It is a fork of Chris Sattinger's django-ajax-selects (http://code.google.com/p/django-ajax-selects/)
Enables editing of ForeignKey, ManyToMany and simple text fields using the Autocomplete - jQuery plugin.
django-ajax-selects will work in any normal form in the admin as well.
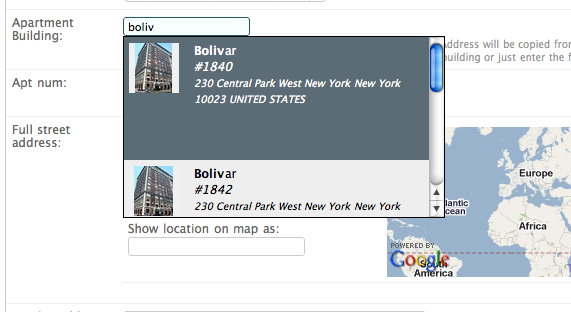
selecting:
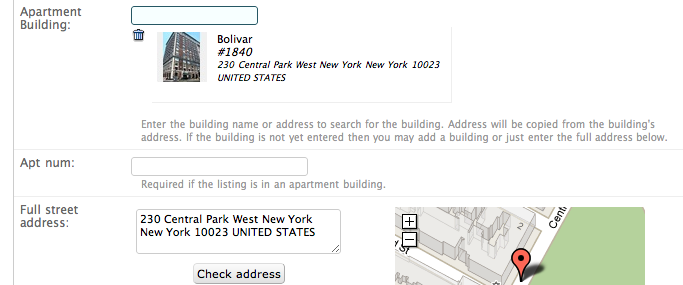
selected:
The user is presented with a text field. They type a search term or a few letters of a name they are looking for, an ajax request is sent to the server, a search channel returns possible results. Results are displayed as a drop down menu. When an item is selected it is added to a display area just below the text field.
A single view services all of the ajax search requests, delegating the searches to named 'channels'.
A channel is a simple class that handles the actual searching, defines how you want to treat the query input (split first name and last name, which fields to search etc.) and returns id and formatted results back to the view which sends it to the browser.
For instance the search channel 'contacts' would search for Contact models. The class would be named ContactLookup. This channel can be used for both AutoCompleteSelect (foreign key, single item) and AutoCompleteSelectMultiple (many-to-many) fields.
Simple search channels can also be automatically generated, you merely specify the model and the field to search against (see examples below).
Custom search channels can be written when you need to do a more complex search, check the user's permissions, format the results differently or customize the sort order of the results.
Tested with Django 1.3
In settings.py :
INSTALLED_APPS = (
...,
'ajax_select'
)
in your settings.py define the channels in use on the site, for example:
AJAX_LOOKUP_CHANNELS = {
# the simplest case, pass a DICT with the model and field to search against :
'track' : dict(model='music.track',search_field='title'),
# this generates a simple channel
# specifying the model Track in the music app, and searching against the 'title' field
# or write a custom search channel and specify that using a TUPLE
'contact' : ('peoplez.lookups', 'ContactLookup'),
# this specifies to look for the class `ContactLookup` in the `peoplez.lookups` module
}
Custom search channels can be written when you need to do a more complex search, check the user's permissions (if the lookup URL should even be accessible to them, and then to perhaps filter which items they are allowed to see), format the results differently or customize the sort order of the results. Search channel objects should implement the 4 methods shown in the following example.
peoplez/lookups.py
from peoplez.models import Contact
from django.db.models import Q
class ContactLookup(object):
def get_query(self,q,request):
""" return a query set. you also have access to request.user if needed """
return Contact.objects.filter(Q(name__istartswith=q) | Q(fname__istartswith=q) | Q(lname__istartswith=q) | Q(email__icontains=q))
def format_result(self,contact):
""" the search results display in the dropdown menu. may contain html and multiple-lines. will remove any | """
return u"%s %s %s (%s)" % (contact.fname, contact.lname,contact.name,contact.email)
def format_item(self,contact):
""" the display of a currently selected object in the area below the search box. html is OK """
return unicode(contact)
def get_objects(self,ids):
""" given a list of ids, return the objects ordered as you would like them on the admin page.
this is for displaying the currently selected items (in the case of a ManyToMany field)
"""
return Contact.objects.filter(pk__in=ids).order_by('name','lname')
HTML is fine in the result or item format. Newlines and pipe chars will be removed and everything will be escaped properly.
Include the urls in your site's urls.py. This adds the lookup view and the pop up admin view.
(r'^ajax_select/', include('ajax_select.urls')),
##It you want to use django-ajax-select in your admin page,
for an example model:
class ContactMailing(models.Model):
""" can mail to multiple contacts, has one author """
contacts = models.ManyToManyField(Contact, blank=True)
author = models.ForeignKey(Contact, blank=False)
...
In the admin.py for this app:
from ajax_select import make_ajax_form
class ContactMailingAdmin(Admin):
form = make_ajax_form(ContactMailing, {'author': 'contact', contacts='contact'))
make_ajax_form( model, fieldlist) is a factory function which will insert the ajax powered form field inputs
so in this example the author field (ForeignKey) uses the 'contact' channel and the contacts field (ManyToMany)
also uses the 'contact' channel
If you need to write your own form class then specify that form for the admin as usual:
from forms import ContactMailingForm
class ContactMailingAdmin(admin.ModelAdmin):
form = ContactMailingForm
admin.site.register(ContactMailing,ContactMailingAdmin)
in forms.py for that app:
from ajax_select.fields import AutoCompleteSelectMultipleField, AutoCompleteSelectField
class ContactMailingForm(models.ModelForm):
# declare a field and specify the named channel that it uses
contacts = AutoCompleteSelectMultipleField('contact', required=False)
author = AutoCompleteSelectField('contact', required=False)
##Using ajax selects in a FormSet
There might be a better way to do this.
forms.py
from django.forms.models import modelformset_factory
from django.forms.models import BaseModelFormSet
from ajax_select.fields import AutoCompleteSelectMultipleField, AutoCompleteSelectField
from models import *
# create a superclass
class BaseTaskFormSet(BaseModelFormSet):
# that adds the field in, overwriting the previous default field
def add_fields(self, form, index):
super(BaseTaskFormSet, self).add_fields(form, index)
form.fields["project"] = AutoCompleteSelectField('project', required=False)
# pass in the base formset class to the factory
TaskFormSet = modelformset_factory(Task,fields=('name','project','area'),extra=0,formset=BaseTaskFormSet)
##Help text
If you are using AutoCompleteSelectMultiple outside of the admin then pass in show_help_text=True.
This is because the admin displays the widget's help text and the widget would also.
But when used outside of the admin you need the help text. This is not the case for AutoCompleteSelect.
##License
Dual licensed under the MIT and GPL licenses: http://www.opensource.org/licenses/mit-license.php http://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html
##Changelog
1.2 - Js files was refactored. All static content is collected into 'static' folder. And example project was written.