Gramado is a 64bit kernel.
Gramado OS is a project that includes the bootloader, the core kernel, and the init process.
Important
Documentation for this distribution is still under development. Folder names are subject to change.
distros/ - Complete distributions are built here.
docs/ - Documentation.
kernel/ - The kernel, including the bootloader, kernel modules, and
applications (see kernel/core/apps/).
tools/ - SDK tools.
kernel/core/deps/:
- Bootloader and kernel modules.
- POSIX commands.
- Display server and client-side GUI applications.
kernel/core/deps/kcore/boot/
kernel/
kernel/core/deps/kcore/modules/
kernel/core/deps/ucore/init/
kernel/core/deps/ucore/drivers/
kernel/core/deps/ucore/servers/
kernel/core/gdeps/preshell/ds/ds00/
kernel/core/gdeps/shell/shell00/
kernel/core/gdeps/shell/shell01/
Important
Gramado OS kernel is in a pre-alpha state and is only suitable for developers.
Gramado OS Kernel includes the bootloader, the core kernel, and the init process.
The kernel initialization in I_kmain():
// ==================================
// Levels:
// + [1] earlyinit()
// + [2:0] mmInitialize(0)
// + [2:1] mmInitialize(1)
// + [3:0] keInitialize(0)
// + [3:1] keInitialize(1)
// + [3:2] keInitialize(2)
// + [4] archinit()
// + [5] deviceinit()
// + [6] lateinit()
// ==================================
GramadoOS is a 64-bit graphical operating system, featuring a bootloader, kernel, and a desktop environment. This is the first distribution created using the Gramado OS kernel.
This image shows the first process that runs after the kernel initialization.

You can install a desktop environment on top of the kernel. The default desktop environment is located in the gdeps/ folder.
Gramado OS is a hobby operating system. It is not a commercial system; it is small and offers only a limited set of features.
Hardware Support
CPU: Intel and AMD, 64-bit only
Memory: Paging, 2MB chunks using 4KB pages
Block device: IDE (Primary master only)
Character devices: PS/2 keyboard, PS/2 mouse (works best in QEMU), Serial port (COM, used for debugging)
Network: Intel e1000 NIC (works in Oracle VirtualBox)
Software
Processes and threads
Round-robin scheduler (threads only)
Syscalls via software interrupts (traps)
IPC: sockets and system messages (queue in thread structure)
4 ring 0 kernel virtual consoles (fullscreen raw mode)
General-use TTYs and PTYs for ring 3 virtual terminals
FAT16 file system for boot partition (no dedicated system partition yet)
POSIX libc: ring 0 implementation for ring 3 libraries
Basic networking: sockets, small ring 0 protocol stack (Ethernet, ARP, IP, UDP, TCP, DHCP)
Display: Bootloader display device (VESA)
Minimal user structure
Loadable ring 0 module (static address)
Display server
Unix-like commands in the virtual console
Some clients connect to the display server via Unix sockets
Ring 3 processes can access I/O ports via syscall (for ring 3 drivers only)
- The network server. (Work in progress)
See deps/ucore/cmds/.
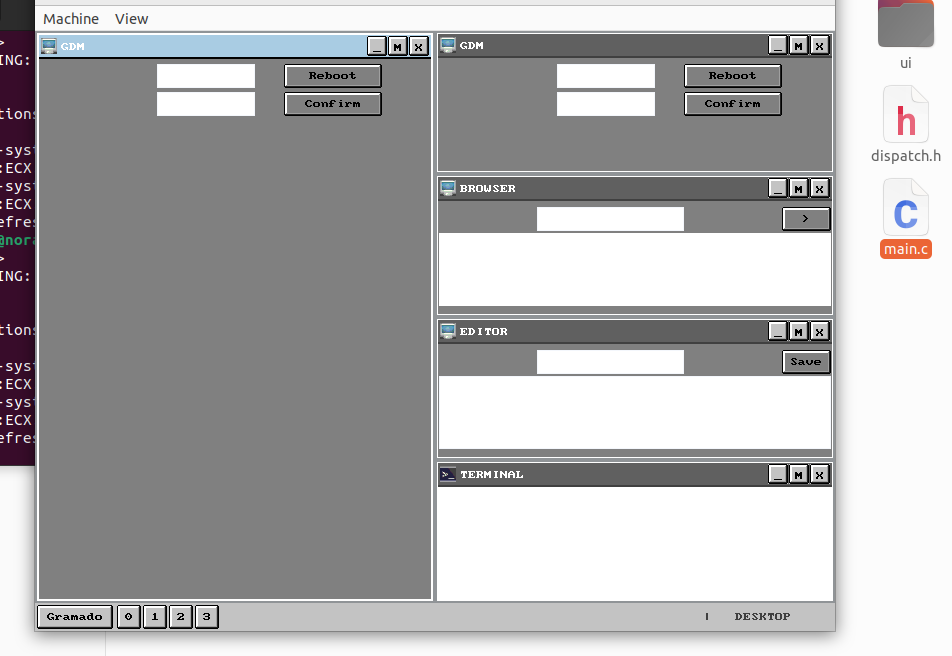
This is a screenshot of the desktop environment running on top of the kernel.
You can find code in the gdeps/ folder.
You can find the API to create client-side GUI application in gdeps/.
