diff --git a/_partials/_devops-cli-get-started.md b/_partials/_devops-cli-get-started.md
index 16eb6a88e5..6b517072a6 100644
--- a/_partials/_devops-cli-get-started.md
+++ b/_partials/_devops-cli-get-started.md
@@ -1,4 +1,6 @@
import RESTPrereqs from "versionContent/_partials/_prereqs-cloud-account-only.mdx";
+import CLIINSTALL from "versionContent/_partials/_devops-cli-install.mdx";
+import CLIREF from "versionContent/_partials/_devops-cli-reference.mdx";
$CLI_LONG is a command-line interface that you use to manage $CLOUD_LONG resources
including VPCs, services, read replicas, and related infrastructure. $CLI_LONG calls $REST_LONG to communicate with
@@ -16,131 +18,22 @@ service.
-1. **Install $CLI_LONG**
-
- Use the terminal to install the $CLI_SHORT:
-
-
-
-
- ```shell
- curl -s https://packagecloud.io/install/repositories/timescale/tiger-cli/script.deb.sh | sudo os=any dist=any bash
- sudo apt-get install tiger-cli
- ```
-
-
-
-
-
- ```shell
- curl -s https://packagecloud.io/install/repositories/timescale/tiger-cli/script.deb.sh | sudo os=any dist=any bash
- sudo apt-get install tiger-cli
- ```
-
-
-
-
- ```shell
- curl -s https://packagecloud.io/install/repositories/timescale/tiger-cli/script.rpm.sh | sudo os=rpm_any dist=rpm_any bash
- sudo yum install tiger-cli
- ```
-
-
-
-
-
- ```shell
- curl -s https://packagecloud.io/install/repositories/timescale/tiger-cli/script.rpm.sh | sudo os=rpm_any dist=rpm_any bash
- sudo yum install tiger-cli
- ```
-
-
-
-
-
- ```shell
- brew install --cask timescale/tap/tiger-cli
- ```
-
-
-
-
-
- ```shell
- curl -fsSL https://tiger-cli-releases.s3.amazonaws.com/install/install.sh | sh
- ```
-
-
-
-
-
-1. **Set up API credentials**
-
- 1. Log $CLI_LONG into your $ACCOUNT_LONG:
-
- ```shell
- tiger auth login
- ```
- $CLI_LONG opens $CONSOLE_SHORT in your browser. Log in, then click `Authorize`.
-
- 1. Log $CLI_LONG into your $ACCOUNT_LONG
-
- ```shell
- tiger auth login
- ```
- $CLI_LONG opens $CONSOLE_SHORT in your browser. Login, then click `Authorize`.
-
- 1. Select a $PROJECT_LONG.
-
- ```terminaloutput
- Auth URL is: https://console.cloud.timescale.com/oauth/authorize?client_id=lotsOfURLstuff
- Opening browser for authentication...
- Select a project:
-
- > 1. Tiger Project (tgrproject)
- 2. YourCompany (Company wide project) (cpnproject)
- 3. YourCompany Department (dptproject)
-
- Use ↑/↓ arrows or number keys to navigate, enter to select, q to quit
- ```
- If only one $PROJECT_SHORT is associated with your $ACCOUNT_SHORT, this step is not shown.
-
- Where possible, $CLI_LONG stores your authentication information in the system keychain/credential manager.
- If that fails, the key is stored in `~/.config/tiger/api-key` with restricted file permissions (600).
- $CLI_LONG stores your configuration in `~/.config/tiger/config.yaml`.
-
-1. **Test your authenticated connection to $CLOUD_LONG by listing services**
-
- ```bash
- tiger service list
- ```
-
- This call returns something like:
- - No services:
- ```terminaloutput
- 🏜️ No services found! Your project is looking a bit empty.
- 🚀 Ready to get started? Create your first service with: tiger service create
- ```
- - One or more services:
-
- ```terminaloutput
- ┌────────────┬─────────────────────┬────────┬─────────────┬──────────────┬──────────────────┐
- │ SERVICE ID │ NAME │ STATUS │ TYPE │ REGION │ CREATED │
- ├────────────┼─────────────────────┼────────┼─────────────┼──────────────┼──────────────────┤
- │ tgrservice │ tiger-agent-service │ READY │ TIMESCALEDB │ eu-central-1 │ 2025-09-25 16:09 │
- └────────────┴─────────────────────┴────────┴─────────────┴──────────────┴──────────────────┘
- ```
+
-## Create your first service
+## Create your first $SERVICE_LONG
Create a new $SERVICE_LONG using $CLI_LONG:
-1. **Submit a service creation request**
+1. **Submit a $SERVICE_SHORT creation request**
+
+ By default, $CLI_LONG creates a $SERVICE_SHORT for you that matches your [pricing plan][pricing-plans]:
+ * **Free plan**: shared CPU/memory and the `time-series` and `ai` capabilities
+ * **Paid plan**: 0.5 CPU and 2 GB memory with the `time-series` capability
```shell
tiger service create
```
@@ -149,12 +42,27 @@ Create a new $SERVICE_LONG using $CLI_LONG:
```terminaloutput
🚀 Creating service 'db-11111' (auto-generated name)...
✅ Service creation request accepted!
- 📋 Service ID: happyservice
+ 📋 Service ID: tgrservice
🔐 Password saved to system keyring for automatic authentication
- 🎯 Set service 'happyservice' as default service.
+ 🎯 Set service 'tgrservice' as default service.
⏳ Waiting for service to be ready (wait timeout: 30m0s)...
- ⏳ Service status: QUEUED...
🎉 Service is ready and running!
+ 🔌 Run 'tiger db connect' to connect to your new service
+ ┌───────────────────┬──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
+ │ PROPERTY │ VALUE │
+ ├───────────────────┼──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
+ │ Service ID │ tgrservice │
+ │ Name │ db-11111 │
+ │ Status │ READY │
+ │ Type │ TIMESCALEDB │
+ │ Region │ us-east-1 │
+ │ CPU │ 0.5 cores (500m) │
+ │ Memory │ 2 GB │
+ │ Direct Endpoint │ tgrservice.tgrproject.tsdb.cloud.timescale.com:39004 │
+ │ Created │ 2025-10-20 20:33:46 UTC │
+ │ Connection String │ postgresql://tsdbadmin@tgrservice.tgrproject.tsdb.cloud.timescale.com:0007/tsdb?sslmode=require │
+ │ Console URL │ https://console.cloud.timescale.com/dashboard/services/tgrservice │
+ └───────────────────┴──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
```
This $SERVICE_SHORT is set as default by the $CLI_SHORT.
@@ -182,56 +90,11 @@ Create a new $SERVICE_LONG using $CLI_LONG:
And that is it, you are ready to use $CLI_LONG to manage your $SERVICE_SHORTs in $CLOUD_LONG.
-## Commands
-
-You can use the following commands with $CLI_LONG. For more information on each command, use the `-h` flag. For example:
-`tiger auth login -h`
-
-| Command | Subcommand | Description |
-|---------|-----------------------------------------------------|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
-| auth | | Manage authentication and the credentials for your $ACCOUNT_LONG |
-| | login | Create an authenticated connection to your $ACCOUNT_LONG |
-| | logout | Remove the credentials used to create authenticated connections to $CLOUD_LONG |
-| | whoami | Show information about the current user |
-| version | | Show information about the currently installed version of $CLI_LONG |
-| | set `` `` | Set a specific value in your configuration. For example, `tiger config set debug true` |
-| config | | Manage your $CLI_LONG configuration |
-| | show | Show the current configuration |
-| | unset `` | Clear the value of a configuration parameter. For example, `tiger config unset debug` |
-| | reset | Reset the configuration to the defaults. This also logs you out from the current $PROJECT_LONG |
-| service | | Manage the $SERVICE_LONGs in this $PROJECT_SHORT |
-| | create `--addons=` | Create a new $SERVICE_SHORT in this $PROJECT_SHORT. Possible addons are: - time-series: with the Timescaledb and Timescaledb Toolkit extensions
- ai: with the Timescaledb, Timescaledb Toolkit, vector and vectorscale extensions
- free: free services have fixed compute of 0.25 CPU, 1 GiB RAM, and up to 500mb storage.
