This repositary contains source code of blockchain node, which is a main part of Evercity's Smart Sustainable Bond project.
The market of green and sustainability-linked bonds is expected to reach a new record of 350 bln USD in 2020. However, there are still challenges preventing market growth: low accuracy and transparency of impact measurement due to lack of on-site data; lack of tools to distribute financial and impact results between projects and investors; high back office costs; relatively low liquidity and profitability of impact finance. Digital technologies have a great potential to solve these challenges, which is confirmed in the UN and EU documents.
Evercity aims to solve these problems by building an open-source blockchain-based Smart Sustainable Bond protocol - digital infrastructure which will enable end to end lifecycle of sustainability-linked bonds with adjustable floating impact-linked coupon rate as well as traditional green bonds. The protocol is supported by Web3 Foundation which nurtures and stewards technologies and applications in the fields of decentralized web software protocols.
Powered by Parity Substrate blockchain engine, Smart Sustainable Bond Protocol is an open-source software which allows participants to issue and monitor innovative sustainability-linked bonds with adjustable floating impact-linked coupon rate. The main idea of the project is to increase accuracy of impact monitoring and reporting eliminating the risk of greenwashing, as well as to enable fair and transparent impact allocation between different stakeholders engaged in sustainability-related projects. The main operations performed are confirmed by blockchain digital signatures and can be traced publicly. The platform stablecoin EVERUSD can only be used in the operations with bonds, which eliminates the risks of money laundering.
Evercity pallet implements actions for three types of entities: accounts and roles, token balances and operations with them and bonds.
Each Evercity account can accommodate one or more roles: MASTER, CUSTODIAN, ISSUER, INVESTOR, AUDITOR, MANAGER. The account only has access to the functions available to its role. The approximate functions of each role in the project are as follows:
- MASTER: the administrative role that can create new accounts and assign roles to them. This role also regulates the launch of bonds to the market, making the final decision on whether the bond meets the requirements.
- CUSTODIAN: the role which can mint and burn the main platform token. This role is assigned to the public account of the partner bank, which exchanges USD --> EVERUSD and EVERUSD --> USD.
- ISSUER: the role which can create bonds. An account with the ISSUER role issues a bond to fund a sustainability-aligned project. After receiving funds from the sale of Bond Units, the ISSUER undertakes to provide data on the impact of the project, which influences the coupon rate that should be paid to the investor. The ISSUER is obliged to replenish the bond balance with the amount necessary to cover its financial obligations.
- INVESTOR: accounts with the INVESTOR role use the EVERUSD token to buy Bond Units and sell them on the secondary market. Each billing period Investor receives a coupon income proportional to its balances of various Bond Units
- AUDITOR: these accounts check and confirm the environmental impact data sent by Issuer, as well as certify the documents uploaded to the platform
- MANAGER: the task of accounts with this role is to help Issuers work with projects, verify data and prepare documents
The EVERUSD platform token is a stablecoin strictly linked 1 to 1 to one of the fiat currencies (USD). The platform token is a reflection of the financial obligations of the participants and is not a means of payment. EVERUSD token cannot be freely sent from one address to another. Any operation that changes EVERUSD balances must have a justification transaction on the platform. It can be: buying Bond Units, receiving a coupon income, selling Bond Units on the secondary market, etc.
The mechanics of EVERUSD are such that it always has verified fiat collateral. Initially, there are 0 EVERUSD-s on the platform. The creation (mint) of new EVERUSD is possible only upon request from accounts that have passed KYC and provided the Bank-Custodian with documents confirming the payment. The same scheme is used to destroy (burn) EVERUSD tokens on users' balances - strictly at their request and with confirmation of the payment of the corresponding amount in fiat currency. Here is an example of how this “mirror” scheme works:
- Investor creates a request for the purchase of 1000 EVERUSD and sends 1000 USD from his account to the bank
- The bank verifies the payment, verifies the Investor's identity, and confirms the application by adding +1000 EVERUSD to the Investor’s balance
- Investor performs transactions on the platform, buying Bond Units, receiving coupon income, organizing transactions in the secondary market, etc., while a part of his EVERUSD goes to the Issuer balance (e.g. 800 EVERUSD)
- Issuer creates a request for withdrawal of 800 USD with burning 800 EVERUSD on its balance
- The bank sees a request for burning of EVERUSD from the Issuer, receives proof of the legality of receiving EVERUSD from observing the contracts on the platform, and confirms the application. Tokens are burned, and 800 USD are sent to Issuer.
