leetcode Daily Challenge on January 23th, 2021.
Difficulty : Medium
Related Topics : Array、Sort
A matrix diagonal is a diagonal line of cells starting from some cell in either the topmost row or leftmost column and going in the bottom-right direction until reaching the matrix's end. For example, the matrix diagonal starting from
mat[2][0], wherematis a6 x 3matrix, includes cellsmat[2][0],mat[3][1], andmat[4][2].Given an
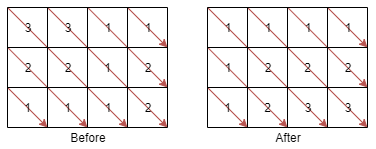
m x nmatrixmatof integers, sort each matrix diagonal in ascending order and return the resulting matrix.Input: mat = [[3,3,1,1],[2,2,1,2],[1,1,1,2]] Output: [[1,1,1,1],[1,2,2,2],[1,2,3,3]]
m == mat.lengthn == mat[i].length1 <= m, n <= 1001 <= mat[i][j] <= 100
- mine
- Java
Runtime: 7 ms, faster than 66.07%, Memory Usage: 40.3 MB, less than 31.04% of Java online submissionspublic int[][] diagonalSort(int[][] mat) { int r = mat.length; int c = mat[0].length; for(int i = r - 1; i >= 0; i--){ List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); int x = i; int y = 0; while(x < r && y < c){ list.add(mat[x++][y++]); } Collections.sort(list); x = i; y = 0; int index = 0; while(x < r && y < c){ mat[x++][y++] = list.get(index++); } } for(int i = 1; i < c; i++){ List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); int x = 0; int y = i; while(x < r && y < c){ list.add(mat[x++][y++]); } Collections.sort(list); x = 0; y = i; int index = 0; while(x < r && y < c){ mat[x++][y++] = list.get(index++); } } return mat; }
- Java
- the faster
Runtime: 0 ms, faster than 100.00%, Memory Usage: 39.7 MB, less than 88.61% of Java online submissionsprivate static final int R = 101; private static int ROW, COL; public int[][] diagonalSort(int[][] mat) { if (mat.length <= 1 || mat[0].length <= 1) return mat; ROW = mat.length; COL = mat[0].length; for (int row = R-2; row > 0; row--) radixSort(mat, row, 0); for (int col = 0; col < COL-1; col++) radixSort(mat, 0, col); return mat; } private void radixSort(int[][] mat, int row, int col) { int[] count = new int[R]; for (int i = row, j = col; i < ROW && j < COL; i++, j++) count[mat[i][j]]++; for (int i = row, j = col, d = 1; i < ROW && j < COL; d++) while (count[d]-- > 0) mat[i++][j++] = d; }