Note
Brought to you by Bytebase, open-source database DevSecOps platform.
DBHub is a universal database gateway implementing the Model Context Protocol (MCP) server interface. This gateway allows MCP-compatible clients to connect to and explore different databases.
+------------------+ +--------------+ +------------------+
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| Claude Desktop +--->+ +--->+ PostgreSQL |
| | | | | |
| Cursor +--->+ DBHub +--->+ SQL Server |
| | | | | |
| | | +--->+ MySQL |
| | | | | |
| | | +--->+ MariaDB |
| | | | | |
+------------------+ +--------------+ +------------------+
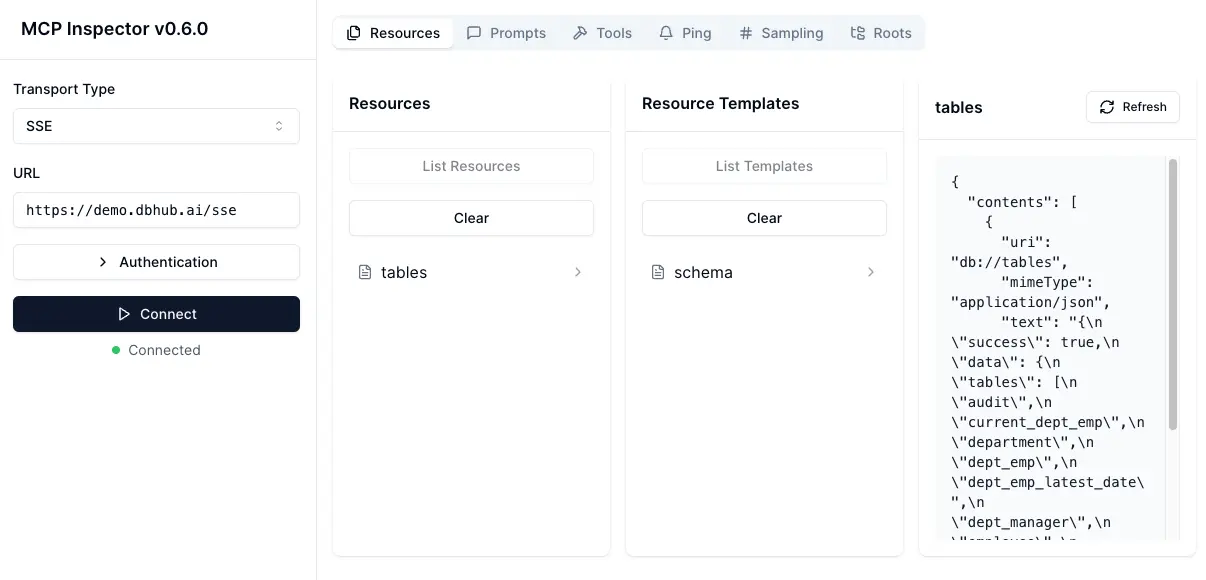
MCP Clients MCP Server Databaseshttps://demo.dbhub.ai/message connects a sample employee database. You can point Cursor or MCP Inspector to it to see it in action.
