Amazon Web Services (AWS) is the world’s most comprehensive and broadly adopted cloud platform, offering over 200 fully featured services from data centers globally. If you are a developer new to AWS, this is where you can learn to build applications on AWS. Choose the programming language and tools familiar to you, learn about core concepts applicable across any service you end up using, and then go build!
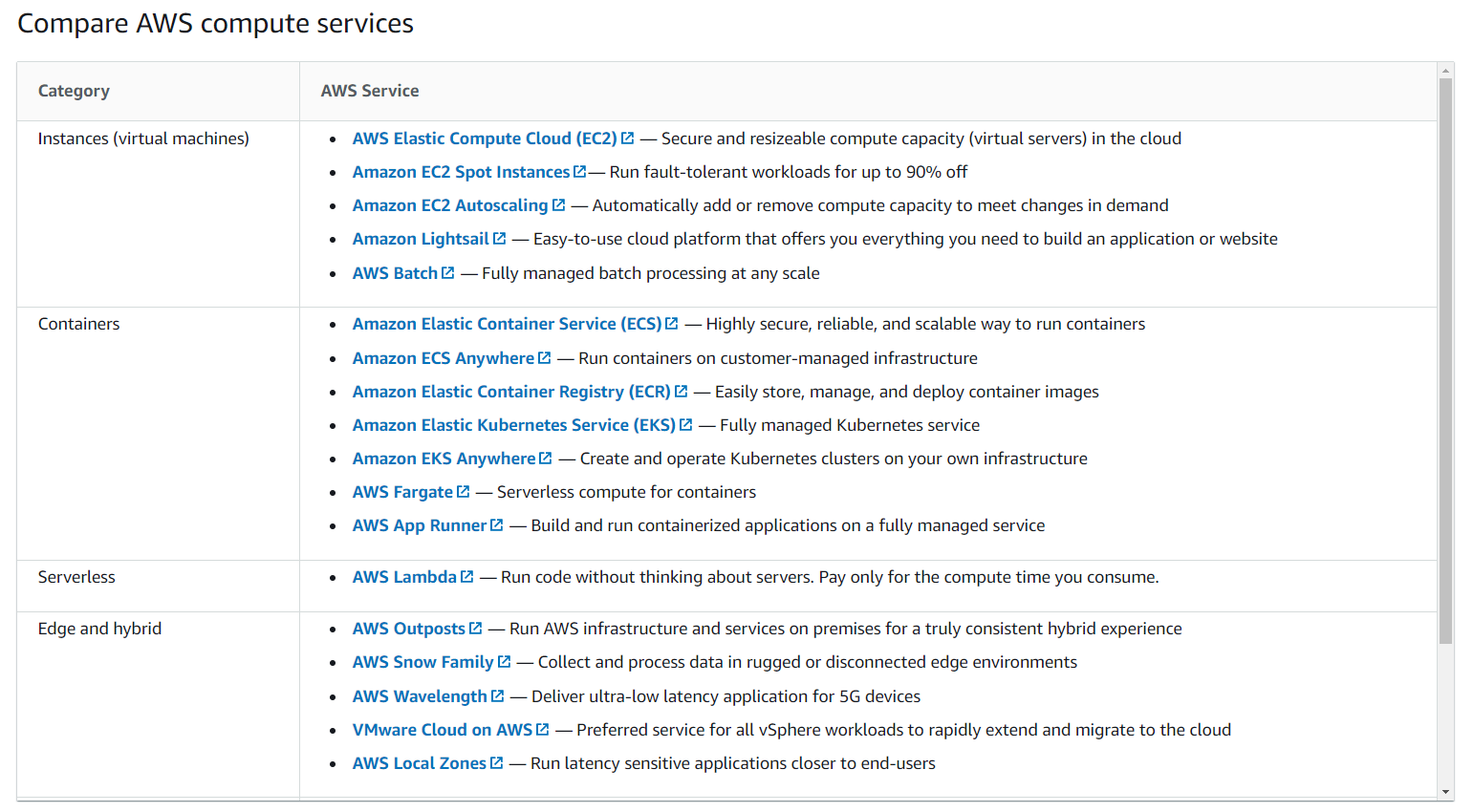
- Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) (弹性云计算)
- Pay for what you need
- AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner exam
Cloud Computing is the on-demand delivery of IT resources (按需求交付IT资源) over the internet with pay-as-you-go pricing
Instead of buying, owning, and maintaining physical data centers and servers, you can access technology services, such as computing power, storage, and databases, on an as-needed basis from a cloud provider like Amazon Web Services (AWS).
Organizations of every type, size, and industry are using the cloud for a wide variety of use cases, such as data backup, disaster recovery, email, virtual desktops, software development and testing, big data analytics, and customer-facing web applications. For example, healthcare companies are using the cloud to develop more personalized treatments for patients. Financial services companies are using the cloud to power real-time fraud detection and prevention. And video game makers are using the cloud to deliver online games to millions of players around the world.