- none: vanilla Postgres
All services have Tiger features such as Tiger Storage, Security, Monitoring and compliance. If you do not use the `addons` flag, the default service is `time-series`. |
-| | describe `` | Show detailed information about a specific $SERVICE_SHORT in this $PROJECT_SHORT |
-| | delete `` | Delete a $SERVICE_SHORT from this $PROJECT_SHORT |
-| | fork `` | Fork of an existing database service. Key features are: - Timing options: `--now`, `--last-snapshot`, `--to-timestamp`
- Resource configuration: `--cpu`, `--memory`
- Naming: `--name ` . Defaults to {source-service-name}-fork
- Wait behavior: `--no-wait`, `--wait-timeout`
- Default service: `--no-set-default`
|
-| | list | List all the $SERVICE_SHORTs in this $PROJECT_SHORT |
-| | update-password `` | Update the password for a $SERVICE_SHORT |
-| db | | Database operations and management |
-| | connect `` | Connect to a $SERVICE_SHORT |
-| | connection-string `` | Retrieve the connection string for a $SERVICE_SHORT |
-| | test-connection `` | Test the connectivity to a $SERVICE_SHORT |
-| mcp | | Manage the $MCP_LONG |
-| | start | Start the $MCP_LONG. This is the same as `tiger mcp start stdio` |
-| | start `stdio` \| `http` | Start the $MCP_LONG with stdio or HTTP transport |
-
-## Flags
-
-You can use the following global flags with $CLI_LONG:
-
-| Flag | Default | Description |
-|--|-----------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------|
-| --analytics | `true` | Set to `false` to disable usage analytics |
-| --config-dir string | `.config/tiger` | Set the directory that holds `config.yaml` |
-| --debug | No debugging | Enable debug logging |
-| -o, --output string | table | Set the output format. Options are `json`, `yaml`, or `table` |
-| --password-storage string | keyring | Set the password storage method. Options are `keyring`, `pgpass`, or `none` |
-| --project-id string | - | Set the $PROJECT_LONG to manage |
-| --service-id string | - | Set the $SERVICE_LONG to manage |
-
-
+
[rest-api-reference]: /api/:currentVersion:/api-reference/
[rest-api-credentials]: https://console.cloud.timescale.com/dashboard/settings
[get-project-id]: /integrations/:currentVersion:/find-connection-details/#find-your-project-and-service-id
[create-client-credentials]: /integrations/:currentVersion:/find-connection-details/#create-client-credentials
-[curl]: https://curl.se/
\ No newline at end of file
+[curl]: https://curl.se/
+[pricing-plans]: /about/:currentVersion:/pricing-and-account-management/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/_partials/_devops-cli-global-flags.md b/_partials/_devops-cli-global-flags.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..1fd8c692dc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/_partials/_devops-cli-global-flags.md
@@ -0,0 +1,11 @@
+
+| Flag | Default | Description |
+|-------------------------------|-------------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------|
+| `--analytics` | `true` | Set to `false` to disable usage analytics |
+| `--color ` | `true` | Set to `false` to disable colored output |
+| `--config-dir` string | `.config/tiger` | Set the directory that holds `config.yaml` |
+| `--debug` | No debugging | Enable debug logging |
+| `--help` | - | Print help about the current command. For example, `tiger service --help` |
+| `--password-storage` string | keyring | Set the password storage method. Options are `keyring`, `pgpass`, or `none` |
+| `--service-id` string | - | Set the $SERVICE_LONG to manage |
+| ` --skip-update-check ` | - | Do not check if a new version of $CLI_LONG is available|
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/_partials/_devops-cli-install.md b/_partials/_devops-cli-install.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d0dab2990e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/_partials/_devops-cli-install.md
@@ -0,0 +1,117 @@
+1. **Install $CLI_LONG**
+
+ Use the terminal to install the $CLI_SHORT:
+
+
+
+
+ ```shell
+ curl -s https://packagecloud.io/install/repositories/timescale/tiger-cli/script.deb.sh | sudo os=any dist=any bash
+ sudo apt-get install tiger-cli
+ ```
+
+
+
+
+
+ ```shell
+ curl -s https://packagecloud.io/install/repositories/timescale/tiger-cli/script.deb.sh | sudo os=any dist=any bash
+ sudo apt-get install tiger-cli
+ ```
+
+
+
+
+ ```shell
+ curl -s https://packagecloud.io/install/repositories/timescale/tiger-cli/script.rpm.sh | sudo os=rpm_any dist=rpm_any bash
+ sudo yum install tiger-cli
+ ```
+
+
+
+
+
+ ```shell
+ curl -s https://packagecloud.io/install/repositories/timescale/tiger-cli/script.rpm.sh | sudo os=rpm_any dist=rpm_any bash
+ sudo yum install tiger-cli
+ ```
+
+
+
+
+
+ ```shell
+ brew install --cask timescale/tap/tiger-cli
+ ```
+
+
+
+
+
+ ```shell
+ curl -fsSL https://cli.tigerdata.com | sh
+ ```
+
+
+
+
+
+1. **Set up API credentials**
+
+ 1. Log $CLI_LONG into your $ACCOUNT_LONG:
+
+ ```shell
+ tiger auth login
+ ```
+ $CLI_LONG opens $CONSOLE_SHORT in your browser. Log in, then click `Authorize`.
+
+ You can have a maximum of 10 active client credentials. If you get an error, open [credentials][rest-api-credentials]
+ and delete an unused credential.
+
+ 1. Select a $PROJECT_LONG:
+
+ ```terminaloutput
+ Auth URL is: https://console.cloud.timescale.com/oauth/authorize?client_id=lotsOfURLstuff
+ Opening browser for authentication...
+ Select a project:
+
+ > 1. Tiger Project (tgrproject)
+ 2. YourCompany (Company wide project) (cpnproject)
+ 3. YourCompany Department (dptproject)
+
+ Use ↑/↓ arrows or number keys to navigate, enter to select, q to quit
+ ```
+ If only one $PROJECT_SHORT is associated with your $ACCOUNT_SHORT, this step is not shown.
+
+ Where possible, $CLI_LONG stores your authentication information in the system keychain/credential manager.
+ If that fails, the credentials are stored in `~/.config/tiger/credentials` with restricted file permissions (600).
+ By default, $CLI_LONG stores your configuration in `~/.config/tiger/config.yaml`.
+
+1. **Test your authenticated connection to $CLOUD_LONG by listing $SERVICE_SHORTs**
+
+ ```bash
+ tiger service list
+ ```
+
+ This call returns something like:
+ - No $SERVICE_SHORTs:
+ ```terminaloutput
+ 🏜️ No services found! Your project is looking a bit empty.
