This repository contains the artifacts (code and supplementary material) for the submission ``SHiFT: An Efficient, Flexible Search Engine for Transfer Learning''. The additional details for replicating the results can be accessed via https://github.com/DS3Lab/shift/blob/main/shift_supplementary.pdf.
Visit the docs for more details!
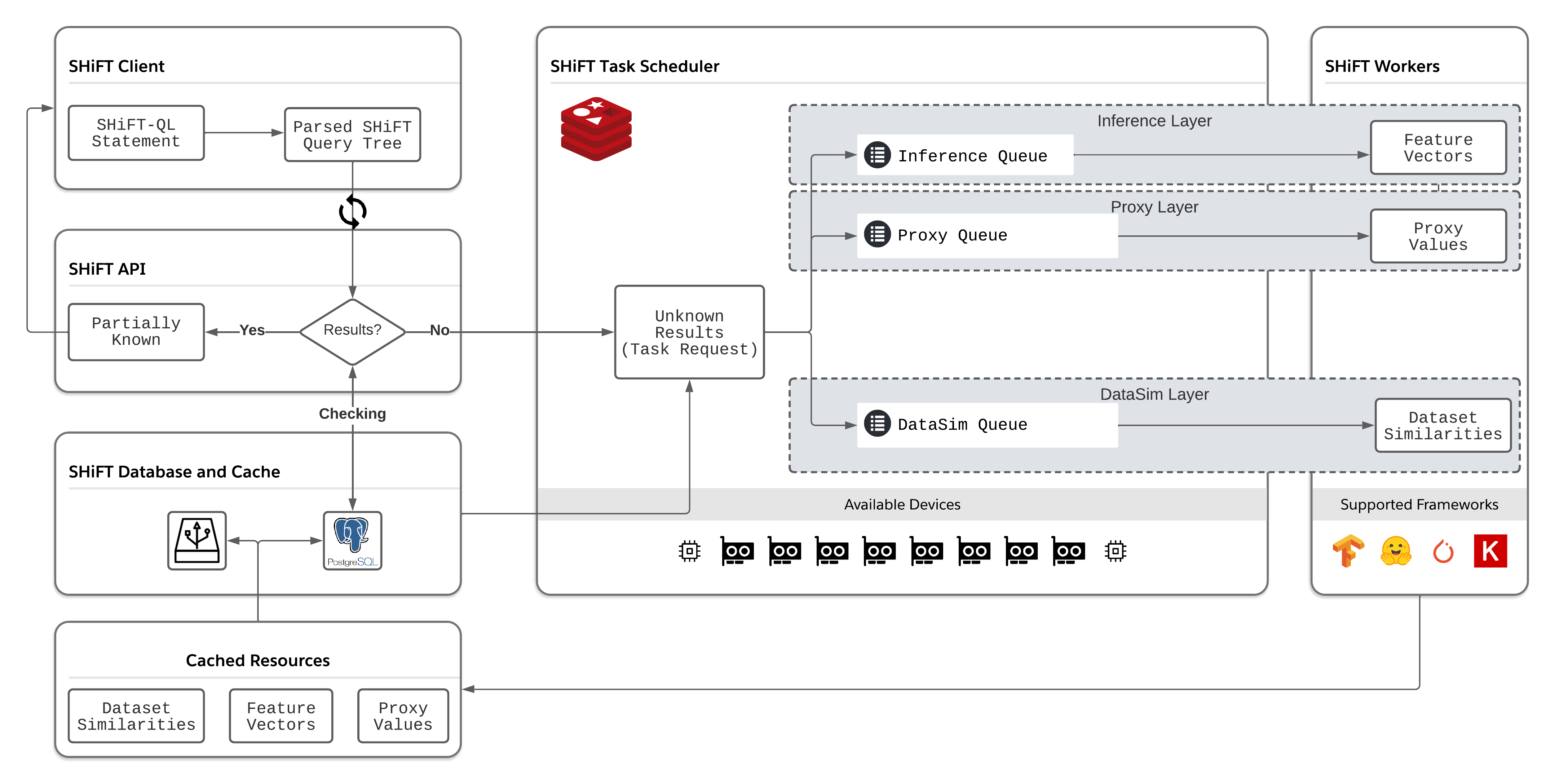
In a transfer learning scenario, an important task for data scientists is to find the best model for a new dataset. Users will have to train, evaluate and tune tons of models to pick the best one, which can be tedious, time-consuming and a waste of resources. To tackle this problem, we proposed SHiFT, with an envision for helping search machine learning models. With SHiFT, users are enabled to type in a structured query along with the dataset and a pool of models, and SHiFT returns the top-ranked models that match the query.