In computing, a client can be a web browser or desktop application that a person interacts with to make requests to computer servers. A server can be services such as Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2), a type of virtual server.
For example, suppose that a client makes a request for a news article, the score in an online game, or a funny video. The server evaluates the details of this request and fulfills it by returning the information to the client.
The three cloud computing deployment models are cloud-based, on-premises, and hybrid.
- Upfront expense: refers to data centers, physical servers, and other resources that you would need to invest in before using them.
- Variable expense: you only pay for computing resources you consume instead of investing heavily in data centers and servers before you know how you’re going to use them.





There are three main models for cloud computing. Each model represents a different part of the cloud computing stack.
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
- Multitenancy: sharing underlying hardware between virtual machines
- provides secure, resizable compute capacity in the cloud as Amazon EC2 instances.

When selecting an instance type, consider the specific needs of your workloads and applications. This might include requirements for compute, memory, or storage capabilities.
With Amazon EC2, you pay only for the compute time that you use. Amazon EC2 offers a variety of pricing options for different use cases. For example, if your use case can withstand interruptions, you can save with Spot Instances. You can also save by committing early and locking in a minimum level of use with Reserved Instances.
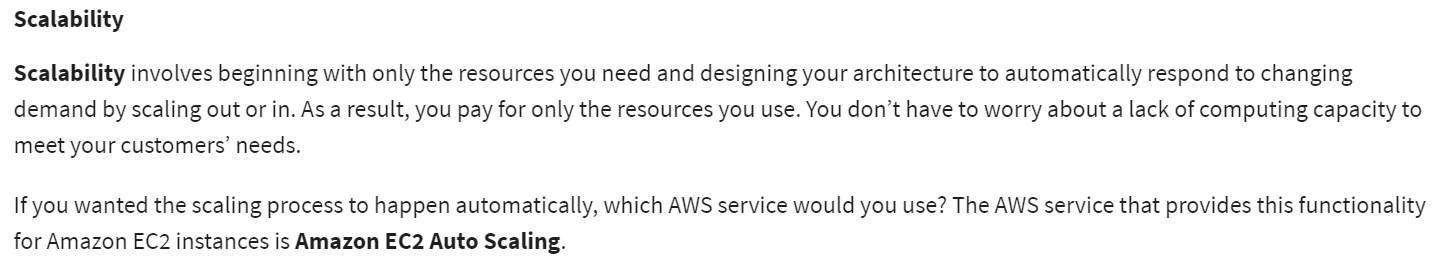
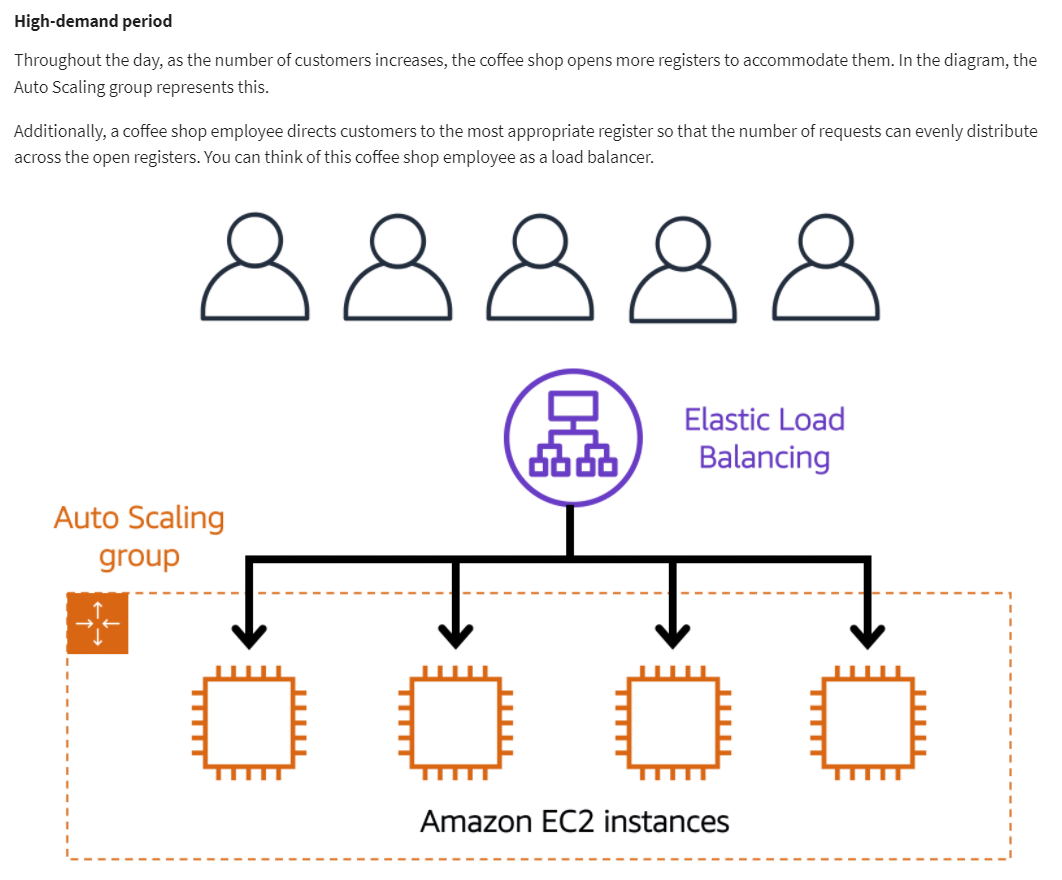
Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling: If you’ve tried to access a website that wouldn’t load and frequently timed out, the website might have received more requests than it was able to handle. This situation is similar to waiting in a long line at a coffee shop, when there is only one barista present to take orders from customers.
Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling enables you to automatically add or remove Amazon EC2 instances in response to changing application demand. By automatically scaling your instances in and out as needed, you are able to maintain a greater sense of application availability.
In the cloud, computing power is a programmatic resource, so you can take a more flexible approach to the issue of scaling. By adding Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling to an application, you can add new instances to the application when necessary and terminate them when no longer needed.
Suppose that you are preparing to launch an application on Amazon EC2 instances. When configuring the size of your Auto Scaling group, you might set the minimum number of Amazon EC2 instances at one. This means that at all times, there must be at least one Amazon EC2 instance running.
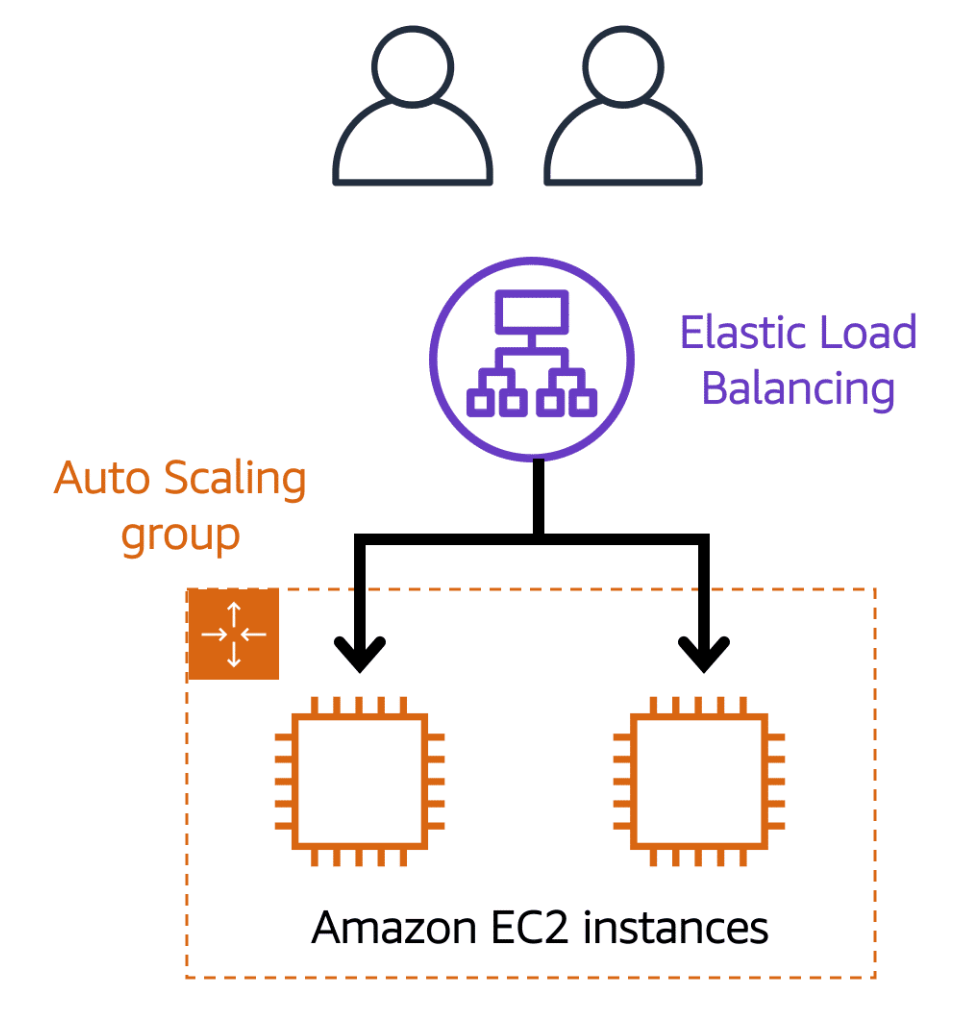
Elastic Load Balancing is the AWS service that automatically distributes incoming application traffic across multiple resources, such as Amazon EC2 instances.
