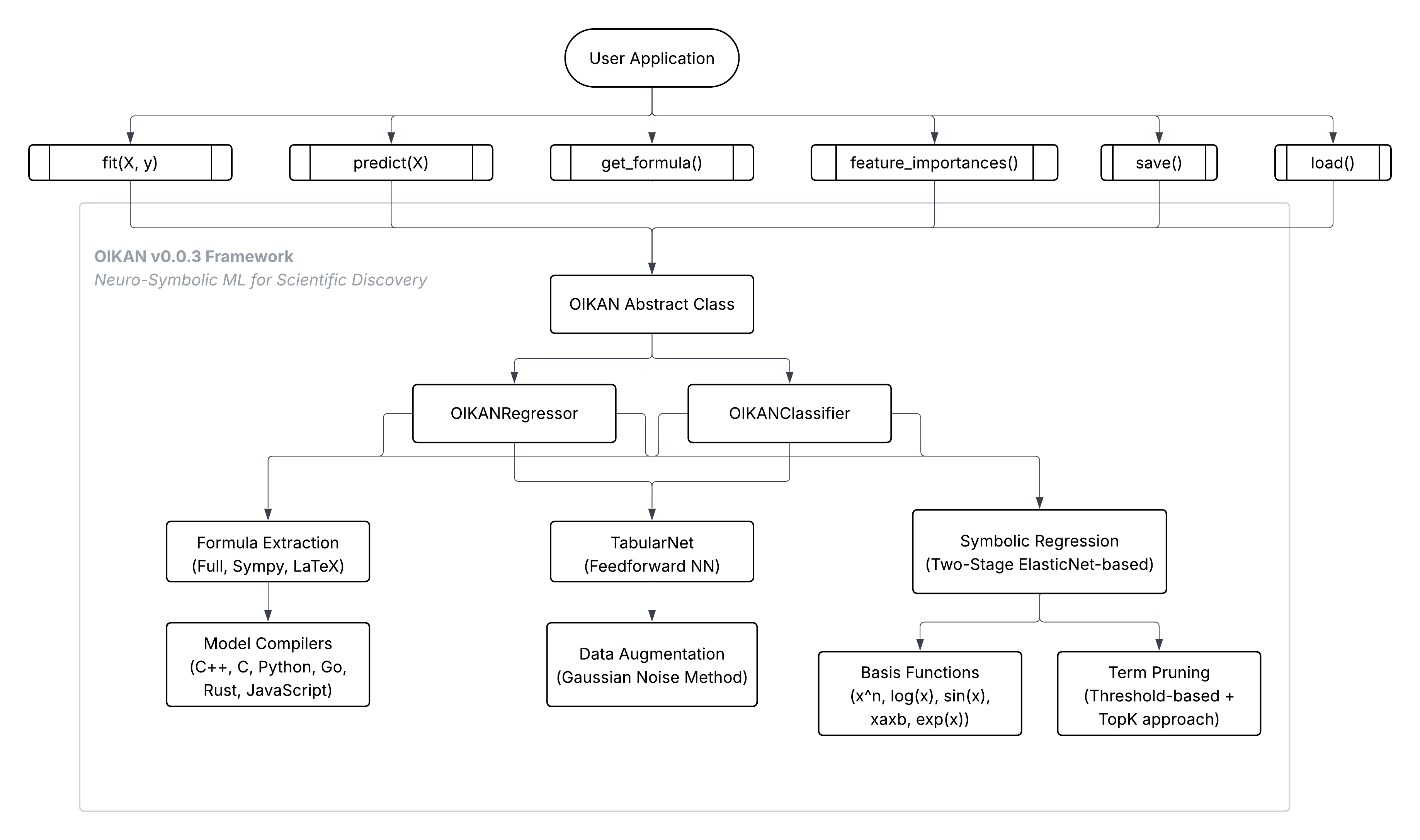
OIKAN is a neuro-symbolic machine learning framework inspired by Kolmogorov-Arnold representation theorem. It combines the power of modern neural networks with techniques for extracting clear, interpretable symbolic formulas from data. OIKAN is designed to make machine learning models both accurate and Interpretable.
