diff --git a/CONTRIBUTING.md b/CONTRIBUTING.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3f953d3f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/CONTRIBUTING.md
@@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
+# Welcome contributors to the DQ Robotics!
+
+We are happy about your interest in our project. Thank you for your time. DQ Robotics is a standalone open-source library and your contributions are always welcome!
+
+This is a set of guidelines for contribuiting to [DQ Robotics](https://dqrobotics.github.io/).
+
+# Workflow
+
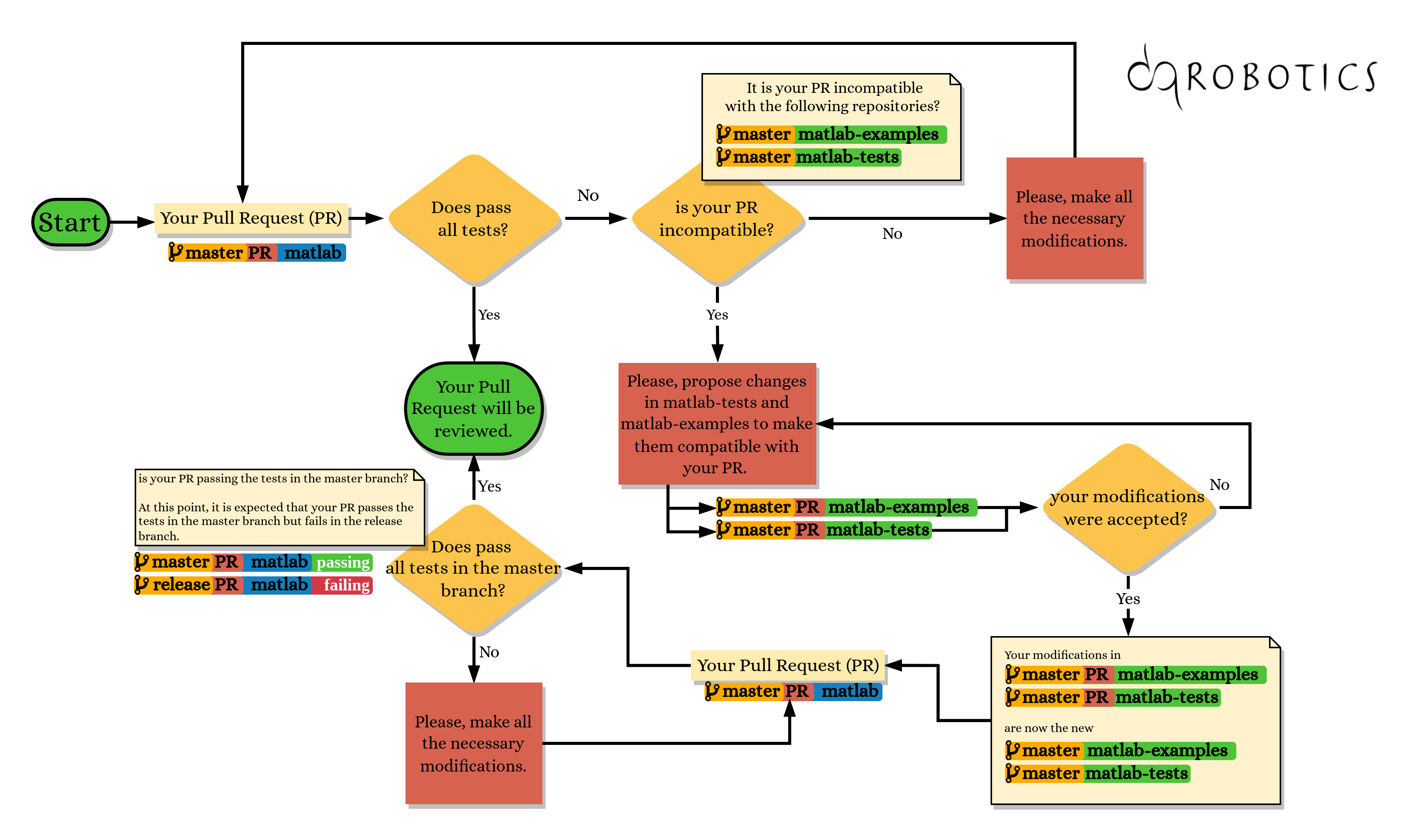
+- Fork the [master branch of the dqrobotics/matlab](https://github.com/dqrobotics/matlab).
+- Propose your modifications and open a draft pull request.
+- Your modifications will be tested automatically by Github actions. Specifically, Github actions runs the tests of [matlab-tests](https://github.com/dqrobotics/matlab-tests), which executes all the examples of [matlab-examples](https://github.com/dqrobotics/matlab-examples).
+- Once your draft pull request passes all the tests, you can switch the status to pull request. (More details [here](https://github.blog/2019-02-14-introducing-draft-pull-requests/)).
+
+
+
+## Case 1 (Common cases)
+
+- If your modifications pass all tests, a designated member of our team will review all the changes and they will accept them after all necessary adjustments if any.
+
+## Case 2 (Very rare cases)
+
+- In some cases, your modifications would fail some tests because of incompatibility with the current version of [matlab-tests](https://github.com/dqrobotics/matlab-tests) and/or [matlab-examples](https://github.com/dqrobotics/matlab-examples). In thoses cases, you would propose changes in [matlab-tests](https://github.com/dqrobotics/matlab-tests) and [matlab-examples](https://github.com/dqrobotics/matlab-examples) to make them compatible with your new version of the dqrobotics/matlab.
+- A designated member of our team will review all the changes proposed in both [matlab-tests](https://github.com/dqrobotics/matlab-tests) and [matlab-examples](https://github.com/dqrobotics/matlab-examples). They will accept the modifications in the master branch after all necessary adjustments. At this point, it is expected that your pull request passes all the tests in the master branch but fails in the release branch.
+
+
+
+- Then, they will test your dqrobotics/matlab pull request making all necessary adjustments until your pull request of dqrobotics/matlab passes all the tests. After that, they will review deeply your modifications.
+- Finally, your modifications will be accepted in the master branch.
+
+# Example
+
+## Fork the [dqrobotics/matlab](https://github.com/dqrobotics/matlab) in your Github account
+
+
+
+## Clone the forked repository
+
+For instance, if your forked matlab respository is https://github.com/juanjqo/matlab, then
+
+Type in your terminal:
+
+- `git clone https://github.com/juanjqo/matlab.git`
+
+
+
+## Make your modifications
+
+Now, you can modify the code with your contributions.
+(In this specific example, as shown in the GIF, I modified the CONTRIBUTING.md file)
+
+
+
+## Add, commit and push your changes
+
+Please indicate in your commit's message the file that was modified using brackets. For instance, if you modified the class DQ_Serialmanipulator, then you would do the following:
+
+- `git commit -m "[DQ_SerialManipulator] your_message_explaining_the modification."`
+
+
+
+## Open a draft pull request (More details [here](https://github.blog/2019-02-14-introducing-draft-pull-requests/))
+
+Now, your draft pull request will be tested by Github actions automatically.
+
+
+
+If your pull request fails the tests, don't worry!, you will see where your code is not working. Pick your pull request in https://github.com/dqrobotics/matlab/pulls. Then, at the end of the page, click on 'Details'.
+
+
diff --git a/robot_modeling/DQ_JointType.m b/robot_modeling/DQ_JointType.m
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..02ea658c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/robot_modeling/DQ_JointType.m
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
+% (C) Copyright 2022 DQ Robotics Developers
+%
+% This file is part of DQ Robotics.
+%
+% DQ Robotics is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
+% it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published
+% by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
+% (at your option) any later version.
+%
+% DQ Robotics is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
+% but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
+% MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
+% GNU Lesser General Public License for more details.
+%
+% You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
+% along with DQ Robotics. If not, see .
+%
+% DQ Robotics website: dqrobotics.github.io
+%
+% Contributors to this file:
+% Juan Jose Quiroz Omana - juanjqo@g.ecc.u-tokyo.ac.jp
+
+classdef DQ_JointType < double
+ enumeration
+ REVOLUTE (1)
+ PRISMATIC (2)
+ end
+end
+
+
+
diff --git a/robot_modeling/DQ_Kinematics.m b/robot_modeling/DQ_Kinematics.m
index d526b1aa..9631108e 100644
--- a/robot_modeling/DQ_Kinematics.m
+++ b/robot_modeling/DQ_Kinematics.m
@@ -1,10 +1,15 @@
% Abstract class that defines an interface to implement robot kinematics.
%
% DQ_Kinematics Properties:
-% base_frame - Frame used to determine the robot physical location.
+% base_frame_ - Frame used to determine the robot physical location.
% name - Unique name that is generated randomly.
-% reference_frame - Reference frame (not always coincident with base_frame).
+% reference_frame_ - Reference frame (not always coincident with base_frame).
% q - Robot configuration vector.
+% dim_configuration_space_ - Dimension of the robot configuration space.
+% lower_q_limit_ - The lower bound of the robot configuration;
+% upper_q_limit_ - The upper bound of the robot configuration;
+% lower_q_dot_limit_ - The lower bound of the robot configuration velocity;
+% upper_q_dot_limit_ - The upper bound of the robot configuration velocity;
%
% DQ_Kinematics Methods (Abstract):
% get_dim_configuration_space - Returns the dimension of the configuration space.
