diff --git a/.github/workflows/docs-build.yml b/.github/workflows/docs-build.yml
index 54699e709f..fd8a2cc6f7 100644
--- a/.github/workflows/docs-build.yml
+++ b/.github/workflows/docs-build.yml
@@ -11,7 +11,7 @@ jobs:
uses: elastic/docs-builder/.github/workflows/preview-build.yml@main
with:
continue-on-error: false
- strict: false
+ strict: true
permissions:
deployments: write
id-token: write
diff --git a/deploy-manage/cloud-organization/billing/manage-subscription.md b/deploy-manage/cloud-organization/billing/manage-subscription.md
index 5d72d1fa5e..c28dbbde1c 100644
--- a/deploy-manage/cloud-organization/billing/manage-subscription.md
+++ b/deploy-manage/cloud-organization/billing/manage-subscription.md
@@ -39,7 +39,7 @@ To change your subscription level:
### Feature usage notifications [ec_feature_usage_notifications]
-:::{applies}
+:::{applies_to}
:hosted: all
:::
diff --git a/deploy-manage/deploy/cloud-enterprise/manage-elastic-stack-versions.md b/deploy-manage/deploy/cloud-enterprise/manage-elastic-stack-versions.md
index a5943cfc0f..746ad592be 100644
--- a/deploy-manage/deploy/cloud-enterprise/manage-elastic-stack-versions.md
+++ b/deploy-manage/deploy/cloud-enterprise/manage-elastic-stack-versions.md
@@ -348,7 +348,7 @@ You can add new Elastic Stack packs to your installation through the Cloud UI, t
To add a new Elastic Stack pack from the Cloud UI:
-1. Download the [Elastic Stack version]() that you want.
+1. Download the Elastic Stack version that you want.
2. [Log into the Cloud UI](log-into-cloud-ui.md).
3. From the **Platform** menu, select **Elastic Stack**.
4. Select **Upload Elastic Stack pack**.
diff --git a/deploy-manage/deploy/cloud-on-k8s/configuration-fleet.md b/deploy-manage/deploy/cloud-on-k8s/configuration-fleet.md
index b7760578bb..ceaa52181a 100644
--- a/deploy-manage/deploy/cloud-on-k8s/configuration-fleet.md
+++ b/deploy-manage/deploy/cloud-on-k8s/configuration-fleet.md
@@ -92,7 +92,7 @@ spec:
* `xpack.fleet.agents.elasticsearch.hosts` must point to the {{es}} cluster where {{agents}} should send data. For ECK-managed {{es}} clusters ECK creates a Service accessible through `https://ES_RESOURCE_NAME-es-http.ES_RESOURCE_NAMESPACE.svc:9200` URL, where `ES_RESOURCE_NAME` is the name of {{es}} resource and `ES_RESOURCE_NAMESPACE` is the namespace it was deployed within. See [Storing local state in host path volume](configuration-examples-standalone.md#k8s_storing_local_state_in_host_path_volume) for details on adjusting this field when running agent as non-root as it becomes required.
* `xpack.fleet.agents.fleet_server.hosts` must point to {{fleet-server}} that {{agents}} should connect to. For ECK-managed {{fleet-server}} instances, ECK creates a Service accessible through `https://FS_RESOURCE_NAME-agent-http.FS_RESOURCE_NAMESPACE.svc:8220` URL, where `FS_RESOURCE_NAME` is the name of {{agent}} resource with {{fleet-server}} enabled and `FS_RESOURCE_NAMESPACE` is the namespace it was deployed in.
* `xpack.fleet.packages` are required packages to enable {{fleet-server}} and {{agents}} to enroll.
-* `xpack.fleet.agentPolicies` policies are needed for {{fleet-server}} and {{agents}} to enroll to, check {{fleet-guide}}/agent-policy.html for more information.
+* `xpack.fleet.agentPolicies` policies are needed for {{fleet-server}} and {{agents}} to enroll to, check https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/fleet/current/agent-policy.html for more information.
## Set referenced resources [k8s-elastic-agent-fleet-configuration-setting-referenced-resources]
diff --git a/deploy-manage/deploy/cloud-on-k8s/logstash-plugins.md b/deploy-manage/deploy/cloud-on-k8s/logstash-plugins.md
index 33b0b2005e..5354c4e05b 100644
--- a/deploy-manage/deploy/cloud-on-k8s/logstash-plugins.md
+++ b/deploy-manage/deploy/cloud-on-k8s/logstash-plugins.md
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@ mapped_pages:
# Logstash plugins [k8s-logstash-plugins]
-The power of {{ls}} is in the plugins--{{logstash-ref}}/input-plugins.html[inputs], [outputs](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/output-plugins.html), [filters,](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/filter-plugins.html) and [codecs](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/codec-plugins.html).
+The power of {{ls}} is in the plugins--[inputs](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/input-plugins.html), [outputs](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/output-plugins.html), [filters,](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/filter-plugins.html) and [codecs](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/codec-plugins.html).
In {{ls}} on ECK, you can use the same plugins that you use for other {{ls}} instances—including Elastic-supported, community-supported, and custom plugins. However, you may have other factors to consider, such as how you configure your {{k8s}} resources, how you specify additional resources, and how you scale your {{ls}} installation.
diff --git a/deploy-manage/deploy/elastic-cloud/manage-integrations-server.md b/deploy-manage/deploy/elastic-cloud/manage-integrations-server.md
index 7fde6a5748..de17eb57ef 100644
--- a/deploy-manage/deploy/elastic-cloud/manage-integrations-server.md
+++ b/deploy-manage/deploy/elastic-cloud/manage-integrations-server.md
@@ -28,8 +28,6 @@ The APM secret token can no longer be reset from the Elasticsearch Service UI. C
This example demonstrates how to use the Elasticsearch Service RESTful API to create a deployment with Integrations Server enabled.
-For more information on how to manage Integrations Server from the UI, check [Manage your Integrations Server]()
-
#### Requirements [ec_requirements_2]
diff --git a/deploy-manage/distributed-architecture/discovery-cluster-formation/modules-discovery-bootstrap-cluster.md b/deploy-manage/distributed-architecture/discovery-cluster-formation/modules-discovery-bootstrap-cluster.md
index ae49a37f79..bce31843f6 100644
--- a/deploy-manage/distributed-architecture/discovery-cluster-formation/modules-discovery-bootstrap-cluster.md
+++ b/deploy-manage/distributed-architecture/discovery-cluster-formation/modules-discovery-bootstrap-cluster.md
@@ -74,7 +74,7 @@ By default each node will automatically bootstrap itself into a single-node clus
* `discovery.seed_hosts`
* `cluster.initial_master_nodes`
-To add a new node into an existing cluster, configure `discovery.seed_hosts` or other relevant discovery settings so that the new node can discover the existing master-eligible nodes in the cluster. To bootstrap a new multi-node cluster, configure `cluster.initial_master_nodes` as described in the [section on cluster bootstrapping]() as well as `discovery.seed_hosts` or other relevant discovery settings.
+To add a new node into an existing cluster, configure `discovery.seed_hosts` or other relevant discovery settings so that the new node can discover the existing master-eligible nodes in the cluster. To bootstrap a new multi-node cluster, configure `cluster.initial_master_nodes` as described in the section on cluster bootstrapping as well as `discovery.seed_hosts` or other relevant discovery settings.
::::{admonition} Forming a single cluster
:name: modules-discovery-bootstrap-cluster-joining
diff --git a/deploy-manage/monitor/logging-configuration/auditing-search-queries.md b/deploy-manage/monitor/logging-configuration/auditing-search-queries.md
index 6c609be5b3..edca7c5558 100644
--- a/deploy-manage/monitor/logging-configuration/auditing-search-queries.md
+++ b/deploy-manage/monitor/logging-configuration/auditing-search-queries.md
@@ -11,7 +11,7 @@ applies:
# Audit Elasticsearch search queries [auditing-search-queries]
-There is no [audit event type]() (asciidocalypse://elasticsearch/docs/reference/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-audit-events) specifically dedicated to search queries. Search queries are analyzed and then processed; the processing triggers authorization actions that are audited. However, the original raw query, as submitted by the client, is not accessible downstream when authorization auditing occurs.
+There is no [audit event type](asciidocalypse://elasticsearch/docs/reference/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-audit-events) specifically dedicated to search queries. Search queries are analyzed and then processed; the processing triggers authorization actions that are audited. However, the original raw query, as submitted by the client, is not accessible downstream when authorization auditing occurs.
Search queries are contained inside HTTP request bodies, however, and some audit events that are generated by the REST layer, on the coordinating node, can be toggled to output the request body to the audit log. Therefore, one must audit request bodies in order to audit search queries.
diff --git a/deploy-manage/monitor/logging-configuration/configuring-audit-logs.md b/deploy-manage/monitor/logging-configuration/configuring-audit-logs.md
index 03f84ee07b..0e85b237f4 100644
--- a/deploy-manage/monitor/logging-configuration/configuring-audit-logs.md
+++ b/deploy-manage/monitor/logging-configuration/configuring-audit-logs.md
@@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ When auditing security events, a single client request might generate multiple a
::::
For a complete description of event details and format, refer to the following resources:
- * [{{es}} audit events details and schema]() asciidocalypse://elasticsearch/docs/reference/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-audit-events
+ * [{{es}} audit events details and schema](asciidocalypse://elasticsearch/docs/reference/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-audit-events)
* [{{es}} log entry output format](/deploy-manage/monitor/logging-configuration/logfile-audit-output.md#audit-log-entry-format)
### Kibana auditing configuration
diff --git a/deploy-manage/monitor/logging-configuration/correlating-kibana-elasticsearch-audit-logs.md b/deploy-manage/monitor/logging-configuration/correlating-kibana-elasticsearch-audit-logs.md
index 25c0e2ca6d..76fe864186 100644
--- a/deploy-manage/monitor/logging-configuration/correlating-kibana-elasticsearch-audit-logs.md
+++ b/deploy-manage/monitor/logging-configuration/correlating-kibana-elasticsearch-audit-logs.md
@@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ When an {{es}} request generates multiple audit events across multiple nodes, yo
This identifier allows you to trace the flow of a request across the {{es}} cluster and reconstruct the full context of an operation.
