Optimizing Python applications without mutilation code.
Use the automatic modification of AST for code optimization, which is transparent to the user and requires the addition of only a few lines.
Decorator:
from opyum import optimize
@optimize
def function_for_optimize():
...Import-hook:
import opyum
opyum.activate()
# other imports"With" syntax:
import opyum
with opyum.activate:
# other importsCommand-line mode:
Show optimized source:
$ opyum show myfile.py
Diff between original source and optimized source:
$ opyum diff myfile.py
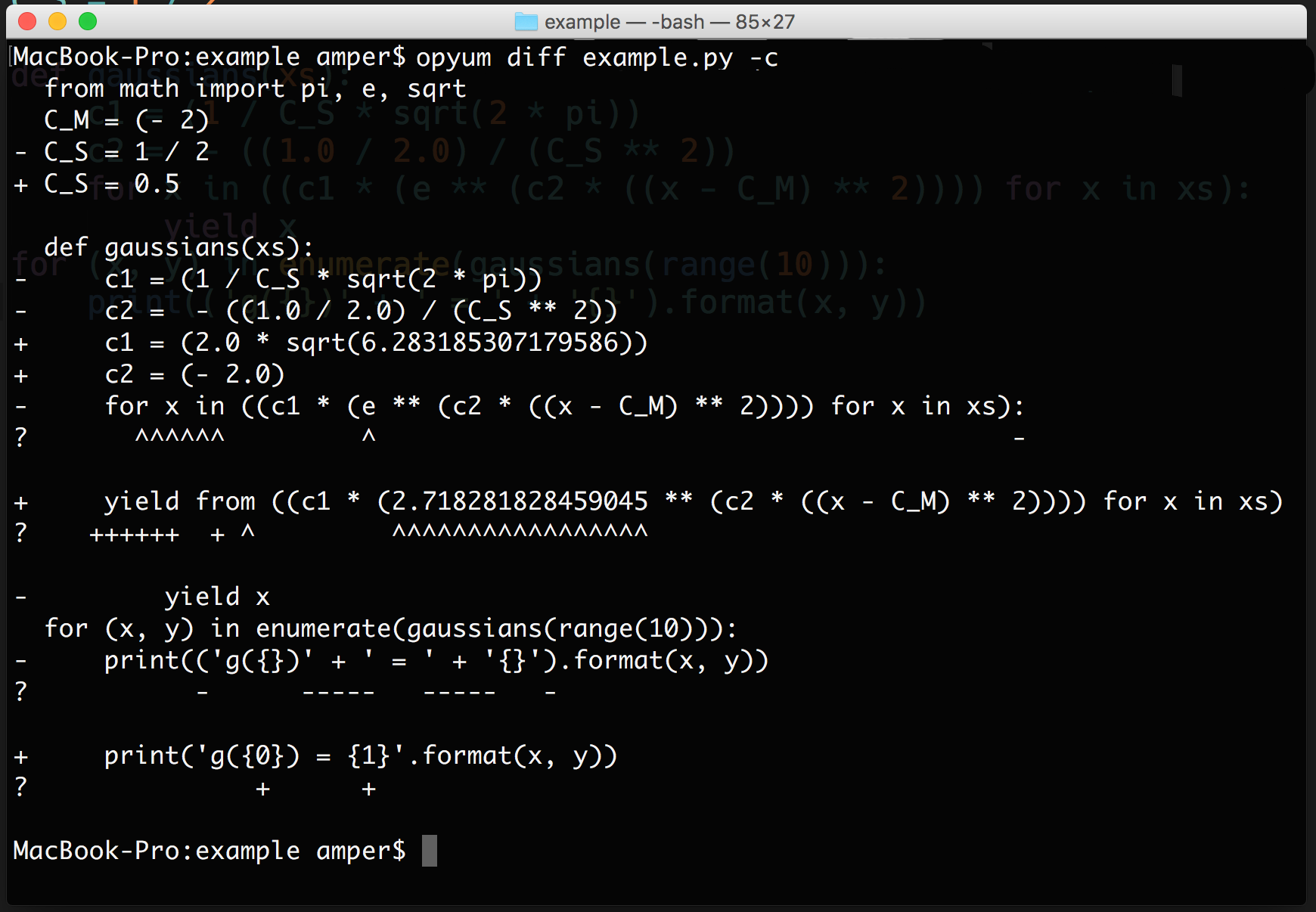
Console diff (with "-c" or "--console" option):
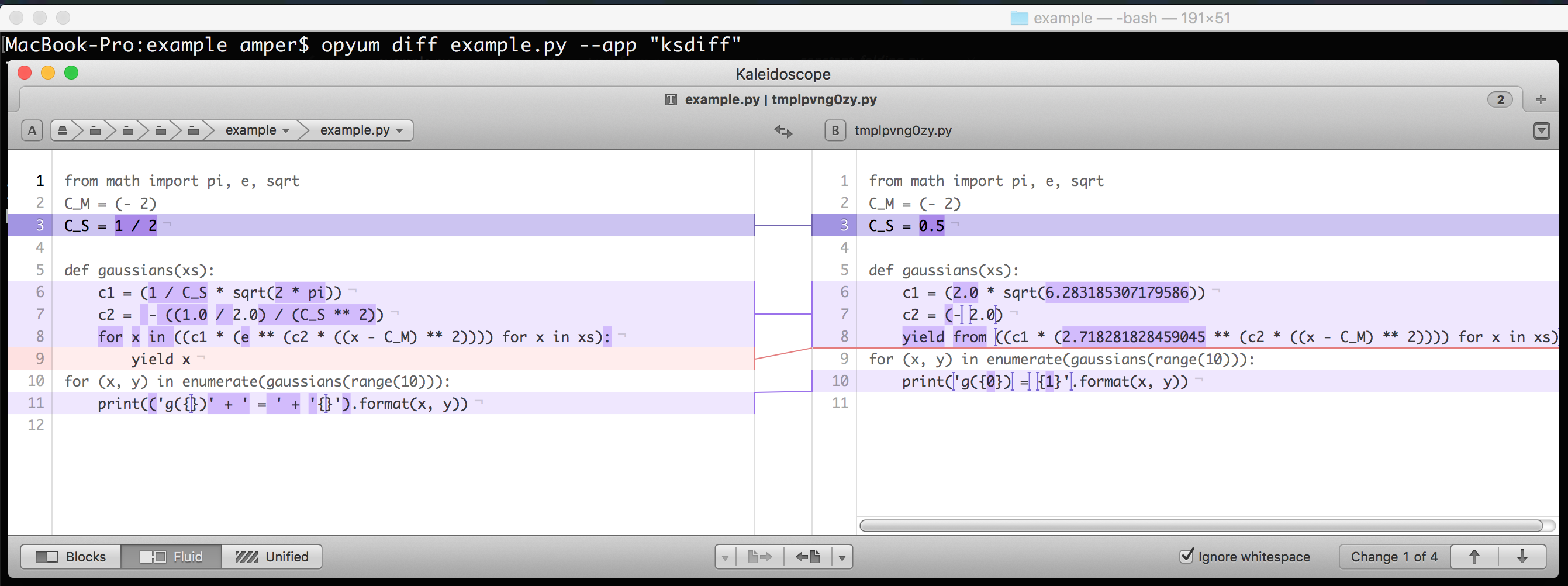
Custom app diff (with "--app" option):
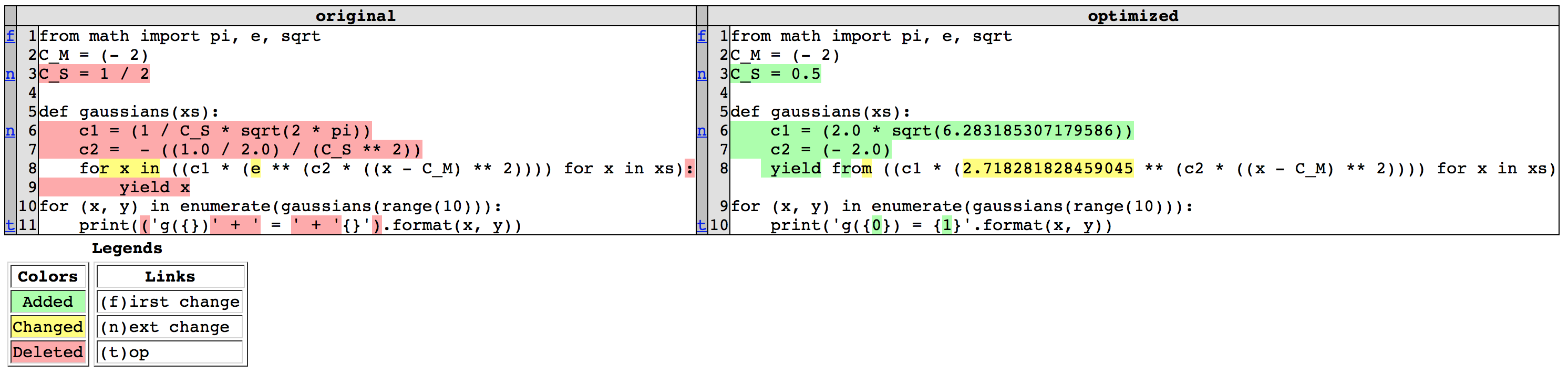
By default, html diff (without options):
####Constant folding
Before:
x = 7 * 24 * 60 * 60
y = [i ** 2 for i in range(10) if i % 2 == 0]
z = sum(range(1000))After:
x = 604800
y = [0, 4, 16, 36, 64]
z = 499500####"'Power' to 'multiplication'" optimization
Before:
x1 = a ** (-2)
x2 = a ** (-1)
x3 = a ** ( 0)
x4 = a ** ( 1)
x5 = a ** ( 2)After:
x1 = 1 / (a * a)
x2 = 1 / a
x3 = 1
x4 = a
x5 = a * a####"'Yield' to 'yield from'" optimization
Before:
for x in some_expression:
yield xAfter
yield from some_expression####Builtin constant propagation
Before:
from math import pi
def circumference(r):
return 2 * pi * rAfter:
from math import pi
def circumference(r):
return 2 * 3.141592653589793 * r####Custom constant propagation
Before:
C_PI = 3.141592653589793
def circumference(r):
return 2 * C_PI * rAfter:
C_PI = 3.141592653589793
def circumference(r):
return 2 * 3.141592653589793 * r####Dead code elimination
Before:
def do_something():
return 1
print('returning 1')
if condition1:
pass
elif condition2:
do_something()
else:
passAfter:
def do_something():
return 1
if not condition1 and condition2:
do_something()Installation is simple with pip:
$ pip install opyum
or with setuptools:
$ easy_install opyum