@@ -69,11 +74,21 @@
properties (SetAccess = protected)
% Reference frame used in fkm() and pose_jacobian methods
- reference_frame;
+ reference_frame_;
% Frame used to determine the robot physical location
- base_frame;
+ base_frame_;
% Robot configuration vector
- q
+ q
+ % Dimension of the robot configuration space
+ dim_configuration_space_;
+ % The lower bound of the robot configuration;
+ lower_q_limit_;
+ % The upper bound of the robot configuration;
+ upper_q_limit_;
+ % The lower bound of the robot configuration velocity;
+ lower_q_dot_limit_;
+ % The upper bound of the robot configuration velocity;
+ upper_q_dot_limit_;
end
methods
@@ -81,27 +96,27 @@
% Both reference_frame and base_frame initially coincide, but
% this can be changed by using set_reference_frame() and
% set_base_frame()
- obj.reference_frame = DQ(1);
- obj.base_frame = DQ(1);
+ obj.reference_frame_ = DQ(1);
+ obj.base_frame_ = DQ(1);
% Define a unique robot name
obj.name = sprintf('%f',rand(1));
end
function ret = get_base_frame(obj)
% Get the physical location of the robot base in the workspace.
- ret = obj.base_frame;
+ ret = obj.base_frame_;
end
function ret = get_reference_frame(obj)
% Get the reference frame used in the calculation of the FKM and all Jacobians.
- ret = obj.reference_frame;
+ ret = obj.reference_frame_;
end
function set_reference_frame(obj,reference_frame)
% SET_REFERENCE_FRAME(reference_frame) sets the reference frame
% used for the fkm() and pose_jacobian() methods
if is_unit(reference_frame)
- obj.reference_frame = reference_frame;
+ obj.reference_frame_ = reference_frame;
else
error('The reference frame must be a unit dual quaternion.');
end
@@ -116,7 +131,7 @@ function set_base_frame(obj, base_frame)
% and it does not necessarily coincides with the reference
% frame.
if is_unit(base_frame)
- obj.base_frame = base_frame;
+ obj.base_frame_ = base_frame;
else
error('The base frame must be a unit dual quaternion.');
end
@@ -125,6 +140,27 @@ function set_base_frame(obj, base_frame)
end
+ methods (Access = protected)
+ function check_to_ith_link(obj, to_ith_link)
+ % Protected method to check if the index to a link is valid.
+ n_links = get_dim_configuration_space(obj);
+ if to_ith_link > n_links || to_ith_link < 0
+ error('Tried to access link index %d , which is unnavailable.', to_ith_link);
+ end
+
+ end
+
+ function check_q_vec(obj, q_vec)
+ % Protected method to check if the size of the vector
+ % of joint values q_vec is valid.
+ n_links = get_dim_configuration_space(obj);
+ if length(q_vec) ~= n_links
+ error('Input vector must have size %d', n_links)
+ end
+ end
+
+ end
+
methods (Abstract)
% GET_DIM_CONFIGURATION_SPACE returns the dimension of the configuration
diff --git a/robot_modeling/DQ_SerialManipulator.m b/robot_modeling/DQ_SerialManipulator.m
index d7356871..dfc5c0fd 100644
--- a/robot_modeling/DQ_SerialManipulator.m
+++ b/robot_modeling/DQ_SerialManipulator.m
@@ -1,19 +1,10 @@
-% Concrete class that defines serial manipulators.
+% Abstract class that defines serial manipulators.
%
-% Usage: robot = DQ_SerialManipulator(A,convention)
-% - 'A' is a 4 x n matrix containing the Denavit-Hartenberg parameters
-% (n is the number of links)
-% A = [theta1 ... thetan;
-% d1 ... dn;
-% a1 ... an;
-% alpha1 ... alphan]
-% - 'convention' is the convention used for the D-H parameters. Accepted
-% values are 'standard' and 'modified'
+% Usage: robot = DQ_SerialManipulator(dim_configuration_space)
+% - 'dim_configuration_space' is the dimension of the
+% configuration space.
%
-% The first row of 'A' contains the joint offsets. More specifically,
-% theta_i is the offset for the i-th joint.
-%
-% DQ_SerialManipulator Methods (Concrete):
+% DQ_SerialManipulator Methods (Abstract):
% get_dim_configuration_space - Return the dimension of the configuration space.
% fkm - Compute the forward kinematics while taking into account base and end-effector's rigid transformations.
% plot - Plots the serial manipulator.
@@ -21,7 +12,22 @@
% pose_jacobian_derivative - Compute the time derivative of the pose Jacobian.
% raw_fkm - Compute the FKM without taking into account base's and end-effector's rigid transformations.
% raw_pose_jacobian - Compute the pose Jacobian without taking into account base's and end-effector's rigid transformations.
+
+%
+% DQ_SerialManipulator Methods (Concrete):
+% get_effector - Get the end-effector rigid transformation with respect to the last frame in the kinematic chain.
% set_effector - Set an arbitrary end-effector rigid transformation with respect to the last frame in the kinematic chain.
+% get_lower_q_limit - Returns the lower bound of the robot configuration.
+% set_lower_q_limit - Sets the lower bound of the robot configuration.
+% get_lower_q_dot_limit - Returns the lower bound of the robot configuration velocity.
+% set_lower_q_dot_limit - Seturns the lower bound of the robot configuration velocity.
+% get_upper_q_limit - Returns the upper bound of the robot configuration.
+% set_upper_q_limit - Sets the upper bound of the robot configuration.
+% get_upper_q_dot_limit - Returns the upper bound of the robot configuration velocity.
+% set_upper_q_dot_limit - Seturns the upper bound of the robot configuration velocity.
+
+
+
% See also DQ_Kinematics.
% (C) Copyright 2011-2020 DQ Robotics Developers
@@ -45,16 +51,16 @@
%
% Contributors to this file:
% Bruno Vihena Adorno - adorno@ufmg.br
+% Juan Jose Quiroz Omana - juanjqogm@gmail.com
% TODO: Remove the virtual joints. Instead of helping, they cause a lot of
% confusion, specially among those trying to learn the library. The
% affected methods are: FKM and Jacobian.
-classdef DQ_SerialManipulator < DQ_Kinematics
- properties
- theta,d,a,alpha;
- convention;
- effector;
+classdef (Abstract) DQ_SerialManipulator < DQ_Kinematics
+ properties
+
+
% Properties for the plot function
plotopt
@@ -65,34 +71,60 @@
% Handle used to access the robot's graphics information. It's used
% mainly in the plot function.
handle
- n_links;
+ effector_;
+
+ end
+
+ methods (Abstract)
+ % RAW_POSE_JACOBIAN(q) returns the Jacobian that satisfies
+ % vec(x_dot) = J * q_dot, where x = fkm(q) and q is the
+ % vector of joint variables.
+ %
+ % RAW_POSE_JACOBIAN(q,ith) returns the Jacobian that
+ % satisfies vec(x_ith_dot) = J * q_dot(1:ith), where
+ % x_ith = fkm(q, ith), that is, the fkm up to the i-th link.
+ %
+ % This function does not take into account any base or
+ % end-effector displacements and should be used mostly
+ % internally in DQ_kinematics
+ J = raw_pose_jacobian(obj, q,to_ith_link);
+
+
+ % RAW_FKM(q) calculates the forward kinematic model and
+ % returns the dual quaternion corresponding to the
+ % last joint (the displacements due to the base and the effector
+ % are not taken into account).
+ %
+ % 'q' is the vector of joint variables
+ % 'to_ith_link' defines until which link the raw_fkm will be
+ % calculated.
+ %
+ % This is an auxiliary function to be used mainly with the
+ % Jacobian function.
+ pose = raw_fkm(obj,q, to_ith_link);
end
methods
- function obj = DQ_SerialManipulator(A,convention)
+ function obj = DQ_SerialManipulator(dim_configuration_space)
if nargin == 0
- error('Input: matrix whose columns contain the DH parameters')
+ error('Input: dimension of the configuration space')
end
+
+ obj.reference_frame_ = DQ(1); %Default base's pose
+ obj.base_frame_ = DQ(1);
+ obj.effector_ = DQ(1); %Default effector's pose
- obj.n_links = size(A,2);
- obj.theta = A(1,:);
- obj.d = A(2,:);
- obj.a = A(3,:);
- obj.alpha = A(4,:);
+ % Define the joint limits
+ obj.lower_q_limit_ = -Inf(dim_configuration_space,1);
+ obj.upper_q_limit_ = Inf(dim_configuration_space,1);
+ obj.lower_q_dot_limit_ = -Inf(dim_configuration_space,1);
+ obj.upper_q_dot_limit_ = Inf(dim_configuration_space,1);
- obj.reference_frame = DQ(1); %Default base's pose
- obj.base_frame = DQ(1);
- obj.effector = DQ(1); %Default effector's pose
+ obj.dim_configuration_space_ = dim_configuration_space;
% Define a unique robot name
obj.name = sprintf('%f',rand(1));
- if nargin==1
- obj.convention='standard';
- else
- obj.convention=convention;
- end
-
%For visualisation
obj.lineopt = {'Color', 'black', 'Linewidth', 2};
obj.plotopt = {};
@@ -100,43 +132,70 @@
end
function ret = get_dim_configuration_space(obj)
- ret = obj.n_links;
+ % GET_DIM_CONFIGURATION_SPACE() returns the dimension of the
+ % configuration space
+ ret = obj.dim_configuration_space_;
end
- function set_effector(obj,effector)
+ function ret = get_effector(obj)
+ % GET_EFFECTOR(effector) gets the pose of the effector
+ ret = obj.effector_;
+ end
+
+ function ret = set_effector(obj,new_effector)
% SET_EFFECTOR(effector) sets the pose of the effector
-
- obj.effector = DQ(effector);
+ obj.effector_ = DQ(new_effector);
+ ret = obj.effector_;
end
- function x = raw_fkm(obj,q, ith)
- % RAW_FKM(q) calculates the forward kinematic model and
- % returns the dual quaternion corresponding to the
- % last joint (the displacements due to the base and the effector
- % are not taken into account).
