diff --git a/docs/IntelOwl/advanced_usage.md b/docs/IntelOwl/advanced_usage.md
index 128b092..4982837 100644
--- a/docs/IntelOwl/advanced_usage.md
+++ b/docs/IntelOwl/advanced_usage.md
@@ -126,6 +126,16 @@ table, th, td {
PhoneInfoga_scan |
PhoneInfoga is one of the most advanced tools to scan international phone numbers. It allows you to first gather basic information such as country, area, carrier and line type, then use various techniques to try to find the VoIP provider or identify the owner. It works with a collection of scanners that must be configured in order for the tool to be effective. PhoneInfoga doesn't automate everything, it's just there to help investigating on phone numbers. here |
+
+ | Phishing Analyzers |
+
+
+ Phishing_ExtractorPhishing_Form_Compiler
+ |
+ This framework tries to render a potential phishing page and extract useful information from it. Also, if the page contains a form, it tries to submit the form using fake data. The goal is to extract IOCs and check whether the page is real phishing or not. |
+
To enable all the optional analyzers you can add the option `--all_analyzers` when starting the project. Example:
@@ -171,7 +181,7 @@ pyintelowl_client.send_file_analysis_request(..., runtime_configuration=runtime_
#### PhoneInfoga
-PhoneInfoga provides several [Scanners](https://sundowndev.github.io/phoneinfoga/getting-started/scanners/) to extract as much information as possible from a given phone number. Those scanners may require authentication, so they're automatically skipped when no authentication credentials are found.
+PhoneInfoga provides several [Scanners](https://sundowndev.github.io/phoneinfoga/getting-started/scanners/) to extract as much information as possible from a given phone number. Those scanners may require authentication, so they are automatically skipped when no authentication credentials are found.
By default the scanner used is `local`.
Go through this [guide](https://sundowndev.github.io/phoneinfoga/getting-started/scanners/) to initiate other required API keys related to this analyzer.
@@ -193,6 +203,24 @@ Additionally, you can also (optionally) set the `output_type` argument.
- "to decimal": `[{"op": "To Decimal", "args": ["Space", False]}]`
+#### Phishing Analyzers
+The framework aims to be extandable and provides two different playbooks connected through a pivot.
+The first playbook, named `PhishingExtractor`, is in charge of extracting useful information from the web page rendered with Selenium-based browser.
+The second playbook is called `PhishingAnalysis` and its main purposes are to extract useful insights on the page itself
+and to try to submit forms with fake data to extract other IOCs.
+
+[XPath](https://www.w3schools.com/xml/xpath_intro.asp) syntax is used to find elements in the page. These selectors are customizable via the plugin's config page.
+The parameter `xpath_form_selector` controls how the form is retrieved from the page and `xpath_js_selector` is used to search
+for JavaScript inside the page.
+
+A mapping is used in order to compile the page with fake data. This is due to the fact that most input tags of type "text"
+do not have a specific role in the page, so there must be some degree of approximation.
+This behaviour is controlled through `*-mapping` parameters. They are a list that must contain the input tag's name to
+compile with fake data.
+
+Here is an example of what a phishing investigation looks like started from `PhishingExtractor` playbook:
+
+
## Analyzers with special configuration
Some analyzers could require a special configuration:
diff --git a/docs/IntelOwl/contribute.md b/docs/IntelOwl/contribute.md
index 76c74c7..f6f89e7 100644
--- a/docs/IntelOwl/contribute.md
+++ b/docs/IntelOwl/contribute.md
@@ -332,7 +332,7 @@ To do so, some utility classes have been made:
| VisualizablePage |
A single page of the final report, made of different levels. Each page added is represented as a new tab in frontend. |
- 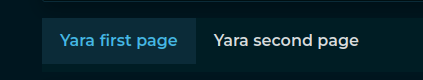 |
+  |
| VisualizableLevel |
@@ -341,37 +341,37 @@ To do so, some utility classes have been made:
VisualizableHorizontalList.