+ 🚀 Ready to get started? Create your first service with: tiger service create
+ ```
+ - One or more $SERVICE_SHORTs:
+
+ ```terminaloutput
+ ┌────────────┬─────────────────────┬────────┬─────────────┬──────────────┬──────────────────┐
+ │ SERVICE ID │ NAME │ STATUS │ TYPE │ REGION │ CREATED │
+ ├────────────┼─────────────────────┼────────┼─────────────┼──────────────┼──────────────────┤
+ │ tgrservice │ tiger-agent-service │ READY │ TIMESCALEDB │ eu-central-1 │ 2025-09-25 16:09 │
+ └────────────┴─────────────────────┴────────┴─────────────┴──────────────┴──────────────────┘
+ ```
+
+
+[rest-api-reference]: /api/:currentVersion:/api-reference/
+[rest-api-credentials]: https://console.cloud.timescale.com/dashboard/settings
+[get-project-id]: /integrations/:currentVersion:/find-connection-details/#find-your-project-and-service-id
+[create-client-credentials]: /integrations/:currentVersion:/find-connection-details/#create-client-credentials
+[curl]: https://curl.se/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/_partials/_devops-cli-reference.md b/_partials/_devops-cli-reference.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c641f17146
--- /dev/null
+++ b/_partials/_devops-cli-reference.md
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
+import GLOBALFLAGS from "versionContent/_partials/_devops-cli-global-flags.mdx";
+
+## Commands
+
+You can use the following commands with $CLI_LONG. For more information on each command, use the `-h` flag. For example:
+`tiger auth login -h`
+
+| Command | Subcommand | Description |
+|---------|----------------------------------------------|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
+| auth | | Manage authentication and credentials for your $ACCOUNT_LONG |
+| | login | Create an authenticated connection to your $ACCOUNT_LONG |
+| | logout | Remove the credentials used to create authenticated connections to $CLOUD_LONG |
+| | status | Show your current authentication status and project ID |
+| version | | Show information about the currently installed version of $CLI_LONG |
+| config | | Manage your $CLI_LONG configuration |
+| | show | Show the current configuration |
+| | set `` `` | Set a specific value in your configuration. For example, `tiger config set debug true` |
+| | unset `` | Clear the value of a configuration parameter. For example, `tiger config unset debug` |
+| | reset | Reset the configuration to the defaults. This also logs you out from the current $PROJECT_LONG |
+| service | | Manage the $SERVICE_LONGs in this $PROJECT_SHORT |
+| | create | Create a new $SERVICE_SHORT in this $PROJECT_SHORT. Possible flags are: - `--name`: service name (auto-generated if not provided)
- `--addons`: addons to enable (time-series, ai, or none for PostgreSQL-only)
- `--region`: region code where the service will be deployed
- `--cpu-memory`: CPU/memory allocation combination
- `--replicas`: number of high-availability replicas
- `--no-wait`: don't wait for the operation to complete
- `--wait-timeout`: wait timeout duration (for example, 30m, 1h30m, 90s)
- `--no-set-default`: don't set this service as the default service
- `--with-password`: include password in output
- `--output, -o`: output format (`json`, `yaml`, table)
Possible `cpu-memory` combinations are: - shared/shared
- 0.5 CPU/2 GB
- 1 CPU/4 GB
- 2 CPU/8 GB
- 4 CPU/16 GB
- 8 CPU/32 GB
- 16 CPU/64 GB
- 32 CPU/128 GB
|
+| | delete `` | Delete a $SERVICE_SHORT from this $PROJECT_SHORT. This operation is irreversible and requires confirmation by typing the service ID |
+| | fork `` | Fork an existing service to create a new independent copy. Key features are: - Timing options: `--now`, `--last-snapshot`, `--to-timestamp`
- Resource configuration: `--cpu-memory`
- Naming: `--name `. Defaults to `{source-service-name}-fork`
- Wait behavior: `--no-wait`, `--wait-timeout`
- Default service: `--no-set-default`
|
+| | get `` (aliases: describe, show) | Show detailed information about a specific $SERVICE_SHORT in this $PROJECT_SHORT |
+| | list | List all the $SERVICE_SHORTs in this $PROJECT_SHORT |
+| | update-password `` | Update the master password for a $SERVICE_SHORT |
+| db | | Database operations and management |
+| | connect `` | Connect to a $SERVICE_SHORT |
+| | connection-string `` | Retrieve the connection string for a $SERVICE_SHORT |
+| | save-password `` | Save the password for a service |
+| | test-connection `` | Test the connectivity to a $SERVICE_SHORT |
+| mcp | | Manage the $MCP_LONG for AI Assistant integration |
+| | install `[client]` | Install and configure $MCP_LONG for a specific client (`claude-code`, `cursor`, `windsurf`, or other). If no client is specified, you'll be prompted to select one interactively |
+| | start | Start the $MCP_LONG. This is the same as `tiger mcp start stdio` |
+| | start stdio | Start the $MCP_LONG with stdio transport (default) |
+| | start http | Start the $MCP_LONG with HTTP transport. Includes flags: `--port` (default: `8080`), `--host` (default: `localhost`) |
+
+
+## Global flags
+
+You can use the following global flags with $CLI_LONG:
+
+
+
+
+## Configuration parameters
+
+By default, $CLI_LONG stores your configuration in `~/.config/tiger/config.yaml`. The name of these
+variables matches the flags you use to update them. However, you can override them using the following
+environmental variables:
+
+- **Configuration parameters**
+ - `TIGER_CONFIG_DIR`: path to configuration directory (default: `~/.config/tiger`)
+ - `TIGER_API_URL`: $REST_LONG base endpoint (default: https://console.cloud.timescale.com/public/api/v1)
+ - `TIGER_CONSOLE_URL`: URL to $CONSOLE (default: https://console.cloud.timescale.com)
+ - `TIGER_GATEWAY_URL`: URL to the $CONSOLE gateway (default: https://console.cloud.timescale.com/api)
+ - `TIGER_DOCS_MCP`: enable/disable docs MCP proxy (default: true)
+ - `TIGER_DOCS_MCP_URL`: URL to the $MCP_SHORT for $COMPANY docs (default: https://mcp.tigerdata.com/docs)
+ - `TIGER_SERVICE_ID`: ID for the $SERVICE_SHORT updated when you call $CLI_SHORT commands
+ - `TIGER_ANALYTICS`: enable or disable analytics (default: `true`)
+ - `TIGER_PASSWORD_STORAGE`: password storage method (keyring, pgpass, or none)
+ - `TIGER_DEBUG`: enable/disable debug logging (default: `false`)
+ - `TIGER_COLOR`: Set to `false` to disable colored output (default: `true`)
+
+
+- **Authentication parameters**
+
+ To authenticate without using the interactive login, either:
+ - Set the following parameters with your [client credentials][rest-api-credentials], then `login`:
+ ```shell
+ TIGER_PUBLIC_KEY= TIGER_SECRET_KEY= TIGER_PROJECT_ID=\
+ tiger auth login
+ ```
+ - Add your [client credentials][rest-api-credentials] to the `login` command:
+ ```shell
+ tiger auth login --public-key= --secret-key= --project-id=
+ ```
+
+[rest-api-reference]: /api/:currentVersion:/api-reference/
+[rest-api-credentials]: https://console.cloud.timescale.com/dashboard/settings
+[get-project-id]: /integrations/:currentVersion:/find-connection-details/#find-your-project-and-service-id
+[create-client-credentials]: /integrations/:currentVersion:/find-connection-details/#create-client-credentials
+[curl]: https://curl.se/
+[rest-api-credentials]: https://console.cloud.timescale.com/dashboard/settings
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/_partials/_devops-mcp-commands-cli.md b/_partials/_devops-mcp-commands-cli.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0f3ba5d10c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/_partials/_devops-mcp-commands-cli.md
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
+
+You can use the following $CLI_LONG commands to run $MCP_SHORT:
+
+Usage: `tiger mcp [subcommand] --`
+
+| Command | Subcommand | Description |
+|---------|--------------------|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
+| mcp | | Manage the $MCP_LONG |
+| | install `[client]` | Install and configure $MCP_SHORT for a specific client installed on your developer device.