- %
- % 'q' is the vector of joint variables
- %
- % This is an auxiliary function to be used mainly with the
- % Jacobian function.
-
- if nargin == 3
- n = ith;
- else
- n = obj.n_links;
- end
-
- if length(q) ~= obj.n_links
- error('Incorrect number of joint variables');
- end
-
- x = DQ(1);
-
- for i=1:n
- x = x*dh2dq(obj,q(i),i);
- end
+ function ret = get_lower_q_limit(obj)
+ % GET_LOWER_Q_LIMIT() returns the lower bound of
+ %the robot configuration;
+ ret = obj.lower_q_limit_;
+ end
+
+ function set_lower_q_limit(obj, new_lower_q_limit)
+ % SET_LOWER_Q_LIMIT(new_lower_q_limit) sets the lower bound of
+ %the robot configuration;
+ obj.lower_q_limit_ = new_lower_q_limit;
+ end
+
+ function ret = get_lower_q_dot_limit(obj)
+ % GET_LOWER_Q_DOT_LIMIT() returns the lower bound of
+ %the robot configuration velocity;
+ ret = obj.lower_q_dot_limit_;
+ end
+
+ function set_lower_q_dot_limit(obj, new_lower_q_dot_limit)
+ % SET_LOWER_Q_DOT_LIMIT() sets the lower bound of
+ %the robot configuration velocity;
+ obj.lower_q_dot_limit = new_lower_q_dot_limit;
+ end
+
+ function ret = get_upper_q_limit(obj)
+ % GET_UPPER_Q_LIMIT() returns the upper bound of
+ %the robot configuration;
+ ret = obj.upper_q_limit_;
+ end
+
+ function set_upper_q_limit(obj, new_upper_q_limit)
+ % SET_UPPER_Q_LIMIT(new_upper_q_dot_limit) sets the
+ %lower bound of the robot configuration;
+ obj.upper_q_limit_ = new_upper_q_limit;
+ end
+
+ function ret = get_upper_q_dot_limit(obj)
+ % GET_UPPER_Q_DOT_LIMIT() returns the upper bound of
+ %the robot configuration velocity;
+ ret = obj.upper_q_dot_limit_;
end
+ function set_upper_q_dot_limit(obj, new_upper_q_dot_limit)
+ % SET_UPPER_Q_DOT_LIMIT(new_upper_q_dot_limit) sets the
+ %lower bound of the robot configuration velocity;
+ obj.upper_q_dot_limit_ = new_upper_q_dot_limit;
+ end
+
function x = fkm(obj,q, ith)
% FKM(q) calculates the forward kinematic model and
% returns the dual quaternion corresponding to the
@@ -152,112 +211,12 @@ function set_effector(obj,effector)
% instead.
if nargin == 3
- x = obj.reference_frame*obj.raw_fkm(q, ith); %Takes into account the base displacement
- else
- x = obj.reference_frame*obj.raw_fkm(q)*obj.effector;
- end
- end
-
- function dq = dh2dq(obj,theta,i)
- % For a given link's DH parameters, calculate the correspondent dual
- % quaternion
- % Usage: dq = dh2dq(theta,i), where
- % theta: joint angle
- % i: link number
-
- if nargin ~= 3
- error('Wrong number of arguments. The parameters are theta and the correspondent link')
- end
- d = obj.d(i);
- a = obj.a(i);
- alpha = obj.alpha(i);
-
- if strcmp(obj.convention,'standard')
- h(1) = cos((theta+obj.theta(i))/2)*cos(alpha/2);
- h(2) = cos((theta+obj.theta(i))/2)*sin(alpha/2);
- h(3) = sin((theta+obj.theta(i))/2)*sin(alpha/2);
- h(4) = sin((theta+obj.theta(i))/2)*cos(alpha/2);
- d2 = d/2;
- a2 = a/2;
-
-
- h(5) = -d2*h(4)-a2*h(2);
- h(6) = -d2*h(3)+a2*h(1);
- h(7) = d2*h(2)+a2*h(4);
- h(8) = d2*h(1)-a2*h(3);
- else
- h1 = cos((theta+obj.theta(i))/2)*cos(alpha/2);
- h2 = cos((theta+obj.theta(i))/2)*sin(alpha/2);
- h3 = sin((theta+obj.theta(i))/2)*sin(alpha/2);
- h4 = sin((theta+obj.theta(i))/2)*cos(alpha/2);
- h(1) = h1;
- h(2) = h2;
- h(3) = -h3;
- h(4) = h4;
- d2 = d/2;
- a2 = a/2;
-
- h(5) = -d2*h4-a2*h2;
- h(6) = -d2*h3+a2*h1;
- h(7) = -(d2*h2+a2*h4);
- h(8) = d2*h1-a2*h3;
- end
-
- dq = DQ(h);
- end
-
- function p = get_z(~,h)
- p(1) = 0;
- p(2) = h(2)*h(4) + h(1)*h(3);
- p(3) = h(3)*h(4) - h(1)* h(2);
- p(4) = (h(4)^2-h(3)^2-h(2)^2+h(1)^2)/2;
- p(5) = 0;
- p(6) = h(2)*h(8)+h(6)*h(4)+h(1)*h(7)+h(5)*h(3);
- p(7) = h(3)*h(8)+h(7)*h(4)-h(1)*h(6)-h(5)*h(2);
- p(8) = h(4)*h(8)-h(3)*h(7)-h(2)*h(6)+h(1)*h(5);
- end
-
- function J = raw_pose_jacobian(obj,q,ith)
- % RAW_POSE_JACOBIAN(q) returns the Jacobian that satisfies
- % vec(x_dot) = J * q_dot, where x = fkm(q) and q is the
- % vector of joint variables.
- %
- % RAW_POSE_JACOBIAN(q,ith) returns the Jacobian that
- % satisfies vec(x_ith_dot) = J * q_dot(1:ith), where
- % x_ith = fkm(q, ith), that is, the fkm up to the i-th link.
- %
- % This function does not take into account any base or
- % end-effector displacements and should be used mostly
- % internally in DQ_kinematics
-
- if nargin == 3
- n = ith;
- x_effector = obj.raw_fkm(q,ith);
+ x = obj.reference_frame_*obj.raw_fkm(q, ith); %Takes into account the base displacement
else
- n = obj.n_links;
- x_effector = obj.raw_fkm(q);
- end
-
- x = DQ(1);
- J = zeros(8,n);
-
- for i = 0:n-1
- % Use the standard DH convention
- if strcmp(obj.convention,'standard')
- z = DQ(obj.get_z(x.q));
- else % Use the modified DH convention
- w = DQ([0,0,-sin(obj.alpha(i+1)),cos(obj.alpha(i+1)),0, ...
- 0,-obj.a(i+1)*cos(obj.alpha(i+1)), ...
- -obj.a(i+1)*sin(obj.alpha(i+1))] );
- z = 0.5*x*w*x';
- end
-
- x = x*obj.dh2dq(q(i+1),i+1);
- j = z * x_effector;
- J(:,i+1) = vec8(j);
+ x = obj.reference_frame_*obj.raw_fkm(q)*obj.effector_;
end
- end
-
+ end
+
function J = pose_jacobian(obj, q, ith)
% POSE_JACOBIAN(q) returns the Jacobian that satisfies
% vec(x_dot) = J * q_dot, where x = fkm(q) and
@@ -265,75 +224,21 @@ function set_effector(obj,effector)
% both base and end-effector displacements (their default
% values are 1).
- if nargin == 3 && ith < obj.n_links
+ if nargin == 3 && ith < obj.dim_configuration_space_
% If the Jacobian is not related to the mapping between the
% end-effector velocities and the joint velocities, it takes
% into account only the base displacement
- J = hamiplus8(obj.reference_frame)*obj.raw_pose_jacobian(...
+ J = hamiplus8(obj.reference_frame_)*obj.raw_pose_jacobian(...
q, ith);
else
% Otherwise, it the Jacobian is related to the
% end-effector velocity, it takes into account both base
% and end-effector (constant) displacements.
- J = hamiplus8(obj.reference_frame)*haminus8(obj.effector)*...
+ J = hamiplus8(obj.reference_frame_)*haminus8(obj.effector_)*...
obj.raw_pose_jacobian(q);
end
- end
-
- function J_dot = pose_jacobian_derivative(obj,q,q_dot, ith)
- % POSE_JACOBIAN_DERIVATIVE(q,q_dot) returns the Jacobian
- % time derivative.
- %
- % POSE_JACOBIAN_DERIVATIVE(q,q_dot,ith) returns the first
- % ith columns of the Jacobian time derivative.
- % This function does not take into account any base or
- % end-effector displacements.
-
- if nargin == 4
- n = ith;
- x_effector = obj.raw_fkm(q,ith);
- J = obj.raw_pose_jacobian(q,ith);
- vec_x_effector_dot = J*q_dot(1:ith);
- else
- n = obj.n_links;
- x_effector = obj.raw_fkm(q);
- J = obj.raw_pose_jacobian(q);
- vec_x_effector_dot = J*q_dot;
- end
-
- x = DQ(1);
- J_dot = zeros(8,n);
-
- for i = 0:n-1
- % Use the standard DH convention
- if strcmp(obj.convention,'standard')
- w = DQ.k;
- z = DQ(obj.get_z(x.q));
- else % Use the modified DH convention
- w = DQ([0,0,-sin(obj.alpha(i+1)),cos(obj.alpha(i+1)),0, ...
- 0,-obj.a(i+1)*cos(obj.alpha(i+1)),...
