Difficulty : Medium
Related Topics : Graph
There are a total of
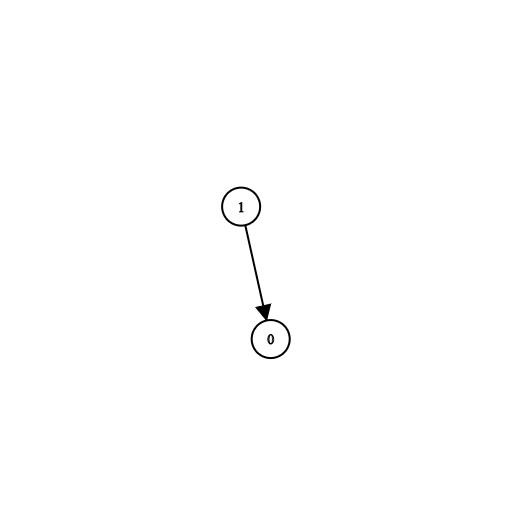
ncourses you have to take, labeled from0ton-1.Some courses may have direct prerequisites, for example, to take course 0 you have first to take course 1, which is expressed as a pair:
[1,0]Given the total number of courses
n, a list of directprerequisitepairs and a list ofqueriespairs.You should answer for each
queries[i]whether the coursequeries[i][0]is a prerequisite of the coursequeries[i][1]or not.Return a list of boolean, the answers to the given
queries.Please note that if course a is a prerequisite of course b and course b is a prerequisite of course c, then, course a is a prerequisite of course c.
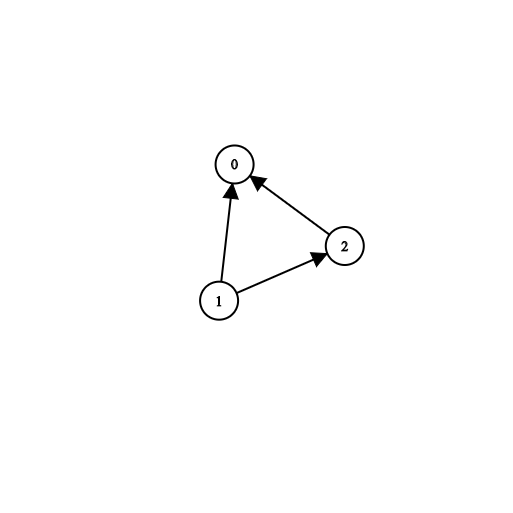
Input: n = 2, prerequisites = [[1,0]], queries = [[0,1],[1,0]] Output: [false,true] Explanation: course 0 is not a prerequisite of course 1 but the opposite is true.Input: n = 2, prerequisites = [], queries = [[1,0],[0,1]] Output: [false,false] Explanation: There are no prerequisites and each course is independent.Input: n = 3, prerequisites = [[1,2],[1,0],[2,0]], queries = [[1,0],[1,2]] Output: [true,true]Input: n = 3, prerequisites = [[1,0],[2,0]], queries = [[0,1],[2,0]] Output: [false,true]Input: n = 5, prerequisites = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,3],[3,4]], queries = [[0,4],[4,0],[1,3],[3,0]] Output: [true,false,true,false]
2 <= n <= 1000 <= prerequisite.length <= (n * (n - 1) / 2)0 <= prerequisite[i][0], prerequisite[i][1] < nprerequisite[i][0] != prerequisite[i][1]- The prerequisites graph has no cycles.
- The prerequisites graph has no repeated edges.
1 <= queries.length <= 10^4queries[i][0] != queries[i][1]
- mine
- Java
- TopologicalSort & BFS
Runtime: 46 ms, faster than 82.56%,Memory Usage: 45.7 MB, less than 51.12% of Java online submissions.// O(N^2)time // O(N^2)space public List<Boolean> checkIfPrerequisite(int n, int[][] prerequisites, int[][] queries) { List<Integer>[] pre = new List[n]; Set<Integer>[] next = new HashSet[n]; int[] nextCount = new int[n]; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { pre[i] = new ArrayList<>(); next[i] = new HashSet<>(); } for (int[] p : prerequisites) { pre[p[1]].add(p[0]); next[p[0]].add(p[1]); nextCount[p[0]]++; } boolean[] used = new boolean[n]; LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (nextCount[i] == 0) { list.add(i); used[i] = true; } } while (!list.isEmpty()) { int remove = list.removeFirst(); for (int i : pre[remove]) { nextCount[i]--; next[i].addAll(next[remove]); if (nextCount[i] == 0) { list.add(i); } } } List<Boolean> res = new ArrayList<>(queries.length); for (int[] q : queries) { res.add(next[q[0]].contains(q[1])); } return res; }
- TopologicalSort & BFS
- Java
- the most votes
- Floyd–Warshall Algorithm
Runtime: 56 ms, faster than 64.51%, Memory Usage: 42.7 MB, less than 51.12% of Java online submissions// O(N^3)time // O(N^2)space public List<Boolean> checkIfPrerequisite(int n, int[][] prerequisites, int[][] queries) { boolean[][] connected = new boolean[n][n]; for (int[] p : prerequisites) connected[p[0]][p[1]] = true; // p[0] -> p[1] for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) connected[i][j] = connected[i][j] || connected[i][k] && connected[k][j]; List<Boolean> ans = new ArrayList<>(); for (int[] q : queries) ans.add(connected[q[0]][q[1]]); return ans; }- DFS
Runtime: 22 ms, faster than 94.77%, Memory Usage: 41.6 MB, less than 99.19% of Java online submissions// O(N^2)time // O(N^2)space Map<Integer, List<Integer>> graph = new HashMap<>(); boolean[][] reachable; public List<Boolean> checkIfPrerequisite(int n, int[][] prerequisites, int[][] queries) { reachable = new boolean[n][n]; populate(n, prerequisites); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { dfs(i, i); } List<Boolean> res = new ArrayList<>(); for (int[] q : queries) { res.add(reachable[q[0]][q[1]]); } return res; } public void dfs(int src, int target) { reachable[src][target] = true; for (int nei : graph.get(target)) { if (!reachable[src][nei]) dfs(src, nei); } } public void populate(int n, int[][] edges) { for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { graph.put(i, new ArrayList<>()); } for (int[] edge : edges) { graph.get(edge[0]).add(edge[1]); } }