- Counting divisible Substrings
- Best Time to Buy And Sell Stock
- Maximum Sum of Subarray
- Trace and Normal of Matrix
- Sort an Array of 0s, 1s and 2s
- Prefix Sum
- First Negative Integer In Every K size Window
- Peak In 1D Array
- Array Operations
- Symmetric matrix
- Reversing of array
- Printing matrix in antispiral form
- Printing matrix for find the missing and repeating number
- Majority Element
- Sort an Array in wave form
- Print the matrix in wave form
- Spiral Traversal of Matrix
 Question:
Question:
You are given a string Str of length N. Each character of the string is a base 10 digit.
Your task is to find the total number of substrings of Str such that the number denoted by the string Str[i...j] is divisible by 6. Since that result can be a very large return it is modulo 10^9+7.
Notes:
- It is given that a number denoted by Str[i..j] can have leading Zeroes.
Input Format The first line contains an integer, N, denoting the length of the given string. The next line contains a string, Str, denoting the given string.
Constrains 1 <= N <= 10^5 1 <= len(Str) <= 10^5
| Sample Input | Sample Output | Explanation |
| 3 328 |
0 | No substring is divisible by 6 |
| 3 318 |
2 | "18","318" divisible by 6 |
| 4 6151 |
1 | "6" divisible by 6 |
The problem states that there is a string that contains only digits. You have to find the number of subsets that can be divisible by 6.
- 1st Select an index in the string from begining that has not been selected before as leftmost prefix and initilize count = 0.
- 2nd initilize number as 0.
- 3rd get the digit from the string by int(string[index])-int('0').
- 4th Now update the number by (suming prefix digit)*10 + current index digits and increment count if number is divisible
- 5th follow step 3rd till the end of string.
- 6th continue step 1-4 till all the element of string is not chosen as most significant digit place.
Time complexity: O(n2) Space complexity: O(1)
The problem states that there is an array or vector that contains N elements and elements stores stocks price at that day. For example: Let the array be [7,1,5,3,6,4] Then i=0 stores stocks price at 1st day that is 7.
- Then part of the problem states that you can not sell before buying and that means we can not
sell at i=0 and buy at i=1 for profit of 6. - The next part of the problem is if it can not have a profit then return 0 meaning
if no profit don't buy anything - example:
Input :[7,1]
Output: 0
- 1st initiate the buying price as
INT_MAXas we want to minimize it in later steps. Let us saybuying pricebe b - 2nd initiate the maximum profit as
0as it is given in the problem to return 0 if in case of no profit. Let us saymaximum profitbe p. - 3rd Now iterate over the array or vector if current element at
i is smaller then the previous elementthen update b to that element. - 4th Check wether the differece of current b with the current element is lager than previous value then update the p value to the value of differnce.
- 5th continue 3rd and 4th step till the lenth of the array or vector.
Time complexity: O(n) Space complexity: O(1)
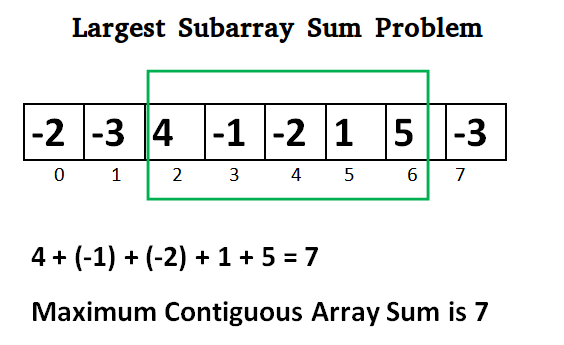
Given an array of integers, the task is to find the maximum subarray sum possible of all the non-empty subarrays.
| Sr. No. | Input | Output | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [-3, -4, 5, -1, 2, -4, 6, -1] | 8 | The subarray [5, -1, 2, -4, 6] has the maximum sum among all subarrays with sum 8. |
| 2 | [-2, 3, -1, 2] | 4 | The subarray [3, -1, 2] has the maximum sum among all subarrays with sum 4. |
| 3 | [-5, 8, 9, -6, 10, -15, 3] | 21 | The subarray [8, 9, -6, 10] has the maximum sum among all subarrays with sum 21. |
| 4 | [-4, -7, -1, 5,-2] | 4 | The subarray [-1, 5] has the maximum sum among all subarrays with sum 4. |
We would be solving the problem by following approaches –
- Brute force approach
- Cumulative sum approach
- Efficient Approach: Kadane’s Algorithm
The simple approach to solve this problem is to run three for loops and For each subarray arr[i..j], calculate its sum. Update maxSum if last calculated sum is smaller than the current sum.
int maxSubarraySum1 ( int a [] , int n)
{
int maxSum = INT_MIN
for(i = 0 to n-1)
{
for(j = i to n-1)
{
int sum = 0
for(k = i to j)
sum = sum + a[k]
Update maxSum if its smaller than sum with the maxSum value
}
}
return maxSum
}
Time Complexity: O(n^3), Where n is the size of the array.
