📦 [2025/10] CTINexus Python package released! Install with pip install ctinexus for seamless integration into your Python projects.
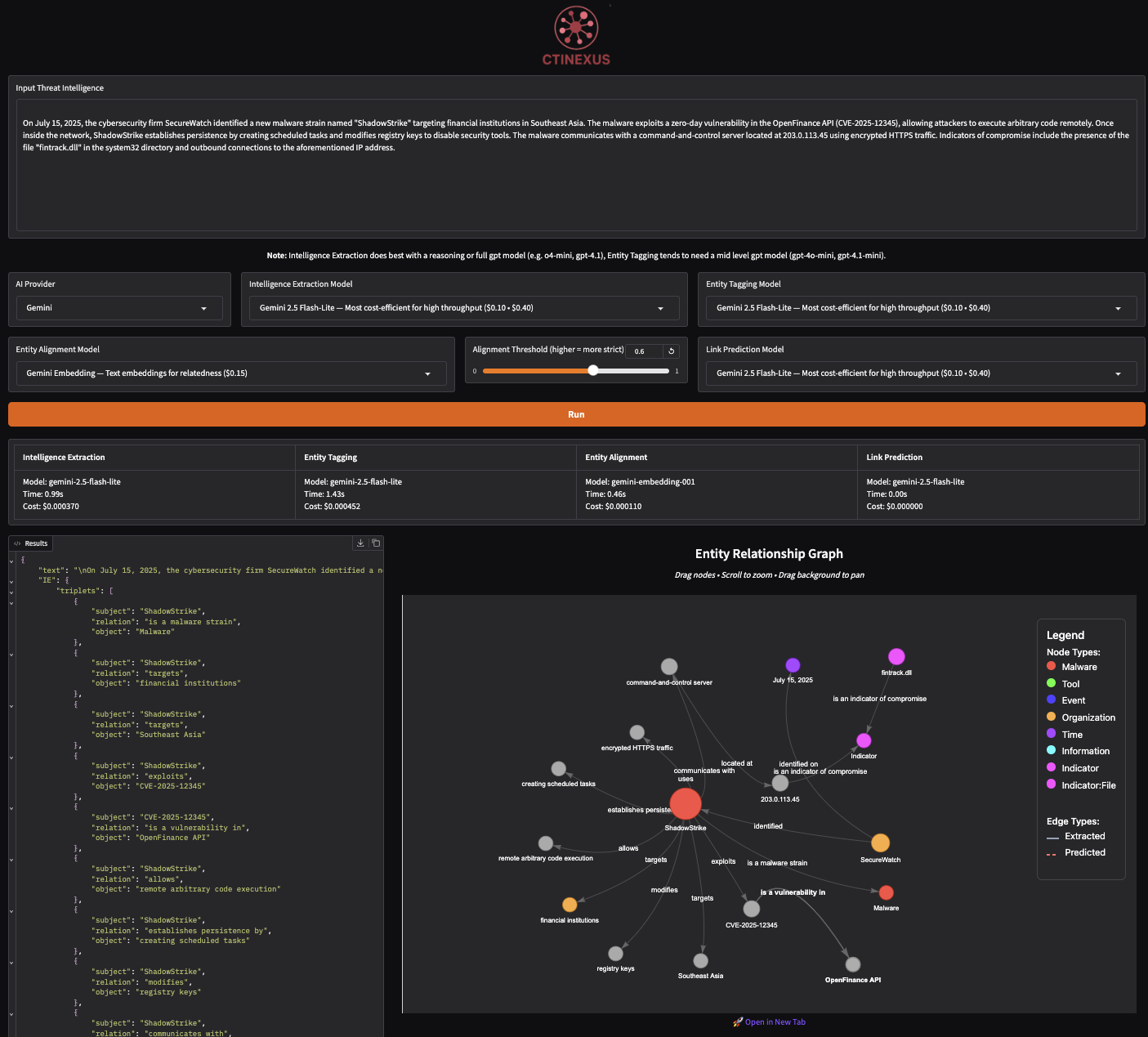
🌟 [2025/07] CTINexus now features an intuitive Gradio interface! Submit threat intelligence text and instantly visualize extracted interactive graphs.
🔥 [2025/04] We released the camera-ready paper on arxiv.
🔥 [2025/02] CTINexus is accepted at 2025 IEEE European Symposium on Security and Privacy (Euro S&P).
