A high-performance, provider-agnostic bulk insert extension for Entity Framework Core 8+. Supports SQL Server, PostgreSQL, SQLite, MySQL and Oracle.
Its main purpose is to provide a fast way to perform simple bulk inserts in Entity Framework Core applications.
- Performance: It is designed to be fast and memory efficient, making it suitable for high-performance applications.
- Provider-agnostic: It works with multiple database providers (SQL Server, PostgreSQL, SQLite and MySQL), allowing you to use it in different environments without changing your code.
- Simplicity: The API is simple and easy to use, making it accessible for developers of all skill levels.
For now, it does not support navigation properties, complex types, owned types, shadow properties, or inheritance, but they are in the roadmap.
Install the NuGet package for your database provider:
# For SQL Server
Install-Package PhenX.EntityFrameworkCore.BulkInsert.SqlServer
# For PostgreSQL
Install-Package PhenX.EntityFrameworkCore.BulkInsert.PostgreSql
# For SQLite
Install-Package PhenX.EntityFrameworkCore.BulkInsert.Sqlite
# For MySql
Install-Package PhenX.EntityFrameworkCore.BulkInsert.MySql
# For Oracle
Install-Package PhenX.EntityFrameworkCore.BulkInsert.OracleRegister the bulk insert provider in your DbContextOptions:
services.AddDbContext<MyDbContext>(options =>
{
options
// .UseSqlServer(connectionString) // or UseNpgsql or UseSqlite, as appropriate
.UseBulkInsertPostgreSql()
// OR
.UseBulkInsertSqlServer()
// OR
.UseBulkInsertSqlite()
// OR
.UseBulkInsertMySql()
// OR
.UseBulkInsertOracle()
;
});// Asynchronously
await dbContext.ExecuteBulkInsertAsync(entities);
// Or synchronously
dbContext.ExecuteBulkInsert(entities);// Common options
await dbContext.ExecuteBulkInsertAsync(entities, options =>
{
options.BatchSize = 1000; // Set the batch size for the insert operation, the default value is different for each provider
});
// Provider specific options, when available, example for SQL Server
await dbContext.ExecuteBulkInsertAsync(entities, (SqlServerBulkInsertOptions o) => // <<< here specify the SQL Server options class
{
options.EnableStreaming = true; // Enable streaming for SQL Server
});
// Provider specific options, supporting multiple providers
await dbContext.ExecuteBulkInsertAsync(entities, o =>
{
o.MoveRows = true;
if (o is SqlServerBulkInsertOptions sqlServerOptions)
{
sqlServerOptions.EnableStreaming = true;
}
else if (o is MySqlBulkInsertOptions mysqlOptions)
{
mysqlOptions.BatchSize = 1000;
}
});await dbContext.ExecuteBulkInsertReturnEntitiesAsync(entities);Conflict resolution works by specifying columns that should be used to detect conflicts and the action to take when
a conflict is detected (e.g., update existing rows), using the onConflict parameter.
- The conflicting columns are specified with the
Matchproperty and must have a unique constraint in the database. - The action to take when a conflict is detected is specified with the
Updateproperty. If not specified, the default action is to do nothing (i.e., skip the conflicting rows). - You can also specify the condition for the update action using either the
Whereor theRawWhereproperty. If not specified, the update action will be applied to all conflicting rows.
await dbContext.ExecuteBulkInsertAsync(entities, onConflict: new OnConflictOptions<TestEntity>
{
Match = e => new
{
e.Name,
// ...other columns to match on
},
// Optional: specify the update action, if not specified, the default action is to do nothing
// Excluded is the row being inserted which is in conflict, and Inserted is the row already in the database.
Update = (inserted, excluded) => new TestEntity
{
Price = inserted.Price // Update the Price column with the new value
},
// Optional: specify the condition for the update action
// Excluded is the row being inserted which is in conflict, and Inserted is the row already in the database.