With this scheme on the platform, any transaction with the EVERUSD token has a strict confirmation on the blockchain, which can be presented as proof of transparency of all the money flows on the platform, and each EVERUSD has a guaranteed collateral.
Bonds are the main essence of the project. The logic of the work of Evercity bonds copies the logic of the traditional issuance of bonds in the financial markets, but links the impact data on the use of proceeds with the financial parameters of the bond. The data on the environmental impact of the project uploaded to the blockchain changes the coupon rate. The parameters for these changes are configured at the stage of bond structuring. This mechanism is described in more detail in the platform operation scenario.
Here is the basic scenario on of Smart Sustainable Bond Protocol:
-
Issuer, having registered on the platform, creates a description of the future project, posts all financial and technical documentation and estimates the minimum and maximum amount of investment that it requires. For these investments, Issuer configures a sustainability-linked bond, the Bond Units of which will be bought by Investors. Documents and data about the project are checked and certified by participants with the role of Auditors, who publicly confirm the accuracy of the information provided by Issuer. After the final approvals, the bond becomes available for study by Investors
-
Investor, having studied the project, decides to invest. To record the fact of buying bonds and transferring funds to Issuer, the Investor needs to exchange fiat funds for a platform token with the help of a custodian bank. In order to do so, he creates an application for the issue of a certain amount of EVERUSD token, which will be sent to its balance as soon as the custodian bank receives all documents confirming the payment
-
Investor deposits the required amount of EVERUSD on the bond balance by purchasing a number of Bond Units. Other Investors do the same. At this stage, the funds invested in EVERUSD are not available to Issuer. If the bond has not collected the minimum investment amount within a specified time, Investors can return their funds, and the project can be revised and put up for auction again
-
If the minimum investment amount is reached (the minimal amount of Bond Units was bought) the bond is released to the market. The remainder of the Bond Units can be freely purchased by any Investor. The Issuer can now withdraw the EVERUSD received from the sale and exchange it to fiat currency by placing a request to burn EVERUSD tokens to the custodian bank. The custodian bank, having access to information about all sources of funds, can issue fiat currency for the implementation of the project, burning the corresponding amount of EVERUSD on the balance of Issuer
-
From the moment the bond is released to the open market and the funds are received, Issuer starts to implement the project. After some time, at the end of each billing period, the Issuer must send data on the project's environmental impact (amount of renewable electricity generated, CO2 emissions saved by the project or other types of impact) to the blockchain, and pay the coupon rate to the Investors. The coupon rate changes depending on the data provided: if the project develops successfully, Issuer should pay less, and if the project is unsuccessful, the Issuer should pay more (the exact configuration is set out at the bond structuring stage). The data sent to the bond is verified by the Auditor, who was previously assigned to a specific project by the platform administrator (Master)
