A blazing-fast reverse proxy with intelligent caching and multi-backend object storage support.
CacheBolt is a high-performance reverse proxy designed to cache and serve responses with minimal latency. It intelligently stores responses in memory and synchronizes them with persistent object storage backends.
This tool is ideal for accelerating APIs, file delivery, and improving reliability under high load.
You can download the latest precompiled binaries for your platform from the latest GitHub release.
| Platform | File |
|---|---|
| macOS (Apple Silicon) | cachebolt-aarch64-apple-darwin.tar.gz |
| macOS (Intel) | cachebolt-x86_64-apple-darwin.tar.gz |
| Linux (ARM64) | cachebolt-aarch64-unknown-linux-gnu.tar.gz |
| Linux (x86_64, musl) | cachebolt-x86_64-unknown-linux-musl.tar.gz |
| Windows (x86_64) | cachebolt-x86_64-pc-windows-gnu.zip |
CacheBolt reads its configuration from a YAML file. By default, it expects a file config.yaml:
Default mode:
./cacheboltCustom config path:
./cachebolt --config ./config/prod.yamlDocker:
docker run --rm -p 3000:3000 \
-v $(pwd)/config:/config \
-v $(pwd)/cache:/data \
-e GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS=/config/adc.json \
ghcr.io/msalinas92/cachebolt:latest \
--config /config/config.yaml- 🔁 Reverse HTTP proxy powered by Axum and Tokio
- 🚀 Fast, concurrent in-memory caching with LRU eviction
- ☁️ Multi-cloud object store support:
- 🟢 Amazon S3
- 🔵 Google Cloud Storage
- 🔶 Azure Blob Storage
- 💽 Local filesystem
- 📉 Memory-based cache eviction (threshold-configurable)
- ⏱️ Latency-based failover policies (regex route rules)
- 🧠 Smart fallback if upstreams are slow or unavailable
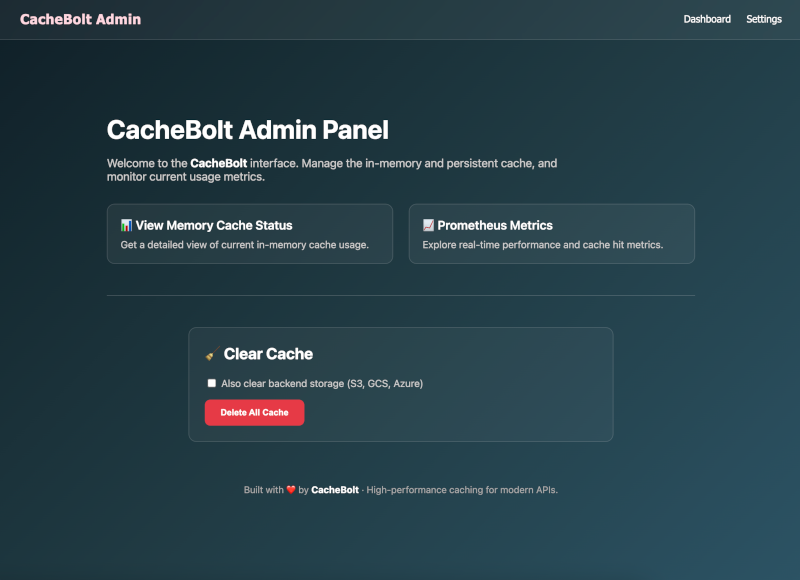
CacheBolt comes with a built-in graphical admin interface accessible via your browser.
This lightweight UI is bundled directly into the binary—no additional server or frontend hosting is required.
Once CacheBolt is running, open:
- 🧠 View memory cache entries in real time
- 🧹 Clear in-memory or persistent cache with a single click
- 📊 Inspect memory usage, TTL, and sizes
- 🛠️ Fully static and bundled – served directly from the binary
This interface is useful for both debugging and administrative operations in production environments.
Client sends GET request
|
v
┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ proxy_handler receives request │
└────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
|
v
Check if URI is marked as degraded (should_failover)
|
├── Yes --> try_cache(key)
│ ├── Hit in memory?
│ │ └── ✅ Serve from memory
│ ├── Else: Hit in storage?
│ │ └── ✅ Load from selected storage backend (GCS, S3, Azure, or Local)
│ │ └── Load into memory + Serve
│ └── Else: ❌ Return 502 (no cache, no backend)
│
└── No
|
v
Check MEMORY_CACHE for key
|
├── Hit --> ✅ Serve from memory
└── Miss
|
v
Acquire semaphore (concurrency guard)
|
├── Denied --> Check memory again
│ ├── Hit --> ✅ Serve
│ └── ❌ Return 502 (overloaded)
|
└── Acquired --> forward_request to backend
|
├── Response latency > threshold?
│ └── Yes --> mark_latency_fail
|
├── Downstream OK?
│ |
│ ├── Build CachedResponse
│ ├── In failover mode?
│ │ ├── Yes --> Skip caching
│ │ └── No:
│ │ ├── Put in MEMORY_CACHE
│ │ └── Send to CACHE_WRITER (persist to backend)
│ └── ✅ Return response
|
└── Downstream failed --> try_cache fallback
To ensure cached responses stay fresh over time, CacheBolt supports probabilistic refreshes.
You can configure a percentage of requests that will intentionally bypass the cache and fetch a fresh version from the backend.
cache:
refresh_percentage: 10In the example above, approximately 1 in every 10 requests to the same cache key will bypass the memory and persistent cache and trigger a revalidation from the upstream server. The refreshed response is then stored again in both memory and persistent storage backends.