- Overview
- Features
- Supported AI Providers
- Getting Started
- Command Line Interface
- Contributing
- Citation
- License
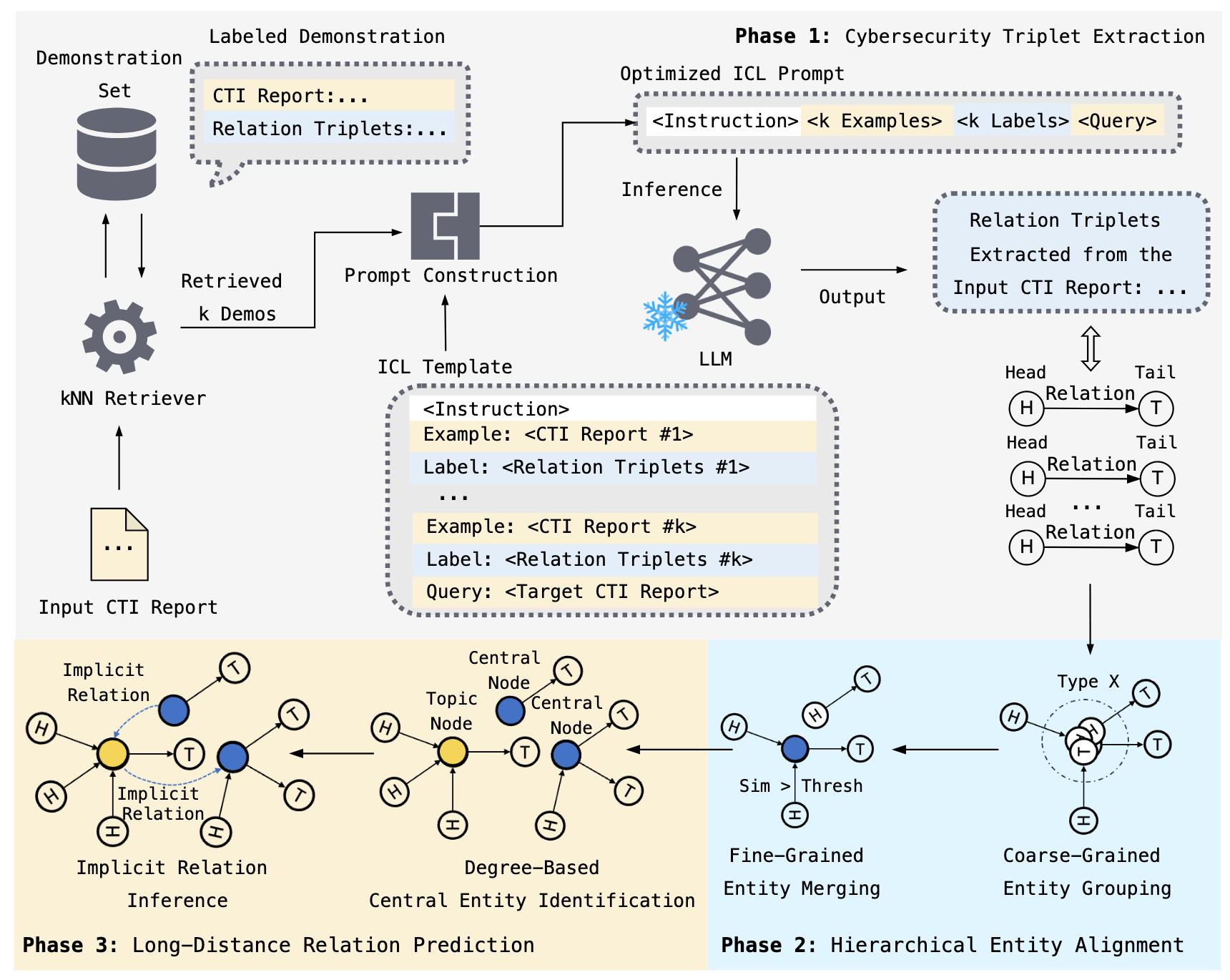
CTINexus is a framework that leverages optimized in-context learning (ICL) of large language models (LLMs) to automatically extract cyber threat intelligence (CTI) from unstructured text and construct cybersecurity knowledge graphs (CSKG).
The framework processes threat intelligence reports to:
- 🔍 Extract cybersecurity entities (malware, vulnerabilities, tactics, IOCs)
- 🔗 Identify relationships between security concepts
- 📊 Construct knowledge graphs with interactive visualizations
- ⚡ Require minimal configuration - no extensive training data or parameter tuning needed
-
Intelligence Extraction (IE)
- Automatically extracts cybersecurity entities and relationships from unstructured text
- Uses optimized prompt construction and demonstration retrieval
-
Hierarchical Entity Alignment
- Entity Typing (ET): Classifies entities by semantic type
- Entity Merging (EM): Canonicalizes entities and removes redundancy with IOC protection
-
Link Prediction (LP)
- Predicts and adds missing relationships to complete the knowledge graph
-
Interactive Visualization
- Network graph visualization of the constructed cybersecurity knowledge graph
CTINexus supports multiple AI providers for flexibility:
| Provider | Models | Setup Required |
|---|---|---|
| OpenAI | GPT-4, GPT-4o, o1, o3, etc. | API Key |
| Google Gemini | Gemini 2.0, 2.5 Flash, etc. | API Key |
| AWS Bedrock | Claude, Nova, Llama, DeepSeek, etc. | AWS Credentials |
| Ollama | Llama, Mistral, Qwen, Gemma, etc. | Local Installation (FREE) |
Note: When using Ollama models, use the 📖 Ollama Setup Guide.
