
+即便执行更多次操作,也无法得到字典序更小的数组。
+注意,执行不同的操作也可能会得到相同的结果。
+
+
+示例 2:
+
+
+输入:nums = [1,7,6,18,2,1], limit = 3
+输出:[1,6,7,18,1,2]
+解释:执行 3 次操作:
+- 交换 nums[1] 和 nums[2] 。数组变为 [1,6,7,18,2,1] 。
+- 交换 nums[0] 和 nums[4] 。数组变为 [2,6,7,18,1,1] 。
+- 交换 nums[0] 和 nums[5] 。数组变为 [1,6,7,18,1,2] 。
+即便执行更多次操作,也无法得到字典序更小的数组。
+
+
+示例 3:
+
+
+输入:nums = [1,7,28,19,10], limit = 3
+输出:[1,7,28,19,10]
+解释:[1,7,28,19,10] 是字典序最小的数组,因为不管怎么选择下标都无法执行操作。
+
+
+
+
+提示:
+
+
+ 1 <= nums.length <= 1051 <= nums[i] <= 1091 <= limit <= 109
+
+## 解法
+
+
+
+
+
+### **Python3**
+
+
+
+```python
+
+```
+
+### **Java**
+
+
+
+```java
+
+```
+
+### **C++**
+
+```cpp
+
+```
+
+### **Go**
+
+```go
+
+```
+
+### **...**
+
+```
+
+```
+
+
diff --git a/solution/2900-2999/2948.Make Lexicographically Smallest Array by Swapping Elements/README_EN.md b/solution/2900-2999/2948.Make Lexicographically Smallest Array by Swapping Elements/README_EN.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..91a0bbe36173f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2900-2999/2948.Make Lexicographically Smallest Array by Swapping Elements/README_EN.md
@@ -0,0 +1,91 @@
+# [2948. Make Lexicographically Smallest Array by Swapping Elements](https://leetcode.com/problems/make-lexicographically-smallest-array-by-swapping-elements)
+
+[中文文档](/solution/2900-2999/2948.Make%20Lexicographically%20Smallest%20Array%20by%20Swapping%20Elements/README.md)
+
+## Description
+
+You are given a 0-indexed array of positive integers nums and a positive integer limit.
+
+In one operation, you can choose any two indices i and j and swap nums[i] and nums[j] if |nums[i] - nums[j]| <= limit.
+
+Return the lexicographically smallest array that can be obtained by performing the operation any number of times.
+
+An array a is lexicographically smaller than an array b if in the first position where a and b differ, array a has an element that is less than the corresponding element in b. For example, the array [2,10,3] is lexicographically smaller than the array [10,2,3] because they differ at index 0 and 2 < 10.
+
+
+Example 1:
+
+
+Input: nums = [1,5,3,9,8], limit = 2
+Output: [1,3,5,8,9]
+Explanation: Apply the operation 2 times:
+- Swap nums[1] with nums[2]. The array becomes [1,3,5,9,8]
+- Swap nums[3] with nums[4]. The array becomes [1,3,5,8,9]
+We cannot obtain a lexicographically smaller array by applying any more operations.
+Note that it may be possible to get the same result by doing different operations.
+
+
+Example 2:
+
+
+Input: nums = [1,7,6,18,2,1], limit = 3
+Output: [1,6,7,18,1,2]
+Explanation: Apply the operation 3 times:
+- Swap nums[1] with nums[2]. The array becomes [1,6,7,18,2,1]
+- Swap nums[0] with nums[4]. The array becomes [2,6,7,18,1,1]
+- Swap nums[0] with nums[5]. The array becomes [1,6,7,18,1,2]
+We cannot obtain a lexicographically smaller array by applying any more operations.
+
+
+Example 3:
+
+
+Input: nums = [1,7,28,19,10], limit = 3
+Output: [1,7,28,19,10]
+Explanation: [1,7,28,19,10] is the lexicographically smallest array we can obtain because we cannot apply the operation on any two indices.