A load balancer acts as a single point of contact for all incoming web traffic to your Auto Scaling group. This means that as you add or remove Amazon EC2 instances in response to the amount of incoming traffic, these requests route to the load balancer first. Then, the requests spread across multiple resources that will handle them. For example, if you have multiple Amazon EC2 instances, Elastic Load Balancing distributes the workload across the multiple instances so that no single instance has to carry the bulk of it.
Although Elastic Load Balancing and Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling are separate services, they work together to help ensure that applications running in Amazon EC2 can provide high performance and availability.
- Tightly Coupled Architecture
- Loosely Coupled Architecture: single failure won't cause cascading failures
Loosely Coupled Architecture:
- Amazon Simple Queue Service (Amazon SQS) 亚马逊简单队列服务
- Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS) Amazon简单通知服务
Monolithic Applications(整体应用程序):
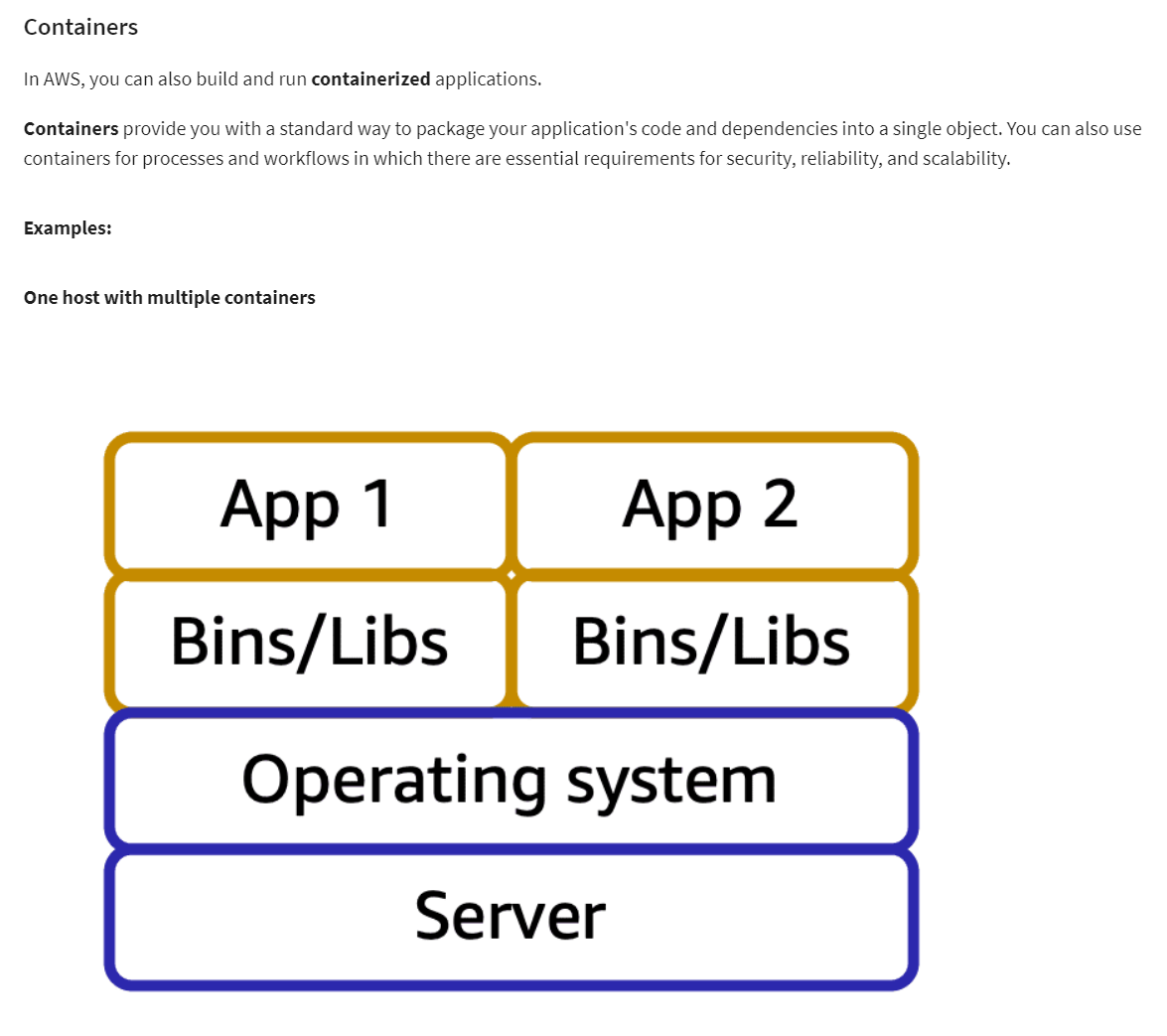
Applications are made of multiple components. The components communicate with each other to transmit data, fulfill requests, and keep the application running.
