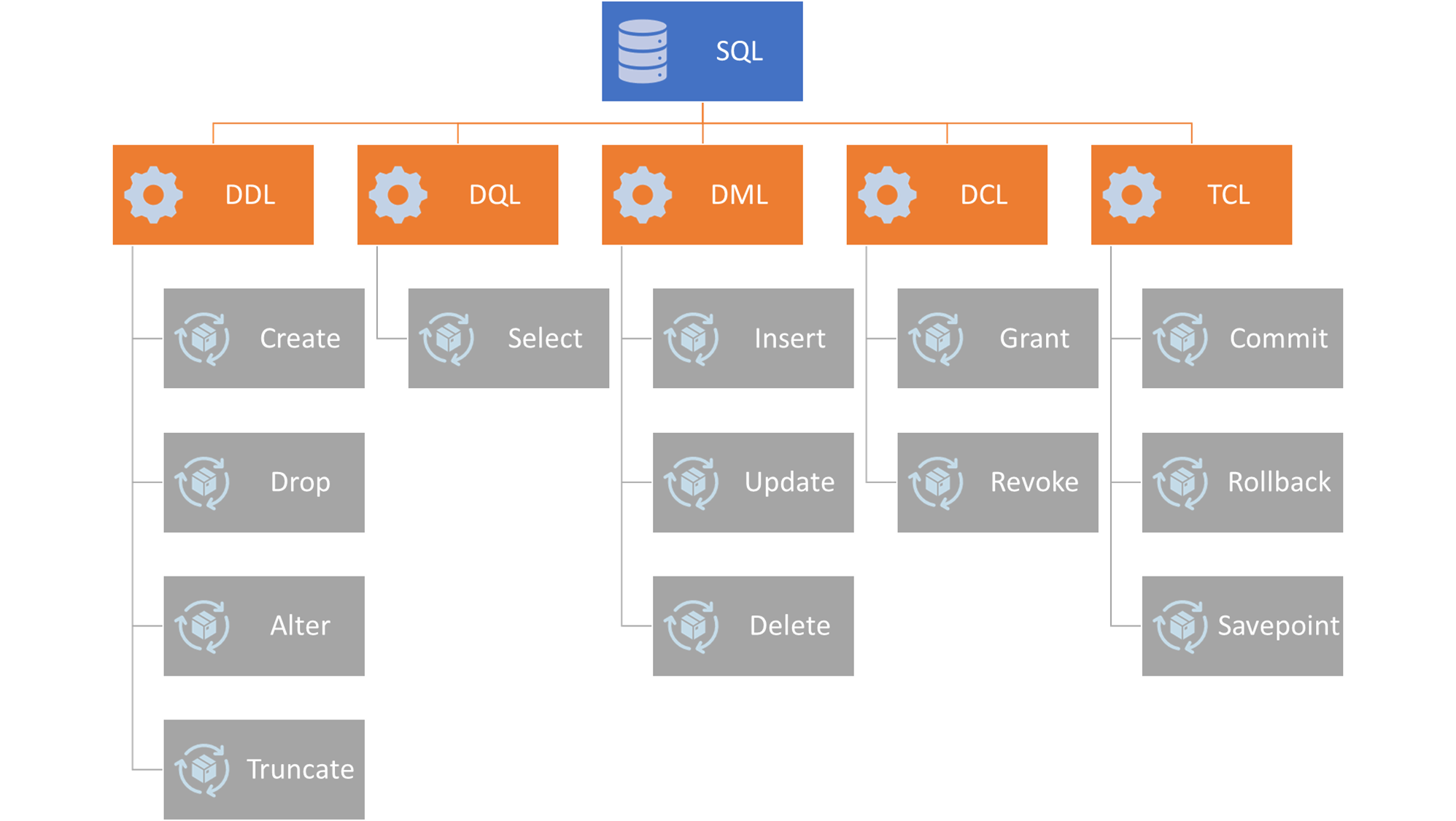
The standard SQL commands to interact with relational databases are CREATE, SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, DROP and few more. These commands can be classified into groups based on their nature:
DDL statements are used to build and modify the structure of your tables and other objects in the database. In simple words these are the commands which define the structure of the table/database/schema. When you execute a DDL statement, it takes effect immediately. Below are the DDL commands with the description of the task it performs.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| CREATE | Creates a new table, a view of a table, or other object in database |
| ALTER | Modifies an existing database object, such as a table |
| DROP | Deletes an entire table, a view of a table or other object in the database. |
| TRUNCATE | Deletes the data inside a table, but not the table itself. |
Syntax: CREATE DATABASE
CREATE DATABASE database_name; Example: Create dpu database
CREATE DATABASE dpu
);Syntax: CREATE TABLE
CREATE TABLE TABLE_NAME (COLUMN_NAME DATATYPES[,....]); Example: Create a Student table with following columns in dpu database
- StudentID
- LastName
- FirstName
- Address
- Mark
CREATE TABLE dpu.Student (
StudendId int,
LastName varchar(255),
FirstName varchar(255),
Address varchar(255),
Mark int
);Syntax: ALTER TABLE
ALTER TABLE: Add Column
ALTER TABLE table_name
ADD column_name datatype;ALTER TABLE: Drop Column
ALTER TABLE table_name
DROP column_name datatype;ALTER TABLE: Modify Column
ALTER TABLE table_name
MODIFY column_name datatype;Example: Add Department column to the existing Student table you just created.
ALTER TABLE dpu.Student
ADD Department varchar(25);Syntax: DROP TABLE
DROP TABLE table_name;Example: Drop the Student table you just created.
DROP TABLE dpu.Student;Note- Please Create the Student table again to make sure next examples work correctly
DML Statements are used to work on the data within the tables or in simple words it helps manipulate data inside table/database. With the help of DML commands, we can insert, delete, change the data inside a table.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| INSERT | Inserts the data into a table |
| UPDATE | Update the existing data in a table |
| DELETE | Delete the data records from a table |
Syntax: INSERT