-Refer to [linkTBD]() asciidocalypse://elasticsearch/docs/reference/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-audit-events for a complete reference of event types and attributes.
+Refer to [Audit events](asciidocalypse://elasticsearch/docs/reference/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-audit-events) for a complete reference of event types and attributes.
## `trace.id` field in {{kib}} audit events
diff --git a/deploy-manage/monitor/logging-configuration/logfile-audit-events-ignore-policies.md b/deploy-manage/monitor/logging-configuration/logfile-audit-events-ignore-policies.md
index 61a41f98ba..5384251743 100644
--- a/deploy-manage/monitor/logging-configuration/logfile-audit-events-ignore-policies.md
+++ b/deploy-manage/monitor/logging-configuration/logfile-audit-events-ignore-policies.md
@@ -35,7 +35,7 @@ xpack.security.audit.logfile.events.ignore_filters:
An audit event generated by the *kibana_system* user and operating over multiple indices , some of which do not match the indices wildcard, will not match. As expected, operations generated by all other users (even operating only on indices that match the *indices* filter) will not match this policy either.
-Audit events of different types may have [different attributes]() asciidocalypse://elasticsearch/docs/reference/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-audit-events/#audit-event-attributes. If an event does not contain an attribute for which some policy defines filters, the event will not match the policy. For example, the following policy will never match `authentication_success` or `authentication_failed` events, irrespective of the user’s roles, because these event schemas do not contain the `role` attribute:
+Audit events of different types may have [different attributes](asciidocalypse://elasticsearch/docs/reference/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-audit-events/#audit-event-attributes). If an event does not contain an attribute for which some policy defines filters, the event will not match the policy. For example, the following policy will never match `authentication_success` or `authentication_failed` events, irrespective of the user’s roles, because these event schemas do not contain the `role` attribute:
```yaml
xpack.security.audit.logfile.events.ignore_filters:
diff --git a/deploy-manage/monitor/logging-configuration/logfile-audit-output.md b/deploy-manage/monitor/logging-configuration/logfile-audit-output.md
index dee12a2559..5e91cdb46c 100644
--- a/deploy-manage/monitor/logging-configuration/logfile-audit-output.md
+++ b/deploy-manage/monitor/logging-configuration/logfile-audit-output.md
@@ -32,4 +32,4 @@ There are however a few attributes that are exceptions to the above format. The
When the `request.body` attribute is present (see [Auditing search queries](auditing-search-queries.md)), it contains a string value containing the full HTTP request body, escaped as per the JSON RFC 4677.
-Refer to [audit event types]() (asciidocalypse://elasticsearch/docs/reference/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-audit-events) for a complete list of fields, as well as examples, for each entry type.
\ No newline at end of file
+Refer to [audit event types](asciidocalypse://elasticsearch/docs/reference/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-audit-events) for a complete list of fields, as well as examples, for each entry type.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/deploy-manage/monitor/logging-configuration/security-event-audit-logging.md b/deploy-manage/monitor/logging-configuration/security-event-audit-logging.md
index ab8a988786..7869f7ebc0 100644
--- a/deploy-manage/monitor/logging-configuration/security-event-audit-logging.md
+++ b/deploy-manage/monitor/logging-configuration/security-event-audit-logging.md
@@ -32,5 +32,5 @@ By following these guidelines, you can effectively audit system activity, enhanc
For a complete description of audit event details and format, refer to:
-* [Elasticsearch audit events]() asciidocalypse://elasticsearch/docs/reference/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-audit-events
-* [Kibana audit events]() asciidocalypse://kibana/docs/reference/kibana-audit-events
+* [Elasticsearch audit events](asciidocalypse://elasticsearch/docs/reference/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-audit-events)
+* [Kibana audit events](asciidocalypse://kibana/docs/reference/kibana-audit-events)
diff --git a/deploy-manage/security/supported-ssltls-versions-by-jdk-version.md b/deploy-manage/security/supported-ssltls-versions-by-jdk-version.md
index 726580b650..376375278a 100644
--- a/deploy-manage/security/supported-ssltls-versions-by-jdk-version.md
+++ b/deploy-manage/security/supported-ssltls-versions-by-jdk-version.md
@@ -107,6 +107,6 @@ To enable your custom security policy, create a file named `java.security.option
SSL/TLS versions can be enabled and disabled within {{es}} via the [`ssl.supported_protocols` settings](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/security-settings.html#ssl-tls-settings).
-{{es}} will only support the TLS versions that are enabled by the [underlying JDK](). If you configure `ssl.supported_procotols` to include a TLS version that is not enabled in your JDK, then it will be silently ignored.
+{{es}} will only support the TLS versions that are enabled by the underlying JDK. If you configure `ssl.supported_procotols` to include a TLS version that is not enabled in your JDK, then it will be silently ignored.
Similarly, a TLS version that is enabled in your JDK, will not be used unless it is configured as one of the `ssl.supported_protocols` in {{es}}.
diff --git a/deploy-manage/tools/snapshot-and-restore/azure-repository.md b/deploy-manage/tools/snapshot-and-restore/azure-repository.md
index 7b78c514b4..50ef1b3ff6 100644
--- a/deploy-manage/tools/snapshot-and-restore/azure-repository.md
+++ b/deploy-manage/tools/snapshot-and-restore/azure-repository.md
@@ -73,15 +73,15 @@ In progress snapshot or restore jobs will not be preempted by a **reload** of th
## Client settings [repository-azure-client-settings]
-The following list describes the available client settings. Those that must be stored in the keystore are marked as ({{ref}}/secure-settings.html[Secure], [reloadable](../../security/secure-settings.md#reloadable-secure-settings)); the other settings must be stored in the `elasticsearch.yml` file. The default `CLIENT_NAME` is `default` but you may configure a client with a different name and specify that client by name when registering a repository.
+The following list describes the available client settings. Those that must be stored in the keystore are marked as ([Secure](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/secure-settings.html), [reloadable](../../security/secure-settings.md#reloadable-secure-settings)); the other settings must be stored in the `elasticsearch.yml` file. The default `CLIENT_NAME` is `default` but you may configure a client with a different name and specify that client by name when registering a repository.
-`azure.client.CLIENT_NAME.account` ({{ref}}/secure-settings.html[Secure], [reloadable](../../security/secure-settings.md#reloadable-secure-settings))
+`azure.client.CLIENT_NAME.account` ([Secure](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/secure-settings.html), [reloadable](../../security/secure-settings.md#reloadable-secure-settings))
: The Azure account name, which is used by the repository’s internal Azure client. This setting is required for all clients.
`azure.client.CLIENT_NAME.endpoint_suffix`
: The Azure endpoint suffix to connect to. The default value is `core.windows.net`.
-`azure.client.CLIENT_NAME.key` ({{ref}}/secure-settings.html[Secure], [reloadable](../../security/secure-settings.md#reloadable-secure-settings))
+`azure.client.CLIENT_NAME.key` ([Secure](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/secure-settings.html), [reloadable](../../security/secure-settings.md#reloadable-secure-settings))
: The Azure secret key, which is used by the repository’s internal Azure client. Alternatively, use `sas_token`.
`azure.client.CLIENT_NAME.max_retries`
@@ -96,7 +96,7 @@ The following list describes the available client settings. Those that must be s
`azure.client.CLIENT_NAME.proxy.type`
: Register a proxy type for the client. Supported values are `direct`, `http`, and `socks`. For example: `azure.client.default.proxy.type: http`. When `proxy.type` is set to `http` or `socks`, `proxy.host` and `proxy.port` must also be provided. The default value is `direct`.
-`azure.client.CLIENT_NAME.sas_token` ({{ref}}/secure-settings.html[Secure], [reloadable](../../security/secure-settings.md#reloadable-secure-settings))
+`azure.client.CLIENT_NAME.sas_token` ([Secure](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/secure-settings.html), [reloadable](../../security/secure-settings.md#reloadable-secure-settings))
: A shared access signatures (SAS) token, which the repository’s internal Azure client uses for authentication. The SAS token must have read (r), write (w), list (l), and delete (d) permissions for the repository base path and all its contents. These permissions must be granted for the blob service (b) and apply to resource types service (s), container (c), and object (o). Alternatively, use `key`.
`azure.client.CLIENT_NAME.timeout`
diff --git a/deploy-manage/tools/snapshot-and-restore/cloud-enterprise.md b/deploy-manage/tools/snapshot-and-restore/cloud-enterprise.md
index ddc461598f..4678a3fd26 100644
--- a/deploy-manage/tools/snapshot-and-restore/cloud-enterprise.md
+++ b/deploy-manage/tools/snapshot-and-restore/cloud-enterprise.md
@@ -99,9 +99,6 @@ To edit a snapshot repository configuration from your Elastic Cloud Enterprise i
1. [Log into the Cloud UI](../../deploy/cloud-enterprise/log-into-cloud-ui.md).
2. From the **Platform** menu, select **Repositories**.
3. Select **Edit** to modify a snapshot repository configuration.
-
- For available options that you can change, check [Add Snapshot Repository Configurations]().
-
4. Select **Save**.
@@ -136,7 +133,7 @@ You might need to update existing Elasticsearch clusters to use a different snap
To change the snapshot repository for an existing Elasticsearch cluster:
1. [Log into the Cloud UI](../../deploy/cloud-enterprise/log-into-cloud-ui.md).
-2. Optional: If you need to use a repository that is not yet listed, [add a snapshot repository configuration]() first.
+2. Optional: If you need to use a repository that is not yet listed, add a snapshot repository configuration first.
3. From the **Deployments** page, select your deployment.
Narrow the list by name, ID, or choose from several other filters. To further define the list, use a combination of filters.
diff --git a/deploy-manage/tools/snapshot-and-restore/google-cloud-storage-repository.md b/deploy-manage/tools/snapshot-and-restore/google-cloud-storage-repository.md
index cd27f5ee31..05c0c99632 100644
--- a/deploy-manage/tools/snapshot-and-restore/google-cloud-storage-repository.md
+++ b/deploy-manage/tools/snapshot-and-restore/google-cloud-storage-repository.md
@@ -123,7 +123,7 @@ bin/elasticsearch-keystore add-file gcs.client.default.credentials_file /path/se
The following are the available client settings. Those that must be stored in the keystore are marked as `Secure`.