// Using raw SQL condition
RawWhere = (insertedTable, excludedTable) => $"{excludedTable}.some_price > {insertedTable}.some_price",
// OR using a lambda expression
Where = (inserted, excluded) => excluded.Price > inserted.Price,
});- Add support for navigation properties
- Add support for complex types
- Add support for owned types
- Add support for shadow properties
- Add support for TPT (Table Per Type) inheritance
- Add support for TPC (Table Per Concrete Type) inheritance
- Add support for TPH (Table Per Hierarchy) inheritance
Benchmark projects are available in the tests/PhenX.EntityFrameworkCore.BulkInsert.Benchmark directory.
Run them to compare performance with raw bulk insert methods and other libraries (https://github.com/borisdj/EFCore.BulkExtensions
and https://entityframework-extensions.net/bulk-extensions), using optimized configuration (local Docker is required).
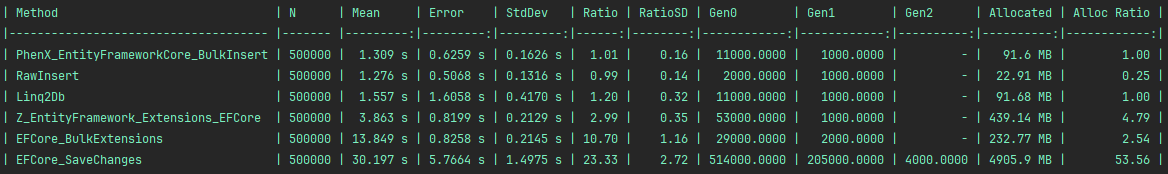
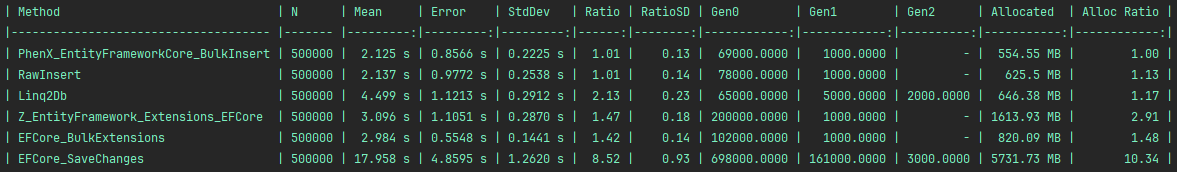
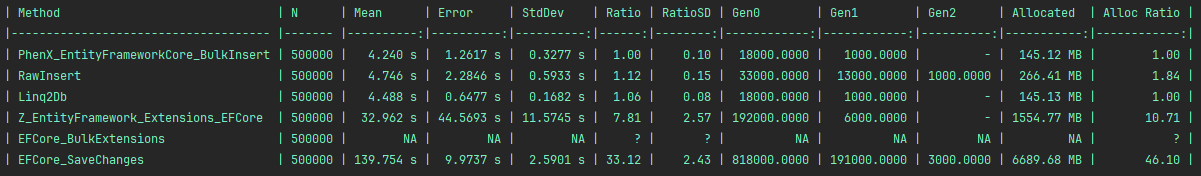
Legend :
PhenX_EntityFrameworkCore_BulkInsert: this libraryRawInsert: naive implementation without any library, using the native provider API (SqlBulkCopy for SQL Server, BeginBinaryImport for PostgreSQL, raw inserts for SQLite)Z_EntityFramework_Extensions_EFCore: https://entityframework-extensions.net/bulk-extensionsEFCore_BulkExtensions: https://github.com/borisdj/EFCore.BulkExtensionsLinq2Db: https://github.com/linq2db/linq2db
SQL Server results with 500 000 rows :
PostgreSQL results with 500 000 rows :
SQLite results with 500 000 rows :
MySQL results with 500 000 rows :
Oracle results with 500 000 rows :
Contributions are welcome! Please open issues or submit pull requests for bug fixes, features, or documentation improvements.
MIT License. See LICENSE for details.