Space Complexity: O(1)
For each subarray arr[i..j], calculate its sum. Using prefix sum can reduce time to calculate the sum of arr[i..j] to O(1)
int maxSubarraySum2 ( int a [] , int n)
{
int currsum[n+1]
Currsum[0] = 0
int maxSum = INT_MIN
for(i = 1 to n-1)
{
cumsum[i] = cumsum[i - 1] + a[i];
}
for(i = 1 to n-1)
{
int sum = 0
for(j = 0 to i)
sum = currsum[i - currsum[j]
Update maxSum if its smaller than sum with the maxSum value
}
return maxSum
}
Time Complexity: O(n^2), Where n is the size of the array.
Space Complexity: O(n)
Kadane’s Algorithm is an iterative dynamic programming algorithm. It calculates the maximum sum subarray ending at a particular position by using the maximum sum subarray ending at the previous position. Basic logic is to start taking the sum of the array, as soon as it gets negative, discard the current subarray, and start a new sum.
Initialize:
currsum = 0
maxSum = INT_MIN
Loop for each element of the array
(a) currsum = currsum + a[i]
(b) if(currsum < 0)
currsum = 0
Othewise maxSum = currsum
return max_so_far
Time complexity: O(n), Where n is the size of the array.
Space complexity: O(1)
The trace of a matrix A, defined by tr(A), is the sum of the diagonal elements of a matrix. Trace of a matrix is only possible for square matrix.
The normal of matrix is the sum of all the elements of a matrix and then the square root of sum.
--> tr(A + B) = tr(A) +tr(B)
--> tr(cA) = ctr(A) ** c represents scalars
--> tr(A) = tr(A^T) ** T means transpose of matrix
we have taken following as the elements of a matrix 2 3 5 7 4 5 8 5 4
we have to add all the elements of the matrix and store it in sum variable,sum = 2+3+5+7+4+5+8+5+4 then we will find the square root of sum we get 6.55 so, normal of matrix = 6.55
Now we will first check the conditions for trace of matrix (i.e. row==column) then we will add all the diagonal elements trace = 2+4+4 so, trace of matrix = 10
1. Enter the order of a matrix (eg: 3X3 or 2X2 etc...)
2. Using loop enter the elements of a matrix .
3. Printing the elements of the matrix .
4. Finding the sum of all the elements of the matrix .
5. Then the square root of the sum using sqrt() to find the normal of the matrix and store it in variable normal.
6. Using the condition row == column we can find the sum of diagonal elements of a matrix , value of sum will be store in
variable trace .
7. Print the value of normal and trace of a matrix .
Time complexity of trace of a matrix is n^2.
Time complexity of normal of a matrix is n^2.
- Symmetric matrix
- Pseudo Code of Symmetric Matrix
- Some properties of Symmetric Matrix
- Example of Symmetric Matrix
- Time complexity/space complexity of Symmetric Matrix
To check weather a matrix is symmetric or not
In linear algebra, a symmetric matrix is defined as the square matrix that is equal to its transpose matrix. The transpose matrix of any given matrix A can be given as A^T. A symmetric matrix A therefore satisfies the condition, A = A^T.
- Input from the user the order r,c of the matrix we wish to check
- Input a matrix of size rxc from the user with the help of nested for loops and store it in a 2-D array of size rxc.
- Set a variable flag = 0.
- Using a nested for loop check if a[i][j] = a[j][i] , if not, set flag = 1 and break out of the loops.
- Out of the loop check if flag = 0 then its symmetric matrix.
- In the else condition, if flag = 1 then its not a symmetric matrix.
- The sum and difference of two symmetric matrices give the resultant as a symmetric matrix.
- The property stated above is not always true for the product: Given the symmetric matrices A and B, then AB is symmetric if and only if A and B follow commutative property of multiplication, i.e., if AB = BA.