pip install ctinexusCreate a .env file in your project directory with credentials for at least one provider. Look at .env.example for reference.
from ctinexus import process_cti_report
from dotenv import load_dotenv
# Load API credentials
load_dotenv()
# Process threat intelligence
text = """
APT29 used PowerShell to download additional malware from command-and-control
server at 192.168.1.100. The attack exploited CVE-2023-1234 in Microsoft Exchange.
"""
result = process_cti_report(
text=text,
provider="openai", # optional: auto-detected if not specified
model="gpt-4", # optional: uses default if not specified
similarity_threshold=0.6,
output="results.json" # optional: save results to file
)
# Access results
print(f"Graph saved to: {result['entity_relation_graph']}")
# Open the HTML file in your browser to view the interactive graphAPI Parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
text |
str | Required | Threat intelligence text to process |
provider |
str | Auto-detect | "openai", "gemini", "aws", or "ollama" |
model |
str | Provider default | Model name (e.g., "gpt-4o", "gemini-2.0-flash") |
embedding_model |
str | Provider default | Embedding model for entity alignment |
similarity_threshold |
float | 0.6 | Entity similarity threshold (0.0-1.0) |
output |
str | None | Path to save JSON results |
Return Value:
The function returns a dictionary with complete analysis results:
{
"text": "Original input text",
"IE": {"triplets": [...]}, # Extracted entities and relationships
"ET": {"typed_triplets": [...]}, # Entities with type classifications
"EA": {"aligned_triplets": [...]}, # Canonicalized entities
"LP": {"predicted_links": [...]}, # Predicted relationships
"entity_relation_graph": "path/to/graph.html" # Interactive visualization
}git clone https://github.com/peng-gao-lab/CTINexus.git
cd CTINexus
# Create and activate virtual environment
python -m venv .venv
# Activate (macOS/Linux)
source .venv/bin/activate
# Activate (Windows)
# .venv\Scripts\activate
# Install the package
pip install -e .# Copy the example environment file
cp .env.example .env
# Edit .env with your credentials1. Launch the application:
ctinexus2. Access the web interface:
Open your browser to: http://127.0.0.1:7860
3. Process threat intelligence:
- Paste threat intelligence text into the input area
- Select your AI provider and model from dropdowns
- Click "Run" to analyze
- View extracted entities, relationships, and interactive graph
- Export results as JSON or save graph images
Prerequisites:
- Install Docker Desktop
Setup:
# Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/peng-gao-lab/CTINexus.git
cd CTINexus
# Copy environment template
cp .env.example .env
# Edit .env with your credentials1. Build and start:
# Run in foreground
docker compose up --build
# OR run in background (detached mode)
docker compose up -d --build
# View logs (if running in background)
docker compose logs -f2. Access the application:
Open your browser to: http://localhost:8000
3. Process threat intelligence:
- Paste threat intelligence text into the input area
- Select your AI provider and model from dropdowns
- Click "Run" to analyze
- View extracted entities, relationships, and interactive graph
- Export results as JSON or save graph images
The CLI works with any installation method and is perfect for automation and batch processing.
# Process a file
ctinexus --input-file report.txt
# Process text directly
ctinexus --text "APT29 exploited CVE-2023-1234 using PowerShell..."
# Specify provider and model
ctinexus -i report.txt --provider openai --model gpt-4o
# Save to custom location
ctinexus -i report.txt --output results/analysis.json📖 Complete CLI Documentation - Detailed examples and all available options.
We warmly welcome contributions from the community! Whether you're interested in:
- 🐛 Fix bugs or add features
- 📖 Improve documentation
- 🎨 Enhance the UI/UX
- 🧪 Add tests or examples
Please check out our Contributing Guide for detailed information on how to get started, development setup, and submission guidelines.
If you use CTINexus in your research, please cite our paper:
@inproceedings{cheng2025ctinexusautomaticcyberthreat,
title={CTINexus: Automatic Cyber Threat Intelligence Knowledge Graph Construction Using Large Language Models},
author={Yutong Cheng and Osama Bajaber and Saimon Amanuel Tsegai and Dawn Song and Peng Gao},
booktitle={2025 IEEE European Symposium on Security and Privacy (EuroS\&P)},
year={2025},
organization={IEEE}
}The source code is licensed under the MIT License. We warmly welcome industry collaboration. If you’re interested in building on CTINexus or exploring joint initiatives, please email yutongcheng@vt.edu or saimon.tsegai@vt.edu, we’d be happy to set up a brief call to discuss ideas.