| Resource Name | URI Format | PostgreSQL | MySQL | MariaDB | SQL Server |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| schemas | db://schemas |
✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| tables_in_schema | db://schemas/{schemaName}/tables |
✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| table_structure_in_schema | db://schemas/{schemaName}/tables/{tableName} |
✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| indexes_in_table | db://schemas/{schemaName}/tables/{tableName}/indexes |
✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| procedures_in_schema | db://schemas/{schemaName}/procedures |
✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| procedure_details_in_schema | db://schemas/{schemaName}/procedures/{procedureName} |
✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Tool | Command Name | Description | PostgreSQL | MySQL | MariaDB | SQL Server |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Execute SQL | execute_sql |
Execute single or multiple SQL statements (separated by semicolons) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Prompt | Command Name | PostgreSQL | MySQL | MariaDB | SQL Server |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Generate SQL | generate_sql |
✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Explain DB Elements | explain_db |
✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
# PostgreSQL example
docker run --rm --init \
--name dbhub \
--publish 8080:8080 \
bytebase/dbhub \
--transport http \
--port 8080 \
--dsn "postgres://user:password@localhost:5432/dbname?sslmode=disable"# PostgreSQL example
npx @bytebase/dbhub --transport http --port 8080 --dsn "postgres://user:password@localhost:5432/dbname?sslmode=disable"- Claude Desktop only supports
stdiotransport https://github.com/orgs/modelcontextprotocol/discussions/16
// claude_desktop_config.json
{
"mcpServers": {
"dbhub-postgres-docker": {
"command": "docker",
"args": [
"run",
"-i",
"--rm",
"bytebase/dbhub",
"--transport",
"stdio",
"--dsn",
// Use host.docker.internal as the host if connecting to the local db
"postgres://user:password@host.docker.internal:5432/dbname?sslmode=disable"
]
},
"dbhub-postgres-npx": {
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"-y",
"@bytebase/dbhub",
"--transport",
"stdio",
"--dsn",
"postgres://user:password@localhost:5432/dbname?sslmode=disable"
]
},
}
}- Cursor supports both
stdioandhttp. - Follow Cursor MCP guide and make sure to use Agent mode.
You can specify the SSL mode using the sslmode parameter in your DSN string:
| Database | sslmode=disable |
sslmode=require |
Default SSL Behavior |
|---|---|---|---|
| PostgreSQL | ✅ | ✅ | Certificate verification |
| MySQL | ✅ | ✅ | Certificate verification |
| MariaDB | ✅ | ✅ | Certificate verification |
| SQL Server | ✅ | ✅ | Certificate verification |
SSL Mode Options:
sslmode=disable: All SSL/TLS encryption is turned off. Data is transmitted in plaintext.sslmode=require: Connection is encrypted, but the server's certificate is not verified. This provides protection against packet sniffing but not against man-in-the-middle attacks. You may use this for trusted self-signed CA.
Without specifying sslmode, most databases default to certificate verification, which provides the highest level of security.
Example usage:
# Disable SSL
postgres://user:password@localhost:5432/dbname?sslmode=disable
# Require SSL without certificate verification
postgres://user:password@localhost:5432/dbname?sslmode=require
# Standard SSL with certificate verification (default)
postgres://user:password@localhost:5432/dbnameYou can run DBHub in read-only mode, which restricts SQL query execution to read-only operations:
# Enable read-only mode
npx @bytebase/dbhub --readonly --dsn "postgres://user:password@localhost:5432/dbname"In read-only mode, only readonly SQL operations are allowed.
This provides an additional layer of security when connecting to production databases.
Warning
If your user/password contains special characters, you need to escape them first. (e.g. pass#word should be escaped as pass%23word)
For real databases, a Database Source Name (DSN) is required. You can provide this in several ways:
-
Command line argument (highest priority):
npx @bytebase/dbhub --dsn "postgres://user:password@localhost:5432/dbname?sslmode=disable" -
Environment variable (second priority):
export DSN="postgres://user:password@localhost:5432/dbname?sslmode=disable" npx @bytebase/dbhub
-
Environment file (third priority):
- For development: Create
.env.localwith your DSN - For production: Create
.envwith your DSN
DSN=postgres://user:password@localhost:5432/dbname?sslmode=disable - For development: Create
Warning
When running in Docker, use host.docker.internal instead of localhost to connect to databases running on your host machine. For example: mysql://user:password@host.docker.internal:3306/dbname
DBHub supports the following database connection string formats:
| Database | DSN Format | Example |
|---|---|---|
| MySQL | mysql://[user]:[password]@[host]:[port]/[database] |
mysql://user:password@localhost:3306/dbname?sslmode=disable |
| MariaDB | mariadb://[user]:[password]@[host]:[port]/[database] |
mariadb://user:password@localhost:3306/dbname?sslmode=disable |
| PostgreSQL | postgres://[user]:[password]@[host]:[port]/[database] |
postgres://user:password@localhost:5432/dbname?sslmode=disable |
| SQL Server | sqlserver://[user]:[password]@[host]:[port]/[database] |
sqlserver://user:password@localhost:1433/dbname?sslmode=disable |
Extra query parameters:
authentication=azure-active-directory-access-token. Only applicable when running from Azure. See DefaultAzureCredential.
