diff --git a/_partials/_devops-cli-install.md b/_partials/_devops-cli-install.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..06fd4b58ba
--- /dev/null
+++ b/_partials/_devops-cli-install.md
@@ -0,0 +1,114 @@
+1. ** Install $CLI_LONG**
+
+ Use the Terminal to install the $CLI_SHORT:
+
+
+
+
+ ```shell
+ curl -s https://packagecloud.io/install/repositories/timescale/tiger-cli/script.deb.sh | sudo os=any dist=any bash
+ sudo apt-get install tiger-cli
+ ```
+
+
+
+
+
+ ```shell
+ curl -s https://packagecloud.io/install/repositories/timescale/tiger-cli/script.deb.sh | sudo os=any dist=any bash
+ sudo apt-get install tiger-cli
+ ```
+
+
+
+
+ ```shell
+ curl -s https://packagecloud.io/install/repositories/timescale/tiger-cli/script.rpm.sh | sudo os=rpm_any dist=rpm_any bash
+ sudo yum install tiger-cli
+ ```
+
+
+
+
+
+ ```shell
+ curl -s https://packagecloud.io/install/repositories/timescale/tiger-cli/script.rpm.sh | sudo os=rpm_any dist=rpm_any bash
+ sudo yum install tiger-cli
+ ```
+
+
+
+
+
+ ```shell
+ brew install --cask timescale/tap/tiger-cli
+ ```
+
+
+
+
+
+ ```shell
+ curl -fsSL https://tiger-cli-releases.s3.amazonaws.com/install/install.sh | sh
+ ```
+
+
+
+
+
+1. **Set up API credentials**
+
+ 1. Log $CLI_LONG into your $ACCOUNT_LONG
+
+ ```shell
+ tiger auth login
+ ```
+ $CLI_LONG opens $CONSOLE_SHORT in your browser. Login, then click `Authorize`.
+
+ 1. Select a $PROJECT_LONG.
+
+ ```terminaloutput
+ Auth URL is: https://console.cloud.timescale.com/oauth/authorize?client_id=lotsOfURLstuff
+ Opening browser for authentication...
+ Select a project:
+
+ > 1. Tiger Project (tgrproject)
+ 2. YourCompany (Company wide project) (cpnproject)
+ 3. YourCompany Department (dptproject)
+
+ Use ↑/↓ arrows or number keys to navigate, enter to select, q to quit
+ ```
+ If only one $PROJECT_SHORT is associated with your $ACCOUNT_SHORT, this step is not shown.
+
+ Where possible, $CLI_LONG stores your authentication information in the system keychain/credential manager.
+ If that fails, the key is stored in `~/.config/tiger/api-key` with restricted file permissions (600).
+ $CLI_LONG stores your configuration in `~/.config/tiger/config.yaml`.
+
+1. **Test your authenticated connection to $CLOUD_LONG by listing services**
+
+ ```bash
+ tiger service list
+ ```
+
+ This call returns something like:
+ - No services:
+ ```terminaloutput
+ 🏜️ No services found! Your project is looking a bit empty.
+ 🚀 Ready to get started? Create your first service with: tiger service create
+ ```
+ - One or more services:
+
+ ```terminaloutput
+ ┌────────────┬─────────────────────┬────────┬─────────────┬──────────────┬──────────────────┐
+ │ SERVICE ID │ NAME │ STATUS │ TYPE │ REGION │ CREATED │
+ ├────────────┼─────────────────────┼────────┼─────────────┼──────────────┼──────────────────┤
+ │ tgrservice │ tiger-agent-service │ READY │ TIMESCALEDB │ eu-central-1 │ 2025-09-25 16:09 │
+ └────────────┴─────────────────────┴────────┴─────────────┴──────────────┴──────────────────┘
+ ```
+
+
+[rest-api-reference]: /api/:currentVersion:/api-reference/
+[rest-api-credentials]: https://console.cloud.timescale.com/dashboard/settings
+[get-project-id]: /integrations/:currentVersion:/find-connection-details/#find-your-project-and-service-id
+[create-client-credentials]: /integrations/:currentVersion:/find-connection-details/#create-client-credentials
+[curl]: https://curl.se/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/_partials/_devops-cli-service-forks.md b/_partials/_devops-cli-service-forks.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..bb43262477
--- /dev/null
+++ b/_partials/_devops-cli-service-forks.md
@@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
+import CLIINSTALL from "versionContent/_partials/_devops-cli-install.mdx";
+
+Modern development is highly iterative. Developers and AI agents need safe spaces to test changes before deploying them
+to production. Forkable $SERVICE_SHORTs make this natural and easy. Spin up a branch, run your test, throw it away, or
+merge it back.
+
+Forks are a powerful way to share production-scale data safely. BI and data science teams often need access to real
+datasets to build models or generate insights. With forkable $SERVICE_SHORTs, you easily create instant, zero-copy
+branches of a production $SERVICE_SHORT that is isolated from production, but contains all the data needed for
+analysis. You share this fork with your analytics teams in seconds. This dramatically reduces friction getting insights
+from live data.
+
+Forks are fully independent. You can query them, run migrations, add indexes, or test new features.
+
+To manage development forks:
+
+
+
+
+
+1. **Fork the $SERVICE_SHORT**
+
+ ```shell
+ tiger service fork tgrservice --now --no-wait --name bob
+ ```
+ You see something like:
+
+ ```terminaloutput
+ 🍴 Forking service 'tgrservice' to create 'bob' at current state...
+ ✅ Fork request accepted!
+ 📋 New Service ID: trgbobserv
+ 🔐 Password saved to system keyring for automatic authentication
+ 🎯 Set service 'trgbobserv' as default service.