-`credentials_file` ({{ref}}/secure-settings.html[Secure], [reloadable](../../security/secure-settings.md#reloadable-secure-settings))
+`credentials_file` ([Secure](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/secure-settings.html), [reloadable](../../security/secure-settings.md#reloadable-secure-settings))
: The service account file that is used to authenticate to the Google Cloud Storage service.
`endpoint`
diff --git a/deploy-manage/tools/snapshot-and-restore/s3-repository.md b/deploy-manage/tools/snapshot-and-restore/s3-repository.md
index 61563dea5d..c3ab673cef 100644
--- a/deploy-manage/tools/snapshot-and-restore/s3-repository.md
+++ b/deploy-manage/tools/snapshot-and-restore/s3-repository.md
@@ -72,13 +72,13 @@ Define the relevant secure settings in each node’s keystore before starting th
The following list contains the available client settings. Those that must be stored in the keystore are marked as "secure" and are **reloadable**; the other settings belong in the `elasticsearch.yml` file.
-`access_key` ({{ref}}/secure-settings.html[Secure], [reloadable](../../security/secure-settings.md#reloadable-secure-settings))
+`access_key` ([Secure](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/secure-settings.html), [reloadable](../../security/secure-settings.md#reloadable-secure-settings))
: An S3 access key. If set, the `secret_key` setting must also be specified. If unset, the client will use the instance or container role instead.
-`secret_key` ({{ref}}/secure-settings.html[Secure], [reloadable](../../security/secure-settings.md#reloadable-secure-settings))
+`secret_key` ([Secure](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/secure-settings.html), [reloadable](../../security/secure-settings.md#reloadable-secure-settings))
: An S3 secret key. If set, the `access_key` setting must also be specified.
-`session_token` ({{ref}}/secure-settings.html[Secure], [reloadable](../../security/secure-settings.md#reloadable-secure-settings))
+`session_token` ([Secure](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/secure-settings.html), [reloadable](../../security/secure-settings.md#reloadable-secure-settings))
: An S3 session token. If set, the `access_key` and `secret_key` settings must also be specified.
`endpoint`
@@ -96,10 +96,10 @@ The following list contains the available client settings. Those that must be st
`proxy.scheme`
: The scheme to use for the proxy connection to S3. Valid values are either `http` or `https`. Defaults to `http`. This setting allows to specify the protocol used for communication with the proxy server
-`proxy.username` ({{ref}}/secure-settings.html[Secure], [reloadable](../../security/secure-settings.md#reloadable-secure-settings))
+`proxy.username` ([Secure](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/secure-settings.html), [reloadable](../../security/secure-settings.md#reloadable-secure-settings))
: The username to connect to the `proxy.host` with.
-`proxy.password` ({{ref}}/secure-settings.html[Secure], [reloadable](../../security/secure-settings.md#reloadable-secure-settings))
+`proxy.password` ([Secure](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/secure-settings.html), [reloadable](../../security/secure-settings.md#reloadable-secure-settings))
: The password to connect to the `proxy.host` with.
`read_timeout`
diff --git a/deploy-manage/tools/snapshot-and-restore/source-only-repository.md b/deploy-manage/tools/snapshot-and-restore/source-only-repository.md
index e94da6100f..acea41d1fe 100644
--- a/deploy-manage/tools/snapshot-and-restore/source-only-repository.md
+++ b/deploy-manage/tools/snapshot-and-restore/source-only-repository.md
@@ -46,7 +46,7 @@ PUT _snapshot/my_src_only_repository
`delegate_type`
: (Optional, string) Delegated repository type. For valid values, see the [`type` parameter](https://www.elastic.co/docs/api/doc/elasticsearch/operation/operation-snapshot-create-repository#put-snapshot-repo-api-request-type).
- `source` repositories can use `settings` properties for its delegated repository type. See [Source-only repository]().
+ `source` repositories can use `settings` properties for its delegated repository type.
`max_number_of_snapshots`
diff --git a/deploy-manage/users-roles.md b/deploy-manage/users-roles.md
index ea35a8fd9c..be5ac7c279 100644
--- a/deploy-manage/users-roles.md
+++ b/deploy-manage/users-roles.md
@@ -29,7 +29,7 @@ Preventing unauthorized access is only one element of a complete security strate
## Cloud organization level
-:::{applies}
+:::{applies_to}
:hosted: all
:serverless: all
:::
@@ -50,7 +50,7 @@ For {{ech}} deployments, you can configure SSO at the organization level, the de
## Orchestrator level
-:::{applies}
+:::{applies_to}
:ece: all
:::
@@ -77,7 +77,7 @@ You can't manage users and roles for {{eck}} clusters at the orchestrator level.
## Project level
-:::{applies}
+:::{applies_to}
:serverless: all
:::
@@ -87,7 +87,7 @@ As an extension of the [predefined instance access roles](/deploy-manage/users-r
## Cluster or deployment level
-:::{applies}
+:::{applies_to}
:ece: all
:hosted: all
:eck: all
diff --git a/deploy-manage/users-roles/cloud-organization.md b/deploy-manage/users-roles/cloud-organization.md
index cee9d93962..038eed2168 100644
--- a/deploy-manage/users-roles/cloud-organization.md
+++ b/deploy-manage/users-roles/cloud-organization.md
@@ -25,7 +25,7 @@ If you're using {{ech}}, then you can also manage users and control access [at t
## Should I use organization-level or deployment-level SSO? [organization-deployment-sso]
-:::{applies}
+:::{applies_to}
:hosted: all
:::
diff --git a/deploy-manage/users-roles/cluster-or-deployment-auth/role-restriction.md b/deploy-manage/users-roles/cluster-or-deployment-auth/role-restriction.md
index 3f4fd02a3a..0afaed671a 100644
--- a/deploy-manage/users-roles/cluster-or-deployment-auth/role-restriction.md
+++ b/deploy-manage/users-roles/cluster-or-deployment-auth/role-restriction.md
@@ -27,7 +27,7 @@ Workflow names are case-sensitive.
### Examples [_examples_5]
-The following example creates an API key with a [restriction]() to the `search_application_query` workflow, which allows to call only [Search Application Search API](https://www.elastic.co/docs/api/doc/elasticsearch/operation/operation-search-application-search):
+The following example creates an API key with a restriction to the `search_application_query` workflow, which allows to call only [Search Application Search API](https://www.elastic.co/docs/api/doc/elasticsearch/operation/operation-search-application-search):
```console
POST /_security/api_key
diff --git a/docset.yml b/docset.yml
index 079107e562..5fcde28fb0 100644
--- a/docset.yml
+++ b/docset.yml
@@ -62,7 +62,7 @@ subs:
apm-lambda-ref: "https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/apm/lambda/current"
apm-attacher-ref: "https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/apm/attacher/current"
docker-logging-ref: "https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/loggingplugin/current"
- esf-ref: "https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/esf/{{esf_version}}"
+ esf-ref: "https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/esf/current"
kinesis-firehose-ref: "https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kinesis/{{kinesis_version}}"
estc-welcome-current: "https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/starting-with-the-elasticsearch-platform-and-its-solutions/current"
estc-welcome: "https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/starting-with-the-elasticsearch-platform-and-its-solutions/current"
@@ -495,189 +495,4 @@ subs:
a-data-source: "a data view"
icon-bug: "pass:[]"
icon-checkInCircleFilled: "pass:[]"
- icon-warningFilled: "pass:[]"
-
-external_hosts:
- - 50.10
- - aka.ms
- - aliyun.com
- - amazon.com
- - amazonaws.com
- - amp.dev
- - android.com
- - ansible.com
- - anthropic.com
- - apache.org
- - apple.com
- - arxiv.org
- - atlassian.com
- - azure.com
- - bouncycastle.org
- - cbor.io
- - census.gov
- - cert-manager.io
- - chromium.org
- - cisa.gov
- - cisecurity.org
- - cmu.edu
- - cncf.io
- - co.
- - codesandbox.io
- - cohere.com
- - columbia.edu
- - concourse-ci.org
- - contentstack.io
- - curl.se
- - dbeaver.io
- - dbvis.com
- - deque.com
- - die.net
- - digitalocean.com
- - direnv.net
- - dnschecker.org
- - docker.com
- - dso.mil
- - eicar.org
- - ela.st
- - elastic-cloud.com
- - elasticsearch.org
- - elstc.co
- - epsg.org
- - example.com
- - falco.org
- - freedesktop.org
- - gdal.org
- - gin-gonic.com
- - git-lfs.com
- - github.io
- - githubusercontent.com
- - go.dev
- - godoc.org
- - golang.org
- - google.com
- - google.dev
- - googleapis.com
- - googleblog.com
- - gorillatoolkit.org
- - gradle.org
- - handlebarsjs.com
- - haxx.se
- - helm.io
- - helm.sh
- - heroku.com
- - huggingface.co
- - ibm.com
- - ietf.org
- - ijmlc.org
- - istio.io
- - jaegertracing.io
- - java.net
- - javadoc.io
- - javalin.io
- - jenkins.io
- - jina.ai
- - json.org
- - kernel.org
- - kubernetes.io
- - letsencrypt.org
- - linkerd.io
- - lmstudio.ai
- - loft.sh
- - man7.org
- - mariadb.org
- - markdownguide.org
- - maven.org
- - maxmind.com
- - metacpan.org
- - micrometer.io
- - microsoft.com
- - microstrategy.com
- - min.io
- - minio.io
- - mistral.ai
- - mit.edu
- - mitre.org
- - momentjs.com
- - mozilla.org
- - mvnrepository.com
- - mysql.com
- - navattic.com
- - nginx.com
- - nginx.org
- - ngrok.com
- - nist.gov
- - nlog-project.org
- - nodejs.dev
- - nodejs.org
- - npmjs.com
- - ntp.org
- - nuget.org
- - numeraljs.com
- - oasis-open.org
- - office.com
- - okta.com
- - openai.com
- - openebs.io
- - opengroup.org
- - openid.net
- - openjdk.org
- - openmaptiles.org
- - openpolicyagent.org
- - openshift.com
- - openssl.org
- - openstreetmap.org
- - opentelemetry.io
- - openweathermap.org
- - operatorhub.io
- - oracle.com
- - osquery.io
- - outlook.com
- - owasp.org
- - pagerduty.com
- - palletsprojects.com
- - pastebin.com
- - playwright.dev
- - podman.io
- - postgresql.org
- - pypi.org
- - python.org
- - qlik.com
- - readthedocs.io
- - recurly.com
- - redhat.com
- - rust-lang.org
- - salesforce.com
- - scikit-learn.org
- - sdkman.io
- - searchkit.co
- - semver.org
- - serilog.net
- - sigstore.dev
- - slack.com
- - snowballstem.org
- - sonatype.org
- - sourceforge.net
- - sourcemaps.info
- - spring.io
- - sql-workbench.eu
- - stackexchange.com
- - stunnel.org
- - swiftype.com
- - tableau.com
- - talosintelligence.com
- - telerik.com
- - terraform.io
- - trimet.org
- - umd.edu
- - urlencoder.org
- - vaultproject.io
- - victorops.com
- - virustotal.com
- - w3.org
- - web.dev
- - webhook.site
- - wikipedia.org
- - wolfi.dev
- - wttr.in
- - yaml.org
- - youtube.com
+ icon-warningFilled: "pass:[]"
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/explore-analyze/alerts-cases/watcher/actions-slack.md b/explore-analyze/alerts-cases/watcher/actions-slack.md
index 7b4d693678..02a0e5f83a 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/alerts-cases/watcher/actions-slack.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/alerts-cases/watcher/actions-slack.md
@@ -174,7 +174,7 @@ xpack.notification.slack:
To notify multiple channels, create a webhook URL for each channel in Slack and multiple Slack accounts in {{es}} (one for each webhook URL).