Supported clients are: `claude-code`, `cursor`, `windsurf`, `codex`, `gemini/gemini-cli`, `vscode/code/vs-code`.
Flags: - `--no-backup`: do not back up the existing configuration
- `--config-path`: open the configuration file at a specific location
|
+| | start | Start the $MCP_SHORT. This is the same as `tiger mcp start stdio` |
+| | start stdio | Start the $MCP_SHORT with stdio transport |
+| | start http | Start the $MCP_SHORT with HTTP transport. This option is for users who wish to access $MCP_LONG without using stdio. For example, your AI Assistant does not support stdio, or you do not want to run $CLI_SHORT on your device.
Flags are: - `--port `: the default is `8000`
- `--host `: the default is `localhost`
|
+
diff --git a/_partials/_devops-mcp-commands.md b/_partials/_devops-mcp-commands.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0b91f74756
--- /dev/null
+++ b/_partials/_devops-mcp-commands.md
@@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
+
+$MCP_LONG exposes the following MCP tools to your AI Assistant:
+
+| Command | Parameter | Required | Description |
+|--------------------------|---------------------|----------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
+| `service_list` | - | - | Returns a list of the $SERVICE_SHORTs in the current $PROJECT_SHORT. |
+| `service_get` | - | - | Returns detailed information about a $SERVICE_SHORT. |
+| | `service_id` | ✓ | The unique identifier of the $SERVICE_SHORT (10-character alphanumeric string). |
+| | `with_password` | - | Set to `true` to include the password in the response and connection string.
**WARNING**: never do this unless the user explicitly requests the password. |
+| `service_create` | - | - | Create a new $SERVICE_SHORT in $CLOUD_LONG.
**WARNING**: creates billable resources. |
+| | `name` | - | Set the human-readable name of up to 128 characters for this $SERVICE_SHORT. |
+| | `addons` | - | Set the array of [addons][create-service] to enable for the $SERVICE_SHORT. Options: - `time-series`: enables $TIMESCALE_DB
- `ai`: enables the AI and vector extensions
Set an empty array for $PG-only. |
+| | `region` | - | Set the [AWS region][cloud-regions] to deploy this $SERVICE_SHORT in. |
+| | `cpu_memory` | - | CPU and memory allocation combination.
Available configurations are: - shared/shared
- 0.5 CPU/2 GB
- 1 CPU/4 GB
- 2 CPU/8 GB
- 4 CPU/16 GB
- 8 CPU/32 GB
- 16 CPU/64 GB
- 32 CPU/128 GB
|
+| | `replicas` | - | Set the number of [high-availability replicas][readreplica] for fault tolerance. |
+| | `wait` | - | Set to `true` to wait for $SERVICE_SHORT to be fully ready before returning. |
+| | `timeout_minutes` | - | Set the timeout in minutes to wait for $SERVICE_SHORT to be ready. Only used when `wait=true`. Default: 30 minutes |
+| | `set_default` | - | By default, the new $SERVICE_SHORT is the default for following commands in $CLI_SHORT. Set to `false` to keep the previous $SERVICE_SHORT as the default. |
+| | `with_password` | - | Set to `true` to include the password for this $SERVICE_SHORT in response and connection string.
**WARNING**: never set to `true` unless user explicitly requests the password. |
+| `service_update_password` | - | - | Update the password for the `tsdbadmin` for this $SERVICE_SHORT. The password change takes effect immediately and may terminate existing connections. |
+| | `service_id` | ✓ | The unique identifier of the $SERVICE_SHORT you want to update the password for. |
+| | `password` | ✓ | The new password for the `tsdbadmin` user. |
+| `db_execute_query` | - | - | Execute a single SQL query against a $SERVICE_SHORT. This command returns column metadata, result rows, affected row count, and execution time. Multi-statement queries are not supported.
**WARNING**: can execute destructive SQL including INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, and DDL commands. |
+| | `service_id` | ✓ | The unique identifier of the $SERVICE_SHORT. Use `tiger_service_list` to find $SERVICE_SHORT IDs. |
+| | `query` | ✓ | The SQL query to execute. Single statement queries are supported. |
+| | `parameters` | - | Query parameters for parameterized queries. Values are substituted for the `$n` placeholders in the query. |
+| | `timeout_seconds` | - | The query timeout in seconds. Default: `30`. |
+| | `role` | - | The $SERVICE_SHORT role/username to connect as. Default: `tsdbadmin`. |
+| | `pooled` | - | Use [connection pooling][Connection pooling]. This is only available if you have already enabled it for the $SERVICE_SHORT. Default: `false`. |
+
+[cloud-regions]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/regions/
+[create-service]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/services/
+[readreplica]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/ha-replicas/read-scaling/
+[Connection pooling]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/services/connection-pooling/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/_partials/_devops-rest-api-get-started.md b/_partials/_devops-rest-api-get-started.md
index fdf27c3062..b62390fdc5 100644
--- a/_partials/_devops-rest-api-get-started.md
+++ b/_partials/_devops-rest-api-get-started.md
@@ -21,13 +21,13 @@ proper authentication headers.
1. **Set up API credentials**
- 1. In $CONSOLE, copy your [project ID][get-project-id] and store it securely using an environment variable:
+ 1. In $CONSOLE [copy your project ID][get-project-id] and store it securely using an environment variable:
```bash
export TIGERDATA_PROJECT_ID="your-project-id"
```
- 1. [Create your client credentials][create-client-credentials] and store them securely using environment variables:
+ 1. In $CONSOLE [create your client credentials][create-client-credentials] and store them securely using environment variables:
```bash
export TIGERDATA_ACCESS_KEY="Public key"
@@ -58,12 +58,12 @@ proper authentication headers.
