UXsim++ (or uxsimpp) is a free, open-source mesoscopic network traffic flow simulator for Python. It simulates the movements of car travelers and traffic congestion in road networks. It is suitable for simulating large-scale (e.g., city-scale) traffic phenomena. UXsim++ would be especially useful for scientific and educational purposes because of its fast, simple, lightweight, and customizable features, but users are free to use UXsim++ for any purpose.
UXsim++ is a significantly faster variant of UXsim, a pure Python-based traffic simulator. Its functionalities and syntax are almost equivalent to UXsim. Meanwhile, the internal simulation engine is thoroughly written in C++, making it 20 to 30 times faster than UXsim. Thanks to pybind11, the C++ engine is fully accessible from Python codes without any dependencies.
This is alpha stage. The codes and docs are work in progress.
If you are interested, please see:
- Tutorial using Jupyter Notebook
- Simple, fast, lightweight, and easy-to-use Python package for modern standard models of dynamic network traffic flow
- Macroscopic traffic simulation: Simulating over 60000 vehicles in a city in 1 second
- Dynamic traffic assignment: Traffic flow simulation with a given network and time-dependent OD demand
- Theoretically valid models commonly used in academic/professional transportation research
- Car-following model (Newell's simplified model)
- Reactive route choice model (dynamic user optimum)
- Significantly faster variant of UXsim, with almost equivalent functionalities and syntax
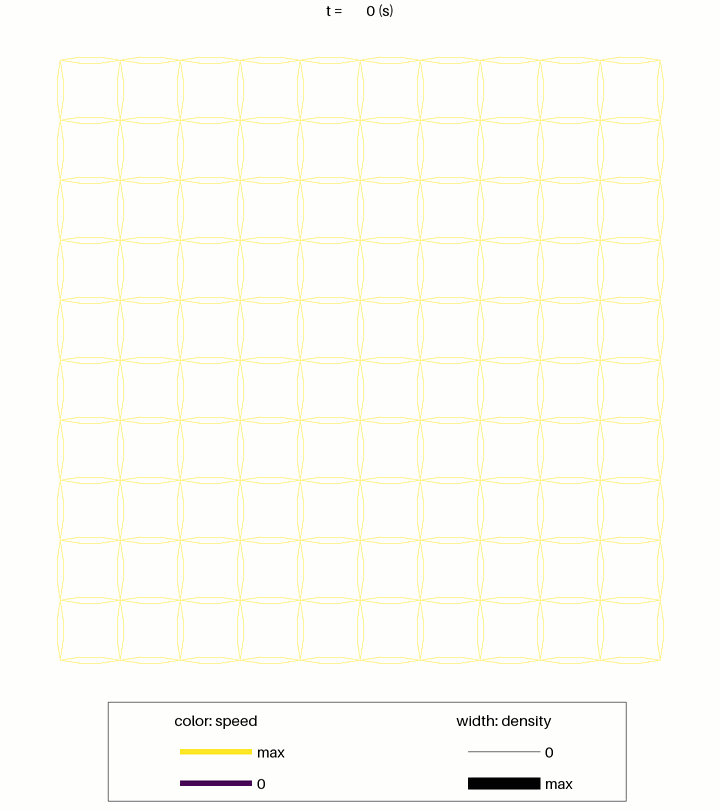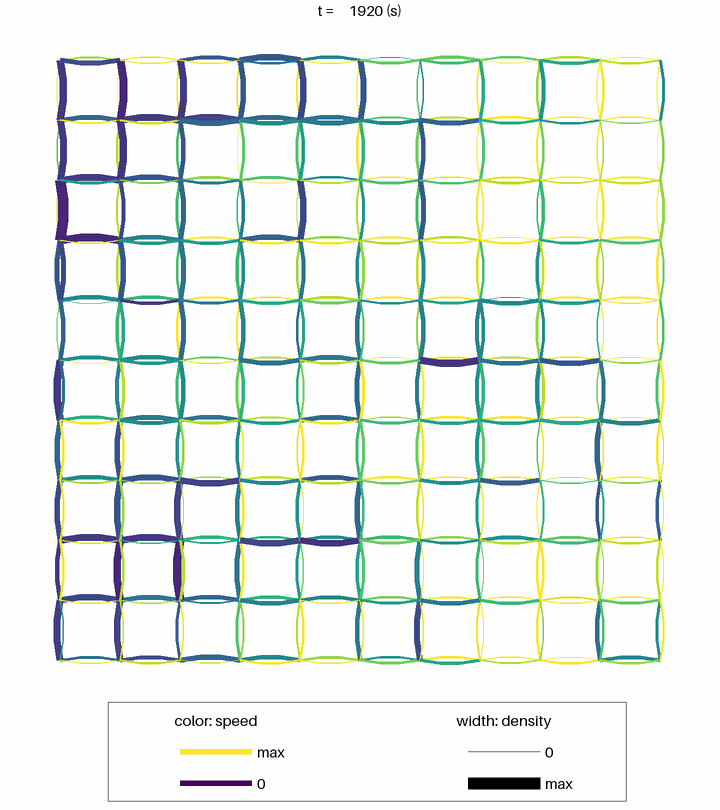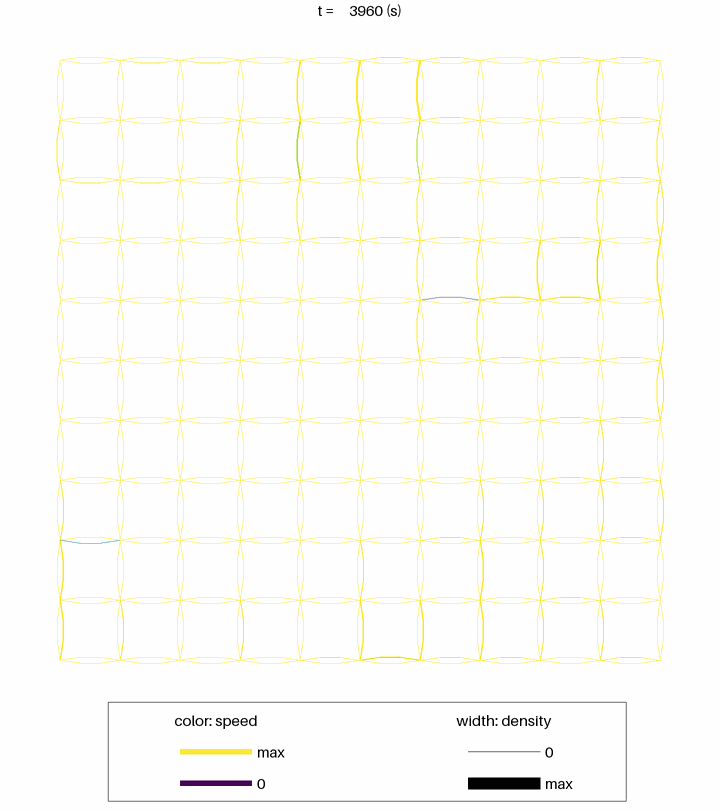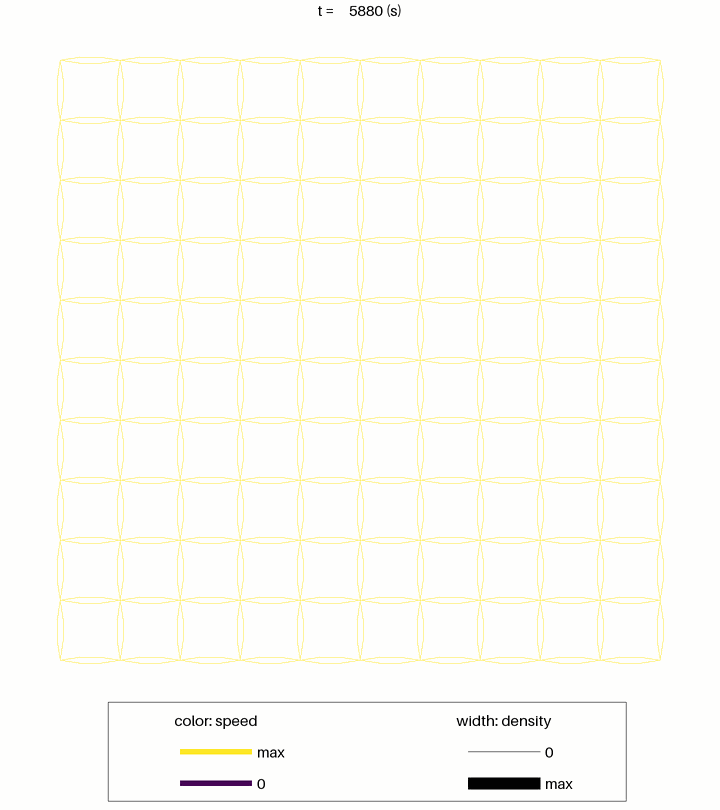
Simulation of about 50 000 vehicles in a 10 km x 10 km grid network. The computation time on a laptop PC was less than 1 second.
