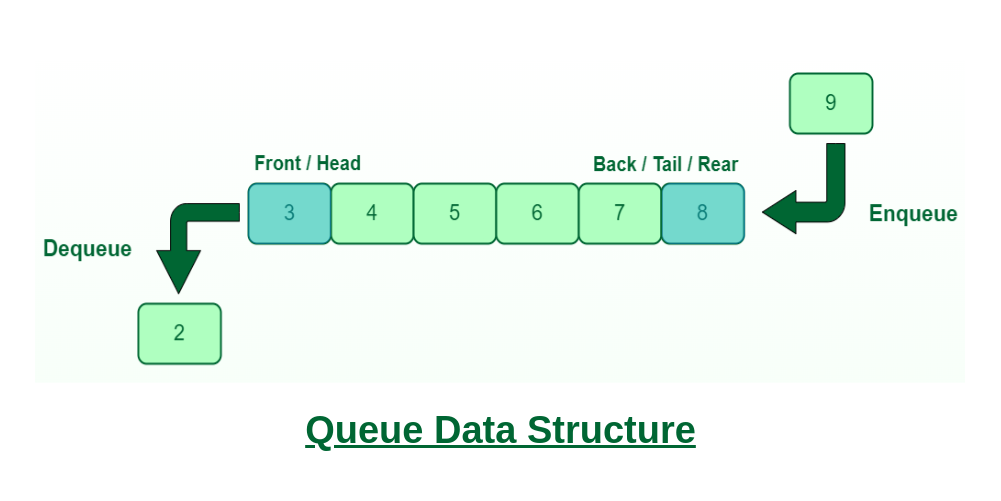
A queue is a linear data structure that follows the First-In-First-Out (FIFO) principle. This means that the first element added to the queue will be the first one to be removed. A queue can be implemented using arrays, linked lists, or other data structures.
A queue is a collection of elements that supports two main operations:
- Enqueue: Add an element to the end of the queue.
- Dequeue: Remove an element from the front of the queue.
Queues are used in various applications, such as task scheduling, buffering data streams, and handling requests. They are fundamental in computer science and are used in various algorithms and systems.
- Simple Queue: A basic queue where elements are added at the rear and removed from the front.
- Circular Queue: A type of queue where the last position is connected to the first position, forming a circle. This helps in utilizing the available space more efficiently.
- Priority Queue: A queue where each element has a priority, and elements with higher priority are dequeued before those with lower priority.
- Double-Ended Queue (Deque): A queue where elements can be added or removed from both the front and rear ends.
Common operations performed on queues include:
- Enqueue: Add an element to the end of the queue.
- Dequeue: Remove an element from the front of the queue.
- Peek/Front: Get the element at the front of the queue without removing it.
- IsEmpty: Check if the queue is empty.
A Double-Ended Queue (Deque) is a generalized form of a queue data structure in which the insertion and deletion operations can be performed from both ends (front and rear).
In an array-based implementation, a queue uses an array to store its elements. Two pointers, front and rear, are maintained to keep track of the beginning and end of the queue, respectively. Elements are added at the position indicated by rear and removed from the position indicated by front.
In a linked list-based implementation, a queue uses a linked list where each node contains data and a reference to the next node. The front and rear pointers keep track of the start and end of the queue. The front pointer is used for dequeuing, and the rear pointer is used for enqueuing.
A queue can be implemented using two stacks. One stack is used for enqueue operations, and the other is used for dequeue operations. When dequeuing, if the second stack is empty, elements are transferred from the first stack to the second stack. This ensures that the order of elements is maintained according to the FIFO principle.
- Queue Implementation: Demonstrates how to implement a queue using arrays, linked lists, and two stacks.
- Circular Queue: An enhancement where the last position connects to the first, utilizing available space more efficiently.
- Priority Queue: Manages tasks with different priorities, processing higher-priority tasks first.