-If you configure multiple Slack accounts, you either need to configure a default account or specify which account the notification should be sent with in the [`slack`]() action.
+If you configure multiple Slack accounts, you either need to configure a default account or specify which account the notification should be sent with in the `slack` action.
```yaml
xpack.notification.slack:
diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards/add-controls.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards/add-controls.md
index 25069b0298..115d618cec 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/dashboards/add-controls.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/dashboards/add-controls.md
@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ There are three types of controls:
* [**Time slider**](#add-time-slider-controls) — Adds a time range slider that allows to filter the data within a specified range of time, advance the time range backward and forward by a unit that you can define, and animate your change in data over the specified time range.
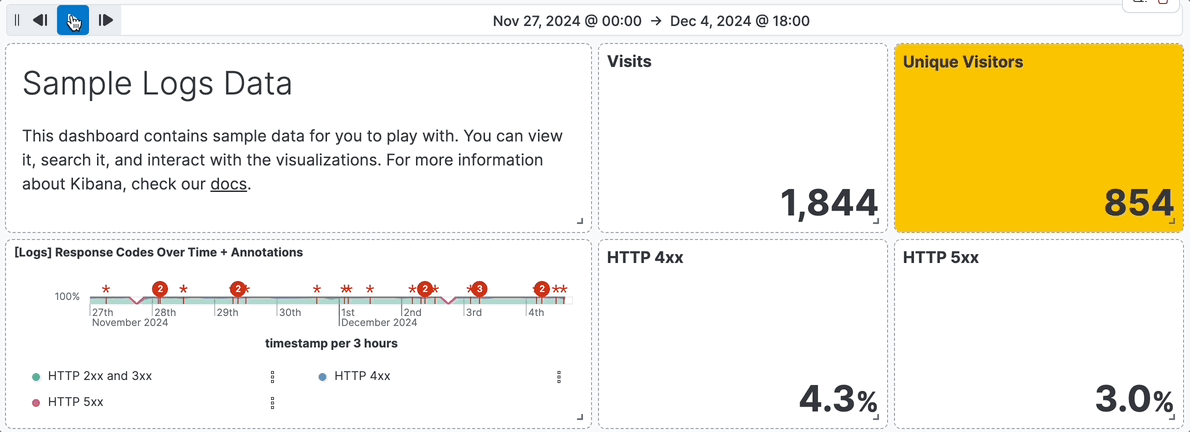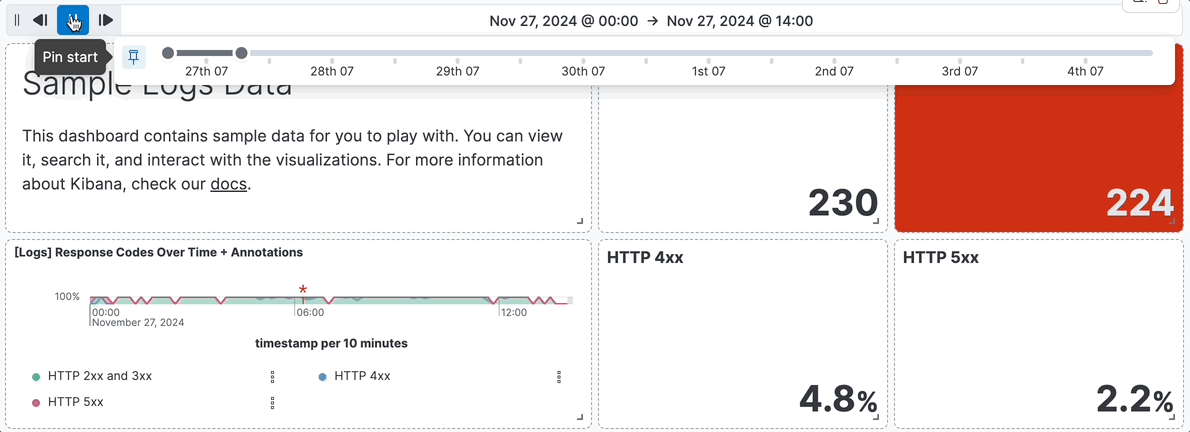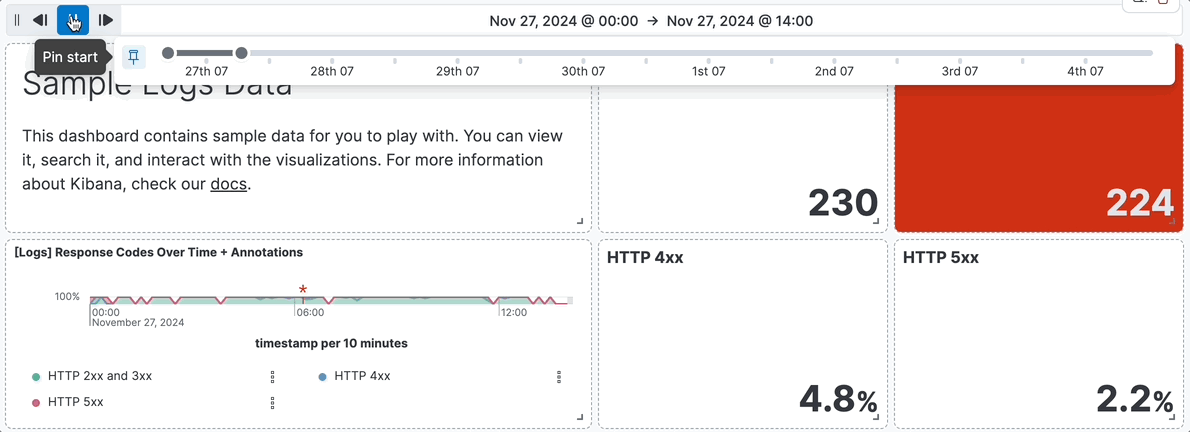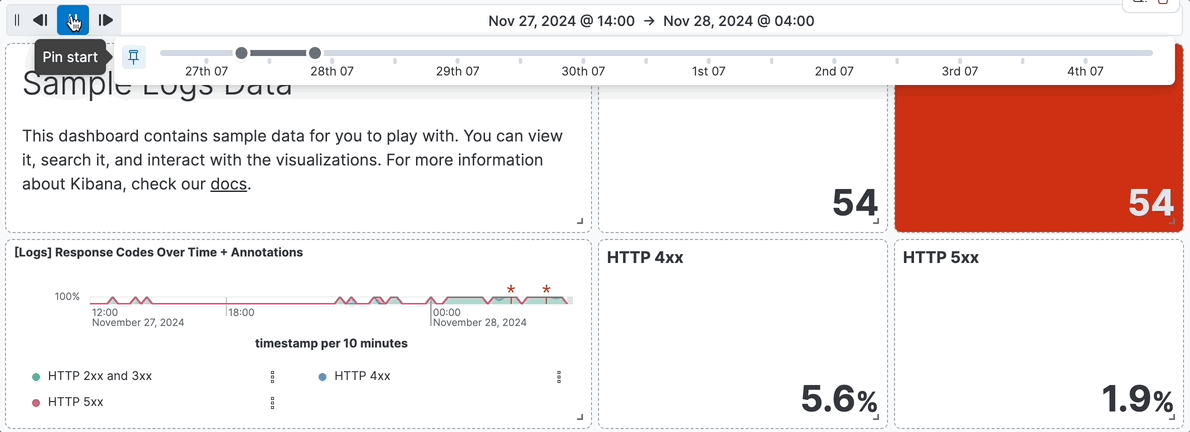
For example, you are using the **[Logs] Web Traffic** dashboard from the sample web logs data, and the global time filter is **Last 7 days**. When you add the time slider, you can click the previous and next buttons to advance the time range backward or forward, and click the play button to watch how the data changes over the last 7 days.
- 
+ 
diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards/create-dashboard-of-panels-with-ecommerce-data.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards/create-dashboard-of-panels-with-ecommerce-data.md
index 14fb1cbed5..5414ee1c9d 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/dashboards/create-dashboard-of-panels-with-ecommerce-data.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/dashboards/create-dashboard-of-panels-with-ecommerce-data.md
@@ -110,7 +110,7 @@ To copy a function, you drag it to the **Add or drag-and-drop a field** area wit
1. Drag the **95th** field to **Add or drag-and-drop a field** for **Vertical axis**.
- :::{image} https://images.contentstack.io/v3/assets/bltefdd0b53724fa2ce/blt8fb6969daa820faf/6700642c363a96bb08f48bee/drag-and-drop-a-field-8.16.0.gif
+ :::{image} ../../images/drag-and-drop-a-field-8.16.0.gif
:alt: Easily duplicate the items with drag and drop
:class: screenshot
:::
diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards/create-dashboard-of-panels-with-web-server-data.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards/create-dashboard-of-panels-with-web-server-data.md
index c05439e3c8..f4b7a0bf48 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/dashboards/create-dashboard-of-panels-with-web-server-data.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/dashboards/create-dashboard-of-panels-with-web-server-data.md
@@ -51,7 +51,7 @@ To create the visualizations in this tutorial, you’ll use the following fields
Click a field name to view more details, such as its top values and distribution.