+ ⏳ Service is being forked. Use 'tiger service list' to check status.
+ ┌───────────────────┬──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
+ │ PROPERTY │ VALUE │
+ ├───────────────────┼──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
+ │ Service ID │ trgbobserv │
+ │ Name │ bob │
+ │ Status │ │
+ │ Type │ TIMESCALEDB │
+ │ Region │ eu-central-1 │
+ │ CPU │ 0.5 cores (500m) │
+ │ Memory │ 2 GB │
+ │ Direct Endpoint │ ..tsdb.cloud.timescale.com: │
+ │ Created │ 2025-10-08 13:58:07 UTC │
+ │ Connection String │ postgresql://tsdbadmin@..tsdb.cloud.timescale.com:/tsdb?sslmode=require │
+ └───────────────────┴──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
+ ```
+
+1. **When you are done, delete your forked $SERVICE_SHORT**
+
+ 1. Use the CLI to request $SERVICE_SHORT delete:
+
+ ```shell
+ tiger service delete trgbobserv
+ ```
+ 1. Validate the $SERVICE_SHORT delete:
+
+ ```terminaloutput
+ Are you sure you want to delete service 'trgbobserv'? This operation cannot be undone.
+ Type the service ID 'trgbobserv' to confirm:
+ trgbobserv
+ ```
+ You see something like:
+ ```terminaloutput
+ 🗑️ Delete request accepted for service 'trgbobserv'.
+ ⏳ Waiting for service 'trgbobserv' to be deleted
+ ✅ Service 'trgbobserv' has been successfully deleted.
+ ```
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/use-timescale/backup-restore.md b/use-timescale/backup-restore.md
index c924306682..7e45c65efb 100644
--- a/use-timescale/backup-restore.md
+++ b/use-timescale/backup-restore.md
@@ -1,24 +1,31 @@
---
-title: Back up and recover your Tiger services
-excerpt: See how and when Tiger backs up your data, making sure you always have something to fall back on in case of disaster recovery
+title: Back up, fork, and recover services
+excerpt: Tiger Cloud backs up your data, making sure you always have something to fall back on for disaster recovery
products: [cloud]
keywords: [backups, restore]
tags: [recovery, failures]
---
-# Back up and recover your $SERVICE_SHORTs
+import CLIFORKS from "versionContent/_partials/_devops-cli-service-forks.mdx";
-$CLOUD_LONG automatically handles backup for your $SERVICE_LONGs using the `pgBackRest` tool. You don't need to perform backups manually. What's more, with [cross-region backup][cross-region], you are protected when an entire AWS region goes down.
+# Back up, fork, and recover $SERVICE_SHORT
-$CLOUD_LONG automatically creates one full backup every week, and
-incremental backups every day in the same region as your $SERVICE_SHORT.
+$CLOUD_LONG provides comprehensive backup and recovery solutions to protect your data, including automatic daily backups,
+cross-region protection, point-in-time recovery, and development forks for testing and collaboration.
-On [$SCALE and $PERFORMANCE][pricing-and-account-management] $PRICING_PLANs, you can check the list of backups for the previous 14 days in $CONSOLE_LONG. To do so, select your $SERVICE_SHORT, then click `Operations` > `Backup and restore` > `Backup history`.
+## Automatic backups
+
+$CLOUD_LONG automatically handles backup for your $SERVICE_LONGs using the `pgBackRest` tool. You don't need to perform
+backups manually. What's more, with [cross-region backup][cross-region], you are protected when an entire AWS region goes down.
-Additionally, all [Write-Ahead Log (WAL)][wal] files are retained back to the oldest full backup. This means that you always have a full backup available for the current and previous week:
+$CLOUD_LONG automatically creates one full backup every week, and incremental backups every day in the same region as
+your $SERVICE_SHORT. Additionally, all [Write-Ahead Log (WAL)][wal] files are retained back to the oldest full backup.