Important Disclaimer: OIKAN is an experimental research project. It is not intended for production use or real-world applications. This framework is designed for research purposes, experimentation, and academic exploration of neuro-symbolic machine learning concepts.
- 🧠 Neuro-Symbolic ML: Combines neural network learning with symbolic mathematics
- 📊 Automatic Formula Extraction: Generates human-readable mathematical expressions
- 🎯 Scikit-learn Compatible: Familiar
.fit()and.predict()interface - 🔬 Research-Focused: Designed for academic exploration and experimentation
- 📈 Multi-Task: Supports both regression and classification problems
-
Neural Implementation: OIKAN uses a specialized architecture combining:
- Feature transformation layers with interpretable basis functions
- Symbolic regression for formula extraction (ElasticNet-based)
- Automatic pruning of insignificant terms
class OIKAN: def __init__(self, hidden_sizes=[64, 64], activation='relu', polynomial_degree=2, alpha=0.1): # Neural network for learning complex patterns self.neural_net = TabularNet(input_size, hidden_sizes, activation) # Data augmentation for better coverage self.augmented_data = self.augment_data(X, y, augmentation_factor=5) # Symbolic regression for interpretable formulas self.symbolic_regression = SymbolicRegression(alpha=alpha)
-
Basis Functions: Core set of interpretable transformations:
SYMBOLIC_FUNCTIONS = { 'linear': 'x', # Direct relationships 'quadratic': 'x^2', # Non-linear patterns 'cubic': 'x^3', # Higher-order relationships 'interaction': 'x_i x_j', # Feature interactions 'higher_order': 'x^n', # Polynomial terms 'trigonometric': 'sin(x)', # Trigonometric functions 'exponential': 'exp(x)', # Exponential growth 'logarithmic': 'log(x)' # Logarithmic relationships }
-
Formula Extraction Process:
- Train neural network on raw data
- Generate augmented samples for better coverage
- Perform ElasticNet-regularization
- Prune terms with coefficients below threshold
- Export human-readable mathematical expressions
pip install -qU oikangit clone https://github.com/silvermete0r/OIKAN.git
cd OIKAN
pip install -e . # Install in development mode| Requirement | Details |
|---|---|
| Python | Version 3.7 or higher |
| Operating System | Platform independent (Windows/macOS/Linux) |
| Memory | Recommended minimum 4GB RAM |
| Disk Space | ~100MB for installation (including dependencies) |
| GPU | Optional (for faster training) |
| Dependencies | torch, numpy, scikit-learn, sympy, tqdm |
Suggestion: Please ensure that the data is normalized using standard scaling (or another suitable normalization method), as Elastic Net assumes that the model intercept has already been accounted for.
from oikan import OIKANRegressor
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
# Initialize model
model = OIKANRegressor(
hidden_sizes=[32, 32], # Hidden layer sizes
activation='relu', # Activation function (other options: 'tanh', 'leaky_relu', 'elu', 'swish', 'gelu')
augmentation_factor=5, # Augmentation factor for data generation
alpha=1.0, # ElasticNet regularization strength (Symbolic regression)
l1_rate=0.5, # ElasticNet mixing parameter (0 <= l1_ratio <= 1). 0 is equivalent to Ridge regression, 1 is equivalent to Lasso (Symbolic regression)
sigma=5, # Standard deviation of Gaussian noise for data augmentation
top_k=5, # Number of top features to select (Symbolic regression)
epochs=100, # Number of training epochs
lr=0.001, # Learning rate
batch_size=32, # Batch size for training
verbose=True, # Verbose output during training
evaluate_nn=True, # Validate neural network performance before full process
random_state=42 # Random seed for reproducibility
)
# Fit the model
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Make predictions
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
# Evaluate performance
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred)
print("Mean Squared Error:", mse)
# Get symbolic formula
formula = model.get_formula() # default: type='original' -> returns all formula without pruning | other options: 'sympy' -> simplified formula using sympy; 'latex' -> LaTeX format
print("Symbolic Formula:", formula)
# Get feature importances
importances = model.feature_importances()
print("Feature Importances:", importances)
# Save the model (optional)
model.save("outputs/model.json")
# Load the model (optional)
loaded_model = OIKANRegressor()
loaded_model.load("outputs/model.json")Example of the saved symbolic formula (regression model): outputs/california_housing_model.json
Suggestion: Please ensure that the data is normalized using standard scaling (or another suitable normalization method), as Elastic Net assumes that the model intercept has already been accounted for.
