Topic modeling is your turf too.
Contextual topic models with representations from transformers.
| SOTA Transformer-based Topic Models | 🧭 S³, 🔑 KeyNMF, 💎 GMM, Clustering Models (BERTopic and Top2Vec), Autoencoding models (ZeroShotTM and CombinedTM), FASTopic |
| Models for all Scenarios | 📈 Dynamic, 🌊 Online, 🌿 Seeded, 🌲 Hierarchical, and 📷 Multimodal topic modeling |
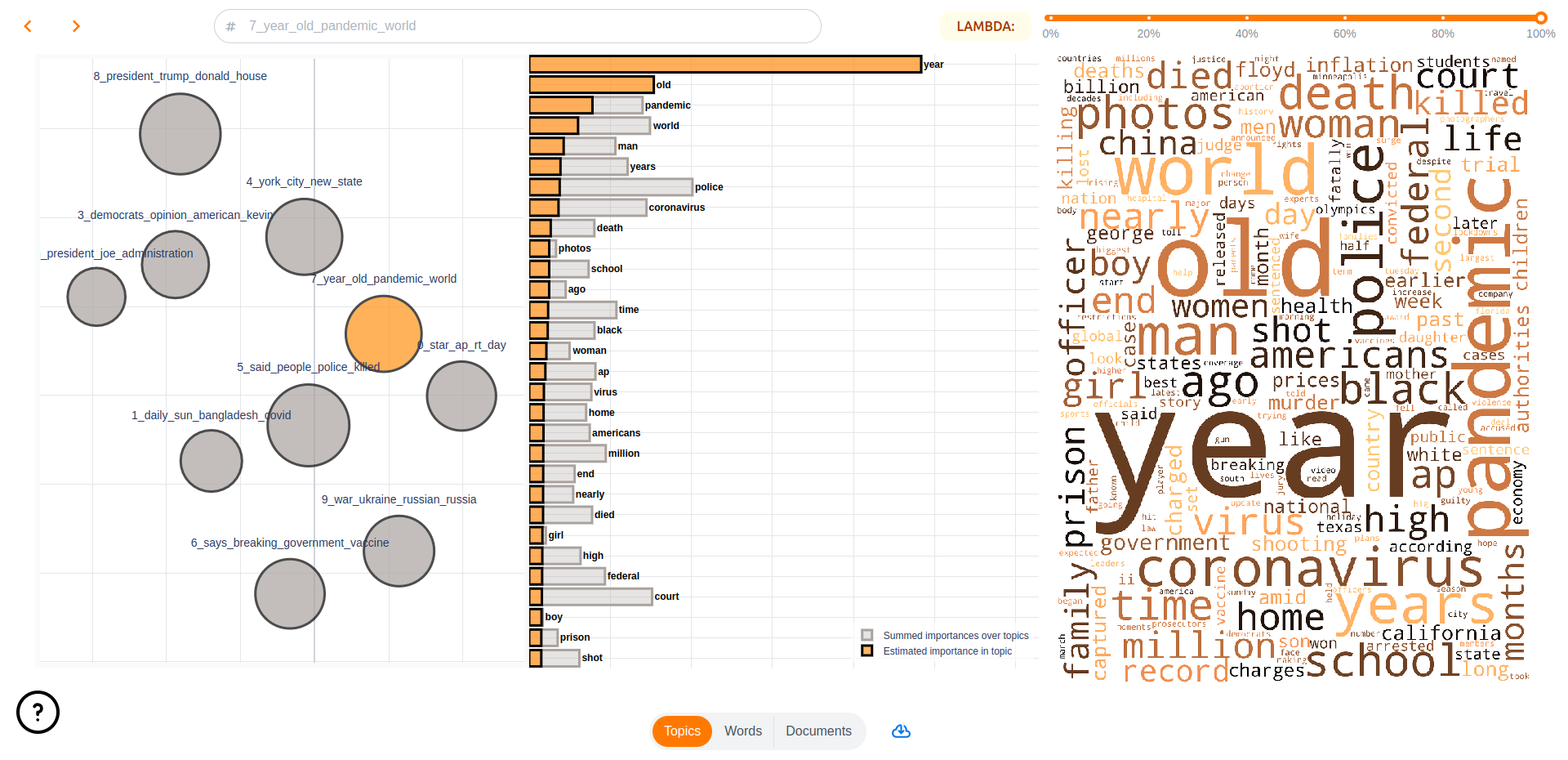
| Easy Interpretation | 📑 Pretty Printing, 📊 Interactive Figures, 🎨 topicwizard compatible |
| Topic Naming | 🤖 LLM-based, N-gram Retrieval, 👋 Manual |
| Informative Topic Descriptions | 🔑 Keyphrases, Noun-phrases, Lemmatization, Stemming |
For more details on a particular topic, you can consult our documentation page:
Turftopic can be installed from PyPI.