Suppose that you have an application with tightly coupled components. These components might include databases, servers, the user interface, business logic, and so on. This type of architecture can be considered a monolithic application.
In this approach to application architecture, if a single component fails, other components fail, and possibly the entire application fails.
Microservices:
To help maintain application availability when a single component fails, you can design your application through a microservices approach.
In a microservices approach, application components are loosely coupled. In this case, if a single component fails, the other components continue to work because they are communicating with each other. The loose coupling prevents the entire application from failing.
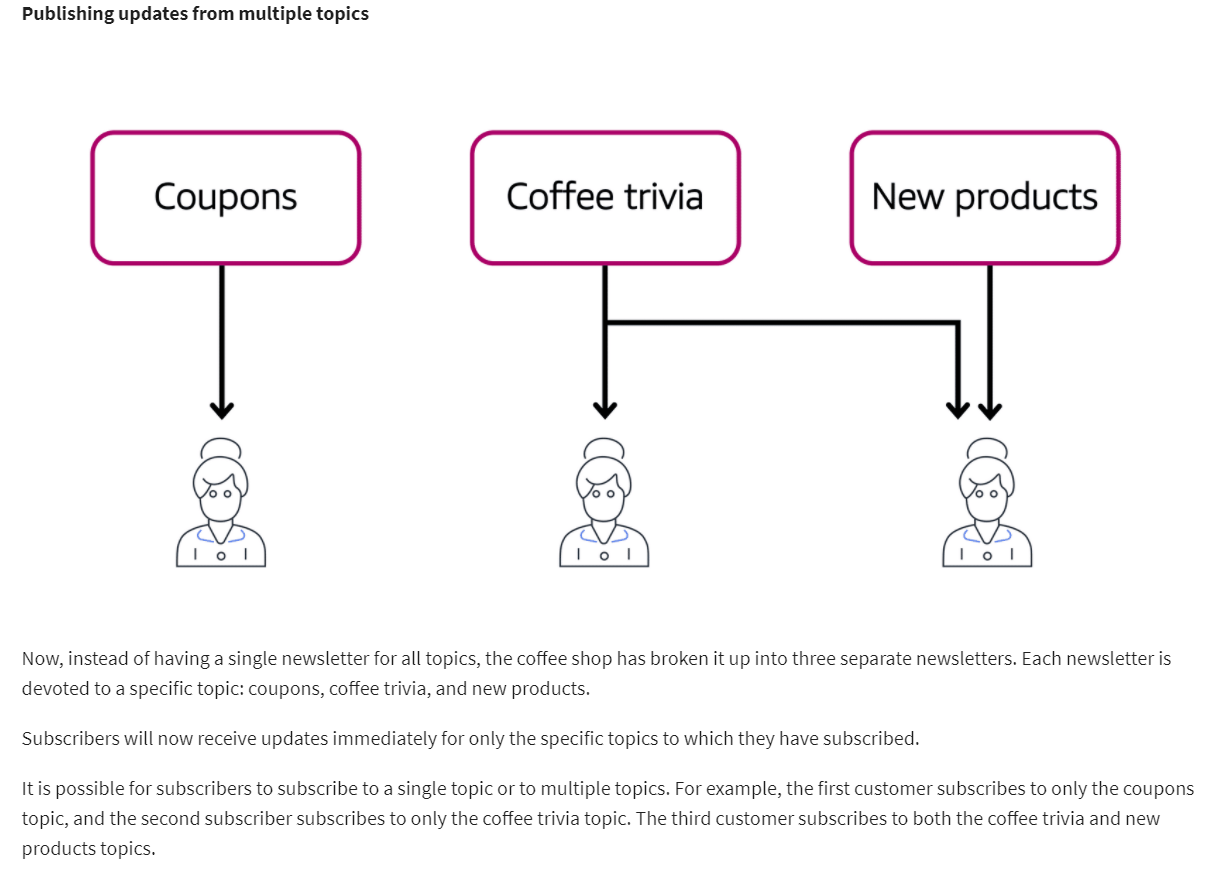
When designing applications on AWS, you can take a microservices approach with services and components that fulfill different functions. Two services facilitate application integration: Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS) and Amazon Simple Queue Service (Amazon SQS).
