leetcode-cn Daily Challenge on May 10th, 2021.
Difficulty : Easy
Related Topics : Tree、DFS
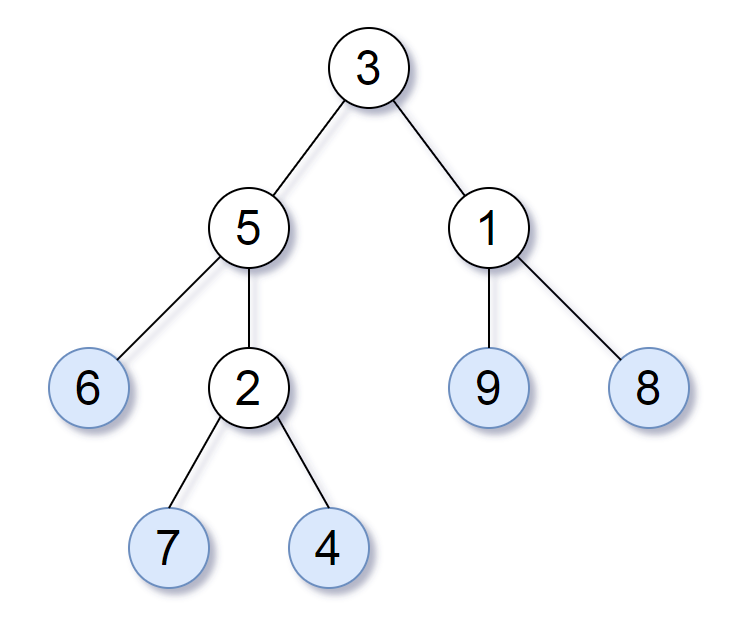
Consider all the leaves of a binary tree. From left to right order, the values of those leaves form a leaf value sequence.
For example, in the given tree above, the leaf value sequence is
(6, 7, 4, 9, 8).Two binary trees are considered leaf-similar if their leaf value sequence is the same.
Return
trueif and only if the two given trees with head nodesroot1 androot2` are leaf-similar.
- Both of the given trees will have between
1and200nodes.- Both of the given trees will have values between
0and200.
- Java
-
mine
DFS
Runtime: 0 ms, faster than 100.00%, Memory Usage: 37.2 MB, less than 7.14% of Java online submissions// O(N)Time O(N)Space public boolean leafSimilar(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) { List<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>(); List<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList<>(); dfs(root1,list1); dfs(root2,list2); if(list1.size() != list2.size()){ return false; } for(int i = 0; i < list1.size(); i++){ if(list1.get(i)!=list2.get(i)){ return false; } } return true; } public TreeNode dfs(TreeNode node, List<Integer> list){ if(node == null){ return null; } TreeNode left = dfs(node.left, list); TreeNode right = dfs(node.right, list); if(left == null && right == null){ list.add(node.val); } return node; } -
the most votes
****
Runtime: 0 ms, faster than 100.00%, Memory Usage: 36.7 MB, less than 89.29% of Java online submissions// O(N)Time O(H)Space public boolean leafSimilar(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) { Stack<TreeNode> s1 = new Stack<>(), s2 = new Stack<>(); s1.push(root1); s2.push(root2); while (!s1.empty() && !s2.empty()) if (dfs(s1) != dfs(s2)) return false; return s1.empty() && s2.empty(); } public int dfs(Stack<TreeNode> s) { while (true) { TreeNode node = s.pop(); if (node.right != null) s.push(node.right); if (node.left != null) s.push(node.left); if (node.left == null && node.right == null) return node.val; } }
-