- One or more $SERVICE_SHORTs:
```terminaloutput
- [{"service_id":"a59clooxoe","project_id":"c8nmagk8zh","name":"events",
- "region_code":"eu-central-1","service_type":"TIMESCALEDB",
- "created":"2025-09-09T08:37:15.816443Z","paused":false,"status":"READY",
- "resources":[{"id":"101228","spec":{"cpu_millis":500,"memory_gbs":2,"volume_type":""}}],
- "metadata":{"environment":"DEV"},"endpoint":{"host":"oh.yeah.tsdb.cloud.timescale.com",
- "port":12345}}]
+ [{"service_id":"tgrservice","project_id":"tgrproject","name":"tiger-eon",
+ "region_code":"us-east-1","service_type":"TIMESCALEDB",
+ "created":"2025-10-20T12:21:28.216172Z","paused":false,"status":"READY",
+ "resources":[{"id":"104977","spec":{"cpu_millis":500,"memory_gbs":2,"volume_type":""}}],
+ "metadata":{"environment":"DEV"},
+ "endpoint":{"host":"tgrservice.tgrproject.tsdb.cloud.timescale.com","port":11111}}]
```
@@ -81,31 +81,29 @@ Create a new $SERVICE_SHORT using the $REST_LONG:
-u "${TIGERDATA_ACCESS_KEY}:${TIGERDATA_SECRET_KEY}" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
- "name": "my-first-service",
- "service_type": "TIMESCALEDB",
- "region_code": "us-east-1",
- "replica_count": 1,
- "cpu_millis": 1000,
- "memory_gbs": 4
- }'
+ "name": "my-first-service",
+ "addons": ["time-series"],
+ "region_code": "us-east-1",
+ "replica_count": 1,
+ "cpu_millis": "1000",
+ "memory_gbs": "4"
+ }'
```
$CLOUD_LONG creates a Development environment for you. That is, no delete protection, high-availability, spooling or
read replication. You see something like:
```terminaloutput
- {
- "service_id":"asdfasdfasdf","project_id":"asdasdfasf","name":"my-first-service",
- "region_code":"us-east-1", "service_type":"TIMESCALEDB",
- "created":"2025-09-09T09:24:31.997767396Z", "paused":false,"status":"READY",
- "resources":[{"id":"101240",
- "spec":{"cpu_millis":1000,"memory_gbs":4,"volume_type":""}}],
- "metadata":{"environment":"PROD"},
- "endpoint":{"host":"oh.yeah.tsdb.cloud.timescale.com","port":123435},
- "initial_password":"very-secret",
- "ha_replicas":{"sync_replica_count":0,"replica_count":1}
- }
+ {"service_id":"tgrservice","project_id":"tgrproject","name":"my-first-service",
+ "region_code":"us-east-1","service_type":"TIMESCALEDB",
+ "created":"2025-10-20T22:29:33.052075713Z","paused":false,"status":"QUEUED",
+ "resources":[{"id":"105120","spec":{"cpu_millis":1000,"memory_gbs":4,"volume_type":""}}],
+ "metadata":{"environment":"PROD"},
+ "endpoint":{"host":"tgrservice.tgrproject.tsdb.cloud.timescale.com","port":00001},
+ "initial_password":"notTellingYou",
+ "ha_replicas":{"sync_replica_count":0,"replica_count":1}}
```
-1. **Save `service_id` from the response to a variable**
+1. Save `service_id` from the response to a variable:
+
```bash
# Extract service_id from the JSON response
export SERVICE_ID="service_id-from-response"
@@ -118,13 +116,15 @@ Create a new $SERVICE_SHORT using the $REST_LONG:
-u "${TIGERDATA_ACCESS_KEY}:${TIGERDATA_SECRET_KEY}" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json"
```
- You see something like:
+You see something like:
```terminaloutput
- {"service_id":"tgrservice","project_id":"tgrproject","name":"my-first-service","region_code":"us-east-1",
- "service_type":"TIMESCALEDB","created":"2025-09-30T12:08:54.438785Z","paused":false,"status":"READY",
- "resources":[{"id":"102879","spec":{"cpu_millis":1000,"memory_gbs":4,"volume_type":""}}],
- "metadata":{"environment":"DEV"},"endpoint":{"host":"ohhhh.yeahhhhh.tsdb.cloud.timescale.com","port":33867},
- "ha_replicas":{"sync_replica_count":0,"replica_count":1}}
+ {"service_id":"tgrservice","project_id":"tgrproject","name":"my-first-service",
+ "region_code":"us-east-1","service_type":"TIMESCALEDB",
+ "created":"2025-10-20T22:29:33.052075Z","paused":false,"status":"READY",
+ "resources":[{"id":"105120","spec":{"cpu_millis":1000,"memory_gbs":4,"volume_type":""}}],
+ "metadata":{"environment":"DEV"},
+ "endpoint":{"host":"tgrservice.tgrproject.tsdb.cloud.timescale.com","port":11111},
+ "ha_replicas":{"sync_replica_count":0,"replica_count":1}}
```
@@ -150,6 +150,7 @@ Follow these security guidelines when working with the $REST_LONG:
- Implement proper backup and recovery procedures for created services
- Follow data residency requirements for your region
+
[rest-api-reference]: /api/:currentVersion:/api-reference/
[rest-api-credentials]: https://console.cloud.timescale.com/dashboard/settings
[get-project-id]: /integrations/:currentVersion:/find-connection-details/#find-your-project-and-service-id
diff --git a/ai/index.md b/ai/index.md
index 0f57113529..df59104433 100644
--- a/ai/index.md
+++ b/ai/index.md
@@ -1,51 +1,83 @@
---
-title: Power your AI apps with Postgres
-excerpt: TigerData pgai is a solution for building search, RAG, and AI agents with Postgres. Learn more about pgai and how to use it
+title: Integrate AI with Tiger Data
+excerpt: Build AI assistants with Tiger Data using pgvector, Tiger Eon, Tiger Agents, and MCP server for seamless data integration
products: [cloud, mst, self_hosted]
-keywords: [ai, vector, pgvector, pgvectorscale, pgai]
-tags: [ai, vector]
+keywords: [ai, vector, pgvector, pgvectorscale, pgai, tiger-eon, tiger-agents, mcp-server]
+tags: [ai, vector, agents, assistants]
---
+# Integrate AI with Tiger Data
-# Power your AI apps with pgai on $CLOUD_LONG
+You can build and deploy AI assistants that understand, analyze, and act on your organizational data using
+$COMPANY. Whether you're building semantic search applications, recommendation systems, or intelligent agents
+that answer complex business questions, $COMPANY provides the tools and infrastructure you need.
-pgai on $CLOUD_LONG is a cloud solution for building search, RAG, and AI agents with $PG. This suite of tools empowers you to deploy production AI applications with $PG as your vector database, storing both vector embeddings, relational data (for example, related metadata), and time-based data in the same database.
+$COMPANY's AI ecosystem combines $PG with advanced vector capabilities, intelligent agents, and seamless
+integrations. Your AI assistants can:
-
+- Access organizational knowledge from Slack, GitHub, Linear, and other data sources
+- Understand context using advanced vector search and embeddings across large datasets
+- Execute tasks, generate reports, and interact with your $SERVICE_LONGs through natural language
+- Scale reliably with enterprise-grade performance for concurrent conversations
-pgai on $CLOUD_LONG is comprised of three extensions: pgvector, pgvectorscale and pgai. pgvector provides the vector data type and HNSW search index. Pgvectorscale provides the StreamingDiskANN index to superpower embedding search and make vector queries performant. pgai allows you to easily call AI embedding and generation models from inside the database. All three extensions are installed in your $CLOUD_LONG instance by default.
+## $EON_LONG for complete organizational AI
+
+[$EON_LONG](/ai/:currentVersion:/tiger-eon/) automatically integrates $AGENTS_LONG with your organizational
+data. You can:
+
+- Get instant access to company knowledge from Slack, GitHub, and Linear
+- Process data in real-time as conversations and updates happen
+- Store data efficiently with time-series partitioning and compression
+- Deploy quickly with Docker and an interactive setup wizard
+
+Use $EON_SHORT when you want to unlock knowledge from your communication and development tools.
+
+## $AGENTS_LONG for enterprise Slack AI
+
+[$AGENTS_LONG](/ai/:currentVersion:/tiger-agents-for-work/) provides enterprise-grade Slack-native AI agents.
+You get:
+
+- Durable event handling with $PG-backed processing
+- Horizontal scalability across multiple $AGENTS_SHORT instances
+- Flexibility to choose AI models and customize prompts
+- Integration with specialized data sources through MCP servers
+- Complete observability and monitoring with Logfire
+
+Use $AGENTS_SHORT when you need reliable, customizable AI agents for high-volume conversations.
+
+## $MCP_SHORT for direct AI Assistant integration
+
+The [$MCP_LONG](/ai/:currentVersion:/mcp-server/) integrates directly with popular AI Assistants. You can:
+
+- Work with Claude Code, Cursor, VS Code, and other editors
+- Manage $SERVICE_SHORTs and optimize queries through natural language
+- Access comprehensive $COMPANY documentation during development
+- Use secure authentication and access control
+
+Use the $MCP_SHORT when you want to manage $COMPANY resources from your AI assistant.