+
+
+
+Constraints:
+
+
+ 1 <= nums.length <= 1051 <= nums[i] <= 1091 <= limit <= 109
+
+## Solutions
+
+
+
+### **Python3**
+
+```python
+
+```
+
+### **Java**
+
+```java
+
+```
+
+### **C++**
+
+```cpp
+
+```
+
+### **Go**
+
+```go
+
+```
+
+### **...**
+
+```
+
+```
+
+
diff --git a/solution/2900-2999/2949.Count Beautiful Substrings II/README.md b/solution/2900-2999/2949.Count Beautiful Substrings II/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..900153ae072c1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2900-2999/2949.Count Beautiful Substrings II/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
+# [2949. 统计美丽子字符串 II](https://leetcode.cn/problems/count-beautiful-substrings-ii)
+
+[English Version](/solution/2900-2999/2949.Count%20Beautiful%20Substrings%20II/README_EN.md)
+
+## 题目描述
+
+
+
+给你一个字符串 s 和一个正整数 k 。
+
+用 vowels 和 consonants 分别表示字符串中元音字母和辅音字母的数量。
+
+如果某个字符串满足以下条件,则称其为 美丽字符串 :
+
+
+ vowels == consonants,即元音字母和辅音字母的数量相等。(vowels * consonants) % k == 0,即元音字母和辅音字母的数量的乘积能被 k 整除。
+
+返回字符串 s 中 非空美丽子字符串 的数量。
+
+子字符串是字符串中的一个连续字符序列。
+
+英语中的 元音字母 为 'a'、'e'、'i'、'o' 和 'u' 。
+
+英语中的 辅音字母 为除了元音字母之外的所有字母。
+
+
+
+示例 1:
+
+
+输入:s = "baeyh", k = 2
+输出:2
+解释:字符串 s 中有 2 个美丽子字符串。
+- 子字符串 "baeyh",vowels = 2(["a","e"]),consonants = 2(["y","h"])。
+可以看出字符串 "aeyh" 是美丽字符串,因为 vowels == consonants 且 vowels * consonants % k == 0 。
+- 子字符串 "baeyh",vowels = 2(["a","e"]),consonants = 2(["b","y"])。
+可以看出字符串 "baey" 是美丽字符串,因为 vowels == consonants 且 vowels * consonants % k == 0 。
+可以证明字符串 s 中只有 2 个美丽子字符串。
+
+
+示例 2:
+
+
+输入:s = "abba", k = 1
+输出:3
+解释:字符串 s 中有 3 个美丽子字符串。
+- 子字符串 "abba",vowels = 1(["a"]),consonants = 1(["b"])。
+- 子字符串 "abba",vowels = 1(["a"]),consonants = 1(["b"])。
+- 子字符串 "abba",vowels = 2(["a","a"]),consonants = 2(["b","b"])。
+可以证明字符串 s 中只有 3 个美丽子字符串。
+
+
+示例 3:
+
+
+输入:s = "bcdf", k = 1
+输出:0
+解释:字符串 s 中没有美丽子字符串。
+
+
+
+
+提示:
+
+
+ 1 <= s.length <= 5 * 1041 <= k <= 1000s 仅由小写英文字母组成。
+
+## 解法
+
+
+
+
+
+### **Python3**
+
+
+
+```python
+
+```
+
+### **Java**
+
+
+
+```java
+
+```
+
+### **C++**
+
+```cpp
+
+```
+
+### **Go**
+
+```go
+
+```
+
+### **...**
+
+```
+
+```
+
+
diff --git a/solution/2900-2999/2949.Count Beautiful Substrings II/README_EN.md b/solution/2900-2999/2949.Count Beautiful Substrings II/README_EN.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..3071fcd40a06a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2900-2999/2949.Count Beautiful Substrings II/README_EN.md
@@ -0,0 +1,103 @@
+# [2949. Count Beautiful Substrings II](https://leetcode.com/problems/count-beautiful-substrings-ii)
+
+[中文文档](/solution/2900-2999/2949.Count%20Beautiful%20Substrings%20II/README.md)
+
+## Description
+
+You are given a string s and a positive integer k.