-:::{image} https://images.contentstack.io/v3/assets/bltefdd0b53724fa2ce/blt25c7a05e0f5daaa3/671966b9b1d3dd705a2ae650/tutorial-field-more-info.gif
+:::{image} ../../images/tutorial-field-more-info.gif
:alt: Clicking a field name to view more details
:class: screenshot
:width: 50%
diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards/sharing.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards/sharing.md
index 76233e40c9..3a26ca1c18 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/dashboards/sharing.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/dashboards/sharing.md
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ mapped_pages:
To share a dashboard with a larger audience, click **Share** in the toolbar. For detailed information about the sharing options, refer to [Reporting](../report-and-share.md).
-:::{image} https://images.contentstack.io/v3/assets/bltefdd0b53724fa2ce/blt9428300b184af4c6/6763173de7201118db0315a7/share-dashboard-copy-link.gif
+:::{image} ../../images/share-dashboard-copy-link.gif
:alt: getting a shareable link for a dashboard
:::
diff --git a/explore-analyze/dashboards/using.md b/explore-analyze/dashboards/using.md
index 1b07132806..6d106ff844 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/dashboards/using.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/dashboards/using.md
@@ -36,7 +36,7 @@ Use filter pills to focus in on the specific data you want.
You can interact with some panel visualizations to explore specific data more in depth. Upon clicking, filter pills are added and applied to the entire dashboard, so that surrounding panels and visualizations also reflect your browsing.
-:::{image} https://images.contentstack.io/v3/assets/bltefdd0b53724fa2ce/blt93fcc34395a310d4/6750e7e9b09fe993fbc0824a/add-filter-pills-8.17.gif
+:::{image} ../../images/add-filter-pills-8.17.gif
:alt: Browsing a chart creates a filter dynamically
:::
@@ -143,7 +143,7 @@ Filter the data within a specified range of time.
4. To animate the data changes over time, click .
5. To clear the specified values, click .
-:::{image} https://images.contentstack.io/v3/assets/bltefdd0b53724fa2ce/blt672f3aaadf9ea5a6/6750dd6c2452f972af0a88b4/dashboard_timeslidercontrol_8.17.0.gif
+:::{image} ../../images/dashboard_timeslidercontrol_8.17.0.gif
:alt: Time slider control
:class: screenshot
:::
diff --git a/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/data-views.md b/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/data-views.md
index d951b9b320..32ba3c8a2e 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/data-views.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/data-views.md
@@ -89,7 +89,7 @@ Want to explore your data or create a visualization without saving it as a data
A temporary {{data-source}} remains in your space until you change apps, or until you save it.
-:::{image} https://images.contentstack.io/v3/assets/bltefdd0b53724fa2ce/blte3a4f3994c44c0cc/637eb0c95834861044c21a25/ad-hoc-data-view.gif
+:::{image} ../../images/ad-hoc-data-view.gif
:alt: how to create an ad-hoc data view
:class: screenshot
:::
@@ -101,7 +101,7 @@ Temporary {{data-sources}} are not available in the **Management** menu.
### Use {{data-sources}} with rolled up data [rollup-data-view]
-::::{applies}
+::::{applies_to}
:serverless: unavailable
:stack: deprecated
::::
@@ -123,7 +123,7 @@ For an example, refer to [Create and visualize rolled up data](/manage-data/life
### Use {{data-sources}} with {{ccs}} [management-cross-cluster-search]
-::::{applies}
+::::{applies_to}
:serverless: unavailable
:stack: ga
::::
diff --git a/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/saved-objects.md b/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/saved-objects.md
index 06d40c4cd1..46fec69eda 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/saved-objects.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/find-and-organize/saved-objects.md
@@ -126,7 +126,7 @@ However, saved objects can only be imported into the same version, a newer minor
| 7.8.1 | 9.0.0 | No |
## Saved Object IDs [saved-object-ids]
-::::{applies}
+::::{applies_to}
:stack:
::::
diff --git a/explore-analyze/machine-learning/nlp/ml-nlp-e5.md b/explore-analyze/machine-learning/nlp/ml-nlp-e5.md
index 156536074b..eacaaa0f25 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/machine-learning/nlp/ml-nlp-e5.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/machine-learning/nlp/ml-nlp-e5.md
@@ -146,7 +146,7 @@ If you want to install E5 in an air-gapped environment, you have the following o
For the `multilingual-e5-small` model, you need the following files in your system:
-```url
+```text
https://ml-models.elastic.co/multilingual-e5-small.metadata.json
https://ml-models.elastic.co/multilingual-e5-small.pt
https://ml-models.elastic.co/multilingual-e5-small.vocab.json
@@ -154,7 +154,7 @@ https://ml-models.elastic.co/multilingual-e5-small.vocab.json
For the optimized version, you need the following files in your system:
-```url
+```text
https://ml-models.elastic.co/multilingual-e5-small_linux-x86_64.metadata.json
https://ml-models.elastic.co/multilingual-e5-small_linux-x86_64.pt
https://ml-models.elastic.co/multilingual-e5-small_linux-x86_64.vocab.json
diff --git a/explore-analyze/machine-learning/nlp/ml-nlp-elser.md b/explore-analyze/machine-learning/nlp/ml-nlp-elser.md
index ea986aa6bc..96d14984ee 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/machine-learning/nlp/ml-nlp-elser.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/machine-learning/nlp/ml-nlp-elser.md
@@ -178,7 +178,7 @@ If you want to deploy ELSER in a restricted or closed network, you have two opti
For the cross-platform verison, you need the following files in your system:
-```url
+```text
https://ml-models.elastic.co/elser_model_2.metadata.json
https://ml-models.elastic.co/elser_model_2.pt
https://ml-models.elastic.co/elser_model_2.vocab.json
@@ -186,7 +186,7 @@ https://ml-models.elastic.co/elser_model_2.vocab.json
For the optimized version, you need the following files in your system:
-```url
+```text
https://ml-models.elastic.co/elser_model_2_linux-x86_64.metadata.json
https://ml-models.elastic.co/elser_model_2_linux-x86_64.pt
https://ml-models.elastic.co/elser_model_2_linux-x86_64.vocab.json
@@ -213,7 +213,7 @@ You can use any HTTP service to deploy ELSER. This example uses the official Ngi
4. Verify that Nginx runs properly by visiting the following URL in your browser:
- ```url
+ ```text
http://{IP_ADDRESS_OR_HOSTNAME}:8080/elser_model_2.metadata.json
```
diff --git a/explore-analyze/machine-learning/nlp/ml-nlp-rerank.md b/explore-analyze/machine-learning/nlp/ml-nlp-rerank.md
index 85897f7b65..5acb7df821 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/machine-learning/nlp/ml-nlp-rerank.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/machine-learning/nlp/ml-nlp-rerank.md
@@ -94,7 +94,7 @@ If you want to deploy the Elastic Rerank model in a restricted or closed network
For the cross-platform version, you need the following files in your system:
-```url
+```text
https://ml-models.elastic.co/rerank-v1.metadata.json
https://ml-models.elastic.co/rerank-v1.pt
https://ml-models.elastic.co/rerank-v1.vocab.json
@@ -121,7 +121,7 @@ You can use any HTTP service to deploy the model. This example uses the official
4. Verify that Nginx runs properly by visiting the following URL in your browser:
- ```url
+ ```text
http://{IP_ADDRESS_OR_HOSTNAME}:8080/rerank-v1.metadata.json
```
diff --git a/explore-analyze/query-filter/languages/esql-kibana.md b/explore-analyze/query-filter/languages/esql-kibana.md
index 6ddbd2c1a7..c8fd9f5dc3 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/query-filter/languages/esql-kibana.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/query-filter/languages/esql-kibana.md
@@ -76,7 +76,7 @@ FROM kibana_sample_data_logs
You can do that using the **Add line breaks on pipes** button from the query editor’s footer.
-:::{image} https://images.contentstack.io/v3/assets/bltefdd0b53724fa2ce/bltd5554518309e10f6/672d153cfeb8f9d479ebcc6e/esql-line-breakdown.gif
+:::{image} ../../../images/esql-line-breakdown.gif
:alt: Automatic line breaks for ES|QL queries
:::
diff --git a/explore-analyze/query-filter/languages/sql-functions-datetime.md b/explore-analyze/query-filter/languages/sql-functions-datetime.md
index 7f8590d224..77a74112c3 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/query-filter/languages/sql-functions-datetime.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/query-filter/languages/sql-functions-datetime.md
@@ -1519,7 +1519,7 @@ EXTRACT(
**Output**: integer
-**Description**: Extract fields from a date/datetime by specifying the name of a [datetime function](). The following
+**Description**: Extract fields from a date/datetime by specifying the name of a datetime function. The following
```sql
SELECT EXTRACT(DAY_OF_YEAR FROM CAST('2018-02-19T10:23:27Z' AS TIMESTAMP)) AS day;
diff --git a/explore-analyze/report-and-share.md b/explore-analyze/report-and-share.md
index 304e08fdcb..3a699a3cd5 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/report-and-share.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/report-and-share.md
@@ -58,7 +58,7 @@ To access the object shared with the link, users need to authenticate.
Anonymous users can also access the link if you have configured [Anonymous authentication](/deploy-manage/users-roles/cluster-or-deployment-auth/user-authentication.md#anonymous-authentication) and your anonymous service account has privileges to access what you want to share.