pip install uxsimppThe following code simulate traffic in simple Y-shaped network.
from uxsimpp import newWorld, Analyzer
W = newWorld(
name="basic",
deltan=5,
tmax=1200,
random_seed=42
)
W.addNode("orig1", 0, 0)
W.addNode("orig2", 0, 2)
W.addNode("merge", 1, 1)
W.addNode("dest", 2, 1)
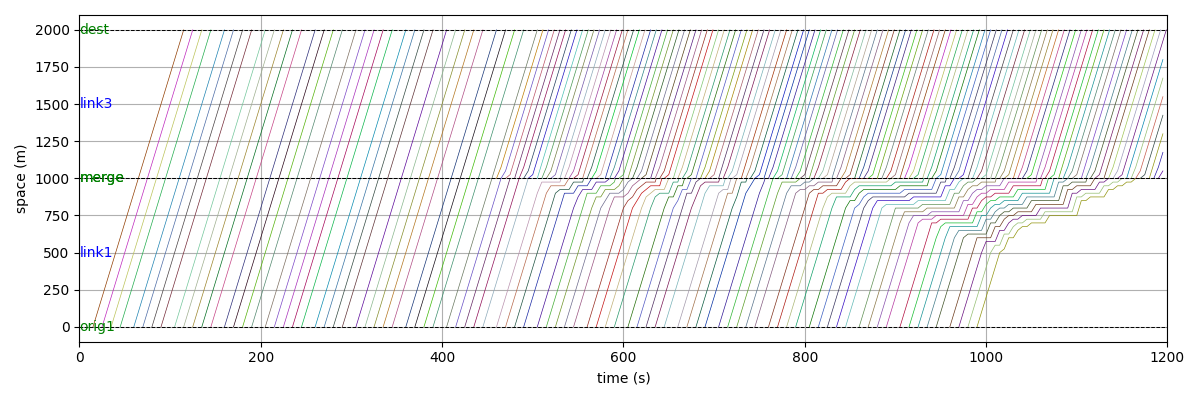
W.addLink("link1", "orig1", "merge", 1000, 20, 0.2, 1)
W.addLink("link2", "orig2", "merge", 1000, 20, 0.2, 1)
W.addLink("link3", "merge", "dest", 1000, 20, 0.2, 1)
W.adddemand("orig1", "dest", 0, 1000, 0.45)
W.adddemand("orig2", "dest", 400, 1000, 0.6)
W.print_scenario_stats()
W.exec_simulation()
W.print_simple_results()
ana = Analyzer(W)
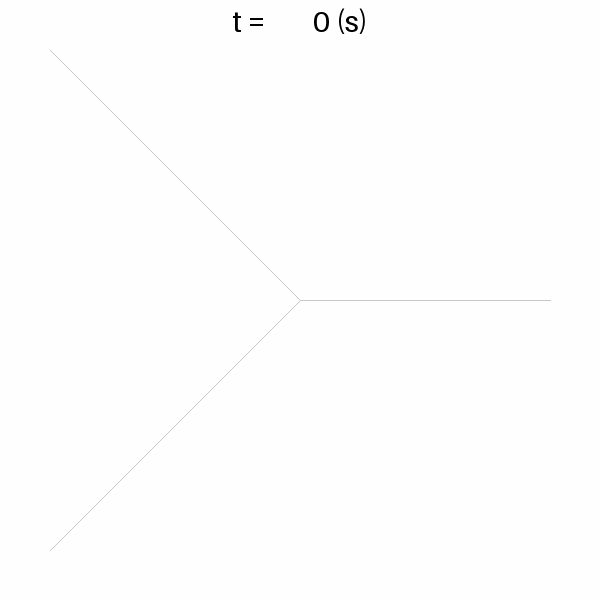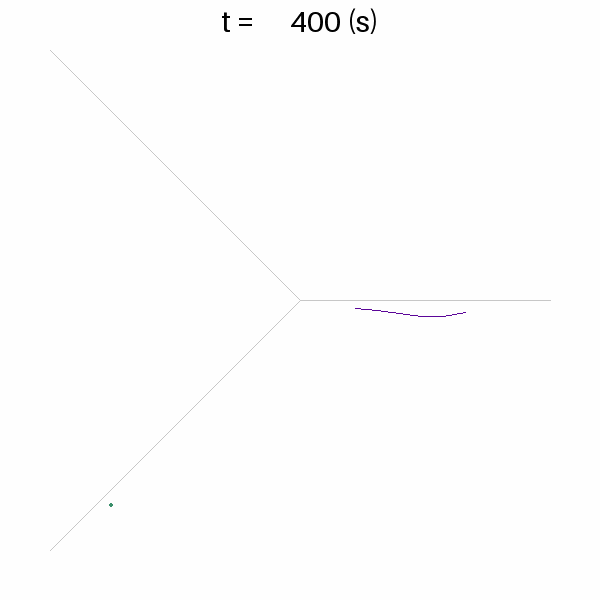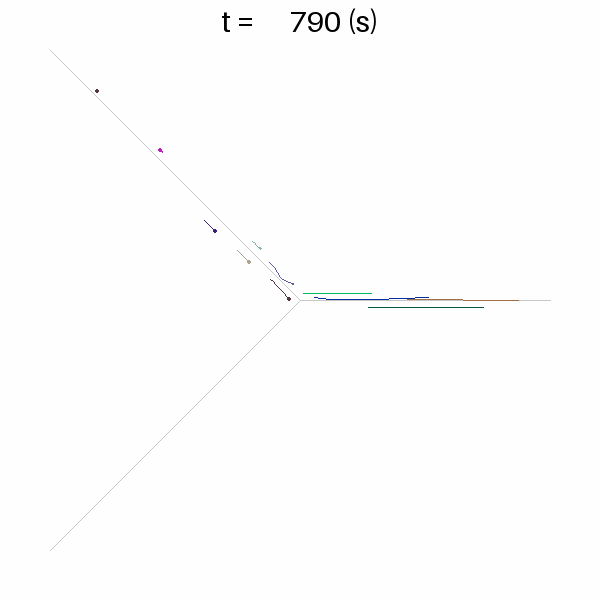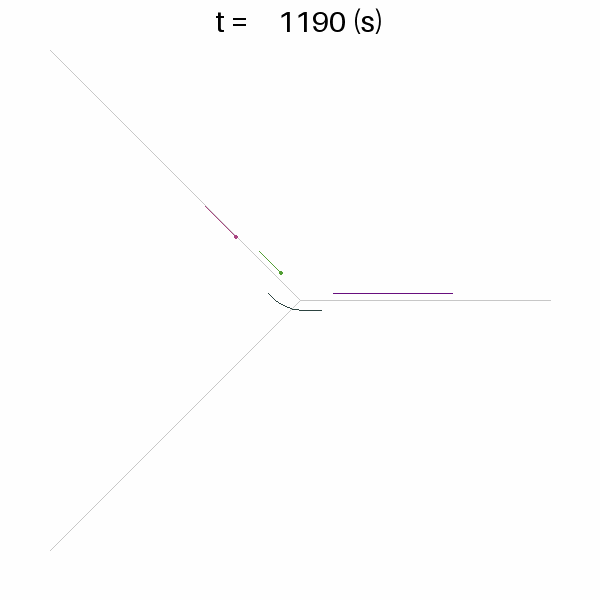
ana.plot_time_space_trajectories(["link1", "link3"])
ana.network_fancy()This will output the following text and images.
Scenario statistics:
duration: 1200 s
timesteps: 240
nodes: 4
links: 3
vehicles: 800 veh
platoon size: 5 veh
platoons: 160
