- 动态规划
- 分治、回溯、递归
- demos
- 解法总结
- 课后思考
- 递归
public void recur(int level,int param){ // terminator if(level > MAX_LEVEL){ // process result return; } // process current logic process(level,param); // drill down recur(level:level+1,newParam); }
- 分治 Divide & Conquer
def divide_conquer(problem,param1,param2,...): # recursion terminator if problem is None: print_result return # prepare data data = prepare_data(problem) subproblems = split_problem(problem,data) # conquer subproblems subresult1 = self.divide_conquer(subproblems[0],p1,...) subresult2 = self.divied_conquer(Subproblems[1],p1,...) subresult3 = self.divied_conquer(Subproblems[2],p1,...) "" # process and generate the final result result = process_result(subresult1,subresult2,subresult3,...) # revert the current level states
- 动态规划 和 递归或者分治 没有根本上的区别
- 关键是看有无最优的子结构
- 共性
- 找到重复子问题
- 差异性
- 最优子结构、中途可以被淘汰次优解
- 最优子结构
- opt[n] = best_of(opt[n-1],opt[n-2],...)
- 储存中间状态
- opt[i]
- 递推公式
- Fib: opt[n] = opt[n-1]+opt[n-2]
- 二维路径:opt[i,j] = opt[i+1][j] + opt[i][j+1]
- 需判断a[i,j]是否可达,如障碍物
- 斐波那契数列
int fib(int n){ if(n <= 1){ return n; } return fib(n-1) + fib(n-2); } int fib(int n){ return n <= 1 ? n : fib(n-1) + fib(n-2) } int fib(int n,int [] meno){ if(n <= 1){ return n; } if(memo[n] == 0){ meno = fib(n-1) + fib(n-2); } return memo[n]; } // Bottom Up F[n] = F[n-1]+F[n-2] a[0] = 0,a[1] = 1; for(int i = 2;i <= n;i++){ a[i] = a[i-1] + a[i-2] } a[n]
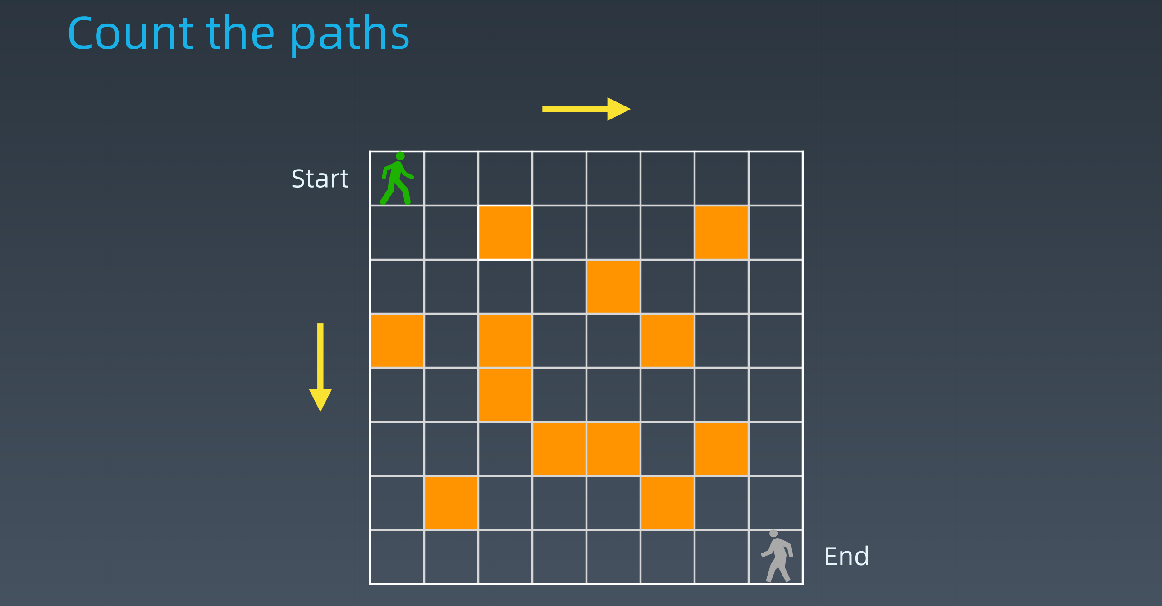
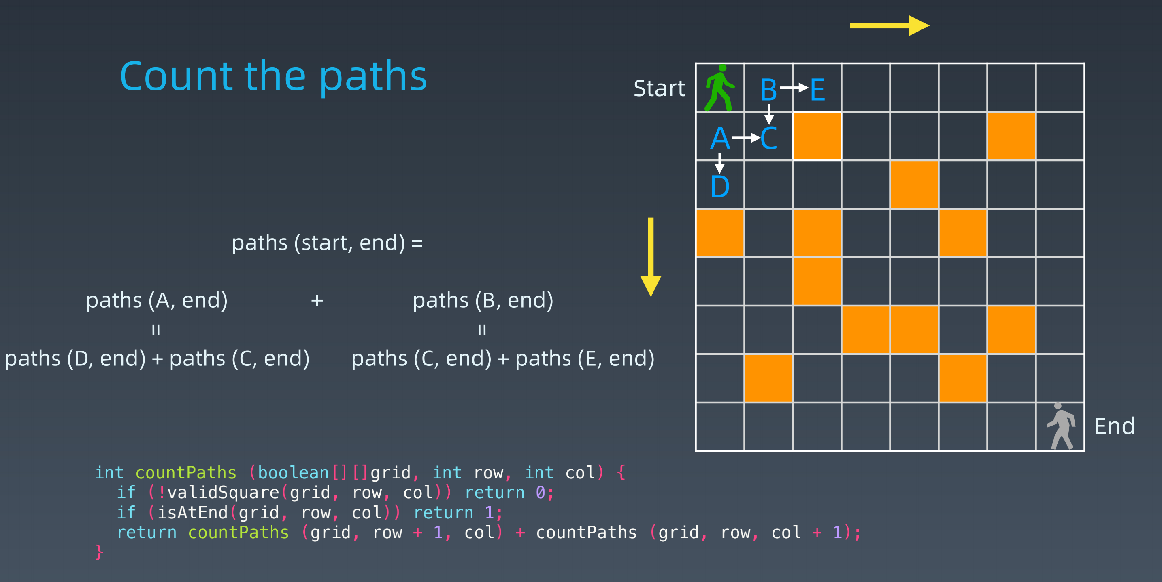
