diff --git a/.amazonq/rules/problem-creation.md b/.amazonq/rules/problem-creation.md
index d67a88a..2fc2a30 100644
--- a/.amazonq/rules/problem-creation.md
+++ b/.amazonq/rules/problem-creation.md
@@ -6,11 +6,17 @@ When user requests a problem by **number** or **name/slug**, the assistant will:
1. **Scrape** problem data using `.templates/leetcode/scrape.py`
2. **Transform** data into proper JSON template format
-3. **Create** JSON file in `.templates/leetcode/json/{problem_name}.json`
-4. **Update** Makefile with `PROBLEM ?= {problem_name}`
-5. **Generate** problem structure using `make p-gen`
-6. **Verify** with `make lint` - fix template issues in JSON if possible, or manually fix generated files if template limitations
-7. **Iterate** if JSON fixes: re-run `make p-gen PROBLEM={problem_name} FORCE=1` and `make lint` until passes to ensure reproducibility
+3. **CRITICAL: Include images** - Extract image URLs from scraped data and add to readme_examples with format: `\n\n` before code blocks
+ - Check scraped data for image URLs in the `raw_content` field
+ - Look for patterns: `https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/...` or ` `
+ - Common patterns: `kthtree1.jpg`, `kthtree2.jpg`, `clone_graph.png`, `container.jpg`
+ - Images provide crucial visual context, especially for tree and graph problems
+ - Always verify images are included in `readme_examples` and accessible
+4. **Create** JSON file in `.templates/leetcode/json/{problem_name}.json`
+5. **Update** Makefile with `PROBLEM ?= {problem_name}`
+6. **Generate** problem structure using `make p-gen`
+7. **Verify** with `make lint` - fix template issues in JSON if possible, or manually fix generated files if template limitations
+8. **Iterate** if JSON fixes: re-run `make p-gen PROBLEM={problem_name} FORCE=1` and `make lint` until passes to ensure reproducibility
## Scraping Commands
@@ -46,7 +52,7 @@ Required fields for `.templates/leetcode/json/{problem_name}.json`:
"readme_description": "Given an array of integers `nums` and an integer `target`, return indices of the two numbers such that they add up to `target`.",
"readme_examples": [
{
- "content": "```\nInput: nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9\nOutput: [0,1]\n```\n**Explanation:** Because nums[0] + nums[1] == 9, we return [0, 1]."
+ "content": "\n\n```\nInput: nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9\nOutput: [0,1]\n```\n**Explanation:** Because nums[0] + nums[1] == 9, we return [0, 1]."
}
],
"readme_constraints": "- 2 <= nums.length <= 10^4\n- -10^9 <= nums[i] <= 10^9\n- -10^9 <= target <= 10^9\n- Only one valid answer exists.",
diff --git a/.templates/leetcode/json/binary_search.json b/.templates/leetcode/json/binary_search.json
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..ed3b7c4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.templates/leetcode/json/binary_search.json
@@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
+{
+ "problem_name": "binary_search",
+ "solution_class_name": "Solution",
+ "problem_number": "704",
+ "problem_title": "Binary Search",
+ "difficulty": "Easy",
+ "topics": "Array, Binary Search",
+ "tags": ["grind-75"],
+ "readme_description": "Given an array of integers `nums` which is sorted in ascending order, and an integer `target`, write a function to search `target` in `nums`. If `target` exists, then return its index. Otherwise, return `-1`.\n\nYou must write an algorithm with `O(log n)` runtime complexity.",
+ "readme_examples": [
+ {
+ "content": "```\nInput: nums = [-1,0,3,5,9,12], target = 9\nOutput: 4\n```\n**Explanation:** 9 exists in nums and its index is 4"
+ },
+ {
+ "content": "```\nInput: nums = [-1,0,3,5,9,12], target = 2\nOutput: -1\n```\n**Explanation:** 2 does not exist in nums so return -1"
+ }
+ ],
+ "readme_constraints": "- `1 <= nums.length <= 10^4`\n- `-10^4 < nums[i], target < 10^4`\n- All the integers in `nums` are **unique**.\n- `nums` is sorted in ascending order.",
+ "readme_additional": "",
+ "solution_imports": "",
+ "solution_methods": [
+ {
+ "name": "search",
+ "parameters": "nums: list[int], target: int",
+ "return_type": "int",
+ "dummy_return": "-1"
+ }
+ ],
+ "test_imports": "import pytest\nfrom leetcode_py.test_utils import logged_test\nfrom .solution import Solution",
+ "test_class_name": "BinarySearch",
+ "test_helper_methods": [
+ { "name": "setup_method", "parameters": "", "body": "self.solution = Solution()" }
+ ],
+ "test_methods": [
+ {
+ "name": "test_search",
+ "parametrize": "nums, target, expected",
+ "parametrize_typed": "nums: list[int], target: int, expected: int",
+ "test_cases": "[([\u22121, 0, 3, 5, 9, 12], 9, 4), ([\u22121, 0, 3, 5, 9, 12], 2, \u22121), ([5], 5, 0), ([5], \u22125, \u22121), ([1, 3, 5, 7, 9], 1, 0), ([1, 3, 5, 7, 9], 9, 4), ([1, 3, 5, 7, 9], 4, \u22121)]",
+ "body": "result = self.solution.search(nums, target)\nassert result == expected"
+ }
+ ],
+ "playground_imports": "from solution import Solution",
+ "playground_test_case": "# Example test case\nnums = [-1, 0, 3, 5, 9, 12]\ntarget = 9\nexpected = 4",
+ "playground_execution": "result = Solution().search(nums, target)\nresult",
+ "playground_assertion": "assert result == expected"
+}
diff --git a/.templates/leetcode/json/k_closest_points_to_origin.json b/.templates/leetcode/json/k_closest_points_to_origin.json
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..25e7cfa
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.templates/leetcode/json/k_closest_points_to_origin.json
@@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
+{
+ "problem_name": "k_closest_points_to_origin",
+ "solution_class_name": "Solution",
+ "problem_number": "973",
+ "problem_title": "K Closest Points to Origin",
+ "difficulty": "Medium",
+ "topics": "Array, Math, Divide and Conquer, Geometry, Sorting, Heap (Priority Queue), Quickselect",
+ "tags": ["grind-75"],
+ "readme_description": "Given an array of `points` where `points[i] = [xi, yi]` represents a point on the **X-Y** plane and an integer `k`, return the `k` closest points to the origin `(0, 0)`.\n\nThe distance between two points on the **X-Y** plane is the Euclidean distance (i.e., `\u221a(x1 - x2)\u00b2 + (y1 - y2)\u00b2`).\n\nYou may return the answer in **any order**. The answer is **guaranteed** to be **unique** (except for the order that it is in).",
+ "readme_examples": [
+ {
+ "content": "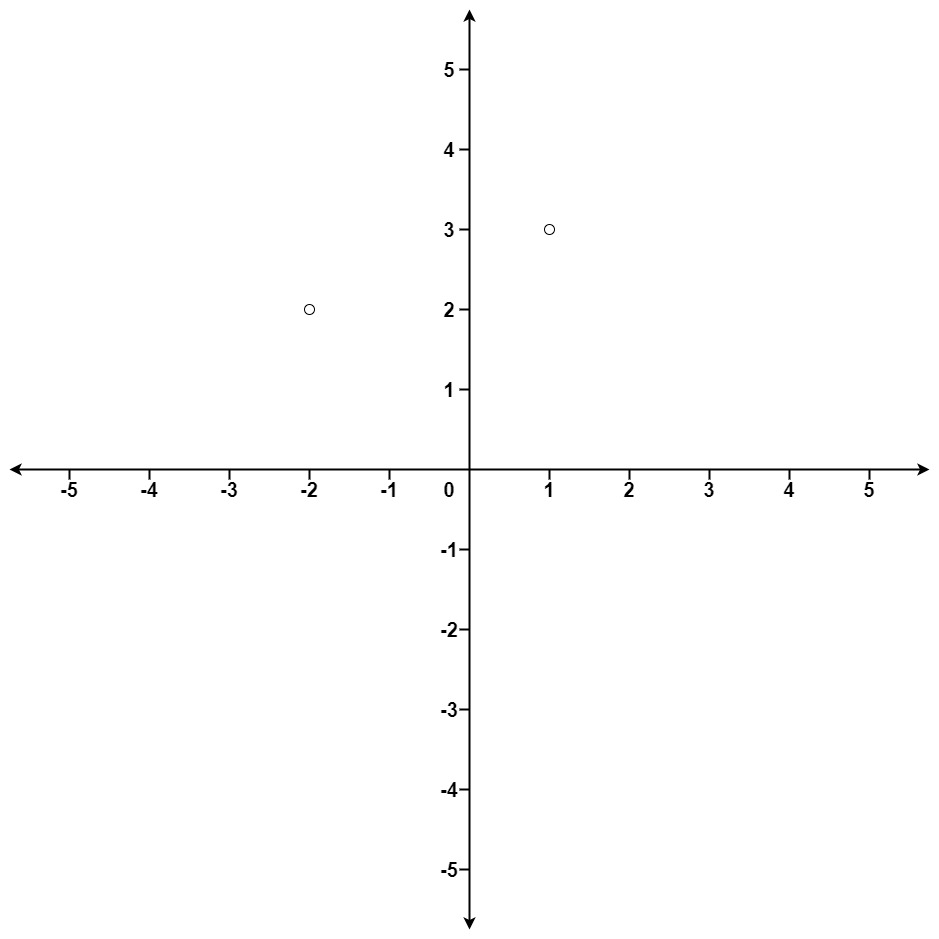\n\n```\nInput: points = [[1,3],[-2,2]], k = 1\nOutput: [[-2,2]]\n```\n**Explanation:** The distance between (1, 3) and the origin is sqrt(10). The distance between (-2, 2) and the origin is sqrt(8). Since sqrt(8) < sqrt(10), (-2, 2) is closer to the origin. We only want the closest k = 1 points from the origin, so the answer is just [[-2,2]]."
+ },
+ {
+ "content": "```\nInput: points = [[3,3],[5,-1],[-2,4]], k = 2\nOutput: [[3,3],[-2,4]]\n```\n**Explanation:** The answer [[-2,4],[3,3]] would also be accepted."
+ }
+ ],
+ "readme_constraints": "- `1 <= k <= points.length <= 10^4`\n- `-10^4 <= xi, yi <= 10^4`",
+ "readme_additional": "",
+ "solution_imports": "",
+ "solution_methods": [
+ {
+ "name": "k_closest",
+ "parameters": "points: list[list[int]], k: int",
+ "return_type": "list[list[int]]",
+ "dummy_return": "[]"
+ }
+ ],
+ "test_imports": "import pytest\nfrom leetcode_py.test_utils import logged_test\nfrom .solution import Solution",
+ "test_class_name": "KClosestPointsToOrigin",
+ "test_helper_methods": [
+ { "name": "setup_method", "parameters": "", "body": "self.solution = Solution()" }
+ ],
+ "test_methods": [
+ {
+ "name": "test_k_closest",
+ "parametrize": "points, k, expected",
+ "parametrize_typed": "points: list[list[int]], k: int, expected: list[list[int]]",
+ "test_cases": "[([[1, 3], [-2, 2]], 1, [[-2, 2]]), ([[3, 3], [5, -1], [-2, 4]], 2, [[3, 3], [-2, 4]]), ([[0, 1], [1, 0]], 2, [[0, 1], [1, 0]]), ([[1, 1], [1, 1], [1, 1]], 2, [[1, 1], [1, 1]])]",
+ "body": "result = self.solution.k_closest(points, k)\n# Sort both result and expected for comparison since order doesn't matter\nresult_sorted = sorted(result)\nexpected_sorted = sorted(expected)\nassert result_sorted == expected_sorted"
+ }
+ ],
+ "playground_imports": "from solution import Solution",
+ "playground_test_case": "# Example test case\npoints = [[1, 3], [-2, 2]]\nk = 1\nexpected = [[-2, 2]]",
+ "playground_execution": "result = Solution().k_closest(points, k)\nresult",
+ "playground_assertion": "assert sorted(result) == sorted(expected)"
+}
diff --git a/.templates/leetcode/json/kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst.json b/.templates/leetcode/json/kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst.json
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..3239379
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.templates/leetcode/json/kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst.json
@@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
+{
+ "problem_name": "kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst",
+ "solution_class_name": "Solution",
+ "problem_number": "230",
+ "problem_title": "Kth Smallest Element in a BST",
+ "difficulty": "Medium",
+ "topics": "Tree, Depth-First Search, Binary Search Tree, Binary Tree",
+ "tags": ["grind-75"],
+ "readme_description": "Given the `root` of a binary search tree, and an integer `k`, return the `k`th smallest value (1-indexed) of all the values of the nodes in the tree.",
+ "readme_examples": [
+ {
+ "content": "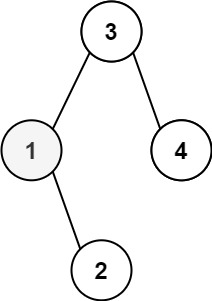\n\n```\nInput: root = [3,1,4,null,2], k = 1\nOutput: 1\n```"
+ },
+ {
+ "content": "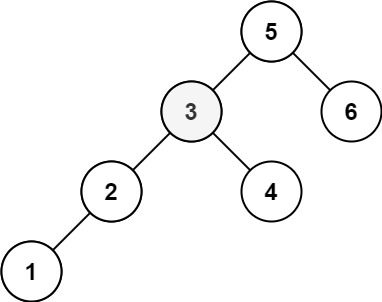\n\n```\nInput: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,null,1], k = 3\nOutput: 3\n```"
+ }
+ ],
+ "readme_constraints": "- The number of nodes in the tree is `n`.\n- `1 <= k <= n <= 10^4`\n- `0 <= Node.val <= 10^4`",
+ "readme_additional": "**Follow up:** If the BST is modified often (i.e., we can do insert and delete operations) and you need to find the kth smallest frequently, how would you optimize?",
+ "solution_imports": "from leetcode_py import TreeNode",
+ "solution_methods": [
+ {
+ "name": "kth_smallest",
+ "parameters": "root: TreeNode | None, k: int",
+ "return_type": "int",
+ "dummy_return": "0"
+ }
+ ],
+ "test_imports": "import pytest\nfrom leetcode_py.test_utils import logged_test\nfrom leetcode_py import TreeNode\nfrom .solution import Solution",
+ "test_class_name": "KthSmallestElementInABst",
+ "test_helper_methods": [
+ { "name": "setup_method", "parameters": "", "body": "self.solution = Solution()" }
+ ],
+ "test_methods": [
+ {
+ "name": "test_kth_smallest",
+ "parametrize": "root_list, k, expected",
+ "parametrize_typed": "root_list: list[int | None], k: int, expected: int",
+ "test_cases": "[([3, 1, 4, None, 2], 1, 1), ([5, 3, 6, 2, 4, None, None, 1], 3, 3), ([1], 1, 1)]",
+ "body": "root = TreeNode.from_list(root_list)\nresult = self.solution.kth_smallest(root, k)\nassert result == expected"
+ }
+ ],
+ "playground_imports": "from solution import Solution\nfrom leetcode_py import TreeNode",
+ "playground_test_case": "# Example test case\nroot_list = [3, 1, 4, None, 2]\nk = 1\nexpected = 1",
+ "playground_execution": "root = TreeNode.from_list(root_list)\nresult = Solution().kth_smallest(root, k)\nresult",
+ "playground_assertion": "assert result == expected"
+}
diff --git a/.templates/leetcode/json/linked_list_cycle.json b/.templates/leetcode/json/linked_list_cycle.json
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..ae5dd54
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.templates/leetcode/json/linked_list_cycle.json
@@ -0,0 +1,55 @@
+{
+ "problem_name": "linked_list_cycle",
+ "solution_class_name": "Solution",
+ "problem_number": "141",
+ "problem_title": "Linked List Cycle",
+ "difficulty": "Easy",
+ "topics": "Hash Table, Linked List, Two Pointers",
+ "tags": ["grind-75"],
+ "readme_description": "Given `head`, the head of a linked list, determine if the linked list has a cycle in it.\n\nThere is a cycle in a linked list if there is some node in the list that can be reached again by continuously following the `next` pointer. Internally, `pos` is used to denote the index of the node that tail's `next` pointer is connected to. **Note that `pos` is not passed as a parameter**.\n\nReturn `true` *if there is a cycle in the linked list*. Otherwise, return `false`.",
+ "readme_examples": [
+ {
+ "content": "\n\n```\nInput: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1\nOutput: true\n```\n**Explanation:** There is a cycle in the linked list, where the tail connects to the 1st node (0-indexed)."
+ },
+ {
+ "content": "\n\n```\nInput: head = [1,2], pos = 0\nOutput: true\n```\n**Explanation:** There is a cycle in the linked list, where the tail connects to the 0th node."
+ },
+ {
+ "content": "\n\n```\nInput: head = [1], pos = -1\nOutput: false\n```\n**Explanation:** There is no cycle in the linked list."
+ }
+ ],
+ "readme_constraints": "- The number of the nodes in the list is in the range `[0, 10^4]`.\n- `-10^5 <= Node.val <= 10^5`\n- `pos` is `-1` or a **valid index** in the linked-list.",
+ "readme_additional": "**Follow up:** Can you solve it using `O(1)` (i.e. constant) memory?",
+ "solution_imports": "from leetcode_py import ListNode",
+ "solution_methods": [
+ {
+ "name": "has_cycle",
+ "parameters": "head: ListNode[int] | None",
+ "return_type": "bool",
+ "dummy_return": "False"
+ }
+ ],
+ "test_imports": "import pytest\nfrom leetcode_py import ListNode\nfrom leetcode_py.test_utils import logged_test\nfrom .solution import Solution",
+ "test_class_name": "LinkedListCycle",
+ "test_helper_methods": [
+ { "name": "setup_method", "parameters": "", "body": "self.solution = Solution()" },
+ {
+ "name": "create_cycle_list",
+ "parameters": "values: list[int], pos: int",
+ "body": "if not values:\n return None\n\nnodes = []\nhead = ListNode(values[0])\nnodes.append(head)\ncurrent = head\n\nfor i in range(1, len(values)):\n current.next = ListNode(values[i])\n current = current.next\n nodes.append(current)\n\nif pos != -1 and pos < len(nodes):\n current.next = nodes[pos]\n\nreturn head"
+ }
+ ],
+ "test_methods": [
+ {
+ "name": "test_has_cycle",
+ "parametrize": "values, pos, expected",
+ "parametrize_typed": "values: list[int], pos: int, expected: bool",
+ "test_cases": "[([3, 2, 0, -4], 1, True), ([1, 2], 0, True), ([1], -1, False), ([], -1, False), ([1, 2, 3], -1, False), ([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], 0, True), ([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], 2, True), ([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], 4, True), ([1], 0, True), ([1, 2], 1, True), ([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8], 3, True), ([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8], -1, False), ([1, 2], -1, False), ([5, 10], 0, True), ([5, 10], 1, True), ([0], -1, False), ([-1, -2, -3], 1, True), ([100, 200, 300], 0, True)]",
+ "body": "head = self.create_cycle_list(values, pos)\nresult = self.solution.has_cycle(head)\nassert result == expected"
+ }
+ ],
+ "playground_imports": "from solution import Solution",
+ "playground_test_case": "import os\nimport sys\nsys.path.append(os.path.join(os.getcwd(), \\\"..\\\"))\nfrom linked_list_cycle.tests import TestLinkedListCycle\n\n# Example test case\nvalues = [3, 2, 0, -4]\npos = 1\nexpected = True",
+ "playground_execution": "head = TestLinkedListCycle().create_cycle_list(values, pos)\nresult = Solution().has_cycle(head)\nresult",
+ "playground_assertion": "assert result == expected"
+}
diff --git a/.templates/leetcode/json/lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree.json b/.templates/leetcode/json/lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree.json
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..eb71d4b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.templates/leetcode/json/lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree.json
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
+{
+ "problem_name": "lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree",
+ "solution_class_name": "Solution",
+ "problem_number": "235",
+ "problem_title": "Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Search Tree",
+ "difficulty": "Medium",
+ "topics": "Tree, Depth-First Search, Binary Search Tree, Binary Tree",
+ "tags": ["grind-75"],
+ "readme_description": "Given a binary search tree (BST), find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) node of two given nodes in the BST.\n\nAccording to the definition of LCA on Wikipedia: \"The lowest common ancestor is defined between two nodes `p` and `q` as the lowest node in `T` that has both `p` and `q` as descendants (where we allow **a node to be a descendant of itself**).\"",
+ "readme_examples": [
+ {
+ "content": "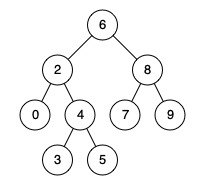\n\n```\nInput: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 8\nOutput: 6\n```\n**Explanation:** The LCA of nodes 2 and 8 is 6."
+ },
+ {
+ "content": "\n\n```\nInput: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 4\nOutput: 2\n```\n**Explanation:** The LCA of nodes 2 and 4 is 2, since a node can be a descendant of itself according to the LCA definition."