+
+Let vowels and consonants be the number of vowels and consonants in a string.
+
+A string is beautiful if:
+
+
+ vowels == consonants.(vowels * consonants) % k == 0, in other terms the multiplication of vowels and consonants is divisible by k.
+
+Return the number of non-empty beautiful substrings in the given string s.
+
+A substring is a contiguous sequence of characters in a string.
+
+Vowel letters in English are 'a', 'e', 'i', 'o', and 'u'.
+
+Consonant letters in English are every letter except vowels.
+
+
+Example 1:
+
+
+Input: s = "baeyh", k = 2
+Output: 2
+Explanation: There are 2 beautiful substrings in the given string.
+- Substring "baeyh", vowels = 2 (["a",e"]), consonants = 2 (["y","h"]).
+You can see that string "aeyh" is beautiful as vowels == consonants and vowels * consonants % k == 0.
+- Substring "baeyh", vowels = 2 (["a",e"]), consonants = 2 (["b","y"]).
+You can see that string "baey" is beautiful as vowels == consonants and vowels * consonants % k == 0.
+It can be shown that there are only 2 beautiful substrings in the given string.
+
+
+Example 2:
+
+
+Input: s = "abba", k = 1
+Output: 3
+Explanation: There are 3 beautiful substrings in the given string.
+- Substring "abba", vowels = 1 (["a"]), consonants = 1 (["b"]).
+- Substring "abba", vowels = 1 (["a"]), consonants = 1 (["b"]).
+- Substring "abba", vowels = 2 (["a","a"]), consonants = 2 (["b","b"]).
+It can be shown that there are only 3 beautiful substrings in the given string.
+
+
+Example 3:
+
+
+Input: s = "bcdf", k = 1
+Output: 0
+Explanation: There are no beautiful substrings in the given string.
+
+
+
+Constraints:
+
+
+ 1 <= s.length <= 5 * 1041 <= k <= 1000s consists of only English lowercase letters.
+
+## Solutions
+
+
+
+### **Python3**
+
+```python
+
+```
+
+### **Java**
+
+```java
+
+```
+
+### **C++**
+
+```cpp
+
+```
+
+### **Go**
+
+```go
+
+```
+
+### **...**
+
+```
+
+```
+
+
diff --git a/solution/CONTEST_README.md b/solution/CONTEST_README.md
index 1ff3c9791e48a..0f7580098c20c 100644
--- a/solution/CONTEST_README.md
+++ b/solution/CONTEST_README.md
@@ -22,6 +22,13 @@
## 往期竞赛
+#### 第 373 场周赛(2023-11-26 10:30, 90 分钟) 参赛人数 3577
+
+- [2946. 循环移位后的矩阵相似检查](/solution/2900-2999/2946.Matrix%20Similarity%20After%20Cyclic%20Shifts/README.md)
+- [2947. 统计美丽子字符串 I](/solution/2900-2999/2947.Count%20Beautiful%20Substrings%20I/README.md)
+- [2948. 交换得到字典序最小的数组](/solution/2900-2999/2948.Make%20Lexicographically%20Smallest%20Array%20by%20Swapping%20Elements/README.md)
+- [2949. 统计美丽子字符串 II](/solution/2900-2999/2949.Count%20Beautiful%20Substrings%20II/README.md)
+
#### 第 118 场双周赛(2023-11-25 22:30, 90 分钟) 参赛人数 2425
- [2942. 查找包含给定字符的单词](/solution/2900-2999/2942.Find%20Words%20Containing%20Character/README.md)
diff --git a/solution/CONTEST_README_EN.md b/solution/CONTEST_README_EN.md
index f38068db63e0d..8afc30b26e3b3 100644
--- a/solution/CONTEST_README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/CONTEST_README_EN.md
