- 作业1.5
*1.5. Consider again a decay problem with two types of nuclei A and B, but now suppose that nuclei of type A decay into ones of type B, while nuclei of type B decay into type A. Strictly speaking, this is not a "decay" process, since it is possible for the type B nuclei to turn back into type A nuclei. A better analogy would be a resonance in which a system can tunnel or move back and forth between two states A and B which have equal energies. The corresponding rate equations are
where for simplicity we have assumed that the two types of decay are characterized by the same time constant,  Solve this system of equations for the numbers of nuclei,
Solve this system of equations for the numbers of nuclei,  and
and  , as functions of time. Consider different initial conditions, such as
, as functions of time. Consider different initial conditions, such as 
 etc., and take
etc., and take 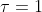 s. Show that your numerical results are consistent with the idea that the system reaches a stteady state in which
s. Show that your numerical results are consistent with the idea that the system reaches a stteady state in which  and
and  are constant. In such a steady state, the time derivatives
are constant. In such a steady state, the time derivatives  and
and  should vanish.
should vanish.
- Double Decay:
#### ProblemJust as the qustion-stems indicates, a better analogy for this problem would be a resonance in which a system can tunnel or move back and forth between two states A and B which have equal energys. Although it is a decay problem with two types of nuclei, considering that the total number of two types of nuclei is constant, we can readily solve it in the same way as in the single decay problem.
- The Euler Method:
#### Still, I choose to use Euler method to deal with this problem. The principle of it, as we have all learned, is Taylor expansion. And the routine process is to substitute the given ordinary differential equation into the first-order derivative of the Taylor expansion and neglect infinitesimals of hiher order.
- 求解析解 观察关系式可知两未知变量地位完全对等且它们的和为一常数,我们不妨设该常数为N并选一个变量进行求解。
- 求数值解
同样,我们可以通过导数的定义得到该结果
首先,完全按照教案上的模板编写并运行第一个程序
我们可以看到,它确实展示了该初始条件下的变化状况,但光这样还不够。
因此,我们再在另两种初始条件下进行数值模拟。
- 情况2: NA = 75, NB = 25
- 情况3: NA = 50, NB = 50
- 汇总对比图
此外,我们还应该将数值模拟的结果与真值进行比较。
由此可见,用该方法求得的比理论值要小, 不难想象这很可能是略去高阶无穷小项所致。
我们改变dt,比较不同大小dt对应的图像。
分别取dt1=0.05s,dt2=0.01s,dt3=0.1s
可以看出dt越小越大,我们有理由认为,dt越小
越趋近于理论值。
从上述模拟实验中,我们可以得出结论,在题设条件下,经过一段时间后, 两种原子核间的衰变达到动态平衡,它们的数目恒定且相等;才用如上数值算法时, 总是比理论值要小,但是当dt取得足够小时,
总是比理论值要小,但是当dt取得足够小时, 就足够逼近理论值。
就足够逼近理论值。
- 蔡老师
- 余康同学
- 田原同学
- 网络上热心分享技巧的大神

.gif?raw=true)
.gif?raw=true)





