UPDATE: code is updated to run in Python 3, and includes exorings3 which is a Python 3 version of the original exorings which runs under Python 2.7.
These are Python tools for displaying and fitting giant extrasolar planet ring systems, as detailed in Kenworthy and Mamajek (2015).
If you need a python 2.7 environment to run the original disk_sim.py, you can set up a conda environment with the appropriate Python modules installed:
conda create --name exo27 -c conda-forge python=2.7 matplotlib numpy scipy astropy
conda activate exo27
then you can copy this repo and run the interactive ring fitter:
git clone https://github.com/mkenworthy/exorings.git
cd exorings/
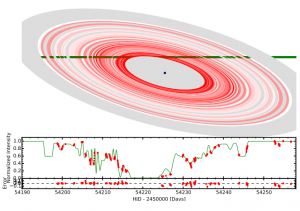
python disk_sim.py -s 33000. -r 54220.65.try9.33kms.fits -d 54220.65.try9.33kms.fits -o 54220.65.try10.33kms.fits
Explanations on how to use the exorings interface are on the Quick Start page, along with all documentation and discussion on the Exorings wiki.
The code is registered at the ASCL at ascl:1501.012 and should be cited in papers as:
Kenworthy, M.A., 2015, Exorings, Astrophysics Source Code Library, record ascl:1501.012
The code is released under an ISC license, which is functionally equivalent to the BSD 2-clause license but removes some language that is no longer necessary.