- -obj.a(i+1)*sin(obj.alpha(i+1))] );
- z = 0.5*x*w*x';
- end
+ end
- % When i = 0 and length(theta) = 1, theta(1,i) returns
- % a 1 x 0 vector, differently from the expected
- % behavior, which is to return a 0 x 1 matrix.
- % Therefore, we have to deal with the case i = 0
- % explictly.
- if i ~= 0
- vec_zdot = 0.5*(haminus8(w*x') + ...
- hamiplus8(x*w)*DQ.C8) * ...
- obj.raw_pose_jacobian(q,i)*q_dot(1:i);
- else
- vec_zdot = zeros(8,1);
- end
- J_dot(:,i+1) = haminus8(x_effector)*vec_zdot +...
- hamiplus8(z)*vec_x_effector_dot;
- x = x*obj.dh2dq(q(i+1),i+1);
- end
- end
-
function plot(robot,q,varargin)
% plot(robot,q,options) plots the robot of type DQ_kinematics.
% q is the vector of joint configurations
@@ -444,7 +349,7 @@ function dq_kinematics_plot(robot, q, varargin)
opt = plot_options(robot, varargin);
end
- n = robot.n_links;
+ n = robot.dim_configuration_space_;
if length(q) ~= n
error('Incorrect number of joints. The correct number is %d', n);
@@ -521,14 +426,14 @@ function dq_kinematics_plot(robot, q, varargin)
% Draw a small plane representing the robot base
if opt.base
- plane = robot.base_frame.'*DQ.k*robot.base_frame';
+ plane = robot.base_frame_.'*DQ.k*robot.base_frame_';
% Since the plane is infinite, the DQ.plot function draws the part
% closest to the origin of the reference frame. We first
% consider the plane that passes through the origin and is aligned with
% the one that supports the base
base_handle = plot(plane.P,'plane',opt.mag,'color','k');
% We then translate the 'visible' plane to the base frame
- base_translation = vec3(translation(robot.base_frame));
+ base_translation = vec3(translation(robot.base_frame_));
plane_vertices = get(base_handle, 'Vertices');
for i = 1:3
plane_vertices(:,i) = plane_vertices(:,i) + base_translation(i);
@@ -539,7 +444,7 @@ function dq_kinematics_plot(robot, q, varargin)
% Write the robot name.
if opt.name
- b = vec3(translation(robot.base_frame));
+ b = vec3(translation(robot.base_frame_));
h.name_handle = text(b(1), b(2) - opt.mag, b(3), [' ' robot.name],...
'FontAngle', 'italic','FontWeight', 'bold');
end
@@ -572,7 +477,7 @@ function dq_kinematics_plot(robot, q, varargin)
end
% Display cylinders (revolute each joint).
- for i = 1:robot.n_links
+ for i = 1:robot.dim_configuration_space_
if opt.joints
%TODO: implement prismatic joints
N = 8;
@@ -622,7 +527,7 @@ function dq_kinematics_plot(robot, q, varargin)
% kinematic robot, and graphics are defined by the handle structure robot.handle,
% which stores the 'graphical robot' as robot.handle.robot.
function update_robot(robot, q)
- n = robot.n_links;
+ n = robot.dim_configuration_space_;
% Get the handle to the graphical robot. Since each kinematic robot
% stores just one graphical handle, if we want to plot the same robot
@@ -632,7 +537,7 @@ function update_robot(robot, q)
% the last view only.
h = robot.handle;
mag = h.mag;
- base = vec3(translation(robot.base_frame));
+ base = vec3(translation(robot.base_frame_));
% Initialize the vector containing the origin of each frame along the
% kinematic chain
@@ -647,7 +552,7 @@ function update_robot(robot, q)
% compute the link transforms, and record the origin of each frame
% for the graphics update.
for j=1:n
- t = vec3(translation(robot.base_frame*robot.raw_fkm(q,j)));
+ t = vec3(translation(robot.base_frame_*robot.raw_fkm(q,j)));
x(j+1) = t(1);
y(j+1) = t(2);
z(j+1) = t(3);
@@ -672,7 +577,7 @@ function update_robot(robot, q)
for k = 1:size(xyz,2)
% 1 + DQ.E*(1/2)*p, where p = xyz(1:3,k);
cylinder_vertex = DQ([1;0;0;0;0;0.5*xyz(1:3,k)]);
- xyz(1:3,k) = vec3(translation(robot.base_frame*fkm_j*cylinder_vertex));
+ xyz(1:3,k) = vec3(translation(robot.base_frame_*fkm_j*cylinder_vertex));
end
% Now that all cylinder vertices are transformed, update the
@@ -695,7 +600,7 @@ function update_robot(robot, q)
if isfield(h, 'x')
% get the end-effector pose (considering the final transformation given
% by set_end_effector()
- t = robot.base_frame*robot.raw_fkm(q)*robot.effector;
+ t = robot.base_frame_*robot.raw_fkm(q)*robot.get_effector();
t1 = vec3(translation(t));
% The following transformations use the Hamilton operators to
@@ -733,6 +638,11 @@ function update_robot(robot, q)
% o = plot_options(robot, options) returns an options structure.
% 'robot' is the kinematic robot and 'options' is an array cell with the plot
% options.
+%
+% TODO:
+% This implementation assumes we are using the DH parametrization.
+% we need to fix it in the future.
+%
function o = plot_options(robot, optin)
% process a cell array of options and return a struct
% define all possible options and their default values
@@ -766,10 +676,13 @@ function update_robot(robot, q)
% simple heuristic to figure the maximum reach of the robot
if isempty(o.workspace)
reach = 0;
- for i=1:robot.n_links
+ for i=1:robot.dim_configuration_space_
% Since the maximum reaching distance are given by the link offset
% and link length, we add them.
- reach = reach + abs(robot.a(i)) + abs(robot.d(i));
+ %reach = reach + abs(robot.a(i)) + abs(robot.d(i));
+ robot_a = robot.get_dh_parameters_a();
+ robot_d = robot.get_dh_parameters_d();
+ reach = reach + abs(robot_a(i)) + abs(robot_d(i));
end
o.workspace = [-reach reach -reach reach -reach reach];
else
diff --git a/robot_modeling/DQ_SerialManipulatorDH.m b/robot_modeling/DQ_SerialManipulatorDH.m
index e906bcc5..f5731dc0 100644
--- a/robot_modeling/DQ_SerialManipulatorDH.m
+++ b/robot_modeling/DQ_SerialManipulatorDH.m
@@ -1,32 +1,34 @@
% Concrete class that extends the DQ_SerialManipulator using the
% Denavit-Hartenberg parameters (DH)
%
-% Usage: robot = DQ_SerialManipulatorDH(A)
-% - 'A' is a 4 x n matrix containing the Denavit-Hartenberg parameters
+% Usage: robot = DQ_SerialManipulatorDH(dh_matrix)
+% - 'dh_matrix' is a 5 x n matrix containing the Denavit-Hartenberg parameters
% (n is the number of links)
-% A = [theta1 ... thetan;
-% d1 ... dn;
-% a1 ... an;
-% alpha1 ... alphan;
-% type1 ... typen]
-% where type is the actuation type, either DQ_SerialManipulatorDH.JOINT_ROTATIONAL
-% or DQ_SerialManipulatorDH.JOINT_PRISMATIC
+% dh_matrix = [theta1 ... thetan;
+% d1 ... dn;
+% a1 ... an;
+% alpha1 ... alphan;
+% type1 ... typen]
+% where type is the actuation type, either DQ_SerialManipulatorDH.REVOLUTE
+% or DQ_SerialManipulatorDH.PRISMATIC
% - The only accepted convention in this subclass is the 'standard' DH
% convention.
%
-% If the joint is of type JOINT_ROTATIONAL, then the first row of A will
-% have the joint offsets. If the joint is of type JOINT_PRISMATIC, then the
-% second row of A will have the joints offsets.
+% If the joint is of type REVOLUTE, then the first row of dh_matrix will
+% have the joint offsets. If the joint is of type PRISMATIC, then the
+% second row of dh_matrix will have the joints offsets.
%
% DQ_SerialManipulatorDH Methods (Concrete):
-% get_dim_configuration_space - Return the dimension of the configuration space.
-% fkm - Compute the forward kinematics while taking into account base and end-effector's rigid transformations.
-% plot - Plots the serial manipulator.
-% pose_jacobian - Compute the pose Jacobian while taking into account base's and end-effector's rigid transformations.
+% get_dh_parameters_theta - Returns the vector containing the theta parameters of the DH table.
+% get_dh_parameters_d - Returns the vector containing the d parameters of the DH table.
+% get_dh_parameters_a - Returns the vector containing the a parameters of the DH table.
+% get_dh_parameters_alpha - Returns the vector containing the alpha parameters of the DH table.
+% get_joint_types - Returns the joint type, which can be either REVOLUTE or PRISMATIC.
% pose_jacobian_derivative - Compute the time derivative of the pose Jacobian.
-% raw_fkm - Compute the FKM without taking into account base's and end-effector's rigid transformations.
% raw_pose_jacobian - Compute the pose Jacobian without taking into account base's and end-effector's rigid transformations.
-% set_effector - Set an arbitrary end-effector rigid transformation with respect to the last frame in the kinematic chain.
+% raw_fkm - Compute the FKM without taking into account base's and end-effector's rigid transformations.
+%
+%
% See also DQ_SerialManipulator.