pip install turftopicIf you intend to use CTMs, make sure to install the package with Pyro as an optional dependency.
pip install "turftopic[pyro-ppl]"If you want to use clustering models like BERTopic or Top2Vec, install:
pip install "turftopic[umap-learn]"Turftopic's models follow the scikit-learn API conventions, and as such they are quite easy to use if you are familiar with scikit-learn workflows.
Here's an example of how you use KeyNMF, one of our models on the 20Newsgroups dataset from scikit-learn.
If you are using a Mac, you might have to install the required SSL certificates on your system in order to be able to download the dataset.
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_20newsgroups
newsgroups = fetch_20newsgroups(
subset="all",
remove=("headers", "footers", "quotes"),
)
corpus: list[str] = newsgroups.data
print(len(corpus)) # 18846Turftopic also comes with interpretation tools that make it easy to display and understand your results.
from turftopic import KeyNMF
model = KeyNMF(20)
document_topic_matrix = model.fit_transform(corpus)Turftopic comes with a number of pretty printing utilities for interpreting the models.
To see the highest the most important words for each topic, use the print_topics() method.
model.print_topics()| Topic ID | Top 10 Words |
|---|---|
| 0 | armenians, armenian, armenia, turks, turkish, genocide, azerbaijan, soviet, turkey, azerbaijani |
| 1 | sale, price, shipping, offer, sell, prices, interested, 00, games, selling |
| 2 | christians, christian, bible, christianity, church, god, scripture, faith, jesus, sin |
| 3 | encryption, chip, clipper, nsa, security, secure, privacy, encrypted, crypto, cryptography |
| .... |
# Print highest ranking documents for topic 0
model.print_representative_documents(0, corpus, document_topic_matrix)| Document | Score |
|---|---|
| Poor 'Poly'. I see you're preparing the groundwork for yet another retreat from your... | 0.40 |
| Then you must be living in an alternate universe. Where were they? An Appeal to Mankind During the... | 0.40 |
| It is 'Serdar', 'kocaoglan'. Just love it. Well, it could be your head wasn't screwed on just right... | 0.39 |
model.print_topic_distribution(
"I think guns should definitely banned from all public institutions, such as schools."
)| Topic name | Score |
|---|---|
| 7_gun_guns_firearms_weapons | 0.05 |
| 17_mail_address_email_send | 0.00 |
| 3_encryption_chip_clipper_nsa | 0.00 |
| 19_baseball_pitching_pitcher_hitter | 0.00 |
| 11_graphics_software_program_3d | 0.00 |
Turftopic now allows you to automatically assign human readable names to topics using LLMs or n-gram retrieval!
