the second one in Weekly Contest 209.
Difficulty : Medium
Related Topics : Tree
A binary tree is named Even-Odd if it meets the following conditions:
- The root of the binary tree is at level index
0, its children are at level index1, their children are at level index2, etc.- For every even-indexed level, all nodes at the level have odd integer values in strictly increasing order (from left to right).
- For every odd-indexed level, all nodes at the level have even integer values in strictly decreasing order (from left to right).
Given the
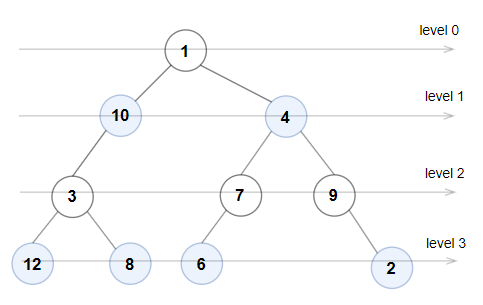
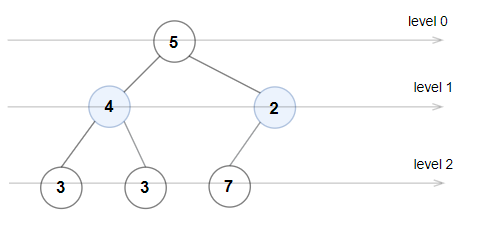
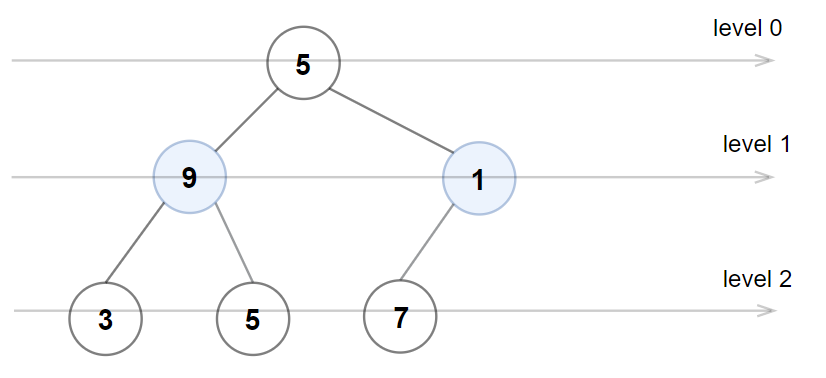
rootof a binary tree, returntrueif the binary tree is Even-Odd, otherwise returnfalse.Input: root = [1,10,4,3,null,7,9,12,8,6,null,null,2] Output: true Explanation: The node values on each level are: Level 0: [1] Level 1: [10,4] Level 2: [3,7,9] Level 3: [12,8,6,2] Since levels 0 and 2 are all odd and increasing, and levels 1 and 3 are all even and decreasing, the tree is Even-Odd.Input: root = [5,4,2,3,3,7] Output: false Explanation: The node values on each level are: Level 0: [5] Level 1: [4,2] Level 2: [3,3,7] Node values in the level 2 must be in strictly increasing order, so the tree is not Even-Odd.Input: root = [5,9,1,3,5,7] Output: false Explanation: Node values in the level 1 should be even integers.Input: root = [1] Output: trueInput: root = [11,8,6,1,3,9,11,30,20,18,16,12,10,4,2,17] Output: true
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 10^5].1 <= Node.val <= 10^6
- mine
- Java
Runtime: 7 ms, faster than 99.92%, Memory Usage: 56.3 MB, less than 5.00% of Java online submissions// O(N)time // O(maxsize(level))space public boolean isEvenOddTree(TreeNode root) { LinkedList<TreeNode> list = new LinkedList<>(); list.add(root); int level = 0; while(!list.isEmpty()){ int size = list.size(); boolean large = level % 2 == 0; int f = large ? Integer.MIN_VALUE : Integer.MAX_VALUE; while(size > 0){ TreeNode node = list.removeFirst(); if(node.left != null) list.add(node.left); if(node.right != null) list.add(node.right); if(large){ if(node.val % 2 == 0) return false; if(node.val > f) f = node.val; else return false; }else{ if(node.val % 2 != 0) return false; if(node.val < f) f = node.val; else return false; } size--; } level++; } return true; }
- Java