The dimension of the level can be customized with the size parameter (1 is the biggest, 6 is the smallest).
- 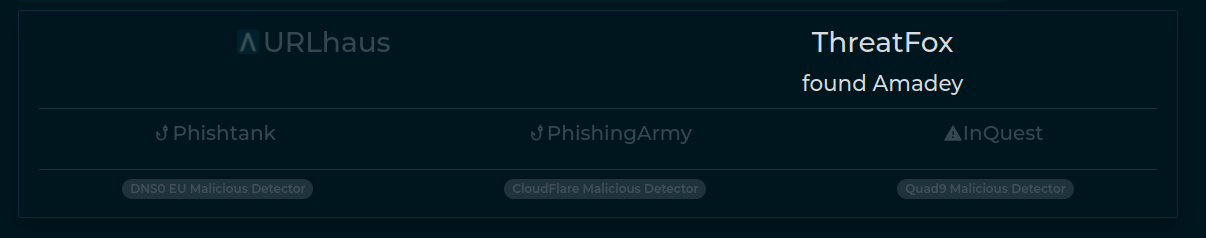 |
+  |
| VisualizableHorizontalList |
An horizontal list of visualizable elements. In the example there is an horizontal list of vertical lists. |
- 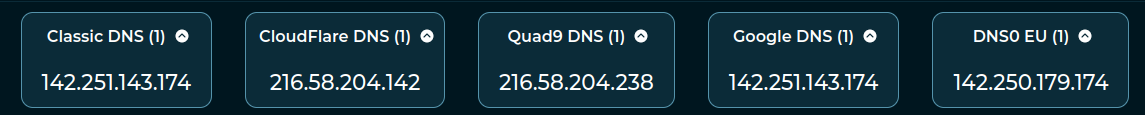 |
+  |
| VisualizableVerticalList |
A vertical list made of a name, a title, and the list of elements. |
- 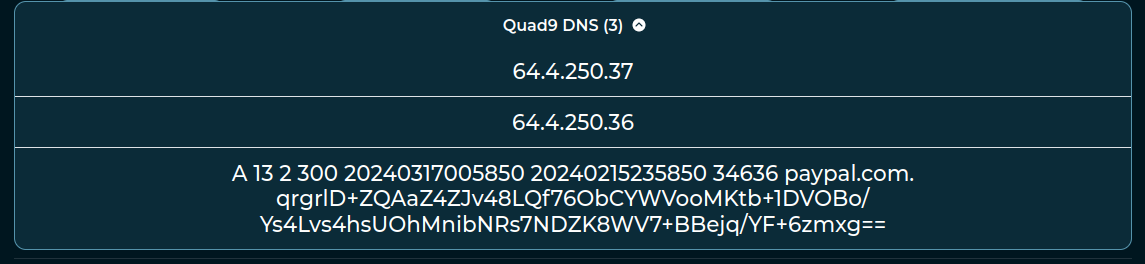 |
+  |
| VisualizableTable |
A table of visualizable elements. In the example there is a table of base and vertical lists. |
-  |
+  |
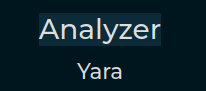
| VisualizableBool |
The representation of a boolean value. It can be enabled or disabled with colors. |
-  |
+  |
| VisualizableTitle |
The representation of a tuple, composed of a title and a value. |
-  |
+  |
| VisualizableBase |
The representation of a base string. Can have a link attached to it and even an icon. The background color can be changed. |
- The title above is composed by two `VisualizableBase` |
+ The title above is composed by two VisualizableBase |
diff --git a/docs/IntelOwl/static/phishing_analysis.png b/docs/IntelOwl/static/phishing_analysis.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..b3610ef
Binary files /dev/null and b/docs/IntelOwl/static/phishing_analysis.png differ