- For integer n, if A is symmetric, ⇒ A^n is symmetric.
- If A^-1 exists, it will be symmetric if and only if A is symmetric.
Time Complexity : O(N x N) space complexity : O(N x N)
- [1. Sort an Array of 0s, 1s and 2s](#1-sort-an-array-of-0s-1s-and-2s)
- [Dutch National Flag Algorithm](#dutch-national-flag-algorithm)
- [Properties](#properties)
- [Sample Output](#sample-output)
Given an array consisting 0s, 1s and 2s. The task is to write a function that sorts the given array. The functions should put all 0s first, then all 1s and all 2s in last.
begin sortArray(array)
int low = 0
int mid = 0
int high = array.size() - 1
while(mid <= high)
if (array[mid] == 0)
swap(array[low], array[mid])
low++
mid++
else if (array[mid] == 1)
mid++
else
swap(array[mid], array[high])
high--
end if
end while
return array
end sortArray
- Time Complexity: O(n)
- Space Complexity: O(1)
- In-Place: Yes
- Stable: Yes
- For More Reference Please Check Out -> Geeks For Geeks
Given an array of N integers. Given Q queries and in each query given L and R print sum of array elements from index L to R (both inclusive)
Use a loop to calculate the sum of numbers from l to r for each query.
Time Complexity: O(N) + O(Q*N) = 10^ 10
Space Complexity: O(1)
Use prefix sum , a pre-computation technique , to calculate the sum .
We declare a prefix[] array which stores the sum of numbers from 1 to ith index. prefix[i] ---> Stores the sum of numbers from 1 to ith index
So, to calculate the sum of numbers from l to r , we deduce a formula:
prefix[r] ----> Stores sum of numbers from 1 to rth index prefix[l-1] ----> Stores sum of numbers from 1 to (l-1)th index
So, to output the sum of numbers from l to r , we use this:
prefix[r]-prefix[l-1] (O(1) time complexity)
Time Complexity: O(N) + O(N) + O(Q) = 10^5
Space Complexity: O(N) + O(N) (Using prefix array)
Given an array and a positive integer k, find the first negative integer for each window(contiguous subarray) of size k. If a window does not contain a negative integer, then print 0 for that window. \
Input : arr[] = {-8, 2, 3, -6, 10}, k = 2
Output : -8 0 -6 -6
First negative integer for each window of size k
{-8, 2} = -8
{2, 3} = 0 (does not contain a negative integer)
{3, -6} = -6
{-6, 10} = -6
Input : arr[] = {12, -1, -7, 8, -15, 30, 16, 28} , k = 3
Output : -1 -1 -7 -15 -15 0
| Sr. No. | Input | Output | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [-3, -4, 5, -1, 2, -4, 6] , 3 | [-3, -4, -1, -1, -4] | [-3, -4, -1, -1, -4] are the first negative integer of every window of size 3. |
| 2 | [-2, 3, -1, 2] , 2 | [-2, -1, -1] | [-2, -1, -1] are the first negative integer of every window of size 2. |
| 3 | [-5, 8, 9, -6, 10, -15, 3] , 3 | [-5, -6 ,-6, -6, -15] | [-5, -6 ,-6, -6, -15] are the first negative integer of every window of size 3. |
| 4 | [-4, -7, 1, 5,2] , 2 | [-4, -7, 0, 0] | [-4, -7, 0, 0] are the first negative integer of every window of size 2. |
For every k size window store every element if negative in deque from rear end using for loop then check size of deque size if greater than 0 then then get the element from front and store it in vector. If deque size is 0 store 0 in vector. Move the window ahead if we have reached or passed the last element of the window.
1. Initialize deque and vector.
2. Use loop for starting window that is till k.
3. Push back the index in deque if element is negative.
4. Push back 0 if element is positive.
5. Check the size of deque after execution of loop if size > 0 get the front element of deque(index) store the element at that index in vector.
6. Else store 0 in vector.
7. Use loop from k till last index of array.
8. Check if deque is not empty && loop variable - front element of deque is not greater than or equal to k.
9. If step 8 is true pop the front element in deque.
10.Repeat steps 5,6 and 8, 9 till execution of loop
Time Complexity = O(n-k), Where n is the size of the array and k is window size.
Space complexity = O(n-k+1), size of vector returned.
Peak element in 1D array is the element which is greater than or equal to its adjacent neighbours. For the first and last element in the array consider only one adjacent neighbour.