% (C) Copyright 2020 DQ Robotics Developers
@@ -49,87 +51,43 @@
% DQ Robotics website: dqrobotics.github.io
%
% Contributors to this file:
+% Bruno Vihena Adorno - bruno.adorno@manchester.ac.uk
% Murilo M. Marinho - murilo@nml.t.u-tokyo.ac.jp
+% Juan Jose Quiroz Omana - juanjqo@g.ecc.u-tokyo.ac.jp
classdef DQ_SerialManipulatorDH < DQ_SerialManipulator
- properties
- type
+
+
+ properties (Access = protected)
+ dh_matrix_;
end
properties (Constant)
% Joints that can be actuated
- % Rotational joint
- JOINT_ROTATIONAL = 1;
+ % Revolute joint
+ JOINT_ROTATIONAL = 1; % Deprecated
% Prismatic joint
- JOINT_PRISMATIC = 2;
+ JOINT_PRISMATIC = 2; % Deprecated
+ Parameter = struct('Theta', 1, 'D',2, 'A', 3, 'Alpha', 4, 'JointType', 5);
+ JointType = struct('REVOLUTE',1, 'PRISMATIC',2);
end
- methods
- function obj = DQ_SerialManipulatorDH(A,convention)
- % These are initialized in the constructor of
- % DQ_SerialManipulator
- %obj.convention = convention;
- %obj.n_links = size(A,2);
- %obj.theta = A(1,:);
- %obj.d = A(2,:);
- %obj.a = A(3,:);
- %obj.alpha = A(4,:);
- obj = obj@DQ_SerialManipulator(A(1:4,:),convention);
-
- if nargin == 0
- error('Input: matrix whose columns contain the DH parameters')
- end
-
- if(size(A,1) ~= 5)
- error('Input: Invalid DH matrix. It should have 5 rows.')
- end
-
- % Add type
- obj.type = A(5,:);
- end
-
- function x = raw_fkm(obj,q,to_ith_link)
- % RAW_FKM(q) calculates the forward kinematic model and
- % returns the dual quaternion corresponding to the
- % last joint (the displacements due to the base and the effector
- % are not taken into account).
- %
- % 'q' is the vector of joint variables
- % 'to_ith_link' defines until which link the raw_fkm will be
- % calculated.
- %
- % This is an auxiliary function to be used mainly with the
- % Jacobian function.
- if nargin == 3
- n = to_ith_link;
- else
- n = obj.n_links;
- end
-
- x = DQ(1);
-
- for i=1:n
- x = x*dh2dq(obj,q(i),i);
- end
- end
-
- function x = fkm(obj,q,to_ith_link)
- % FKM(q) calculates the forward kinematic model and
- % returns the dual quaternion corresponding to the
- % end-effector pose. This function takes into account the
- % displacement due to the base's and effector's poses.
- %
- % 'q' is the vector of joint variables
- % 'to_ith_link' defines up to which link the fkm will be
- % calculated. If to_ith_link corresponds to the last link,
- % the method DOES NOT take into account the transformation
- % given by set_effector. If you want to take into account
- % that transformation, use FKM(q) instead.
-
- if nargin == 3
- x = obj.reference_frame*obj.raw_fkm(q, to_ith_link); %Takes into account the base displacement
+ methods (Access = protected)
+ function w = get_w(obj,ith)
+ % This method returns the term 'w' related with the time derivative of
+ % the unit dual quaternion pose using the Standard DH convention.
+ % See. eq (2.32) of 'Two-arm Manipulation: From Manipulators to Enhanced
+ % Human-Robot Collaboration' by Bruno Adorno.
+ % Usage: w = get_w(ith), where
+ % ith: link number
+ joint_type = obj.dh_matrix_(5,ith);
+ if joint_type == DQ_JointType.REVOLUTE
+ w = DQ.k;
else
- x = obj.reference_frame*obj.raw_fkm(q)*obj.effector;
+ % see Table 1 of "Dynamics of Mobile Manipulators using Dual Quaternion Algebra."
+ % by Silva, F. F. A., Quiroz-Omaña, J. J., and Adorno, B. V. (April 12, 2022).
+ % ASME. J. Mechanisms Robotics. doi: https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4054320
+ w = DQ.E*DQ.k;
end
end
@@ -141,33 +99,20 @@
% ith: link number
if nargin ~= 3
- error('Wrong number of arguments. The parameters are joint value and the correspondent link')
+ error(['Wrong number of arguments. The parameters are joint ' ...
+ 'value and the correspondent link'])
end
-
- %The unoptimized standard dh2dq calculation is commented below
- %if obj.type(ith) == obj.JOINT_ROTATIONAL
- % % If joint is rotational
- % h1 = cos((obj.theta(ith)+q)/2.0)+DQ.k*sin((obj.theta(ith)+q)/2.0);
- % h2 = 1 + DQ.E*0.5*obj.d(ith)*DQ.k;
- %else
- % % If joint is prismatic
- % h1 = cos(obj.theta(ith)/2.0)+DQ.k*sin(obj.theta(ith)/2.0);
- % h2 = 1 + DQ.E*0.5*(obj.d(ith)+q)*DQ.k;
- %end
- %h3 = 1 + DQ.E*0.5*obj.a(ith)*DQ.i;
- %h4 = cos(obj.alpha(ith)/2.0)+DQ.i*sin(obj.alpha(ith)/2.0);
- %dq = h1*h2*h3*h4;
-
- % The optimized standard dh2dq calculation
+
% Store half angles and displacements
- half_theta = obj.theta(ith)/2.0;
- d = obj.d(ith);
- a = obj.a(ith);
- half_alpha = obj.alpha(ith)/2.0;
+ half_theta = obj.dh_matrix_(1,ith)/2.0; %obj.theta(ith)/2.0;
+ d = obj.dh_matrix_(2,ith); %obj.d(ith);
+ a = obj.dh_matrix_(3,ith); %obj.a(ith);
+ half_alpha = obj.dh_matrix_(4,ith)/2.0; %obj.alpha(ith)/2.0;
+ joint_type = obj.dh_matrix_(5,ith);
- % Add the effect of the joint value
- if obj.type(ith) == obj.JOINT_ROTATIONAL
- % If joint is rotational
+ % Add the effect of the joint value
+ if joint_type == DQ_JointType.REVOLUTE
+ % If joint is revolute
half_theta = half_theta + (q/2.0);
else
% If joint is prismatic
@@ -180,35 +125,189 @@
sine_of_half_alpha = sin(half_alpha);
cosine_of_half_alpha = cos(half_alpha);
- % Return the optimized standard dh2dq calculation
- dq = DQ([
- cosine_of_half_alpha*cosine_of_half_theta
-
- sine_of_half_alpha*cosine_of_half_theta
-
- sine_of_half_alpha*sine_of_half_theta
-
- cosine_of_half_alpha*sine_of_half_theta
-
- -(a*sine_of_half_alpha*cosine_of_half_theta) /2.0...
- - (d*cosine_of_half_alpha*sine_of_half_theta)/2.0
+ d2 = d/2;
+ a2 = a/2;
+ h(1) = cosine_of_half_alpha*cosine_of_half_theta;
+ h(2) = sine_of_half_alpha*cosine_of_half_theta;
+ h(3) = sine_of_half_alpha*sine_of_half_theta;
+ h(4) = cosine_of_half_alpha*sine_of_half_theta;
+ h(5) = -a2*h(2) - d2*h(4);
+ h(6) = a2*h(1) - d2*h(3);
+ h(7) = a2*h(4) + d2*h(2);
+ h(8) = d2*h(1) - a2*h(3);
+ dq = DQ(h);
+ end
+
+ end
+
+ methods
+ function obj = DQ_SerialManipulatorDH(dh_matrix, convention)
+ % These are initialized in the constructor of
+ % DQ_SerialManipulator, where dh_matrix is given as follows
+ % dh_matrix = [theta1 ... thetan;
+ % d1 ... dn;
+ % a1 ... an;
+ % alpha1 ... alphan;
+ % type1 ... typen]
+ str = ['DQ_SerialManipulatorDH(dh_matrix), where ' ...
+ 'dh_matrix = [theta1 ... thetan; ' ...
+ ' d1 ... dn; ' ...
+ ' a1 ... an; ' ...
+ ' alpha1 ... alphan; ' ...
+ ' type1 ... typen]'];
+
+
+ if nargin == 0
+ error(['Input: matrix whose columns contain the DH parameters' ...
+ ' and type of joints. Example: ' str])
+ end
+ if nargin == 2
+ warning(['DQ_SerialManipulatorDH(dh_matrix, convention) is deprecated.' ...
+ ' Please use DQ_SerialManipulatorDH(dh_matrix) instead.']);
- (a*cosine_of_half_alpha*cosine_of_half_theta)/2.0...
- - (d*sine_of_half_alpha*sine_of_half_theta )/2.0
+ end
+
+ if(size(dh_matrix,1) ~= 5)
+ error(['Input: Invalid DH matrix. It should have 5 rows. ' ...
+ 'Example: ' str])
+ end
+
+ obj = obj@DQ_SerialManipulator(size(dh_matrix,2));
+ obj.dh_matrix_ = dh_matrix;
+
+ end
+
+ function ret = get_parameters(obj, parameter)
+ %GET_PARAMETERS(parameter) Returns the vector containing the
+ % parameter specified. The parameter can be the DH parameters as
+ % Theta, A, D, Alpha, or can be JointType.
+ % Example:
+ % robot = DQ_SerialManipulatorDH(dh_matrix);
+ % dh_alphas = robot.get_parameters(robot.Parameter.Alpha)
+ ret = obj.dh_matrix_(parameter,:);
+ end
+
+ function ret = get_parameter(obj, parameter, ith)
+ %GET_PARAMETERS(parameter, ith) Returns the scalar containing the
+ % parameter specified of the ith joint.
+ % The parameter can be the DH parameters as
+ % Theta, A, D, Alpha, or can be JointType.