from oikan import OIKANClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
# Initialize model
model = OIKANClassifier(
hidden_sizes=[32, 32], # Hidden layer sizes
activation='relu', # Activation function (other options: 'tanh', 'leaky_relu', 'elu', 'swish', 'gelu')
augmentation_factor=10, # Augmentation factor for data generation
alpha=1.0, # ElasticNet regularization strength (Symbolic regression)
l1_rate=0.5, # ElasticNet mixing parameter (0 <= l1_ratio <= 1). 0 is equivalent to Ridge regression, 1 is equivalent to Lasso (Symbolic regression)
sigma=5, # Standard deviation of Gaussian noise for data augmentation
top_k=5, # Number of top features to select (Symbolic regression)
epochs=100, # # Number of training epochs
lr=0.001, # Learning rate
batch_size=32, # Batch size for training
verbose=True, # Verbose output during training
evaluate_nn=True, # Validate neural network performance before full process
random_state=42 # Random seed for reproducibility
)
# Fit the model
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Make predictions
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
# Evaluate performance
accuracy = model.score(X_test, y_test)
print("Accuracy:", accuracy)
# Get symbolic formulas for each class
formulas = model.get_formula() # default: type='original' -> returns all formula without pruning | other options: 'sympy' -> simplified formula using sympy; 'latex' -> LaTeX format
for i, formula in enumerate(formulas):
print(f"Class {i} Formula:", formula)
# Get feature importances
importances = model.feature_importances()
print("Feature Importances:", importances)
# Save the model (optional)
model.save("outputs/model.json")
# Load the model (optional)
loaded_model = OIKANClassifier()
loaded_model.load("outputs/model.json")Example of the saved symbolic formula (classification model): outputs/iris_model.json
OIKAN provides a set of symbolic model compilers to convert the symbolic formulas generated by the OIKAN model into different programming languages.
Currently, we support: Python, C++, C, JavaScript, Rust, and Go. This allows users to easily integrate the generated formulas into their applications or systems.
All compilers: model_compilers/
- Regression Model:
import numpy as np
import json
def predict(X, symbolic_model):
X = np.asarray(X)
X_transformed = evaluate_basis_functions(X, symbolic_model['basis_functions'],
symbolic_model['n_features'])
return np.dot(X_transformed, symbolic_model['coefficients'])
if __name__ == "__main__":
with open('outputs/california_housing_model.json', 'r') as f:
symbolic_model = json.load(f)
X = np.random.rand(10, symbolic_model['n_features'])
y_pred = predict(X, symbolic_model)
print(y_pred)- Classification Model:
import numpy as np
import json
def predict(X, symbolic_model):
X = np.asarray(X)
X_transformed = evaluate_basis_functions(X, symbolic_model['basis_functions'],
symbolic_model['n_features'])
logits = np.dot(X_transformed, np.array(symbolic_model['coefficients_list']).T)
probabilities = np.exp(logits) / np.sum(np.exp(logits), axis=1, keepdims=True)
return np.argmax(probabilities, axis=1)
if __name__ == "__main__":
with open('outputs/iris_model.json', 'r') as f:
symbolic_model = json.load(f)
X = np.array([[5.1, 3.5, 1.4, 0.2],
[7.0, 3.2, 4.7, 1.4],
[6.3, 3.3, 6.0, 2.5]])
y_pred = predict(X, symbolic_model)
print(y_pred)We welcome contributions! Key areas of interest:
- Model architecture improvements
- Novel basis function implementations
- Improved symbolic extraction algorithms
- Real-world case studies and applications
- Performance optimizations
Please see CONTRIBUTING.md for guidelines.
If you use OIKAN in your research, please cite:
@software{oikan2025,
title = {OIKAN: Neuro-Symbolic ML for Scientific Discovery},
author = {Zhalgasbayev, Arman},
year = {2025},
url = {https://github.com/silvermete0r/OIKAN}
}This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details.







-architecture-oop.png)