Option 1: Provide the column names in INSERT INTO statement
INSERT INTO TABLE_NAME (col1, col2, col3,.... col N)
VALUES (value1, value2, value3, .... valueN); Option 2: No need to provide column names and the values will be inserted into columns as per the order they appear in table.
INSERT INTO TABLE_NAME
VALUES (value1, value2, value3, .... valueN);Example: Insert data into students table
INSERT INTO dpu.Student (StudendId, FirstName, LastName, Address, Mark)
VALUES (001, "Ankit", "Mittal", "Pune", 78),
(002, "Hitesh", "Mishra", "Bangalore", 83),
(003, "Deepak", "Singh", "Mumbai", 84),
(004, "Ashok", "Surendran", "Pune", 77)
(005, "Abhishek", "Jain", "Mumbai", 65);Syntax: UPDATE
UPDATE TABLE_NAME
SET column1 = value1, column2 = value2
WHERE condition;Example: Update the Marks of Abhishek Jain to 63
UPDATE dpu.Student
SET Mark = 63
WHERE FirstName='Abhishek';Syntax: DELETE
DELETE FROM TABLE_NAME
WHERE condition;Example: Delete the data for Deepak Singh
DELETE FROM dpu.Student
WHERE FirstName='Deepak' AND LastName='Singh';DQL statement is used to fetch the data from the database. With the help of DQL query we can get the data from the database to perform actions or operations like analysing the data.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| SELECT | Retrives data from one or more tables |
Syntax: SELECT
SELECT column1, column2....columnN
FROM table_name;Example: Select FirstName, LastName and Address of all the students from Student Table
SELECT FirstName, LastName, Address
FROM dpu.Student;DCL commands are used to give rights and permissions on database system.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| GRANT | To give user access privileges to a database. |
| REVOKE | To withdraw the user’s access privileges given by using the GRANT command. |
TCL commands are used to control the transaction performed using DML commands to maintain database consistency.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| COMMIT | To save the data permanently after a DML command is used |
| ROLLBACK | To get the data or restore the data to the last savepoint or last committed state |
| SAVEPOINT | To save the data at a particular point temporarily, so that whenever needed can be rollback to that particular point |
By this time you already know major SQL Commands and when to use which one, just that we need some practice.
Let's go to Next chapter>>