+ },
+ { "content": "```\nInput: root = [2,1], p = 2, q = 1\nOutput: 2\n```" }
+ ],
+ "readme_constraints": "- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range `[2, 10^5]`.\n- `-10^9 <= Node.val <= 10^9`\n- All `Node.val` are **unique**.\n- `p != q`\n- `p` and `q` will exist in the BST.",
+ "readme_additional": "",
+ "solution_imports": "from leetcode_py import TreeNode",
+ "solution_methods": [
+ {
+ "name": "lowest_common_ancestor",
+ "parameters": "root: TreeNode[int] | None, p: TreeNode[int], q: TreeNode[int]",
+ "return_type": "TreeNode[int] | None",
+ "dummy_return": "None"
+ }
+ ],
+ "test_imports": "import pytest\nfrom leetcode_py import TreeNode\nfrom leetcode_py.test_utils import logged_test\nfrom .solution import Solution",
+ "test_class_name": "LowestCommonAncestorOfABinarySearchTree",
+ "test_helper_methods": [
+ { "name": "setup_method", "parameters": "", "body": "self.solution = Solution()" },
+ {
+ "name": "_find_node",
+ "parameters": "root: TreeNode[int], val: int",
+ "body": "if not root:\n return None\nif root.val == val:\n return root\nleft = self._find_node(root.left, val)\nif left:\n return left\nreturn self._find_node(root.right, val)"
+ }
+ ],
+ "test_methods": [
+ {
+ "name": "test_lowest_common_ancestor",
+ "parametrize": "root_list, p_val, q_val, expected_val",
+ "parametrize_typed": "root_list: list[int | None], p_val: int, q_val: int, expected_val: int",
+ "test_cases": "[([6, 2, 8, 0, 4, 7, 9, None, None, 3, 5], 2, 8, 6), ([6, 2, 8, 0, 4, 7, 9, None, None, 3, 5], 2, 4, 2), ([2, 1], 2, 1, 2), ([2, 1], 1, 2, 2), ([6, 2, 8, 0, 4, 7, 9], 0, 4, 2), ([6, 2, 8, 0, 4, 7, 9], 7, 9, 8)]",
+ "body": "root = TreeNode[int].from_list(root_list)\nassert root is not None\np = self._find_node(root, p_val)\nq = self._find_node(root, q_val)\nassert p is not None and q is not None\nresult = self.solution.lowest_common_ancestor(root, p, q)\nassert result is not None\nassert result.val == expected_val"
+ }
+ ],
+ "playground_imports": "from leetcode_py import TreeNode\nfrom solution import Solution",
+ "playground_test_case": "# Example test case\nroot_list = [6, 2, 8, 0, 4, 7, 9, None, None, 3, 5]\np_val = 2\nq_val = 8\nexpected_val = 6",
+ "playground_execution": "root = TreeNode[int].from_list(root_list)\np = find_node(root, p_val)\nq = find_node(root, q_val)\nresult = Solution().lowest_common_ancestor(root, p, q)\nresult.val if result else None",
+ "playground_assertion": "assert result and result.val == expected_val"
+}
diff --git a/.templates/leetcode/json/maximum_subarray.json b/.templates/leetcode/json/maximum_subarray.json
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..50da7c2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.templates/leetcode/json/maximum_subarray.json
@@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
+{
+ "problem_name": "maximum_subarray",
+ "solution_class_name": "Solution",
+ "problem_number": "53",
+ "problem_title": "Maximum Subarray",
+ "difficulty": "Medium",
+ "topics": "Array, Divide and Conquer, Dynamic Programming",
+ "tags": ["grind-75"],
+ "readme_description": "Given an integer array `nums`, find the subarray with the largest sum, and return its sum.",
+ "readme_examples": [
+ {
+ "content": "```\nInput: nums = [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4]\nOutput: 6\n```\n**Explanation:** The subarray [4,-1,2,1] has the largest sum 6."
+ },
+ {
+ "content": "```\nInput: nums = [1]\nOutput: 1\n```\n**Explanation:** The subarray [1] has the largest sum 1."
+ },
+ {
+ "content": "```\nInput: nums = [5,4,-1,7,8]\nOutput: 23\n```\n**Explanation:** The subarray [5,4,-1,7,8] has the largest sum 23."
+ }
+ ],
+ "readme_constraints": "- `1 <= nums.length <= 10^5`\n- `-10^4 <= nums[i] <= 10^4`",
+ "readme_additional": "**Follow up:** If you have figured out the `O(n)` solution, try coding another solution using the **divide and conquer** approach, which is more subtle.",
+ "solution_imports": "",
+ "solution_methods": [
+ {
+ "name": "max_sub_array",
+ "parameters": "nums: list[int]",
+ "return_type": "int",
+ "dummy_return": "0"
+ }
+ ],
+ "test_imports": "import pytest\nfrom leetcode_py.test_utils import logged_test\nfrom .solution import Solution",
+ "test_class_name": "MaximumSubarray",
+ "test_helper_methods": [
+ { "name": "setup_method", "parameters": "", "body": "self.solution = Solution()" }
+ ],
+ "test_methods": [
+ {
+ "name": "test_max_sub_array",
+ "parametrize": "nums, expected",
+ "parametrize_typed": "nums: list[int], expected: int",
+ "test_cases": "[([-2, 1, -3, 4, -1, 2, 1, -5, 4], 6), ([1], 1), ([5, 4, -1, 7, 8], 23), ([-1], -1), ([-2, -1], -1), ([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], 15), ([-5, -2, -8, -1], -1)]",
+ "body": "result = self.solution.max_sub_array(nums)\nassert result == expected"
+ }
+ ],
+ "playground_imports": "from solution import Solution",
+ "playground_test_case": "# Example test case\nnums = [-2, 1, -3, 4, -1, 2, 1, -5, 4]\nexpected = 6",
+ "playground_execution": "result = Solution().max_sub_array(nums)\nresult",
+ "playground_assertion": "assert result == expected"
+}
diff --git a/.templates/leetcode/json/minimum_window_substring.json b/.templates/leetcode/json/minimum_window_substring.json
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..a4d151b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.templates/leetcode/json/minimum_window_substring.json
@@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
+{
+ "problem_name": "minimum_window_substring",
+ "solution_class_name": "Solution",
+ "problem_number": "76",
+ "problem_title": "Minimum Window Substring",
+ "difficulty": "Hard",
+ "topics": "Hash Table, String, Sliding Window",
+ "tags": ["grind-75"],
+ "readme_description": "Given two strings `s` and `t` of lengths `m` and `n` respectively, return the **minimum window substring** of `s` such that every character in `t` (including duplicates) is included in the window. If there is no such substring, return the empty string `\"\"`.\n\nThe testcases will be generated such that the answer is unique.",
+ "readme_examples": [
+ {
+ "content": "```\nInput: s = \"ADOBECODEBANC\", t = \"ABC\"\nOutput: \"BANC\"\n```\n**Explanation:** The minimum window substring \"BANC\" includes 'A', 'B', and 'C' from string t."
+ },
+ {
+ "content": "```\nInput: s = \"a\", t = \"a\"\nOutput: \"a\"\n```\n**Explanation:** The entire string s is the minimum window."
+ },
+ {
+ "content": "```\nInput: s = \"a\", t = \"aa\"\nOutput: \"\"\n```\n**Explanation:** Both 'a's from t must be included in the window. Since the largest window of s only has one 'a', return empty string."
+ }
+ ],
+ "readme_constraints": "- `m == s.length`\n- `n == t.length`\n- `1 <= m, n <= 10^5`\n- `s` and `t` consist of uppercase and lowercase English letters.",
+ "readme_additional": "**Follow up:** Could you find an algorithm that runs in `O(m + n)` time?",
+ "solution_imports": "",
+ "solution_methods": [
+ {
+ "name": "min_window",
+ "parameters": "s: str, t: str",
+ "return_type": "str",
+ "dummy_return": "\"\""
+ }
+ ],
+ "test_imports": "import pytest\nfrom leetcode_py.test_utils import logged_test\nfrom .solution import Solution",
+ "test_class_name": "MinimumWindowSubstring",
+ "test_helper_methods": [
+ { "name": "setup_method", "parameters": "", "body": "self.solution = Solution()" }
+ ],
+ "test_methods": [
+ {
+ "name": "test_min_window",
+ "parametrize": "s, t, expected",
+ "parametrize_typed": "s: str, t: str, expected: str",
+ "test_cases": "[(\"ADOBECODEBANC\", \"ABC\", \"BANC\"), (\"a\", \"a\", \"a\"), (\"a\", \"aa\", \"\")]",
+ "body": "result = self.solution.min_window(s, t)\nassert result == expected"
+ }
+ ],
+ "playground_imports": "from solution import Solution",
+ "playground_test_case": "# Example test case\ns = \\\"ADOBECODEBANC\\\"\nt = \\\"ABC\\\"\nexpected = \\\"BANC\\\"",
+ "playground_execution": "result = Solution().min_window(s, t)\nresult",
+ "playground_assertion": "assert result == expected"
+}
diff --git a/.templates/leetcode/json/reverse_linked_list_ii.json b/.templates/leetcode/json/reverse_linked_list_ii.json
index 7c904e2..4eeb724 100644
--- a/.templates/leetcode/json/reverse_linked_list_ii.json
+++ b/.templates/leetcode/json/reverse_linked_list_ii.json
@@ -5,7 +5,7 @@
"problem_title": "Reverse Linked List II",
"difficulty": "Medium",
"topics": "Linked List",
- "tags": ["grind-75"],
+ "tags": [],
"readme_description": "Given the `head` of a singly linked list and two integers `left` and `right` where `left <= right`, reverse the nodes of the list from position `left` to position `right`, and return the reversed list.",
"readme_examples": [
{ "content": "```\nInput: head = [1,2,3,4,5], left = 2, right = 4\nOutput: [1,4,3,2,5]\n```" },
diff --git a/.templates/leetcode/json/search_in_rotated_sorted_array.json b/.templates/leetcode/json/search_in_rotated_sorted_array.json
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..1235416
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.templates/leetcode/json/search_in_rotated_sorted_array.json
@@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
+{
+ "problem_name": "search_in_rotated_sorted_array",
+ "solution_class_name": "Solution",
+ "problem_number": "33",
+ "problem_title": "Search in Rotated Sorted Array",
+ "difficulty": "Medium",
+ "topics": "Array, Binary Search",
+ "tags": ["grind-75"],
+ "readme_description": "There is an integer array `nums` sorted in ascending order (with **distinct** values).\n\nPrior to being passed to your function, `nums` is **possibly left rotated** at an unknown index `k` (`1 <= k < nums.length`) such that the resulting array is `[nums[k], nums[k+1], ..., nums[n-1], nums[0], nums[1], ..., nums[k-1]]` (**0-indexed**). For example, `[0,1,2,4,5,6,7]` might be left rotated by 3 indices and become `[4,5,6,7,0,1,2]`.\n\nGiven the array `nums` **after** the possible rotation and an integer `target`, return *the index of* `target` *if it is in* `nums`*, or* `-1` *if it is not in* `nums`.\n\nYou must write an algorithm with `O(log n)` runtime complexity.",
+ "readme_examples": [
+ { "content": "```\nInput: nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 0\nOutput: 4\n```" },
+ { "content": "```\nInput: nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 3\nOutput: -1\n```" },
+ { "content": "```\nInput: nums = [1], target = 0\nOutput: -1\n```" }
+ ],
+ "readme_constraints": "- `1 <= nums.length <= 5000`\n- `-10^4 <= nums[i] <= 10^4`\n- All values of `nums` are **unique**.\n- `nums` is an ascending array that is possibly rotated.\n- `-10^4 <= target <= 10^4`",
+ "readme_additional": "",
+ "solution_imports": "",
+ "solution_methods": [
+ {
+ "name": "search",
+ "parameters": "nums: list[int], target: int",
+ "return_type": "int",
+ "dummy_return": "-1"
+ }
+ ],
+ "test_imports": "import pytest\nfrom leetcode_py.test_utils import logged_test\nfrom .solution import Solution",
+ "test_class_name": "SearchInRotatedSortedArray",
+ "test_helper_methods": [
+ { "name": "setup_method", "parameters": "", "body": "self.solution = Solution()" }
+ ],
+ "test_methods": [
+ {
+ "name": "test_search",
+ "parametrize": "nums, target, expected",
+ "parametrize_typed": "nums: list[int], target: int, expected: int",
+ "test_cases": "[([4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 1, 2], 0, 4), ([4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 1, 2], 3, -1), ([1], 0, -1), ([1], 1, 0), ([3, 1], 1, 1)]",
+ "body": "result = self.solution.search(nums, target)\nassert result == expected"
+ }
+ ],
+ "playground_imports": "from solution import Solution",
+ "playground_test_case": "# Example test case\nnums = [4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 1, 2]\ntarget = 0\nexpected = 4",
+ "playground_execution": "result = Solution().search(nums, target)\nresult",
+ "playground_assertion": "assert result == expected"
+}
diff --git a/.templates/leetcode/json/valid_palindrome.json b/.templates/leetcode/json/valid_palindrome.json
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..cb4b861
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.templates/leetcode/json/valid_palindrome.json
@@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
+{
+ "problem_name": "valid_palindrome",
+ "solution_class_name": "Solution",
+ "problem_number": "125",
+ "problem_title": "Valid Palindrome",
+ "difficulty": "Easy",
+ "topics": "Two Pointers, String",
+ "tags": ["grind-75"],
+ "readme_description": "A phrase is a **palindrome** if, after converting all uppercase letters into lowercase letters and removing all non-alphanumeric characters, it reads the same forward and backward. Alphanumeric characters include letters and numbers.\n\nGiven a string `s`, return `true` if it is a **palindrome**, or `false` otherwise.",
+ "readme_examples": [
+ {
+ "content": "```\nInput: s = \"A man, a plan, a canal: Panama\"\nOutput: true\n```\n**Explanation:** \"amanaplanacanalpanama\" is a palindrome."
+ },
+ {
+ "content": "```\nInput: s = \"race a car\"\nOutput: false\n```\n**Explanation:** \"raceacar\" is not a palindrome."
+ },
+ {
+ "content": "```\nInput: s = \" \"\nOutput: true\n```\n**Explanation:** s is an empty string \"\" after removing non-alphanumeric characters. Since an empty string reads the same forward and backward, it is a palindrome."
+ }
+ ],
+ "readme_constraints": "- `1 <= s.length <= 2 * 10^5`\n- `s` consists only of printable ASCII characters.",
+ "readme_additional": "",
+ "solution_imports": "",
+ "solution_methods": [
+ {
+ "name": "is_palindrome",
+ "parameters": "s: str",
+ "return_type": "bool",
+ "dummy_return": "False"
+ }
+ ],
+ "test_imports": "import pytest\nfrom leetcode_py.test_utils import logged_test\nfrom .solution import Solution",
+ "test_class_name": "ValidPalindrome",
+ "test_helper_methods": [
+ { "name": "setup_method", "parameters": "", "body": "self.solution = Solution()" }
+ ],
+ "test_methods": [
+ {
+ "name": "test_is_palindrome",
+ "parametrize": "s, expected",
+ "parametrize_typed": "s: str, expected: bool",
+ "test_cases": "[(\"A man, a plan, a canal: Panama\", True), (\"race a car\", False), (\" \", True), (\"\", True), (\"a\", True), (\"Madam\", True), (\"No 'x' in Nixon\", True), (\"Mr. Owl ate my metal worm\", True)]",
+ "body": "result = self.solution.is_palindrome(s)\nassert result == expected"
+ }
+ ],
+ "playground_imports": "from solution import Solution",
+ "playground_test_case": "# Example test case\ns = \"A man, a plan, a canal: Panama\"\nexpected = True",
+ "playground_execution": "result = Solution().is_palindrome(s)\nresult",
+ "playground_assertion": "assert result == expected"
+}
diff --git a/Makefile b/Makefile
index 91a7d24..d49ed4d 100644
--- a/Makefile
+++ b/Makefile
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
PYTHON_VERSION = 3.13
-PROBLEM ?= task_scheduler
+PROBLEM ?= k_closest_points_to_origin
FORCE ?= 0
sync_submodules:
diff --git a/leetcode/binary_search/README.md b/leetcode/binary_search/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..16d0461
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/binary_search/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
+# Binary Search
+
+**Difficulty:** Easy
+**Topics:** Array, Binary Search
+**Tags:** grind-75
+
+**LeetCode:** [Problem 704](https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-search/description/)
+
+## Problem Description
+
+Given an array of integers `nums` which is sorted in ascending order, and an integer `target`, write a function to search `target` in `nums`. If `target` exists, then return its index. Otherwise, return `-1`.
+
+You must write an algorithm with `O(log n)` runtime complexity.
+
+## Examples
+
+### Example 1:
+
+```
+Input: nums = [-1,0,3,5,9,12], target = 9
+Output: 4
+```
+
+**Explanation:** 9 exists in nums and its index is 4
+
+### Example 2:
+
+```
+Input: nums = [-1,0,3,5,9,12], target = 2
+Output: -1
+```
+
+**Explanation:** 2 does not exist in nums so return -1
+
+## Constraints
+
+- `1 <= nums.length <= 10^4`
+- `-10^4 < nums[i], target < 10^4`
+- All the integers in `nums` are **unique**.
+- `nums` is sorted in ascending order.
diff --git a/leetcode/binary_search/__init__.py b/leetcode/binary_search/__init__.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e69de29
diff --git a/leetcode/binary_search/playground.ipynb b/leetcode/binary_search/playground.ipynb
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..d7a58c0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/binary_search/playground.ipynb
@@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
+{
+ "cells": [
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "imports",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "from solution import Solution"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "setup",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "# Example test case\n",
+ "nums = [-1, 0, 3, 5, 9, 12]\n",
+ "target = 9\n",
+ "expected = 4"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "execute",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "result = Solution().search(nums, target)\n",
+ "result"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "test",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "assert result == expected"
+ ]
+ }
+ ],
+ "metadata": {
+ "kernelspec": {
+ "display_name": "leetcode-py-py3.13",
+ "language": "python",
+ "name": "python3"
+ },
+ "language_info": {
+ "codemirror_mode": {
+ "name": "ipython",
+ "version": 3
+ },
+ "file_extension": ".py",
+ "mimetype": "text/x-python",
+ "name": "python",
+ "nbconvert_exporter": "python3",
+ "pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
+ "version": "3.13.7"
+ }
+ },
+ "nbformat": 4,
+ "nbformat_minor": 5
+}
diff --git a/leetcode/binary_search/solution.py b/leetcode/binary_search/solution.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..7bc15e6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/binary_search/solution.py
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+class Solution:
+ # Time: O(log n)
+ # Space: O(1)
+ def search(self, nums: list[int], target: int) -> int:
+ left, right = 0, len(nums) - 1
+
+ while left <= right:
+ mid = (left + right) // 2
+
+ if nums[mid] == target:
+ return mid
+ elif nums[mid] < target:
+ left = mid + 1
+ else:
+ right = mid - 1
+
+ return -1
diff --git a/leetcode/binary_search/tests.py b/leetcode/binary_search/tests.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..0842386
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/binary_search/tests.py
@@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
+import pytest
+
+from leetcode_py.test_utils import logged_test
+
+from .solution import Solution
+
+
+class TestBinarySearch:
+ def setup_method(self):
+ self.solution = Solution()
+
+ @pytest.mark.parametrize(
+ "nums, target, expected",
+ [
+ # Original examples
+ ([-1, 0, 3, 5, 9, 12], 9, 4),
+ ([-1, 0, 3, 5, 9, 12], 2, -1),
+ # Single element
+ ([5], 5, 0),
+ ([5], -5, -1),
+ # Target at boundaries
+ ([1, 3, 5, 7, 9], 1, 0),
+ ([1, 3, 5, 7, 9], 9, 4),
+ # Target not found
+ ([1, 3, 5, 7, 9], 4, -1),
+ # Two elements
+ ([1, 3], 1, 0),
+ ([1, 3], 3, 1),
+ ([1, 3], 2, -1),
+ # Negative numbers
+ ([-5, -2, 0, 3, 7], -2, 1),
+ ([-5, -2, 0, 3, 7], 0, 2),
+ ([-5, -2, 0, 3, 7], -1, -1),
+ ],
+ )
+ @logged_test
+ def test_search(self, nums: list[int], target: int, expected: int):
+ result = self.solution.search(nums, target)
+ assert result == expected
diff --git a/leetcode/container_with_most_water/tests.py b/leetcode/container_with_most_water/tests.py
index ebc66be..2713d8d 100644
--- a/leetcode/container_with_most_water/tests.py
+++ b/leetcode/container_with_most_water/tests.py
@@ -10,7 +10,29 @@ def setup_method(self):
self.solution = Solution()
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
- "height, expected", [([1, 8, 6, 2, 5, 4, 8, 3, 7], 49), ([1, 1], 1), ([1, 2, 1], 2)]
+ "height, expected",
+ [
+ # Original cases
+ ([1, 8, 6, 2, 5, 4, 8, 3, 7], 49),
+ ([1, 1], 1),
+ ([1, 2, 1], 2),
+ # Edge cases
+ ([2, 1], 1),
+ ([1, 2], 1),
+ ([0, 2], 0),
+ ([2, 0], 0),
+ # Increasing heights
+ ([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], 6),
+ # Decreasing heights
+ ([5, 4, 3, 2, 1], 6),
+ # Same heights
+ ([3, 3, 3, 3], 9),
+ # Large differences
+ ([1, 1000, 1], 2),
+ ([1000, 1, 1000], 2000),
+ # Multiple peaks
+ ([2, 3, 4, 5, 18, 17, 6], 17),
+ ],
)
@logged_test
def test_max_area(self, height: list[int], expected: int):
diff --git a/leetcode/evaluate_reverse_polish_notation/tests.py b/leetcode/evaluate_reverse_polish_notation/tests.py
index 82c126b..f353e1f 100644
--- a/leetcode/evaluate_reverse_polish_notation/tests.py
+++ b/leetcode/evaluate_reverse_polish_notation/tests.py
@@ -12,9 +12,24 @@ def setup_method(self):
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
"tokens, expected",
[
+ # Original cases
(["2", "1", "+", "3", "*"], 9),
(["4", "13", "5", "/", "+"], 6),
(["10", "6", "9", "3", "+", "-11", "*", "/", "*", "17", "+", "5", "+"], 22),
+ # Single number
+ (["42"], 42),
+ # Negative numbers
+ (["-1"], -1),
+ (["1", "-1", "+"], 0),
+ # Basic operations
+ (["3", "4", "+"], 7),
+ (["5", "2", "-"], 3),
+ (["6", "3", "*"], 18),
+ (["8", "2", "/"], 4),
+ # Division with negatives
+ (["-3", "4", "+", "2", "*", "1", "-"], 1),
+ # Complex expression
+ (["15", "7", "1", "1", "+", "/", "/", "3", "*", "2", "1", "1", "+", "+", "-"], 11),
],
)
@logged_test
diff --git a/leetcode/insert_interval/tests.py b/leetcode/insert_interval/tests.py
index 6968af7..ee51e8f 100644
--- a/leetcode/insert_interval/tests.py
+++ b/leetcode/insert_interval/tests.py
@@ -12,8 +12,25 @@ def setup_method(self):
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
"intervals, new_interval, expected",
[
+ # Original cases
([[1, 3], [6, 9]], [2, 5], [[1, 5], [6, 9]]),
([[1, 2], [3, 5], [6, 7], [8, 10], [12, 16]], [4, 8], [[1, 2], [3, 10], [12, 16]]),
+ # Empty intervals
+ ([], [5, 7], [[5, 7]]),
+ # Insert at beginning
+ ([[3, 5], [6, 9]], [1, 2], [[1, 2], [3, 5], [6, 9]]),
+ # Insert at end
+ ([[1, 3], [6, 9]], [10, 12], [[1, 3], [6, 9], [10, 12]]),
+ # No overlap
+ ([[1, 2], [4, 5]], [3, 3], [[1, 2], [3, 3], [4, 5]]),
+ # Complete overlap
+ ([[1, 5]], [2, 3], [[1, 5]]),
+ # Merge all intervals
+ ([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]], [0, 7], [[0, 7]]),
+ # Adjacent intervals
+ ([[1, 3], [6, 9]], [4, 5], [[1, 3], [4, 5], [6, 9]]),
+ # Touch boundaries
+ ([[1, 3], [6, 9]], [3, 6], [[1, 9]]),
],
)
@logged_test
diff --git a/leetcode/k_closest_points_to_origin/README.md b/leetcode/k_closest_points_to_origin/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..54395ba
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/k_closest_points_to_origin/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
+# K Closest Points to Origin
+
+**Difficulty:** Medium
+**Topics:** Array, Math, Divide and Conquer, Geometry, Sorting, Heap (Priority Queue), Quickselect
+**Tags:** grind-75
+
+**LeetCode:** [Problem 973](https://leetcode.com/problems/k-closest-points-to-origin/description/)
+
+## Problem Description
+
+Given an array of `points` where `points[i] = [xi, yi]` represents a point on the **X-Y** plane and an integer `k`, return the `k` closest points to the origin `(0, 0)`.