-
-## pgvectorscale ❤️ pgvector
+## pgvectorscale and️ pgvector
+
[Pgvector](https://github.com/pgvector/pgvector) is a popular open source extension for vector storage and similarity search in $PG and [pgvectorscale](https://github.com/timescale/pgvectorscale) adds advanced indexing capabilities to pgvector. pgai on $CLOUD_LONG offers both extensions so you can use all the capabilities already available in pgvector (like HNSW and ivfflat indexes) and also make use of the StreamingDiskANN index in pgvectorscale to speed up vector search.
This makes it easy to migrate your existing pgvector deployment and take advantage of the additional performance features in pgvectorscale. You also have the flexibility to create different index types suited to your needs. See the [vector search indexing][vector-search-indexing] section for more information.
-## What are vector embeddings?
Embeddings offer a way to represent the semantic essence of data and to allow comparing data according to how closely related it is in terms of meaning. In the database context, this is extremely powerful: think of this as full-text search on steroids. Vector databases allow storing embeddings associated with data and then searching for embeddings that are similar to a given query.
-## Applications of vector embeddings
-
-There are many applications where vector embeddings can be useful.
-
-### Semantic search
-Transcend the limitations of traditional keyword-driven search methods by creating systems that understand the intent and contextual meaning of a query, thereby returning more relevant results. Semantic search doesn't just seek exact word matches; it grasps the deeper intent behind a user's query. The result? Even if search terms differ in phrasing, relevant results are surfaced. Taking advantage of hybrid search, which marries lexical and semantic search methodologies, offers users a search experience that's both rich and accurate. It's not just about finding direct matches anymore; it's about tapping into contextually and conceptually similar content to meet user needs.
+- Semantic search: transcend the limitations of traditional keyword-driven search methods by creating systems that understand the intent and contextual meaning of a query, thereby returning more relevant results. Semantic search doesn't just seek exact word matches; it grasps the deeper intent behind a user's query. The result? Even if search terms differ in phrasing, relevant results are surfaced. Taking advantage of hybrid search, which marries lexical and semantic search methodologies, offers users a search experience that's both rich and accurate. It's not just about finding direct matches anymore; it's about tapping into contextually and conceptually similar content to meet user needs.
-### Recommendation systems
-Imagine a user who has shown interest in several articles on a singular topic. With embeddings, the recommendation engine can delve deep into the semantic essence of those articles, surfacing other database items that resonate with the same theme. Recommendations, thus, move beyond just the superficial layers like tags or categories and dive into the very heart of the content.
+- Recommendation systems: imagine a user who has shown interest in several articles on a singular topic. With embeddings, the recommendation engine can delve deep into the semantic essence of those articles, surfacing other database items that resonate with the same theme. Recommendations, thus, move beyond just the superficial layers like tags or categories and dive into the very heart of the content.
-### Retrieval augmented generation (RAG)
-Supercharge generative AI by providing additional context to Large Language Models (LLMs) like OpenAI's GPT-4, Anthropic's Claude 2, and open source modes like Llama 2. When a user poses a query, relevant database content is fetched and used to supplement the query as additional information for the LLM. This helps reduce LLM hallucinations, as it ensures the model's output is more grounded in specific and relevant information, even if it wasn't part of the model's original training data.
+- Retrieval augmented generation (RAG): supercharge generative AI by providing additional context to Large Language Models (LLMs) like OpenAI's GPT-4, Anthropic's Claude 2, and open source modes like Llama 2. When a user poses a query, relevant database content is fetched and used to supplement the query as additional information for the LLM. This helps reduce LLM hallucinations, as it ensures the model's output is more grounded in specific and relevant information, even if it wasn't part of the model's original training data.
-### Clustering
-Embeddings also offer a robust solution for clustering data. Transforming data into these vectorized forms allows for nuanced comparisons between data points in a high-dimensional space. Through algorithms like K-means or hierarchical clustering, data can be categorized into semantic categories, offering insights that surface-level attributes might miss. This surfaces inherent data patterns, enriching both exploration and decision-making processes.
+- Clustering: embeddings also offer a robust solution for clustering data. Transforming data into these vectorized forms allows for nuanced comparisons between data points in a high-dimensional space. Through algorithms like K-means or hierarchical clustering, data can be categorized into semantic categories, offering insights that surface-level attributes might miss. This surfaces inherent data patterns, enriching both exploration and decision-making processes.
-## Vector similarity search: How does it work
+### Vector similarity search: How does it work
On a high level, embeddings help a database to look for data that is similar to a given piece of information (similarity search). This process includes a few steps:
@@ -56,7 +88,7 @@ On a high level, embeddings help a database to look for data that is similar to
Under the hood, embeddings are represented as a vector (a list of numbers) that capture the essence of the data. To determine the similarity of two pieces of data, the database uses mathematical operations on vectors to get a distance measure (commonly Euclidean or cosine distance). During a search, the database should return those stored items where the distance between the query embedding and the stored embedding is as small as possible, suggesting the items are most similar.
-## Embedding models
+### Embedding models
pgai on $CLOUD_LONG works with the most popular embedding models that have output vectors of 2,000 dimensions or less.:
diff --git a/ai/mcp-server.md b/ai/mcp-server.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..13228c8f33
--- /dev/null
+++ b/ai/mcp-server.md
@@ -0,0 +1,233 @@
+---
+title: Integrate Tiger Cloud with your AI Assistant
+excerpt: Manage your services and optimize your schema and queries using your AI Assistant
+products: [cloud, self_hosted]
+keywords: [ai, mcp, server, security]
+tags: [ai]
+---
+
+import RESTPrereqs from "versionContent/_partials/_prereqs-cloud-account-only.mdx";
+import CLIINSTALL from "versionContent/_partials/_devops-cli-install.mdx";
+import MCPCOMMANDS from "versionContent/_partials/_devops-mcp-commands.mdx";
+import MCPCOMMANDSCLI from "versionContent/_partials/_devops-mcp-commands-cli.mdx";
+import GLOBALFLAGS from "versionContent/_partials/_devops-cli-global-flags.mdx";
+
+
+# Integrate Tiger Cloud with your AI Assistant
+
+The $MCP_LONG provides access to your $CLOUD_LONG resources through Claude and other AI Assistants. $MCP_SHORT
+mirrors the functionality of $CLI_LONG and is integrated directly into the $CLI_SHORT binary. You manage your
+$CLOUD_LONG resources using natural language from your AI Assistant. As $MCP_SHORT is integrated with the
+$COMPANY documentation, ask any question and you will get the best answer.
+
+This page shows you how to install $CLI_LONG and set up secure authentication for $MCP_SHORT, then manage the
+resources in your $ACCOUNT_LONG through the $MCP_LONG using your AI Assistant.
+
+## Prerequisites
+
+
+
+* An AI Assistant installed on your developer device with an active API key
+
+ The following AI Assistants are automatically configured by the $MCP_LONG: `claude-code`, `cursor`, `windsurf`, `codex`, `gemini/gemini-cli`, `vscode/code/vs-code`
+ You can also [manually configure][manual-config] $MCP_SHORT.
+
+## Install and configure $MCP_SHORT
+
+The $MCP_SHORT is bundled with $CLI_LONG:
+
+
+
+
+
+1. **Configure your AI Assistant to interact with the $PROJECT_SHORT and $SERVICE_SHORTs in your $ACCOUNT_LONG**
+
+ For example:
+ ```shell
+ tiger mcp install
+ ```
+
+1. **Choose the client to integrate with, then press `Enter` **
+
+ ```shell
+ Select an MCP client to configure:
+
+ > 1. Claude Code
+ 2. Codex
+ 3. Cursor
+ 4. Gemini CLI
+ 5. VS Code
+ 6. Windsurf
+
+ Use ↑/↓ arrows or number keys to navigate, enter to select, q to quit
+ ```
+
+
+
+And that is it, you are ready to use the $MCP_LONG to manage your $SERVICE_SHORTs in $CLOUD_LONG.