@@ -25,6 +25,13 @@ Get your rating changes right after the completion of LeetCode contests, https:/
## Past Contests
+#### Weekly Contest 373
+
+- [2946. Matrix Similarity After Cyclic Shifts](/solution/2900-2999/2946.Matrix%20Similarity%20After%20Cyclic%20Shifts/README_EN.md)
+- [2947. Count Beautiful Substrings I](/solution/2900-2999/2947.Count%20Beautiful%20Substrings%20I/README_EN.md)
+- [2948. Make Lexicographically Smallest Array by Swapping Elements](/solution/2900-2999/2948.Make%20Lexicographically%20Smallest%20Array%20by%20Swapping%20Elements/README_EN.md)
+- [2949. Count Beautiful Substrings II](/solution/2900-2999/2949.Count%20Beautiful%20Substrings%20II/README_EN.md)
+
#### Biweekly Contest 118
- [2942. Find Words Containing Character](/solution/2900-2999/2942.Find%20Words%20Containing%20Character/README_EN.md)
diff --git a/solution/README.md b/solution/README.md
index 651981efc5cd4..ae4a38f871961 100644
--- a/solution/README.md
+++ b/solution/README.md
@@ -2956,6 +2956,10 @@
| 2943 | [最大化网格图中正方形空洞的面积](/solution/2900-2999/2943.Maximize%20Area%20of%20Square%20Hole%20in%20Grid/README.md) | | 中等 | 第 118 场双周赛 |
| 2944 | [购买水果需要的最少金币数](/solution/2900-2999/2944.Minimum%20Number%20of%20Coins%20for%20Fruits/README.md) | | 中等 | 第 118 场双周赛 |
| 2945 | [找到最大非递减数组的长度](/solution/2900-2999/2945.Find%20Maximum%20Non-decreasing%20Array%20Length/README.md) | | 困难 | 第 118 场双周赛 |
+| 2946 | [循环移位后的矩阵相似检查](/solution/2900-2999/2946.Matrix%20Similarity%20After%20Cyclic%20Shifts/README.md) | | 简单 | 第 373 场周赛 |
+| 2947 | [统计美丽子字符串 I](/solution/2900-2999/2947.Count%20Beautiful%20Substrings%20I/README.md) | | 中等 | 第 373 场周赛 |
+| 2948 | [交换得到字典序最小的数组](/solution/2900-2999/2948.Make%20Lexicographically%20Smallest%20Array%20by%20Swapping%20Elements/README.md) | | 中等 | 第 373 场周赛 |
+| 2949 | [统计美丽子字符串 II](/solution/2900-2999/2949.Count%20Beautiful%20Substrings%20II/README.md) | | 困难 | 第 373 场周赛 |
## 版权
diff --git a/solution/README_EN.md b/solution/README_EN.md
index 557af085ee4f1..18ad5c812ecbd 100644
--- a/solution/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/README_EN.md
@@ -2954,6 +2954,10 @@ Press Control + F(or Command + F on
| 2943 | [Maximize Area of Square Hole in Grid](/solution/2900-2999/2943.Maximize%20Area%20of%20Square%20Hole%20in%20Grid/README_EN.md) | | Medium | Biweekly Contest 118 |
| 2944 | [Minimum Number of Coins for Fruits](/solution/2900-2999/2944.Minimum%20Number%20of%20Coins%20for%20Fruits/README_EN.md) | | Medium | Biweekly Contest 118 |
| 2945 | [Find Maximum Non-decreasing Array Length](/solution/2900-2999/2945.Find%20Maximum%20Non-decreasing%20Array%20Length/README_EN.md) | | Hard | Biweekly Contest 118 |
+| 2946 | [Matrix Similarity After Cyclic Shifts](/solution/2900-2999/2946.Matrix%20Similarity%20After%20Cyclic%20Shifts/README_EN.md) | | Easy | Weekly Contest 373 |
+| 2947 | [Count Beautiful Substrings I](/solution/2900-2999/2947.Count%20Beautiful%20Substrings%20I/README_EN.md) | | Medium | Weekly Contest 373 |