+
+The distance between two points on the **X-Y** plane is the Euclidean distance (i.e., `√(x1 - x2)² + (y1 - y2)²`).
+
+You may return the answer in **any order**. The answer is **guaranteed** to be **unique** (except for the order that it is in).
+
+## Examples
+
+### Example 1:
+
+
+
+```
+Input: points = [[1,3],[-2,2]], k = 1
+Output: [[-2,2]]
+```
+
+**Explanation:** The distance between (1, 3) and the origin is sqrt(10). The distance between (-2, 2) and the origin is sqrt(8). Since sqrt(8) < sqrt(10), (-2, 2) is closer to the origin. We only want the closest k = 1 points from the origin, so the answer is just [[-2,2]].
+
+### Example 2:
+
+```
+Input: points = [[3,3],[5,-1],[-2,4]], k = 2
+Output: [[3,3],[-2,4]]
+```
+
+**Explanation:** The answer [[-2,4],[3,3]] would also be accepted.
+
+## Constraints
+
+- `1 <= k <= points.length <= 10^4`
+- `-10^4 <= xi, yi <= 10^4`
diff --git a/leetcode/k_closest_points_to_origin/__init__.py b/leetcode/k_closest_points_to_origin/__init__.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e69de29
diff --git a/leetcode/k_closest_points_to_origin/playground.ipynb b/leetcode/k_closest_points_to_origin/playground.ipynb
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..49a9238
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/k_closest_points_to_origin/playground.ipynb
@@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
+{
+ "cells": [
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "imports",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": ["from solution import Solution"]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "setup",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": ["# Example test case\npoints = [[1, 3], [-2, 2]]\nk = 1\nexpected = [[-2, 2]]"]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "execute",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": ["result = Solution().k_closest(points, k)\nresult"]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "test",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": ["assert sorted(result) == sorted(expected)"]
+ }
+ ],
+ "metadata": {
+ "kernelspec": {
+ "display_name": "leetcode-py-py3.13",
+ "language": "python",
+ "name": "python3"
+ },
+ "language_info": {
+ "codemirror_mode": {
+ "name": "ipython",
+ "version": 3
+ },
+ "file_extension": ".py",
+ "mimetype": "text/x-python",
+ "name": "python",
+ "nbconvert_exporter": "python3",
+ "pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
+ "version": "3.13.7"
+ }
+ },
+ "nbformat": 4,
+ "nbformat_minor": 5
+}
diff --git a/leetcode/k_closest_points_to_origin/solution.py b/leetcode/k_closest_points_to_origin/solution.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..d053d9b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/k_closest_points_to_origin/solution.py
@@ -0,0 +1,16 @@
+import heapq
+
+
+class Solution:
+ # Time: O(n log k)
+ # Space: O(k)
+ def k_closest(self, points: list[list[int]], k: int) -> list[list[int]]:
+ heap: list[tuple[int, list[int]]] = []
+
+ for x, y in points:
+ dist = x * x + y * y
+ heapq.heappush(heap, (-dist, [x, y]))
+ if len(heap) > k:
+ heapq.heappop(heap)
+
+ return [point for _, point in heap]
diff --git a/leetcode/k_closest_points_to_origin/tests.py b/leetcode/k_closest_points_to_origin/tests.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..296af1b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/k_closest_points_to_origin/tests.py
@@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
+import pytest
+
+from leetcode_py.test_utils import logged_test
+
+from .solution import Solution
+
+
+class TestKClosestPointsToOrigin:
+ def setup_method(self):
+ self.solution = Solution()
+
+ @pytest.mark.parametrize(
+ "points, k, expected",
+ [
+ # Basic examples
+ ([[1, 3], [-2, 2]], 1, [[-2, 2]]),
+ ([[3, 3], [5, -1], [-2, 4]], 2, [[3, 3], [-2, 4]]),
+ ([[0, 1], [1, 0]], 2, [[0, 1], [1, 0]]),
+ ([[1, 1], [1, 1], [1, 1]], 2, [[1, 1], [1, 1]]),
+ # Edge cases
+ ([[0, 0]], 1, [[0, 0]]), # Origin point
+ ([[1, 0], [0, 1], [-1, 0], [0, -1]], 1, [[1, 0]]), # Unit circle points
+ ([[2, 2], [1, 1], [3, 3]], 3, [[1, 1], [2, 2], [3, 3]]), # All points
+ # Negative coordinates
+ ([[-1, -1], [-2, -2], [1, 1]], 2, [[-1, -1], [1, 1]]),
+ # Large coordinates
+ ([[100, 100], [1, 1], [50, 50]], 1, [[1, 1]]),
+ # Same distances
+ ([[1, 0], [0, 1], [-1, 0], [0, -1]], 2, [[1, 0], [0, 1]]),
+ ],
+ )
+ @logged_test
+ def test_k_closest(self, points: list[list[int]], k: int, expected: list[list[int]]):
+ result = self.solution.k_closest(points, k)
+ # Sort both result and expected for comparison since order doesn't matter
+ result_sorted = sorted(result)
+ expected_sorted = sorted(expected)
+ assert result_sorted == expected_sorted
diff --git a/leetcode/kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/README.md b/leetcode/kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..fefde64
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
+# Kth Smallest Element in a BST
+
+**Difficulty:** Medium
+**Topics:** Tree, Depth-First Search, Binary Search Tree, Binary Tree
+**Tags:** grind-75
+
+**LeetCode:** [Problem 230](https://leetcode.com/problems/kth-smallest-element-in-a-bst/description/)
+
+## Problem Description
+
+Given the `root` of a binary search tree, and an integer `k`, return the `k`th smallest value (1-indexed) of all the values of the nodes in the tree.
+
+## Examples
+
+### Example 1:
+
+
+
+```
+Input: root = [3,1,4,null,2], k = 1
+Output: 1
+```
+
+### Example 2:
+
+
+
+```
+Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,null,1], k = 3
+Output: 3
+```
+
+## Constraints
+
+- The number of nodes in the tree is `n`.
+- `1 <= k <= n <= 10^4`
+- `0 <= Node.val <= 10^4`
+
+**Follow up:** If the BST is modified often (i.e., we can do insert and delete operations) and you need to find the kth smallest frequently, how would you optimize?
diff --git a/leetcode/kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/__init__.py b/leetcode/kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/__init__.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e69de29
diff --git a/leetcode/kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/playground.ipynb b/leetcode/kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/playground.ipynb
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..da34058
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/playground.ipynb
@@ -0,0 +1,160 @@
+{
+ "cells": [
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 1,
+ "id": "imports",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "from solution import Solution\n",
+ "\n",
+ "from leetcode_py import TreeNode"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 2,
+ "id": "setup",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "# Example test case\n",
+ "root_list = [3, 1, 4, None, 2]\n",
+ "k = 1\n",
+ "expected = 1"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 3,
+ "id": "execute",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [
+ {
+ "data": {
+ "text/plain": [
+ "1"
+ ]
+ },
+ "execution_count": 3,
+ "metadata": {},
+ "output_type": "execute_result"
+ }
+ ],
+ "source": [
+ "root = TreeNode.from_list(root_list)\n",
+ "result = Solution().kth_smallest(root, k)\n",
+ "result"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 4,
+ "id": "6dc42838",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [
+ {
+ "data": {
+ "text/html": [
+ "\n",
+ "\n",
+ "\n",
+ "\n",
+ "\n"
+ ],
+ "text/plain": [
+ "TreeNode([3, 1, 4, None, 2])"
+ ]
+ },
+ "execution_count": 4,
+ "metadata": {},
+ "output_type": "execute_result"
+ }
+ ],
+ "source": [
+ "root"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 5,
+ "id": "test",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "assert result == expected"
+ ]
+ }
+ ],
+ "metadata": {
+ "kernelspec": {
+ "display_name": "leetcode-py-py3.13",
+ "language": "python",
+ "name": "python3"
+ },
+ "language_info": {
+ "codemirror_mode": {
+ "name": "ipython",
+ "version": 3
+ },
+ "file_extension": ".py",
+ "mimetype": "text/x-python",
+ "name": "python",
+ "nbconvert_exporter": "python",
+ "pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
+ "version": "3.13.7"
+ }
+ },
+ "nbformat": 4,
+ "nbformat_minor": 5
+}
diff --git a/leetcode/kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/solution.py b/leetcode/kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/solution.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..57bd5db
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/solution.py
@@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
+from leetcode_py import TreeNode
+
+
+class Solution:
+ # Inorder Recursive
+ # Time: O(k)
+ # Space: O(h)
+ def kth_smallest(self, root: TreeNode | None, k: int) -> int:
+ def inorder(node: TreeNode | None):
+ if not node:
+ return
+ yield from inorder(node.left)
+ yield node.val
+ yield from inorder(node.right)
+
+ for i, val in enumerate(inorder(root)):
+ if i == k - 1:
+ return val
+
+ raise ValueError(f"Tree has fewer than {k} nodes")
+
+
+# Binary Tree Traversal Patterns
+#
+# def inorder(node):
+# if node:
+# inorder(node.left)
+# print(node.val)
+# inorder(node.right)
+#
+# def preorder(node):
+# if node:
+# print(node.val)
+# preorder(node.left)
+# preorder(node.right)
+#
+# def postorder(node):
+# if node:
+# postorder(node.left)
+# postorder(node.right)
+# print(node.val)
diff --git a/leetcode/kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/tests.py b/leetcode/kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/tests.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..1e52c52
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/tests.py
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
+import pytest
+
+from leetcode_py import TreeNode
+from leetcode_py.test_utils import logged_test
+
+from .solution import Solution
+
+
+class TestKthSmallestElementInABst:
+ def setup_method(self):
+ self.solution = Solution()
+
+ @pytest.mark.parametrize(
+ "root_list, k, expected",
+ [([3, 1, 4, None, 2], 1, 1), ([5, 3, 6, 2, 4, None, None, 1], 3, 3), ([1], 1, 1)],
+ )
+ @logged_test
+ def test_kth_smallest(self, root_list: list[int | None], k: int, expected: int):
+ root = TreeNode.from_list(root_list)
+ result = self.solution.kth_smallest(root, k)
+ assert result == expected
diff --git a/leetcode/linked_list_cycle/README.md b/leetcode/linked_list_cycle/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..4ec75c4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/linked_list_cycle/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
+# Linked List Cycle
+
+**Difficulty:** Easy
+**Topics:** Hash Table, Linked List, Two Pointers
+**Tags:** grind-75
+
+**LeetCode:** [Problem 141](https://leetcode.com/problems/linked-list-cycle/description/)
+
+## Problem Description
+
+Given `head`, the head of a linked list, determine if the linked list has a cycle in it.
+
+There is a cycle in a linked list if there is some node in the list that can be reached again by continuously following the `next` pointer. Internally, `pos` is used to denote the index of the node that tail's `next` pointer is connected to. **Note that `pos` is not passed as a parameter**.
+
+Return `true` _if there is a cycle in the linked list_. Otherwise, return `false`.
+
+## Examples
+
+### Example 1:
+
+
+
+```
+Input: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
+Output: true
+```
+
+**Explanation:** There is a cycle in the linked list, where the tail connects to the 1st node (0-indexed).
+
+### Example 2:
+
+
+
+```
+Input: head = [1,2], pos = 0
+Output: true
+```
+
+**Explanation:** There is a cycle in the linked list, where the tail connects to the 0th node.
+
+### Example 3:
+
+
+
+```
+Input: head = [1], pos = -1
+Output: false
+```
+
+**Explanation:** There is no cycle in the linked list.
+
+## Constraints
+
+- The number of the nodes in the list is in the range `[0, 10^4]`.
+- `-10^5 <= Node.val <= 10^5`
+- `pos` is `-1` or a **valid index** in the linked-list.
+
+**Follow up:** Can you solve it using `O(1)` (i.e. constant) memory?
diff --git a/leetcode/linked_list_cycle/__init__.py b/leetcode/linked_list_cycle/__init__.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e69de29
diff --git a/leetcode/linked_list_cycle/playground.ipynb b/leetcode/linked_list_cycle/playground.ipynb
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..7f74fb3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/linked_list_cycle/playground.ipynb
@@ -0,0 +1,87 @@
+{
+ "cells": [
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 1,
+ "id": "imports",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "from solution import Solution"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 2,
+ "id": "setup",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "import os\n",
+ "import sys\n",
+ "\n",
+ "sys.path.append(os.path.join(os.getcwd(), \"..\"))\n",
+ "from linked_list_cycle.tests import TestLinkedListCycle\n",
+ "\n",
+ "# Example test case\n",
+ "values = [3, 2, 0, -4]\n",
+ "pos = 1\n",
+ "expected = True"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 3,
+ "id": "execute",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [
+ {
+ "data": {
+ "text/plain": [
+ "True"
+ ]
+ },
+ "execution_count": 3,
+ "metadata": {},
+ "output_type": "execute_result"
+ }
+ ],
+ "source": [
+ "head = TestLinkedListCycle().create_cycle_list(values, pos)\n",
+ "result = Solution().has_cycle(head)\n",
+ "result"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 4,
+ "id": "test",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "assert result == expected"
+ ]
+ }
+ ],
+ "metadata": {
+ "kernelspec": {
+ "display_name": "leetcode-py-py3.13",
+ "language": "python",
+ "name": "python3"
+ },
+ "language_info": {
+ "codemirror_mode": {
+ "name": "ipython",
+ "version": 3
+ },
+ "file_extension": ".py",
+ "mimetype": "text/x-python",
+ "name": "python",
+ "nbconvert_exporter": "python",
+ "pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
+ "version": "3.13.7"
+ }
+ },
+ "nbformat": 4,
+ "nbformat_minor": 5
+}
diff --git a/leetcode/linked_list_cycle/solution.py b/leetcode/linked_list_cycle/solution.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..6c3f838
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/linked_list_cycle/solution.py
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
+from leetcode_py import ListNode
+
+
+class Solution:
+ # Time: O(n)
+ # Space: O(1)
+ def has_cycle(self, head: ListNode[int] | None) -> bool:
+ fast = head
+ slow = head
+
+ while fast and fast.next:
+ assert slow is not None
+ fast = fast.next.next
+ slow = slow.next
+ if fast is slow:
+ return True
+
+ return False
diff --git a/leetcode/linked_list_cycle/tests.py b/leetcode/linked_list_cycle/tests.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..8af1b82
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/linked_list_cycle/tests.py
@@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
+import pytest
+
+from leetcode_py import ListNode
+from leetcode_py.test_utils import logged_test
+
+from .solution import Solution
+
+
+class TestLinkedListCycle:
+ def setup_method(self):
+ self.solution = Solution()
+
+ def create_cycle_list(self, values: list[int], pos: int):
+ if not values:
+ return None
+
+ nodes = []
+ head = ListNode(values[0])
+ nodes.append(head)
+ current = head
+
+ for i in range(1, len(values)):
+ current.next = ListNode(values[i])
+ current = current.next
+ nodes.append(current)
+
+ if pos != -1 and pos < len(nodes):
+ current.next = nodes[pos]
+
+ return head
+
+ @pytest.mark.parametrize(
+ "values, pos, expected",
+ [
+ ([3, 2, 0, -4], 1, True),
+ ([1, 2], 0, True),
+ ([1], -1, False),
+ ([], -1, False),
+ ([1, 2, 3], -1, False),
+ ([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], 0, True),
+ ([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], 2, True),
+ ([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], 4, True),
+ ([1], 0, True),
+ ([1, 2], 1, True),
+ ([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8], 3, True),
+ ([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8], -1, False),
+ ([1, 2], -1, False),
+ ([5, 10], 0, True),
+ ([5, 10], 1, True),
+ ([0], -1, False),
+ ([-1, -2, -3], 1, True),
+ ([100, 200, 300], 0, True),
+ ],
+ )
+ @logged_test
+ def test_has_cycle(self, values: list[int], pos: int, expected: bool):
+ head = self.create_cycle_list(values, pos)
+ result = self.solution.has_cycle(head)
+ assert result == expected
diff --git a/leetcode/lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree/README.md b/leetcode/lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..a5b2f27
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
+# Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Search Tree
+
+**Difficulty:** Medium
+**Topics:** Tree, Depth-First Search, Binary Search Tree, Binary Tree
+**Tags:** grind-75
+
+**LeetCode:** [Problem 235](https://leetcode.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-search-tree/description/)
+
+## Problem Description
+
+Given a binary search tree (BST), find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) node of two given nodes in the BST.
+
+According to the definition of LCA on Wikipedia: "The lowest common ancestor is defined between two nodes `p` and `q` as the lowest node in `T` that has both `p` and `q` as descendants (where we allow **a node to be a descendant of itself**)."
+
+## Examples
+
+### Example 1:
+
+
+
+```
+Input: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 8
+Output: 6
+```
+
+**Explanation:** The LCA of nodes 2 and 8 is 6.
+
+### Example 2:
+
+
+
+```
+Input: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 4
+Output: 2
+```
+
+**Explanation:** The LCA of nodes 2 and 4 is 2, since a node can be a descendant of itself according to the LCA definition.
+
+### Example 3:
+
+```
+Input: root = [2,1], p = 2, q = 1
+Output: 2
+```
+
+## Constraints
+
+- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range `[2, 10^5]`.
+- `-10^9 <= Node.val <= 10^9`
+- All `Node.val` are **unique**.
+- `p != q`
+- `p` and `q` will exist in the BST.
diff --git a/leetcode/lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree/__init__.py b/leetcode/lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree/__init__.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e69de29
diff --git a/leetcode/lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree/playground.ipynb b/leetcode/lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree/playground.ipynb
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..763d0ea
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree/playground.ipynb
@@ -0,0 +1,75 @@
+{
+ "cells": [
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "imports",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "from solution import Solution\n",
+ "\n",
+ "from leetcode_py import TreeNode"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "setup",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "# Example test case\n",
+ "root_list = [6, 2, 8, 0, 4, 7, 9, None, None, 3, 5]\n",
+ "p_val = 2\n",
+ "q_val = 8\n",
+ "expected_val = 6"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "execute",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "root = TreeNode[int].from_list(root_list)\n",
+ "p = find_node(root, p_val)\n",
+ "q = find_node(root, q_val)\n",
+ "result = Solution().lowest_common_ancestor(root, p, q)\n",
+ "result.val if result else None"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "test",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "assert result and result.val == expected_val"
+ ]
+ }
+ ],
+ "metadata": {
+ "kernelspec": {
+ "display_name": "leetcode-py-py3.13",
+ "language": "python",
+ "name": "python3"
+ },
+ "language_info": {
+ "codemirror_mode": {
+ "name": "ipython",
+ "version": 3
+ },
+ "file_extension": ".py",
+ "mimetype": "text/x-python",
+ "name": "python",
+ "nbconvert_exporter": "python3",
+ "pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
+ "version": "3.13.7"
+ }
+ },
+ "nbformat": 4,
+ "nbformat_minor": 5
+}
diff --git a/leetcode/lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree/solution.py b/leetcode/lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree/solution.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..f6f5dcd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree/solution.py
@@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
+from leetcode_py import TreeNode
+
+
+class Solution:
+ # Time: O(log n) average, O(n) worst case
+ # Space: O(1) iterative, O(log n) recursive
+ def lowest_common_ancestor(
+ self, root: TreeNode[int] | None, p: TreeNode[int], q: TreeNode[int]
+ ) -> TreeNode[int] | None:
+ while root:
+ # Both nodes are in left subtree
+ if p.val < root.val and q.val < root.val:
+ root = root.left
+ # Both nodes are in right subtree
+ elif p.val > root.val and q.val > root.val:
+ root = root.right
+ # Split point - one node on each side or one is the root
+ else:
+ return root
+ return None
diff --git a/leetcode/lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree/tests.py b/leetcode/lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree/tests.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..33767fe
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree/tests.py
@@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
+import pytest
+
+from leetcode_py import TreeNode
+from leetcode_py.test_utils import logged_test
+
+from .solution import Solution
+
+
+class TestLowestCommonAncestorOfABinarySearchTree:
+ def setup_method(self):
+ self.solution = Solution()
+
+ def _find_node(self, root: TreeNode[int] | None, val: int):
+ if not root:
+ return None
+ if root.val == val:
+ return root
+ left = self._find_node(root.left, val)
+ if left:
+ return left
+ return self._find_node(root.right, val)
+
+ @pytest.mark.parametrize(
+ "root_list, p_val, q_val, expected_val",
+ [
+ ([6, 2, 8, 0, 4, 7, 9, None, None, 3, 5], 2, 8, 6),
+ ([6, 2, 8, 0, 4, 7, 9, None, None, 3, 5], 2, 4, 2),
+ ([2, 1], 2, 1, 2),
+ ([2, 1], 1, 2, 2),
+ ([6, 2, 8, 0, 4, 7, 9], 0, 4, 2),
+ ([6, 2, 8, 0, 4, 7, 9], 7, 9, 8),
+ ],
+ )
+ @logged_test
+ def test_lowest_common_ancestor(
+ self, root_list: list[int | None], p_val: int, q_val: int, expected_val: int
+ ):
+ root = TreeNode[int].from_list(root_list)
+ assert root is not None
+ p = self._find_node(root, p_val)
+ q = self._find_node(root, q_val)
+ assert p is not None and q is not None
+ result = self.solution.lowest_common_ancestor(root, p, q)
+ assert result is not None
+ assert result.val == expected_val
diff --git a/leetcode/maximum_subarray/README.md b/leetcode/maximum_subarray/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e4d7afa
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/maximum_subarray/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
+# Maximum Subarray
+
+**Difficulty:** Medium
+**Topics:** Array, Divide and Conquer, Dynamic Programming
+**Tags:** grind-75
+
+**LeetCode:** [Problem 53](https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-subarray/description/)
+
+## Problem Description
+
+Given an integer array `nums`, find the subarray with the largest sum, and return its sum.
