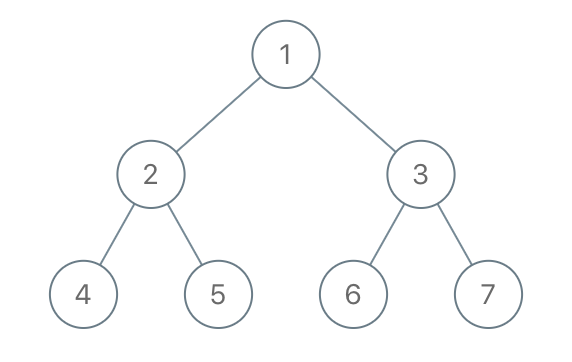
Given the
rootof a binary tree, each node in the tree has a distinct value.After deleting all nodes with a value in
to_delete, we are left with a forest (a disjoint union of trees).Return the roots of the trees in the remaining forest. You may return the result in any order.
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7], to_delete = [3,5] Output: [[1,2,null,4],[6],[7]]
- The number of nodes in the given tree is at most
1000.- Each node has a distinct value between
1and1000.to_delete.length <= 1000to_deletecontains distinct values between1and1000.
- java
-
mine
DFS
Runtime: 1 ms, faster than 98.74%, Memory Usage: 39.8 MB, less than 100.00% of Java online submissions//O(N + N*D)time O(N-D)space public List<TreeNode> delNodes(TreeNode root, int[] to_delete) { List<TreeNode> res = new ArrayList<>(); dfs(root, to_delete, res, true); return res; } public TreeNode dfs(TreeNode node, int[] to_delete, List<TreeNode> res, boolean noParent) { if (node == null) { return null; } boolean isDeleteNode = isDeleteNode(node, to_delete); node.left = dfs(node.left, to_delete, res, isDeleteNode); node.right = dfs(node.right, to_delete, res, isDeleteNode); if (isDeleteNode) { return null; } if (noParent) { res.add(node); } return node; } public boolean isDeleteNode(TreeNode node, int[] to_delete) { if (node == null) { return false; } for (int delete : to_delete) { if (node.val == delete) { return true; } } return false; } -
the most votes
Recursion
Runtime: 1 ms, faster than 98.74%, Memory Usage: 40 MB, less than 100.00% of Java online submissions//Time O(N) Space O(H + N) Set<Integer> to_delete_set; List<TreeNode> res; public List<TreeNode> delNodes(TreeNode root, int[] to_delete) { to_delete_set = new HashSet<>(); res = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i : to_delete) to_delete_set.add(i); helper(root, true); return res; } private TreeNode helper(TreeNode node, boolean is_root) { if (node == null) return null; boolean deleted = to_delete_set.contains(node.val); if (is_root && !deleted) res.add(node); node.left = helper(node.left, deleted); node.right = helper(node.right, deleted); return deleted ? null : node; }
-