This strategy helps:
Keep long-lived cache entries updated
Avoid cache staleness without needing manual invalidation
Distribute backend load gradually and intelligently
If set to 0, no automatic refresh will occur unless the cache is manually purged.
The config is written in YAML. Example:
# 🔧 Unique identifier for this CacheBolt instance
app_id: my-service
# 🌐 Port to bind the main proxy server (default: 3000)
proxy_port: 3000
# 🛠️ Port to bind the admin interface and /metrics (default: 3001)
admin_port: 3001
# 🚦 Maximum number of concurrent outbound requests to the downstream service
max_concurrent_requests: 200
# 🌐 Base URL of the upstream API/backend to which requests are proxied
downstream_base_url: http://localhost:4000
# 💾 Backend used for persistent cache storage
# Available options: gcs, s3, azure, local
storage_backend: s3
# 🪣 Name of the Google Cloud Storage bucket (used if storage_backend is 'gcs')
gcs_bucket: cachebolt
# 🪣 Name of the Amazon S3 bucket (used if storage_backend is 's3')
s3_bucket: my-cachebolt-bucket
# 📦 Name of the Azure Blob Storage container (used if storage_backend is 'azure')
azure_container: cachebolt-container
# 🧠 Memory cache configuration
cache:
# 🚨 System memory usage threshold (%) above which in-memory cache will start evicting entries
memory_threshold: 80
# 🔁 Percentage of requests (per key) that should trigger a refresh from backend instead of using cache
# Example: 10% means 1 in every 10 requests will bypass cache
refresh_percentage: 10
# ⚠️ Latency-based failover configuration
latency_failover:
# ⌛ Default maximum allowed latency in milliseconds for any request
default_max_latency_ms: 3000
# 🛣️ Path-specific latency thresholds
path_rules:
- pattern: "^/api/v1/products/.*"
max_latency_ms: 1500
- pattern: "^/auth/.*"
max_latency_ms: 1000
# 🚫 List of request headers to ignore when computing cache keys (case-insensitive)
ignored_headers:
- postman-token
- if-none-matchDepending on the storage backend, you'll need to configure credentials via environment variables:
- Must be authenticated using Application Default Credentials (ADC), which you can set via:
export GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS="/path/to/service-account.json"- Required environment variables:
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=your-access-key-id
export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=your-secret-key
export AWS_REGION=us-east-1 # or your specific region- Required environment variables:
export AZURE_STORAGE_ACCOUNT=your_account_name
export AZURE_STORAGE_ACCESS_KEY=your_access_key- No additional credentials required. Cache files will be saved locally.
To build locally:
cargo build --releaseTo cross-compile:
See .github/workflows/release.yml for cross-target examples.
CacheBolt exposes Prometheus-compatible metrics at the /metrics endpoint on port 3000. These metrics allow you to monitor request flow, latency thresholds, memory caching, and backend persistence.
-
cachebolt_proxy_requests_total{uri}
Total number of proxy requests received, labeled by URI. -
cachebolt_downstream_failures_total{uri}
Count of downstream request failures per URI. -
cachebolt_rejected_due_to_concurrency_total{uri}
Requests rejected due to max concurrency being exceeded. -
cachebolt_failover_total{uri}
Requests served via failover mode due to recent high latency.
-
cachebolt_memory_hits_total{uri}
Requests served directly from the in-memory cache. -
cachebolt_memory_store_total{uri}
Responses stored into the in-memory cache. -
cachebolt_memory_fallback_hits_total
Failover-mode requests served from memory cache.
-
cachebolt_proxy_request_latency_ms{uri}
Histogram of proxy request latency in milliseconds. -
cachebolt_latency_exceeded_ms{uri}
Histogram of requests whose latency exceeded the configured threshold. -
cachebolt_latency_exceeded_total{uri}
Count of latency threshold violations per URI.
-
cachebolt_persist_attempts_total{backend}
Number of attempts to persist cache entries into the selected backend. -
cachebolt_persist_errors_total{backend}
Number of failed attempts to persist cache entries. -
cachebolt_persistent_fallback_hits_total
Requests served from persistent storage (GCS, S3, Azure, or local) during failover. -
cachebolt_fallback_miss_total
Count of failover attempts that missed both memory and persistent storage.
You can clear the entire cache (both in-memory and persistent storage) using the /cache?backend=true endpoint. This is useful when deploying major updates or invalidating stale content globally.
- When
backend=true, CacheBolt will delete all cache entries stored in:- 🟢 Amazon S3
- 🔵 Google Cloud Storage
- 🔶 Azure Blob Storage
- 💽 Local Filesystem
curl -X DELETE "http://localhost:3001/admin/cache?backend=true"CacheBolt includes an endpoint to inspect the current in-memory cache state in real time.
curl --location 'http://localhost:3001/admin/status-memory'Returns a JSON object where each key is a hashed cache key, and the value includes metadata:
{
"e43bd17d...": {
"path": "/api/v1/products/123",
"inserted_at": "2025-06-15T21:54:31Z",
"size_bytes": 879,
"ttl_remaining_secs": 173
},
"a128be77...": {
"path": "/auth/session",
"inserted_at": "2025-06-15T21:50:12Z",
"size_bytes": 1601,
"ttl_remaining_secs": 0
}
}
Licensed under the Apache License 2.0.