+
+## Examples
+
+### Example 1:
+
+```
+Input: nums = [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4]
+Output: 6
+```
+
+**Explanation:** The subarray [4,-1,2,1] has the largest sum 6.
+
+### Example 2:
+
+```
+Input: nums = [1]
+Output: 1
+```
+
+**Explanation:** The subarray [1] has the largest sum 1.
+
+### Example 3:
+
+```
+Input: nums = [5,4,-1,7,8]
+Output: 23
+```
+
+**Explanation:** The subarray [5,4,-1,7,8] has the largest sum 23.
+
+## Constraints
+
+- `1 <= nums.length <= 10^5`
+- `-10^4 <= nums[i] <= 10^4`
+
+**Follow up:** If you have figured out the `O(n)` solution, try coding another solution using the **divide and conquer** approach, which is more subtle.
diff --git a/leetcode/maximum_subarray/__init__.py b/leetcode/maximum_subarray/__init__.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e69de29
diff --git a/leetcode/maximum_subarray/playground.ipynb b/leetcode/maximum_subarray/playground.ipynb
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..2cbaa51
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/maximum_subarray/playground.ipynb
@@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
+{
+ "cells": [
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "imports",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": ["from solution import Solution"]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "setup",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": ["# Example test case\nnums = [-2, 1, -3, 4, -1, 2, 1, -5, 4]\nexpected = 6"]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "execute",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": ["result = Solution().max_sub_array(nums)\nresult"]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "test",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": ["assert result == expected"]
+ }
+ ],
+ "metadata": {
+ "kernelspec": {
+ "display_name": "leetcode-py-py3.13",
+ "language": "python",
+ "name": "python3"
+ },
+ "language_info": {
+ "codemirror_mode": {
+ "name": "ipython",
+ "version": 3
+ },
+ "file_extension": ".py",
+ "mimetype": "text/x-python",
+ "name": "python",
+ "nbconvert_exporter": "python3",
+ "pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
+ "version": "3.13.7"
+ }
+ },
+ "nbformat": 4,
+ "nbformat_minor": 5
+}
diff --git a/leetcode/maximum_subarray/solution.py b/leetcode/maximum_subarray/solution.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..2176165
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/maximum_subarray/solution.py
@@ -0,0 +1,11 @@
+class Solution:
+ # Time: O(n)
+ # Space: O(1)
+ def max_sub_array(self, nums: list[int]) -> int:
+ max_sum = current_sum = nums[0]
+
+ for i in range(1, len(nums)):
+ current_sum = max(nums[i], current_sum + nums[i])
+ max_sum = max(max_sum, current_sum)
+
+ return max_sum
diff --git a/leetcode/maximum_subarray/tests.py b/leetcode/maximum_subarray/tests.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..f186921
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/maximum_subarray/tests.py
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
+import pytest
+
+from leetcode_py.test_utils import logged_test
+
+from .solution import Solution
+
+
+class TestMaximumSubarray:
+ def setup_method(self):
+ self.solution = Solution()
+
+ @pytest.mark.parametrize(
+ "nums, expected",
+ [
+ ([-2, 1, -3, 4, -1, 2, 1, -5, 4], 6),
+ ([1], 1),
+ ([5, 4, -1, 7, 8], 23),
+ ([-1], -1),
+ ([-2, -1], -1),
+ ([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], 15),
+ ([-5, -2, -8, -1], -1),
+ ],
+ )
+ @logged_test
+ def test_max_sub_array(self, nums: list[int], expected: int):
+ result = self.solution.max_sub_array(nums)
+ assert result == expected
diff --git a/leetcode/minimum_window_substring/README.md b/leetcode/minimum_window_substring/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..f54b7da
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/minimum_window_substring/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
+# Minimum Window Substring
+
+**Difficulty:** Hard
+**Topics:** Hash Table, String, Sliding Window
+**Tags:** grind-75
+
+**LeetCode:** [Problem 76](https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-window-substring/description/)
+
+## Problem Description
+
+Given two strings `s` and `t` of lengths `m` and `n` respectively, return the **minimum window substring** of `s` such that every character in `t` (including duplicates) is included in the window. If there is no such substring, return the empty string `""`.
+
+The testcases will be generated such that the answer is unique.
+
+## Examples
+
+### Example 1:
+
+```
+Input: s = "ADOBECODEBANC", t = "ABC"
+Output: "BANC"
+```
+
+**Explanation:** The minimum window substring "BANC" includes 'A', 'B', and 'C' from string t.
+
+### Example 2:
+
+```
+Input: s = "a", t = "a"
+Output: "a"
+```
+
+**Explanation:** The entire string s is the minimum window.
+
+### Example 3:
+
+```
+Input: s = "a", t = "aa"
+Output: ""
+```
+
+**Explanation:** Both 'a's from t must be included in the window. Since the largest window of s only has one 'a', return empty string.
+
+## Constraints
+
+- `m == s.length`
+- `n == t.length`
+- `1 <= m, n <= 10^5`
+- `s` and `t` consist of uppercase and lowercase English letters.
+
+**Follow up:** Could you find an algorithm that runs in `O(m + n)` time?
diff --git a/leetcode/minimum_window_substring/__init__.py b/leetcode/minimum_window_substring/__init__.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e69de29
diff --git a/leetcode/minimum_window_substring/playground.ipynb b/leetcode/minimum_window_substring/playground.ipynb
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..1f99f98
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/minimum_window_substring/playground.ipynb
@@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
+{
+ "cells": [
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 1,
+ "id": "imports",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "from solution import Solution"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 2,
+ "id": "setup",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "# Example test case\n",
+ "s = \"ADOBECODEBANC\"\n",
+ "t = \"ABC\"\n",
+ "expected = \"BANC\""
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 3,
+ "id": "execute",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [
+ {
+ "data": {
+ "text/plain": [
+ "'BANC'"
+ ]
+ },
+ "execution_count": 3,
+ "metadata": {},
+ "output_type": "execute_result"
+ }
+ ],
+ "source": [
+ "result = Solution().min_window(s, t)\n",
+ "result"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 4,
+ "id": "test",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "assert result == expected"
+ ]
+ }
+ ],
+ "metadata": {
+ "kernelspec": {
+ "display_name": "leetcode-py-py3.13",
+ "language": "python",
+ "name": "python3"
+ },
+ "language_info": {
+ "codemirror_mode": {
+ "name": "ipython",
+ "version": 3
+ },
+ "file_extension": ".py",
+ "mimetype": "text/x-python",
+ "name": "python",
+ "nbconvert_exporter": "python",
+ "pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
+ "version": "3.13.7"
+ }
+ },
+ "nbformat": 4,
+ "nbformat_minor": 5
+}
diff --git a/leetcode/minimum_window_substring/solution.py b/leetcode/minimum_window_substring/solution.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..60bcb89
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/minimum_window_substring/solution.py
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
+from collections import Counter
+
+
+class Solution:
+ # Sliding Window
+ # Time: O(m + n) where m = len(s), n = len(t)
+ # Space: O(k) where k is unique chars in t
+ def min_window(self, s: str, t: str) -> str:
+ if not t or len(t) > len(s):
+ return ""
+
+ need = Counter(t)
+
+ left = 0
+ formed = 0
+ required = len(need)
+ window_counts: dict[str, int] = {}
+
+ # Result: (window length, left, right)
+ ans: tuple[float, int | None, int | None] = (float("inf"), None, None)
+
+ for right in range(len(s)):
+ char = s[right]
+ window_counts[char] = window_counts.get(char, 0) + 1
+
+ # Check if current char frequency matches desired frequency in t
+ if char in need and window_counts[char] == need[char]:
+ formed += 1
+
+ # Contract window until it's no longer valid
+ while left <= right and formed == required:
+ char = s[left]
+
+ # Update result if this window is smaller
+ if right - left + 1 < ans[0]:
+ ans = (right - left + 1, left, right)
+
+ # Remove from left
+ window_counts[char] -= 1
+ if char in need and window_counts[char] < need[char]:
+ formed -= 1
+
+ left += 1
+
+ if ans[0] == float("inf"):
+ return ""
+ assert ans[1] is not None and ans[2] is not None
+ return s[ans[1] : ans[2] + 1]
diff --git a/leetcode/minimum_window_substring/tests.py b/leetcode/minimum_window_substring/tests.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..8a3e16a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/minimum_window_substring/tests.py
@@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
+import pytest
+
+from leetcode_py.test_utils import logged_test
+
+from .solution import Solution
+
+
+class TestMinimumWindowSubstring:
+ def setup_method(self):
+ self.solution = Solution()
+
+ @pytest.mark.parametrize(
+ "s, t, expected",
+ [
+ # Basic cases
+ ("ADOBECODEBANC", "ABC", "BANC"),
+ ("a", "a", "a"),
+ ("a", "aa", ""),
+ # Edge cases
+ ("", "a", ""), # Empty s
+ ("a", "", ""), # Empty t
+ ("", "", ""), # Both empty
+ ("ab", "ba", "ab"), # Same length
+ ("abc", "cba", "abc"), # Entire string needed
+ # Duplicates
+ ("ADOBECODEBANC", "AABC", "ADOBECODEBA"), # Correct: needs 2 A's, 1 B, 1 C
+ ("aa", "aa", "aa"),
+ # No solution
+ ("abc", "def", ""),
+ ("a", "b", ""),
+ # Multiple valid windows
+ ("ADOBECODEBANC", "AB", "BA"), # Correct: "BA" is shorter than "ADOB"
+ ("abcdef", "cf", "cdef"),
+ ],
+ )
+ @logged_test
+ def test_min_window(self, s: str, t: str, expected: str):
+ result = self.solution.min_window(s, t)
+ assert result == expected
diff --git a/leetcode/reverse_linked_list_ii/README.md b/leetcode/reverse_linked_list_ii/README.md
index 7c005a6..1f7a098 100644
--- a/leetcode/reverse_linked_list_ii/README.md
+++ b/leetcode/reverse_linked_list_ii/README.md
@@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
**Difficulty:** Medium
**Topics:** Linked List
-**Tags:** grind-75
+**Tags:**
**LeetCode:** [Problem 92](https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-linked-list-ii/description/)
diff --git a/leetcode/search_in_rotated_sorted_array/README.md b/leetcode/search_in_rotated_sorted_array/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..f74397c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/search_in_rotated_sorted_array/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
+# Search in Rotated Sorted Array
+
+**Difficulty:** Medium
+**Topics:** Array, Binary Search
+**Tags:** grind-75
+
+**LeetCode:** [Problem 33](https://leetcode.com/problems/search-in-rotated-sorted-array/description/)
+
+## Problem Description
+
+There is an integer array `nums` sorted in ascending order (with **distinct** values).
+
+Prior to being passed to your function, `nums` is **possibly left rotated** at an unknown index `k` (`1 <= k < nums.length`) such that the resulting array is `[nums[k], nums[k+1], ..., nums[n-1], nums[0], nums[1], ..., nums[k-1]]` (**0-indexed**). For example, `[0,1,2,4,5,6,7]` might be left rotated by 3 indices and become `[4,5,6,7,0,1,2]`.
+
+Given the array `nums` **after** the possible rotation and an integer `target`, return _the index of_ `target` _if it is in_ `nums`_, or_ `-1` _if it is not in_ `nums`.
+
+You must write an algorithm with `O(log n)` runtime complexity.
+
+## Examples
+
+### Example 1:
+
+```
+Input: nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 0
+Output: 4
+```
+
+### Example 2:
+
+```
+Input: nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 3
+Output: -1
+```
+
+### Example 3:
+
+```
+Input: nums = [1], target = 0
+Output: -1
+```
+
+## Constraints
+
+- `1 <= nums.length <= 5000`
+- `-10^4 <= nums[i] <= 10^4`
+- All values of `nums` are **unique**.
+- `nums` is an ascending array that is possibly rotated.
+- `-10^4 <= target <= 10^4`
diff --git a/leetcode/search_in_rotated_sorted_array/__init__.py b/leetcode/search_in_rotated_sorted_array/__init__.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e69de29
diff --git a/leetcode/search_in_rotated_sorted_array/playground.ipynb b/leetcode/search_in_rotated_sorted_array/playground.ipynb
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..357fb33
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/search_in_rotated_sorted_array/playground.ipynb
@@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
+{
+ "cells": [
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 1,
+ "id": "imports",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "from solution import Solution"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 2,
+ "id": "setup",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "# Example test case\n",
+ "nums = [4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 1, 2]\n",
+ "target = 0\n",
+ "expected = 4"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 3,
+ "id": "execute",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [
+ {
+ "data": {
+ "text/plain": [
+ "4"
+ ]
+ },
+ "execution_count": 3,
+ "metadata": {},
+ "output_type": "execute_result"
+ }
+ ],
+ "source": [
+ "result = Solution().search(nums, target)\n",
+ "result"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 4,
+ "id": "test",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "assert result == expected"
+ ]
+ }
+ ],
+ "metadata": {
+ "kernelspec": {
+ "display_name": "leetcode-py-py3.13",
+ "language": "python",
+ "name": "python3"
+ },
+ "language_info": {
+ "codemirror_mode": {
+ "name": "ipython",
+ "version": 3
+ },
+ "file_extension": ".py",
+ "mimetype": "text/x-python",
+ "name": "python",
+ "nbconvert_exporter": "python",
+ "pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
+ "version": "3.13.7"
+ }
+ },
+ "nbformat": 4,
+ "nbformat_minor": 5
+}
diff --git a/leetcode/search_in_rotated_sorted_array/solution.py b/leetcode/search_in_rotated_sorted_array/solution.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..d8af000
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/search_in_rotated_sorted_array/solution.py
@@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
+class Solution:
+ # Time: O(log n)
+ # Space: O(1)
+ def search(self, nums: list[int], target: int) -> int:
+ left, right = 0, len(nums) - 1
+
+ while left <= right:
+ mid = (left + right) // 2
+
+ if nums[mid] == target:
+ return mid
+
+ # Left half is sorted
+ if nums[left] <= nums[mid]:
+ if nums[left] <= target < nums[mid]:
+ right = mid - 1
+ else:
+ left = mid + 1
+ # Right half is sorted
+ else:
+ if nums[mid] < target <= nums[right]:
+ left = mid + 1
+ else:
+ right = mid - 1
+
+ return -1
diff --git a/leetcode/search_in_rotated_sorted_array/tests.py b/leetcode/search_in_rotated_sorted_array/tests.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..90cc27f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/search_in_rotated_sorted_array/tests.py
@@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
+import pytest
+
+from leetcode_py.test_utils import logged_test
+
+from .solution import Solution
+
+
+class TestSearchInRotatedSortedArray:
+ def setup_method(self):
+ self.solution = Solution()
+
+ @pytest.mark.parametrize(
+ "nums, target, expected",
+ [
+ # Original test cases
+ ([4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 1, 2], 0, 4),
+ ([4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 1, 2], 3, -1),
+ ([1], 0, -1),
+ ([1], 1, 0),
+ ([3, 1], 1, 1),
+ # No rotation (sorted array)
+ ([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], 3, 2),
+ ([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], 6, -1),
+ # Different rotation points
+ ([6, 7, 0, 1, 2, 4, 5], 0, 2),
+ ([6, 7, 0, 1, 2, 4, 5], 4, 5),
+ ([6, 7, 0, 1, 2, 4, 5], 7, 1),
+ ([2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 1], 0, 6),
+ # Target at boundaries
+ ([4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 1, 2], 4, 0),
+ ([4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 1, 2], 2, 6),
+ # Two elements
+ ([2, 1], 1, 1),
+ ([2, 1], 2, 0),
+ ([1, 3], 3, 1),
+ ],
+ )
+ @logged_test
+ def test_search(self, nums: list[int], target: int, expected: int):
+ result = self.solution.search(nums, target)
+ assert result == expected
diff --git a/leetcode/spiral_matrix/tests.py b/leetcode/spiral_matrix/tests.py
index bb12705..8e3233c 100644
--- a/leetcode/spiral_matrix/tests.py
+++ b/leetcode/spiral_matrix/tests.py
@@ -12,8 +12,26 @@ def setup_method(self):
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
"matrix, expected",
[
+ # Original cases
([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]], [1, 2, 3, 6, 9, 8, 7, 4, 5]),
([[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8], [9, 10, 11, 12]], [1, 2, 3, 4, 8, 12, 11, 10, 9, 5, 6, 7]),
+ # Single element
+ ([[1]], [1]),
+ # Single row
+ ([[1, 2, 3, 4]], [1, 2, 3, 4]),
+ # Single column
+ ([[1], [2], [3]], [1, 2, 3]),
+ # 2x2 matrix
+ ([[1, 2], [3, 4]], [1, 2, 4, 3]),
+ # 1x2 matrix
+ ([[1, 2]], [1, 2]),
+ # 2x1 matrix
+ ([[1], [2]], [1, 2]),
+ # Larger square matrix
+ (
+ [[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8], [9, 10, 11, 12], [13, 14, 15, 16]],
+ [1, 2, 3, 4, 8, 12, 16, 15, 14, 13, 9, 5, 6, 7, 11, 10],
+ ),
],
)
@logged_test
diff --git a/leetcode/valid_palindrome/README.md b/leetcode/valid_palindrome/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e2444ef
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/valid_palindrome/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
+# Valid Palindrome
+
+**Difficulty:** Easy
+**Topics:** Two Pointers, String
+**Tags:** grind-75
+
+**LeetCode:** [Problem 125](https://leetcode.com/problems/valid-palindrome/description/)
+
+## Problem Description
+
+A phrase is a **palindrome** if, after converting all uppercase letters into lowercase letters and removing all non-alphanumeric characters, it reads the same forward and backward. Alphanumeric characters include letters and numbers.
+
+Given a string `s`, return `true` if it is a **palindrome**, or `false` otherwise.
+
+## Examples
+
+### Example 1:
+
+```
+Input: s = "A man, a plan, a canal: Panama"
+Output: true
+```
+
+**Explanation:** "amanaplanacanalpanama" is a palindrome.
+
+### Example 2:
+
+```
+Input: s = "race a car"
+Output: false
+```
+
+**Explanation:** "raceacar" is not a palindrome.
+
+### Example 3:
+
+```
+Input: s = " "
+Output: true
+```
+
+**Explanation:** s is an empty string "" after removing non-alphanumeric characters. Since an empty string reads the same forward and backward, it is a palindrome.
+
+## Constraints
+
+- `1 <= s.length <= 2 * 10^5`
+- `s` consists only of printable ASCII characters.
diff --git a/leetcode/valid_palindrome/__init__.py b/leetcode/valid_palindrome/__init__.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e69de29
diff --git a/leetcode/valid_palindrome/playground.ipynb b/leetcode/valid_palindrome/playground.ipynb
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..981f5a4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/valid_palindrome/playground.ipynb
@@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
+{
+ "cells": [
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "imports",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": ["from solution import Solution"]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "setup",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": ["# Example test case\ns = \"A man, a plan, a canal: Panama\"\nexpected = True"]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "execute",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": ["result = Solution().is_palindrome(s)\nresult"]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "test",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": ["assert result == expected"]
+ }
+ ],
+ "metadata": {
+ "kernelspec": {
+ "display_name": "leetcode-py-py3.13",
+ "language": "python",
+ "name": "python3"
+ },
+ "language_info": {
+ "codemirror_mode": {
+ "name": "ipython",
+ "version": 3
+ },
+ "file_extension": ".py",
+ "mimetype": "text/x-python",
+ "name": "python",
+ "nbconvert_exporter": "python3",
+ "pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
+ "version": "3.13.7"
+ }
+ },
+ "nbformat": 4,
+ "nbformat_minor": 5
+}
diff --git a/leetcode/valid_palindrome/solution.py b/leetcode/valid_palindrome/solution.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e2eba71
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/valid_palindrome/solution.py
@@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
+class Solution:
+ # Time: O(n)
+ # Space: O(1)
+ def is_palindrome(self, s: str) -> bool:
+ left, right = 0, len(s) - 1
+
+ while left < right:
+ while left < right and not s[left].isalnum():
+ left += 1
+ while left < right and not s[right].isalnum():
+ right -= 1
+
+ if s[left].lower() != s[right].lower():
+ return False
+
+ left += 1
+ right -= 1
+
+ return True
diff --git a/leetcode/valid_palindrome/tests.py b/leetcode/valid_palindrome/tests.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..a029400
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/valid_palindrome/tests.py
@@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
+import pytest
+
+from leetcode_py.test_utils import logged_test
+
+from .solution import Solution
+
+
+class TestValidPalindrome:
+ def setup_method(self):
+ self.solution = Solution()
+
+ @pytest.mark.parametrize(
+ "s, expected",
+ [
+ ("A man, a plan, a canal: Panama", True),
+ ("race a car", False),
+ (" ", True),
+ ("", True),
+ ("a", True),
+ ("Madam", True),
+ ("No 'x' in Nixon", True),
+ ("Mr. Owl ate my metal worm", True),
+ ],
+ )
+ @logged_test
+ def test_is_palindrome(self, s: str, expected: bool):
+ result = self.solution.is_palindrome(s)
+ assert result == expected
diff --git a/leetcode_py/data_structures/list_node.py b/leetcode_py/data_structures/list_node.py
index c5b5409..0d873b7 100644
--- a/leetcode_py/data_structures/list_node.py
+++ b/leetcode_py/data_structures/list_node.py
@@ -20,24 +20,111 @@ def from_list(cls, arr: list[T]) -> "ListNode[T] | None":
current = current.next
return head
- def to_list(self) -> list[T]:
- result = []
+ def _has_cycle(self) -> bool:
+ """Use Floyd's algorithm to detect if list has a cycle."""
+ slow = fast = self
+ while fast and fast.next and fast.next.next:
+ assert slow.next is not None
+ slow = slow.next
+ fast = fast.next.next
+ if slow is fast: # Use identity comparison to avoid recursion
+ return True
+ return False
+
+ def to_list(self, max_length: int = 1000) -> list[T]:
+ result: list[T] = []
current: "ListNode[T] | None" = self
- while current:
+ visited: set[int] = set()
+
+ while current and len(result) < max_length:
+ if id(current) in visited:
+ # Cycle detected
+ break
+ visited.add(id(current))
result.append(current.val)
current = current.next
return result
def __str__(self) -> str:
- return " -> ".join(str(val) for val in self.to_list())
+ if self._has_cycle():
+ # Show cycle with target value
+ result: list[str] = []
+ current: "ListNode[T] | None" = self
+ visited: dict[int, int] = {}
+ position = 0
+
+ while current:
+ if id(current) in visited:
+ cycle_pos = visited[id(current)]
+ cycle_val = result[cycle_pos]
+ result_str = " -> ".join(result)
+ return f"{result_str} -> ... (cycle back to {cycle_val})"
+
+ visited[id(current)] = position
+ result.append(str(current.val))
+ current = current.next
+ position += 1
+
+ values = self.to_list()
+ result_str = " -> ".join(str(val) for val in values)
+ if len(values) >= 1000:
+ result_str += " -> ... (long list)"
+ return result_str
def __repr__(self) -> str:
return f"{self.__class__.__name__}({self.to_list()})"
def _repr_html_(self) -> str:
- return self.__str__()
+ """Generate HTML representation using Graphviz for Jupyter notebooks."""
