leetcode-cn Daily Challenge on August 12th, 2020.
leetcode Daily Challenge on October 20th, 2020.
Difficulty : Medium
Related Topics : DFS、BFS、Graph
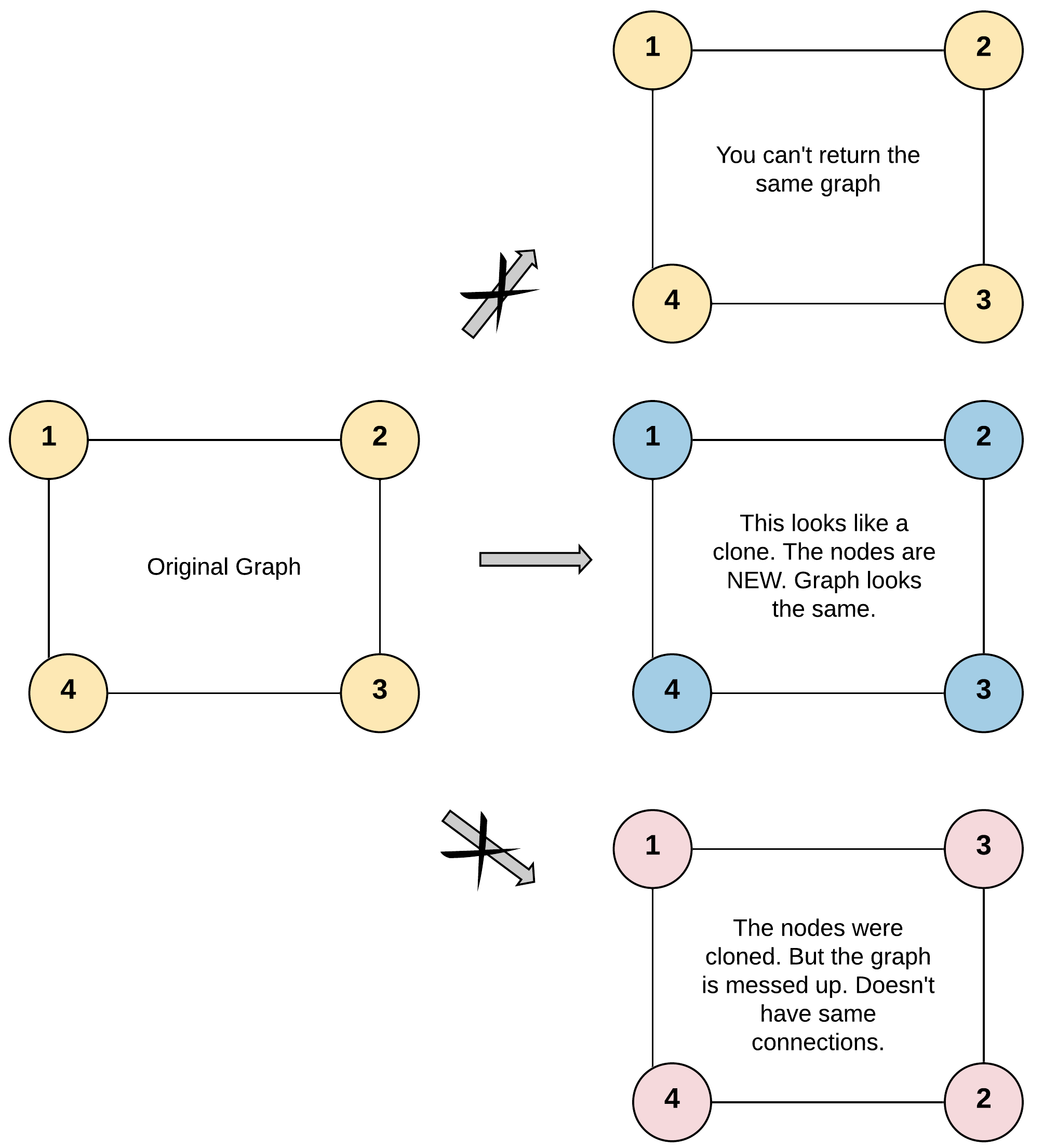
Given a reference of a node in a connected undirected graph.
Return a deep copy (clone) of the graph.
Each node in the graph contains a val (
int) and a list (List[Node]) of its neighbors.class Node { public int val; public List<Node> neighbors; }Test case format:
For simplicity sake, each node's value is the same as the node's index (1-indexed). For example, the first node with
val = 1, the second node withval = 2, and so on. The graph is represented in the test case using an adjacency list.Adjacency list is a collection of unordered lists used to represent a finite graph. Each list describes the set of neighbors of a node in the graph.
The given node will always be the first node with
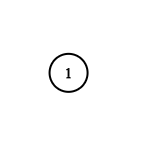
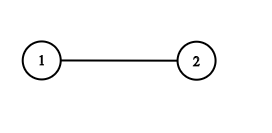
val = 1. You must return the copy of the given node as a reference to the cloned graph.Input: adjList = [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]] Output: [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]] Explanation: There are 4 nodes in the graph. 1st node (val = 1)'s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4). 2nd node (val = 2)'s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3). 3rd node (val = 3)'s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4). 4th node (val = 4)'s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3).Input: adjList = [[]] Output: [[]] Explanation: Note that the input contains one empty list. The graph consists of only one node with val = 1 and it does not have any neighbors.Input: adjList = [] Output: [] Explanation: This an empty graph, it does not have any nodes.Input: adjList = [[2],[1]] Output: [[2],[1]]
1 <= Node.val <= 100- Node.val is unique for each node.
- Number of Nodes will not exceed 100.
- There is no repeated edges and no self-loops in the graph.
- The Graph is connected and all nodes can be visited starting from the given node.
- mine
- Java
- DFS
Runtime: 26 ms, faster than 97.42%, Memory Usage: 39.9 MB, less than 50.09% of Java online submissions// O(N)time // O(N)space HashMap<Integer,Node> cache = new HashMap<>(); public Node cloneGraph(Node node) { if(node == null) return node; dfs(node); return cache.get(node.val); } void dfs(Node node){ if(cache.containsKey(node.val)){ return; } Node copy = new Node(node.val); cache.put(node.val, copy); for(Node n : node.neighbors){ dfs(n); copy.neighbors.add(cache.get(n.val)); } }
- DFS
- Java