System Design & Implementation
Dataset: SGSC_Weather_Sensor_Data.csv (Southern Grampians Weather Sensors)
This repository implements a real-time IoT analytics prototype for weather anomaly detection.
Main components:
-
prototype.py- Loads and cleans a public IoT weather dataset
- Trains Isolation Forest (IF) and a Deep Autoencoder (AE)
- Simulates real-time streaming and writes results to
stream_output.csv
-
app.py- A Streamlit dashboard that continuously reads
stream_output.csv - Visualises live sensor trends
- Highlights anomaly points from both models
- Shows basic KPIs and an anomaly table
- A Streamlit dashboard that continuously reads
The goal is to show a clear offline → online pipeline:
historical training + model building, then real-time anomaly scoring and monitoring.
- Source: Southern Grampians Shire Council (SGSC) Weather Sensor Data – data.gov.au
- Local file:
SGSC_Weather_Sensor_Data.csv(auto-downloaded if missing) - Download URL: defined as
DATA_URLinprototype.py
Time information in the raw dataset is stored in a numeric field with the format YYYYMMDDHHMMSS,
sometimes as integers, sometimes as scientific notation (e.g. 2.01806E+13).
prototype.py:
- Parses this field into a proper
datetimecolumn - Filters the data into a configurable time window (default 2018–2021)
prototype.py– Offline training + real-time streaming (IF + AE)app.py– Streamlit dashboard for live anomaly visualisationSGSC_Weather_Sensor_Data.csv– Local cache of raw dataset (auto-downloaded if absent)stream_output.csv– Streaming output consumed by the dashboard (generated at runtime)
- Download and cache the SGSC dataset if needed.
- Standardise column names (lowercase, stripped).
- Locate and parse the time / timestamp column:
- Convert
YYYYMMDDHHMMSS(including scientific notation) todatetime.
- Convert
- Filter records between
YEAR_STARTandYEAR_END(defaults: 2018–2021). - Select numeric sensor features, for example:
airtemp,relativehumidity,windspeed,solar,
vapourpressure,atmosphericpressure,gustspeed,winddirection. - Handle missing values using forward/backward fill.
- Optionally downsample to
SAMPLE_SIZErows for a faster demo.
Using the historical window (early part of the time-ordered data):
-
Train–stream split
- Split in temporal order with
TRAIN_RATIO(e.g. 70% train, 30% stream).
- Split in temporal order with
-
Isolation Forest (IF)
- Implemented with
sklearn.ensemble.IsolationForest. - Key hyperparameters:
contamination– expected anomaly proportion (e.g. 0.05)n_estimators– number of trees
- Output flag per record:
IF_Flag = 1if predicted as an outlier (-1), else0.
- Implemented with
-
Autoencoder (AE)
- Fully-connected encoder–decoder network:
- Input = scaled sensor features (
StandardScaler) - Latent bottleneck to compress normal patterns
- Input = scaled sensor features (
- Training configuration:
- Optimiser: Adam
- Loss: MSE reconstruction loss
AE_EPOCHS,AE_BATCH_SIZE,AE_LRcontrol training length and speed.
- Threshold:
- Compute reconstruction error on the training set
- Threshold =
mean(error) + 3 × std(error) AE_Flag = 1if current reconstruction error exceeds threshold.
- Fully-connected encoder–decoder network:
-
The streaming partition (future window) is processed row by row.
