the last one in Weekly Contest 200.
Difficulty : Hard
Related Topics : Dynamic Programming
You are given two sorted arrays of distinct integers
nums1andnums2.A valid path is defined as follows:
- Choose array nums1 or nums2 to traverse (from index-0).
- Traverse the current array from left to right.
- If you are reading any value that is present in
nums1andnums2you are allowed to change your path to the other array. (Only one repeated value is considered in the valid path).Score is defined as the sum of uniques values in a valid path.
Return the maximum score you can obtain of all possible valid paths.
Since the answer may be too large, return it modulo 10^9 + 7.
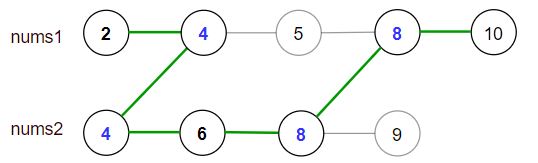
Input: nums1 = [2,4,5,8,10], nums2 = [4,6,8,9] Output: 30 Explanation: Valid paths: [2,4,5,8,10], [2,4,5,8,9], [2,4,6,8,9], [2,4,6,8,10], (starting from nums1) [4,6,8,9], [4,5,8,10], [4,5,8,9], [4,6,8,10] (starting from nums2) The maximum is obtained with the path in green [2,4,6,8,10].Input: nums1 = [1,3,5,7,9], nums2 = [3,5,100] Output: 109 Explanation: Maximum sum is obtained with the path [1,3,5,100].Input: nums1 = [1,2,3,4,5], nums2 = [6,7,8,9,10] Output: 40 Explanation: There are no common elements between nums1 and nums2. Maximum sum is obtained with the path [6,7,8,9,10].Input: nums1 = [1,4,5,8,9,11,19], nums2 = [2,3,4,11,12] Output: 61
1 <= nums1.length <= 10^51 <= nums2.length <= 10^51 <= nums1[i], nums2[i] <= 10^7nums1andnums2are strictly increasing.
- mine
- Java
Runtime: 44 ms, faster than 80.00%, Memory Usage: 51.9 MB, less than 100.00% of Java online submissions// O(N)time // O(N)space public int maxSum(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) { int mod = 1000000007; int res = 0; //save value's index Map<Integer, Integer> map1 = new HashMap<>(); Map<Integer, Integer> map2 = new HashMap<>(); LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < nums1.length; i++) { map1.put(nums1[i], i); } for (int i = 0; i < nums2.length; i++) { map2.put(nums2[i], i); //save the same value if (map1.containsKey(nums2[i])) { list.add(nums2[i]); } } //need use long to save value, we can not mod first Map<Integer, Long> memo = new HashMap<>(); while (!list.isEmpty()) { int same = list.removeLast(); long m = getSum(map1.get(same), memo, nums1); long n = getSum(map2.get(same), memo, nums2); memo.put(same, Math.max(m, n)); } long m = getSum(0, memo, nums1); long n = getSum(0, memo, nums2); return (int) (Math.max(m, n) % mod); } //get nums the max sum form i long getSum(int i, Map<Integer, Long> memo, int[] nums) { long m = 0; while (i < nums.length) { if (memo.containsKey(nums[i])) { m += memo.get(nums[i]); break; } m += nums[i]; i++; } return m; }
- Java
- the most votes
- Two Pointers
Runtime: 4 ms, faster than 100.00%, Memory Usage: 48.7 MB, less than 100.00% of Java online submissions// O(N)time // O(1)space public int maxSum(int[] A, int[] B) { int i = 0, j = 0, n = A.length, m = B.length; long a = 0, b = 0, mod = (long)1e9 + 7; while (i < n || j < m) { if (i < n && (j == m || A[i] < B[j])) { a += A[i++]; } else if (j < m && (i == n || A[i] > B[j])) { b += B[j++]; } else { a = b = Math.max(a, b) + A[i]; i++; j++; } } return (int)(Math.max(a, b) % mod); }