-:::{image} https://images.contentstack.io/v3/assets/bltefdd0b53724fa2ce/blt49f2b5a80ec89a34/66b9e919af508f4ac182c194/share-dashboard.gif
+:::{image} ../images/share-dashboard.gif
:alt: getting a shareable link for a dashboard
:::
diff --git a/explore-analyze/report-and-share/reporting-troubleshooting-csv.md b/explore-analyze/report-and-share/reporting-troubleshooting-csv.md
index ba8355836e..b015c8f45f 100644
--- a/explore-analyze/report-and-share/reporting-troubleshooting-csv.md
+++ b/explore-analyze/report-and-share/reporting-troubleshooting-csv.md
@@ -78,7 +78,7 @@ The listing of reports in **Stack Management > Reporting** allows you to inspect
3. Click **Inspect query in Console** in the **Actions** menu.
4. This will open the **Console** application, pre-filled with the queries used to generate the CSV export.
-:::{image} https://images.contentstack.io/v3/assets/bltefdd0b53724fa2ce/blt4758e67aaec715d9/67897d0be92e090a6dc626a8/inspect-query-from-csv-export.gif
+:::{image} ../../images/inspect-query-from-csv-export.gif
:alt: Inspect the query used for CSV export
:class: screenshot
:::
diff --git a/get-started/installing-elastic-stack.md b/get-started/installing-elastic-stack.md
index 808ee13285..a1a1423860 100644
--- a/get-started/installing-elastic-stack.md
+++ b/get-started/installing-elastic-stack.md
@@ -29,12 +29,12 @@ For more information on supported network configurations, refer to [{{es}} Inges
Install the Elastic Stack products you want to use in the following order:
-1. [Elasticsearch]({{ref}}/install-elasticsearch.html)
-2. [Kibana]({{kibana-ref}}/install.html)
-3. [Logstash]({{logstash-ref}}/installing-logstash.html)
-4. [Elastic Agent]({{fleet-guide}}/elastic-agent-installation.html) or [Beats]({{beats-ref}}/getting-started.html)
-5. [APM]({{apm-guide-ref}}/apm-quick-start.html)
-6. [Elasticsearch Hadoop]({{hadoop-ref}}/install.html)
+1. [Elasticsearch](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/install-elasticsearch.html)
+2. [Kibana](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/install.html)
+3. [Logstash](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/installing-logstash.html)
+4. [Elastic Agent](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/fleet/current/elastic-agent-installation.html) or [Beats](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/libbeat/current/getting-started.html)
+5. [APM](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/apm/guide/current/apm-quick-start.html)
+6. [Elasticsearch Hadoop](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/hadoop/current/install.html)
Installing in this order ensures that the components each product depends on are in place.
diff --git a/images/ad-hoc-data-view.gif b/images/ad-hoc-data-view.gif
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8592e39fc7
Binary files /dev/null and b/images/ad-hoc-data-view.gif differ
diff --git a/images/add-filter-pills-8.17.gif b/images/add-filter-pills-8.17.gif
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..91ec4937f4
Binary files /dev/null and b/images/add-filter-pills-8.17.gif differ
diff --git a/images/dashboard_timeslidercontrol_8.17.0.gif b/images/dashboard_timeslidercontrol_8.17.0.gif
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..441020543a
Binary files /dev/null and b/images/dashboard_timeslidercontrol_8.17.0.gif differ
diff --git a/images/drag-and-drop-a-field-8.16.0.gif b/images/drag-and-drop-a-field-8.16.0.gif
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..02156d9194
Binary files /dev/null and b/images/drag-and-drop-a-field-8.16.0.gif differ
diff --git a/images/esql-line-breakdown.gif b/images/esql-line-breakdown.gif
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..a67c292644
Binary files /dev/null and b/images/esql-line-breakdown.gif differ
diff --git a/images/inspect-query-from-csv-export.gif b/images/inspect-query-from-csv-export.gif
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..61546ea3ff
Binary files /dev/null and b/images/inspect-query-from-csv-export.gif differ
diff --git a/images/share-dashboard-copy-link.gif b/images/share-dashboard-copy-link.gif
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..90054f8483
Binary files /dev/null and b/images/share-dashboard-copy-link.gif differ
diff --git a/images/share-dashboard.gif b/images/share-dashboard.gif
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..3e0d47eb74
Binary files /dev/null and b/images/share-dashboard.gif differ
diff --git a/images/tutorial-field-more-info.gif b/images/tutorial-field-more-info.gif
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..f46e4de313
Binary files /dev/null and b/images/tutorial-field-more-info.gif differ
diff --git a/raw-migrated-files/cloud/cloud/ec-cloud-ingest-data.md b/raw-migrated-files/cloud/cloud/ec-cloud-ingest-data.md
index 1ceecbe26f..fcb63ded40 100644
--- a/raw-migrated-files/cloud/cloud/ec-cloud-ingest-data.md
+++ b/raw-migrated-files/cloud/cloud/ec-cloud-ingest-data.md
@@ -42,25 +42,25 @@ This diagram focuses on *timestamped* data.
Process data using and forward it with .
Use Logstash plugins
-filter plugins
-output plugins
+filter plugins
+output plugins
Use with Elastic Agent or Beats.
Use runtime fields
-runtime fields
+runtime fields
Use a pipeline for or .
Use ingest pipelines
-Elastic Agent
-Beats
+Elastic Agent
+Beats
For Elastic Agent integrations, use an . For Beats, use a .
Use processors
Beats processor
-Agent processor
+Agent processor
something
else
@@ -81,8 +81,8 @@ This diagram focuses on *timestamped* data.
using one (or more) .
Use Logstash
-Get started
-input plugins
+Get started
+input plugins
no
@@ -93,14 +93,14 @@ This diagram focuses on *timestamped* data.
with the Beat.
Set up Beats
-Get started
+Get started
relevant
yes
Look for your data source in the list of and their modules.
-Beats
+Beats
Beats module
Is a Beat or available?
diff --git a/raw-migrated-files/docs-content/serverless/observability-add-logs-service-name.md b/raw-migrated-files/docs-content/serverless/observability-add-logs-service-name.md
index be3e2db3df..9838b8bc4d 100644
--- a/raw-migrated-files/docs-content/serverless/observability-add-logs-service-name.md
+++ b/raw-migrated-files/docs-content/serverless/observability-add-logs-service-name.md
@@ -51,5 +51,5 @@ For more ways to add a field to your mapping, refer to [add a field to an existi
The {{stack}} provides additional ways to process your data:
-* **{{ref}}/ingest.html[Ingest pipelines]:** convert data to ECS, normalize field data, or enrich incoming data.
-* **{{logstash-ref}}/introduction.html[Logstash]:** enrich your data using input, output, and filter plugins.
+* **https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/ingest.html[Ingest pipelines]:** convert data to ECS, normalize field data, or enrich incoming data.
+* **https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/introduction.html[Logstash]:** enrich your data using input, output, and filter plugins.
diff --git a/raw-migrated-files/docs-content/serverless/security-endpoints-page.md b/raw-migrated-files/docs-content/serverless/security-endpoints-page.md
index fb4dbe60d3..be89fc3749 100644
--- a/raw-migrated-files/docs-content/serverless/security-endpoints-page.md
+++ b/raw-migrated-files/docs-content/serverless/security-endpoints-page.md
@@ -137,7 +137,7 @@ If you need help troubleshooting a configuration failure, refer to [Endpoint man
### Filter endpoints [security-endpoints-page-filter-endpoints]
-To filter the Endpoints list, use the search bar to enter a query using **{{kibana-ref}}/kuery-query.html[{{kib}} Query Language (KQL)]**. To refresh the search results, click **Refresh**.
+To filter the Endpoints list, use the search bar to enter a query using **https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/kuery-query.html[{{kib}} Query Language (KQL)]**. To refresh the search results, click **Refresh**.
::::{note}
The date and time picker on the right side of the page allows you to set a time interval to automatically refresh the Endpoints list — for example, to check if new endpoints were added or deleted.
diff --git a/raw-migrated-files/observability-docs/observability/add-logs-service-name.md b/raw-migrated-files/observability-docs/observability/add-logs-service-name.md
index 663953a63a..7064eace41 100644
--- a/raw-migrated-files/observability-docs/observability/add-logs-service-name.md
+++ b/raw-migrated-files/observability-docs/observability/add-logs-service-name.md
@@ -52,5 +52,5 @@ For more ways to add a field to your mapping, refer to [add a field to an existi
The {{stack}} provides additional ways to process your data:
-* **{{ref}}/ingest.html[Ingest pipelines]:** convert data to ECS, normalize field data, or enrich incoming data.
-* **{{logstash-ref}}/introduction.html[Logstash]:** enrich your data using input, output, and filter plugins.
+* **https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/ingest.html[Ingest pipelines]:** convert data to ECS, normalize field data, or enrich incoming data.
+* **https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/introduction.html[Logstash]:** enrich your data using input, output, and filter plugins.
diff --git a/solutions/observability/apps/api-keys.md b/solutions/observability/apps/api-keys.md
index db4ac1f1f0..4d247f65c2 100644
--- a/solutions/observability/apps/api-keys.md
+++ b/solutions/observability/apps/api-keys.md
@@ -46,8 +46,6 @@ apm-server.auth.api_key.limit: 50 <2>
1. Enables API keys
2. Restricts the number of unique API keys that {{es}} allows each minute. This value should be the number of unique API keys configured in your monitored services.
-
-All other configuration options are described in [API keys]().
::::::
:::::::
diff --git a/solutions/observability/apps/configure-elasticsearch-output.md b/solutions/observability/apps/configure-elasticsearch-output.md
index 977a75f7be..3f89b807fd 100644
--- a/solutions/observability/apps/configure-elasticsearch-output.md
+++ b/solutions/observability/apps/configure-elasticsearch-output.md
@@ -292,5 +292,4 @@ Authentication is specified in the APM Server configuration file:
More information on sending data to a secured cluster is available in the configuration reference:
-* [{{es}}]()
* [SSL/TLS output settings](ssltls-output-settings.md)
diff --git a/solutions/observability/apps/create-assign-feature-roles-to-apm-server-users.md b/solutions/observability/apps/create-assign-feature-roles-to-apm-server-users.md
index 49cd9af89a..8c96bcc61f 100644
--- a/solutions/observability/apps/create-assign-feature-roles-to-apm-server-users.md
+++ b/solutions/observability/apps/create-assign-feature-roles-to-apm-server-users.md
@@ -76,7 +76,7 @@ If you have explicitly disabled Elastic security *and* you are *not* using tail-
1. Assign the **general writer role** to APM Server users who need to publish APM data.
::::{note}
-Assign [additional APM feature roles]() to users as needed including the *Central configuration management role*, which is [required in most cases](#apm-central-config-role-note).