+ % Example:
+ % robot = DQ_SerialManipulatorDH(dh_matrix);
+ % dh_alpha = robot.get_parameter(robot.Parameter.Alpha, 3)
+ ret = obj.dh_matrix_(parameter,ith);
+ end
+
+ function th = get_dh_parameters_theta(obj)
+ %GET_DH_PARAMETERS_THETA() Returns the vector containing the
+ % theta parameters of the DH table.
+ th = obj.dh_matrix_(1,:); %obj.theta;
+ end
+
+ function ds = get_dh_parameters_d(obj)
+ % GET_DH_PARAMETERS_D() Returns the vector containing the d
+ % parameters of the DH table.
+ ds = obj.dh_matrix_(2,:); %obj.d;
+ end
+
+ function as = get_dh_parameters_a(obj)
+ % GET_DH_PARAMETERS_A() Returns the vector containing the a
+ % parameters of the DH table.
+ as = obj.dh_matrix_(3,:); %obj.a;
+ end
+
+ function alphas = get_dh_parameters_alpha(obj)
+ % GET_DH_PARAMETERS_ALPHA() Returns the vector containing
+ % the alpha parameters of the DH table.
+ alphas = obj.dh_matrix_(4,:); %obj.alpha;
+ end
+
+ function types = get_joint_types(obj)
+ % GET_JOINT_TYPES() Returns the joint type, which can be
+ % either REVOLUTE or PRISMATIC.
+ types = obj.dh_matrix_(5,:); %obj.type;
+ end
+
+ % TODO:
+ % This method is not defined in the DQ_Kinematics superclass
+ % we need to fix it in the future.
+ function J_dot = pose_jacobian_derivative(obj,q,q_dot, to_ith_link)
+ % POSE_JACOBIAN_DERIVATIVE(q,q_dot) returns the Jacobian
+ % time derivative.
+ %
+ % POSE_JACOBIAN_DERIVATIVE(q,q_dot,to_ith_link) returns the first
+ % to_ith_link columns of the Jacobian time derivative.
+ % This function does not take into account any base or
+ % end-effector displacements.
+ obj.check_q_vec(q);
+ obj.check_q_vec(q_dot);
+
+ if nargin == 4
+ n = to_ith_link;
+ x_effector = obj.raw_fkm(q,to_ith_link);
+ J = obj.raw_pose_jacobian(q,to_ith_link);
+ vec_x_effector_dot = J*q_dot(1:to_ith_link);
+ else
+ n = obj.dim_configuration_space_;
+ obj.check_to_ith_link(n);
+ x_effector = obj.raw_fkm(q);
+ J = obj.raw_pose_jacobian(q);
+ vec_x_effector_dot = J*q_dot;
+ end
+
+ x = DQ(1);
+ J_dot = zeros(8,n);
+
+ for i = 0:n-1
+ % Use the standard DH convention
- (a*cosine_of_half_alpha*sine_of_half_theta) /2.0...
- + (d*sine_of_half_alpha*cosine_of_half_theta)/2.0
+ w = obj.get_w(i+1); %w = DQ.k;
+ %z = DQ(obj.get_z(x.q));
+ z = 0.5*x*w*conj(x);
- (d*cosine_of_half_alpha*cosine_of_half_theta)/2.0...
- - (a*sine_of_half_alpha*sine_of_half_theta )/2.0
- ]);
+ % When i = 0 and length(theta) = 1, theta(1,i) returns
+ % a 1 x 0 vector, differently from the expected
+ % behavior, which is to return a 0 x 1 matrix.
+ % Therefore, we have to deal with the case i = 0
+ % explictly.
+ if i ~= 0
+ vec_zdot = 0.5*(haminus8(w*x') + ...
+ hamiplus8(x*w)*DQ.C8) * ...
+ obj.raw_pose_jacobian(q,i)*q_dot(1:i);
+ else
+ vec_zdot = zeros(8,1);
+ end
+ J_dot(:,i+1) = haminus8(x_effector)*vec_zdot +...
+ hamiplus8(z)*vec_x_effector_dot;
+ x = x*obj.dh2dq(q(i+1),i+1);
+ end
end
- function w = get_w(obj,ith)
- if obj.type(ith) == obj.JOINT_ROTATIONAL
- w = DQ.k;
+ function x = raw_fkm(obj,q,to_ith_link)
+ % RAW_FKM(q) calculates the forward kinematic model and
+ % returns the dual quaternion corresponding to the
+ % last joint (the displacements due to the base and the effector
+ % are not taken into account).
+ %
+ % 'q' is the vector of joint variables
+ % 'to_ith_link' defines until which link the raw_fkm will be
+ % calculated.
+ %
+ % This is an auxiliary function to be used mainly with the
+ % Jacobian function.
+ obj.check_q_vec(q);
+
+ if nargin == 3
+ n = to_ith_link;
else
- w = DQ.E*DQ.k;
+ n = obj.dim_configuration_space_;
+ end
+
+ obj.check_to_ith_link(n);
+ x = DQ(1);
+
+ for i=1:n
+ x = x*dh2dq(obj,q(i),i);
end
end
@@ -224,23 +323,29 @@
% This function does not take into account any base or
% end-effector displacements and should be used mostly
% internally in DQ_kinematics
-
- if nargin < 3
- to_ith_link = obj.n_links;
+ obj.check_q_vec(q);
+
+ if nargin == 3
+ n = to_ith_link;
+ else
+ n = obj.dim_configuration_space_;
end
- x_effector = obj.raw_fkm(q,to_ith_link);
-
+
+ obj.check_to_ith_link(n);
+ x_effector = obj.raw_fkm(q,n);
+
x = DQ(1);
- J = zeros(8,to_ith_link);
+ J = zeros(8,n);
- for i = 0:to_ith_link-1
- w = obj.get_w(i+1);
+ for i = 1:n
+ w = obj.get_w(i);
z = 0.5*Ad(x,w);
- x = x*obj.dh2dq(q(i+1),i+1);
+ x = x*obj.dh2dq(q(i),i);
j = z * x_effector;
- J(:,i+1) = vec8(j);
+ J(:,i) = vec8(j);
end
end
end
-end
\ No newline at end of file
+end
+
diff --git a/robot_modeling/DQ_SerialManipulatorMDH.m b/robot_modeling/DQ_SerialManipulatorMDH.m
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..258adabb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/robot_modeling/DQ_SerialManipulatorMDH.m
@@ -0,0 +1,310 @@
+% Concrete class that extends the DQ_SerialManipulator using the Modified
+% Denavit-Hartenberg parameters (MDH)
+%
+% Usage: robot = DQ_SerialManipulatorMDH(A)
+% - 'A' is a 5 x n matrix containing the Denavit-Hartenberg parameters
+% (n is the number of links)
+% A = [theta1 ... thetan;
+% d1 ... dn;
+% a1 ... an;
+% alpha1 ... alphan;
+% type1 ... typen]
+% where type is the actuation type, either DQ_SerialManipulatorDH.REVOLUTE
+% or DQ_SerialManipulatorDH.PRISMATIC
+% - The only accepted convention in this subclass is the 'standard' DH
+% convention.
+%
+% If the joint is of type REVOLUTE, then the first row of A will
+% have the joint offsets. If the joint is of type JOINT_PRISMATIC, then the
+% second row of A will have the joints offsets.
+%
+% DQ_SerialManipulatorDH Methods (Concrete):
+% get_dh_parameters_theta - Returns the vector containing the theta parameters of the MDH table.
+% get_dh_parameters_d - Returns the vector containing the d parameters of the MDH table.
+% get_dh_parameters_a - Returns the vector containing the a parameters of the MDH table.
+% get_dh_parameters_alpha - Returns the vector containing the alpha parameters of the MDH table.
+% get_joint_types - Returns the joint type, which can be either REVOLUTE or PRISMATIC.
+% pose_jacobian_derivative - Compute the time derivative of the pose Jacobian.
+% raw_fkm - Compute the FKM without taking into account base's and end-effector's rigid transformations.
+% raw_pose_jacobian - Compute the pose Jacobian without taking into account base's and end-effector's rigid transformations.
+
+
+% (C) Copyright 2022 DQ Robotics Developers
+%
+% This file is part of DQ Robotics.
+%
+% DQ Robotics is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
+% it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published
+% by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
+% (at your option) any later version.
+%
+% DQ Robotics is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
+% but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
+% MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
+% GNU Lesser General Public License for more details.
+%
+% You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
+% along with DQ Robotics. If not, see .
+%
+% DQ Robotics website: dqrobotics.github.io
+%
+% Contributors to this file:
+% Bruno Vihena Adorno - bruno.adorno@manchester.ac.uk
+% Murilo M. Marinho - murilo@nml.t.u-tokyo.ac.jp
+% Juan Jose Quiroz Omana - juanjqo@g.ecc.u-tokyo.ac.jp
+
+classdef DQ_SerialManipulatorMDH < DQ_SerialManipulator
+
+
+ properties (Access = protected)
+ mdh_matrix_;
+
+ end
+
+ properties (Constant)
+ % Joints that can be actuated
+ % Revolute joint
+ JOINT_ROTATIONAL = 1;
+ % Prismatic joint
+ JOINT_PRISMATIC = 2;
+ end
+
+ methods (Access = protected)
+ function w = get_w(obj,ith)
+ % This method returns the term 'w' related with the time derivative of
+ % the unit dual quaternion pose using the Modified DH convention.
+ % See. eq (2.32) of 'Two-arm Manipulation: From Manipulators to Enhanced
+ % Human-Robot Collaboration' by Bruno Adorno.
+ % Usage: w = get_w(ith), where
+ % ith: link number
+ joint_type = obj.mdh_matrix_(5,ith);
+ alpha = obj.mdh_matrix_(4,ith);
+ a = obj.mdh_matrix_(3,ith);
+
+ if joint_type == DQ_JointType.REVOLUTE
+ w = -DQ.j*sin(alpha)+ DQ.k*cos(alpha)...