Example 1:
Example 2:
Example 3:
Traverse the array linearly and check wheather the element is peak or not, by comparing with it's adjacent neighbours.
- If size of the array is 1 then then return that element.
- Checking for the corner cases:
- In the array if the first element is greater than or equal to second element then we return 0 (index of the first element).
- In the array if the last element is greater than or equal to second last element then we return n-1 (index of the last element).
- Traverse the array from second element to second last element.
- If the element is greater than or equal to both of it's adjacent neighbours then return the index of that element.
int simplePeak(vector<int> &arr,int n){
if(n==1) return 0
if(arr[0]>=arr[1]) return 0
if(arr[n-1]>=arr[n-2]) return n-1
for(int i=1;i<n-1;i++){
if(arr[i]>=arr[i+1] && arr[i]>=arr[i-1]) return i
}
}
Time Complexity: O(n)
Auxillary Space: O(1)
- Make two variables,start=0 and end=n-1.
- Iterate till start is less than end.
- Check if the mid value is peak or not ,if yes then return mid.
- If the element on the left side of mid element is more then update end=mid-1.
- If the element on the right side of mid element is more then update start=mid+1.
begin efficientPeak(array,n)
if(n == 1) return 0
if(array[0] >= array[1]) return 0;
if(array[n-1] >= array[n-2]) return n-1;
int start = 0
int mid = 0
int end= n-1
while(start <= end)
mid = (start + end)/2
if((array[mid] >= array[mid-1]) && (array[mid] >= array[mid+1]))
return mid
else if(array[mid] < array[mid-1])
end=mid-1
else
start=mid+1
end if
end while
end efficientPeak
Time Complexity: O(log n)
Auxillary Space: O(1)
Array is a container which can hold fix number of items of same data type. Syntax for declaring an array is: datatype array_name[size];
Most of the Data Structures use arrays to implement algorithms. Some basics operations can be performed in an array. The Operations which can be performed are as follows:
- Traversal
- Insertion
- Deletion
- Searching- a) Linear Search b) Binary Search
- 1st START OF THE PROGRAM
- 2st Create an array of fixed size i.e the maximum capacity/elements the array can store.
- 3nd Input the size of array you want to create & the elements of array from the user.
- 4rd Create a traversal function which takes array & size of the array as its arguments so that every element of the array can be traversed as well as printed(with the help of for loop which iterate with the size of array).
- 5th For Insertion, create an insert function i.e insert(array,new element,index of new element,size,capacity). Check the condition whether element can be inserted or not & if the index number is valid or not.If yes, then insert the new element by shifting the previous elements in forward direction & put the new element at the required index
-
for (int i = size - 1; i >= index; i--) { arr[i + 1] = arr[i]; } arr[index] = element; - 6th For Deletion, create a delete function which takes array, size & index as arguments. Deletion can be done directly by shifting the elements in backward direction from the index number
-
for (int i = index; i < size - 1; i++) { arr[i] = arr[i + 1]; } - 7st In order to Search elements in the Array, there are 2 methods i.e LINEAR SEARCH ALGORITHM & another is BINARY SEARCH ALGORITHM.
- LINEAR SEARCH -
- In this algorithm, a sequential search is made over all elements one by one & if a match is found(i.e key==element),then index of that element is returned.
-
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { if (arr[i] == key) { return i; } } - BINARY SEARCH -
- NOTE:: This algorithm works only for SORTED ARRAYS
- In this algorithm, search begins by comparing the key with the element in the middle of the array.If match is found then index is returned. But, if the key is less than middle element, then the search continues in the lower half of the array(i.e BINARY SEARCH will again work from low index to the middle index). And if the key is greater than the middle element,then search continues in the upper half(i.e from middle index to high index)
-
int low = 0; int mid; int high = size - 1; while (low <= high) { mid = (low + high) / 2; if (arr[mid] == key) { return mid; } else if (arr[mid] < key) { low = mid + 1; } else { high = mid - 1; } } - 8st END OF THE PROGRAM
-
SAMPLE INPUT - arr[10]={1,2,3,4,5}; Traversal-> traversal(arr,size); O/P- 1 2 3 4 5 Insertion-> insert(arr, new element, index, size, capacity); (let new element be 9 & index be 2) O/P- 1 2 9 3 4 5 Deletion-> delete(arr,size,index); (let index=1) O/P- 1 9 3 4 5 Linear Search-> linear(arr,key,size); (let key=3) O/P- Element 3 is found at index 2 Binary Search-> binary(arr,key,size); (let key=9) O/P- Element 9 is found at index 1 (if key=3) O/P- Element not Found as Binary search works only for sorted array
For TRAVERSAL-
Time complexity is O(n).