-
In the end of bond duration period Issuer returns full debt to bond's balance, and Investors can receive their funds back
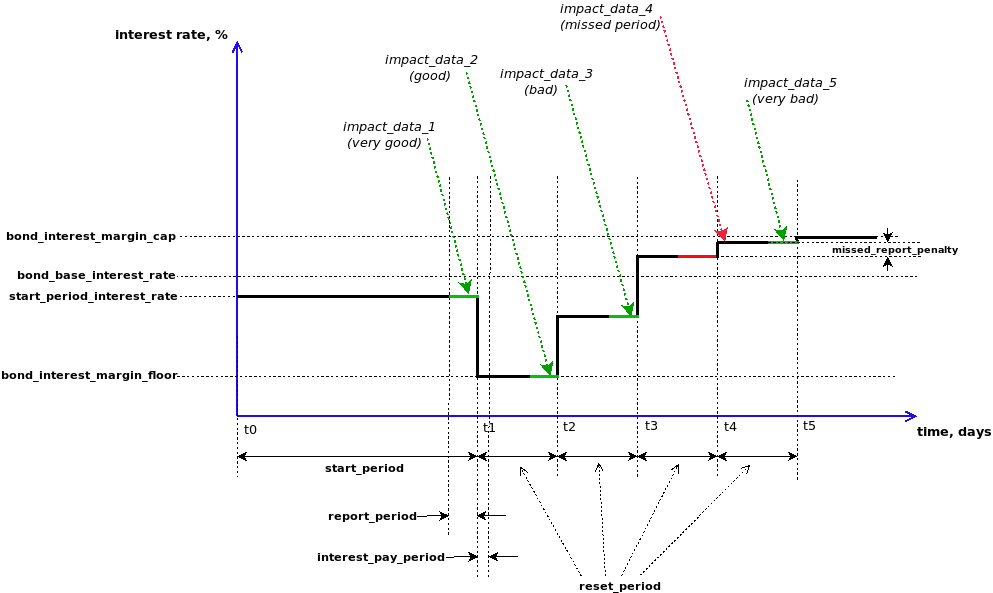
An illustration of how the coupon rate changes depending on the data on the environmental impact of the project is shown in the figure:
The parameters shown on the figure(interest rate base, cap, floor, periods, penalty, etc...) are set out by Issuer at the bond structuring stage and allow him to flexibly set the financial policy of the bond. It is possible to provide any combination of penalties / rewards (for example, there can be bonds without penalties), as well as to set short periods (for regular data feed by automatic sensors). The project can accommodate financial models of almost any complexity and the reception of data of different types and formats.
Issuer pays the coupon rate calculated on the basis of impact data to Investors, replenishing the bond balance with the required amount of EVERUSD. At the end of the bond circulation period, the Issuer must repay all debt to Investors within a specified time.
In case of a shortage of funds on the balance sheet of the bond, the bond is considered bankrupt, and the funds on its balance sheet are distributed to Investors in proportion to the amount of accumulated obligations in relation to each Investor.
Also, during the life of a bond, Investors can put their bonds for sale, and other Investors can buy them.
Any significant operations with a token, bond, accounts and roles (including commissions for exchanging tokens or for the operation of supplementary accounts) are reflected in the blockchain and serve as a justification for receiving / spending funds. 1 to 1 linkage of the token to fiat currency excludes manipulations with the exchange rate and allows to use the transaction history in the blockchain as a source for the financial reporting of the participants, which cannot be faked without disrupting the functionality of the platform.
Methods of pallet-evercity are described in Rust documentation here [TEMP]
git clone https://github.com/EvercityEcosystem/smart-sustainable-bond.git
cd evercity-substrate
cargo build --releasePurge any existing dev chain state:
./target/release/evercity-node purge-chain --dev[WARNING] All chains data is usually located in $HOME/.local/share/evercity-node/chains/*
Removing of all chains: "dev", "local-testnet", and any others to launch all chains from block "0" can be made by:
rm -rf $HOME/.local/share/evercity-node/chains/*
./target/release/evercity-node --devcargo build --release
mv ./target/release/evercity-node ./docker
docker build --tag evercity-node:1.0 ./docker/Build
cargo build --releaseCopy ./target/release/evercity-node into /usr/bin/evercity/. Create /var/run/evercity directory.
Put evercity.service in /etc/systemd/system/
[Unit]
Description=Evercity substrate test service
After=network.target
StartLimitIntervalSec=0
[Service]
Type=simple
Restart=always
RestartSec=1
User=evercity
ExecStart=/usr/bin/evercity/evercity-node --dev --rpc-external --ws-external --ws-port 9940 --rpc-port 9930 --port 30300 --base-path /var/run/evercity
systemctl enable evercitystart service
systemctl start evercitycargo test./target/release/evercity-node --devcargo doc