diff --git a/src/main/java/g0301_0400/s0357_count_numbers_with_unique_digits/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g0301_0400/s0357_count_numbers_with_unique_digits/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..1c1a816ba
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g0301_0400/s0357_count_numbers_with_unique_digits/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+package g0301_0400.s0357_count_numbers_with_unique_digits;
+
+// #Medium #Dynamic_Programming #Math #Backtracking
+
+public class Solution {
+ public int countNumbersWithUniqueDigits(int n) {
+ int ans = 1;
+ for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
+ int mul = 1;
+ for (int j = 1; j < i; j++) {
+ mul *= (10 - j);
+ }
+ ans = ans + 9 * mul;
+ }
+ return ans;
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g0301_0400/s0357_count_numbers_with_unique_digits/readme.md b/src/main/java/g0301_0400/s0357_count_numbers_with_unique_digits/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..771542b65
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g0301_0400/s0357_count_numbers_with_unique_digits/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+357\. Count Numbers with Unique Digits
+
+Medium
+
+Given an integer `n`, return the count of all numbers with unique digits, `x`, where 0 <= x < 10n.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 2
+
+**Output:** 91
+
+**Explanation:** The answer should be the total numbers in the range of 0 ≤ x < 100, excluding 11,22,33,44,55,66,77,88,99
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 0
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `0 <= n <= 8`
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g0301_0400/s0363_max_sum_of_rectangle_no_larger_than_k/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g0301_0400/s0363_max_sum_of_rectangle_no_larger_than_k/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..6d7db52ed
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g0301_0400/s0363_max_sum_of_rectangle_no_larger_than_k/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,130 @@
+package g0301_0400.s0363_max_sum_of_rectangle_no_larger_than_k;
+
+// #Hard #Array #Dynamic_Programming #Binary_Search #Matrix #Ordered_Set
+
+/*
+*
+* Basic idea is the same as previous approach but we solve the problem in Step 2 differently.
+* Here we leverage divide and conquer technique. Basically we perform merge sort on prefix sum values and
+* calculate result during merge step.
+* One might remember the idea of using merge sort to count inversions in an array. This is very similar.
+
+* So how exactly do we compute result during merge step?
+* Suppose we are merging left prefix subarray and right prefix subarray.
+* Remember from previous approach, for each index we're trying to find an old prefix sum which is just greater than or
+* equal to current prefix sum - k.
+* So we can iterate over right subarray and for each index j, keep incrementing the pointer
+* in left array i (initialized to start index) till that situation is false (or basically prefix[i] < prefix[j] - k).
+* This way, we can compute the result for all cross subarrays (i.e. i in left subarray and j in right subarray)
+* in linear time.
+* After this, we do the standard merging part of merge sort.
+*
+*/
+
+import java.util.Arrays;
+
+public class Solution {
+ private int[] m;
+
+ private int merge(int[] a, int l, int m, int r, int k) {
+ int res = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
+ for (int j = m + 1; j <= r; j++) {
+ int i = l;
+ while (i <= m && a[j] - a[i] > k) {
+ i++;
+ }
+ if (i > m) {
+ break;
+ }
+ res = Math.max(res, a[j] - a[i]);
+ if (res == k) {
+ return res;
+ }
+ }
+ int i = l;
+ int j = m + 1;
+ int t = 0;
+ while (i <= m && j <= r) {
+ this.m[t++] = a[i] <= a[j] ? a[i++] : a[j++];
+ }
+ while (i <= m) {
+ this.m[t++] = a[i++];
+ }
+ while (j <= r) {
+ this.m[t++] = a[j++];
+ }
+ for (i = l; i <= r; i++) {
+ a[i] = this.m[i - l];
+ }
+ return res;
+ }
+
+ private int mergeSort(int[] a, int l, int r, int k) {
+ if (l == r) {
+ return a[l] <= k ? a[l] : Integer.MIN_VALUE;
+ }
+ int localM = l + ((r - l) >> 1);
+ int res = mergeSort(a, l, localM, k);
+ if (res == k) {
+ return res;
+ }
+ res = Math.max(res, mergeSort(a, localM + 1, r, k));
+ if (res == k) {
+ return res;
+ }
+ return Math.max(res, merge(a, l, localM, r, k));
+ }