We apply several optimisations to SHiFT, including proxy classifiers, successive halving and incremental execution. With all these optimisations, we show that we can be 20 times faster than fine-tuning all the models in the pool.
SHiFT consists of the following main components:
- SHiFT-QL: SHiFT-QL is a query language specifically designed for searching machine learning models. Under
client/shiftql/repl, we provide a REPL (Read Eval Print Loop) for SHiFT-QL. Users can type in a query and get the results. An example of SHiFT-QL is shown below:
SELECT * FROM Models
WHERE NumParams < 10M AND Input == 'Vision'
ORDER BY UpstreamAccuracy DESC LIMIT 1-
Scheduler: It manages the scheduling of the computing devices (including both GPUs and CPUs). Whenever a new request comes to the system, the scheduler checks whether there is a free device available. If there is, the scheduler asks the worker to execute this request on the free device. The source code for scheduler is under
server/scheduler/. -
Worker: It executes the task on a given device. The source code for worker is under
server/worker_general. Our worker supports four types of tasks:- Inference Task: An inference task is a task that is used to infer the output of a model. The input to the inference task is a single data point, and the inference task outputs the feature vector of the data point.
- Classification Task: A classification task is a task that is used to classify the input data, based on the feature vector calculated by the inference task.
- Task2Vec Task: A task2vec task is a task to transform the entire dataset into a single vector.
- Fine-tune Task: A fine-tune task is a task that is used to fine-tune the model on the entire dataset.
-
RESTful API: SHiFT is organised in a client-server structure. The RESTful provides access to all functionalities of SHiFT, including querying models, checking job status, and so on. The source code for RESTful API is under
server/rest/. -
Task Queues: The scheduler and worker form a producer/consumer model: the scheduler produces the tasks and the worker consumes the tasks. These two components communicated with each other by a task queue. The source code for the task queue is under
server/common/db_tools/queues. -
Database Utilities: All operations related to database accesses are under
server/common/db_tools/. -
Successive Halving Simulator: We have implemented a simulator for running successive halving with some parameters, including the chunk size, budget, cost of models, etc. The simulator can be found at
client/simulator/. -
Fine-tune Accuracies for Benchmark Module: We provide the fine-tune accuracies on VTAB tasks and HuggingFace transformers, which can be found here.
-
Parse: The SHiFT-QL statement is first parsed into a query tree at the client-side, which is similar to the query tree in database systems.
-
Query Composition: The client then transforms the parsed query tree into an HTTP request, which is sent to the server afterwards. The server then starts to process the query.
-
Evaluation: Once the server receives the query, it starts to evaluate the performance of the candidate models. There might be two cases for the evaluation:
- The accuracies or some other performance metrics for some models have already been calculated and are stored. If all results are known, SHiFT returns the results immediately.
- The accuracies or some other performance metrics for some models have not been calculated before. In this case, SHiFT will start to lazily evaluate the performance of the candidate models and goes to the next step.
-
Task Processing: SHiFT then starts to process the remaining unknown tasks. A task in SHiFT includes three parts: a model, a training dataset and a testing dataset. SHiFT creates three jobs correspondingly:
- An inference task for the training dataset.
- An inference task for the testing dataset.
- A classification task predicting the labels of the testing dataset.