-
For each record:
-
Score with Isolation Forest →
IF_Flag. -
Scale features and score with the Autoencoder →
AE_Flag. -
Attach ground-truth label
GT_Label(see Section 5). -
Append a new row into
stream_output.csv:Index, Time, <features…>, IF_Flag, AE_Flag, GT_Label
-
-
app.pyruns as a Streamlit app and:- Continuously reloads
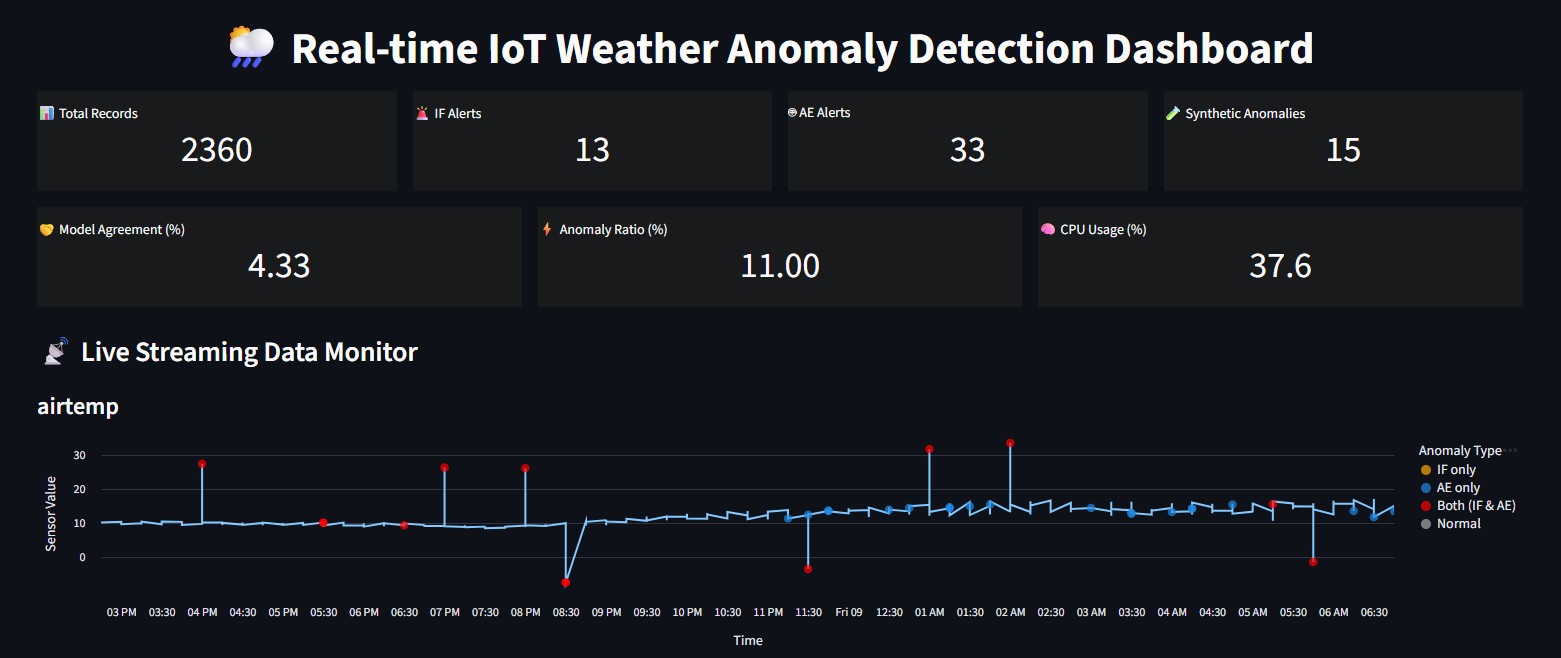
stream_output.csv. - Shows KPIs (total records, IF/AE alerts, synthetic anomalies, model agreement, anomaly ratio).
- Plots time-series for selected features with anomaly markers.
- Displays a table of recent anomaly rows.
- Continuously reloads
To make anomalies clearer and support simple evaluation:
prototype.pycan inject synthetic anomalies into the streaming set whenSYNTHETIC = True.- A subset of rows (
SYNTH_POINTS) is selected at random. - For each selected row:
- One or more feature values are perturbed by a multiple of that feature’s standard deviation.
- A ground-truth label
gt_anomaly = 1is set, and later written asGT_Labelinstream_output.csv.
The dashboard uses GT_Label to:
- Count synthetic anomalies,
- Highlight them visually on the plots (e.g. vertical markers),
- Compare IF/AE alerts against a simple ground truth.
Install the required Python packages:
pip install pandas numpy scikit-learn torch streamlit altair psutilStart the Streaming Engine
python prototype.pyLaunch the Streamlit Dashboard
streamlit run app.pyThen open the URL printed in the terminal (normally): http://localhost:8501