+Assign additional APM feature roles to users as needed including the *Central configuration management role*, which is [required in most cases](#apm-central-config-role-note).
::::
@@ -118,7 +118,7 @@ The previous privileges should be sufficient for APM agent central configuration
| Spaces | `Read` on Applications UI | Allow APM Server to manage central configurations via the Applications UI |
::::{note}
-Assign [additional APM feature roles]() to users as needed including the *Writer role*, which is [required in most cases](#apm-privileges-to-publish-events).
+Assign additional APM feature roles to users as needed including the *Writer role*, which is [required in most cases](#apm-privileges-to-publish-events).
::::
@@ -177,7 +177,7 @@ If you don’t use the `apm_system` user, you can create a custom role:
2. Assign the **monitoring role** to APM Server users who need to write monitoring data to {{es}}.
::::{note}
-Assign [additional APM feature roles]() to users as needed including the [*Writer role*](#apm-privileges-to-publish-events) and [*Central configuration management role*](#apm-central-config-role-note), both of which are required in most cases.
+Assign additional APM feature roles to users as needed including the [*Writer role*](#apm-privileges-to-publish-events) and [*Central configuration management role*](#apm-central-config-role-note), both of which are required in most cases.
::::
@@ -214,7 +214,7 @@ If you don’t use the `remote_monitoring_user` user, you can create a custom us
::::{note}
-Assign [additional APM feature roles]() to users as needed including the [*Writer role*](#apm-privileges-to-publish-events) and [*Central configuration management role*](#apm-central-config-role-note), both of which are required in most cases.
+Assign additional APM feature roles to users as needed including the [*Writer role*](#apm-privileges-to-publish-events) and [*Central configuration management role*](#apm-central-config-role-note), both of which are required in most cases.
::::
@@ -239,7 +239,7 @@ To grant users the required privileges for viewing monitoring data:
::::{note}
-Assign [additional APM feature roles]() to users as needed including the [*Writer role*](#apm-privileges-to-publish-events) and [*Central configuration management role*](#apm-central-config-role-note), both of which are required in most cases.
+Assign additional APM feature roles to users as needed including the [*Writer role*](#apm-privileges-to-publish-events) and [*Central configuration management role*](#apm-central-config-role-note), both of which are required in most cases.
::::
@@ -257,7 +257,7 @@ To grant an APM Server user with the required privileges for reading RUM source
| Index | `read` on `.apm-source-map` index | Allow APM Server to read RUM source maps from {{es}} |
::::{note}
-Assign [additional APM feature roles]() to users as needed including the [*Writer role*](#apm-privileges-to-publish-events) and [*Central configuration management role*](#apm-central-config-role-note), both of which are required in most cases.
+Assign additional APM feature roles to users as needed including the [*Writer role*](#apm-privileges-to-publish-events) and [*Central configuration management role*](#apm-central-config-role-note), both of which are required in most cases.
::::
diff --git a/solutions/observability/apps/ssltls-input-settings.md b/solutions/observability/apps/ssltls-input-settings.md
index 74d50f4b5f..a0d5d63fa0 100644
--- a/solutions/observability/apps/ssltls-input-settings.md
+++ b/solutions/observability/apps/ssltls-input-settings.md
@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ These settings apply to SSL/TLS communication between the APM Server and APM Age
:::::::{tab-set}
::::::{tab-item} Fleet-managed
-Enable TLS in the APM integration settings and use the [SSL/TLS input settings]() to set the path to the server certificate and key.
+Enable TLS in the APM integration settings and use the SSL/TLS input settings to set the path to the server certificate and key.
::::::
::::::{tab-item} APM Server binary
@@ -30,8 +30,6 @@ apm-server.ssl.certificate: "/path/to/apm-server.crt"
apm-server.ssl.key: "/path/to/apm-server.key"
```
-A full list of configuration options is available in [SSL/TLS input settings]().
-
::::{tip}
If APM agents are authenticating themselves using a certificate that cannot be authenticated through known CAs (e.g. self signed certificates), use the `ssl.certificate_authorities` to set a custom CA. This will automatically modify the `ssl.client_authentication` configuration to require authentication.
::::
diff --git a/solutions/observability/cloud/monitor-amazon-web-services-aws-with-amazon-data-firehose.md b/solutions/observability/cloud/monitor-amazon-web-services-aws-with-amazon-data-firehose.md
index b5412fe155..c875be84a1 100644
--- a/solutions/observability/cloud/monitor-amazon-web-services-aws-with-amazon-data-firehose.md
+++ b/solutions/observability/cloud/monitor-amazon-web-services-aws-with-amazon-data-firehose.md
@@ -60,7 +60,7 @@ For advanced use cases, source records can be transformed by invoking a custom L
* `include_cw_extracted_fields`: This parameter is optional and can be set when using a CloudWatch logs subscription filter as the Firehose data source. When set to true, extracted fields generated by the filter pattern in the subscription filter will be collected. Setting this parameter can add many fields into each record and may significantly increase data volume in Elasticsearch. As such, use of this parameter should be carefully considered and used only when the extracted fields are required for specific filtering and/or aggregation.
* `set_es_document_id`: This parameter is optional and can be set to allow Elasticsearch to assign each document a random ID or use a calculated unique ID for each document. Default is true. When set to false, a random ID will be used for each document which will help indexing performance.
- 1. In the **Backup settings** panel, it is recommended to configure S3 backup for failed records. It’s then possible to configure workflows to automatically retry failed records, for example by using [Elastic Serverless Forwarder](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/esf/{{esf_version}}/aws-elastic-serverless-forwarder.html).
+ 1. In the **Backup settings** panel, it is recommended to configure S3 backup for failed records. It’s then possible to configure workflows to automatically retry failed records, for example by using [Elastic Serverless Forwarder](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/esf/current/aws-elastic-serverless-forwarder.html).
diff --git a/solutions/observability/cloud/monitor-amazon-web-services-aws-with-elastic-serverless-forwarder.md b/solutions/observability/cloud/monitor-amazon-web-services-aws-with-elastic-serverless-forwarder.md
index bad74e0daa..9f2ce49941 100644
--- a/solutions/observability/cloud/monitor-amazon-web-services-aws-with-elastic-serverless-forwarder.md
+++ b/solutions/observability/cloud/monitor-amazon-web-services-aws-with-elastic-serverless-forwarder.md
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@ mapped_pages:
# Monitor Amazon Web Services (AWS) with Elastic Serverless Forwarder [monitor-aws-esf]
-The Elastic Serverless Forwarder (ESF) is an Amazon Web Services (AWS) Lambda function that ships logs from your AWS environment to Elastic. Elastic Serverless Forwarder is published in the AWS Serverless Application Repository (SAR). For more information on ESF, check the [Elastic Serverless Forwarder Guide](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/esf/{{esf_version}}/aws-elastic-serverless-forwarder.html).
+The Elastic Serverless Forwarder (ESF) is an Amazon Web Services (AWS) Lambda function that ships logs from your AWS environment to Elastic. Elastic Serverless Forwarder is published in the AWS Serverless Application Repository (SAR). For more information on ESF, check the [Elastic Serverless Forwarder Guide](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/esf/current/aws-elastic-serverless-forwarder.html).
## What you’ll learn [aws-esf-what-you-learn]
diff --git a/solutions/observability/infra-and-hosts/universal-profiling.md b/solutions/observability/infra-and-hosts/universal-profiling.md
index c610e28ce1..6fa6fa0b01 100644
--- a/solutions/observability/infra-and-hosts/universal-profiling.md
+++ b/solutions/observability/infra-and-hosts/universal-profiling.md
@@ -161,7 +161,7 @@ The functions view presents an ordered list of functions that Universal Profilin
## Filtering [profiling-filtering-intro]
-In all of the Universal Profiling views, the search bar accepts a filter in the {{kib}} Query Language ({{kibana-ref}}/kuery-query.html[KQL]).
+In all of the Universal Profiling views, the search bar accepts a filter in the {{kib}} Query Language (https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/kuery-query.html[KQL]).
Most notably, you may want to filter on:
diff --git a/solutions/observability/unknown-bucket/monitor-aws-with-amazon-data-firehose.md b/solutions/observability/unknown-bucket/monitor-aws-with-amazon-data-firehose.md
index d6069d56d8..0ff01ce696 100644
--- a/solutions/observability/unknown-bucket/monitor-aws-with-amazon-data-firehose.md
+++ b/solutions/observability/unknown-bucket/monitor-aws-with-amazon-data-firehose.md
@@ -60,7 +60,7 @@ For advanced use cases, source records can be transformed by invoking a custom L
* `include_cw_extracted_fields`: This parameter is optional and can be set when using a CloudWatch logs subscription filter as the Firehose data source. When set to true, extracted fields generated by the filter pattern in the subscription filter will be collected. Setting this parameter can add many fields into each record and may significantly increase data volume in Elasticsearch. As such, use of this parameter should be carefully considered and used only when the extracted fields are required for specific filtering and/or aggregation.
* `set_es_document_id`: This parameter is optional and can be set to allow Elasticsearch to assign each document a random ID or use a calculated unique ID for each document. Default is true. When set to false, a random ID will be used for each document which will help indexing performance.
- 1. In the **Backup settings** panel, it is recommended to configure S3 backup for failed records. It’s then possible to configure workflows to automatically retry failed records, for example by using [Elastic Serverless Forwarder](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/esf/{{esf_version}}/aws-elastic-serverless-forwarder.html).
+ 1. In the **Backup settings** panel, it is recommended to configure S3 backup for failed records. It’s then possible to configure workflows to automatically retry failed records, for example by using [Elastic Serverless Forwarder](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/esf/current/aws-elastic-serverless-forwarder.html).
diff --git a/solutions/search/get-started.md b/solutions/search/get-started.md
index 790b1d0a47..3656fd8944 100644
--- a/solutions/search/get-started.md
+++ b/solutions/search/get-started.md
@@ -19,7 +19,7 @@ Building a search experience with {{es}} requires a number of fundamental implem
1. [**Ingestion**](ingest-for-search.md): What tools will you use to get your content into {{es}}?