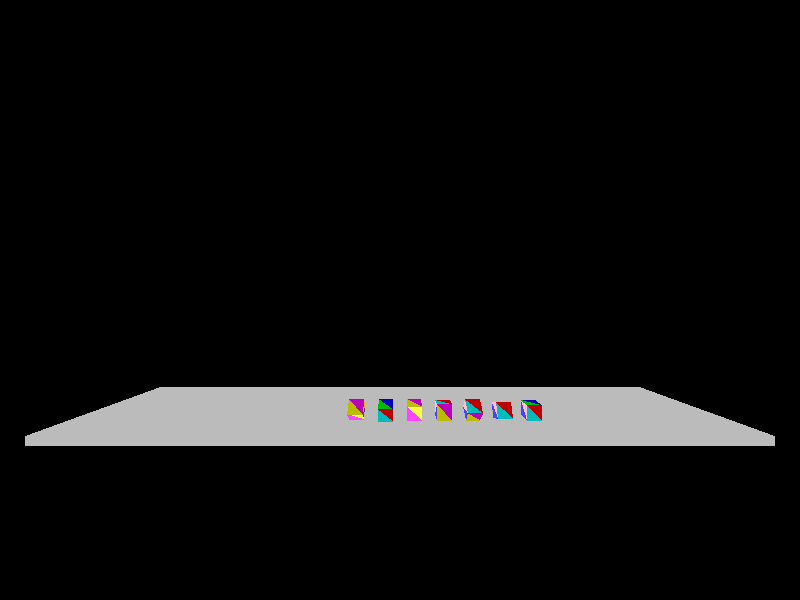
This is a screenshot of 3D demo running on top of the kernel.
You can find code in the zde/aurora/ folder.

You can find the source code on Github on the internet,
where you can clone the repository, contribute to the project or
download the code. The address is https://github.com/frednora/gramado.
Building an operating system is a great way to learn how systems work and
to understand the full software stack required to run applications.
However, if your goal is to make money, high demand is typically found in
application development (web front-end and back-end).
- Main Developer: Fred Nora, a Brazilian developer (creator and maintainer)
- Contributions: All are welcome!
Important
Build instruction
$ make
$ ./runps: Do NOT use the fancy '-j' thingy for now.
$ make clean-all
- Gramado OS has been compiled and tested on Ubuntu LTS releases, including WSL2 on Windows and various Ubuntu versions.
- A typical build environment:
Host machine: Windows 10, wsl2 with Ubuntu.
Linux kernel: 5.15.146.1-microsoft-standard-WSL2
gcc (Ubuntu) 11.4.0
GNU ld (GNU Binutils for Ubuntu) 2.38
NASM version 2.15.05
Host machine: Ubuntu 20.04.5 LTS
Linux 5.4.0-146-generic x86_64
gcc (Ubuntu) 9.4.0
GNU ld (GNU Binutils for Ubuntu) 2.34
NASM version 2.14.02
Host machine: Ubuntu 22.04.2 LTS
Linux 5.15.0-78-generic x86_64
gcc (Ubuntu) 11.4.0
GNU ld (GNU Binutils for Ubuntu) 2.38
NASM version 2.15.05
Host machine: Ubuntu 22.04.2 LTS
Linux 5.15.0-83-generic x86_64
gcc (Ubuntu) 11.4.0
GNU ld (GNU Binutils for Ubuntu) 2.38
NASM version 2.15.05
Host machine: Ubuntu 22.04.2 LTS
Linux 5.15.0-84-generic x86_64
gcc (Ubuntu) 11.4.0
GNU ld (GNU Binutils for Ubuntu) 2.38
NASM version 2.15.05
Host machine: Ubuntu 22.04.2 LTS
Linux 5.15.0-87-generic x86_64
gcc (Ubuntu) 11.4.0
GNU ld (GNU Binutils for Ubuntu) 2.38
NASM version 2.15.05
Host machine: Ubuntu 22.04.2 LTS
Linux 5.15.0-89-generic x86_64
gcc (Ubuntu) 11.4.0
GNU ld (GNU Binutils for Ubuntu) 2.38
NASM version 2.15.05
- Virtual Machines: Tested on QEMU, QEMU with KVM, and VirtualBox.
- Physical Machines: Older versions tested on real hardware (e.g., Intel Core 2 Duo, VIA chipset).
Yes, you can test the system on a virtual machine. The system has been tested by Fred Nora on qemu, qemu with kvm and virtualbox. Now, Fred Nora is testing the system only on qemu and virtualbox.
Yes, we can test the system in the real machines. This way we can improve the system. The older versions of the system were tested for a long period of time on a real machine. That machine was a Gigabyte machine with an Intel Core 2 Duo processor and a VIA chipset.
Feedback from users and developers is appreciated! Feel free to comment on GitHub or contact Fred Nora directly.
- Fred Nora - Fred Nora's X account
- Fred Nora - Fred Nora's Facebook account
- Fred Nora - Fred Nora's X account
- Fred Nora 2 - Fred Nora's Facebook account
See the Gramado OS build instructions
You're reaching the boring area of this document!
Documentation and design notes are in the docs/ folder.
See the docs.
The project is looking for some people to create a better documentation, for free, as a contribuition to the open source community. To create this new documentation we can use the documentation in docs/ and the design notes found all over the project.
Gramado OS is Free and Open Source. The source code uses the MIT License.
"Orthodox church"