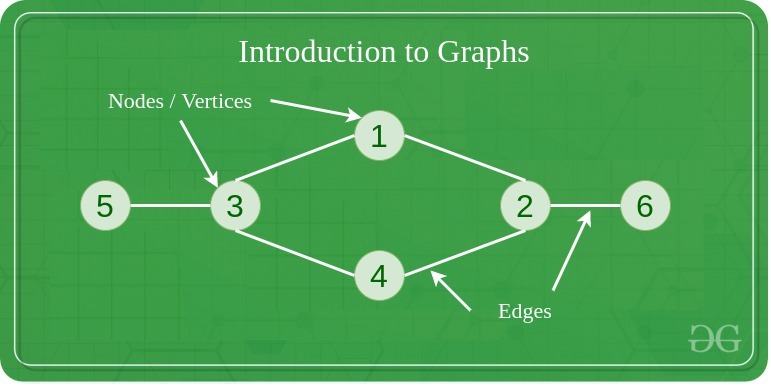
A graph is a data structure that consists of a finite set of vertices (or nodes) connected by edges. It is used to model relationships between objects, representing nodes as entities and edges as relationships. Graphs are highly useful in representing real-world scenarios, such as networks, web pages, and social connections.
- Undirected Graph: A graph where edges do not have a direction.
- Directed Graph (Digraph): A graph where each edge has a direction.
- Weighted Graph: A graph where each edge has an associated weight, representing the cost or distance between vertices.
-
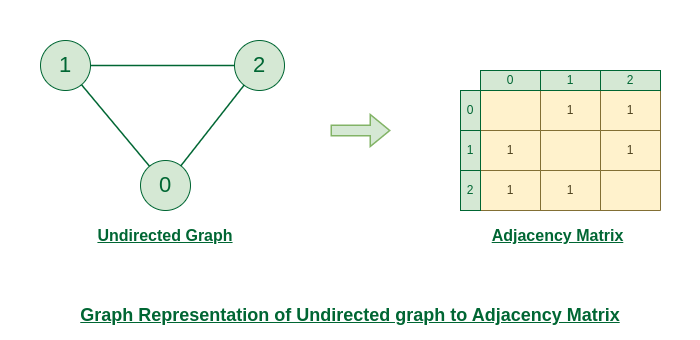
Adjacency Matrix: A 2D array where each cell
(i, j)represents an edge from vertexito vertexj. -
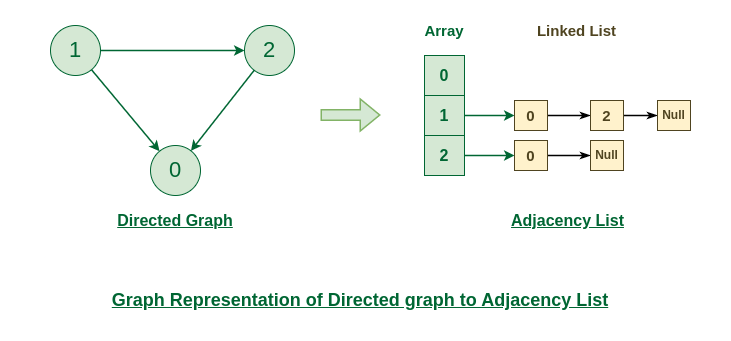
Adjacency List: An array of lists where each list contains the neighboring vertices of a vertex.
- Add Vertex: Insert a new vertex into the graph.
- Add Edge: Insert a new edge between two vertices.
- Remove Vertex: Delete a vertex and all its edges.
- Remove Edge: Delete a specific edge between two vertices.
DFS explores as far as possible along each branch before backtracking.
BFS explores all neighbors at the present depth before moving on to nodes at the next depth level.
- Social Networks: To represent connections among users.
- Web Crawling: For web page traversal.
- Routing Algorithms: Used in networking for finding shortest paths.
- Recommendation Systems: Graphs are used to model relationships between items and users.
Graphs are versatile structures widely used in computer science. Understanding graphs and their various representations, operations, and traversal methods like BFS and DFS is crucial for solving complex problems in data analysis, networking, and other computational fields.