+| 2948 | [Make Lexicographically Smallest Array by Swapping Elements](/solution/2900-2999/2948.Make%20Lexicographically%20Smallest%20Array%20by%20Swapping%20Elements/README_EN.md) | | Medium | Weekly Contest 373 |
+| 2949 | [Count Beautiful Substrings II](/solution/2900-2999/2949.Count%20Beautiful%20Substrings%20II/README_EN.md) | | Hard | Weekly Contest 373 |
## Copyright
diff --git a/solution/summary.md b/solution/summary.md
index 3965b3aa48d51..256bad0d309f1 100644
--- a/solution/summary.md
+++ b/solution/summary.md
@@ -3003,3 +3003,7 @@
- [2943.最大化网格图中正方形空洞的面积](/solution/2900-2999/2943.Maximize%20Area%20of%20Square%20Hole%20in%20Grid/README.md)
- [2944.购买水果需要的最少金币数](/solution/2900-2999/2944.Minimum%20Number%20of%20Coins%20for%20Fruits/README.md)
- [2945.找到最大非递减数组的长度](/solution/2900-2999/2945.Find%20Maximum%20Non-decreasing%20Array%20Length/README.md)
+ - [2946.循环移位后的矩阵相似检查](/solution/2900-2999/2946.Matrix%20Similarity%20After%20Cyclic%20Shifts/README.md)
+ - [2947.统计美丽子字符串 I](/solution/2900-2999/2947.Count%20Beautiful%20Substrings%20I/README.md)
+ - [2948.交换得到字典序最小的数组](/solution/2900-2999/2948.Make%20Lexicographically%20Smallest%20Array%20by%20Swapping%20Elements/README.md)
+ - [2949.统计美丽子字符串 II](/solution/2900-2999/2949.Count%20Beautiful%20Substrings%20II/README.md)
diff --git a/solution/summary_en.md b/solution/summary_en.md
index 855df355b87e1..a0318b11865c9 100644
--- a/solution/summary_en.md
+++ b/solution/summary_en.md
@@ -3003,3 +3003,7 @@
- [2943.Maximize Area of Square Hole in Grid](/solution/2900-2999/2943.Maximize%20Area%20of%20Square%20Hole%20in%20Grid/README_EN.md)
- [2944.Minimum Number of Coins for Fruits](/solution/2900-2999/2944.Minimum%20Number%20of%20Coins%20for%20Fruits/README_EN.md)
- [2945.Find Maximum Non-decreasing Array Length](/solution/2900-2999/2945.Find%20Maximum%20Non-decreasing%20Array%20Length/README_EN.md)
+ - [2946.Matrix Similarity After Cyclic Shifts](/solution/2900-2999/2946.Matrix%20Similarity%20After%20Cyclic%20Shifts/README_EN.md)
+ - [2947.Count Beautiful Substrings I](/solution/2900-2999/2947.Count%20Beautiful%20Substrings%20I/README_EN.md)
+ - [2948.Make Lexicographically Smallest Array by Swapping Elements](/solution/2900-2999/2948.Make%20Lexicographically%20Smallest%20Array%20by%20Swapping%20Elements/README_EN.md)
+ - [2949.Count Beautiful Substrings II](/solution/2900-2999/2949.Count%20Beautiful%20Substrings%20II/README_EN.md)
 +
+初始矩阵如图一所示。
+图二表示对奇数行右移一次且对偶数行左移一次后的矩阵状态。
+图三是经过两次循环移位后的最终矩阵状态,与初始矩阵相同。
+因此,返回 true 。
+
+
+初始矩阵如图一所示。
+图二表示对奇数行右移一次且对偶数行左移一次后的矩阵状态。
+图三是经过两次循环移位后的最终矩阵状态,与初始矩阵相同。
+因此,返回 true 。
++ +初始矩阵如图一所示。 +图二表示对奇数行右移一次且对偶数行左移一次后的矩阵状态。 +图三是经过两次循环移位后的最终矩阵状态,与初始矩阵相同。 +因此,返回 true 。 +
+ +Initially, the matrix looks like the first figure. +Second figure represents the state of the matrix after one right and left cyclic shifts to even and odd indexed rows. +Third figure is the final state of the matrix after two cyclic shifts which is similar to the initial matrix. +Therefore, return true. +