+This means that you always have a full backup available for the current and previous week:
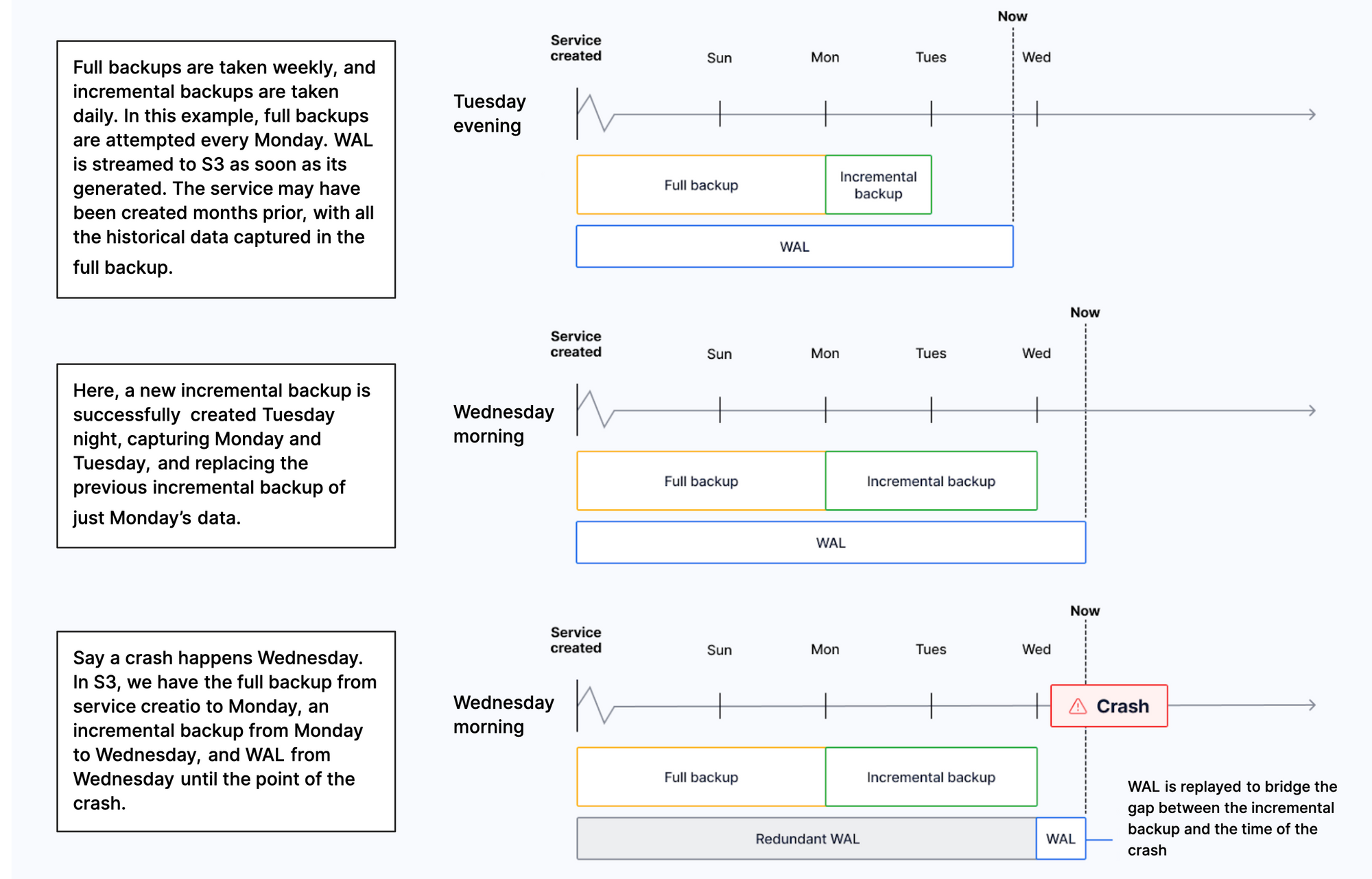
+On [$SCALE and $PERFORMANCE][pricing-and-account-management] $PRICING_PLANs, you can check the list of backups for the previous 14 days in $CONSOLE_LONG. To do so, select your $SERVICE_SHORT, then click `Operations` > `Backup and restore` > `Backup history`.
+
In the event of a storage failure, a $SERVICE_SHORT automatically recovers from a backup
to the point of failure. If the whole availability zone goes down, your $SERVICE_LONGs are recovered in a different zone. In the event of a user error, you can [create a point-in-time recovery fork][create-fork].
@@ -107,6 +114,11 @@ You initiate a point-in-time recovery from a same-region or cross-region backup
+## Create a development fork
+
+
+
+
[console]: https://console.cloud.timescale.com/dashboard/services
[ha-replicas]: /about/use-timescale/:currentVersion:/ha-replicas/
[pricing-and-account-management]: /about/:currentVersion:/pricing-and-account-management/
diff --git a/use-timescale/page-index/page-index.js b/use-timescale/page-index/page-index.js
index e35af9c4b1..8da68c44a3 100644
--- a/use-timescale/page-index/page-index.js
+++ b/use-timescale/page-index/page-index.js
@@ -156,6 +156,28 @@ module.exports = [
href: "service-management",
excerpt: "Tiger services operations, Service management tab",
},
+ {
+ title: "Service forks",
+ href: "forks",
+ excerpt: "Fork databases for testing, development, CI/CD, and disaster recovery",
+ children: [
+ {
+ title: "Quick start",
+ href: "quickstart",
+ excerpt: "Create your first fork with Console, CLI, or GitHub Actions",
+ },
+ {
+ title: "Strategies and limitations",
+ href: "performance",
+ excerpt: "Fork strategies, trade-offs, and important constraints",
+ },
+ {
+ title: "GitHub Actions integration",
+ href: "github-actions",
+ excerpt: "Automate fork creation in CI/CD workflows",
+ },
+ ],
+ },
{
title: "Manually change resources",
href: "change-resources",
@@ -601,7 +623,7 @@ module.exports = [
],
},
{
- title: "Back up and recover your services",
+ title: "Back up, fork, and recover services",
href: "backup-restore",
},
{
diff --git a/use-timescale/services/forks/github-actions.md b/use-timescale/services/forks/github-actions.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0578b88c07
--- /dev/null
+++ b/use-timescale/services/forks/github-actions.md
@@ -0,0 +1,124 @@
+---
+title: Forking with GitHub Actions
+excerpt: Automate database fork creation in CI/CD workflows for testing, pull request validation, and ephemeral environments
+products: [cloud]
+keywords: [forks, github actions, CI/CD, automation, testing]
+tags: [forks, github, ci/cd, devops, automation]
+---
+
+# Forking with GitHub Actions
+
+The [Tiger Data Fork Service action][github-action] enables you to automate database fork creation in your GitHub workflows. This is ideal for:
+
+- Testing pull requests against production-like data
+- Running integration tests on isolated database copies
+- Creating ephemeral test environments
+- Validating [migrations and upgrades][upgrades] before applying to production
+
+## Installation
+
+The action is available on the [GitHub Actions Marketplace][github-action]. Add it to your workflow YAML files to start forking databases as part of your CI/CD pipeline.
+
+## Example: Pull request testing with automatic cleanup
+
+This workflow demonstrates a common pattern: forking a database when a pull request is opened, running tests against the fork, and automatically cleaning up when the workflow completes.
+
+```yaml
+name: Test on Fork
+on: pull_request
+
+jobs:
+ test:
+ runs-on: ubuntu-latest
+ steps:
+ - uses: actions/checkout@v4
+
+ - name: Fork Database
+ id: fork
+ uses: timescale/fork-service@v1
+ with:
+ project_id: ${{ secrets.TIGERDATA_PROJECT_ID }}
+ service_id: ${{ secrets.TIGERDATA_SERVICE_ID }}
+ api_key: ${{ secrets.TIGERDATA_API_KEY }}
+ fork_strategy: last-snapshot
+ cleanup: true
+ name: pr-${{ github.event.pull_request.number }}
+
+ - name: Run Integration Tests
+ env:
+ DATABASE_URL: postgresql://tsdbadmin:${{ steps.fork.outputs.initial_password }}@${{ steps.fork.outputs.host }}:${{ steps.fork.outputs.port }}/tsdb?sslmode=require
+ run: |
+ npm install
+ npm test
+
+ - name: Run Migrations
+ env:
+ DATABASE_URL: postgresql://tsdbadmin:${{ steps.fork.outputs.initial_password }}@${{ steps.fork.outputs.host }}:${{ steps.fork.outputs.port }}/tsdb?sslmode=require
+ run: npm run migrate
+```
+
+## Key features
+
+### Automatic cleanup
+
+Set `cleanup: true` to automatically delete the forked service when the workflow completes. This prevents orphaned test databases and keeps costs down.
+
+For more control over cleanup timing, use the [Tiger Data Delete Service action][delete-action] to delete forks on your own schedule.
+
+### Fork strategies
+
+Choose the best strategy for your use case:
+
+- **`last-snapshot`**: Fastest option, uses the most recent automatic backup (ideal for CI/CD)
+- **`now`**: Creates a new snapshot before forking (most up-to-date data)
+- **`timestamp`**: Fork from a specific point in time (requires `target_time` parameter)
+
+See [Fork strategies, limitations, and trade-offs][strategies-and-limitations] for detailed guidance on when to use each option.
+
+### Connection outputs
+
+The action outputs all [connection details][connection-details] needed to connect to your fork:
+
+- `host`: Database hostname
+- `port`: Database port
+- `initial_password`: Initial password for the `tsdbadmin` user
+- `service_id`: The forked service ID
+- `name`: The forked service name
+
+Use these outputs with `steps..outputs.` to construct connection strings.
+
+## API key management
+
+Store your Tiger API key as a GitHub Actions secret:
+
+1. Navigate to your repository settings
+2. Go to `Secrets and variables` > `Actions`
+3. Create a new secret named `TIGERDATA_API_KEY`
+4. Set the value to your API key in format `publicKey:secretKey`
+
+
+
+Never commit API keys directly to your repository. Always use GitHub Actions secrets or other secure secret management solutions.
+
+
+
+## Complete reference
+
+For the full list of inputs, outputs, and configuration options, see the [Tiger Data Fork Service action on GitHub Marketplace][github-action].
+
+Additional GitHub Actions for Tiger Cloud:
+- [Tiger Data Delete Service][delete-action] - Delete services programmatically
+
+## Next steps
+
+- [Quick start guide][quickstart] - Get started with forking using other methods
+- [Fork strategies, limitations, and trade-offs][strategies-and-limitations] - Choosing the right strategy and understanding constraints
+- [Service Forks overview][forks-overview] - Complete guide to forking
+
+[github-action]: https://github.com/marketplace/actions/tiger-data-fork-service
+[delete-action]: https://github.com/marketplace/actions/tiger-data-delete-service
+[forks-overview]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/services/forks/
+[quickstart]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/services/forks/quickstart/
+[strategies-and-limitations]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/services/forks/strategies/
+[connection-details]: /integrations/:currentVersion:/find-connection-details/
+[upgrades]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/upgrades/
diff --git a/use-timescale/services/forks/index.md b/use-timescale/services/forks/index.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..a506a01ac2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/use-timescale/services/forks/index.md
@@ -0,0 +1,90 @@
+---
+title: Service Forks
+excerpt: Create isolated copies of your Tiger database for testing, development, CI/CD, and point-in-time recovery
+products: [cloud]
+keywords: [forks, development, testing, CI/CD, point-in-time recovery]
+tags: [forks, clone, copy, snapshot, branching]
+cloud_ui:
+ path:
+ - [services, :serviceId, operations, management]
+ - [create_services, fork, :serviceId]
+---
+
+# Service Forks
+
+Service Forks allow you to create isolated copies of your Tiger $SERVICE_SHORT for testing, development, CI/CD pipelines, and disaster recovery. A fork is an exact copy of your database at a specific point in time, with its own independent data and configuration.
+
+## What is a fork?
+
+A fork creates a complete copy of your $SERVICE_SHORT, including:
+- All database data and schema
+- Configuration settings (which can be customized during fork creation)
+- An independent `tsdbadmin` user with a new password
+
+Once created, a fork operates independently from its parent. Changes to the fork don't affect the parent $SERVICE_SHORT, and vice versa. Forks appear in your services dashboard with a label indicating their parent $SERVICE_SHORT.
+
+## Why fork a database?
+
+Common use cases for database forks include:
+
+- **Testing and development**:
+ - Create isolated development environments from production data to test schema migrations and application changes safely.
+ - Or share realistic datasets with your team without exposing production.
+
+- **CI/CD automation**:
+ - Spin up fresh database copies for each pull request using [GitHub Actions][github-action] and automatically clean up after workflows complete.
+ - Run integration tests against production-like data or test any migrations before applying them to production.
+
+- **Disaster recovery**:
+ - Recover from destructive operations (accidental deletes, bad migrations) by using [point-in-time recovery][backup-restore] forks.
+
+- **Major upgrades**:
+ - Test [PostgreSQL major version upgrades][upgrades] on a fork before applying to production.
+ - Estimate upgrade duration and identify potential issues.
+
+## Getting started
+
+Ready to create your first fork? See the [Quick start guide][quickstart] for step-by-step instructions using:
+- Console UI
+- Tiger CLI
+- GitHub Actions
+
+## Fork strategies and limitations
+
+Tiger Cloud offers three fork strategies (`now`, `last-snapshot`, and `timestamp`), each with different trade-offs for speed, data freshness, and use case fit. Understanding these strategies along with important limitations helps you make informed decisions.
+
+For detailed guidance on choosing strategies, storage architecture differences, tier restrictions, and cost considerations, see [Fork strategies, limitations, and trade-offs][performance].
+
+
+## Key limitations to know
+
+Before forking, be aware of these important constraints:
+
+- Services must have a status of `Running` or `Paused` (not `In progress`)
+- Fork passwords differ from the parent—[connection strings][connection-details] must be updated
+- Forks capture a point-in-time snapshot—ongoing parent writes are not included
+
+For complete details on limitations, tier restrictions, and resource constraints, see [Fork strategies, limitations, and trade-offs][performance].
+
+## Next steps
+
+- [Quick start guide][quickstart] - Create your first fork
+- [Fork strategies, limitations, and trade-offs][performance] - Choosing the right approach for your use case
+- [GitHub Actions integration][github-actions-guide] - Automate forks in CI/CD workflows
+- [Service management][service-management] - Managing forks after creation
+- [Backup and recovery][backup-restore] - Using forks for disaster recovery
+- [Data tiering with forks][tiered-forks] - Understanding zero-copy mechanics
+
+[quickstart]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/services/forks/quickstart/
+[tiger-cli]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/run-tiger-cloud-cli/
+[service-management-cli]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/services/service-management/#create-a-development-fork
+[service-management]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/services/service-management/
+[backup-restore]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/backup-restore/
+[pricing]: /about/:currentVersion:/pricing-and-account-management/
+[data-tiering]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/data-tiering/
+[tiered-forks]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/data-tiering/tiered-data-replicas-forks/
+[performance]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/services/forks/strategies/
+[github-actions-guide]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/services/forks/github-actions/
+[github-action]: https://github.com/marketplace/actions/tiger-data-fork-service
+[upgrades]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/upgrades/
+[connection-details]: /integrations/:currentVersion:/find-connection-details/
diff --git a/use-timescale/services/forks/quickstart.md b/use-timescale/services/forks/quickstart.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..672f35fff4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/use-timescale/services/forks/quickstart.md
@@ -0,0 +1,107 @@
+---
+title: Fork a database - Quick start
+excerpt: Get started quickly with Service forks using Console UI, CLI, GitHub Actions, or REST API
+products: [cloud]
+keywords: [forks, quickstart, getting started, tutorial]
+tags: [forks, quickstart, tutorial]
+---
+
+# Fork a database - Quick start
+
+This guide shows you how to create your first database fork using different methods. Choose the approach that best fits your workflow.
+
+## Fork from Console
+
+
+
+1. In $CONSOLE_LONG, from the `Services` list, click the name of the $SERVICE_SHORT you want to fork. The $SERVICE_SHORT must have a status of `Running` or `Paused`.
+1. Navigate to the `Operations` tab.
+1. In the `Service management` section, click `Fork service`.
+1. To customize your fork's resources or configuration, click `Advanced options`. You can set different compute and storage options, separate from your original $SERVICE_SHORT.
+1. Confirm by clicking `Fork service`.
+
+The forked $SERVICE_SHORT appears in the `Services` dashboard with a label indicating its parent. Provisioning typically takes a few minutes, but can vary based on your [storage architecture][performance].
+
+![]() +
+
+
+## Fork with CLI
+
+You can fork $SERVICE_SHORTs using the [Tiger CLI][tiger-cli]. For complete CLI documentation, see [Service management][service-management-cli].
+
+```bash
+tiger service fork
+```
+
+### Common CLI options
+
+```bash
+# Fork with a custom name
+tiger service fork --name my-test-fork --now
+
+# Fork with specific resources
+tiger service fork --cpu-millis 1000 --memory-gbs 4 --now
+
+# Fork to free tier with shared resources
+tiger service fork --cpu-millis shared --memory-gbs shared --now
+```
+
+## Fork with GitHub Actions
+
+Automate fork creation in your CI/CD workflows using the [Tiger Data Fork Service action][github-action].
+
+### Basic example
+
+```yaml
+- name: Fork Database
+ id: fork
+ uses: timescale/fork-service@v1
+ with:
+ project_id: ${{ secrets.TIGERDATA_PROJECT_ID }}
+ service_id: ${{ secrets.TIGERDATA_SERVICE_ID }}
+ api_key: ${{ secrets.TIGERDATA_API_KEY }}
+ fork_strategy: now
+ cleanup: true
+```
+
+See the [GitHub Actions integration guide][github-actions-guide] for complete examples and configuration options.
+
+## Choose your fork strategy
+
+When creating a fork, you'll need to choose a strategy:
+
+- **`last-snapshot`** - Fastest option, uses the most recent automatic backup (ideal for CI/CD)
+- **`now`** - Creates a new snapshot before forking (most up-to-date data)
+- **`timestamp`** - Fork from a specific point in time for disaster recovery
+
+For detailed guidance on when to use each strategy, trade-offs, and limitations, see [Fork strategies, limitations, and trade-offs][strategies-and-limitations].
+
+## What happens when you fork?
+
+When you create a fork:
+
+1. A new $SERVICE_SHORT is provisioned with the same configuration as the parent
+2. Data is restored to the fork at your chosen point in time
+3. The fork gets a new, independent `tsdbadmin` password
+4. The fork appears in your services dashboard with a label showing its parent
+
+The fork operates completely independently from its parent. Changes to one don't affect the other.
+
+## Next steps
+
+- [Fork strategies, limitations, and trade-offs][strategies-and-limitations] - Learn when to use each strategy and understand constraints
+- [GitHub Actions integration][github-actions-guide] - Set up automated forking in CI/CD
+- [Service Forks overview][forks-overview] - Complete guide to forking features
+
+[tiger-cli]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/run-tiger-cloud-cli/
+[service-management-cli]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/services/service-management/#create-a-development-fork
+[github-action]: https://github.com/marketplace/actions/tiger-data-fork-service
+[github-actions-guide]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/services/forks/github-actions/
+[strategies-and-limitations]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/services/forks/strategies/
+[forks-overview]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/services/forks/
diff --git a/use-timescale/services/forks/strategies.md b/use-timescale/services/forks/strategies.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..971e795d2c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/use-timescale/services/forks/strategies.md
@@ -0,0 +1,112 @@
+---
+title: Fork strategies, limitations, and trade-offs
+excerpt: Understanding fork strategies, storage architectures, and important limitations when forking databases
+products: [cloud]
+keywords: [forks, strategies, limitations, storage, copy-on-write, CoW]
+tags: [forks, strategies, limitations, tradeoffs]
+---
+
+# Fork strategies, limitations, and trade-offs
+
+When forking databases, understanding the available strategies and their trade-offs helps you choose the right approach for your use case while being aware of current limitations.
+
+## Fork strategies
+
+Tiger Cloud offers three fork strategies, each optimized for different scenarios:
+
+### `now` - Create fork at the current time
+
+Creates a fresh fork of your database at the current time.
+
+**Use when:**
+- You need the absolute latest data
+- Recent changes must be included in the fork
+
+### `last-snapshot` - Uses existing snapshot or backup
+
+Forks from the most recent automatic backup or snapshot. The frequency of these depends on your plan.
+
+**Use when:**
+- Pipelines where speed matters
+- Slightly behind current data is acceptable
+- You want the fastest possible fork creation
+
+### `timestamp` - Point-in-time recovery
+
+Forks from a specific point in time within your [retention period][pricing].
+
+**Use when:**
+- Disaster recovery from a known-good state
+- Investigating issues that occurred at a specific time
+- Testing "what-if" scenarios from historical data
+
+**Retention periods for point-in-time recovery:**
+- Free plan: 1 day
+- Scale plan: 3 days
+- Performance plan: 14 days
+- Enterprise plan: 14 days
+
+
+## Storage architecture differences
+
+Fork creation speed varies based on your underlying storage architecture.
+
+
+
+Tiger Data has developed a new Copy-on-Write storage architecture that is currently available on the free plan. We will slowly roll this out to paid plans but want to ensure absolute stability when we do so.
+
+
+### Copy-on-Write (CoW) storage
+
+- **Availability**: Free plan (rolling out to all paid plans)
+- **Fork speed**: ~30-90 seconds, independent of database size
+- **Mechanism**: Zero-copy storage level shared between forks and parent
+- **Billing**: Pay only for blocks that diverge from parent (or nothing currently on free plan)
+
+### Traditional storage
+
+- **Availability**: Current default for paid plans
+- **Fork speed**: Varies with database size (typically 5-20+ minutes)
+- **Mechanism**: Backup restore + WAL replay
+- **Billing**: Full database size billed immediately
+
+
+### Plan restrictions
+
+- **You cannot fork from paid plan to free plan**: Forks from Scale, Performance, or Enterprise plan services cannot target the free plan
+- Free plan services can fork to any plan
+
+## Service configuration
+
+- **By default, match parent resources**: Omit resource parameters to inherit parent's allocation
+- **Custom resources**: Specify `cpu_millis` and `memory_gbs` for dedicated resources (only on paid plans)
+- **Underpowered forks**: Small compute allocations may slow data-intensive operations (only on free plan)
+
+
+## Tiered storage billing
+
+If you use [data tiering][data-tiering], tiered data is shared across forks also on traditional storage:
+
+- Tiered chunks are only billed once, regardless of fork count
+- Only new or modified chunks in a fork incur additional costs
+
+For details, see [Replicas and forks with tiered data][tiered-forks].
+
+
+## Next steps
+
+- [Quick start guide][quickstart] - Create your first fork
+- [Service Forks overview][forks-overview] - Complete guide to forking
+- [GitHub Actions integration][github-actions] - Automate forking in CI/CD
+- [Backup and recovery][backup-restore] - Using forks for disaster recovery
+- [Data tiering with forks][tiered-forks] - Understanding shared storage mechanics
+
+[quickstart]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/services/forks/quickstart/
+[forks-overview]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/services/forks/
+[github-actions]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/services/forks/github-actions/
+[backup-restore]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/backup-restore/
+[data-tiering]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/data-tiering/
+[tiered-forks]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/data-tiering/tiered-data-replicas-forks/
+[pricing]: /about/:currentVersion:/pricing-and-account-management/
+[connection-details]: /integrations/:currentVersion:/find-connection-details/
+[upgrades]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/upgrades/
diff --git a/use-timescale/services/service-management.md b/use-timescale/services/service-management.md
index 98500bbfa4..0307c67e3a 100644
--- a/use-timescale/services/service-management.md
+++ b/use-timescale/services/service-management.md
@@ -10,6 +10,8 @@ cloud_ui:
- [create_services, fork, :serviceId]
---
+import CLIFORKS from "versionContent/_partials/_devops-cli-service-forks.mdx";
+
# $SERVICE_SHORT_CAP management
In the `Service management` section of the `Operations` dashboard, you can fork
@@ -46,8 +48,6 @@ data discrepancy between $SERVICE_SHORTs.
-### Forking a $SERVICE_SHORT
-
1. In $CONSOLE_LONG, from the `Services` list, ensure the $SERVICE_SHORT
you want to form has a status of `Running` or `Paused`, then click the name
of the $SERVICE_SHORT you want to fork.
@@ -72,7 +72,12 @@ alt="Fork a Tiger service"
-### Reset your $SERVICE_SHORT password
+## Create a development fork
+
+
+
+
+## Reset your $SERVICE_SHORT password
You can reset your $SERVICE_SHORT password from the `Operations` dashboard. This is the
password you use to connect to your $SERVICE_SHORT, not the password for $CONSOLE. To reset your $CONSOLE_SHORT password, navigate to the `Account` page.
@@ -86,14 +91,14 @@ digest algorithm 5) are cryptographic authentication mechanisms. $CONSOLE_LONG
uses SCRAM by default. It is more secure and strongly recommended. The MD5
option is provided for compatibility with older clients.
-### Pause a $SERVICE_SHORT
+## Pause a $SERVICE_SHORT
You can pause a $SERVICE_SHORT if you want to stop it running temporarily. When you
pause a $SERVICE_SHORT, you are no longer billed for compute resources. However, you do
need to continue paying for any storage you are using. Pausing a $SERVICE_SHORT ensures
that it is still available, and is ready to be restarted at any time.
-### Delete a $SERVICE_SHORT
+## Delete a $SERVICE_SHORT
You can delete a $SERVICE_SHORT to remove it completely. This removes the $SERVICE_SHORT
and its underlying data from the server. You cannot recover a deleted
+
+
+
+## Fork with CLI
+
+You can fork $SERVICE_SHORTs using the [Tiger CLI][tiger-cli]. For complete CLI documentation, see [Service management][service-management-cli].
+
+```bash
+tiger service fork
+```
+
+### Common CLI options
+
+```bash
+# Fork with a custom name
+tiger service fork --name my-test-fork --now
+
+# Fork with specific resources
+tiger service fork --cpu-millis 1000 --memory-gbs 4 --now
+
+# Fork to free tier with shared resources
+tiger service fork --cpu-millis shared --memory-gbs shared --now
+```
+
+## Fork with GitHub Actions
+
+Automate fork creation in your CI/CD workflows using the [Tiger Data Fork Service action][github-action].
+
+### Basic example
+
+```yaml
+- name: Fork Database
+ id: fork
+ uses: timescale/fork-service@v1
+ with:
+ project_id: ${{ secrets.TIGERDATA_PROJECT_ID }}
+ service_id: ${{ secrets.TIGERDATA_SERVICE_ID }}
+ api_key: ${{ secrets.TIGERDATA_API_KEY }}
+ fork_strategy: now
+ cleanup: true
+```
+
+See the [GitHub Actions integration guide][github-actions-guide] for complete examples and configuration options.
+
+## Choose your fork strategy
+
+When creating a fork, you'll need to choose a strategy:
+
+- **`last-snapshot`** - Fastest option, uses the most recent automatic backup (ideal for CI/CD)
+- **`now`** - Creates a new snapshot before forking (most up-to-date data)
+- **`timestamp`** - Fork from a specific point in time for disaster recovery
+
+For detailed guidance on when to use each strategy, trade-offs, and limitations, see [Fork strategies, limitations, and trade-offs][strategies-and-limitations].
+
+## What happens when you fork?
+
+When you create a fork:
+
+1. A new $SERVICE_SHORT is provisioned with the same configuration as the parent
+2. Data is restored to the fork at your chosen point in time
+3. The fork gets a new, independent `tsdbadmin` password
+4. The fork appears in your services dashboard with a label showing its parent
+
+The fork operates completely independently from its parent. Changes to one don't affect the other.
+
+## Next steps
+
+- [Fork strategies, limitations, and trade-offs][strategies-and-limitations] - Learn when to use each strategy and understand constraints
+- [GitHub Actions integration][github-actions-guide] - Set up automated forking in CI/CD
+- [Service Forks overview][forks-overview] - Complete guide to forking features
+
+[tiger-cli]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/run-tiger-cloud-cli/
+[service-management-cli]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/services/service-management/#create-a-development-fork
+[github-action]: https://github.com/marketplace/actions/tiger-data-fork-service
+[github-actions-guide]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/services/forks/github-actions/
+[strategies-and-limitations]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/services/forks/strategies/
+[forks-overview]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/services/forks/
diff --git a/use-timescale/services/forks/strategies.md b/use-timescale/services/forks/strategies.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..971e795d2c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/use-timescale/services/forks/strategies.md
@@ -0,0 +1,112 @@
+---
+title: Fork strategies, limitations, and trade-offs
+excerpt: Understanding fork strategies, storage architectures, and important limitations when forking databases
+products: [cloud]
+keywords: [forks, strategies, limitations, storage, copy-on-write, CoW]
+tags: [forks, strategies, limitations, tradeoffs]
+---
+
+# Fork strategies, limitations, and trade-offs
+
+When forking databases, understanding the available strategies and their trade-offs helps you choose the right approach for your use case while being aware of current limitations.
+
+## Fork strategies
+
+Tiger Cloud offers three fork strategies, each optimized for different scenarios:
+
+### `now` - Create fork at the current time
+
+Creates a fresh fork of your database at the current time.
+
+**Use when:**
+- You need the absolute latest data
+- Recent changes must be included in the fork
+
+### `last-snapshot` - Uses existing snapshot or backup
+
+Forks from the most recent automatic backup or snapshot. The frequency of these depends on your plan.
+
+**Use when:**
+- Pipelines where speed matters
+- Slightly behind current data is acceptable
+- You want the fastest possible fork creation
+
+### `timestamp` - Point-in-time recovery
+
+Forks from a specific point in time within your [retention period][pricing].
+
+**Use when:**
+- Disaster recovery from a known-good state
+- Investigating issues that occurred at a specific time
+- Testing "what-if" scenarios from historical data
+
+**Retention periods for point-in-time recovery:**
+- Free plan: 1 day
+- Scale plan: 3 days
+- Performance plan: 14 days
+- Enterprise plan: 14 days
+
+
+## Storage architecture differences
+
+Fork creation speed varies based on your underlying storage architecture.
+
+
+
+Tiger Data has developed a new Copy-on-Write storage architecture that is currently available on the free plan. We will slowly roll this out to paid plans but want to ensure absolute stability when we do so.
+
+
+### Copy-on-Write (CoW) storage
+
+- **Availability**: Free plan (rolling out to all paid plans)
+- **Fork speed**: ~30-90 seconds, independent of database size
+- **Mechanism**: Zero-copy storage level shared between forks and parent
+- **Billing**: Pay only for blocks that diverge from parent (or nothing currently on free plan)
+
+### Traditional storage
+
+- **Availability**: Current default for paid plans
+- **Fork speed**: Varies with database size (typically 5-20+ minutes)
+- **Mechanism**: Backup restore + WAL replay
+- **Billing**: Full database size billed immediately
+
+
+### Plan restrictions
+
+- **You cannot fork from paid plan to free plan**: Forks from Scale, Performance, or Enterprise plan services cannot target the free plan
+- Free plan services can fork to any plan
+
+## Service configuration
+
+- **By default, match parent resources**: Omit resource parameters to inherit parent's allocation
+- **Custom resources**: Specify `cpu_millis` and `memory_gbs` for dedicated resources (only on paid plans)
+- **Underpowered forks**: Small compute allocations may slow data-intensive operations (only on free plan)
+
+
+## Tiered storage billing
+
+If you use [data tiering][data-tiering], tiered data is shared across forks also on traditional storage:
+
+- Tiered chunks are only billed once, regardless of fork count
+- Only new or modified chunks in a fork incur additional costs
+
+For details, see [Replicas and forks with tiered data][tiered-forks].
+
+
+## Next steps
+
+- [Quick start guide][quickstart] - Create your first fork
+- [Service Forks overview][forks-overview] - Complete guide to forking
+- [GitHub Actions integration][github-actions] - Automate forking in CI/CD
+- [Backup and recovery][backup-restore] - Using forks for disaster recovery
+- [Data tiering with forks][tiered-forks] - Understanding shared storage mechanics
+
+[quickstart]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/services/forks/quickstart/
+[forks-overview]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/services/forks/
+[github-actions]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/services/forks/github-actions/
+[backup-restore]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/backup-restore/
+[data-tiering]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/data-tiering/
+[tiered-forks]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/data-tiering/tiered-data-replicas-forks/
+[pricing]: /about/:currentVersion:/pricing-and-account-management/
+[connection-details]: /integrations/:currentVersion:/find-connection-details/
+[upgrades]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/upgrades/
diff --git a/use-timescale/services/service-management.md b/use-timescale/services/service-management.md
index 98500bbfa4..0307c67e3a 100644
--- a/use-timescale/services/service-management.md
+++ b/use-timescale/services/service-management.md
@@ -10,6 +10,8 @@ cloud_ui:
- [create_services, fork, :serviceId]
---
+import CLIFORKS from "versionContent/_partials/_devops-cli-service-forks.mdx";
+
# $SERVICE_SHORT_CAP management
In the `Service management` section of the `Operations` dashboard, you can fork
@@ -46,8 +48,6 @@ data discrepancy between $SERVICE_SHORTs.
-### Forking a $SERVICE_SHORT
-
1. In $CONSOLE_LONG, from the `Services` list, ensure the $SERVICE_SHORT
you want to form has a status of `Running` or `Paused`, then click the name
of the $SERVICE_SHORT you want to fork.
@@ -72,7 +72,12 @@ alt="Fork a Tiger service"
-### Reset your $SERVICE_SHORT password
+## Create a development fork
+
+
+
+
+## Reset your $SERVICE_SHORT password
You can reset your $SERVICE_SHORT password from the `Operations` dashboard. This is the
password you use to connect to your $SERVICE_SHORT, not the password for $CONSOLE. To reset your $CONSOLE_SHORT password, navigate to the `Account` page.
@@ -86,14 +91,14 @@ digest algorithm 5) are cryptographic authentication mechanisms. $CONSOLE_LONG
uses SCRAM by default. It is more secure and strongly recommended. The MD5
option is provided for compatibility with older clients.
-### Pause a $SERVICE_SHORT
+## Pause a $SERVICE_SHORT
You can pause a $SERVICE_SHORT if you want to stop it running temporarily. When you
pause a $SERVICE_SHORT, you are no longer billed for compute resources. However, you do
need to continue paying for any storage you are using. Pausing a $SERVICE_SHORT ensures
that it is still available, and is ready to be restarted at any time.
-### Delete a $SERVICE_SHORT
+## Delete a $SERVICE_SHORT
You can delete a $SERVICE_SHORT to remove it completely. This removes the $SERVICE_SHORT
and its underlying data from the server. You cannot recover a deleted