+
+ private int maxSumSubArray(int[] a) {
+ int min = 0;
+ int res = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
+ for (int sum : a) {
+ res = Math.max(res, sum - min);
+ min = Math.min(min, sum);
+ }
+ return res;
+ }
+
+ private int maxSumSubArray(int[] a, int k) {
+ int res = maxSumSubArray(a);
+ if (res <= k) {
+ return res;
+ }
+ return mergeSort(a.clone(), 0, a.length - 1, k);
+ }
+
+ public int maxSumSubMatrix(int[][] matrix, int k) {
+ int localM = matrix.length;
+ int localN = localM == 0 ? 0 : matrix[0].length;
+ int res = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
+ boolean groupingRows = true;
+ if (localM > localN) {
+ int temp = localM;
+ localM = localN;
+ localN = temp;
+ groupingRows = false;
+ }
+ int[] sum = new int[localN];
+ this.m = new int[localN];
+ for (int i = 0; i < localM; i++) {
+ Arrays.fill(sum, 0);
+ for (int j = i; j < localM; j++) {
+ int pre = 0;
+ if (groupingRows) {
+ for (int t = 0; t < localN; t++) {
+ sum[t] += pre += matrix[j][t];
+ }
+ } else {
+ for (int t = 0; t < localN; t++) {
+ sum[t] += pre += matrix[t][j];
+ }
+ }
+ res = Math.max(res, maxSumSubArray(sum, k));
+ if (res == k) {
+ return res;
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return res;
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g0301_0400/s0363_max_sum_of_rectangle_no_larger_than_k/readme.md b/src/main/java/g0301_0400/s0363_max_sum_of_rectangle_no_larger_than_k/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..4a08bcc6e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g0301_0400/s0363_max_sum_of_rectangle_no_larger_than_k/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+363. Max Sum of Rectangle No Larger Than K
+
+Hard
+
+Given an `m x n` matrix `matrix` and an integer `k`, return _the max sum of a rectangle in the matrix such that its sum is no larger than_ `k`.
+
+It is **guaranteed** that there will be a rectangle with a sum no larger than `k`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
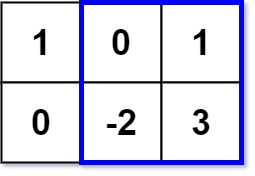
+**Input:** matrix = [[1,0,1],[0,-2,3]], k = 2
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** Because the sum of the blue rectangle [[0, 1], [-2, 3]] is 2, and 2 is the max number no larger than k (k = 2).
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** matrix = [[2,2,-1]], k = 3
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `m == matrix.length`
+* `n == matrix[i].length`
+* `1 <= m, n <= 100`
+* `-100 <= matrix[i][j] <= 100`
+* -105 <= k <= 105
+
+**Follow up:** What if the number of rows is much larger than the number of columns?
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/test/java/g0301_0400/s0357_count_numbers_with_unique_digits/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g0301_0400/s0357_count_numbers_with_unique_digits/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..f52a2feda
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g0301_0400/s0357_count_numbers_with_unique_digits/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
+package g0301_0400.s0357_count_numbers_with_unique_digits;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void countNumbersWithUniqueDigits() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().countNumbersWithUniqueDigits(2), equalTo(91));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void countNumbersWithUniqueDigits2() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().countNumbersWithUniqueDigits(0), equalTo(1));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g0301_0400/s0363_max_sum_of_rectangle_no_larger_than_k/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g0301_0400/s0363_max_sum_of_rectangle_no_larger_than_k/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..e250cbbb5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g0301_0400/s0363_max_sum_of_rectangle_no_larger_than_k/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
+package g0301_0400.s0363_max_sum_of_rectangle_no_larger_than_k;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void maxSumSubMatrix() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution().maxSumSubMatrix(new int[][] {{1, 0, 1}, {0, -2, 3}}, 2), equalTo(2));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void maxSumSubMatrix2() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().maxSumSubMatrix(new int[][] {{2, 2, -1}}, 3), equalTo(3));
+ }
+}