For INSERTION-
- Best Case Time Complexity is O(1)
- Worst Case Time Complexity is O(n)
For DELETION-
- Best Case Time Complexity is O(1)
- Worst Case Time Complexity is O(n)
For LINEAR SEARCH-
- Best Case Time Complexity is O(1)
- Worst Case Time Complexity is O(n)
For BINARY SEARCH-
- Best Case Time Complexity is O(1)
- Worst Case Time Complexity is O(log n)
1.Take input the size of the array and the elements of the array. 2.Consider a function reverse1 which takes the parameters-the array(say arr) and the size of the array(say n). 3.Inside the function, a new array (with the array size of the first array, arr) is initialized. The array arr[] is iterated from the first element, and each element of array arr[] is placed in the new array from the back, i.e., the new array is iterated from its last element. 4.In this way, all the elements of the array arr[] are placed reversely in the new array. 5.Further, we can iterate through the new array from the beginning and print the elements of the array.
Time-complexity-->O(n) Space-complexity-->O(n)
The reverse2 method uses a similar code for the inputting and printing of the array. However, we don’t create a new array like the above method. Instead, we reverse the original array itself. In this method, we swap the elements of the array. The first element is swapped with the last element. The second element is swapped with the last but one element and so on. For instance, consider array [1, 2, 3, …., n-2, n-1, n]. We swap 1 with n, 2 with n-1, 3 with n-2 and further.
Properties Time-complexity-->O(n) Space-complexity-->O(1)
The problem is that you are given a 2D array and the task is to print matrix in anti spiral form.
> Note you must be well aware with the printing matrix in spiral form algorithm
to properly understand the printing matrix in antispiral form
Input :
arr[][4] = {1, 2, 3, 4
5, 6, 7, 8
9, 10, 11, 12
13, 14, 15, 16};
Output :
10 11 7 6 5 9 13 14 15 16 12 8 4 3 2 1
-
The idea is simple, we traverse matrix in spiral form and put all traversed elements in a stack.
-
Finally one by one elements from stack and print them.
-
Understanding spiral method :
-
In spiral method the problem can be solved by dividing the matrix into boundaries.
-
It is visible that elements of the outer loop are printed in a clockwise manner, and then the elements from the inner loop are printed.
-
So, we can imagine the outer loop as four boundaries, namely row_start, col_start, row_end, col_end.
-
row_start: elements in the path of the matrix where we move from left to right.
-
row_end: elements in the path of the matrix where we move from right to left.
-
col_start: elements in the path of the matrix where we move from up to down.
-
col_end: elements in the path of the matrix where we move from down to up.
-
We print elements covered by each boundary in a clockwise manner using four loops, and after each iteration, reduce the dimension of the boundary to form an inner loop of the matrix.
-
Now, the new boundary conditions become our new matrix.
Time Complexity: O ( m * n )
Space Complexity: O (m * n )
Given an unsorted array of size n. Array elements are in the range from 1 to n. One number from set {1, 2, …n} is missing and one number occurs twice in the array.
Find these two numbers.
Input:
arr[] = {3, 1, 3}
Output:
Missing = 2, Repeating = 3
Explanation: In the array,
2 is missing and 3 occurs twice
-
Given an array and its size first we need to traverse the array.
-
While traversing, use the absolute value of every element as an index.
-
Make the value at this index as negative to mark it visited.
-
If something is already marked negative then this is the repeating element.
-
To find missing, traverse the array again and look for a positive value.
-
This question can also be solved using sorting.
-
But using this approach is better as it solves the question in O(n) complexity whereas in sorting it would need O(nlogn) complexity.
-
In sorting approach you would need to sort the input array and then traverse and check for elements.
-
This would lead to O(nlogn) complexity.
Time Complexity: O (n)
Space Complexity: O (n)
The problem is given an array you have to print the majority element. A majority element in an array A[] of size n is an element that appears more than n/2 times.
Input :
{3, 3, 4, 2, 4, 4, 2, 4, 4}
Output : 4
Explanation: The frequency of 4 is 5 which is greater
than the half of the size of the array size.
-
Given an array we take two loops and keep track of the maximum count for all different elements.