1. [**Search approaches**](search-approaches.md): What search techniques and algorithms will you use to find relevant results?
1. **Implementation tools**: How will you write queries and interact with {{es}}?
- - Which [programming language client]() matches your application?
+ - Which programming language client matches your application?
- Which API endpoints and [query language(s)](querying-for-search.md) will you use to express your search logic?
Each decision builds on the previous ones, offering flexibility to mix and match approaches based on your needs.
diff --git a/solutions/search/search-templates.md b/solutions/search/search-templates.md
index dcb4675474..083af50312 100644
--- a/solutions/search/search-templates.md
+++ b/solutions/search/search-templates.md
@@ -546,7 +546,7 @@ POST _render/template
## Search template examples with Mustache [search-template-with-mustache-examples]
-The mustache templating language defines various tag types you can use within templates. The following sections describe some of these tag types and provide examples of using them in {{es}} [search templates]().
+The mustache templating language defines various tag types you can use within templates. The following sections describe some of these tag types and provide examples of using them in {{es}} search templates.
### Mustache variables [search-template-mustache-variable]
diff --git a/solutions/search/site-or-app.md b/solutions/search/site-or-app.md
index 026c3f7fc5..0038b2ce3a 100644
--- a/solutions/search/site-or-app.md
+++ b/solutions/search/site-or-app.md
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@ applies:
The following tools are available to help you add search to your site or app:
-- [Clients](): Use programming language clients to integrate {{es}} with your application.
+- Clients: Use programming language clients to integrate {{es}} with your application.
- [Search UI](site-or-app/search-ui.md): Use the Search UI library to build a user interface for your search application.
- [Behavioral analytics](site-or-app/behavioral-analytics.md): Use Behavioral Analytics to track user behavior and improve search relevance.
- [Search Applications](search-applications.md): Use Search Applications to simplify the process of building search experiences, by leveraging [search templates](search-templates.md).
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solutions/security/get-started/elastic-security-ui.md b/solutions/security/get-started/elastic-security-ui.md
index 6cb155d917..7c3f174ab3 100644
--- a/solutions/security/get-started/elastic-security-ui.md
+++ b/solutions/security/get-started/elastic-security-ui.md
@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ The {{security-app}} is a highly interactive workspace designed for security ana
## Search [search-overview]
-Filter for alerts, events, processes, and other important security data by entering **{{kibana-ref}}/kuery-query.html[{{kib}} Query Language (KQL)]** queries in the search bar, which appears at the top of each page throughout the app. A date/time filter set to `Today` is enabled by default, but can be changed to any time range.
+Filter for alerts, events, processes, and other important security data by entering **https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/kuery-query.html[{{kib}} Query Language (KQL)]** queries in the search bar, which appears at the top of each page throughout the app. A date/time filter set to `Today` is enabled by default, but can be changed to any time range.
:::{image} ../../../images/security-search-bar.png
:alt: search bar
diff --git a/solutions/security/manage-elastic-defend/endpoints.md b/solutions/security/manage-elastic-defend/endpoints.md
index f8fde6357f..3d172d9b4e 100644
--- a/solutions/security/manage-elastic-defend/endpoints.md
+++ b/solutions/security/manage-elastic-defend/endpoints.md
@@ -153,7 +153,7 @@ If you need help troubleshooting a configuration failure, refer to [Endpoint man
### Filter endpoints [_filter_endpoints]
-To filter the Endpoints list, use the search bar to enter a query using **{{kibana-ref}}/kuery-query.html[{{kib}} Query Language (KQL)]**. To refresh the search results, click **Refresh**.
+To filter the Endpoints list, use the search bar to enter a query using **https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/kuery-query.html[{{kib}} Query Language (KQL)]**. To refresh the search results, click **Refresh**.
:::{image} ../../../images/security-filter-endpoints.png
:alt: filter endpoints
diff --git a/troubleshoot/elasticsearch/clusters.md b/troubleshoot/elasticsearch/clusters.md
index 501e3410b3..92db29786c 100644
--- a/troubleshoot/elasticsearch/clusters.md
+++ b/troubleshoot/elasticsearch/clusters.md
@@ -18,5 +18,3 @@ Use the topics in this section to troubleshoot {{es}} clusters:
* [](/troubleshoot/elasticsearch/remote-clusters.md)
* [](/troubleshoot/elasticsearch/diagnose-unassigned-shards.md)
* [](/troubleshoot/elasticsearch/troubleshooting-shards-capacity-issues.md)
-* []()
-
diff --git a/troubleshoot/ingest.md b/troubleshoot/ingest.md
index c26eeb9075..ea67be43fc 100644
--- a/troubleshoot/ingest.md
+++ b/troubleshoot/ingest.md
@@ -15,11 +15,3 @@ Use the topics in this section to troubleshoot ingestion tools:
* [](/troubleshoot/ingest/logstash.md)
* [](/troubleshoot/ingest/fleet/fleet-elastic-agent.md)
* [](/troubleshoot/ingest/beats-loggingplugin/elastic-logging-plugin-for-docker.md)
-* []()
-* []()
-* []()
-* []()
-* []()
-* []()
-* []()
-
diff --git a/troubleshoot/observability/apm/common-problems.md b/troubleshoot/observability/apm/common-problems.md
index 120632a44f..4afa220d74 100644
--- a/troubleshoot/observability/apm/common-problems.md
+++ b/troubleshoot/observability/apm/common-problems.md
@@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ This section describes common problems you might encounter when using APM Server
## No data is indexed [apm-no-data-indexed]
-:::{applies}
+:::{applies_to}
:stack: all
:::
@@ -83,7 +83,7 @@ APM Server currently relies on {{es}} to create indices that do not exist. As a
:::::::
## Common SSL-related problems [apm-common-ssl-problems]
-:::{applies}
+:::{applies_to}
:stack: all
:::
@@ -134,7 +134,7 @@ A firewall is refusing the connection. Check if a firewall is blocking the traff
## I/O Timeout [apm-io-timeout]
-:::{applies}
+:::{applies_to}
:stack: all
:::
@@ -177,7 +177,7 @@ In the agent logs, you won’t see a sign of failures as the APM server asynchro
## Tail-based sampling causing high system memory usage and high disk IO [apm-tail-based-sampling-memory-disk-io]
-:::{applies}
+:::{applies_to}
:stack: all
:::
@@ -185,7 +185,7 @@ Tail-based sampling requires minimal memory to run, and there should not be a no
## Too many unique transaction names [troubleshooting-too-many-transactions]
-:::{applies}
+:::{applies_to}
:stack: all
:::
@@ -231,7 +231,7 @@ If your problem is occurring in a different APM agent, the tips above still appl
## Unknown route [troubleshooting-unknown-route]
-:::{applies}
+:::{applies_to}
:stack: all
:::
@@ -245,7 +245,7 @@ To resolve this, you’ll need to head over to the relevant [APM agent documenta
## Fields are not searchable [troubleshooting-fields-unsearchable]
-:::{applies}
+:::{applies_to}
:stack: all
:::
@@ -262,7 +262,7 @@ As an example, some APM agents store cookie values in `http.request.cookies`. Si
## Service Maps: no connection between client and server [service-map-rum-connections]
-:::{applies}
+:::{applies_to}
:stack: all
:::
@@ -272,7 +272,7 @@ This setting is necessary, for example, for cross-origin requests. If you have a
## No data shown in the infrastructure tab [troubleshooting-apm-infra-data]
-:::{applies}
+:::{applies_to}
:stack: all
:::
@@ -292,7 +292,7 @@ For example, if the APM agent is not configured to use the correct host name, th
## Common response codes [observability-apm-troubleshooting-common-response-codes]
-:::{applies}
+:::{applies_to}
:serverless: all
:::
diff --git a/troubleshoot/observability/troubleshoot-logs.md b/troubleshoot/observability/troubleshoot-logs.md
index a538d37778..533b41a372 100644
--- a/troubleshoot/observability/troubleshoot-logs.md
+++ b/troubleshoot/observability/troubleshoot-logs.md
@@ -63,7 +63,7 @@ You need to either:
### Failed to create API key [logs-troubleshooting-API-key-failed]
-:::{applies}
+:::{applies_to}
:stack: all
:::
diff --git a/troubleshoot/observability/troubleshoot-service-level-objectives-slos.md b/troubleshoot/observability/troubleshoot-service-level-objectives-slos.md
index af2a79d347..ed0a4eca14 100644
--- a/troubleshoot/observability/troubleshoot-service-level-objectives-slos.md
+++ b/troubleshoot/observability/troubleshoot-service-level-objectives-slos.md
@@ -191,7 +191,7 @@ Refer to [SLO API calls](https://www.elastic.co/docs/api/doc/kibana/v8/operation
## Upgrade from beta to GA [slo-troubleshoot-beta]
-:::{applies}
+:::{applies_to}
:stack: all
:::
diff --git a/troubleshoot/observability/troubleshooting-synthetics.md b/troubleshoot/observability/troubleshooting-synthetics.md
index 0483a4c424..367ab2e77e 100644
--- a/troubleshoot/observability/troubleshooting-synthetics.md
+++ b/troubleshoot/observability/troubleshooting-synthetics.md
@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ For debugging synthetic tests locally, you can set an environment variable, `DEB
### Monitors stopped running after upgrading to 8.8.0 or above [synthetics-troubleshooting-missing-api-key]
-:::{applies}
+:::{applies_to}
:stack: all
:::
@@ -128,7 +128,7 @@ There are a few ways to fix this:
::::
### You do not have permission to use Elastic managed locations [synthetics-troubleshooting-public-locations-disabled]
-:::{applies}
+:::{applies_to}
:stack: all
:::
diff --git a/troubleshoot/security/detection-rules.md b/troubleshoot/security/detection-rules.md
index a8442b50af..8585d398bd 100644
--- a/troubleshoot/security/detection-rules.md
+++ b/troubleshoot/security/detection-rules.md
@@ -182,7 +182,7 @@ For example, say an event occurred at 10:00 but wasn’t ingested into {{es}} un
### Troubleshoot missing alerts for {{ml}} jobs [ml-job-compatibility]
-:::{applies}
+:::{applies_to}
:serverless: unavailable
:::
% doesn't apply to serverless