+
+## Manage the resources in your $ACCOUNT_LONG through your AI Assistant
+
+Your AI Assistant is connected to your $ACCOUNT_LONG and the $COMPANY documentation, you can now use it to
+manage your $SERVICE_SHORTs and learn more about how to implement $CLOUD_LONG features. For example:
+
+
+
+1. **Run your AI Assistant**
+ ```shell
+ claude
+ ```
+ Claude automatically runs the $MCP_SHORT server that enables you to interact with $CLOUD_LONG from your
+ AI Assistant.
+
+1. **Check your $MCP_LONG configuration**
+ ```shell
+ > is the tigerdata mcp server active for you?
+ ```
+ You see something like:
+ ```shell
+ MCP server is active. I can see the following Tiger Data-related tools available:
+
+ - mcp__tiger__get_guide - Retrieve TimescaleDB guides and best practices
+ - mcp__tiger__semantic_search_postgres_docs - Search PostgreSQL documentation
+ - mcp__tiger__semantic_search_tiger_docs - Search Tiger Cloud and TimescaleDB documentation
+ - mcp__tiger__tiger_service_create - Create new database services
+ - mcp__tiger__tiger_service_list - List all database services
+ - mcp__tiger__tiger_service_show - Show detailed service information
+ - mcp__tiger__tiger_service_update_password - Update service passwords
+
+ Is there something specific you'd like to do with the Tiger Data MCP server?
+ ```
+
+1. **Ask a basic question about your $SERVICE_SHORTs**
+ ```shell
+ > can you list my active services please
+ ```
+ You see something like:
+ ```shell
+ ⏺ You have 3 active services, all with the same name "my-first-service":
+
+ 1. tgrservice1 - READY - TimescaleDB - us-east-1 - 1 CPU/4GB - Created: 2025-09-30
+ 2. tgrservice1 - READY - TimescaleDB - us-east-1 - 1 CPU/4GB - Created: 2025-09-30
+ 3. tgrservice1 - READY - TimescaleDB - us-east-1 - 1 CPU/4GB - Created: 2025-09-30
+ ```
+
+1. **Manage your $SERVICE_SHORTs without having to learn how to**
+
+ For example:
+ ```shell
+ Can you create a new ai service called bob with a replica for me please
+ ```
+ You see something like:
+ ```shell
+ tiger - Create Database Service (MCP)(name: "bob", addons: ["ai"], replicas: 1, wait: false)
+ ```
+
+1. **Find best practice for things you need to do**
+
+ For example:
+ ```shell
+ > I need to migrate a database with 25 million rows of data to Tiger Cloud,
+ please tell me what service optimizations i should do before migration.
+
+ ```
+
+ You see something like:
+
+ ```shell
+ ⏺ For migrating a database with 25 million rows to Tiger Cloud, here are the key service optimizations to do before migration:
+
+ Pre-Migration Service Optimizations
+
+ 1. Right-size your compute resources:
+ - For 25M rows, start with at least 2 CPU/8GB or 4 CPU/16GB
+ - You can scale up during migration if needed, then scale down after
+
+ 2. Enable the appropriate addons:
+ - Use time-series addon if you are working with time-series data
+ - Use ai addon if you need vector/AI capabilities
+
+ 3. Choose optimal region:
+ - Select the region closest to your current database to minimize network transfer time
+ - This significantly reduces migration duration
+
+ 4. Consider enhanced storage (Enterprise only):
+ - If you expect high write throughput during migration, enhanced storage provides better IOPS (up to 32,000)
+
+ 5. Skip replicas initially:
+ - Start with 0 replicas during migration
+ - Add replicas after migration completes to avoid duplicate data copying
+
+ 6. Plan for storage space:
+ - Estimate your uncompressed data size
+ - Allocate sufficient high-performance storage (scales automatically but good to plan)
+ - You can enable tiered storage later for older data
+
+ During Migration Best Practices
+
+ Migration method selection:
+ - 25M rows: Use schema-then-data migration (migrate schema first, then copy data in chunks)
+ - Allows restart if a copy operation fails
+ - Better for databases >10GB
+
+ Database configuration to set AFTER migration:
+ - Set up compression policies (once data is loaded)
+ - Configure retention policies
+ - Create continuous aggregates
+ - Enable tiered storage for cost optimization
+
+ Connection settings:
+ - Use the pooled connection endpoint for better performance during bulk inserts
+ - Disable unnecessary constraints/indexes during migration, re-enable after
+
+ Would you like me to help you create an optimized service for this migration?
+ ```
+
+
+
+That beats working. Let the $MCP_SHORT do it all for you.
+
+## Manually configure the $MCP_SHORT
+
+If your MCP client is not supported by `tiger mcp install`. follow the client's instructions to install
+MCP servers. For example, many clients use a JSON file like the following that use `tiger mcp start` to
+start $MCP_LONG:
+
+```json
+{
+ "mcpServers": {
+ "tiger": {
+ "command": "tiger",
+ "args": [
+ "mcp",
+ "start"
+ ]
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+## $MCP_LONG commands
+
+
+
+## $CLI_LONG commands for $MCP_SHORT
+
+
+
+## Global flags
+
+You can use the following $CLI_LONG global flags when you run the $MCP_SHORT:
+
+
+
+
+[rest-api-reference]: /api/:currentVersion:/api-reference/
+[rest-api-credentials]: https://console.cloud.timescale.com/dashboard/settings
+[get-project-id]: /integrations/:currentVersion:/find-connection-details/#find-your-project-and-service-id
+[create-client-credentials]: /integrations/:currentVersion:/find-connection-details/#create-client-credentials
+[curl]: https://curl.se/
+[cloud-regions]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/regions/
+[readreplica]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/ha-replicas/read-scaling/
+[manual-config]: /ai/:currentVersion:/mcp-server/#manually-configure-the-tiger-mcp-server
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/ai/page-index/page-index.js b/ai/page-index/page-index.js
index 4bc352130d..b3735bbc4d 100644
--- a/ai/page-index/page-index.js
+++ b/ai/page-index/page-index.js
@@ -1,13 +1,18 @@
module.exports = [
{
- title: "AI and Vector",
+ title: "Integrate AI with Tiger Data",
href: "ai",
filePath: "index.md",
pageComponents: ["featured-cards"],
excerpt:
- "Information about pgai on TigerData and how to use it.",
+ "Integrate AI with your Tiger Data products",
children: [
{
+ title: "Integrate Tiger Cloud with your AI Assistant",
+ href: "mcp-server",
+ excerpt: "Manage your services and optimize your schema and queries with your AI Assistant",
+ },
+ {
title: "Aggregate organizational data with AI agents",
href: "tiger-eon",
excerpt: "Unify company knowledge with slack-native AI agents",
diff --git a/api/api-reference.md b/api/api-reference.md
index d682b84a4d..de6baf5b27 100644
--- a/api/api-reference.md
+++ b/api/api-reference.md
@@ -32,12 +32,14 @@ curl -X GET "https://console.cloud.timescale.com/public/api/v1/projects/{project
## Service Management
-You use this endpoint to create and manage the following Tiger Postgres services:
+You use this endpoint to create a Tiger Cloud service with one of more of the following addons:
-- `TIMESCALEDB`: a Tiger Postgres instance optimized for real-time analytics service For time-stamped data like events,
- prices, metrics, sensor readings, or any information that changes over time
-- `POSTGRES`: a vanilla Postgres instance
-- `VECTOR`: a Tiger Postgres instance with vector extensions
+- `time-series`: a Tiger Cloud service optimized for real-time analytics. For time-stamped data like events,
+ prices, metrics, sensor readings, or any information that changes over time.