-
If maximum count becomes greater than n/2 then break the loops and return the element having maximum count.
-
If the maximum count doesn’t become more than n/2 then the majority element doesn’t exist.
-
Create a variable to store the max count, count = 0
-
Traverse through the array from start to end.
-
For every element in the array run another loop to find the count of similar elements in the given array.
-
If the count is greater than the max count update the max count and store the index in another variable.
-
If the maximum count is greater than the half the size of the array, print the element. Else print there is no majority element.
Time Complexity: O(n*n)
Space Complexity: O(1)
Given an unsorted array of integers, sort the array into a wave like array. An array ‘arr[0..n-1]’ is sorted in wave form if arr[0] >= arr[1] <= arr[2] >= arr[3] <= arr[4] >= …..
Input:
arr[] = {10, 5, 6, 3, 2, 20, 100, 80}
Output:
arr[] = {10, 5, 6, 2, 20, 3, 100, 80} OR
{20, 5, 10, 2, 80, 6, 100, 3} OR
any other array that is in wave form
-
Given an array of size n first sort the input array.
-
Then swap all the adjacent elements.
-
For example, let the input array be {3, 6, 5, 10, 7, 20}.
-
After sorting, we get {3, 5, 6, 7, 10, 20}.
-
After swapping adjacent elements, we get {5, 3, 7, 6, 20, 10}.
Time Complexity: O(nlogn)
Space Complexity: O(1)
For a 2D integer array "matrix" of size m x n (where m and n are the number of rows and columns respectively), print the ‘matrix’ in wave order, i.e. print the first column top to bottom, next column bottom to top, and so on.
Input :
1,2,3
4,5,6
7,8,9
Output : 1 4 7 8 5 2 3 6 9
- Run a loop from col_no = 0 to n ( Toal number of columns).
- If the col_no(current column) is even, then the elements will be printed from top to bottom.
- Run an inner loop from row_no = 0 to m (Total number of rows) Print all the elements.
- Else if the current row is odd, then the elements will be printed from bottom to top.
- Run another inner loop from row no = m - 1 to 0
- Print all the elements.
Time Complexity: O(N2)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
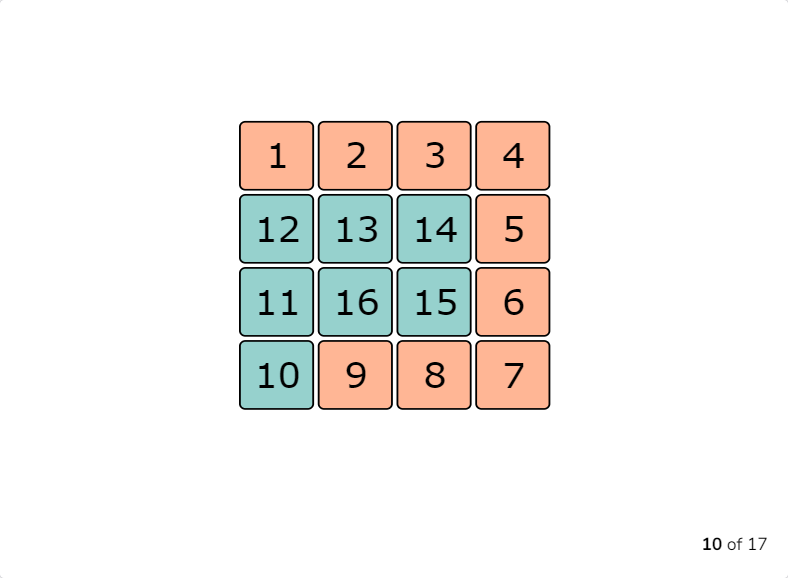
The Spiral Matrix problem takes a 2-Dimensional array with N rows and M columns as input and prints the elements in spiral order. The spiral starts at the top left corner of the input matrix and prints all of the elements it encounters as it loops clockwise towards the centre.
- First, four variables containing the indices for the corner points of the array are initialized.
- From the top left corner of the array, the algorithm traverses the first row from left to right. It does not need to revisit the row once it has traversed it, so it increments the top corner index.
- It then traverses the rightmost column from top to bottom. Once this is done, there is no need to go back to the rightmost column, so the right corner index is decremented.
- Next, the algorithm traverses the bottommost row and decrements the bottom corner index afterward.
- Finally, the algorithm goes through the leftmost column, incrementing the left corner index once it's done.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |