- In programming languages, loops are used to execute a particular statement/set of instructions again and again.
- The execution of the loop starts when some conditions become true.
- For example, print 1 to 1000, print multiplication table of 7, etc.
- Loops make it easy for us to tell the computer that a given set of instructions need to be executed repeatedly.
- Primarily, there are three types of loops in Java:
- While loop
- do-while loop
- for loop
- Let's look into these, one by one.
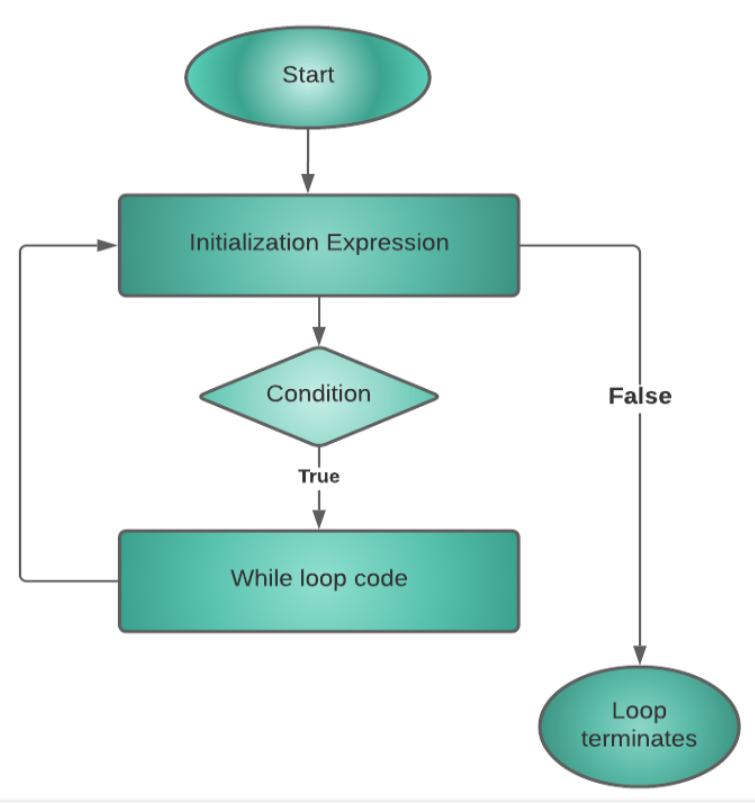
- The while loop in Java is used when we need to execute a block of code again and again based on a given boolean condition.
- Use a while loop if the exact number of iterations is not known.
- If the condition never becomes false, the while loop keeps getting executed. Such a loop is known as an infinite loop.
/*
while (Boolean condition)
{
// Statements -> This keeps executing as long as the condition is true.
}
*/
- Example
int i=10;
while(i>0){
System.out.println(i);
i--;
}
Quick Quiz: Write a program to print natural numbers from 100 to 200.
public class cwh_21_ch5_loops {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(1);
System.out.println(2);
System.out.println(3);
System.out.println("Using Loops:");
int i = 100;
while(i<=200){
System.out.println(i);
i++;
}
System.out.println("Finish Running While Loop!");
// while(true){
// System.out.println("I am an infinite while loop!");
// }
}
}
- This is all for this tutorial, and we will discuss the do-while loop in the next tutorial.
Handwritten Notes: Click to Download
Ultimate Java Cheatsheet: Click To Download