This repo aims to create a pytorch warehouse for (medical) image analysis consisting of classification, detection, segmentation (2D and 3D). The codes/methods should be easily applied to other types of images due to the fact that all images are matrices storing intensity values. There might be special python packages need to be installed to handle the specific MRI or CT image format (i.e. dicom).
The goal for this part is to train a classifier that can predict whether a patient's X-Ray indicates the presence of pneumonia or not. To achieve this, we will be utilizing the RSNA Pneumonia Detection Challenge dataset, which can be found at the following link: https://www.kaggle.com/c/rsna-pneumonia-detection-challenge/data
The task is a typical binary classification problem with samples shown below. Here the input is the image and output is a label (1 indicates positive while 0 indicates negative).
The code does not use handle imbalance issue for this dataset as for now. The resnet neural network is used for the algorithn. Cross entropy is used as the loss function and accuracy is used as a metric for evaluation.
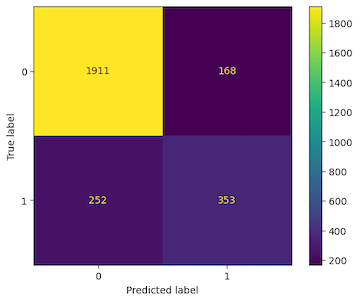
The confusion matrix for the validation dataset is shown below
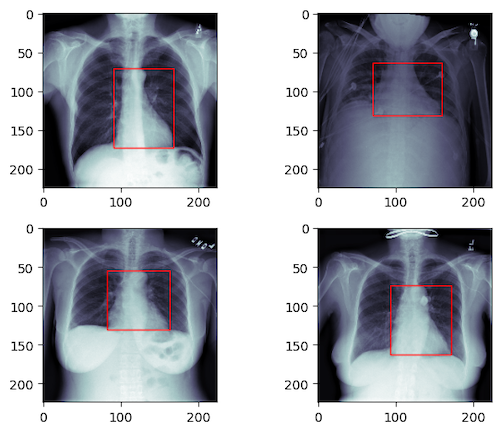
The goal for this part is to predict a bounding box containg heart in the above X-Ray images.
The task can be formulated as a regression problem. Again the input is the image but the output is a 4d vector (xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax) which defines the location of the heart as illustrated below. Here the Mean Square Error is used as the loss function.
After training for 100 epochs, the MSE for the algorithm is ~40 indication the predicted bounding box are about 3 ~ 5 pixel off the ground truth.
The goal for this part is to train a 2D UNET model that segment atrium of a heart. The input is the image and the output is an image with the same size indicating the object.
After training for 70 epochs, the algorithm can achieve a Dice value ~0.95.
Instead of performing segmentation for each 2D slice as above, the goal for this part is to train a 3D UNET model to segment atrium of a heart for the same 3D MR dataset as in the Section above.
The 3D unet model requires huge amount of VRAM. The general idea to overcome this challenge is "divide and conquer". The 3D data stack is devided into small cubes. The training is done per each cube first and then combined for the whole data stack. Torchio has specific module to handle the dividing and combining process. A demo result is shown below.