You will need to
pip install "turftopic[openai]"for this to work.
from turftopic import KeyNMF
from turftopic.namers import OpenAITopicNamer
model = KeyNMF(10).fit(corpus)
namer = OpenAITopicNamer("gpt-4o-mini")
model.rename_topics(namer)
model.print_topics()| Topic ID | Topic Name | Highest Ranking |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Operating Systems and Software | windows, dos, os, ms, microsoft, unix, nt, memory, program, apps |
| 1 | Atheism and Belief Systems | atheism, atheist, atheists, belief, religion, religious, theists, beliefs, believe, faith |
| 2 | Computer Architecture and Performance | motherboard, ram, memory, cpu, bios, isa, speed, 486, bus, performance |
| 3 | Storage Technologies | disk, drive, scsi, drives, disks, floppy, ide, dos, controller, boot |
| ... |
You can use a set of custom vectorizers for topic modeling over phrases, as well as lemmata and stems.
You will need to
pip install "turftopic[spacy]"for this to work.
from turftopic import BERTopic
from turftopic.vectorizers.spacy import NounPhraseCountVectorizer
model = BERTopic(
n_components=10,
vectorizer=NounPhraseCountVectorizer("en_core_web_sm"),
)
model.fit(corpus)
model.print_topics()| Topic ID | Highest Ranking |
|---|---|
| ... | |
| 3 | fanaticism, theism, fanatism, all fanatism, theists, strong theism, strong atheism, fanatics, precisely some theists, all theism |
| 4 | religion foundation darwin fish bumper stickers, darwin fish, atheism, 3d plastic fish, fish symbol, atheist books, atheist organizations, negative atheism, positive atheism, atheism index |
| ... |
Turftopic comes with a number of visualization and pretty printing utilities for specific models and specific contexts, such as hierarchical or dynamic topic modelling. You will find an overview of these in the Interpreting and Visualizing Models section of our documentation.
pip install "turftopic[datamapplot, openai]"
from turftopic import ClusteringTopicModel
from turftopic.namers import OpenAITopicNamer
model = ClusteringTopicModel(feature_importance="centroid").fit(corpus)
namer = OpenAITopicNamer("gpt-4o-mini")
model.rename_topics(namer)
fig = model.plot_clusters_datamapplot()
fig.show()In addition, Turftopic is natively supported in topicwizard, an interactive topic model visualization library, is compatible with all models from Turftopic.
pip install "turftopic[topic-wizard]"By far the easiest way to visualize your models for interpretation is to launch the topicwizard web app.
import topicwizard
topicwizard.visualize(corpus, model=model)Alternatively you can use the Figures API in topicwizard for individual HTML figures.
- Kardos, M., Kostkan, J., Vermillet, A., Nielbo, K., Enevoldsen, K., & Rocca, R. (2024, June 13).
$S^3$ - Semantic Signal separation. arXiv.org. https://arxiv.org/abs/2406.09556 - Wu, X., Nguyen, T., Zhang, D. C., Wang, W. Y., & Luu, A. T. (2024). FASTopic: A Fast, Adaptive, Stable, and Transferable Topic Modeling Paradigm. ArXiv Preprint ArXiv:2405.17978.
- Grootendorst, M. (2022, March 11). BERTopic: Neural topic modeling with a class-based TF-IDF procedure. arXiv.org. https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.05794
- Angelov, D. (2020, August 19). Top2VEC: Distributed representations of topics. arXiv.org. https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.09470
- Bianchi, F., Terragni, S., & Hovy, D. (2020, April 8). Pre-training is a Hot Topic: Contextualized Document Embeddings Improve Topic Coherence. arXiv.org. https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.03974
- Bianchi, F., Terragni, S., Hovy, D., Nozza, D., & Fersini, E. (2021). Cross-lingual Contextualized Topic Models with Zero-shot Learning. In Proceedings of the 16th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Main Volume (pp. 1676–1683). Association for Computational Linguistics.
- Kristensen-McLachlan, R. D., Hicke, R. M. M., Kardos, M., & Thunø, M. (2024, October 16). Context is Key(NMF): Modelling Topical Information Dynamics in Chinese Diaspora Media. arXiv.org. https://arxiv.org/abs/2410.12791