+ try:
+ import graphviz
+ except ImportError:
+ return f"
`
+ - Common patterns: `kthtree1.jpg`, `kthtree2.jpg`, `clone_graph.png`, `container.jpg`
+ - Images provide crucial visual context, especially for tree and graph problems
+ - Always verify images are included in `readme_examples` and accessible
+4. **Create** JSON file in `.templates/leetcode/json/{problem_name}.json`
+5. **Update** Makefile with `PROBLEM ?= {problem_name}`
+6. **Generate** problem structure using `make p-gen`
+7. **Verify** with `make lint` - fix template issues in JSON if possible, or manually fix generated files if template limitations
+8. **Iterate** if JSON fixes: re-run `make p-gen PROBLEM={problem_name} FORCE=1` and `make lint` until passes to ensure reproducibility
## Scraping Commands
@@ -46,7 +52,7 @@ Required fields for `.templates/leetcode/json/{problem_name}.json`:
"readme_description": "Given an array of integers `nums` and an integer `target`, return indices of the two numbers such that they add up to `target`.",
"readme_examples": [
{
- "content": "```\nInput: nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9\nOutput: [0,1]\n```\n**Explanation:** Because nums[0] + nums[1] == 9, we return [0, 1]."
+ "content": "\n\n```\nInput: nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9\nOutput: [0,1]\n```\n**Explanation:** Because nums[0] + nums[1] == 9, we return [0, 1]."
}
],
"readme_constraints": "- 2 <= nums.length <= 10^4\n- -10^9 <= nums[i] <= 10^9\n- -10^9 <= target <= 10^9\n- Only one valid answer exists.",
diff --git a/.templates/leetcode/json/binary_search.json b/.templates/leetcode/json/binary_search.json
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..ed3b7c4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.templates/leetcode/json/binary_search.json
@@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
+{
+ "problem_name": "binary_search",
+ "solution_class_name": "Solution",
+ "problem_number": "704",
+ "problem_title": "Binary Search",
+ "difficulty": "Easy",
+ "topics": "Array, Binary Search",
+ "tags": ["grind-75"],
+ "readme_description": "Given an array of integers `nums` which is sorted in ascending order, and an integer `target`, write a function to search `target` in `nums`. If `target` exists, then return its index. Otherwise, return `-1`.\n\nYou must write an algorithm with `O(log n)` runtime complexity.",
+ "readme_examples": [
+ {
+ "content": "```\nInput: nums = [-1,0,3,5,9,12], target = 9\nOutput: 4\n```\n**Explanation:** 9 exists in nums and its index is 4"
+ },
+ {
+ "content": "```\nInput: nums = [-1,0,3,5,9,12], target = 2\nOutput: -1\n```\n**Explanation:** 2 does not exist in nums so return -1"
+ }
+ ],
+ "readme_constraints": "- `1 <= nums.length <= 10^4`\n- `-10^4 < nums[i], target < 10^4`\n- All the integers in `nums` are **unique**.\n- `nums` is sorted in ascending order.",
+ "readme_additional": "",
+ "solution_imports": "",
+ "solution_methods": [
+ {
+ "name": "search",
+ "parameters": "nums: list[int], target: int",
+ "return_type": "int",
+ "dummy_return": "-1"
+ }
+ ],
+ "test_imports": "import pytest\nfrom leetcode_py.test_utils import logged_test\nfrom .solution import Solution",
+ "test_class_name": "BinarySearch",
+ "test_helper_methods": [
+ { "name": "setup_method", "parameters": "", "body": "self.solution = Solution()" }
+ ],
+ "test_methods": [
+ {
+ "name": "test_search",
+ "parametrize": "nums, target, expected",
+ "parametrize_typed": "nums: list[int], target: int, expected: int",
+ "test_cases": "[([\u22121, 0, 3, 5, 9, 12], 9, 4), ([\u22121, 0, 3, 5, 9, 12], 2, \u22121), ([5], 5, 0), ([5], \u22125, \u22121), ([1, 3, 5, 7, 9], 1, 0), ([1, 3, 5, 7, 9], 9, 4), ([1, 3, 5, 7, 9], 4, \u22121)]",
+ "body": "result = self.solution.search(nums, target)\nassert result == expected"
+ }
+ ],
+ "playground_imports": "from solution import Solution",
+ "playground_test_case": "# Example test case\nnums = [-1, 0, 3, 5, 9, 12]\ntarget = 9\nexpected = 4",
+ "playground_execution": "result = Solution().search(nums, target)\nresult",
+ "playground_assertion": "assert result == expected"
+}
diff --git a/.templates/leetcode/json/k_closest_points_to_origin.json b/.templates/leetcode/json/k_closest_points_to_origin.json
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..25e7cfa
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.templates/leetcode/json/k_closest_points_to_origin.json
@@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
+{
+ "problem_name": "k_closest_points_to_origin",
+ "solution_class_name": "Solution",
+ "problem_number": "973",
+ "problem_title": "K Closest Points to Origin",
+ "difficulty": "Medium",
+ "topics": "Array, Math, Divide and Conquer, Geometry, Sorting, Heap (Priority Queue), Quickselect",
+ "tags": ["grind-75"],
+ "readme_description": "Given an array of `points` where `points[i] = [xi, yi]` represents a point on the **X-Y** plane and an integer `k`, return the `k` closest points to the origin `(0, 0)`.\n\nThe distance between two points on the **X-Y** plane is the Euclidean distance (i.e., `\u221a(x1 - x2)\u00b2 + (y1 - y2)\u00b2`).\n\nYou may return the answer in **any order**. The answer is **guaranteed** to be **unique** (except for the order that it is in).",
+ "readme_examples": [
+ {
+ "content": "\n\n```\nInput: points = [[1,3],[-2,2]], k = 1\nOutput: [[-2,2]]\n```\n**Explanation:** The distance between (1, 3) and the origin is sqrt(10). The distance between (-2, 2) and the origin is sqrt(8). Since sqrt(8) < sqrt(10), (-2, 2) is closer to the origin. We only want the closest k = 1 points from the origin, so the answer is just [[-2,2]]."
+ },
+ {
+ "content": "```\nInput: points = [[3,3],[5,-1],[-2,4]], k = 2\nOutput: [[3,3],[-2,4]]\n```\n**Explanation:** The answer [[-2,4],[3,3]] would also be accepted."
+ }
+ ],
+ "readme_constraints": "- `1 <= k <= points.length <= 10^4`\n- `-10^4 <= xi, yi <= 10^4`",
+ "readme_additional": "",
+ "solution_imports": "",
+ "solution_methods": [
+ {
+ "name": "k_closest",
+ "parameters": "points: list[list[int]], k: int",
+ "return_type": "list[list[int]]",
+ "dummy_return": "[]"
+ }
+ ],
+ "test_imports": "import pytest\nfrom leetcode_py.test_utils import logged_test\nfrom .solution import Solution",
+ "test_class_name": "KClosestPointsToOrigin",
+ "test_helper_methods": [
+ { "name": "setup_method", "parameters": "", "body": "self.solution = Solution()" }
+ ],
+ "test_methods": [
+ {
+ "name": "test_k_closest",
+ "parametrize": "points, k, expected",
+ "parametrize_typed": "points: list[list[int]], k: int, expected: list[list[int]]",
+ "test_cases": "[([[1, 3], [-2, 2]], 1, [[-2, 2]]), ([[3, 3], [5, -1], [-2, 4]], 2, [[3, 3], [-2, 4]]), ([[0, 1], [1, 0]], 2, [[0, 1], [1, 0]]), ([[1, 1], [1, 1], [1, 1]], 2, [[1, 1], [1, 1]])]",
+ "body": "result = self.solution.k_closest(points, k)\n# Sort both result and expected for comparison since order doesn't matter\nresult_sorted = sorted(result)\nexpected_sorted = sorted(expected)\nassert result_sorted == expected_sorted"
+ }
+ ],
+ "playground_imports": "from solution import Solution",
+ "playground_test_case": "# Example test case\npoints = [[1, 3], [-2, 2]]\nk = 1\nexpected = [[-2, 2]]",
+ "playground_execution": "result = Solution().k_closest(points, k)\nresult",
+ "playground_assertion": "assert sorted(result) == sorted(expected)"
+}
diff --git a/.templates/leetcode/json/kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst.json b/.templates/leetcode/json/kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst.json
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..3239379
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.templates/leetcode/json/kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst.json
@@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
+{
+ "problem_name": "kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst",
+ "solution_class_name": "Solution",
+ "problem_number": "230",
+ "problem_title": "Kth Smallest Element in a BST",
+ "difficulty": "Medium",
+ "topics": "Tree, Depth-First Search, Binary Search Tree, Binary Tree",
+ "tags": ["grind-75"],
+ "readme_description": "Given the `root` of a binary search tree, and an integer `k`, return the `k`th smallest value (1-indexed) of all the values of the nodes in the tree.",
+ "readme_examples": [
+ {
+ "content": "\n\n```\nInput: root = [3,1,4,null,2], k = 1\nOutput: 1\n```"
+ },
+ {
+ "content": "\n\n```\nInput: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,null,1], k = 3\nOutput: 3\n```"
+ }
+ ],
+ "readme_constraints": "- The number of nodes in the tree is `n`.\n- `1 <= k <= n <= 10^4`\n- `0 <= Node.val <= 10^4`",
+ "readme_additional": "**Follow up:** If the BST is modified often (i.e., we can do insert and delete operations) and you need to find the kth smallest frequently, how would you optimize?",
+ "solution_imports": "from leetcode_py import TreeNode",
+ "solution_methods": [
+ {
+ "name": "kth_smallest",
+ "parameters": "root: TreeNode | None, k: int",
+ "return_type": "int",
+ "dummy_return": "0"
+ }
+ ],
+ "test_imports": "import pytest\nfrom leetcode_py.test_utils import logged_test\nfrom leetcode_py import TreeNode\nfrom .solution import Solution",
+ "test_class_name": "KthSmallestElementInABst",
+ "test_helper_methods": [
+ { "name": "setup_method", "parameters": "", "body": "self.solution = Solution()" }
+ ],
+ "test_methods": [
+ {
+ "name": "test_kth_smallest",
+ "parametrize": "root_list, k, expected",
+ "parametrize_typed": "root_list: list[int | None], k: int, expected: int",
+ "test_cases": "[([3, 1, 4, None, 2], 1, 1), ([5, 3, 6, 2, 4, None, None, 1], 3, 3), ([1], 1, 1)]",
+ "body": "root = TreeNode.from_list(root_list)\nresult = self.solution.kth_smallest(root, k)\nassert result == expected"
+ }
+ ],
+ "playground_imports": "from solution import Solution\nfrom leetcode_py import TreeNode",
+ "playground_test_case": "# Example test case\nroot_list = [3, 1, 4, None, 2]\nk = 1\nexpected = 1",
+ "playground_execution": "root = TreeNode.from_list(root_list)\nresult = Solution().kth_smallest(root, k)\nresult",
+ "playground_assertion": "assert result == expected"
+}
diff --git a/.templates/leetcode/json/linked_list_cycle.json b/.templates/leetcode/json/linked_list_cycle.json
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..ae5dd54
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.templates/leetcode/json/linked_list_cycle.json
@@ -0,0 +1,55 @@
+{
+ "problem_name": "linked_list_cycle",
+ "solution_class_name": "Solution",
+ "problem_number": "141",
+ "problem_title": "Linked List Cycle",
+ "difficulty": "Easy",
+ "topics": "Hash Table, Linked List, Two Pointers",
+ "tags": ["grind-75"],
+ "readme_description": "Given `head`, the head of a linked list, determine if the linked list has a cycle in it.\n\nThere is a cycle in a linked list if there is some node in the list that can be reached again by continuously following the `next` pointer. Internally, `pos` is used to denote the index of the node that tail's `next` pointer is connected to. **Note that `pos` is not passed as a parameter**.\n\nReturn `true` *if there is a cycle in the linked list*. Otherwise, return `false`.",
+ "readme_examples": [
+ {
+ "content": "\n\n```\nInput: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1\nOutput: true\n```\n**Explanation:** There is a cycle in the linked list, where the tail connects to the 1st node (0-indexed)."
+ },
+ {
+ "content": "\n\n```\nInput: head = [1,2], pos = 0\nOutput: true\n```\n**Explanation:** There is a cycle in the linked list, where the tail connects to the 0th node."
+ },
+ {
+ "content": "\n\n```\nInput: head = [1], pos = -1\nOutput: false\n```\n**Explanation:** There is no cycle in the linked list."
+ }
+ ],
+ "readme_constraints": "- The number of the nodes in the list is in the range `[0, 10^4]`.\n- `-10^5 <= Node.val <= 10^5`\n- `pos` is `-1` or a **valid index** in the linked-list.",
+ "readme_additional": "**Follow up:** Can you solve it using `O(1)` (i.e. constant) memory?",
+ "solution_imports": "from leetcode_py import ListNode",
+ "solution_methods": [
+ {
+ "name": "has_cycle",
+ "parameters": "head: ListNode[int] | None",
+ "return_type": "bool",
+ "dummy_return": "False"
+ }
+ ],
+ "test_imports": "import pytest\nfrom leetcode_py import ListNode\nfrom leetcode_py.test_utils import logged_test\nfrom .solution import Solution",
+ "test_class_name": "LinkedListCycle",
+ "test_helper_methods": [
+ { "name": "setup_method", "parameters": "", "body": "self.solution = Solution()" },
+ {
+ "name": "create_cycle_list",
+ "parameters": "values: list[int], pos: int",
+ "body": "if not values:\n return None\n\nnodes = []\nhead = ListNode(values[0])\nnodes.append(head)\ncurrent = head\n\nfor i in range(1, len(values)):\n current.next = ListNode(values[i])\n current = current.next\n nodes.append(current)\n\nif pos != -1 and pos < len(nodes):\n current.next = nodes[pos]\n\nreturn head"
+ }
+ ],
+ "test_methods": [
+ {
+ "name": "test_has_cycle",
+ "parametrize": "values, pos, expected",
+ "parametrize_typed": "values: list[int], pos: int, expected: bool",
+ "test_cases": "[([3, 2, 0, -4], 1, True), ([1, 2], 0, True), ([1], -1, False), ([], -1, False), ([1, 2, 3], -1, False), ([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], 0, True), ([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], 2, True), ([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], 4, True), ([1], 0, True), ([1, 2], 1, True), ([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8], 3, True), ([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8], -1, False), ([1, 2], -1, False), ([5, 10], 0, True), ([5, 10], 1, True), ([0], -1, False), ([-1, -2, -3], 1, True), ([100, 200, 300], 0, True)]",
+ "body": "head = self.create_cycle_list(values, pos)\nresult = self.solution.has_cycle(head)\nassert result == expected"
+ }
+ ],
+ "playground_imports": "from solution import Solution",
+ "playground_test_case": "import os\nimport sys\nsys.path.append(os.path.join(os.getcwd(), \\\"..\\\"))\nfrom linked_list_cycle.tests import TestLinkedListCycle\n\n# Example test case\nvalues = [3, 2, 0, -4]\npos = 1\nexpected = True",
+ "playground_execution": "head = TestLinkedListCycle().create_cycle_list(values, pos)\nresult = Solution().has_cycle(head)\nresult",
+ "playground_assertion": "assert result == expected"
+}
diff --git a/.templates/leetcode/json/lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree.json b/.templates/leetcode/json/lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree.json
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..eb71d4b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.templates/leetcode/json/lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree.json
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
+{
+ "problem_name": "lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree",
+ "solution_class_name": "Solution",
+ "problem_number": "235",
+ "problem_title": "Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Search Tree",
+ "difficulty": "Medium",
+ "topics": "Tree, Depth-First Search, Binary Search Tree, Binary Tree",
+ "tags": ["grind-75"],
+ "readme_description": "Given a binary search tree (BST), find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) node of two given nodes in the BST.\n\nAccording to the definition of LCA on Wikipedia: \"The lowest common ancestor is defined between two nodes `p` and `q` as the lowest node in `T` that has both `p` and `q` as descendants (where we allow **a node to be a descendant of itself**).\"",
+ "readme_examples": [
+ {
+ "content": "\n\n```\nInput: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 8\nOutput: 6\n```\n**Explanation:** The LCA of nodes 2 and 8 is 6."
+ },
+ {
+ "content": "\n\n```\nInput: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 4\nOutput: 2\n```\n**Explanation:** The LCA of nodes 2 and 4 is 2, since a node can be a descendant of itself according to the LCA definition."
+ },
+ { "content": "```\nInput: root = [2,1], p = 2, q = 1\nOutput: 2\n```" }
+ ],
+ "readme_constraints": "- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range `[2, 10^5]`.\n- `-10^9 <= Node.val <= 10^9`\n- All `Node.val` are **unique**.\n- `p != q`\n- `p` and `q` will exist in the BST.",
+ "readme_additional": "",
+ "solution_imports": "from leetcode_py import TreeNode",
+ "solution_methods": [
+ {
+ "name": "lowest_common_ancestor",
+ "parameters": "root: TreeNode[int] | None, p: TreeNode[int], q: TreeNode[int]",
+ "return_type": "TreeNode[int] | None",
+ "dummy_return": "None"
+ }
+ ],
+ "test_imports": "import pytest\nfrom leetcode_py import TreeNode\nfrom leetcode_py.test_utils import logged_test\nfrom .solution import Solution",
+ "test_class_name": "LowestCommonAncestorOfABinarySearchTree",
+ "test_helper_methods": [
+ { "name": "setup_method", "parameters": "", "body": "self.solution = Solution()" },
+ {
+ "name": "_find_node",
+ "parameters": "root: TreeNode[int], val: int",
+ "body": "if not root:\n return None\nif root.val == val:\n return root\nleft = self._find_node(root.left, val)\nif left:\n return left\nreturn self._find_node(root.right, val)"
+ }
+ ],
+ "test_methods": [
+ {
+ "name": "test_lowest_common_ancestor",
+ "parametrize": "root_list, p_val, q_val, expected_val",
+ "parametrize_typed": "root_list: list[int | None], p_val: int, q_val: int, expected_val: int",
+ "test_cases": "[([6, 2, 8, 0, 4, 7, 9, None, None, 3, 5], 2, 8, 6), ([6, 2, 8, 0, 4, 7, 9, None, None, 3, 5], 2, 4, 2), ([2, 1], 2, 1, 2), ([2, 1], 1, 2, 2), ([6, 2, 8, 0, 4, 7, 9], 0, 4, 2), ([6, 2, 8, 0, 4, 7, 9], 7, 9, 8)]",
+ "body": "root = TreeNode[int].from_list(root_list)\nassert root is not None\np = self._find_node(root, p_val)\nq = self._find_node(root, q_val)\nassert p is not None and q is not None\nresult = self.solution.lowest_common_ancestor(root, p, q)\nassert result is not None\nassert result.val == expected_val"
+ }
+ ],
+ "playground_imports": "from leetcode_py import TreeNode\nfrom solution import Solution",
+ "playground_test_case": "# Example test case\nroot_list = [6, 2, 8, 0, 4, 7, 9, None, None, 3, 5]\np_val = 2\nq_val = 8\nexpected_val = 6",
+ "playground_execution": "root = TreeNode[int].from_list(root_list)\np = find_node(root, p_val)\nq = find_node(root, q_val)\nresult = Solution().lowest_common_ancestor(root, p, q)\nresult.val if result else None",
+ "playground_assertion": "assert result and result.val == expected_val"
+}
diff --git a/.templates/leetcode/json/maximum_subarray.json b/.templates/leetcode/json/maximum_subarray.json
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..50da7c2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.templates/leetcode/json/maximum_subarray.json
@@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
+{
+ "problem_name": "maximum_subarray",
+ "solution_class_name": "Solution",
+ "problem_number": "53",
+ "problem_title": "Maximum Subarray",
+ "difficulty": "Medium",
+ "topics": "Array, Divide and Conquer, Dynamic Programming",
+ "tags": ["grind-75"],
+ "readme_description": "Given an integer array `nums`, find the subarray with the largest sum, and return its sum.",
+ "readme_examples": [
+ {
+ "content": "```\nInput: nums = [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4]\nOutput: 6\n```\n**Explanation:** The subarray [4,-1,2,1] has the largest sum 6."
+ },
+ {
+ "content": "```\nInput: nums = [1]\nOutput: 1\n```\n**Explanation:** The subarray [1] has the largest sum 1."
+ },
+ {
+ "content": "```\nInput: nums = [5,4,-1,7,8]\nOutput: 23\n```\n**Explanation:** The subarray [5,4,-1,7,8] has the largest sum 23."
+ }
+ ],
+ "readme_constraints": "- `1 <= nums.length <= 10^5`\n- `-10^4 <= nums[i] <= 10^4`",
+ "readme_additional": "**Follow up:** If you have figured out the `O(n)` solution, try coding another solution using the **divide and conquer** approach, which is more subtle.",
+ "solution_imports": "",
+ "solution_methods": [
+ {
+ "name": "max_sub_array",
+ "parameters": "nums: list[int]",
+ "return_type": "int",
+ "dummy_return": "0"
+ }
+ ],
+ "test_imports": "import pytest\nfrom leetcode_py.test_utils import logged_test\nfrom .solution import Solution",
+ "test_class_name": "MaximumSubarray",
+ "test_helper_methods": [
+ { "name": "setup_method", "parameters": "", "body": "self.solution = Solution()" }
+ ],
+ "test_methods": [
+ {
+ "name": "test_max_sub_array",
+ "parametrize": "nums, expected",
+ "parametrize_typed": "nums: list[int], expected: int",
+ "test_cases": "[([-2, 1, -3, 4, -1, 2, 1, -5, 4], 6), ([1], 1), ([5, 4, -1, 7, 8], 23), ([-1], -1), ([-2, -1], -1), ([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], 15), ([-5, -2, -8, -1], -1)]",
+ "body": "result = self.solution.max_sub_array(nums)\nassert result == expected"
+ }
+ ],
+ "playground_imports": "from solution import Solution",
+ "playground_test_case": "# Example test case\nnums = [-2, 1, -3, 4, -1, 2, 1, -5, 4]\nexpected = 6",
+ "playground_execution": "result = Solution().max_sub_array(nums)\nresult",
+ "playground_assertion": "assert result == expected"
+}
diff --git a/.templates/leetcode/json/minimum_window_substring.json b/.templates/leetcode/json/minimum_window_substring.json
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..a4d151b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.templates/leetcode/json/minimum_window_substring.json
@@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
+{
+ "problem_name": "minimum_window_substring",
+ "solution_class_name": "Solution",
+ "problem_number": "76",
+ "problem_title": "Minimum Window Substring",
+ "difficulty": "Hard",
+ "topics": "Hash Table, String, Sliding Window",
+ "tags": ["grind-75"],
+ "readme_description": "Given two strings `s` and `t` of lengths `m` and `n` respectively, return the **minimum window substring** of `s` such that every character in `t` (including duplicates) is included in the window. If there is no such substring, return the empty string `\"\"`.\n\nThe testcases will be generated such that the answer is unique.",
+ "readme_examples": [
+ {
+ "content": "```\nInput: s = \"ADOBECODEBANC\", t = \"ABC\"\nOutput: \"BANC\"\n```\n**Explanation:** The minimum window substring \"BANC\" includes 'A', 'B', and 'C' from string t."