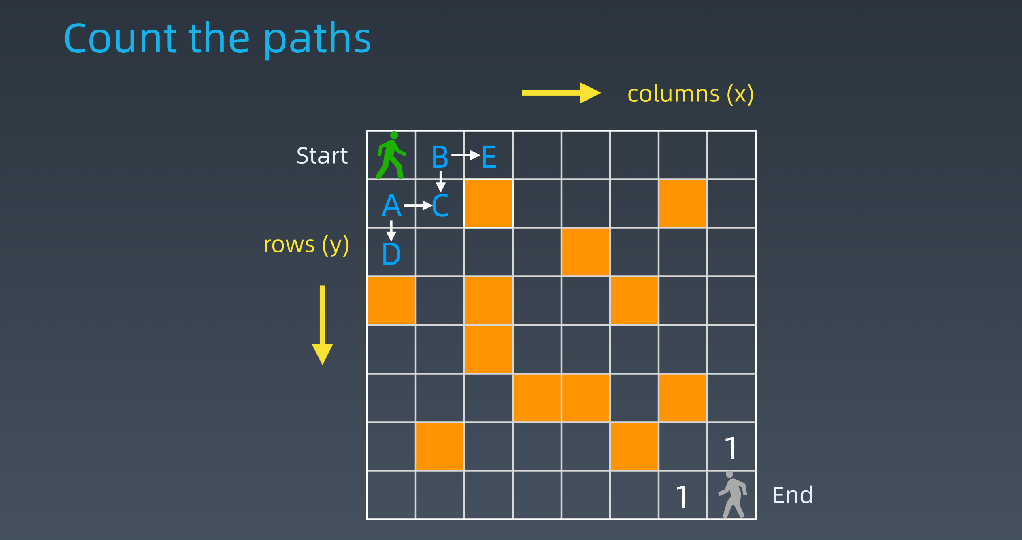
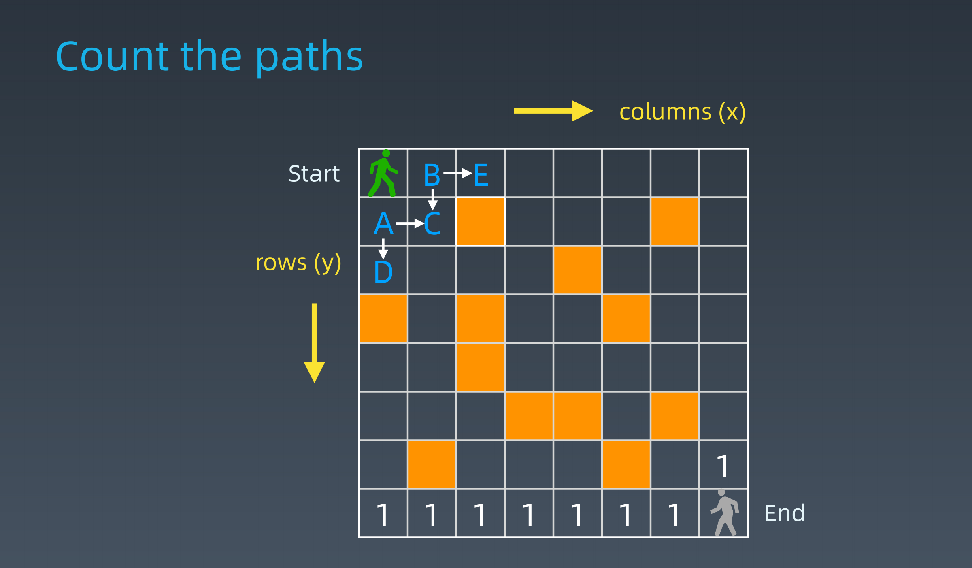
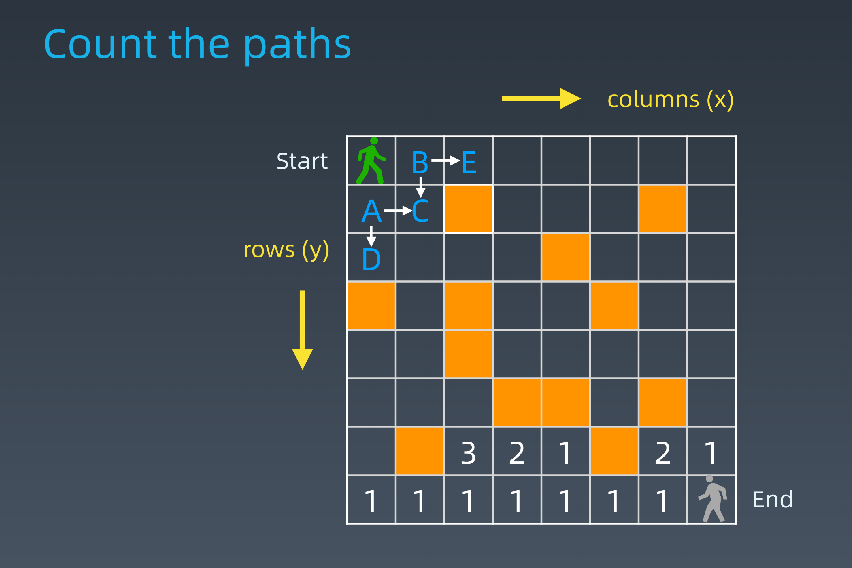
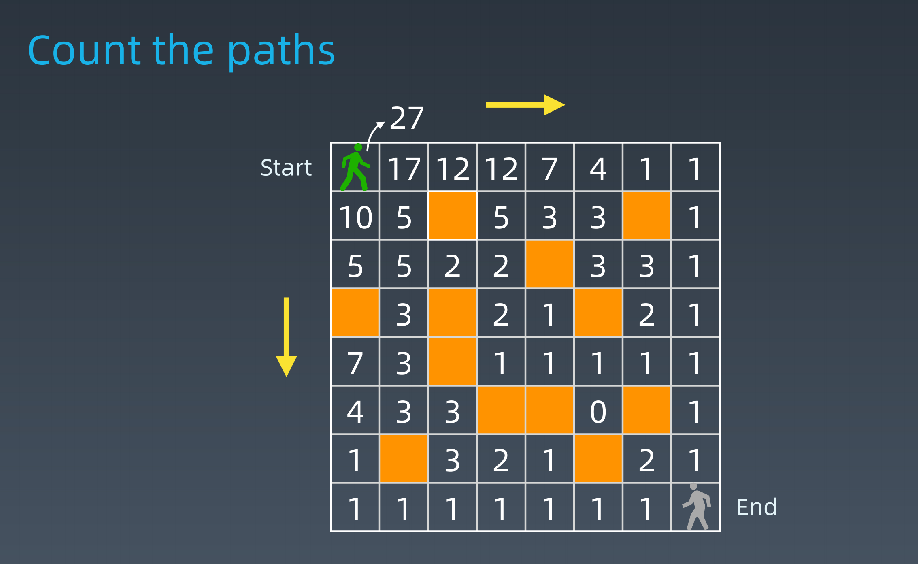
- 路径计数
int countParts(boolean[][]grid,int row,int col){ if(!validSquare(grid,row,col)) return 0; if(isAtEnd(grid,row,col)) return 1; return countPaths(grid,row+1,col) + countPaths(grid,row,col+1); }
- 求状态转移方程(DP方程)
- opt[i,j] = opt[i+1,j] + opt[i,j+1]
- if a[i,j] = '空地';
- opt[i,j] = opt[i+1,j]+opt[i,j+1]
- else
- opt[i,j] = 0
- 其它dp题型
- 1、define subproblems
- 进行分治:总问题分解为子问题
- 2、guess(part of solution)
- 猜递归方程形式
- 3、relate subproblem solutions
- 将n个子问题的解联系起来 <=> 合并子问题的解
- 4、recurse && memorize 或者 build DP table bottom-up
- 递归+备忘录搜索 或者 建立一个自底向上的表来递推