vehicles: 800 veh
Simulating...
time| # of vehicles| ave speed
0 s| 0 veh| 0.00 m/s
120 s| 45 veh| 20.00 m/s
240 s| 45 veh| 20.00 m/s
360 s| 45 veh| 17.78 m/s
480 s| 90 veh| 16.67 m/s
600 s| 125 veh| 14.40 m/s
720 s| 160 veh| 10.31 m/s
840 s| 190 veh| 8.95 m/s
960 s| 205 veh| 8.29 m/s
1080 s| 160 veh| 6.72 m/s
Stats:
Average speed: 11.14
Average speed ratio: 0.56
Trips completion: 735.00 / 800.00
generating animation...
ArXiv preprint will be added.
The simulation model is almost the same to that of UXsim. If you are interested in, please refer to its documents:
- https://toruseo.jp/UXsim/docs/
- Toru Seo. UXsim: lightweight mesoscopic traffic flow simulator in pure Python. Journal of Open Source Software, Vol. 10, No. 106, p. 7617, 2025.
- Toru Seo. Macroscopic Traffic Flow Simulation: Fundamental Mathematical Theory and Python Implementation. Corona Publishing Co., Ltd., 2023.
- Toru Seo. UXsim: An open source macroscopic and mesoscopic traffic simulator in Python-a technical overview. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2309.17114, 2023.
MIT License