+ },
+ {
+ "content": "```\nInput: s = \"a\", t = \"a\"\nOutput: \"a\"\n```\n**Explanation:** The entire string s is the minimum window."
+ },
+ {
+ "content": "```\nInput: s = \"a\", t = \"aa\"\nOutput: \"\"\n```\n**Explanation:** Both 'a's from t must be included in the window. Since the largest window of s only has one 'a', return empty string."
+ }
+ ],
+ "readme_constraints": "- `m == s.length`\n- `n == t.length`\n- `1 <= m, n <= 10^5`\n- `s` and `t` consist of uppercase and lowercase English letters.",
+ "readme_additional": "**Follow up:** Could you find an algorithm that runs in `O(m + n)` time?",
+ "solution_imports": "",
+ "solution_methods": [
+ {
+ "name": "min_window",
+ "parameters": "s: str, t: str",
+ "return_type": "str",
+ "dummy_return": "\"\""
+ }
+ ],
+ "test_imports": "import pytest\nfrom leetcode_py.test_utils import logged_test\nfrom .solution import Solution",
+ "test_class_name": "MinimumWindowSubstring",
+ "test_helper_methods": [
+ { "name": "setup_method", "parameters": "", "body": "self.solution = Solution()" }
+ ],
+ "test_methods": [
+ {
+ "name": "test_min_window",
+ "parametrize": "s, t, expected",
+ "parametrize_typed": "s: str, t: str, expected: str",
+ "test_cases": "[(\"ADOBECODEBANC\", \"ABC\", \"BANC\"), (\"a\", \"a\", \"a\"), (\"a\", \"aa\", \"\")]",
+ "body": "result = self.solution.min_window(s, t)\nassert result == expected"
+ }
+ ],
+ "playground_imports": "from solution import Solution",
+ "playground_test_case": "# Example test case\ns = \\\"ADOBECODEBANC\\\"\nt = \\\"ABC\\\"\nexpected = \\\"BANC\\\"",
+ "playground_execution": "result = Solution().min_window(s, t)\nresult",
+ "playground_assertion": "assert result == expected"
+}
diff --git a/.templates/leetcode/json/reverse_linked_list_ii.json b/.templates/leetcode/json/reverse_linked_list_ii.json
index 7c904e2..4eeb724 100644
--- a/.templates/leetcode/json/reverse_linked_list_ii.json
+++ b/.templates/leetcode/json/reverse_linked_list_ii.json
@@ -5,7 +5,7 @@
"problem_title": "Reverse Linked List II",
"difficulty": "Medium",
"topics": "Linked List",
- "tags": ["grind-75"],
+ "tags": [],
"readme_description": "Given the `head` of a singly linked list and two integers `left` and `right` where `left <= right`, reverse the nodes of the list from position `left` to position `right`, and return the reversed list.",
"readme_examples": [
{ "content": "```\nInput: head = [1,2,3,4,5], left = 2, right = 4\nOutput: [1,4,3,2,5]\n```" },
diff --git a/.templates/leetcode/json/search_in_rotated_sorted_array.json b/.templates/leetcode/json/search_in_rotated_sorted_array.json
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..1235416
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.templates/leetcode/json/search_in_rotated_sorted_array.json
@@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
+{
+ "problem_name": "search_in_rotated_sorted_array",
+ "solution_class_name": "Solution",
+ "problem_number": "33",
+ "problem_title": "Search in Rotated Sorted Array",
+ "difficulty": "Medium",
+ "topics": "Array, Binary Search",
+ "tags": ["grind-75"],
+ "readme_description": "There is an integer array `nums` sorted in ascending order (with **distinct** values).\n\nPrior to being passed to your function, `nums` is **possibly left rotated** at an unknown index `k` (`1 <= k < nums.length`) such that the resulting array is `[nums[k], nums[k+1], ..., nums[n-1], nums[0], nums[1], ..., nums[k-1]]` (**0-indexed**). For example, `[0,1,2,4,5,6,7]` might be left rotated by 3 indices and become `[4,5,6,7,0,1,2]`.\n\nGiven the array `nums` **after** the possible rotation and an integer `target`, return *the index of* `target` *if it is in* `nums`*, or* `-1` *if it is not in* `nums`.\n\nYou must write an algorithm with `O(log n)` runtime complexity.",
+ "readme_examples": [
+ { "content": "```\nInput: nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 0\nOutput: 4\n```" },
+ { "content": "```\nInput: nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 3\nOutput: -1\n```" },
+ { "content": "```\nInput: nums = [1], target = 0\nOutput: -1\n```" }
+ ],
+ "readme_constraints": "- `1 <= nums.length <= 5000`\n- `-10^4 <= nums[i] <= 10^4`\n- All values of `nums` are **unique**.\n- `nums` is an ascending array that is possibly rotated.\n- `-10^4 <= target <= 10^4`",
+ "readme_additional": "",
+ "solution_imports": "",
+ "solution_methods": [
+ {
+ "name": "search",
+ "parameters": "nums: list[int], target: int",
+ "return_type": "int",
+ "dummy_return": "-1"
+ }
+ ],
+ "test_imports": "import pytest\nfrom leetcode_py.test_utils import logged_test\nfrom .solution import Solution",
+ "test_class_name": "SearchInRotatedSortedArray",
+ "test_helper_methods": [
+ { "name": "setup_method", "parameters": "", "body": "self.solution = Solution()" }
+ ],
+ "test_methods": [
+ {
+ "name": "test_search",
+ "parametrize": "nums, target, expected",
+ "parametrize_typed": "nums: list[int], target: int, expected: int",
+ "test_cases": "[([4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 1, 2], 0, 4), ([4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 1, 2], 3, -1), ([1], 0, -1), ([1], 1, 0), ([3, 1], 1, 1)]",
+ "body": "result = self.solution.search(nums, target)\nassert result == expected"
+ }
+ ],
+ "playground_imports": "from solution import Solution",
+ "playground_test_case": "# Example test case\nnums = [4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 1, 2]\ntarget = 0\nexpected = 4",
+ "playground_execution": "result = Solution().search(nums, target)\nresult",
+ "playground_assertion": "assert result == expected"
+}
diff --git a/.templates/leetcode/json/valid_palindrome.json b/.templates/leetcode/json/valid_palindrome.json
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..cb4b861
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.templates/leetcode/json/valid_palindrome.json
@@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
+{
+ "problem_name": "valid_palindrome",
+ "solution_class_name": "Solution",
+ "problem_number": "125",
+ "problem_title": "Valid Palindrome",
+ "difficulty": "Easy",
+ "topics": "Two Pointers, String",
+ "tags": ["grind-75"],
+ "readme_description": "A phrase is a **palindrome** if, after converting all uppercase letters into lowercase letters and removing all non-alphanumeric characters, it reads the same forward and backward. Alphanumeric characters include letters and numbers.\n\nGiven a string `s`, return `true` if it is a **palindrome**, or `false` otherwise.",
+ "readme_examples": [
+ {
+ "content": "```\nInput: s = \"A man, a plan, a canal: Panama\"\nOutput: true\n```\n**Explanation:** \"amanaplanacanalpanama\" is a palindrome."
+ },
+ {
+ "content": "```\nInput: s = \"race a car\"\nOutput: false\n```\n**Explanation:** \"raceacar\" is not a palindrome."
+ },
+ {
+ "content": "```\nInput: s = \" \"\nOutput: true\n```\n**Explanation:** s is an empty string \"\" after removing non-alphanumeric characters. Since an empty string reads the same forward and backward, it is a palindrome."
+ }
+ ],
+ "readme_constraints": "- `1 <= s.length <= 2 * 10^5`\n- `s` consists only of printable ASCII characters.",
+ "readme_additional": "",
+ "solution_imports": "",
+ "solution_methods": [
+ {
+ "name": "is_palindrome",
+ "parameters": "s: str",
+ "return_type": "bool",
+ "dummy_return": "False"
+ }
+ ],
+ "test_imports": "import pytest\nfrom leetcode_py.test_utils import logged_test\nfrom .solution import Solution",
+ "test_class_name": "ValidPalindrome",
+ "test_helper_methods": [
+ { "name": "setup_method", "parameters": "", "body": "self.solution = Solution()" }
+ ],
+ "test_methods": [
+ {
+ "name": "test_is_palindrome",
+ "parametrize": "s, expected",
+ "parametrize_typed": "s: str, expected: bool",
+ "test_cases": "[(\"A man, a plan, a canal: Panama\", True), (\"race a car\", False), (\" \", True), (\"\", True), (\"a\", True), (\"Madam\", True), (\"No 'x' in Nixon\", True), (\"Mr. Owl ate my metal worm\", True)]",
+ "body": "result = self.solution.is_palindrome(s)\nassert result == expected"
+ }
+ ],
+ "playground_imports": "from solution import Solution",
+ "playground_test_case": "# Example test case\ns = \"A man, a plan, a canal: Panama\"\nexpected = True",
+ "playground_execution": "result = Solution().is_palindrome(s)\nresult",
+ "playground_assertion": "assert result == expected"
+}
diff --git a/Makefile b/Makefile
index 91a7d24..d49ed4d 100644
--- a/Makefile
+++ b/Makefile
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
PYTHON_VERSION = 3.13
-PROBLEM ?= task_scheduler
+PROBLEM ?= k_closest_points_to_origin
FORCE ?= 0
sync_submodules:
diff --git a/leetcode/binary_search/README.md b/leetcode/binary_search/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..16d0461
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/binary_search/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
+# Binary Search
+
+**Difficulty:** Easy
+**Topics:** Array, Binary Search
+**Tags:** grind-75
+
+**LeetCode:** [Problem 704](https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-search/description/)
+
+## Problem Description
+
+Given an array of integers `nums` which is sorted in ascending order, and an integer `target`, write a function to search `target` in `nums`. If `target` exists, then return its index. Otherwise, return `-1`.
+
+You must write an algorithm with `O(log n)` runtime complexity.
+
+## Examples
+
+### Example 1:
+
+```
+Input: nums = [-1,0,3,5,9,12], target = 9
+Output: 4
+```
+
+**Explanation:** 9 exists in nums and its index is 4
+
+### Example 2:
+
+```
+Input: nums = [-1,0,3,5,9,12], target = 2
+Output: -1
+```
+
+**Explanation:** 2 does not exist in nums so return -1
+
+## Constraints
+
+- `1 <= nums.length <= 10^4`
+- `-10^4 < nums[i], target < 10^4`
+- All the integers in `nums` are **unique**.
+- `nums` is sorted in ascending order.
diff --git a/leetcode/binary_search/__init__.py b/leetcode/binary_search/__init__.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e69de29
diff --git a/leetcode/binary_search/playground.ipynb b/leetcode/binary_search/playground.ipynb
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..d7a58c0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/binary_search/playground.ipynb
@@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
+{
+ "cells": [
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "imports",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "from solution import Solution"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "setup",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "# Example test case\n",
+ "nums = [-1, 0, 3, 5, 9, 12]\n",
+ "target = 9\n",
+ "expected = 4"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "execute",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "result = Solution().search(nums, target)\n",
+ "result"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "test",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "assert result == expected"
+ ]
+ }
+ ],
+ "metadata": {
+ "kernelspec": {
+ "display_name": "leetcode-py-py3.13",
+ "language": "python",
+ "name": "python3"
+ },
+ "language_info": {
+ "codemirror_mode": {
+ "name": "ipython",
+ "version": 3
+ },
+ "file_extension": ".py",
+ "mimetype": "text/x-python",
+ "name": "python",
+ "nbconvert_exporter": "python3",
+ "pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
+ "version": "3.13.7"
+ }
+ },
+ "nbformat": 4,
+ "nbformat_minor": 5
+}
diff --git a/leetcode/binary_search/solution.py b/leetcode/binary_search/solution.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..7bc15e6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/binary_search/solution.py
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+class Solution:
+ # Time: O(log n)
+ # Space: O(1)
+ def search(self, nums: list[int], target: int) -> int:
+ left, right = 0, len(nums) - 1
+
+ while left <= right:
+ mid = (left + right) // 2
+
+ if nums[mid] == target:
+ return mid
+ elif nums[mid] < target:
+ left = mid + 1
+ else:
+ right = mid - 1
+
+ return -1
diff --git a/leetcode/binary_search/tests.py b/leetcode/binary_search/tests.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..0842386
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/binary_search/tests.py
@@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
+import pytest
+
+from leetcode_py.test_utils import logged_test
+
+from .solution import Solution
+
+
+class TestBinarySearch:
+ def setup_method(self):
+ self.solution = Solution()
+
+ @pytest.mark.parametrize(
+ "nums, target, expected",
+ [
+ # Original examples
+ ([-1, 0, 3, 5, 9, 12], 9, 4),
+ ([-1, 0, 3, 5, 9, 12], 2, -1),
+ # Single element
+ ([5], 5, 0),
+ ([5], -5, -1),
+ # Target at boundaries
+ ([1, 3, 5, 7, 9], 1, 0),
+ ([1, 3, 5, 7, 9], 9, 4),
+ # Target not found
+ ([1, 3, 5, 7, 9], 4, -1),
+ # Two elements
+ ([1, 3], 1, 0),
+ ([1, 3], 3, 1),
+ ([1, 3], 2, -1),
+ # Negative numbers
+ ([-5, -2, 0, 3, 7], -2, 1),
+ ([-5, -2, 0, 3, 7], 0, 2),
+ ([-5, -2, 0, 3, 7], -1, -1),
+ ],
+ )
+ @logged_test
+ def test_search(self, nums: list[int], target: int, expected: int):
+ result = self.solution.search(nums, target)
+ assert result == expected
diff --git a/leetcode/container_with_most_water/tests.py b/leetcode/container_with_most_water/tests.py
index ebc66be..2713d8d 100644
--- a/leetcode/container_with_most_water/tests.py
+++ b/leetcode/container_with_most_water/tests.py
@@ -10,7 +10,29 @@ def setup_method(self):
self.solution = Solution()
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
- "height, expected", [([1, 8, 6, 2, 5, 4, 8, 3, 7], 49), ([1, 1], 1), ([1, 2, 1], 2)]
+ "height, expected",
+ [
+ # Original cases
+ ([1, 8, 6, 2, 5, 4, 8, 3, 7], 49),
+ ([1, 1], 1),
+ ([1, 2, 1], 2),
+ # Edge cases
+ ([2, 1], 1),
+ ([1, 2], 1),
+ ([0, 2], 0),
+ ([2, 0], 0),
+ # Increasing heights
+ ([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], 6),
+ # Decreasing heights
+ ([5, 4, 3, 2, 1], 6),
+ # Same heights
+ ([3, 3, 3, 3], 9),
+ # Large differences
+ ([1, 1000, 1], 2),
+ ([1000, 1, 1000], 2000),
+ # Multiple peaks
+ ([2, 3, 4, 5, 18, 17, 6], 17),
+ ],
)
@logged_test
def test_max_area(self, height: list[int], expected: int):
diff --git a/leetcode/evaluate_reverse_polish_notation/tests.py b/leetcode/evaluate_reverse_polish_notation/tests.py
index 82c126b..f353e1f 100644
--- a/leetcode/evaluate_reverse_polish_notation/tests.py
+++ b/leetcode/evaluate_reverse_polish_notation/tests.py
@@ -12,9 +12,24 @@ def setup_method(self):
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
"tokens, expected",
[
+ # Original cases
(["2", "1", "+", "3", "*"], 9),
(["4", "13", "5", "/", "+"], 6),
(["10", "6", "9", "3", "+", "-11", "*", "/", "*", "17", "+", "5", "+"], 22),
+ # Single number
+ (["42"], 42),
+ # Negative numbers
+ (["-1"], -1),
+ (["1", "-1", "+"], 0),
+ # Basic operations
+ (["3", "4", "+"], 7),
+ (["5", "2", "-"], 3),
+ (["6", "3", "*"], 18),
+ (["8", "2", "/"], 4),
+ # Division with negatives
+ (["-3", "4", "+", "2", "*", "1", "-"], 1),
+ # Complex expression
+ (["15", "7", "1", "1", "+", "/", "/", "3", "*", "2", "1", "1", "+", "+", "-"], 11),
],
)
@logged_test
diff --git a/leetcode/insert_interval/tests.py b/leetcode/insert_interval/tests.py
index 6968af7..ee51e8f 100644
--- a/leetcode/insert_interval/tests.py
+++ b/leetcode/insert_interval/tests.py
@@ -12,8 +12,25 @@ def setup_method(self):
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
"intervals, new_interval, expected",
[
+ # Original cases
([[1, 3], [6, 9]], [2, 5], [[1, 5], [6, 9]]),
([[1, 2], [3, 5], [6, 7], [8, 10], [12, 16]], [4, 8], [[1, 2], [3, 10], [12, 16]]),
+ # Empty intervals
+ ([], [5, 7], [[5, 7]]),
+ # Insert at beginning
+ ([[3, 5], [6, 9]], [1, 2], [[1, 2], [3, 5], [6, 9]]),
+ # Insert at end
+ ([[1, 3], [6, 9]], [10, 12], [[1, 3], [6, 9], [10, 12]]),
+ # No overlap
+ ([[1, 2], [4, 5]], [3, 3], [[1, 2], [3, 3], [4, 5]]),
+ # Complete overlap
+ ([[1, 5]], [2, 3], [[1, 5]]),
+ # Merge all intervals
+ ([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]], [0, 7], [[0, 7]]),
+ # Adjacent intervals
+ ([[1, 3], [6, 9]], [4, 5], [[1, 3], [4, 5], [6, 9]]),
+ # Touch boundaries
+ ([[1, 3], [6, 9]], [3, 6], [[1, 9]]),
],
)
@logged_test
diff --git a/leetcode/k_closest_points_to_origin/README.md b/leetcode/k_closest_points_to_origin/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..54395ba
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/k_closest_points_to_origin/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
+# K Closest Points to Origin
+
+**Difficulty:** Medium
+**Topics:** Array, Math, Divide and Conquer, Geometry, Sorting, Heap (Priority Queue), Quickselect
+**Tags:** grind-75
+
+**LeetCode:** [Problem 973](https://leetcode.com/problems/k-closest-points-to-origin/description/)
+
+## Problem Description
+
+Given an array of `points` where `points[i] = [xi, yi]` represents a point on the **X-Y** plane and an integer `k`, return the `k` closest points to the origin `(0, 0)`.
+
+The distance between two points on the **X-Y** plane is the Euclidean distance (i.e., `√(x1 - x2)² + (y1 - y2)²`).
+
+You may return the answer in **any order**. The answer is **guaranteed** to be **unique** (except for the order that it is in).
+
+## Examples
+
+### Example 1:
+
+
+
+```
+Input: points = [[1,3],[-2,2]], k = 1
+Output: [[-2,2]]
+```
+
+**Explanation:** The distance between (1, 3) and the origin is sqrt(10). The distance between (-2, 2) and the origin is sqrt(8). Since sqrt(8) < sqrt(10), (-2, 2) is closer to the origin. We only want the closest k = 1 points from the origin, so the answer is just [[-2,2]].
+
+### Example 2:
+
+```
+Input: points = [[3,3],[5,-1],[-2,4]], k = 2
+Output: [[3,3],[-2,4]]
+```
+
+**Explanation:** The answer [[-2,4],[3,3]] would also be accepted.
+
+## Constraints
+
+- `1 <= k <= points.length <= 10^4`
+- `-10^4 <= xi, yi <= 10^4`
diff --git a/leetcode/k_closest_points_to_origin/__init__.py b/leetcode/k_closest_points_to_origin/__init__.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e69de29
diff --git a/leetcode/k_closest_points_to_origin/playground.ipynb b/leetcode/k_closest_points_to_origin/playground.ipynb
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..49a9238
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/k_closest_points_to_origin/playground.ipynb
@@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
+{
+ "cells": [
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "imports",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": ["from solution import Solution"]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "setup",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": ["# Example test case\npoints = [[1, 3], [-2, 2]]\nk = 1\nexpected = [[-2, 2]]"]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "execute",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": ["result = Solution().k_closest(points, k)\nresult"]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "test",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": ["assert sorted(result) == sorted(expected)"]
+ }
+ ],
+ "metadata": {
+ "kernelspec": {
+ "display_name": "leetcode-py-py3.13",
+ "language": "python",
+ "name": "python3"
+ },
+ "language_info": {
+ "codemirror_mode": {
+ "name": "ipython",
+ "version": 3
+ },
+ "file_extension": ".py",
+ "mimetype": "text/x-python",
+ "name": "python",
+ "nbconvert_exporter": "python3",
+ "pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
+ "version": "3.13.7"
+ }
+ },
+ "nbformat": 4,
+ "nbformat_minor": 5
+}
diff --git a/leetcode/k_closest_points_to_origin/solution.py b/leetcode/k_closest_points_to_origin/solution.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..d053d9b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/k_closest_points_to_origin/solution.py
@@ -0,0 +1,16 @@
+import heapq
+
+
+class Solution:
+ # Time: O(n log k)
+ # Space: O(k)
+ def k_closest(self, points: list[list[int]], k: int) -> list[list[int]]:
+ heap: list[tuple[int, list[int]]] = []
+
+ for x, y in points:
+ dist = x * x + y * y
+ heapq.heappush(heap, (-dist, [x, y]))
+ if len(heap) > k:
+ heapq.heappop(heap)
+
+ return [point for _, point in heap]
diff --git a/leetcode/k_closest_points_to_origin/tests.py b/leetcode/k_closest_points_to_origin/tests.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..296af1b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/k_closest_points_to_origin/tests.py
@@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
+import pytest
+
+from leetcode_py.test_utils import logged_test
+
+from .solution import Solution
+
+
+class TestKClosestPointsToOrigin:
+ def setup_method(self):
+ self.solution = Solution()
+
+ @pytest.mark.parametrize(
+ "points, k, expected",
+ [
+ # Basic examples
+ ([[1, 3], [-2, 2]], 1, [[-2, 2]]),
+ ([[3, 3], [5, -1], [-2, 4]], 2, [[3, 3], [-2, 4]]),
+ ([[0, 1], [1, 0]], 2, [[0, 1], [1, 0]]),
+ ([[1, 1], [1, 1], [1, 1]], 2, [[1, 1], [1, 1]]),
+ # Edge cases
+ ([[0, 0]], 1, [[0, 0]]), # Origin point
+ ([[1, 0], [0, 1], [-1, 0], [0, -1]], 1, [[1, 0]]), # Unit circle points
+ ([[2, 2], [1, 1], [3, 3]], 3, [[1, 1], [2, 2], [3, 3]]), # All points
+ # Negative coordinates
+ ([[-1, -1], [-2, -2], [1, 1]], 2, [[-1, -1], [1, 1]]),
+ # Large coordinates
+ ([[100, 100], [1, 1], [50, 50]], 1, [[1, 1]]),
+ # Same distances
+ ([[1, 0], [0, 1], [-1, 0], [0, -1]], 2, [[1, 0], [0, 1]]),
+ ],
+ )
+ @logged_test
+ def test_k_closest(self, points: list[list[int]], k: int, expected: list[list[int]]):
+ result = self.solution.k_closest(points, k)
+ # Sort both result and expected for comparison since order doesn't matter
+ result_sorted = sorted(result)
+ expected_sorted = sorted(expected)
+ assert result_sorted == expected_sorted
diff --git a/leetcode/kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/README.md b/leetcode/kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..fefde64
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
+# Kth Smallest Element in a BST
+
+**Difficulty:** Medium
+**Topics:** Tree, Depth-First Search, Binary Search Tree, Binary Tree
+**Tags:** grind-75
+
+**LeetCode:** [Problem 230](https://leetcode.com/problems/kth-smallest-element-in-a-bst/description/)
+
+## Problem Description
+
+Given the `root` of a binary search tree, and an integer `k`, return the `k`th smallest value (1-indexed) of all the values of the nodes in the tree.