+- `ai`: a Tiger Cloud service instance with vector extensions.
+
+To have multiple addons when you create a new service, set `"addons": ["time-series", "ai"]`. To create a
+vanilla Postgres instance, set `addons` to an empty list `[]`.
### List All Services
@@ -83,13 +85,13 @@ Retrieve all services within a project.
POST /projects/{project_id}/services
```
-Create a new Tiger Postgres service. This is an asynchronous operation.
+Create a new Tiger Cloud service. This is an asynchronous operation.
**Request Body:**
```json
{
"name": "test-2",
- "service_type": "TIMESCALEDB",
+ "addons": ["time-series"],
"region_code": "eu-central-1",
"cpu_millis": 1000,
"memory_gbs": 4
@@ -129,10 +131,10 @@ Create a new Tiger Postgres service. This is an asynchronous operation.
```
**Service Types:**
-- `TIMESCALEDB`: a Tiger Postgres instance optimized for real-time analytics service For time-stamped data like events,
+- `TIMESCALEDB`: a Tiger Cloud service instance optimized for real-time analytics service For time-stamped data like events,
prices, metrics, sensor readings, or any information that changes over time
- `POSTGRES`: a vanilla Postgres instance
-- `VECTOR`: a Tiger Postgres instance with vector extensions
+- `VECTOR`: a Tiger Cloud service instance with vector extensions
### Get a Service
@@ -304,6 +306,7 @@ Deactivate the connection pooler for a service.
{
"message": "Connection pooler disabled successfully"
}
+```
### Fork a Service
diff --git a/api/glossary.md b/api/glossary.md
index e3c3be4d29..1faadb53f1 100644
--- a/api/glossary.md
+++ b/api/glossary.md
@@ -163,6 +163,8 @@ This glossary defines technical terms, concepts, and terminology used in $COMPAN
**Euclidean distance**: a measure of the straight-line distance between two points in multidimensional space.
+**Exactly-once**: a message is delivered and processed precisely once. There is no loss and no duplicates.
+
**Explain**: a $PG command that shows the execution plan for a query, useful for performance analysis.
**Event sourcing**: an architectural pattern storing all changes as a sequence of events, naturally fitting time-series database capabilities.
diff --git a/getting-started/get-started-devops-as-code.md b/getting-started/get-started-devops-as-code.md
index 1258de6b64..33e82b78a9 100644
--- a/getting-started/get-started-devops-as-code.md
+++ b/getting-started/get-started-devops-as-code.md
@@ -13,28 +13,25 @@ tags:
- authentication
---
-
import RESTGS from "versionContent/_partials/_devops-rest-api-get-started.mdx";
import CLIGS from "versionContent/_partials/_devops-cli-get-started.mdx";
-
# DevOps as code with $CLOUD_LONG
-$COMPANY supplies a clean, programmatic control layer for $CLOUD_LONG. This includes RESTful APIs, $CLI commands, and
-MCP commands that let humans, machines, and AI agents easily provision, configure, and manage $SERVICE_LONGs
-programmatically.
+$COMPANY supplies a clean, programmatic control layer for $CLOUD_LONG. This includes RESTful APIs and CLI commands
+that enable humans, machines, and AI agents easily provision, configure, and manage $SERVICE_LONG programmatically.
-
+
-
+
-
+
-
+
diff --git a/integrations/find-connection-details.md b/integrations/find-connection-details.md
index 1dca134090..95953aef44 100644
--- a/integrations/find-connection-details.md
+++ b/integrations/find-connection-details.md
@@ -37,7 +37,7 @@ Retrieve the connection details for your $SERVICE_LONG:
## Find your project and service ID
-To retrieve the connection details for your $CLOUD_LONG project and $SERVICE_LONG:
+To retrieve the connection details for your $PROJECT_LONG and $SERVICE_LONG:
@@ -78,6 +78,31 @@ such as Terraform or the [$CLOUD_LONG REST API][rest-api-reference]:
+## Create client credentials
+
+You use client credentials to obtain access tokens outside of the user context.
+
+To retrieve the connection details for your $CLOUD_LONG project for programmatic usage
+such as Terraform or the [$CLOUD_LONG REST API][rest-api-reference]:
+
+
+
+1. **Open the settings for your project**:
+
+ In [$CONSOLE][console-services], click your project name in the upper left corner, then click `Project settings`.
+
+1. **Create client credentials**:
+
+ 1. Click `Create credentials`, then copy `Public key` and `Secret key` locally.
+
+ 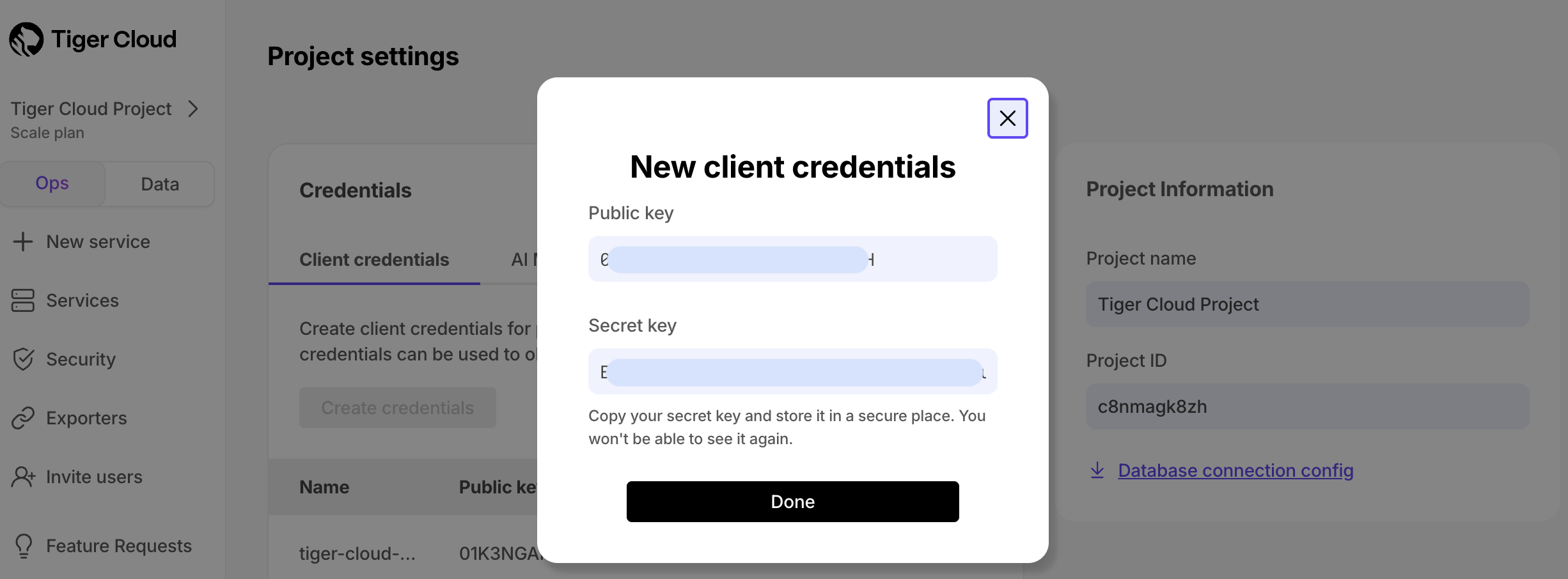
+
+ This is the only time you see the `Secret key`. After this, only the `Public key` is visible in this page.
+
+ 1. Click `Done`.
+
+
+