+ -DQ.E*a*(DQ.j*cos(alpha) + DQ.k*sin(alpha));
+ else
+ w = DQ.E*(cos(alpha)*DQ.k - sin(alpha)*DQ.j);
+ end
+ end
+
+ function dq = mdh2dq(obj,q,ith)
+ % For a given link's Extended MDH parameters, calculate the correspondent dual
+ % quaternion
+ % Usage: dq = dh2dq(q,ith), where
+ % q: joint value
+ % ith: link number
+
+ if nargin ~= 3
+ error('Wrong number of arguments. The parameters are joint value and the correspondent link')
+ end
+
+
+ half_theta = obj.mdh_matrix_(1,ith)/2.0;
+ d = obj.mdh_matrix_(2,ith);
+ a = obj.mdh_matrix_(3,ith);
+ half_alpha = obj.mdh_matrix_(4,ith)/2.0;
+ joint_type = obj.mdh_matrix_(5,ith);
+
+ % Add the effect of the joint value
+ if joint_type == DQ_JointType.REVOLUTE
+ % If joint is revolute
+ half_theta = half_theta + (q/2.0);
+ else
+ % If joint is prismatic
+ d = d + q;
+ end
+
+ % Pre-calculate cosines and sines
+ sine_of_half_theta = sin(half_theta);
+ cosine_of_half_theta = cos(half_theta);
+ sine_of_half_alpha = sin(half_alpha);
+ cosine_of_half_alpha = cos(half_alpha);
+
+ d2 = d/2;
+ a2 = a/2;
+ h(1) = cosine_of_half_alpha*cosine_of_half_theta;
+ h(2) = sine_of_half_alpha*cosine_of_half_theta;
+ h(3) = -sine_of_half_alpha*sine_of_half_theta;
+ h(4) = cosine_of_half_alpha*sine_of_half_theta;
+ h(5) = -a2*h(2) - d2*h(4);
+ h(6) = a2*h(1) - d2*-h(3);
+ h(7) = -a2*h(4) - d2*h(2);
+ h(8) = d2*h(1) - a2*-h(3);
+ dq = DQ(h);
+ end
+ end
+
+ methods
+ function obj = DQ_SerialManipulatorMDH(A)
+ % These are initialized in the constructor of
+ % DQ_SerialManipulator
+ str = ['DQ_SerialManipulatorMDH(A), where ' ...
+ 'A = [theta1 ... thetan; ' ...
+ ' d1 ... dn; ' ...
+ ' a1 ... an; ' ...
+ ' alpha1 ... alphan; ' ...
+ ' type1 ... typen]'];
+ if nargin == 0
+ error(['Input: matrix whose columns contain the MDH parameters' ...
+ ' and type of joints. Example: ' str])
+ end
+
+ if(size(A,1) ~= 5)
+ error(['Input: Invalid DH matrix. It should have 5 rows.' ...
+ ' Example: ' str])
+ end
+
+ obj = obj@DQ_SerialManipulator(size(A,2));
+ obj.mdh_matrix_ = A;
+
+ end
+
+
+
+ function th = get_dh_parameters_theta(obj)
+ %GET_DH_PARAMETERS_THETA() Returns the vector containing the theta parameters of the MDH table.
+ th = obj.mdh_matrix_(1,:);
+ end
+
+ function ds = get_dh_parameters_d(obj)
+ % GET_DH_PARAMETERS_D() Returns the vector containing the d parameters of the MDH table.
+ ds = obj.mdh_matrix_(2,:);
+ end
+
+ function as = get_dh_parameters_a(obj)
+ % GET_DH_PARAMETERS_A() Returns the vector containing the a parameters of the MDH table.
+ as = obj.mdh_matrix_(3,:);
+ end
+
+ function alphas = get_dh_parameters_alpha(obj)
+ % GET_DH_PARAMETERS_ALPHA() Returns the vector containing the alpha parameters of the MDH table.
+ alphas = obj.mdh_matrix_(4,:);
+ end
+
+ function types = get_joint_types(obj)
+ % GET_JOINT_TYPES() Returns the joint type, which can be either REVOLUTE or PRISMATIC.
+ types = obj.mdh_matrix_(5,:);
+ end
+
+ % TODO:
+ % This method is not defined in the DQ_Kinematics superclass
+ % we need to fix it in the future.
+ function J_dot = pose_jacobian_derivative(obj,q,q_dot, to_ith_link)
+ % POSE_JACOBIAN_DERIVATIVE(q,q_dot) returns the Jacobian
+ % time derivative.
+ %
+ % POSE_JACOBIAN_DERIVATIVE(q,q_dot,to_ith_link) returns the first
+ % to_ith_link columns of the Jacobian time derivative.
+ % This function does not take into account any base or
+ % end-effector displacements.
+ obj.check_q_vec(q);
+ obj.check_q_vec(q_dot);
+
+ if nargin == 4
+ n = to_ith_link;
+ x_effector = obj.raw_fkm(q,to_ith_link);
+ J = obj.raw_pose_jacobian(q,to_ith_link);
+ vec_x_effector_dot = J*q_dot(1:to_ith_link);
+ else
+ n = obj.dim_configuration_space_;
+ obj.check_to_ith_link(n);
+ x_effector = obj.raw_fkm(q);
+ J = obj.raw_pose_jacobian(q);
+ vec_x_effector_dot = J*q_dot;
+ end
+
+
+ x = DQ(1);
+ J_dot = zeros(8,n);
+
+ for i = 0:n-1
+ % Use the standard DH convention
+ w = obj.get_w(i+1);
+ z = 0.5*x*w*conj(x);
+
+ % When i = 0 and length(theta) = 1, theta(1,i) returns
+ % a 1 x 0 vector, differently from the expected
+ % behavior, which is to return a 0 x 1 matrix.
+ % Therefore, we have to deal with the case i = 0
+ % explictly.
+ if i ~= 0
+ vec_zdot = 0.5*(haminus8(w*x') + ...
+ hamiplus8(x*w)*DQ.C8) * ...
+ obj.raw_pose_jacobian(q,i)*q_dot(1:i);
+ else
+ vec_zdot = zeros(8,1);
+ end
+ J_dot(:,i+1) = haminus8(x_effector)*vec_zdot +...
+ hamiplus8(z)*vec_x_effector_dot;
+ x = x*obj.mdh2dq(q(i+1),i+1);
+ end
+ end
+
+ function x = raw_fkm(obj,q,to_ith_link)
+ % RAW_FKM(q) calculates the forward kinematic model and
+ % returns the dual quaternion corresponding to the
+ % last joint (the displacements due to the base and the effector
+ % are not taken into account).
+ %
+ % 'q' is the vector of joint variables
+ % 'to_ith_link' defines until which link the raw_fkm will be
+ % calculated.
+ %
+ % This is an auxiliary function to be used mainly with the
+ % Jacobian function.
+
+ obj.check_q_vec(q);
+
+ if nargin == 3
+ n = to_ith_link;
+ else
+ n = obj.dim_configuration_space_;
+ end
+
+ obj.check_to_ith_link(n);
+ x = DQ(1);
+
+ for i=1:n
+ x = x*mdh2dq(obj,q(i),i);
+ end
+ end
+
+ function J = raw_pose_jacobian(obj,q,to_ith_link)
+ % RAW_POSE_JACOBIAN(q) returns the Jacobian that satisfies
+ % vec(x_dot) = J * q_dot, where x = fkm(q) and q is the
+ % vector of joint variables.
+ %
+ % RAW_POSE_JACOBIAN(q,ith) returns the Jacobian that
+ % satisfies vec(x_ith_dot) = J * q_dot(1:ith), where
+ % x_ith = fkm(q, ith), that is, the fkm up to the i-th link.
