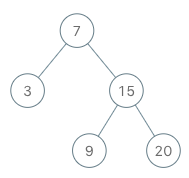
Implement an iterator over a binary search tree (BST). Your iterator will be initialized with the root node of a BST.
Calling next() will return the next smallest number in the BST.
Example:
BSTIterator iterator = new BSTIterator(root); iterator.next(); // return 3 iterator.next(); // return 7 iterator.hasNext(); // return true iterator.next(); // return 9 iterator.hasNext(); // return true iterator.next(); // return 15 iterator.hasNext(); // return true iterator.next(); // return 20 iterator.hasNext(); // return false
Note:
next()andhasNext()should run in average O(1) time and uses O(h) memory, where h is the height of the tree.- You may assume that
next()call will always be valid, that is, there will be at least a next smallest number in the BST whennext()is called.
- Binary Tree Inorder Traversal (Medium)
- Flatten 2D Vector (Medium)
- Zigzag Iterator (Medium)
- Peeking Iterator (Medium)
- Inorder Successor in BST (Medium)