+
+## Examples
+
+### Example 1:
+
+
+
+```
+Input: root = [3,1,4,null,2], k = 1
+Output: 1
+```
+
+### Example 2:
+
+
+
+```
+Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,null,1], k = 3
+Output: 3
+```
+
+## Constraints
+
+- The number of nodes in the tree is `n`.
+- `1 <= k <= n <= 10^4`
+- `0 <= Node.val <= 10^4`
+
+**Follow up:** If the BST is modified often (i.e., we can do insert and delete operations) and you need to find the kth smallest frequently, how would you optimize?
diff --git a/leetcode/kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/__init__.py b/leetcode/kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/__init__.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e69de29
diff --git a/leetcode/kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/playground.ipynb b/leetcode/kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/playground.ipynb
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..da34058
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/playground.ipynb
@@ -0,0 +1,160 @@
+{
+ "cells": [
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 1,
+ "id": "imports",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "from solution import Solution\n",
+ "\n",
+ "from leetcode_py import TreeNode"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 2,
+ "id": "setup",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "# Example test case\n",
+ "root_list = [3, 1, 4, None, 2]\n",
+ "k = 1\n",
+ "expected = 1"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 3,
+ "id": "execute",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [
+ {
+ "data": {
+ "text/plain": [
+ "1"
+ ]
+ },
+ "execution_count": 3,
+ "metadata": {},
+ "output_type": "execute_result"
+ }
+ ],
+ "source": [
+ "root = TreeNode.from_list(root_list)\n",
+ "result = Solution().kth_smallest(root, k)\n",
+ "result"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 4,
+ "id": "6dc42838",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [
+ {
+ "data": {
+ "text/html": [
+ "\n",
+ "\n",
+ "\n",
+ "\n",
+ "\n"
+ ],
+ "text/plain": [
+ "TreeNode([3, 1, 4, None, 2])"
+ ]
+ },
+ "execution_count": 4,
+ "metadata": {},
+ "output_type": "execute_result"
+ }
+ ],
+ "source": [
+ "root"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 5,
+ "id": "test",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "assert result == expected"
+ ]
+ }
+ ],
+ "metadata": {
+ "kernelspec": {
+ "display_name": "leetcode-py-py3.13",
+ "language": "python",
+ "name": "python3"
+ },
+ "language_info": {
+ "codemirror_mode": {
+ "name": "ipython",
+ "version": 3
+ },
+ "file_extension": ".py",
+ "mimetype": "text/x-python",
+ "name": "python",
+ "nbconvert_exporter": "python",
+ "pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
+ "version": "3.13.7"
+ }
+ },
+ "nbformat": 4,
+ "nbformat_minor": 5
+}
diff --git a/leetcode/kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/solution.py b/leetcode/kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/solution.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..57bd5db
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/solution.py
@@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
+from leetcode_py import TreeNode
+
+
+class Solution:
+ # Inorder Recursive
+ # Time: O(k)
+ # Space: O(h)
+ def kth_smallest(self, root: TreeNode | None, k: int) -> int:
+ def inorder(node: TreeNode | None):
+ if not node:
+ return
+ yield from inorder(node.left)
+ yield node.val
+ yield from inorder(node.right)
+
+ for i, val in enumerate(inorder(root)):
+ if i == k - 1:
+ return val
+
+ raise ValueError(f"Tree has fewer than {k} nodes")
+
+
+# Binary Tree Traversal Patterns
+#
+# def inorder(node):
+# if node:
+# inorder(node.left)
+# print(node.val)
+# inorder(node.right)
+#
+# def preorder(node):
+# if node:
+# print(node.val)
+# preorder(node.left)
+# preorder(node.right)
+#
+# def postorder(node):
+# if node:
+# postorder(node.left)
+# postorder(node.right)
+# print(node.val)
diff --git a/leetcode/kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/tests.py b/leetcode/kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/tests.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..1e52c52
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/kth_smallest_element_in_a_bst/tests.py
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
+import pytest
+
+from leetcode_py import TreeNode
+from leetcode_py.test_utils import logged_test
+
+from .solution import Solution
+
+
+class TestKthSmallestElementInABst:
+ def setup_method(self):
+ self.solution = Solution()
+
+ @pytest.mark.parametrize(
+ "root_list, k, expected",
+ [([3, 1, 4, None, 2], 1, 1), ([5, 3, 6, 2, 4, None, None, 1], 3, 3), ([1], 1, 1)],
+ )
+ @logged_test
+ def test_kth_smallest(self, root_list: list[int | None], k: int, expected: int):
+ root = TreeNode.from_list(root_list)
+ result = self.solution.kth_smallest(root, k)
+ assert result == expected
diff --git a/leetcode/linked_list_cycle/README.md b/leetcode/linked_list_cycle/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..4ec75c4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/linked_list_cycle/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
+# Linked List Cycle
+
+**Difficulty:** Easy
+**Topics:** Hash Table, Linked List, Two Pointers
+**Tags:** grind-75
+
+**LeetCode:** [Problem 141](https://leetcode.com/problems/linked-list-cycle/description/)
+
+## Problem Description
+
+Given `head`, the head of a linked list, determine if the linked list has a cycle in it.
+
+There is a cycle in a linked list if there is some node in the list that can be reached again by continuously following the `next` pointer. Internally, `pos` is used to denote the index of the node that tail's `next` pointer is connected to. **Note that `pos` is not passed as a parameter**.
+
+Return `true` _if there is a cycle in the linked list_. Otherwise, return `false`.
+
+## Examples
+
+### Example 1:
+
+
+
+```
+Input: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
+Output: true
+```
+
+**Explanation:** There is a cycle in the linked list, where the tail connects to the 1st node (0-indexed).
+
+### Example 2:
+
+
+
+```
+Input: head = [1,2], pos = 0
+Output: true
+```
+
+**Explanation:** There is a cycle in the linked list, where the tail connects to the 0th node.
+
+### Example 3:
+
+
+
+```
+Input: head = [1], pos = -1
+Output: false
+```
+
+**Explanation:** There is no cycle in the linked list.
+
+## Constraints
+
+- The number of the nodes in the list is in the range `[0, 10^4]`.
+- `-10^5 <= Node.val <= 10^5`
+- `pos` is `-1` or a **valid index** in the linked-list.
+
+**Follow up:** Can you solve it using `O(1)` (i.e. constant) memory?
diff --git a/leetcode/linked_list_cycle/__init__.py b/leetcode/linked_list_cycle/__init__.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e69de29
diff --git a/leetcode/linked_list_cycle/playground.ipynb b/leetcode/linked_list_cycle/playground.ipynb
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..7f74fb3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/linked_list_cycle/playground.ipynb
@@ -0,0 +1,87 @@
+{
+ "cells": [
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 1,
+ "id": "imports",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "from solution import Solution"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 2,
+ "id": "setup",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "import os\n",
+ "import sys\n",
+ "\n",
+ "sys.path.append(os.path.join(os.getcwd(), \"..\"))\n",
+ "from linked_list_cycle.tests import TestLinkedListCycle\n",
+ "\n",
+ "# Example test case\n",
+ "values = [3, 2, 0, -4]\n",
+ "pos = 1\n",
+ "expected = True"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 3,
+ "id": "execute",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [
+ {
+ "data": {
+ "text/plain": [
+ "True"
+ ]
+ },
+ "execution_count": 3,
+ "metadata": {},
+ "output_type": "execute_result"
+ }
+ ],
+ "source": [
+ "head = TestLinkedListCycle().create_cycle_list(values, pos)\n",
+ "result = Solution().has_cycle(head)\n",
+ "result"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 4,
+ "id": "test",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "assert result == expected"
+ ]
+ }
+ ],
+ "metadata": {
+ "kernelspec": {
+ "display_name": "leetcode-py-py3.13",
+ "language": "python",
+ "name": "python3"
+ },
+ "language_info": {
+ "codemirror_mode": {
+ "name": "ipython",
+ "version": 3
+ },
+ "file_extension": ".py",
+ "mimetype": "text/x-python",
+ "name": "python",
+ "nbconvert_exporter": "python",
+ "pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
+ "version": "3.13.7"
+ }
+ },
+ "nbformat": 4,
+ "nbformat_minor": 5
+}
diff --git a/leetcode/linked_list_cycle/solution.py b/leetcode/linked_list_cycle/solution.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..6c3f838
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/linked_list_cycle/solution.py
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
+from leetcode_py import ListNode
+
+
+class Solution:
+ # Time: O(n)
+ # Space: O(1)
+ def has_cycle(self, head: ListNode[int] | None) -> bool:
+ fast = head
+ slow = head
+
+ while fast and fast.next:
+ assert slow is not None
+ fast = fast.next.next
+ slow = slow.next
+ if fast is slow:
+ return True
+
+ return False
diff --git a/leetcode/linked_list_cycle/tests.py b/leetcode/linked_list_cycle/tests.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..8af1b82
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/linked_list_cycle/tests.py
@@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
+import pytest
+
+from leetcode_py import ListNode
+from leetcode_py.test_utils import logged_test
+
+from .solution import Solution
+
+
+class TestLinkedListCycle:
+ def setup_method(self):
+ self.solution = Solution()
+
+ def create_cycle_list(self, values: list[int], pos: int):
+ if not values:
+ return None
+
+ nodes = []
+ head = ListNode(values[0])
+ nodes.append(head)
+ current = head
+
+ for i in range(1, len(values)):
+ current.next = ListNode(values[i])
+ current = current.next
+ nodes.append(current)
+
+ if pos != -1 and pos < len(nodes):
+ current.next = nodes[pos]
+
+ return head
+
+ @pytest.mark.parametrize(
+ "values, pos, expected",
+ [
+ ([3, 2, 0, -4], 1, True),
+ ([1, 2], 0, True),
+ ([1], -1, False),
+ ([], -1, False),
+ ([1, 2, 3], -1, False),
+ ([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], 0, True),
+ ([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], 2, True),
+ ([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], 4, True),
+ ([1], 0, True),
+ ([1, 2], 1, True),
+ ([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8], 3, True),
+ ([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8], -1, False),
+ ([1, 2], -1, False),
+ ([5, 10], 0, True),
+ ([5, 10], 1, True),
+ ([0], -1, False),
+ ([-1, -2, -3], 1, True),
+ ([100, 200, 300], 0, True),
+ ],
+ )
+ @logged_test
+ def test_has_cycle(self, values: list[int], pos: int, expected: bool):
+ head = self.create_cycle_list(values, pos)
+ result = self.solution.has_cycle(head)
+ assert result == expected
diff --git a/leetcode/lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree/README.md b/leetcode/lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..a5b2f27
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
+# Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Search Tree
+
+**Difficulty:** Medium
+**Topics:** Tree, Depth-First Search, Binary Search Tree, Binary Tree
+**Tags:** grind-75
+
+**LeetCode:** [Problem 235](https://leetcode.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-search-tree/description/)
+
+## Problem Description
+
+Given a binary search tree (BST), find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) node of two given nodes in the BST.
+
+According to the definition of LCA on Wikipedia: "The lowest common ancestor is defined between two nodes `p` and `q` as the lowest node in `T` that has both `p` and `q` as descendants (where we allow **a node to be a descendant of itself**)."
+
+## Examples
+
+### Example 1:
+
+
+
+```
+Input: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 8
+Output: 6
+```
+
+**Explanation:** The LCA of nodes 2 and 8 is 6.
+
+### Example 2:
+
+
+
+```
+Input: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 4
+Output: 2
+```
+
+**Explanation:** The LCA of nodes 2 and 4 is 2, since a node can be a descendant of itself according to the LCA definition.
+
+### Example 3:
+
+```
+Input: root = [2,1], p = 2, q = 1
+Output: 2
+```
+
+## Constraints
+
+- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range `[2, 10^5]`.
+- `-10^9 <= Node.val <= 10^9`
+- All `Node.val` are **unique**.
+- `p != q`
+- `p` and `q` will exist in the BST.
diff --git a/leetcode/lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree/__init__.py b/leetcode/lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree/__init__.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e69de29
diff --git a/leetcode/lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree/playground.ipynb b/leetcode/lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree/playground.ipynb
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..763d0ea
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree/playground.ipynb
@@ -0,0 +1,75 @@
+{
+ "cells": [
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "imports",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "from solution import Solution\n",
+ "\n",
+ "from leetcode_py import TreeNode"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "setup",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "# Example test case\n",
+ "root_list = [6, 2, 8, 0, 4, 7, 9, None, None, 3, 5]\n",
+ "p_val = 2\n",
+ "q_val = 8\n",
+ "expected_val = 6"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "execute",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "root = TreeNode[int].from_list(root_list)\n",
+ "p = find_node(root, p_val)\n",
+ "q = find_node(root, q_val)\n",
+ "result = Solution().lowest_common_ancestor(root, p, q)\n",
+ "result.val if result else None"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "test",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "assert result and result.val == expected_val"
+ ]
+ }
+ ],
+ "metadata": {
+ "kernelspec": {
+ "display_name": "leetcode-py-py3.13",
+ "language": "python",
+ "name": "python3"
+ },
+ "language_info": {
+ "codemirror_mode": {
+ "name": "ipython",
+ "version": 3
+ },
+ "file_extension": ".py",
+ "mimetype": "text/x-python",
+ "name": "python",
+ "nbconvert_exporter": "python3",
+ "pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
+ "version": "3.13.7"
+ }
+ },
+ "nbformat": 4,
+ "nbformat_minor": 5
+}
diff --git a/leetcode/lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree/solution.py b/leetcode/lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree/solution.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..f6f5dcd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree/solution.py
@@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
+from leetcode_py import TreeNode
+
+
+class Solution:
+ # Time: O(log n) average, O(n) worst case
+ # Space: O(1) iterative, O(log n) recursive
+ def lowest_common_ancestor(
+ self, root: TreeNode[int] | None, p: TreeNode[int], q: TreeNode[int]
+ ) -> TreeNode[int] | None:
+ while root:
+ # Both nodes are in left subtree
+ if p.val < root.val and q.val < root.val:
+ root = root.left
+ # Both nodes are in right subtree
+ elif p.val > root.val and q.val > root.val:
+ root = root.right
+ # Split point - one node on each side or one is the root
+ else:
+ return root
+ return None
diff --git a/leetcode/lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree/tests.py b/leetcode/lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree/tests.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..33767fe
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/lowest_common_ancestor_of_a_binary_search_tree/tests.py
@@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
+import pytest
+
+from leetcode_py import TreeNode
+from leetcode_py.test_utils import logged_test
+
+from .solution import Solution
+
+
+class TestLowestCommonAncestorOfABinarySearchTree:
+ def setup_method(self):
+ self.solution = Solution()
+
+ def _find_node(self, root: TreeNode[int] | None, val: int):
+ if not root:
+ return None
+ if root.val == val:
+ return root
+ left = self._find_node(root.left, val)
+ if left:
+ return left
+ return self._find_node(root.right, val)
+
+ @pytest.mark.parametrize(
+ "root_list, p_val, q_val, expected_val",
+ [
+ ([6, 2, 8, 0, 4, 7, 9, None, None, 3, 5], 2, 8, 6),
+ ([6, 2, 8, 0, 4, 7, 9, None, None, 3, 5], 2, 4, 2),
+ ([2, 1], 2, 1, 2),
+ ([2, 1], 1, 2, 2),
+ ([6, 2, 8, 0, 4, 7, 9], 0, 4, 2),
+ ([6, 2, 8, 0, 4, 7, 9], 7, 9, 8),
+ ],
+ )
+ @logged_test
+ def test_lowest_common_ancestor(
+ self, root_list: list[int | None], p_val: int, q_val: int, expected_val: int
+ ):
+ root = TreeNode[int].from_list(root_list)
+ assert root is not None
+ p = self._find_node(root, p_val)
+ q = self._find_node(root, q_val)
+ assert p is not None and q is not None
+ result = self.solution.lowest_common_ancestor(root, p, q)
+ assert result is not None
+ assert result.val == expected_val
diff --git a/leetcode/maximum_subarray/README.md b/leetcode/maximum_subarray/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e4d7afa
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/maximum_subarray/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
+# Maximum Subarray
+
+**Difficulty:** Medium
+**Topics:** Array, Divide and Conquer, Dynamic Programming
+**Tags:** grind-75
+
+**LeetCode:** [Problem 53](https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-subarray/description/)
+
+## Problem Description
+
+Given an integer array `nums`, find the subarray with the largest sum, and return its sum.
+
+## Examples
+
+### Example 1:
+
+```
+Input: nums = [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4]
+Output: 6
+```
+
+**Explanation:** The subarray [4,-1,2,1] has the largest sum 6.
+
+### Example 2:
+
+```
+Input: nums = [1]
+Output: 1
+```
+
+**Explanation:** The subarray [1] has the largest sum 1.
+
+### Example 3:
+
+```
+Input: nums = [5,4,-1,7,8]
+Output: 23
+```
+
+**Explanation:** The subarray [5,4,-1,7,8] has the largest sum 23.
+
+## Constraints
+
+- `1 <= nums.length <= 10^5`
+- `-10^4 <= nums[i] <= 10^4`
+
+**Follow up:** If you have figured out the `O(n)` solution, try coding another solution using the **divide and conquer** approach, which is more subtle.
diff --git a/leetcode/maximum_subarray/__init__.py b/leetcode/maximum_subarray/__init__.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e69de29
diff --git a/leetcode/maximum_subarray/playground.ipynb b/leetcode/maximum_subarray/playground.ipynb
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..2cbaa51
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/maximum_subarray/playground.ipynb
@@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
+{
+ "cells": [
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "imports",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": ["from solution import Solution"]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "setup",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": ["# Example test case\nnums = [-2, 1, -3, 4, -1, 2, 1, -5, 4]\nexpected = 6"]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "execute",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": ["result = Solution().max_sub_array(nums)\nresult"]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "test",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": ["assert result == expected"]
+ }
+ ],
+ "metadata": {
+ "kernelspec": {
+ "display_name": "leetcode-py-py3.13",
+ "language": "python",
+ "name": "python3"
+ },
+ "language_info": {
+ "codemirror_mode": {
+ "name": "ipython",
+ "version": 3
+ },
+ "file_extension": ".py",
+ "mimetype": "text/x-python",
+ "name": "python",
+ "nbconvert_exporter": "python3",
+ "pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
+ "version": "3.13.7"
+ }
+ },
+ "nbformat": 4,
+ "nbformat_minor": 5
+}
diff --git a/leetcode/maximum_subarray/solution.py b/leetcode/maximum_subarray/solution.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..2176165
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/maximum_subarray/solution.py
@@ -0,0 +1,11 @@
+class Solution:
+ # Time: O(n)
+ # Space: O(1)
+ def max_sub_array(self, nums: list[int]) -> int:
+ max_sum = current_sum = nums[0]
+
+ for i in range(1, len(nums)):
+ current_sum = max(nums[i], current_sum + nums[i])
+ max_sum = max(max_sum, current_sum)
+
+ return max_sum
diff --git a/leetcode/maximum_subarray/tests.py b/leetcode/maximum_subarray/tests.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..f186921
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/maximum_subarray/tests.py
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
+import pytest
+
+from leetcode_py.test_utils import logged_test
+
+from .solution import Solution
+
+
+class TestMaximumSubarray:
+ def setup_method(self):
+ self.solution = Solution()
+
+ @pytest.mark.parametrize(
+ "nums, expected",
+ [
+ ([-2, 1, -3, 4, -1, 2, 1, -5, 4], 6),
+ ([1], 1),
+ ([5, 4, -1, 7, 8], 23),
+ ([-1], -1),
+ ([-2, -1], -1),
+ ([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], 15),
+ ([-5, -2, -8, -1], -1),
+ ],
+ )
+ @logged_test
+ def test_max_sub_array(self, nums: list[int], expected: int):
+ result = self.solution.max_sub_array(nums)
+ assert result == expected
diff --git a/leetcode/minimum_window_substring/README.md b/leetcode/minimum_window_substring/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..f54b7da
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/minimum_window_substring/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
+# Minimum Window Substring
+
+**Difficulty:** Hard
+**Topics:** Hash Table, String, Sliding Window
+**Tags:** grind-75
+
+**LeetCode:** [Problem 76](https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-window-substring/description/)
+
+## Problem Description
+
+Given two strings `s` and `t` of lengths `m` and `n` respectively, return the **minimum window substring** of `s` such that every character in `t` (including duplicates) is included in the window. If there is no such substring, return the empty string `""`.
+
+The testcases will be generated such that the answer is unique.
+
+## Examples
+
+### Example 1:
+
+```
+Input: s = "ADOBECODEBANC", t = "ABC"
+Output: "BANC"
+```
+
+**Explanation:** The minimum window substring "BANC" includes 'A', 'B', and 'C' from string t.
+
+### Example 2:
+
+```
+Input: s = "a", t = "a"
+Output: "a"
+```
+
+**Explanation:** The entire string s is the minimum window.
+
+### Example 3:
+
+```
+Input: s = "a", t = "aa"
+Output: ""
+```
+
+**Explanation:** Both 'a's from t must be included in the window. Since the largest window of s only has one 'a', return empty string.
+
+## Constraints
+
+- `m == s.length`
+- `n == t.length`
+- `1 <= m, n <= 10^5`
+- `s` and `t` consist of uppercase and lowercase English letters.
+
+**Follow up:** Could you find an algorithm that runs in `O(m + n)` time?
diff --git a/leetcode/minimum_window_substring/__init__.py b/leetcode/minimum_window_substring/__init__.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e69de29
diff --git a/leetcode/minimum_window_substring/playground.ipynb b/leetcode/minimum_window_substring/playground.ipynb
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..1f99f98
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/minimum_window_substring/playground.ipynb
@@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
+{
+ "cells": [
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 1,
+ "id": "imports",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "from solution import Solution"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 2,
+ "id": "setup",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "# Example test case\n",
+ "s = \"ADOBECODEBANC\"\n",
+ "t = \"ABC\"\n",
+ "expected = \"BANC\""
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 3,
+ "id": "execute",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [
+ {
+ "data": {
+ "text/plain": [
+ "'BANC'"
+ ]
+ },
+ "execution_count": 3,
+ "metadata": {},
+ "output_type": "execute_result"
+ }
+ ],
+ "source": [
+ "result = Solution().min_window(s, t)\n",
+ "result"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 4,
+ "id": "test",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "assert result == expected"
+ ]
+ }
+ ],
+ "metadata": {
+ "kernelspec": {
+ "display_name": "leetcode-py-py3.13",
+ "language": "python",
+ "name": "python3"
+ },
+ "language_info": {
+ "codemirror_mode": {
+ "name": "ipython",
+ "version": 3
+ },
+ "file_extension": ".py",
+ "mimetype": "text/x-python",
+ "name": "python",
+ "nbconvert_exporter": "python",
+ "pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
+ "version": "3.13.7"
+ }
+ },
+ "nbformat": 4,
+ "nbformat_minor": 5
+}
diff --git a/leetcode/minimum_window_substring/solution.py b/leetcode/minimum_window_substring/solution.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..60bcb89
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/minimum_window_substring/solution.py
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
+from collections import Counter
+
+
+class Solution:
+ # Sliding Window
+ # Time: O(m + n) where m = len(s), n = len(t)
+ # Space: O(k) where k is unique chars in t
+ def min_window(self, s: str, t: str) -> str:
+ if not t or len(t) > len(s):
+ return ""
+
+ need = Counter(t)
+
+ left = 0
+ formed = 0
+ required = len(need)
+ window_counts: dict[str, int] = {}
+
+ # Result: (window length, left, right)
+ ans: tuple[float, int | None, int | None] = (float("inf"), None, None)
+
+ for right in range(len(s)):
+ char = s[right]
+ window_counts[char] = window_counts.get(char, 0) + 1
+
+ # Check if current char frequency matches desired frequency in t
+ if char in need and window_counts[char] == need[char]:
+ formed += 1
+
+ # Contract window until it's no longer valid
+ while left <= right and formed == required:
+ char = s[left]
+
+ # Update result if this window is smaller
+ if right - left + 1 < ans[0]:
+ ans = (right - left + 1, left, right)
+
+ # Remove from left
+ window_counts[char] -= 1
+ if char in need and window_counts[char] < need[char]:
+ formed -= 1
+
+ left += 1
+
+ if ans[0] == float("inf"):
+ return ""
+ assert ans[1] is not None and ans[2] is not None
+ return s[ans[1] : ans[2] + 1]
diff --git a/leetcode/minimum_window_substring/tests.py b/leetcode/minimum_window_substring/tests.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..8a3e16a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/minimum_window_substring/tests.py
@@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
+import pytest
+
+from leetcode_py.test_utils import logged_test
+
+from .solution import Solution
+
+
+class TestMinimumWindowSubstring:
+ def setup_method(self):
+ self.solution = Solution()
+
+ @pytest.mark.parametrize(
+ "s, t, expected",
+ [
+ # Basic cases
+ ("ADOBECODEBANC", "ABC", "BANC"),
+ ("a", "a", "a"),
+ ("a", "aa", ""),
+ # Edge cases
+ ("", "a", ""), # Empty s
+ ("a", "", ""), # Empty t
+ ("", "", ""), # Both empty
+ ("ab", "ba", "ab"), # Same length
+ ("abc", "cba", "abc"), # Entire string needed
+ # Duplicates
+ ("ADOBECODEBANC", "AABC", "ADOBECODEBA"), # Correct: needs 2 A's, 1 B, 1 C
+ ("aa", "aa", "aa"),
+ # No solution
+ ("abc", "def", ""),
+ ("a", "b", ""),
+ # Multiple valid windows
+ ("ADOBECODEBANC", "AB", "BA"), # Correct: "BA" is shorter than "ADOB"
+ ("abcdef", "cf", "cdef"),
+ ],
+ )
+ @logged_test
+ def test_min_window(self, s: str, t: str, expected: str):
+ result = self.solution.min_window(s, t)
+ assert result == expected
diff --git a/leetcode/reverse_linked_list_ii/README.md b/leetcode/reverse_linked_list_ii/README.md
index 7c005a6..1f7a098 100644
--- a/leetcode/reverse_linked_list_ii/README.md
+++ b/leetcode/reverse_linked_list_ii/README.md
@@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
**Difficulty:** Medium
**Topics:** Linked List
-**Tags:** grind-75
+**Tags:**
**LeetCode:** [Problem 92](https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-linked-list-ii/description/)
diff --git a/leetcode/search_in_rotated_sorted_array/README.md b/leetcode/search_in_rotated_sorted_array/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..f74397c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/search_in_rotated_sorted_array/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
+# Search in Rotated Sorted Array
+
+**Difficulty:** Medium
+**Topics:** Array, Binary Search
+**Tags:** grind-75
+
+**LeetCode:** [Problem 33](https://leetcode.com/problems/search-in-rotated-sorted-array/description/)
+
+## Problem Description
+
+There is an integer array `nums` sorted in ascending order (with **distinct** values).
+
+Prior to being passed to your function, `nums` is **possibly left rotated** at an unknown index `k` (`1 <= k < nums.length`) such that the resulting array is `[nums[k], nums[k+1], ..., nums[n-1], nums[0], nums[1], ..., nums[k-1]]` (**0-indexed**). For example, `[0,1,2,4,5,6,7]` might be left rotated by 3 indices and become `[4,5,6,7,0,1,2]`.
+
+Given the array `nums` **after** the possible rotation and an integer `target`, return _the index of_ `target` _if it is in_ `nums`_, or_ `-1` _if it is not in_ `nums`.
+
+You must write an algorithm with `O(log n)` runtime complexity.
+
+## Examples
+
+### Example 1:
+
+```
+Input: nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 0
+Output: 4
+```
+
+### Example 2:
+
+```
+Input: nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 3
+Output: -1
+```
+
+### Example 3:
+
+```
+Input: nums = [1], target = 0
+Output: -1
+```
+
+## Constraints
+
+- `1 <= nums.length <= 5000`
+- `-10^4 <= nums[i] <= 10^4`
+- All values of `nums` are **unique**.
+- `nums` is an ascending array that is possibly rotated.
+- `-10^4 <= target <= 10^4`
diff --git a/leetcode/search_in_rotated_sorted_array/__init__.py b/leetcode/search_in_rotated_sorted_array/__init__.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e69de29
diff --git a/leetcode/search_in_rotated_sorted_array/playground.ipynb b/leetcode/search_in_rotated_sorted_array/playground.ipynb
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..357fb33
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/search_in_rotated_sorted_array/playground.ipynb
@@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
+{
+ "cells": [
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 1,
+ "id": "imports",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "from solution import Solution"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 2,
+ "id": "setup",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "# Example test case\n",
+ "nums = [4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 1, 2]\n",
+ "target = 0\n",
+ "expected = 4"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 3,
+ "id": "execute",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [
+ {
+ "data": {
+ "text/plain": [
+ "4"
+ ]
+ },
+ "execution_count": 3,
+ "metadata": {},
+ "output_type": "execute_result"
+ }
+ ],
+ "source": [
+ "result = Solution().search(nums, target)\n",
+ "result"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": 4,
+ "id": "test",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "assert result == expected"
+ ]
+ }
+ ],
+ "metadata": {
+ "kernelspec": {
+ "display_name": "leetcode-py-py3.13",
+ "language": "python",
+ "name": "python3"
+ },
+ "language_info": {
+ "codemirror_mode": {
+ "name": "ipython",
+ "version": 3
+ },
+ "file_extension": ".py",
+ "mimetype": "text/x-python",
+ "name": "python",
+ "nbconvert_exporter": "python",
+ "pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
+ "version": "3.13.7"
+ }
+ },
+ "nbformat": 4,
+ "nbformat_minor": 5
+}
diff --git a/leetcode/search_in_rotated_sorted_array/solution.py b/leetcode/search_in_rotated_sorted_array/solution.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..d8af000
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/search_in_rotated_sorted_array/solution.py
@@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
+class Solution:
+ # Time: O(log n)
+ # Space: O(1)
+ def search(self, nums: list[int], target: int) -> int:
+ left, right = 0, len(nums) - 1
+
+ while left <= right:
+ mid = (left + right) // 2
+
+ if nums[mid] == target:
+ return mid
+
+ # Left half is sorted
+ if nums[left] <= nums[mid]:
+ if nums[left] <= target < nums[mid]:
+ right = mid - 1
+ else:
+ left = mid + 1
+ # Right half is sorted
+ else:
+ if nums[mid] < target <= nums[right]:
+ left = mid + 1
+ else:
+ right = mid - 1
+
+ return -1
diff --git a/leetcode/search_in_rotated_sorted_array/tests.py b/leetcode/search_in_rotated_sorted_array/tests.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..90cc27f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/search_in_rotated_sorted_array/tests.py
@@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
+import pytest
+
+from leetcode_py.test_utils import logged_test
+
+from .solution import Solution
+
+
+class TestSearchInRotatedSortedArray:
+ def setup_method(self):
+ self.solution = Solution()
+
+ @pytest.mark.parametrize(
+ "nums, target, expected",
+ [
+ # Original test cases
+ ([4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 1, 2], 0, 4),
+ ([4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 1, 2], 3, -1),
+ ([1], 0, -1),
+ ([1], 1, 0),
+ ([3, 1], 1, 1),
+ # No rotation (sorted array)
+ ([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], 3, 2),
+ ([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], 6, -1),
+ # Different rotation points
+ ([6, 7, 0, 1, 2, 4, 5], 0, 2),
+ ([6, 7, 0, 1, 2, 4, 5], 4, 5),
+ ([6, 7, 0, 1, 2, 4, 5], 7, 1),
+ ([2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 1], 0, 6),
+ # Target at boundaries
+ ([4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 1, 2], 4, 0),
+ ([4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 1, 2], 2, 6),
+ # Two elements
+ ([2, 1], 1, 1),
+ ([2, 1], 2, 0),
+ ([1, 3], 3, 1),
+ ],
+ )
+ @logged_test
+ def test_search(self, nums: list[int], target: int, expected: int):
+ result = self.solution.search(nums, target)
+ assert result == expected
diff --git a/leetcode/spiral_matrix/tests.py b/leetcode/spiral_matrix/tests.py
index bb12705..8e3233c 100644
--- a/leetcode/spiral_matrix/tests.py
+++ b/leetcode/spiral_matrix/tests.py
@@ -12,8 +12,26 @@ def setup_method(self):
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
"matrix, expected",
[
+ # Original cases
([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]], [1, 2, 3, 6, 9, 8, 7, 4, 5]),
([[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8], [9, 10, 11, 12]], [1, 2, 3, 4, 8, 12, 11, 10, 9, 5, 6, 7]),
+ # Single element
+ ([[1]], [1]),
+ # Single row
+ ([[1, 2, 3, 4]], [1, 2, 3, 4]),
+ # Single column
+ ([[1], [2], [3]], [1, 2, 3]),
+ # 2x2 matrix
+ ([[1, 2], [3, 4]], [1, 2, 4, 3]),
+ # 1x2 matrix
+ ([[1, 2]], [1, 2]),
+ # 2x1 matrix
+ ([[1], [2]], [1, 2]),
+ # Larger square matrix
+ (
+ [[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8], [9, 10, 11, 12], [13, 14, 15, 16]],
+ [1, 2, 3, 4, 8, 12, 16, 15, 14, 13, 9, 5, 6, 7, 11, 10],
+ ),
],
)
@logged_test
diff --git a/leetcode/valid_palindrome/README.md b/leetcode/valid_palindrome/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e2444ef
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/valid_palindrome/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
+# Valid Palindrome
+
+**Difficulty:** Easy
+**Topics:** Two Pointers, String
+**Tags:** grind-75
+
+**LeetCode:** [Problem 125](https://leetcode.com/problems/valid-palindrome/description/)
+
+## Problem Description
+
+A phrase is a **palindrome** if, after converting all uppercase letters into lowercase letters and removing all non-alphanumeric characters, it reads the same forward and backward. Alphanumeric characters include letters and numbers.
+
+Given a string `s`, return `true` if it is a **palindrome**, or `false` otherwise.
+
+## Examples
+
+### Example 1:
+
+```
+Input: s = "A man, a plan, a canal: Panama"
+Output: true
+```
+
+**Explanation:** "amanaplanacanalpanama" is a palindrome.
+
+### Example 2:
+
+```
+Input: s = "race a car"
+Output: false
+```
+
+**Explanation:** "raceacar" is not a palindrome.
+
+### Example 3:
+
+```
+Input: s = " "
+Output: true
+```
+
+**Explanation:** s is an empty string "" after removing non-alphanumeric characters. Since an empty string reads the same forward and backward, it is a palindrome.
+
+## Constraints
+
+- `1 <= s.length <= 2 * 10^5`
+- `s` consists only of printable ASCII characters.
diff --git a/leetcode/valid_palindrome/__init__.py b/leetcode/valid_palindrome/__init__.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e69de29
diff --git a/leetcode/valid_palindrome/playground.ipynb b/leetcode/valid_palindrome/playground.ipynb
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..981f5a4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/valid_palindrome/playground.ipynb
@@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
+{
+ "cells": [
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "imports",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": ["from solution import Solution"]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "setup",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": ["# Example test case\ns = \"A man, a plan, a canal: Panama\"\nexpected = True"]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "execute",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": ["result = Solution().is_palindrome(s)\nresult"]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "id": "test",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": ["assert result == expected"]
+ }
+ ],
+ "metadata": {
+ "kernelspec": {
+ "display_name": "leetcode-py-py3.13",
+ "language": "python",
+ "name": "python3"
+ },
+ "language_info": {
+ "codemirror_mode": {
+ "name": "ipython",
+ "version": 3
+ },
+ "file_extension": ".py",
+ "mimetype": "text/x-python",
+ "name": "python",
+ "nbconvert_exporter": "python3",
+ "pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
+ "version": "3.13.7"
+ }
+ },
+ "nbformat": 4,
+ "nbformat_minor": 5
+}
diff --git a/leetcode/valid_palindrome/solution.py b/leetcode/valid_palindrome/solution.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e2eba71
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/valid_palindrome/solution.py
@@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
+class Solution:
+ # Time: O(n)
+ # Space: O(1)
+ def is_palindrome(self, s: str) -> bool:
+ left, right = 0, len(s) - 1
+
+ while left < right:
+ while left < right and not s[left].isalnum():
+ left += 1
+ while left < right and not s[right].isalnum():
+ right -= 1
+
+ if s[left].lower() != s[right].lower():
+ return False
+
+ left += 1
+ right -= 1
+
+ return True
diff --git a/leetcode/valid_palindrome/tests.py b/leetcode/valid_palindrome/tests.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..a029400
--- /dev/null
+++ b/leetcode/valid_palindrome/tests.py
@@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
+import pytest
+
+from leetcode_py.test_utils import logged_test
+
+from .solution import Solution
+
+
+class TestValidPalindrome:
+ def setup_method(self):
+ self.solution = Solution()
+
+ @pytest.mark.parametrize(
+ "s, expected",
+ [
+ ("A man, a plan, a canal: Panama", True),
+ ("race a car", False),
+ (" ", True),
+ ("", True),
+ ("a", True),
+ ("Madam", True),
+ ("No 'x' in Nixon", True),
+ ("Mr. Owl ate my metal worm", True),
+ ],
+ )
+ @logged_test
+ def test_is_palindrome(self, s: str, expected: bool):
+ result = self.solution.is_palindrome(s)
+ assert result == expected
diff --git a/leetcode_py/data_structures/list_node.py b/leetcode_py/data_structures/list_node.py
index c5b5409..0d873b7 100644
--- a/leetcode_py/data_structures/list_node.py
+++ b/leetcode_py/data_structures/list_node.py
@@ -20,24 +20,111 @@ def from_list(cls, arr: list[T]) -> "ListNode[T] | None":
current = current.next
return head
- def to_list(self) -> list[T]:
- result = []
+ def _has_cycle(self) -> bool:
+ """Use Floyd's algorithm to detect if list has a cycle."""
+ slow = fast = self
+ while fast and fast.next and fast.next.next:
+ assert slow.next is not None
+ slow = slow.next
+ fast = fast.next.next
+ if slow is fast: # Use identity comparison to avoid recursion
+ return True
+ return False
+
+ def to_list(self, max_length: int = 1000) -> list[T]:
+ result: list[T] = []
current: "ListNode[T] | None" = self
- while current:
+ visited: set[int] = set()
+
+ while current and len(result) < max_length:
+ if id(current) in visited:
+ # Cycle detected
+ break
+ visited.add(id(current))
result.append(current.val)
current = current.next
return result
def __str__(self) -> str:
- return " -> ".join(str(val) for val in self.to_list())
+ if self._has_cycle():
+ # Show cycle with target value
+ result: list[str] = []
+ current: "ListNode[T] | None" = self
+ visited: dict[int, int] = {}
+ position = 0
+
+ while current:
+ if id(current) in visited:
+ cycle_pos = visited[id(current)]
+ cycle_val = result[cycle_pos]
+ result_str = " -> ".join(result)
+ return f"{result_str} -> ... (cycle back to {cycle_val})"
+
+ visited[id(current)] = position
+ result.append(str(current.val))
+ current = current.next
+ position += 1
+
+ values = self.to_list()
+ result_str = " -> ".join(str(val) for val in values)
+ if len(values) >= 1000:
+ result_str += " -> ... (long list)"
+ return result_str
def __repr__(self) -> str:
return f"{self.__class__.__name__}({self.to_list()})"
def _repr_html_(self) -> str:
- return self.__str__()
+ """Generate HTML representation using Graphviz for Jupyter notebooks."""
+ try:
+ import graphviz
+ except ImportError:
+ return f"{self.__str__()}"
+
+ dot = graphviz.Digraph(comment="LinkedList")
+ dot.attr(rankdir="LR") # Left to right layout
+ dot.attr("node", shape="box", style="rounded,filled", fillcolor="lightblue")
+ dot.attr("edge", color="black")
+
+ current: "ListNode[T] | None" = self
+ visited: dict[int, int] = {}
+ node_id = 0
+
+ # First pass: create all nodes and track positions
+ while current:
+ if id(current) in visited:
+ # Cycle detected - add edge back to existing node
+ cycle_target = visited[id(current)]
+ dot.edge(
+ f"node_{node_id - 1}",
+ f"node_{cycle_target}",
+ color="red",
+ style="dashed",
+ label="cycle",
+ )
+ break
+
+ visited[id(current)] = node_id
+ dot.node(f"node_{node_id}", str(current.val))
+
+ # Only add edge if next node exists and we haven't seen it (no cycle)
+ if current.next and id(current.next) not in visited:
+ dot.edge(f"node_{node_id}", f"node_{node_id + 1}")
+ elif current.next and id(current.next) in visited:
+ # Next iteration will detect cycle, don't add regular edge
+ pass
+
+ current = current.next
+ node_id += 1
+
+ return dot.pipe(format="svg", encoding="utf-8")
def __eq__(self, other: object) -> bool:
if not isinstance(other, ListNode):
return False
+
+ # If either has a cycle, we can't do simple comparison
+ if self._has_cycle() or other._has_cycle():
+ return False # For simplicity, consider cyclic lists as not equal
+
return self.to_list() == other.to_list()
diff --git a/tests/data_structures/test_list_node.py b/tests/data_structures/test_list_node.py
index cc1bb9d..233e20f 100644
--- a/tests/data_structures/test_list_node.py
+++ b/tests/data_structures/test_list_node.py
@@ -84,7 +84,6 @@ def test_string_representations(
assert node is not None
assert str(node) == expected_str
assert repr(node) == expected_repr
- assert node._repr_html_() == expected_str
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
"list1,list2, should_equal",
@@ -118,3 +117,49 @@ def test_roundtrip_conversion(self, test_list: list[Any]) -> None:
assert node is not None
result = node.to_list()
assert result == test_list
+
+ def test_has_cycle_no_cycle(self) -> None:
+ # Test linear list has no cycle
+ node = ListNode.from_list([1, 2, 3])
+ assert node is not None
+ assert not node._has_cycle()
+
+ def test_has_cycle_with_cycle(self) -> None:
+ # Create a cycle: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 2 (cycle back to node 2)
+ node1 = ListNode(1)
+ node2 = ListNode(2)
+ node3 = ListNode(3)
+ node1.next = node2
+ node2.next = node3
+ node3.next = node2 # Create cycle
+
+ assert node1._has_cycle()
+
+ def test_str_with_cycle(self) -> None:
+ # Create a cycle and test string representation
+ node1 = ListNode(1)
+ node2 = ListNode(2)
+ node1.next = node2
+ node2.next = node1 # Create cycle
+
+ result = str(node1)
+ assert "-> ... (cycle back to 1)" in result
+
+ def test_equality_with_cycles(self) -> None:
+ # Create two cyclic lists
+ node1 = ListNode(1)
+ node2 = ListNode(2)
+ node1.next = node2
+ node2.next = node1 # Create cycle
+
+ node3 = ListNode(1)
+ node4 = ListNode(2)
+ node3.next = node4
+ node4.next = node3 # Create cycle
+
+ # Cyclic lists should not be equal (for simplicity)
+ assert node1 != node3
+
+ # Test cyclic vs non-cyclic
+ linear_node = ListNode.from_list([1, 2])
+ assert node1 != linear_node