+ %
+ % This function does not take into account any base or
+ % end-effector displacements and should be used mostly
+ % internally in DQ_kinematics
+ obj.check_q_vec(q);
+
+ if nargin == 3
+ n = to_ith_link;
+ else
+ n = obj.dim_configuration_space_;
+ end
+
+ obj.check_to_ith_link(n);
+ x_effector = obj.raw_fkm(q,n);
+
+ x = DQ(1);
+ J = zeros(8,n);
+ for i = 1:n
+ w = obj.get_w(i);
+ z = 0.5*Ad(x,w);
+ x = x*obj.mdh2dq(q(i),i);
+ j = z * x_effector;
+ J(:,i) = vec8(j);
+ end
+
+ end
+
+ end
+end
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/robot_modeling/DQ_SerialWholeBody.m b/robot_modeling/DQ_SerialWholeBody.m
index 777db3bd..ada5d2ce 100644
--- a/robot_modeling/DQ_SerialWholeBody.m
+++ b/robot_modeling/DQ_SerialWholeBody.m
@@ -198,11 +198,11 @@ function add_reversed(obj, robot)
if nargin > 4
error('Invalid number of arguments');
elseif nargin == 4
- x = obj.reference_frame * raw_fkm_by_chain(obj,q,ith,jth);
+ x = obj.reference_frame_ * raw_fkm_by_chain(obj,q,ith,jth);
elseif nargin == 3
- x = obj.reference_frame * raw_fkm_by_chain(obj,q,ith);
+ x = obj.reference_frame_ * raw_fkm_by_chain(obj,q,ith);
else
- x = obj.reference_frame * raw_fkm_by_chain(obj,q);
+ x = obj.reference_frame_ * raw_fkm_by_chain(obj,q);
end
end
diff --git a/robot_modeling/DQ_WholeBody.m b/robot_modeling/DQ_WholeBody.m
index af8f57d5..587e1074 100644
--- a/robot_modeling/DQ_WholeBody.m
+++ b/robot_modeling/DQ_WholeBody.m
@@ -164,11 +164,11 @@ function add_reversed(obj, robot)
if nargin > 4
error('Invalid number of arguments');
elseif nargin == 4
- x = obj.reference_frame * raw_fkm(obj,q,ith,jth);
+ x = obj.reference_frame_ * raw_fkm(obj,q,ith,jth);
elseif nargin == 3
- x = obj.reference_frame * raw_fkm(obj,q,ith);
+ x = obj.reference_frame_ * raw_fkm(obj,q,ith);
else
- x = obj.reference_frame * raw_fkm(obj,q);
+ x = obj.reference_frame_ * raw_fkm(obj,q);
end
end
diff --git a/robots/Ax18ManipulatorRobot.m b/robots/Ax18ManipulatorRobot.m
index 9ddf9c09..efb7af8b 100644
--- a/robots/Ax18ManipulatorRobot.m
+++ b/robots/Ax18ManipulatorRobot.m
@@ -28,7 +28,7 @@
ax18_DH_d = [0.167 0 0 0.1225 0]; % d
ax18_DH_a = [0 0.159 0.02225 0 0.170]; % a
ax18_DH_alpha = [-pi/2 0 -pi/2 -pi/2 0]; % alpha
- ax18_DH_type = repmat(DQ_SerialManipulatorDH.JOINT_ROTATIONAL,1,5);
+ ax18_DH_type = double([repmat(DQ_JointType.REVOLUTE,1,5)]);
ax18_DH_matrix = [ ax18_DH_theta;
ax18_DH_d;
@@ -37,7 +37,7 @@
ax18_DH_type;
]; % D&H parameters matrix for the arm model
- ax = DQ_SerialManipulatorDH(ax18_DH_matrix,'standard'); % Defines robot model using dual quaternions
+ ax = DQ_SerialManipulatorDH(ax18_DH_matrix); % Defines robot model using dual quaternions
end
end
end
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/robots/BarrettWamArmRobot.m b/robots/BarrettWamArmRobot.m
index 80a8c014..7b7bf97c 100644
--- a/robots/BarrettWamArmRobot.m
+++ b/robots/BarrettWamArmRobot.m
@@ -29,14 +29,14 @@
wam_DH_d = [0, 0, 0.55, 0, 0.3, 0, 0.0609];
wam_DH_a = [0, 0, 0.045, -0.045, 0, 0, 0];
wam_DH_alpha = pi*[-0.5, 0.5, -0.5, 0.5, -0.5, 0.5, 0];
- wam_DH_type = repmat(DQ_SerialManipulatorDH.JOINT_ROTATIONAL,1,7);
+ wam_DH_type = double([repmat(DQ_JointType.REVOLUTE,1,7)]);
wam_DH_matrix = [wam_DH_theta;
wam_DH_d;
wam_DH_a;
wam_DH_alpha;
wam_DH_type];
- wam = DQ_SerialManipulatorDH(wam_DH_matrix,'standard');
+ wam = DQ_SerialManipulatorDH(wam_DH_matrix);
end
end
end
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/robots/ComauSmartSixRobot.m b/robots/ComauSmartSixRobot.m
index 71935483..d48b387b 100644
--- a/robots/ComauSmartSixRobot.m
+++ b/robots/ComauSmartSixRobot.m
@@ -32,14 +32,16 @@
comau_DH_d = [-0.45, 0, 0, -0.64707, 0, -0.095];
comau_DH_a = [0, 0.150, 0.590, 0.13, 0, 0];
comau_DH_alpha = [pi, pi/2, pi, -pi/2, -pi/2, pi/2];
+ comau_DH_type = double([repmat(DQ_JointType.REVOLUTE,1,6)]);
comau_DH_matrix = [comau_DH_theta;
comau_DH_d;
comau_DH_a;
- comau_DH_alpha];
+ comau_DH_alpha;
+ comau_DH_type];
- comau = DQ_SerialManipulator(comau_DH_matrix, 'modified');
-
+ comau = DQ_SerialManipulatorMDH(comau_DH_matrix);
+
% There is a final transformation for the end-effector given by
% a rotation of pi around the local x-axis followed by a
% rotation of pi around the local z-axis
diff --git a/robots/FrankaEmikaPandaRobot.m b/robots/FrankaEmikaPandaRobot.m
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..92b4db77
--- /dev/null
+++ b/robots/FrankaEmikaPandaRobot.m
@@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
+% (C) Copyright 2011-2022 DQ Robotics Developers
+%
+% This file is part of DQ Robotics.
+%
+% DQ Robotics is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
+% it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by
+% the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
+% (at your option) any later version.
+%
+% DQ Robotics is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
+% but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
+% MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
+% GNU Lesser General Public License for more details.
+%
+% You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
+% along with DQ Robotics. If not, see .
+%
+% DQ Robotics website: https://dqrobotics.github.io/
+%
+% Contributors to this file:
+% Juan Jose Quiroz Omana - juanjqogm@gmail.com
+
+classdef FrankaEmikaPandaRobot
+ methods (Static)
+ function ret = kinematics()
+ %Modified D-H of FrankaEmikaPanda
+ franka_DH_theta=[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0];
+ franka_DH_d = [0.333, 0, 3.16e-1, 0, 3.84e-1, 0, 0]; %1.07e-1
+ franka_DH_a = [0, 0, 0, 8.25e-2, -8.25e-2, 0, 8.8e-2];
+ franka_DH_alpha = [0, -pi/2, pi/2, pi/2, -pi/2, pi/2, pi/2];
+ franka_DH_type = double([repmat(DQ_JointType.REVOLUTE,1,7)]);
+ franka_DH_matrix = [franka_DH_theta;
+ franka_DH_d;
+ franka_DH_a;
+ franka_DH_alpha;
+ franka_DH_type];
+
+ ret = DQ_SerialManipulatorMDH(franka_DH_matrix);
+ % There is a final transformation for the end-effector given by
+ % a translation of d=1.07e-1 along around the local z-axis.
+ ret.set_effector(1+DQ.E*0.5*DQ.k*1.07e-1);
+
+ % If you want to describe the FrankaEmikaPanda robot using the
+ % standard DH convention, there is no need to perform the
+ % additional final transformation. In that case, the robot is
+ % described as:
+ % Standard D-H of FrankaEmikaPanda
+ % franka_DH_theta=[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0];
+ % franka_DH_d = [0.333, 0, 3.16e-1, 0, 3.84e-1, 0, 1.07e-1];
+ % franka_DH_a = [0, 0, 8.25e-2, -8.25e-2, 0, 8.8e-2, 0];
+ % franka_DH_alpha = [-pi/2, pi/2, pi/2, -pi/2, pi/2, pi/2, 0];
+ % franka_DH_type = repmat(DQ_SerialManipulatorDH.JOINT_ROTATIONAL,1,7);
+ % franka_DH_matrix = [franka_DH_theta;
+ % franka_DH_d;
+ % franka_DH_a;
+ % franka_DH_alpha;
+ % franka_DH_type];
+ % ret = DQ_SerialManipulatorDH(franka_DH_matrix);
+ end
+ end
+end
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/robots/KukaLwr4Robot.m b/robots/KukaLwr4Robot.m
index 759130f8..f7510c11 100644
--- a/robots/KukaLwr4Robot.m
+++ b/robots/KukaLwr4Robot.m
@@ -32,14 +32,14 @@
kuka_DH_d = [0.310, 0, 0.4, 0, 0.39, 0, 0];
kuka_DH_a = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0];
kuka_DH_alpha = [pi/2, -pi/2, -pi/2, pi/2, pi/2, -pi/2, 0];
- kuka_DH_type = repmat(DQ_SerialManipulatorDH.JOINT_ROTATIONAL,1,7);
+ kuka_DH_type = double([repmat(DQ_JointType.REVOLUTE,1,7)]);
kuka_DH_matrix = [kuka_DH_theta;
kuka_DH_d;
kuka_DH_a;
kuka_DH_alpha;
kuka_DH_type];
- ret = DQ_SerialManipulatorDH(kuka_DH_matrix,'standard');
+ ret = DQ_SerialManipulatorDH(kuka_DH_matrix);
end
end
end
diff --git a/robots/KukaYoubot.m b/robots/KukaYoubotRobot.m
similarity index 93%
rename from robots/KukaYoubot.m
rename to robots/KukaYoubotRobot.m
index a664701e..8960d188 100644
--- a/robots/KukaYoubot.m
+++ b/robots/KukaYoubotRobot.m
@@ -26,7 +26,7 @@
% Contributors to this file:
% Bruno Vihena Adorno - adorno@ufmg.br
-classdef KukaYoubot
+classdef KukaYoubotRobot
methods (Static)
function robot = kinematics()
@@ -40,14 +40,14 @@
arm_DH_d = [ 0.147, 0, 0, 0, 0.218];
arm_DH_a = [ 0, 0.155, 0.135, 0, 0];
arm_DH_alpha = [pi2, 0, 0, pi2, 0];
- arm_DH_type = repmat(DQ_SerialManipulatorDH.JOINT_ROTATIONAL,1,5);
+ arm_DH_type = double([repmat(DQ_JointType.REVOLUTE,1,5)]);
arm_DH_matrix = [arm_DH_theta;
arm_DH_d;
arm_DH_a;
arm_DH_alpha;
arm_DH_type];
- arm = DQ_SerialManipulatorDH(arm_DH_matrix,'standard');
+ arm = DQ_SerialManipulatorDH(arm_DH_matrix);
base = DQ_HolonomicBase();
include_namespace_dq