-
stdio (default) - for direct integration with tools like Claude Desktop:
npx @bytebase/dbhub --transport stdio --dsn "postgres://user:password@localhost:5432/dbname?sslmode=disable" -
http - for browser and network clients:
npx @bytebase/dbhub --transport http --port 5678 --dsn "postgres://user:password@localhost:5432/dbname?sslmode=disable"
| Option | Environment Variable | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| dsn | DSN |
Database connection string | Required |
| transport | TRANSPORT |
Transport mode: stdio or http |
stdio |
| port | PORT |
HTTP server port (only applicable when using --transport=http) |
8080 |
| readonly | READONLY |
Restrict SQL execution to read-only operations | false |
-
Install dependencies:
pnpm install
-
Run in development mode:
pnpm dev
-
Build for production:
pnpm build pnpm start --transport stdio --dsn "postgres://user:password@localhost:5432/dbname?sslmode=disable"
The project uses Vitest for comprehensive unit and integration testing:
- Run all tests:
pnpm test - Run tests in watch mode:
pnpm test:watch - Run integration tests:
pnpm test:integration
DBHub includes comprehensive integration tests for all supported database connectors using Testcontainers. These tests run against real database instances in Docker containers, ensuring full compatibility and feature coverage.
- Docker: Ensure Docker is installed and running on your machine
- Docker Resources: Allocate sufficient memory (recommended: 4GB+) for multiple database containers
- Network Access: Ability to pull Docker images from registries
Note: This command runs all integration tests in parallel, which may take 5-15 minutes depending on your system resources and network speed.
# Run all database integration tests
pnpm test:integration# Run only PostgreSQL integration tests
pnpm test src/connectors/__tests__/postgres.integration.test.ts
# Run only MySQL integration tests
pnpm test src/connectors/__tests__/mysql.integration.test.ts
# Run only MariaDB integration tests
pnpm test src/connectors/__tests__/mariadb.integration.test.ts
# Run only SQL Server integration tests
pnpm test src/connectors/__tests__/sqlserver.integration.test.ts
# Run JSON RPC integration tests
pnpm test src/__tests__/json-rpc-integration.test.tsAll integration tests follow these patterns:
- Container Lifecycle: Start database container → Connect → Setup test data → Run tests → Cleanup
- Shared Test Utilities: Common test patterns implemented in
IntegrationTestBaseclass - Database-Specific Features: Each database includes tests for unique features and capabilities
- Error Handling: Comprehensive testing of connection errors, invalid SQL, and edge cases
Container Startup Issues:
# Check Docker is running
docker ps
# Check available memory
docker system df
# Pull images manually if needed
docker pull postgres:15-alpine
docker pull mysql:8.0
docker pull mariadb:10.11
docker pull mcr.microsoft.com/mssql/server:2019-latestSQL Server Timeout Issues:
- SQL Server containers require significant startup time (3-5 minutes)
- Ensure Docker has sufficient memory allocated (4GB+ recommended)
- Consider running SQL Server tests separately if experiencing timeouts
Network/Resource Issues:
# Run tests with verbose output
pnpm test:integration --reporter=verbose
# Run single database test to isolate issues
pnpm test:integration -- --testNamePattern="PostgreSQL"
# Check Docker container logs if tests fail
docker logs <container_id>The project includes pre-commit hooks to run tests automatically before each commit:
-
After cloning the repository, set up the pre-commit hooks:
./scripts/setup-husky.sh
-
This ensures the test suite runs automatically whenever you create a commit, preventing commits that would break tests.
Debug with MCP Inspector
# PostgreSQL example
TRANSPORT=stdio DSN="postgres://user:password@localhost:5432/dbname?sslmode=disable" npx @modelcontextprotocol/inspector node /path/to/dbhub/dist/index.js# Start DBHub with HTTP transport
pnpm dev --transport=http --port=8080
# Start the MCP Inspector in another terminal
npx @modelcontextprotocol/inspectorConnect to the DBHub server /message endpoint