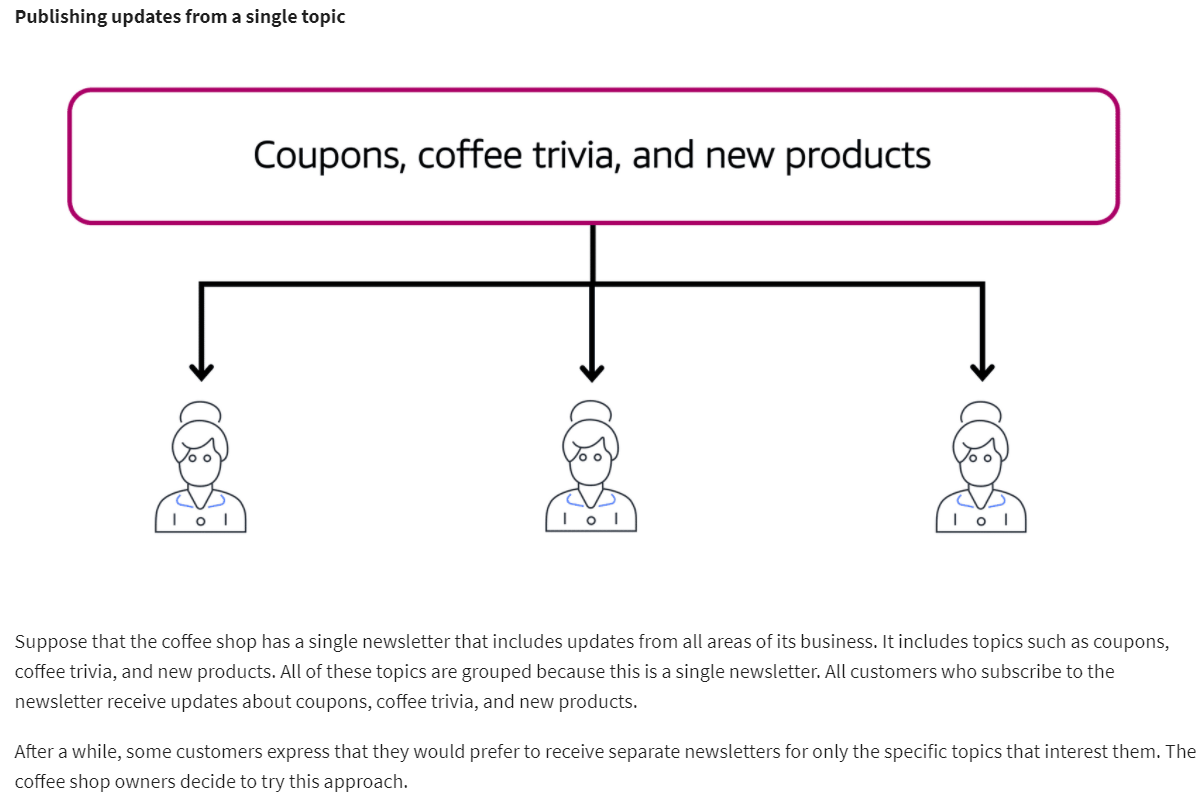
Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS) is a publish/subscribe service. Using Amazon SNS topics, a publisher publishes messages to subscribers. This is similar to the coffee shop; the cashier provides coffee orders to the barista who makes the drinks.
In Amazon SNS, subscribers can be web servers, email addresses, AWS Lambda functions, or several other options.
Amazon Simple Queue Service (Amazon SQS) is a message queuing service.
Using Amazon SQS, you can send, store, and receive messages between software components, without losing messages or requiring other services to be available. In Amazon SQS, an application sends messages into a queue. A user or service retrieves a message from the queue, processes it, and then deletes it from the queue.
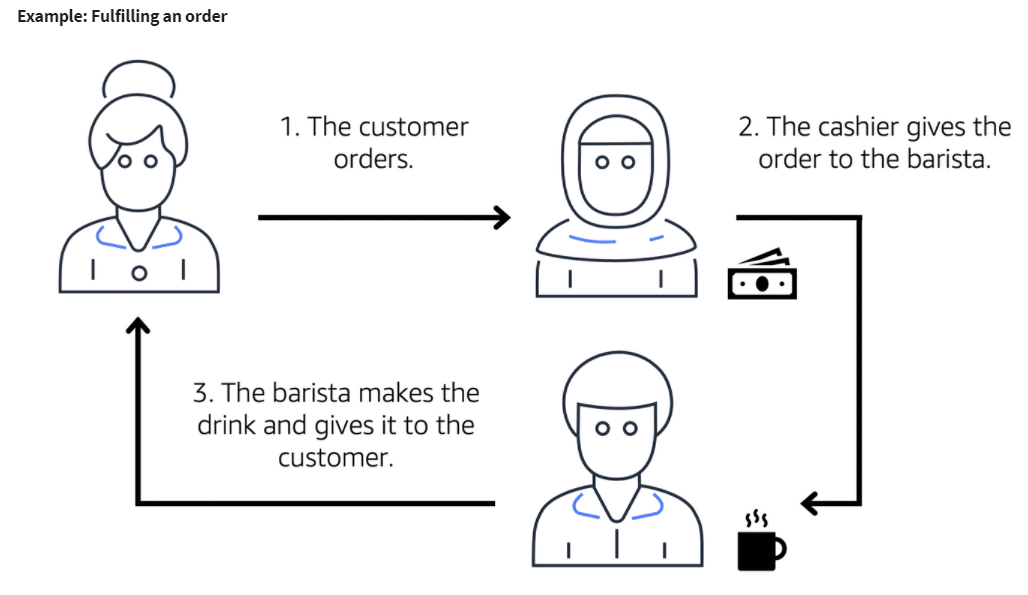
Suppose that the coffee shop has an ordering process in which a cashier takes orders, and a barista makes the orders. Think of the cashier and the barista as two separate components of an application.
