An autoencoder (AE) is a neural network that is trained to copy its input to its output.
It has one or more hidden layers that each describe a code used to represent the input.
The network may be viewed as consisting of two parts:
an encoder h=f(x) that produces the code and a decoder that produces a reconstruction of the datar=g(h).
The encoder is tasked with finding a (usually) reduced representation of the data, extracting the most prominentfeatures of the original data and representing the input in terms of these features in a way the Decoder can understand.
The Decoder learns to read these codes and regenerate the data from them. The entire AE aims to minimize a loss-function while reconstructing.
In their simplest form encoder and decoder are fully-connected feedforward neuralnetworks.
When the inputs are images, it makes sense to use convolutional neural networks (CNNs) instead, obtaininga convolutional autoencoder (CAE).
A CAE uses the convolutional filters to extract features. CAEs learn to encode the input as a combination ofautonomously learned signals and then to reconstruct the input from this encoding.
CAEs learn in what can be seenas an unsupervised learning setup, since they don’t require labels and instead aim to reconstruct the input. Theoutput is evaluated by comparing the reconstructed image by the original one, using a Mean Squared Error (MSE)cost function.
We will be using the CIFAR-10 dataset: •CIFAR-10 dataset (https://www.cs.toronto.edu/ ̃kriz/cifar.html).
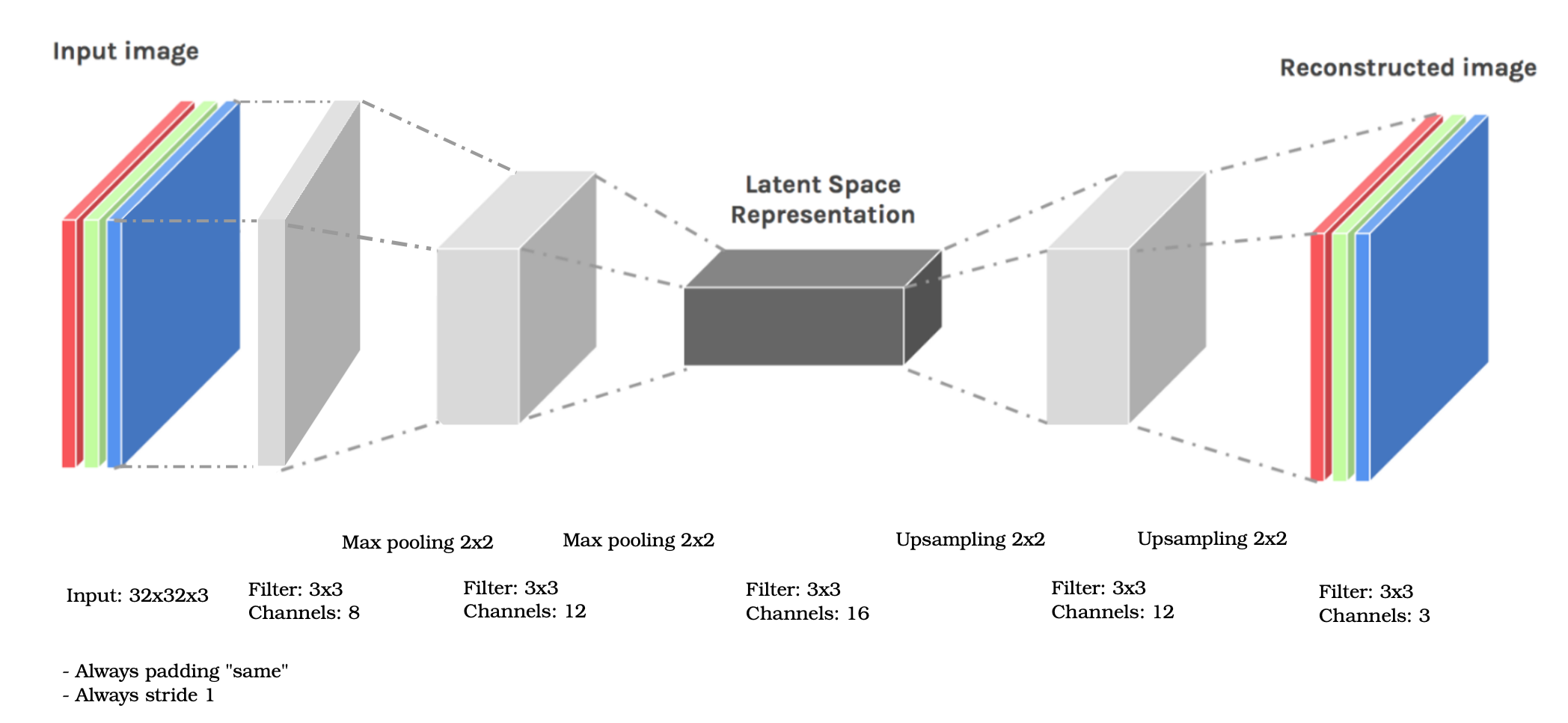
And the architect we are using is:
- Reconstruction:
- Dividing the dataset into training (80%), validation (10%) and test (10%).
- Normaling the data.
- Implementing the autoencoder network specified above.
- Runing the training and ploting the evolution of the error with epochs.
- Reporting also the test error.
- Colorization:
- Adapting the network from the previous part such that it learns to reconstruct colors by feeding in gray scale images but predicting all RGB channels.
- As a starting point, the hyperparameters are used (including the network architecture) that can identified to yield the best performance.
- Reporting the results and reason about potential shortcomings of the network.
The program is in Jupyter Notebook
In order to use the code you need to install the following packages
- Typical libraries
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow- For the dataset
from keras.datasets import cifar10- For the neural network
from keras.utils import np_utils #encoding to transform the labels in categorical
from keras.layers import Input, Dense, Conv2D, MaxPooling2D, #import the layers
from keras.layers import Dropout, Flatten, UpSampling2D #import the layers
from keras.models import Sequential #import the model
from tensorflow.keras import optimizers #import the optimizer
from keras.preprocessing import image #for visualisation of the image data
from keras import backend as K #for cleaning the memory
from keras.callbacks import Callback #import the callback