First, the cashier takes an order and writes it down on a piece of paper. Next, the cashier delivers the paper to the barista. Finally, the barista makes the drink and gives it to the customer.
When the next order comes in, the process repeats. This process runs smoothly as long as both the cashier and the barista are coordinated.
What might happen if the cashier took an order and went to deliver it to the barista, but the barista was out on a break or busy with another order? The cashier would need to wait until the barista is ready to accept the order. This would cause delays in the ordering process and require customers to wait longer to receive their orders.
As the coffee shop has become more popular and the ordering line is moving more slowly, the owners notice that the current ordering process is time consuming and inefficient. They decide to try a different approach that uses a queue.
Recall that the cashier and the barista are two separate components of an application. A message queuing service such as Amazon SQS enables messages between decoupled application components.
In this example, the first step in the process remains the same as before: a customer places an order with the cashier.
The cashier puts the order into a queue. You can think of this as an order board that serves as a buffer between the cashier and the barista. Even if the barista is out on a break or busy with another order, the cashier can continue placing new orders into the queue.
Next, the barista checks the queue and retrieves the order.
The barista prepares the drink and gives it to the customer.
The barista then removes the completed order from the queue.
While the barista is preparing the drink, the cashier is able to continue taking new orders and add them to the queue.
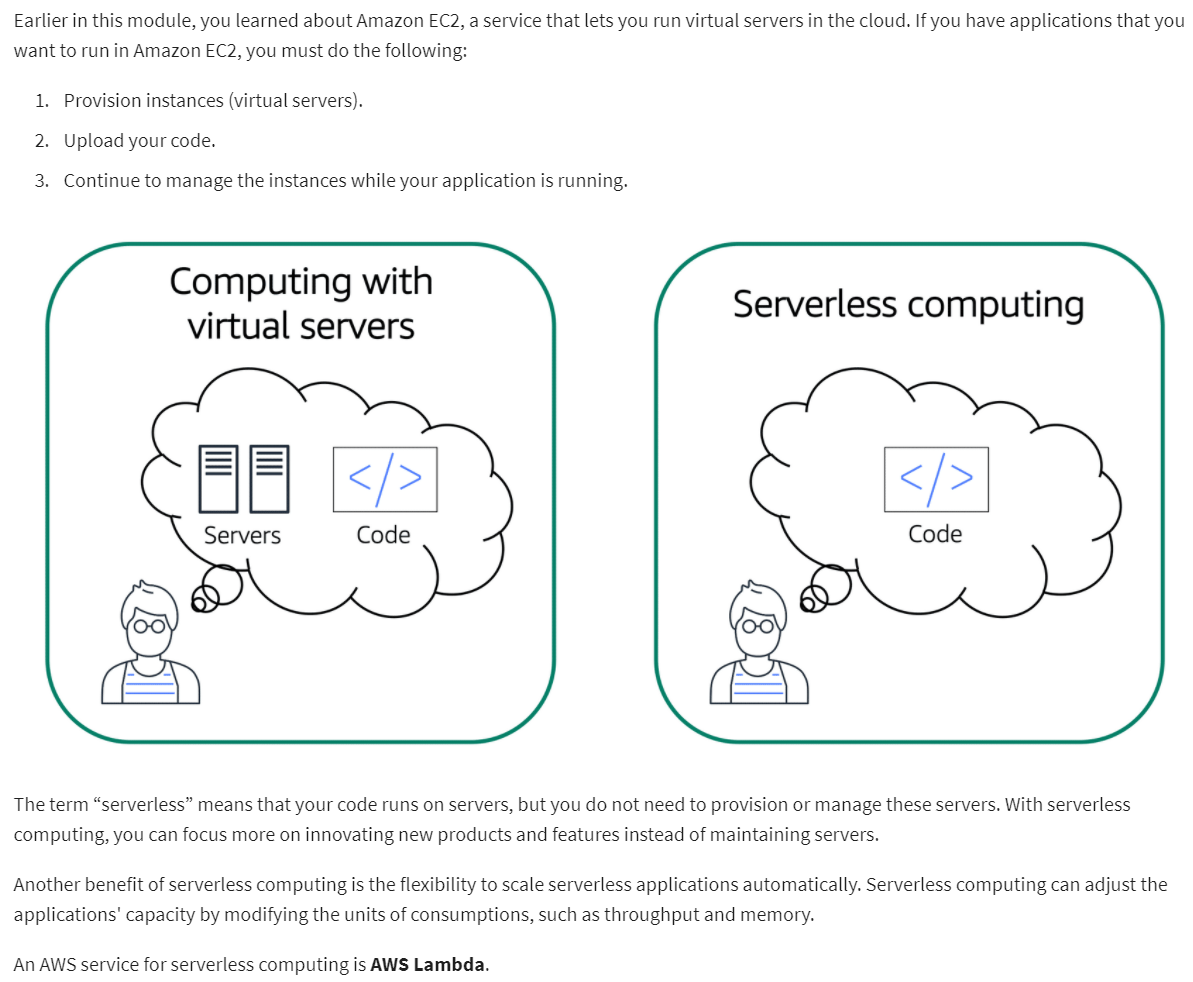
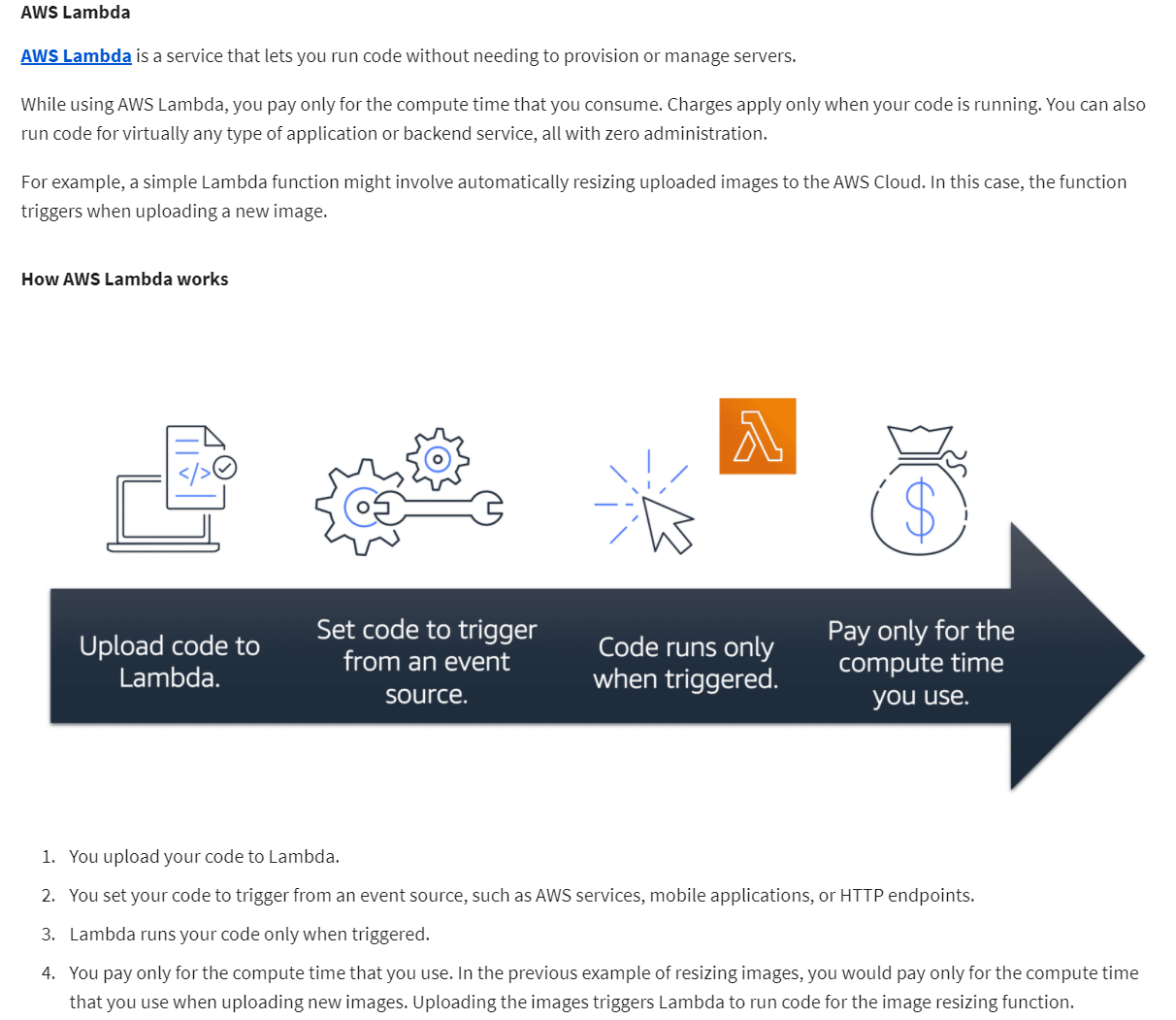
- An AWS service for serverless computing is AWS Lambda
- AWS Lambda is a service that lets you run code without needing to provision or manage servers.
https://aws.amazon.com/products/compute/ https://docs.aws.amazon.com/whitepapers/latest/aws-overview/compute-services.html